Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem
2.1. The Model
2.2. Classical Optimal Dividend Problem
2.3. Exploratory Formulation
- (i)
- for any , where is a set of probability density functions with support ;
- (ii)
- the stochastic differential equation (9) has a unique solution under π;
- (iii)
- .
3. Exploratory HJB Equation
3.1. Exploratory Dividend Policy
3.2. Verification Theorem
3.3. Solution to Exploratory HJB
- (i)
- if , is non-increasing.
- (ii)
- if , is non-decreasing.
- (iii)
- if , .
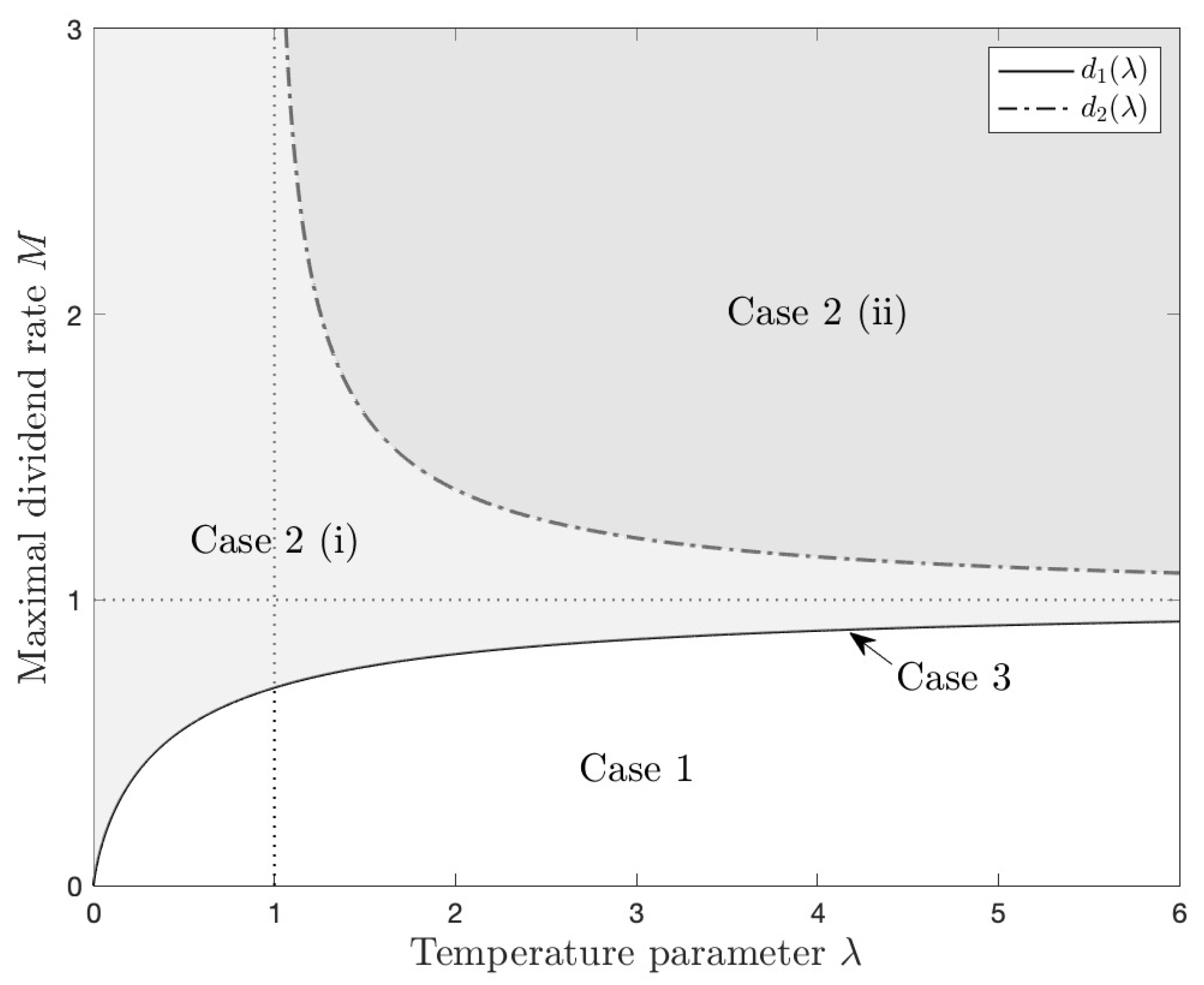
4. Discussion
-
(b) DefineThen , and is decreasing on . Therefore, and .
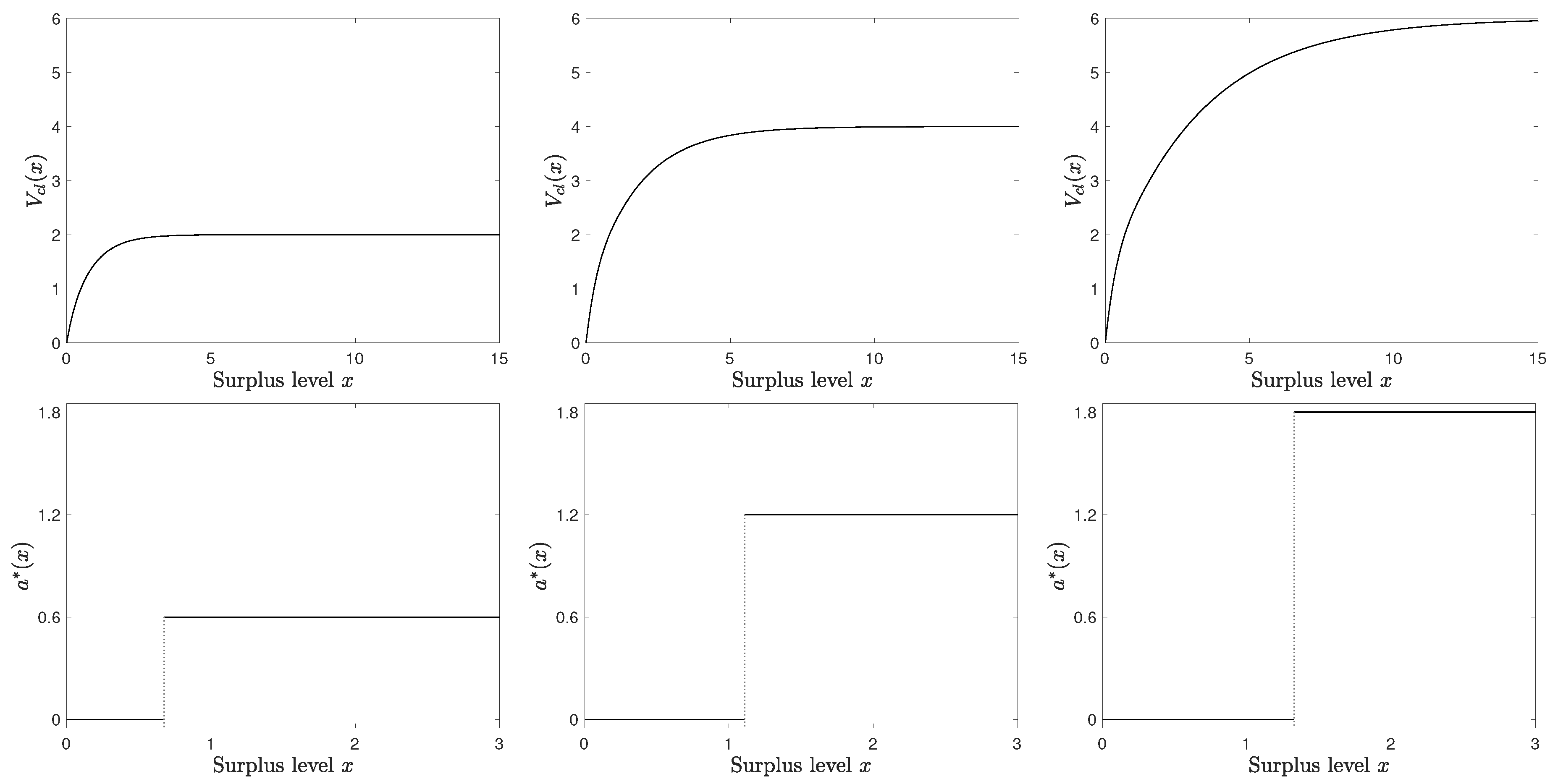
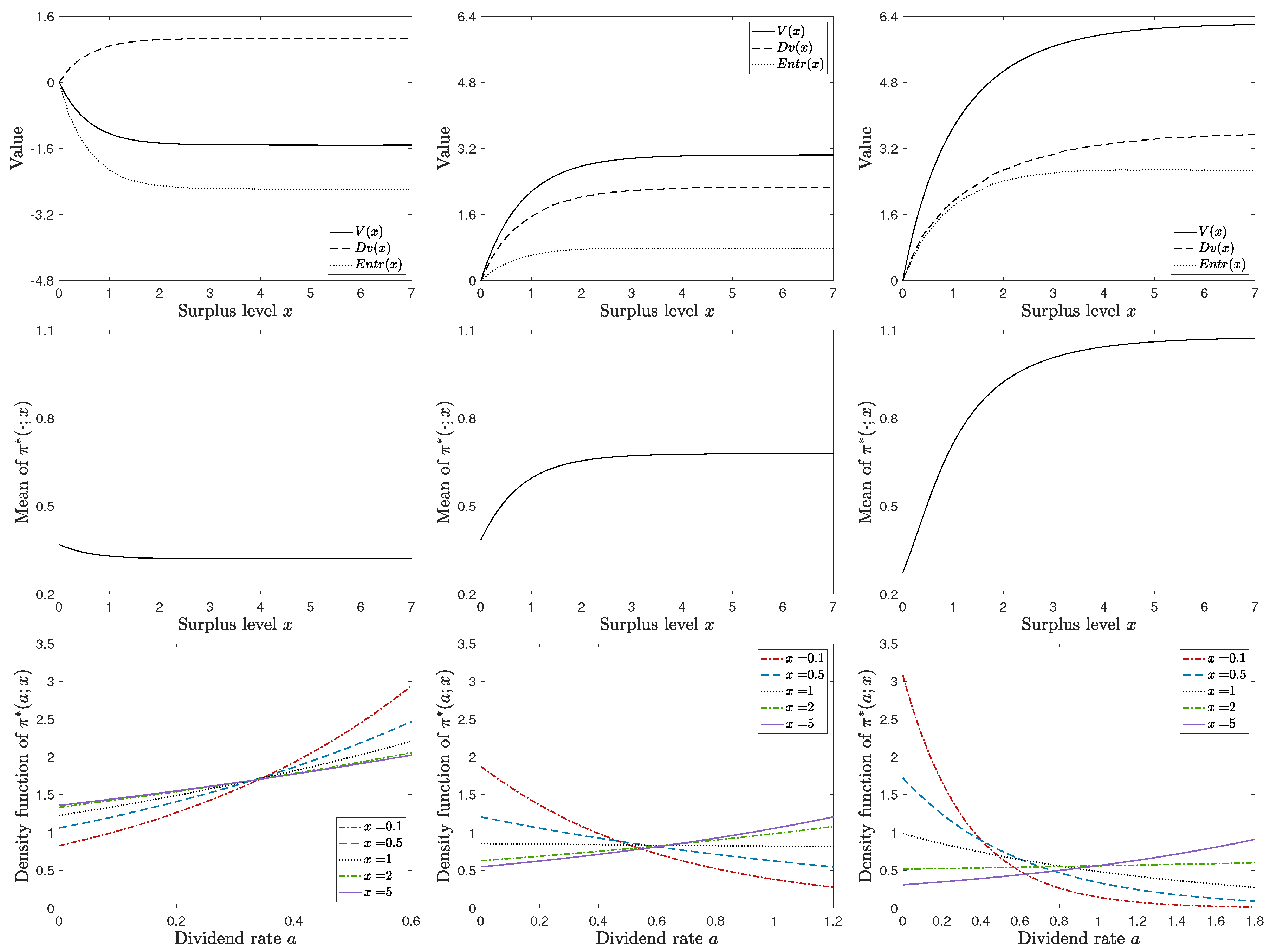
5. Numerical Examples
6. Conclusion
Appendix A. Proof
- (i)
- is continuous and decreasing in x;
- (ii)
- there exists a unique such that ;
- (iii)
- , for some constant which depends on k only;
- (iv)
- , .
- (b) Note that for , . Therefore, .
References
- Wang, H.; Zariphopoulou, T.; Zhou, X.Y. Reinforcement Learning in Continuous Time and Space: A Stochastic Control Approach. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2020, 21, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, F. Approximerad framställning af sannolikhetsfunktionen. Återförsäkring af kollektivrisker. Akademisk afhandling; Almqvist &Wiksells, 1903.
- De Finetti, B. Su un’impostazione alternativa della teoria collettiva del rischio. Transactions of the XVth international congress of Actuaries. New York, 1957, Vol. 2, pp. 433–443.
- Gerber, H.U. Entscheidungskriterien für den zusammengesetzten Poisson-Prozess. PhD thesis, ETH Zurich, 1969.
- Schmidli, H. Stochastic control in insurance; Springer Science & Business Media, 2007.
- Jeanblanc-Picqué, M.; Shiryaev, A.N. Optimization of the flow of dividends. Uspekhi Matematicheskikh Nauk 1995, 50, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, S.; Taksar, M. Controlled diffusion models for optimal dividend pay-out. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 1997, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jgaard, B.H.; Taksar, M. Controlling risk exposure and dividends payout schemes: insurance company example. Mathematical Finance 1999, 9, 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, S.; Højgaard, B.; Taksar, M. Optimal risk control and dividend distribution policies. Example of excess-of loss reinsurance for an insurance corporation. Finance and Stochastics 2000, 4, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcue, P.; Muler, N. Optimal reinsurance and dividend distribution policies in the Cramér-Lundberg model. Mathematical Finance: An International Journal of Mathematics, Statistics and Financial Economics 2005, 15, 261–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcue, P.; Muler, N. Optimal investment policy and dividend payment strategy in an insurance company. The Annals of Applied Probability 2010, 20, 1253–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaier, J.; Grandits, P.; Schachermayer, W. Asymptotic ruin probabilities and optimal investment. The Annals of Applied Probability 2003, 13, 1054–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulenko, N.; Schmidli, H. Optimal dividend strategies in a Cramér–Lundberg model with capital injections. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 2008, 43, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, L. Optimal investment for insurer with jump-diffusion risk process. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 2005, 37, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choulli, T.; Taksar, M.; Zhou, X.Y. A diffusion model for optimal dividend distribution for a company with constraints on risk control. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 2003, 41, 1946–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.U.; Shiu, E.S. On optimal dividend strategies in the compound Poisson model. North American Actuarial Journal 2006, 10, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, F.; Palmowski, Z.; Pistorius, M.R. On the optimal dividend problem for a spectrally negative Lévy process. The Annals of Applied Probability 2007, 17, 156–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wen, Y. Optimal dividend problem with a terminal value for spectrally positive Levy processes. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 2013, 53, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kosorok, M.R.; Zeng, D. Reinforcement learning design for cancer clinical trials. Statistics in medicine 2009, 28, 3294–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorowski, M.; Celi, L.A.; Badawi, O.; Gordon, A.C.; Faisal, A.A. The artificial intelligence clinician learns optimal treatment strategies for sepsis in intensive care. Nature medicine 2018, 24, 1716–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirowski, P.; Pascanu, R.; Viola, F.; Soyer, H.; Ballard, A.J.; Banino, A.; Denil, M.; Goroshin, R.; Sifre, L.; Kavukcuoglu, K. ; others. Learning to navigate in complex environments. arXiv:1611.03673. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mottaghi, R.; Kolve, E.; Lim, J.J.; Gupta, A.; Fei-Fei, L.; Farhadi, A. Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning. 2017 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2017, pp. 3357–3364. [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Jozefowicz, R.; Sutskever, I. Learning to generate reviews and discovering sentiment. arXiv:1704.01444. [CrossRef]
- Paulus, R.; Xiong, C.; Socher, R. A deep reinforced model for abstractive summarization. arXiv:1705.04304. [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; others. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaderberg, M.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Dunning, I.; Marris, L.; Lever, G.; Castaneda, A.G.; Beattie, C.; Rabinowitz, N.C.; Morcos, A.S.; Ruderman, A.; others. Human-level performance in 3D multiplayer games with population-based reinforcement learning. Science 2019, 364, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; others. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Schrittwieser, J.; Simonyan, K.; Antonoglou, I.; Huang, A.; Guez, A.; Hubert, T.; Baker, L.; Lai, M.; Bolton, A.; others. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature 2017, 550, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, P.; Cesa-Bianchi, N.; Fischer, P. Finite-time analysis of the multiarmed bandit problem. Machine learning 2002, 47, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa-Bianchi, N.; Gentile, C.; Lugosi, G.; Neu, G. Boltzmann exploration done right. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Todorov, E. Linearly-solvable Markov decision problems. Advances in neural information processing systems 2006, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ziebart, B.D.; Maas, A.L.; Bagnell, J.A.; Dey, A.K. ; others. Maximum entropy inverse reinforcement learning. Aaai. Chicago, IL, USA, 2008, Vol. 8, pp. 1433–1438.
- Nachum, O.; Norouzi, M.; Xu, K.; Schuurmans, D. Bridging the gap between value and policy based reinforcement learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.Y. Continuous-time mean–variance portfolio selection: A reinforcement learning framework. Mathematical Finance 2020, 30, 1273–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Dong, Y.; Jia, Y. Learning equilibrium mean-variance strategy. Mathematical Finance 2023, 33, 1166–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Gamage, T.; Ma, J.; Xie, P. Reinforcement Learning for optimal dividend problem under diffusion model. arXiv:math/2309.10242. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhou, X.Y. Exploratory HJB equations and their convergence. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 2022, 60, 3191–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.Y. State-dependent temperature control for Langevin diffusions. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 2022, 60, 1250–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strulovici, B.; Szydlowski, M. On the smoothness of value functions and the existence of optimal strategies in diffusion models. Journal of Economic Theory 2015, 159, 1016–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | For example, the dividend paying rate under the threshold strategy is the maximal rate if the surplus exceeds the threshold; otherwise, it pays nothing. Since the threshold is determined by the model parameters, the change in the estimated parameters may dramatically change the dividend paying rate from zero to the maximal rate, or conversely. |
| 2 | |
| 3 | For each initial surplus x, we discretize the continuous time into small pieces () and sample 2000 independent surplus processes to simulate and . |
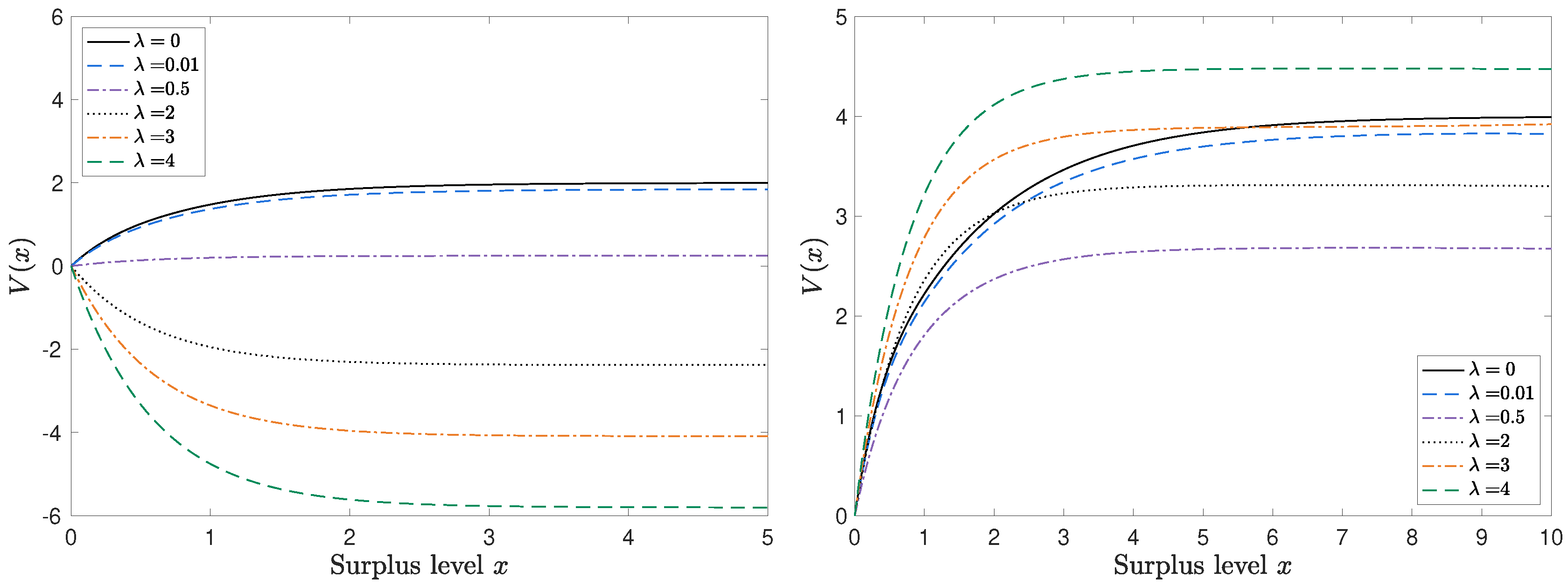
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




