1. Introduction
Recruitment, a pivotal component of Human Resource Management (HRM) in identifying, evaluating, and selecting potential candidates to fill organizational positions, ensuring their seamless integration [
1]. It significantly enhances performance, fosters employee growth, and decreases turnover rate [
2]. Traditional recruitment processes consist of multiple stages, including identifying applicants, attracting candidates, processing applications, and communicating with them. This process involves a time-consuming, location-bound, and costly process relying on face-to-face interactions and paper-based [
3,
4]. Recruitment currently heavily relies on manual tasks like resume review, profile assessment, initial contact, pre-screening interviews, and providing feedback to applicants [
5]. The most challenge for recruiters is to find candidates who align with their company culture, which is narrowing the already limited pool of potential hires [
6].
The digital era revolutionizes recruitment, utilizing technologies, e.g., Artificial Intelligence (AI), to enhance management practices and decision-making [
7]. Digital recruitment, or e-recruitment, utilizes websites and social media for cost-effective and efficient candidate engagement [
8,
9]. Online testing gains popularity for evaluating applicants, ensuring selection based on both hard and soft skills [
10]. AI becomes pervasive in our lives, from voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to applications in online banking and social networks, promising enhanced efficiency and convenience [
11]. AI's influence extends to education with ChatGPT [
12], healthcare areas like medical image diagnostics and virtual patient care through wearables [
13,
14] and the recruitment field is no exception. AI streamlines various aspects of the hiring process, such as screening, interview scheduling, and candidate interactions, improving efficiency and the candidate experience tasks [
15,
16]. AI enhances the recruitment process by automating time-consuming tasks from resume screening, candidate matching to onboarding process [
17,
18]. This automation enables recruiters to concentrate more on strategic matters. A prime example is HireVue, a prominent AI platform, which reduced recruitment time by 90% and boosted employment diversity by 16% through the use of voice and facial recognition, along with proprietary algorithms [
19,
20]. AI promotes fairness by considering all candidate traits equally and prioritizing job fit over performance comparisons, excluding demographic information to eliminate bias [
21]. It overcomes data processing issues, handles large datasets, and uses predictive algorithms to enhance decision-making [
22].
Thailand, a newly industrialized country in Southeast Asia, aspires to transition from a developing nation to a developed one. Their goal is to raise the GDP per capita to
$15,000 within the next two decades. To tackle economic challenges and an aging population, the current Thai Government has introduced a new national development strategy known as "Thailand 4.0" [
23], a 20-year national strategy spanning from 2017 to 2036. This strategy aligns closely with the concept of Industry 4.0 and emphasizes advanced technology industries for sustainable economic growth [
24], incorporating Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 8 to sustain economic growth per capita considering the specific conditions of the country [
25,
26]. Thus, the demand for highly skilled professionals is increasing, leading to high competition in the job market. This drives companies to invest in technology to enhance their talent acquisition processes. Effective talent recruitment is critical for capitalizing on the opportunities presented by this digital era [
24]. The potential to enhance the competitiveness of Thai companies lies in the incorporation of AI technology into their recruitment processes. This integration also aligns with the principles of Sustainable Development Goal 9, which focuses on the significance of industry, innovation, and infrastructure in promoting sustainable economic growth and societal well-being, as well as advancing technological innovation and skill development [
27].
Nonetheless, the adoption of AI in recruitment in Thailand is currently not widespread, mainly due to a range of concerns. AI in recruitment faces limitations, including dependence on human-created data and algorithms, leading to potential decision uncertainty. Concerns exist about AI replicating human biases and its ability to replicate the nuanced human touch in assessing intangible qualities not visible in resumes judgment [
28]. Challenges also arise in trustworthiness, data privacy, and the replacement of human recruiters persist [
29,
30]. It is essential to consider the readiness of the Personal Data Protection Act of Thailand (PDPA) and make necessary preparations for the integration of AI. This includes incorporating AI regulations within the PDPA framework and bolstering security and privacy infrastructure [
31].
This research is aimed to explore perspectives of HR and recruitment professionals in Thailand regarding the integration of AI in the recruitment domain, acknowledging its crucial contribution to achieving sustainable success within an organization. Given the widespread applications of the Unified Theory for Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) [
32] model in numerous studies examining the acceptance of new information technology and AI-driven innovations in areas such as mobile applications, educational, and public services. It is well-regarded for its substantial capacity to explain behaviors related to new technology adoption [
33]. Thus, this study is specially tailored to construct a fresh structural model by integrating UTAUT components with additional factors that are in the context of recruitment practices in Thai companies.
The research is designed to achieve these objectives: (1) Gaining insights and analyzing the perspectives of HR and recruitment professionals in Thailand regarding the integration of AI technology in recruitment processes. (2) Examining professionals' viewpoints on AI in recruitment with the identification of influential factors related to AI use in recruitment, (3) Assessing the structural model through quantitative evaluation. and (4) Assessing of the feasibility of AI adoption in the recruitment domain.
The research structure aligns with the intended purpose and objectives, comprising
Section 2, which provides a concise literature review,
Section 3, which explains the research approach and sources of data,
Section 4, dedicated to presenting empirical findings of the structural model measurement,
Section 5 where discussion and results are presented and
Section 6, which delves into conclusion.
2. Literature Reviews
2.1. Recruitment Overview
Recruitment is a process involving a search to attract and appoint individuals to fulfill designated job roles, with the primary goal of identifying the most appropriate candidate for a specific position [
34]. The recruitment process marks the initial interaction between an employee and an employer, representing the initial stage experienced by both parties. Its main objective is to match candidates with particular roles and ensure their seamless integration into the organization [
1,
35]. From the perspective of the employee, recruitment involves matching their skills with what the organization offers, and this alignment is highly valued by candidates during the recruitment process. To stay effective, organizations must regularly adjust their recruitment strategies by monitoring market conditions and evaluating how shifting demands affect their resource requirements [
1,
2,
36].
Recruitment encompasses internal and external approaches. Internal recruitment focuses on talent development and is cost-effective due to its understanding of candidate profile [
37]. External recruitment addresses skills gaps by seeking candidates outside the organization, especially when internal candidates move to different roles, and emphasizes the importance of cultural fit to reduce turnover [
34,
38]. The usual recruitment process includes job analysis, profile creation, scheduling, interviews, testing, shortlisting, contracts, and onboarding [
39]. Traditional recruitment, as described by [
4], follows a model with four primary tasks. First, it involves identifying applicants, where job requirements and descriptions are formulated to understand the needed skills and responsibilities. The second step is attracting applicants, traditionally achieved through advertising in various media to engage potential candidates. Processing incoming applicants is the third task, which includes sorting and screening applicants and communication with the hiring team. The final step is communicating with applicants, notifying them about the next steps or rejection. Similarly according to [
40], typical recruitment's steps, include recruitment planning, strategic development, sourcing and attraction, screening, evaluation, and tracking. These steps involve identifying job vacancies, creating job descriptions with soft skill criteria, sourcing and screening candidates, shortlisting for interviews, and making the final selection [
41]. However, conventional recruitment is commonly known as in-person and paper-based, with newspapers, manual job boards, and face-to-face interactions in specific locations being the primary methods for attracting candidates [
34].
2.2. Digital Era and Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment
The digital era has brought about significant transformations in the domain of recruitment. The evolving digital technologies of the past few decades played an increasingly prominent role for both employees and Human Resource Management (HRM) [
34]. Electronic Human Resource Management involves information technology to streamline HR processes like recruitment, training, and compensation. Digital recruitment, also known as e-recruitment, uses websites and social media platforms to attract skilled job candidates and provides a cost-effective and efficient means of searching [
8,
9]. The use of online assessment is on the rise for appraising candidates, guaranteeing a selection process that takes into account both technical and interpersonal skills [
10]. Advantages of e-recruitment include wider exposure across local, national, and global markets, reduced advertising costs, 24/7 job postings, unlimited advertising content, and improved online communication [
42]. As the competition for skilled employees intensifies, automation is crucial for expediting the recruitment process [
43].
Artificial Intelligence (AI) permeates various aspects of our lives, including voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, robotics, loan and credit card processing, online banking, and social networks, offering potential improvements in efficiency and convenience well-being [
11]. In recent years, as the global economy expanded, talent recruitment became highly competitive, prompting widespread adoption of AI in the recruitment field [
17]. This integration notably improved candidate selection from a vast pool candidates [
44]. AI's capabilities include initial resume screening, identifying promising candidates and matching them with suitable positions. Virtual assistants engage candidates through various communication platforms services [
17]. AI ensures bias-free, precise job descriptions and automates the entire recruitment process from creation to onboarding, reducing the need for human involvement others [
18]. L'Oreal used AI to achieve gender balance in recruitment, employing machine learning to focus on important tasks. A chatbot, Mya, managed candidate inquiries, and AI conducted interviews and pre-screening, enhancing efficiency and reducing processing time [
45].
Leading AI recruitment platforms play vital roles in different recruitment stages. In job postings, Textio employs Natural Language Processing (NLP) to refine language, reducing bias and enhancing response rates, with organizations like Atos and McDonald's utilizing its software [
41]. Knockri, a Canadian company has developed bias-free hiring software that aims to boost diversity by employing AI and NLP technology. This software incorporates video interviews, audio assessments, and written evaluations in the recruitment process. It assesses the content of these behavioral evaluations using NLP and AI algorithms. The company's algorithm assesses a candidate's qualifications solely based on their skills, ensuring there is no discrimination [
27]. For sourcing candidates, Arya enhances talent search by efficiently sourcing candidates from over 50 social platforms while fostering interaction between candidates and recruitment teams [
46]. In the screening phase, Pomato uses machine learning and pattern recognition to shortlist candidates, and Textkernel and SAP's Resume Matcher process applications and rank applicants based on job requirements teams [
46,
47]. For candidate pre-assessment, GoBe, a recruitment chatbot, manages initial assessments, and Mya Systems streamlines the hiring process using conversational AI, benefiting organizations like L'Oréal and Deloitte. [
20,
28]. These platforms enhance recruitment sustainability, improving efficiency and objectivity.
Intense competition for talent leads to challenges in traditional recruitment processes due to time and effort requirements. Utilizing AI can improve recruitment efficiency, as seen in companies like L'Oreal, Unilever, IKEA and Amazon [
34]. Thus, with AI implementation, recruitment processes can be significantly automated, reducing the need for human involvement. AI now can handle tasks like CV screening, automated messaging, interview scheduling, and reference checks. This automation not only facilitates the swift resolution of employee inquiries but also ensures timely responses [
19]. AI-driven recruitment not only widens a company's scope but also assesses candidate-job compatibility deeply. Nvidia uses AI chips to analyze behavior and speech, aligning candidates with suitable roles. Companies like eBay, IBM, Intel, and Verizon employ AI-powered tools like Hiretual to evaluate candidates' availability, skills, and market value, comparing them against a vast database of over 700 million professional profiles from 30 web-based platforms [
48].
2.3. Technology Adoption Theories and Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT)
The Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), introduced by Icek Ajzen and Martin Fishbein in 1975, emphasizes that human behavior is influenced by the intention to engage in that behavior, which is shaped by one's attitude and subjective norms [
49]. In 1989, the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) was developed as a framework for understanding technology acceptance behavior. It builds upon the TRA, focusing on perceived usefulness (PU), perceived ease of use (PEOU), attitude, and intention to use [
50]. Expanding on TRA, Icek Ajzen introduced the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) in 1991, emphasizing that actual behavior is guided by behavioral intention, which is influenced by attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control [
51]. Thompson and colleagues introduced the Model of Personal Computer Utilization (MPCU) in 1991, modifying an existing behavior model to forecast personal computer usage based on attitudes, social norms, habits, and anticipated outcomes [
52].The Motivational Model (MM), introduced in 1992, focuses on intrinsic and extrinsic motivations as drivers of technology usage, highlighting the importance of perceived benefits and enjoyment computers [
53]. The Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT), introduced in 1995, concentrates on the spread of innovations in a social system, considering factors like the innovation-decision process, characteristics of the innovation, and characteristics of adopters [
54]. In 1999, the Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) applied Bandura's theory to study computer self-efficacy, outcome expectations, emotions, and anxiety's impact on computer use, highlighting the relationship between self-efficacy, emotions, and computer use [
55,
56].
The Unified Theory for Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) [
32], developed by Venkatesh and colleagues in 2003, integrates various technology adoption models, including the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) [
50], Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) [
49], Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) [
51], Model of PC Utilization (MPCU) [
52], Motivational Model (MM) [
53], Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) [
55,
56], and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) ) [
54]. UTAUT addresses TAM's limitations and provides insights into users' intentions to adopt technology. UTAUT comprises four key constructs including: Performance Expectancy (PE), Effort Expectancy (EE), Social Influence (SI), and Facilitating Conditions (FC) [
33].
2.4. UTAUT and Development of Influencing Factors toward the intention to use AI in Recruitment
The Unified Theory for Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) serves as the foundational structure for illustrating the technology adoption within the realms of employees, employers and managers [
32,
57]. The UTAUT model finds extensive application in various technology adoption studies. It predicts Behavioral Intention to use new technology. To adapt to the evolving AI adoption landscape, additional factors are introduced alongside the original UTAUT model, especially in Thailand's economy. The users’ intention to adopt AI integrated software in recruitment correlates with these factors:
2.4.1. Performance Expectancy
Performance Expectancy signifies the users’ perception of how using the particular system will impact their job performance at a specific. It is closely related to the concept of perceived usefulness in Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) [
32]. In the prior studies, the researchers identified a noteworthy impact of performance expectancy on behavioral intention across various areas including a study on TAM [
50] in e-HRM from Fortune Global 500 firms in Malaysia [
58], adoption of mobile Health Services in a developing country [
59] and AI based recruitment adoption among HR staffs in Bangladesh [
60]. Hence, individuals’ perception of how effective new technology, such as AI in talent recruitment, can impact their willingness to use it.
2.4.2. Effort Expectancy
When users believe that a new system simplifies tasks and requires less effort to operate, they are more inclined to embrace it. This factor assesses how user-friendly the technology is and is associated with the notion of "perceived ease of use" in TAM [
32,
52]. The theory posits that when an information system is perceived as complex and challenging to navigate, it diminishes the user's inclination to use it [
32,
61]. In a study of the Acceptance and Integration of Enterprise Resource Planning among HR professionals indicated that Effort Expectancy has a direct and noteworthy impact on the intention to use the ERP [
62]. Likewise, research conducted among human resources personnel in the Indian IT industries reveals that a favorable perception of ease of use had a positive impact on employees' willingness to embrace AI [
63,
64]. People tend to avoid using technology when they find it difficult to use. Therefore, a hypothesis can be formed that effort expectancy contributes to shaping the willingness to integrate AI into recruitment.
Furthermore, drawing from previous research on mobile payment and mobile self-checkout adoption, it was evident that effort expectancy significantly influences performance expectancy [
65,
66]. Thus, new hypotheses concerning this relationship can be formulated.
2.4.3. Social Influence
The concept of social influence in technology adoption involves how users' perceptions are influenced by their social environment, including peers, superiors, and management. Social Influence refers to how much people believe that significant individuals in their lives, such as family and friends, think they should utilize a specific technology [
32,
67]. It's noted that social influence holds a vital role in technology use across different areas including mobile technology in healthcare [
59], AI based talent acquisition in the view of job applicants [
68] and adopting ERP in the corporates [
62]. Based on the earlier research, HR and recruiting professionals can gain access to guidance, advice, and valuable information regarding AI software in recruitment, enhancing their confidence in making decisions to use the system, thereby assessing the hypothesis.
In addition to its direct influence on user intention, social influence has been identified as a factor directly affecting security [
65] and perceived value [
69] in the prior research within the realm of mobile payment adoption. It's essential to consider these factor associations.
2.4.4. Facilitating Conditions
Facilitating conditions relate to how people perceive the available resources and support for executing a specific behavior [
67]. To embrace new technology, it is essential to integrate the new technology into both the organizational and technical infrastructure of the technology itself [
62]. In a research of ERP acceptance in an organization presents that the perception of organizational support in providing necessary infrastructure increases the likelihood of the system adoption and implementation [
70]. Additionally, support in facilitating conditions plays a crucial role in the adoption of new technological systems in various domains, such as chatbot acceptance for public transport [
71], the implementation of e-commerce platforms by SMEs [
72], and the adoption of IT tools by medical doctors [
73]. Consequently, it is hypothesized that facilitating conditions can directly influence the intention of HR and recruitment specialists to use AI in talent acquisition.
2.4.5. Privacy and Security
This study primarily concentrates on informational privacy. Some people choose to limit "privacy" to specific categories of personal information. When it comes to "private" data, there are undoubtedly worries about ensuring its safety, which are referred to as "security concerns." This essentially recognizes the significance of safeguarding private information and classifies this as a security issue [
74]. Adopting modern technology in organizations entails security and privacy risks, demanding the formulation of practical policies. Senior management should balance these concerns to avoid hindering technological adoption in the name of security and privacy [
75]. Secure systems with privacy safeguards show a positive impact on technology adoption across various domains, including mobile payment [
65], mobile self-checkout [
66] and AI adoption in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) application [
75]. In Thailand, the Personal Data Protection Act of Thailand (PDPA) aims to protect personal information of both individuals and organizations, outlining regulations for “personal data processing” [
76] and the act becomes fully enforceable in June 2022 [
77]. To prepare for AI integration, Microsoft Thailand recommended integrating AI regulations into the PDPA, enhancing security and privacy infrastructure. The PDPA is poised to transform personal data protection in Thailand, mandating consent from data owners and consumers before data storage, sharing, or utilization [
31]. Through the information provided, privacy and security factor can be considered as a positive impact on the intent of HR and hiring professionals to use AI driven hiring tools.
2.4.6. Trust in Technology of AI
Trust is recognized as a valuable strategy for navigating the growing intricacies of technology, organizations, and interpersonal relationships that individuals encounter [
78]. As trust gains greater importance in shaping the adoption of emerging technologies like AI, there is a growing awareness among corporations, governments, and the general public regarding AI's potential influence [
79,
80]. This prompts a significant focus on building trustworthy AI systems. In recent years, government organizations, tech giant firms like Google and Microsoft, and professional associations such as the IEEE released guidelines emphasizing the need to design AI systems with trustworthiness as a core principle [
79]. A study on technology acceptance shows that trust is a crucial factor in encouraging the use of information systems. It indicates that the extent of trust that users place in both the information system and the technology provider significantly impacts their willingness to embrace the new system [
80]. Moreover, trust plays a critical role in shaping users' willingness to embrace emerging technologies including AI-driven CRM [
75], AI-integrated HR system [
81], sustainable mobile banking app acceptance [
82] or transportation service powered by AI chatbot [
71]. Therefore, trust in new technology as AI can be a direct impact on users’ intention to adopt the new system like AI in recruitment.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that trust was observed to directly impact both performance expectancy and effort expectancy, as evidenced by studies on the adoption of emerging technologies in various domains, including mobile payment [
65], information system [
80], and e-document authority [
83]. Therefore, it is pertinent to evaluate these connections.
2.4.7. Perceived Values
The term of perceived value, initially introduced by Dodds and Monroe [
84], centers around the balance between how customers perceive quality or benefits and what they are willing to pay or sacrifice. Perceived value involves assessing the overall usefulness by comparing the benefits gained with the sacrifices incurred [
85,
86]. A study in a journal focused on the adoption of intelligent personal assistants discovered that customers' readiness to use the product is notably affected by their perception of functional, social, and knowledge-related values [
86]. Furthermore, additional research studies identified that the perception of value has a direct impact on the willingness to embrace various forms of information technology, for instance, the acceptance of mobile payment solutions [
69] and adoption of assistance products such as smart speaker, voice assistance, home appliances [
87]. Therefore, considering the evidence presented, it is clear that perceived value plays a pivotal role in motivating users to adopt AI-integrated recruitment software.
2.4.8. Perceived Autonomy
Autonomy is crucial for human well-being and growth, defined as the ability to make self-directed choices and govern oneself. According to self-determination theory, autonomy means choices initiated by one's conscious self and informed decisions after evaluating options. A broader perspective on autonomy is vital for rebuilding trust in human-machine interactions [
88]. AI autonomy is defined as the ability of AI technology to perform tasks that originate from human actions without the need for direct human involvement. In the research of intelligent personal assistants, AI autonomy is categorized as sensing, thought and action which have a direct impact on the perception of intelligent personal assistants which also directly influences the use intention [
89]. Similarly from other studies, perceived autonomy is found to have a notable influence on the adoption of IoT [
57] and the utilization of online courses [
90]. Therefore, it is anticipated that perceived autonomy will positively affect the intention to incorporate AI into the hiring process.
2.5. Proposed Structural Model
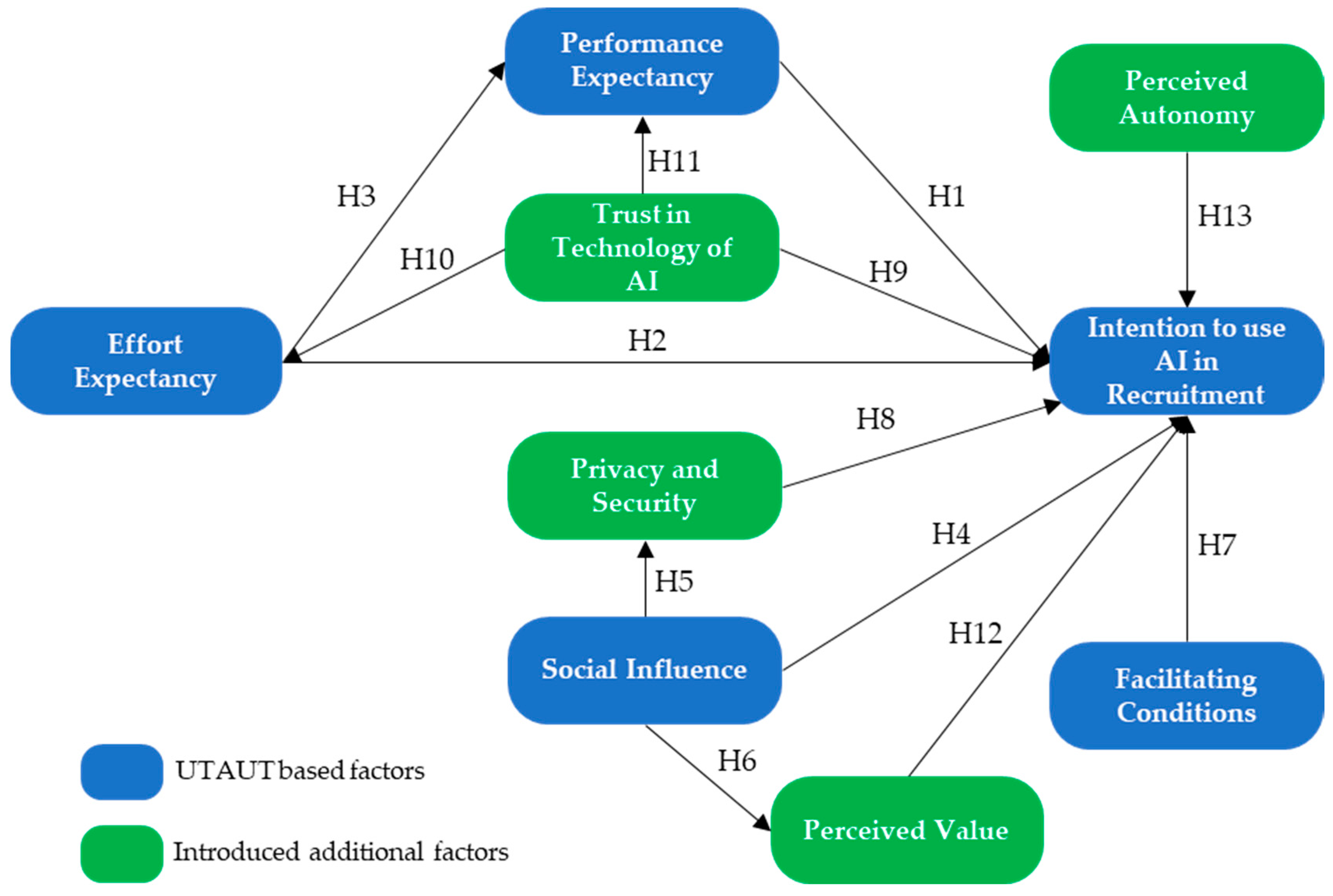
Based on prior research, the hypotheses are established and the structural model is developed as follows:
H1: Performance expectancy (PE) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H2: Effort expectancy (EE) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H3: Effort expectancy (EE) significantly affects performance expectancy (PE).
H4: Social influence (SI) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H5: Social influence (SI) significantly affects privacy and security (PS).
H6: Social influence (SI) significantly affects perceived value (PV).
H7: Facilitating conditions (FC) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H8: Privacy and security (PS) significantly affect the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H9: Trust in technology of AI (TA) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H10: Trust in technology of AI (TA) significantly affects effort expectancy (EE).
H11: Trust in technology of AI (TA) significantly affects performance expectancy (PE).
H12: Perceived value (PV) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
H13: Perceived autonomy (PA) significantly affects the user’s intention to use AI in recruitment (IU).
The structural model is depicted in
Figure 1.
3. Research Design and Methodology
The research utilized both quantitative and qualitative methods. Secondary data was initially used to develop the research model. Subsequently, in-depth interviews were conducted to validate important factors in the proposed model and enhance the questionnaire framework for an upcoming survey, aiming to ensure its suitability in the context of recruitment in Thailand.
3.1. Research Design
3.1.1. Secondary Research
The information was collected from reliable sources, including e-journals, business articles, research reports, and online news. This data acquisition marked the initial phase in enhancing researchers' comprehension of AI technology's features and its application in recruitment, as well as the motivating factors and other pertinent insights.
3.1.2. In-Dept Interviews
Twenty comprehensive interviews were conducted, involving 7 jobseekers (J1-J7), 8 HR professionals (HR1-HR8), and 5 hiring managers (HM1-HM5) across different sectors, representing diverse age groups encompassing both Generation Y and Generation Z and technological experience levels. The interviews aimed to gather insights and validation for a research model that combines elements from UTAUT with additional factors. The open-ended questions covered topics including expectations, benefits, challenges, concerns, contributing factors, and recommendations regarding AI use in recruitment. Interview findings revealed a consensus among the majority of participants, affirming the validity of critical elements in the proposed research model, as follows:
Table 1.
Comprehensive interview outcome summary.
Table 1.
Comprehensive interview outcome summary.
| No. |
Age |
Education Level |
Occupation/Position |
PE |
EE |
SI |
FC |
PS |
TA |
PV |
PA |
| J1 |
37 |
Bachelor |
Engineer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
| J2 |
32 |
PhD |
Market researcher |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| J3 |
36 |
Bachelor |
Engineer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
| J4 |
34 |
Bachelor |
Business developer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| J5 |
32 |
Master |
Data scientist |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
|
x |
|
| J6 |
36 |
Master |
Programmer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| J7 |
23 |
Bachelor |
Business analyst |
x |
x |
|
x |
x |
|
|
|
| HR1 |
23 |
Bachelor |
HR/Recruitment officer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
x |
| HR2 |
25 |
Bachelor |
HR/Recruitment officer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| HR3 |
24 |
Bachelor |
HR/Recruitment officer |
x |
x |
|
x |
|
x |
x |
|
| HR4 |
39 |
Master |
HR Manager |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| HR5 |
33 |
Master |
HR/Recruitment officer |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| HR6 |
30 |
Master |
HR generalist |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| HR7 |
40 |
Master |
People Director |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
x |
x |
|
| HR8 |
39 |
Master |
General manager - HR |
x |
x |
x |
|
x |
x |
x |
x |
| HM1 |
34 |
Master |
Business development |
x |
x |
x |
|
x |
x |
x |
|
| HM2 |
37 |
Bachelor |
Digital head |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
x |
| HM3 |
36 |
Master |
Production manager |
x |
x |
|
|
|
x |
x |
x |
| HM4 |
37 |
Master |
Head of Marketing |
x |
|
x |
x |
x |
|
|
|
| HM5 |
42 |
Bachelor |
Managing Director |
x |
x |
|
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
3.1.3. Questionnaire
The research utilizes survey questionnaire items designed with the previous literature and inputs from interview participants were to ensure its relevance to the recruitment process within Thai companies. The questionnaire, presented in the Thai language for accessibility, is structured into three primary sections. The initial part contains general inquiries, including a screening question to identify HR/recruiting roles and additional queries aimed at collecting demographic data from respondents, such as gender, age group, occupation, academic background, professional experience, business type, and organization size. The second part consists of 35 Likert-scale questions related to the eight factors influencing AI adoption in recruitment, employing a Likert scale for multi-item measurement. Respondents express their opinions on these factors using a five-point Likert scale, with 5 indicating "strongly agree," 4 representing "agree," 3 denoting "neutral," 2 indicating "disagree," and 1 signifying "strongly disagree." [
91].
3.2. Sampling Plan
The research is focused on HR and recruiting professionals in the Bangkok metropolitan area, chosen for its significance as a major economic and business center with diverse industries and a presence of both national and international companies. Surveying HR and recruiting professionals in this area provides valuable insights across various business sectors and corporate settings. Sample size determination follows guidelines from Structure Equation Modeling (SEM) [
92,
93], recommending a sample size of 5 to 10 times the total number of indicators and variables. Ensuring a minimum of 100 respondents is crucial. The research will employ a deliberate online sampling approach, distributing the survey via digital platforms such as LinkedIn and email.
Table 2.
Analysis of demographic characteristics.
Table 2.
Analysis of demographic characteristics.
| Categories |
Dimensions |
N |
% |
| Gender |
Male |
153 |
42% |
| |
Female |
211 |
58% |
| Age |
Younger than 25 years |
25 |
7% |
| |
25 - 34 years |
165 |
45% |
| |
35 - 44 years |
121 |
33% |
| |
45 - 54 years |
45 |
12% |
| |
55 years or older |
8 |
2% |
| Education Level |
Doctorate |
4 |
1% |
| |
Master’s |
148 |
41% |
| |
Bachelor’s |
212 |
58% |
| Position Level |
Officer/ Staff |
131 |
36% |
| |
Supervisor / Team Leader |
82 |
23% |
| |
Manager / Department Head |
119 |
33% |
| |
Director/ Executive |
32 |
9% |
| Work Experience |
0-3 years |
43 |
12% |
| |
3-5 years |
53 |
15% |
| |
5-10 years |
99 |
27% |
| |
10-15 years |
78 |
21% |
| |
15 years or more |
91 |
25% |
Organization Size
(# of Employees) |
Less than 25 |
13 |
4% |
| 26-50 |
43 |
12% |
| 51-200 |
93 |
26% |
| 201-500 |
78 |
21% |
| More than 500 |
137 |
38% |
| Business Sector |
Agro & Food Industry |
19 |
5% |
| |
Information Technology |
67 |
18% |
| |
Manufacturers |
57 |
16% |
| |
Medical and Healthcare |
16 |
4% |
| |
Financials |
27 |
7% |
| |
Consultancy |
36 |
10% |
| |
Services |
43 |
12% |
| |
Energy and Utilities |
27 |
7% |
| |
Consumer Products |
33 |
9% |
| |
Others |
39 |
11% |
| Do you know AI based recruitment software before? |
Yes |
299 |
82% |
| No |
65 |
18% |
| Have you ever used AI based recruitment software before? |
Yes |
110 |
30% |
| No |
254 |
70% |
| Do you think AI based recruitment can replace human? |
Yes |
128 |
35% |
| No |
236 |
65% |
| |
Total |
364 |
100% |
The sample size was calculated using the method proposed by [
92,
93], which involves multiplying the number of indicators by a factor of 5 to 10. Thus, the minimum sample size required should have been at least 35 indicators multiplied by 5, resulting in 175 respondents. The survey was conducted from July 2022 to March 2023 involving a range of participants across different gender, age, and academic qualification categories. Among the 364 valid respondents, comprising 42% men and 58% women, who were HR and recruiting professionals in the Bangkok metropolitan area, there was a diversity in professional roles, with 131 (36%) in officer positions, 119 (33%) in managerial roles, 82 (23%) in supervisory positions, and 32 (9%) directorial positions.
3.3. Data Analysis
To assess the framework model and quantify the concurrent influences among its factors, the gathered data were structured in SPSS and then subjected to analysis using the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) technique, performed with SmartPLS 4 software [
94]. Regression analysis was employed to examine the association between the independent and dependent variables. The incorporation of PLS algorithms facilitated the evaluation of the structural relationships among the model's elements and the verification of research hypotheses. Partial Least Squares (PLS) regression models are frequently used in the modeling of technology adoption and have been the subject of extensive research exploration [
57,
62,
95,
96].
4. Model Measurement
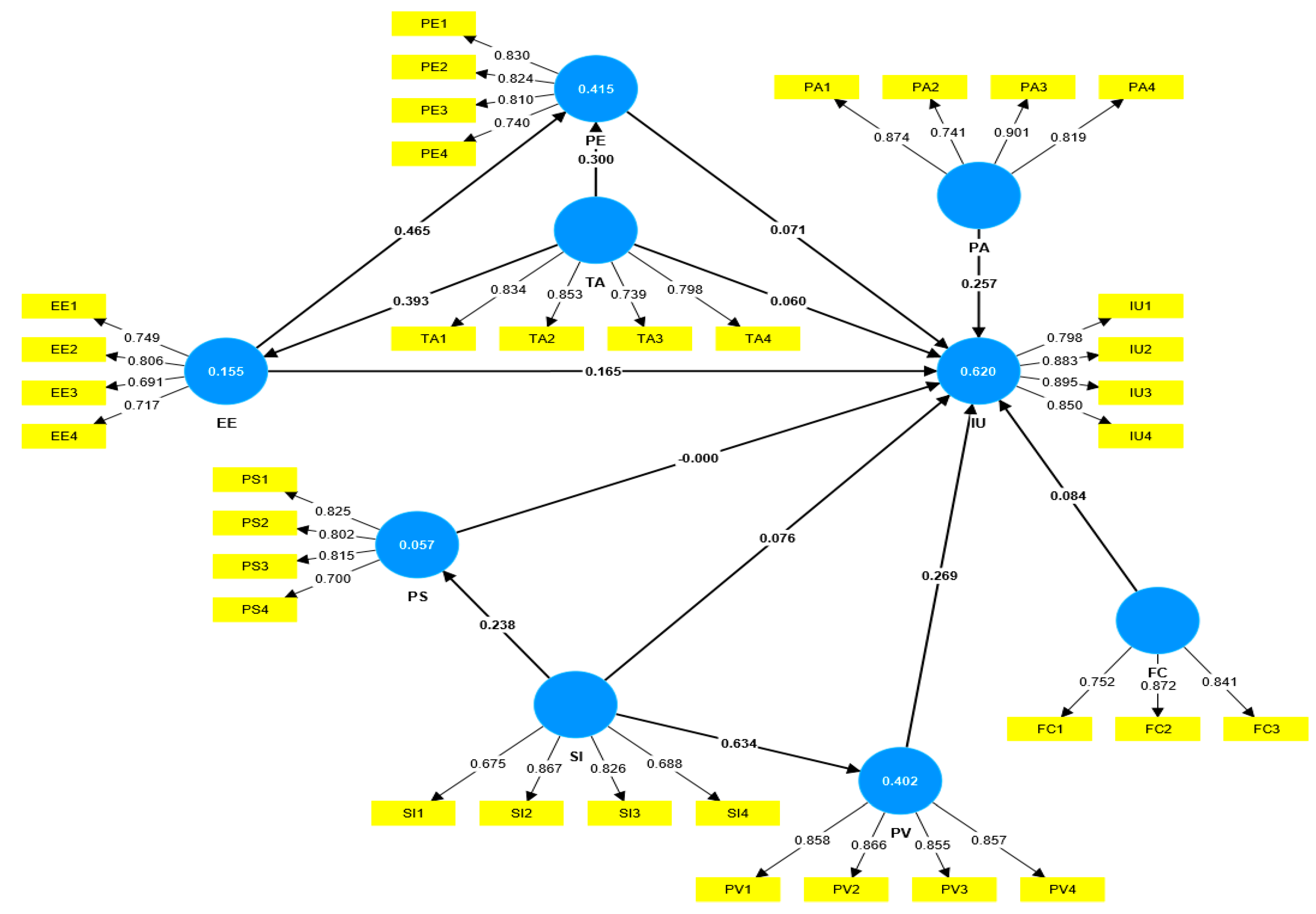
The results of employing PLS-SEM, a statistical method used for scrutinizing relationships between variables in research, are depicted in
Figure 3. This visual presentation enhances the understanding of insights and discoveries from PLS-SEM, contributing to a more profound comprehension of the study's outcomes.
4.1. Reliability and Validity
Based on the outcomes presented in
Table 3, it can be inferred that the measurement for PE, EE, SI, FC, PS, TA, PV, PA, and IU demonstrate reliability. This conclusion is drawn from the fact that the Cronbach's alpha values for each variable surpassed 0.7, indicating good for constructs validated in this study [
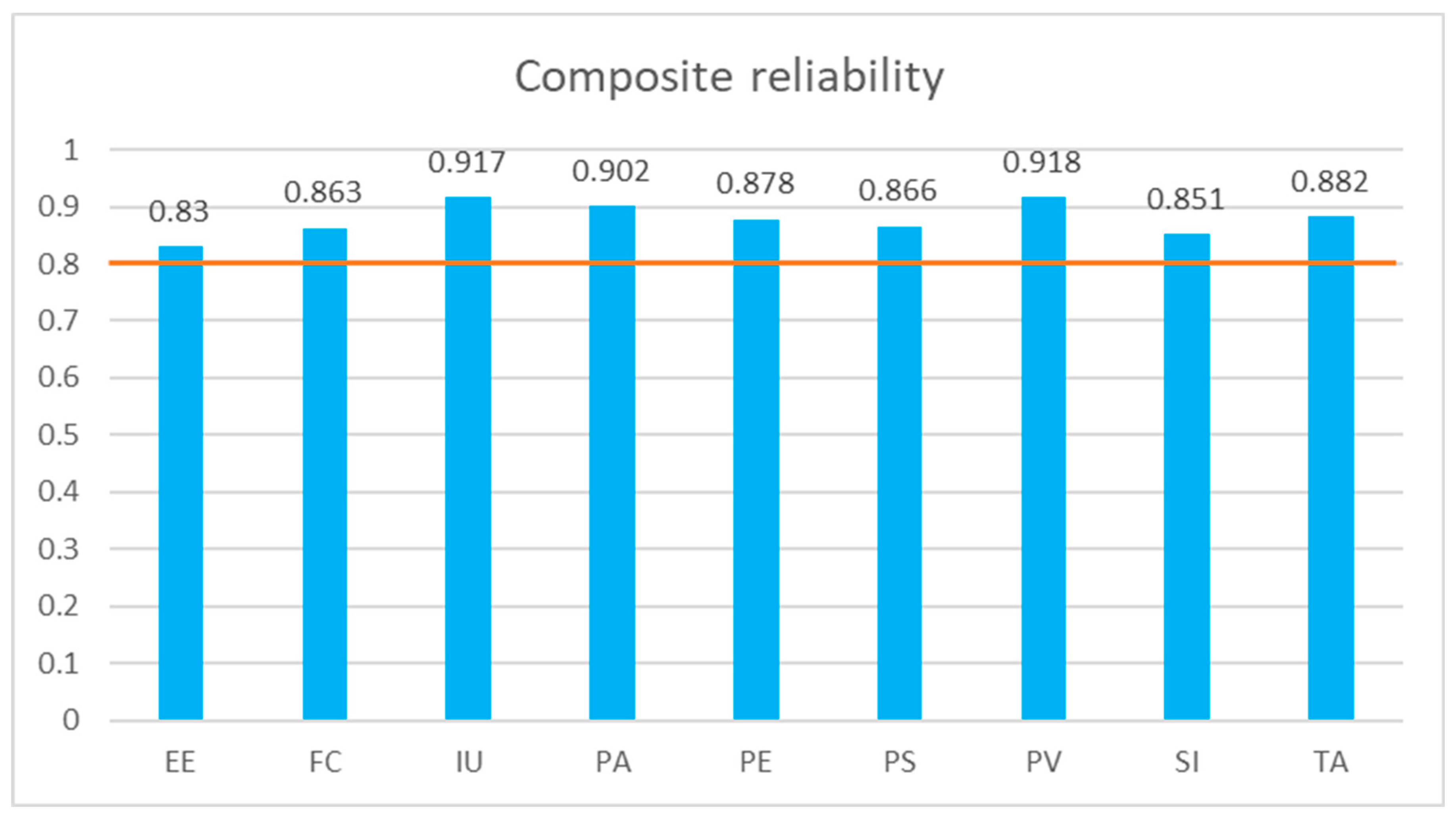
97]. The composite reliability values of each factors are greater than 0.80, which is very high for the proposed construct [
98,
99]. Therefore, the suggested model meets the requirement for construct reliability. Additionally, Average Variance Extracted (AVE) remains the preferred metric for evaluating convergent validity. The AVE values exceeding the recommended minimum threshold of 0.5 confirm the existence of convergent validity. As all AVE values surpass the 0.5 threshold, this can be concluded that the structural model meets the requirements for convergent validity [
100].
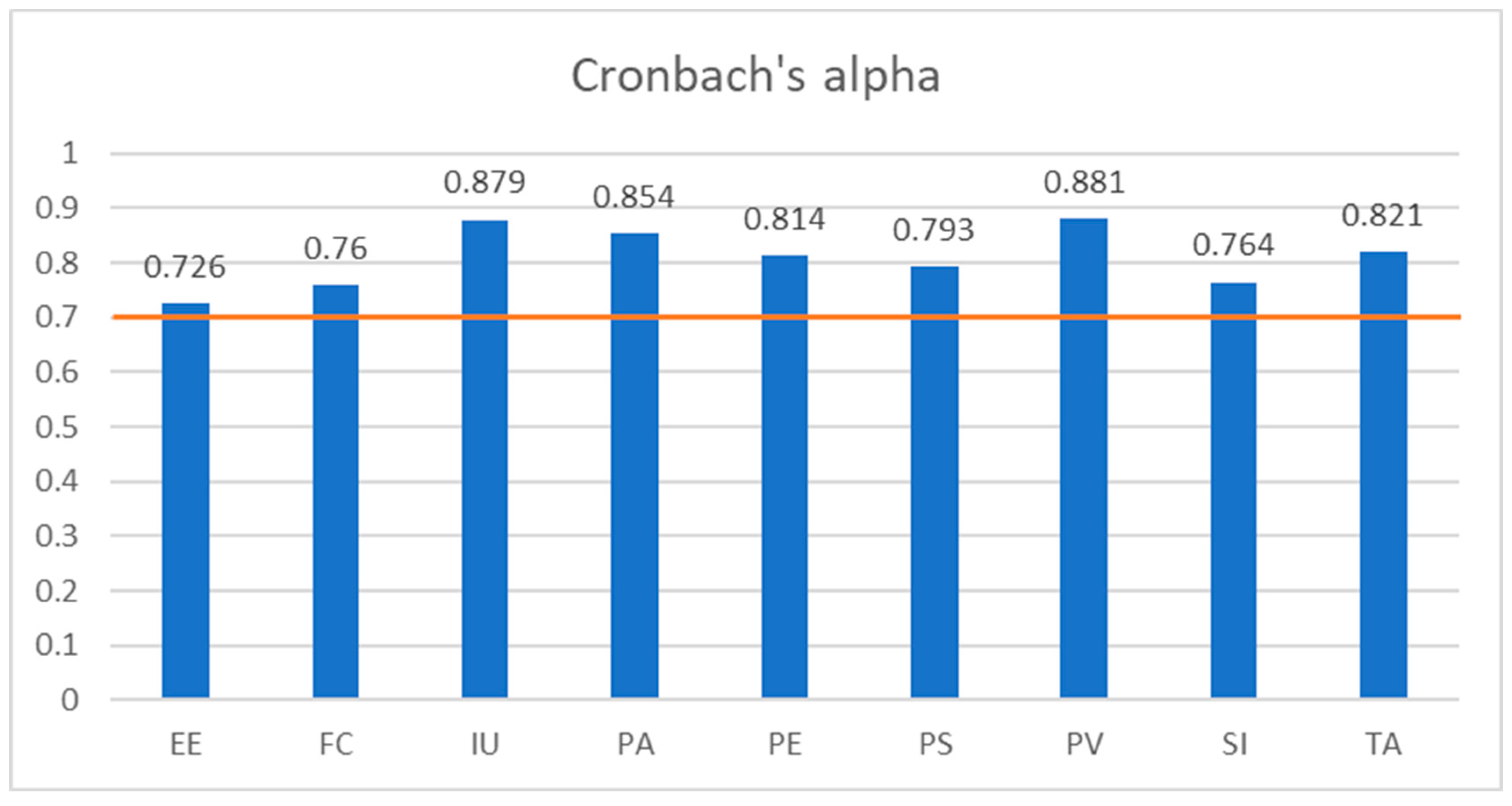
Cronbach's Alpha, which varies between 0 and 1, signifies greater reliability as its value increases. For assessing convergent validity in a construct model, it is recommended that the indicators for variables should be equal to or greater than 0.6, and with a range of 0.7 or higher is typically considered good [
97]. All factors, namely EE (0.732), FC (0.766), IU (0.884), PA (0.852), PE (0.799), PS (0.793), PV (0.882), SI (0.767), TA (0.812) were assessed at a good level as all values are above 7 (see
Figure 4). Consequently, the suggested model meets the requirement for good reliability.
In the context of the construct model under consideration, the assessment of convergent validity was conducted using the composite reliability indicator (CR), with a threshold of CR > 0.8 which is very high for the proposed construct [
98,
99]. In this research finding, the composite reliability indicator (CR) demonstrates a range of values spanning from 0.83 to 0.918 as illustrated in
Figure 5.
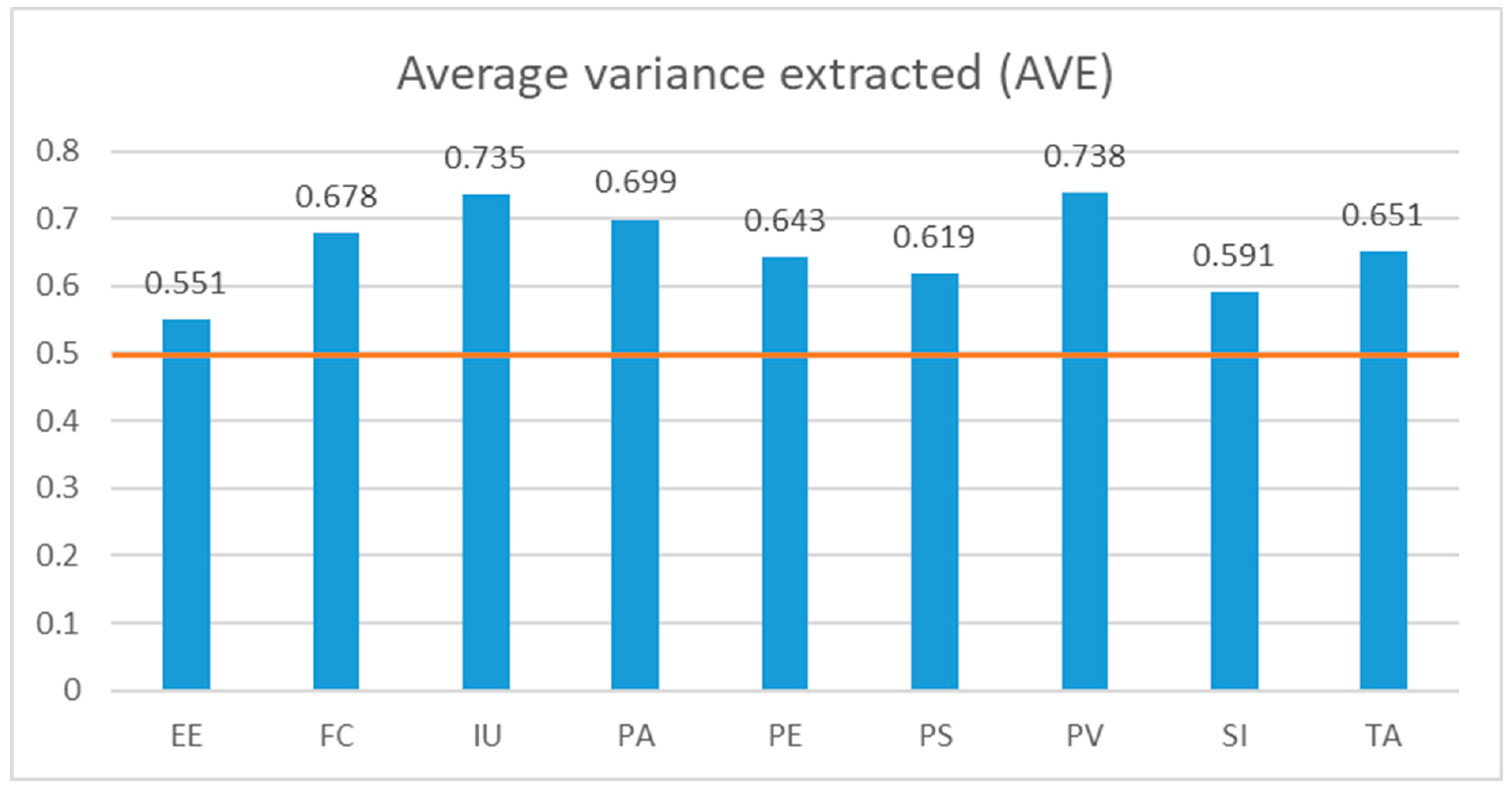
In the realm of convergent validity, it's worth noting that the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) is the recommended measure for evaluating convergent validity. When dealing with the structural models, confirming convergent validity is achieved if AVE values for factors surpass the recommended minimum threshold of 0.5 [
100]. In the structural model, the AVE falls within the range of 0.551 to 0.738, all surpassing the 0.5 threshold (as depicted in
Figure 6). Thus, the confirmation of convergent validity for the proposed construct model is affirmed.
4.2. Discriminant Validity Test
By examining
Table 4, it is evident that regarding Fornell and Larcker's criteria [
101], the constructs demonstrate discriminant validity the square root of AVE values on the diagonal for constructs exceeds the correlations between constructs [
101,
102]. The square root of the AVE for IU, measuring 0.857, surpasses both the vertical (0.694, 0.626, 0.319, 0.714, 0.598, 0.532) and horizontal (0.581, 0.372) correlation values. As a result, the construct model fulfills the condition of discriminant validity.
The standardized average residual square root (SRMR) serves as a measure of the appropriateness of the model under consideration. When the distinction between the observed correlation matrix and the anticipated correlation matrix is under 0.08 [
103], it demonstrates the model's appropriateness. In this study, the average difference (SRMR) was 0.075, which is below 0.80, the proposed model is both effective and pertinent.
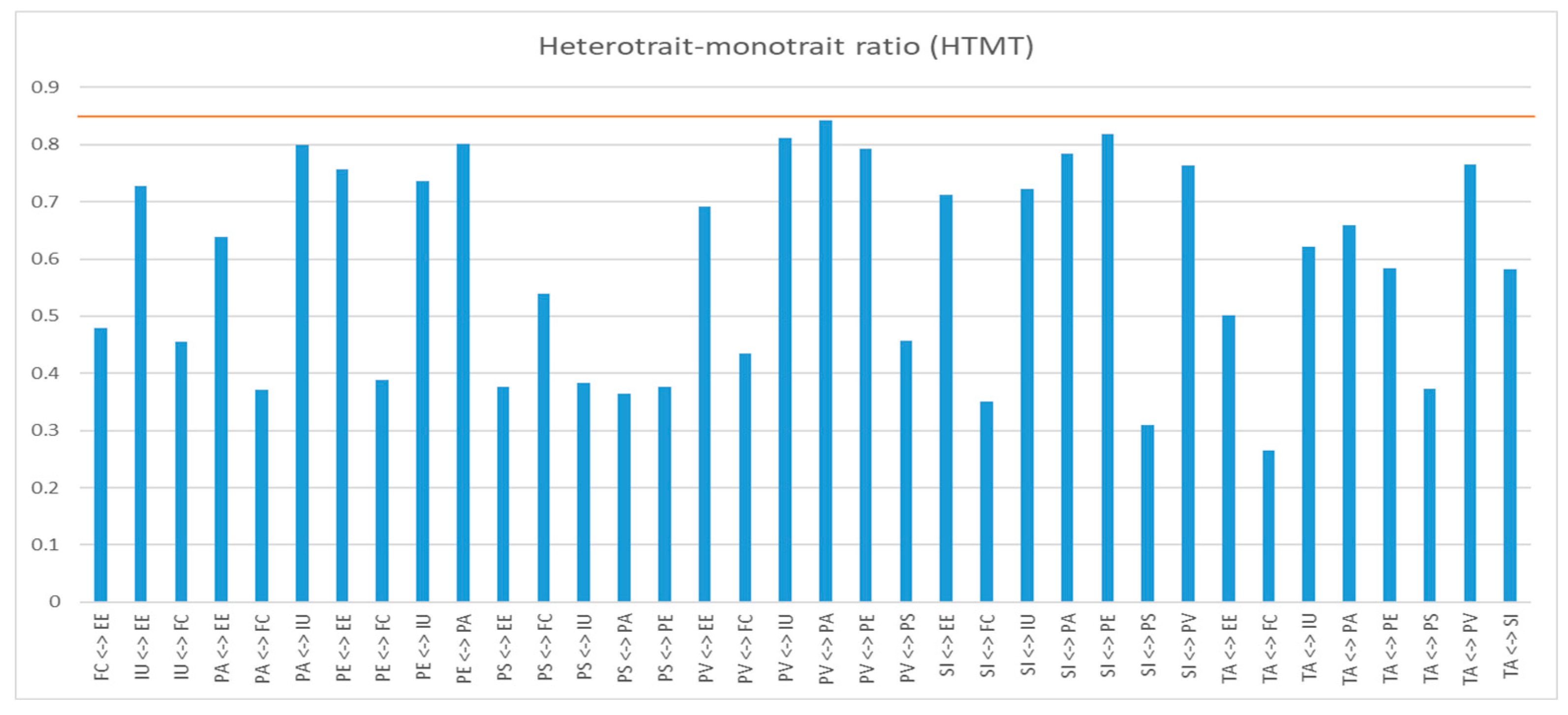
Another approach for assessing discriminant validity is by applying the Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT) criterion, which implies that the variations between correlations among different constructs should not exceed 0.85 [
104]. The variances between these correlations for the variables in the model are found to be below the 0.85 threshold as described in
Figure 7.
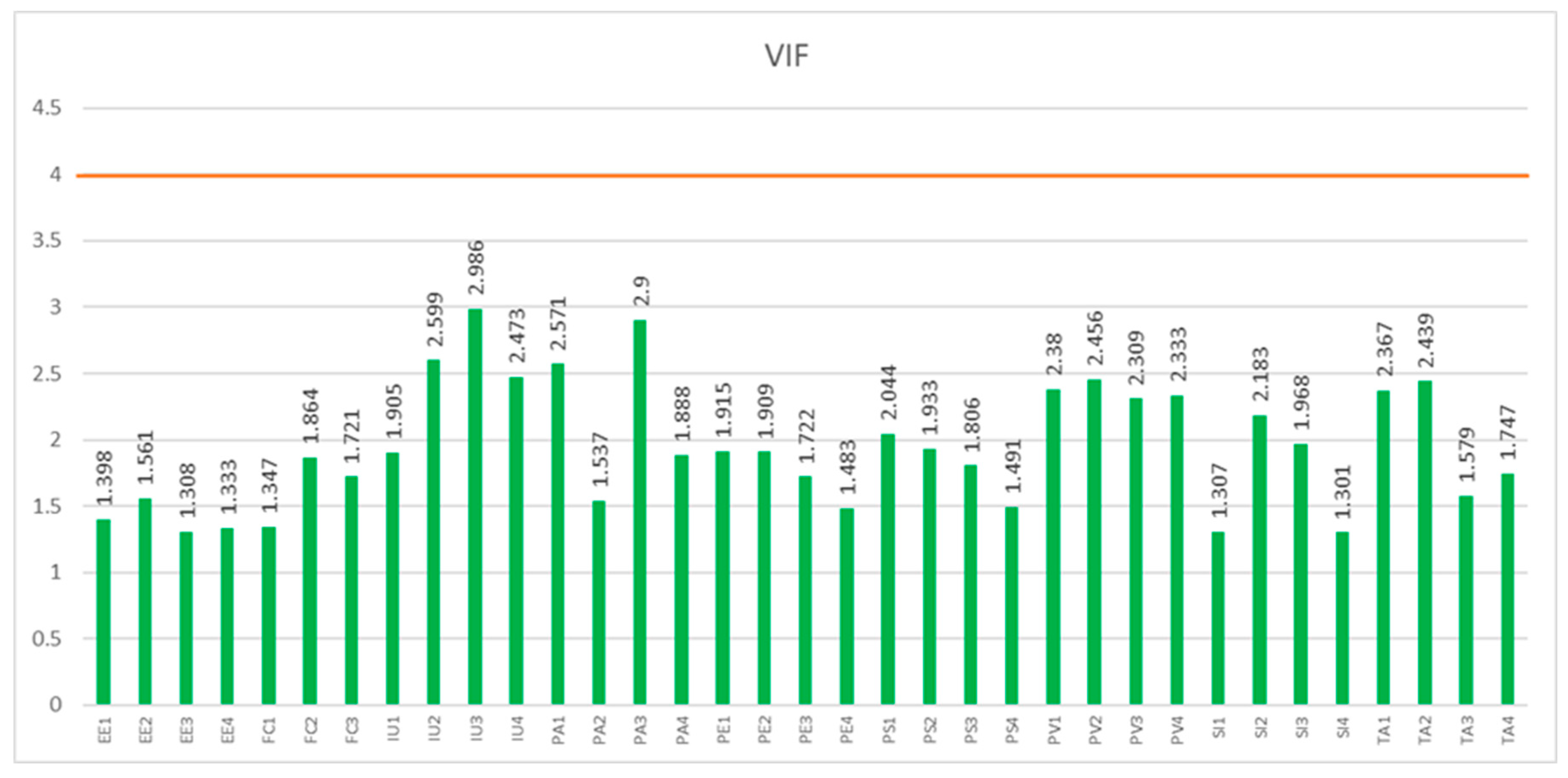
4.3. Multicollinearity Test
Multicollinearity is a situation where independent variables in a statistical model display strong correlations, potentially resulting in unreliable and unstable estimates in regression model. In the assessment of the measurement model, the final step involved the examination of both the outer and inner VIF (Variance Inflation Factor) values. Multicollinearity becomes an issue when the VIF surpasses 4.0. In the structural model, there is no concern about multicollinearity, as the VIF values for all 35 items are below the 4.0 threshold, denoted as
Figure 8 [
98]. This indicates that the variables in the model are not excessively interrelated, rendering the data suitable for further structural analysis. In
Figure 8, the highest VIF values from each element were EE2 (1.561), FC2 (1.864), IU3 (2.986), PA3 (2.9), PE2 (1.909), PS1 (2.044), PV2 (2.456), SI2 (2.183), TA2 (2.439), which are all below 4.0.
4.4. Structural Model Analysis
Table 5 displays the outcomes of correlations among construct variables, Path coefficients (β), T-Statistics, and associated
p-values. These results are obtained through the use of PLS algorithms, which enable the evaluation of structural relationships between model constructs and the testing of research hypotheses. The analysis also includes Bootstrapping and Blindfolding procedures performed within SmartPLS4, with 1000 iterations.
Table 5 presents the outcomes of hypothesis testing, revealing that hypotheses H2, H3, H5, H6, H7, H10, H11, H12, and H13 were statistically significant at the 0.01 probability level, while H7 reached significance at the 0.05 level (with provided path coefficients and p-values). In contrast, H1, H4, H8, and H9 were found to be statistically insignificant at the 0.05 significance level with
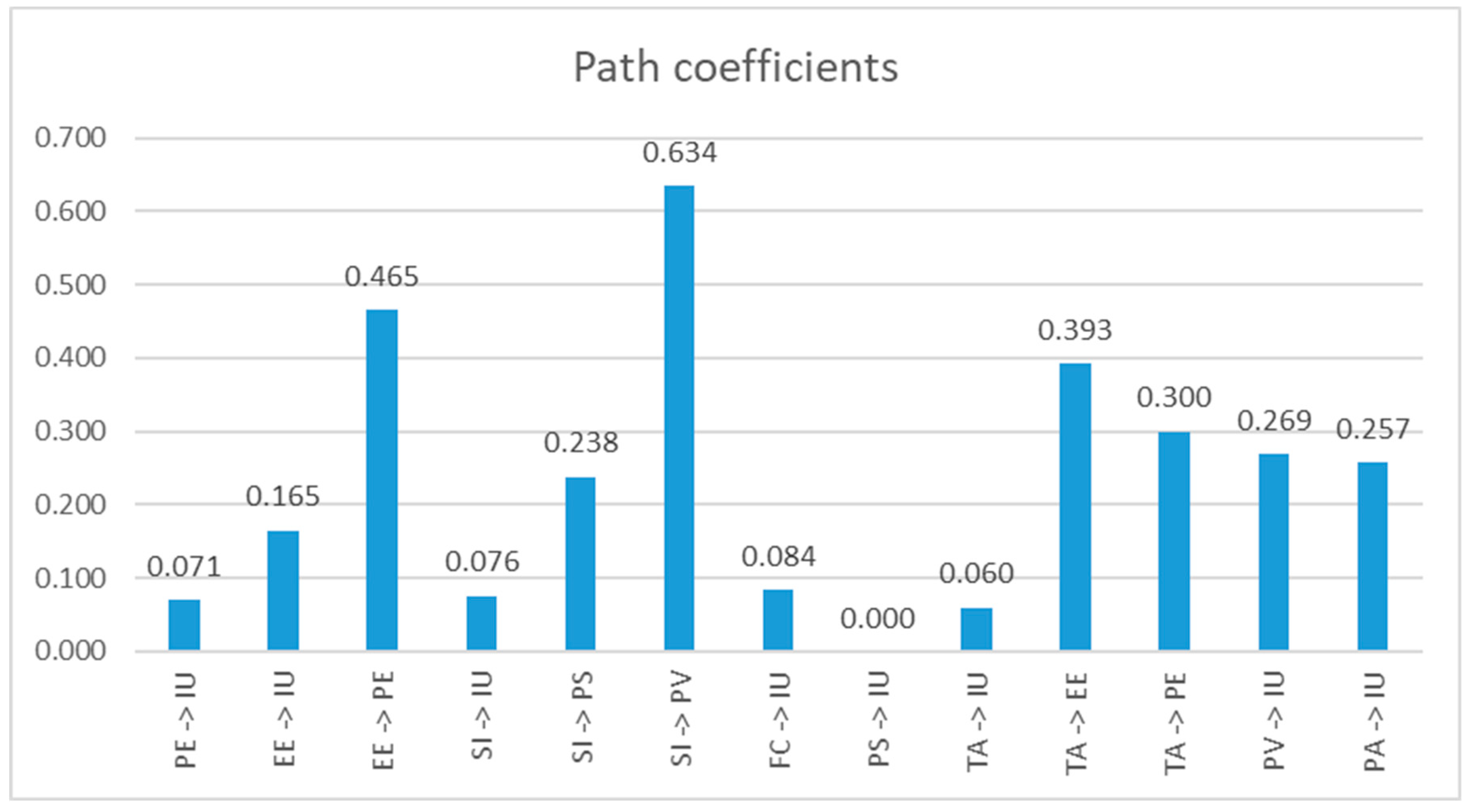
p-values of 0.287, 0.229, 0.995, and 0.201, respectively. Thus, this study supports hypotheses H2, H3, H5, H6, H7, H10, H11, H12, and H13 regarding significant and positive effects, while H1, H4, H8, and H9 do not receive support.
Path coefficients (β) reveal relationships within a structural model organization. Significantly, perceived value (PV) positively affects the intention to use AI-based recruitment software with a coefficient of 0.269. Additionally, perceived autonomy (PA) directly impacts the intention to use with a coefficient of 0.257. Positive contributions to the intention to use AI in recruitment are made by the effort expectancy (EE), which has a path coefficient of 0.165, and facilitating conditions (FC) also directly affect users' intent to accept AI-based recruitment software, with a path coefficient of 0.084.
In the case of other indirect factors, social influence (SI) significantly affects the perceived value (path coefficient of 0.634), which in turn directly influences the intention to use AI-based recruitment systems. Trust in AI technology (TA) has a positive effect on the effort expectancy (EE) with a path coefficient of 0.393. Despite the substantial influence of the effort expectancy (EE) on performance expectancy (PE), as reflected in a path coefficient of 0.465, performance expectancy (PE) does not significantly impact users' intention to adopt AI in the recruitment process.
The research also highlights the complex social influence factor, as seen in its impact on privacy and security (with a path coefficient of 0.238). This underscores the role of the social context in shaping users' perceptions of AI adoption. However, privacy and security (PS) do not have a direct effect on IU, as indicated by a coefficient of 0.00.
The overall indicator of the effect size in the structural model,
, can be categorized as "high" (
> 0.5), "moderate" (
> 0.30), or "weak" (
> 0.1) [
100]. The R-squared (
) value for Intention to Use AI-based recruitment software (IU) is impressively high at 0.620, indicating that approximately 62% of the variance is explained by all eight factors (PE, EE, SI, FC, PS, TA, PV, and PA) working in concert. Among these factors, Effort Expectancy (EE) and Trust in Technology of AI (TA) collectively contribute to around 41.5% of the variability in Performance Expectancy (PE). In the case of Perceived Value (PV), Social Influence (SI) alone significantly accounts for 40.2% of the variance in PV. The adjusted R-squared, being nearly identical to the R-squared, indicates that the added predictors have an insignificant contribution to additional explanatory value [
57]
5. Results and Discussions
This research delves into the determinants impacting the intention of HR and recruiting professionals to adopt AI integration in their recruitment procedures. To adapt to Thailand's unique AI adoption landscape, the study extended the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model, creating a new conceptual framework that includes eight independent variables. These variables comprise Performance Expectancy (PE), Effort Expectancy (EE), Social Influence (SI), Facilitating Conditions (FC) from the UTAUT model, and additional elements: Privacy and Security (PS), Trust in AI Technology (TA), Perceived Value (PV), and Perceived Autonomy (PA). A thorough survey involving 364 HR and recruiting professionals in the Bangkok metropolitan area formed the empirical foundation of this research.
Using Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), the study tested various hypotheses. The structural model accounts for 62% of the variation in the intention to adopt AI-based recruitment software, indicating that approximately 62% of the variance in this intention can be explained by the proposed model. In line with the research findings, the intention towards adoption of AI in recruitment is positively affected by variables that demonstrated statistical significance, including:
1) Perceived Value, which has a direct impact on the intention to adopt AI in recruitment, PV -> IU (β =, 0.269,
p-value = 0.000 < 0.01 confidence level), aligns with findings from Liao and colleagues [
105] about sustainable e-learning system, AI smart product acceptance studied by Sohn and Kwon [
87] and technological interface and digital payment enablers by Gupta and co-authors [
96]. Perceived Value has a substantial influence on the intention to use AI in recruitment. This means that HR professionals must perceive the advantages and benefits of AI in the recruitment process. To encourage adoption, organizations need to effectively convey and demonstrate how AI can enhance efficiency and candidate selection.
2) Perceived Autonomy positively affects the intention to embrace AI in the hiring process, PA -> IU (β =, 0.257,
p-value = 0.001 < 0.01 confidence level), in alignment with findings from Tűrkes and co-authors, [
57] about IoT adoption and the work of Khalid and colleagues regarding online learning [
90]. Perceived Autonomy directly impacts the intent to adopt AI in recruitment. This underscores the significance of granting HR and recruitment professionals the autonomy to make choices regarding AI incorporation. By allowing them to participate in the decision-making process, organizations can heighten the chances of a successful AI adoption.
3) Effort Expectancy positively contributes to shaping the inclination to embrace AI in recruitment, EE -> IU (β = 0.165,
p-value = 0.001 < 0.01 confidence level), coinciding with the research of Jena [
106] in e-banking adoption and the work of Jorge and Jaume [
107] according to chatbot adoption. In the domain of AI in hiring process, organizations and AI software developers should prioritize the ease of use, making AI tools user-friendly to minimize the effort required for HR professionals to embrace AI.
4) Facilitating conditions also directly influence the users’ intent in accepting AI based recruitment software, FC -> IU (
p-value = 0.027 < 0.05 confidence level), which is also stated by Chaveesuk and colleagues [
108] in accordance with autonomous car adoption and the paper of Menon and Shilpa [
109] with regards of ChatGPT adoption. Facilitating Conditions are essential and this finding highlights the importance of creating a supportive environment for AI integration. Organizations need to provide the necessary conditions, resources, and infrastructure to facilitate a smooth AI adoption process.
For other indirect variables, it is worth highlighting the influence of Social Influence (SI) on Perceived Value (PV), where a substantial path coefficient (β = 0.634) is observed, and the associated
p-value (0.000) indicates statistical significance at a confidence level below 0.01. This suggests that Social Influence has a clear and positive impact on Perceived Value, which, in turn, plays a direct role in shaping individuals' intentions to adopt AI-based recruitment systems, underlining the influence of colleagues in shaping how AI adoption is viewed. This relationship is consistent with the findings in the research conducted by Fatima and colleagues [
69] in their study on mobile payment.
Similarly, Trust in AI Technology (TA) is found to have a positive effect on Effort Expectancy (EE), and this relationship is statistically significant with a low
p-value (0.001) at a confidence level below 0.01. This implies that individuals' trust in AI technology directly influences their expectations regarding the ease of using AI systems. It's crucial for organizations to acknowledge the influence of these indirect factors on decisions related to AI adoption. This link is substantiated by a study conducted by Khalilzadeh and their research team in the context of mobile payment adoption [
65] in mobile payment adoption.
Furthermore, Social Influence is a crucial driver, explaining 40.2% of the variance in Perceived Value. The combined impact of Effort Expectancy (EE) and Trust in AI Technology (TA) accounts for approximately 41.5% of the fluctuations in Performance Expectancy (PE). Despite the substantial influence of the effort expectancy (EE) on performance expectancy (PE), as reflected in a path coefficient of 0.465, Performance Expectancy (PE) does not significantly impact users' intention to adopt AI in the recruitment process. Similarly, Privacy and Security (PS) do not have a direct effect on the Intention to Use AI recruitment software (IU), as indicated by a coefficient of 0.00.
Although Privacy and Security may not directly impact the intention to use AI in the hiring process, respondents exhibited strong expectations regarding safety and data privacy in AI-based recruitment. However, they were somewhat uncertain about external oversight and the honesty of AI developers. Nevertheless, it remains crucial to establish a strong foundation for privacy and security when implementing AI platforms in recruitment, in accordance with Thailand's PDPA law. This compliance is essential for both employing organizations and AI developers to ensure trust and reliability in adhering to this legislation.
6. Conclusions
This research offers practical significance for a wide range of stakeholders, including HR professionals, organizations, and AI developers. By understanding the determinants influencing the intention to adopt AI in recruitment, these stakeholders can make more informed decisions, optimize their processes, and ultimately benefit from the enhanced efficiency, improved candidate selection, and competitive advantages that AI integration can bring to the field of HR recruitment.
HR and Recruiting Professionals: This report serves as a valuable resource for HR and recruiting professionals in Thailand and beyond. It provides them with a deeper understanding of the factors influencing their peers' intentions to embrace AI in recruitment. By leveraging the insights from this study, HR practitioners can make informed decisions about integrating AI technology into their recruitment processes. They can focus on enhancing user-friendliness, providing necessary support. This knowledge empowers them to optimize their recruitment procedures, expedite processes, and increase efficiency while maintaining the quality of their candidate selection.
Organizations: For companies and organizations looking to stay competitive and efficient in the recruitment process, this research provides practical guidance. The study highlights the importance of user-friendliness (Effort Expectancy), the influence of colleagues (Social Influence), and the perceived value of AI integration. Organizations can use these findings to design and implement AI-based recruitment solutions that are more likely to be accepted and accepted by HR and recruiting teams. By addressing concerns related to AI, organizations can foster trust among their employees.
AI Developers: Developers and technology providers specializing in AI-based recruitment tools can gain valuable insights from this research. They can use the information to enhance the user-friendliness of their products, address privacy and security concerns in accordance with Thailand’s PDPA law, and build trust with HR and recruiting professionals. By aligning their products with the factors identified as significant in this study, AI developers can better meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
This research, while providing valuable insights, is not exempt from its limitations. One noteworthy constraint is that only 30% of the surveyed individuals had hands-on experience with AI-based recruitment software, and in general the majority of HR and recruiting professionals do not possess extensive expertise in the domain of AI or sophisticated IT. Future research should aim to bridge this gap by either offering education in the application of AI specifically in recruitment or by involving individuals with practical experience and expertise in utilizing such technology. These will shed light on the motivations and impediments that influence professionals when transitioning to AI-based recruitment tools. Furthermore, it is important to recognize that UTAUT has its own set of limitations, like other theories. UTAUT was initially designed to explain the adoption of general information technology, which may not effectively address the distinct characteristics and challenges specific to AI. To address this, future research should be conducted after AI implementation in a variety of organizational settings. This approach will allow researchers to identify more specific factors related to AI's distinct use cases, leading to the development of a more practical and tailored conceptual model.
Author Contributions
Framework design, P.W. and T.T.; methodology, P.W. and T.T; formal analysis, P.W. and T.T; writing—original draft preparation, P.W.; writing—review and editing, T.T. and P.W.; Supervision, T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Thammasat Research Unit in Data Innovation and Artificial Intelligence.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Table A1.
Constructs and Measurement Items.
Table A1.
Constructs and Measurement Items.
| Construct |
Measurement item |
Source |
| Performance Expectancy |
PE1: I think AI is useful in recruitment |
[32,60] |
| PE2: I think that AI will make recruitment process faster |
[32,60] |
| PE3: I think AI can increase efficiency of recruitment work |
[32,60] |
| PE4: I think using AI can help analyze candidates more accurately |
[32,60,61] |
Effort
Expectancy |
EE1: I would find the AI based recruitment software easy to use |
[32,60] |
| EE2: I think it would be easy to learn how to use the interface of AI based recruitment software |
[32,60] |
| EE3: For me, it will not take long to be skillful in using AI in recruitment |
[32,60] |
| EE4: I think AI in recruitment would be flexible for use. |
[32,60] |
Social
Influence |
SI1: My decision to use AI in recruitment would be based on proportion of coworkers who use the software or system |
[32,60,61] |
| SI2: Those who use AI in recruitment would have more advantages than those who do not |
[32,60,61] |
| SI3: With the rapid technology trend, AI integrated in recruitment is necessary for my company |
[32,60,61] |
| SI4: I think the introduction of AI in recruitment into our company will be trendy in my industry |
[32,60,61] |
Facilitating
Conditions |
FC1: I expect to call a technical support team in case of facing any problems |
[32,60,61] |
| FC2: I expect that the system would be available in both computer and mobile devices |
[32,60,61] |
| FC3: I think guidance would be available in AI based recruitment system |
[32,60,61] |
| Privacy and Security |
PS1: I expect that AI based recruitment software will be safe and secure |
[57] |
| PS2: I expect AI based recruitment software will strictly comply data privacy policy regarding Personal Data Protection Act |
[57] |
| PS3: I feel safe and protected by the use of encryption |
[57] |
| PS4: I think AI software developer will protect and ensure safety of users' personal data. |
[57] |
| Trust in Technology of AI |
TA1: I trust that AI algorithm is reliable in screening candidates to match organization's requirement |
[79,82,110] |
| TA2: I trust that AI based recruitment software has reliable database to complete recruitment |
[110] |
| TA3: I think there will be a government organization to ensure AI based recruitment software is secured |
[79,82] |
| TA4: I trust that AI software developer is honest and will not take advantage over user's information |
[79] |
Perceived
Value |
PV1: I think that using AI in recruitment is worth investing |
[86] |
| PV2: I feel that using AI can remain quality of recruitment process consistently. |
[86] |
| PV3: I realize that using AI in recruitment will give the organization the social approve |
[86] |
| PV4: I feel that using AI in recruitment will make impression on candidates |
[86] |
Perceived
Autonomy |
PA1: Using AI in recruitment will allow recruiters/ HR officers to have more freedom to develop preferred skills and tasks |
[57] |
| PA2: Using AI will give recruiters/ HR officers the opportunity to better coordinate with candidates |
[57] |
| PA3: Utilizing AI will provide recruiters and HR officers with more flexibility to manage other essential responsibilities more effectively |
[57] |
| PA4: I think AI in recruitment will reduce the number of decisions to get the optimal results |
[57] |
| Intention to Use |
IU1: Using AI based recruitment software is a good and modern idea |
[50] |
| IU2: I like the idea of using AI in recruitment |
[32] |
| IU3: The AI based recruitment software makes me more interested |
[8] |
| IU4: I have a high wiliness to use AI in recruitment |
[61] |
References
- Saroj Bandi, G.N.; Kumar, D.G.P. A STUDY ON RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION PRACTICES - A THEORETICAL APPROACH. IJRDO J. Bus. Manag. 2017, 3, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Nanor, A.; Owusu, E.; Senyah, M.M.; Owusu, E.K.O.; Agyei, S.K. Recruitment and Selection Policies and Procedures and Their Effects on Organizational Performance: A Case Study. Tech. Soc. Sci. J. 2022, 35, 405–417. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, D.S.; Webster, J. The Use of Technologies in the Recruiting, Screening, and Selection Processes for Job Candidates. Int. J. Sel. Assess. 2003, 11, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.B. E-recruitment: Towards an Ubiquitous Recruitment Process and Candidate Relationship Management. Ger. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, D. HRM in the Organization: An Overview. In Management Science: Foundations and Innovations, Machado, C., Davim, J.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 75–110. [Google Scholar]
-
Talent Trends 2022 Michael Page The Great X Report Thailand 2022.
- Jatoba, M.; Gutierriz, I.; Fernandes, P.O.; Teixeira, J.P.; Moscon, D. ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN THE RECRUITMENT & SELECTION: INNOVATION AND IMPACTS FOR THE HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT. 2019, 96-104.
- Johnson, R.D.; Stone, D.L.; Lukaszewski, K.M. The benefits of eHRM and AI for talent acquisition. J. Tour. Futures 2021, 7, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamija, P. E-RECRUITMENT: A ROADMAP TOWARDS E- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT. Res. World 2012, 3, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- van Esch, P.; Black, J.S.; Ferolie, J. Marketing AI recruitment: The next phase in job application and selection. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 90, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, V.; Sharma, Y.; Burate, M.; Prof, A.; Jagdishprasad, S.; Tibrewala, J. Application in Artificial Intelligence. 2021.
- Kamalov, F.; Santandreu Calonge, D.; Gurrib, I. New Era of Artificial Intelligence in Education: Towards a Sustainable Multifaceted Revolution. Sustainability 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kuwaiti, A.; Nazer, K.; Al-Reedy, A.; Al-Shehri, S.; Al-Muhanna, A.; Subbarayalu, A.V.; Al Muhanna, D.; Al-Muhanna, F.A. A Review of the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanantong, T.; Nantajeewarawat, E.; Thiemjarus, S. False Alarm Reduction in BSN-Based Cardiac Monitoring Using Signal Quality and Activity Type Information. Sensors 2015, 15, 3952–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.T. Five Ways AI Is Disrupting Human Resources Management. 2021.
- Nidhi, O.; Majdi, K.; Ayman, A. RECRUITMENT IN THE ERA OF INDUSTRY 4.0: USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN RECRUITMENT AND ITS IMPACT. PalArch's J. Archaeol. Egypt / Egyptol. 2020, 17, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Khandelwal, K. Applying artificial intelligence: implications for recruitment. Strateg. HR Rev. 2018, 17, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rąb-Kettler, K.; Lehnervp, B. Recruitment in the Times of Machine Learning. Manag. Syst. Prod. Eng. 2019, 27, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Gankar, S.S. "Impact of HR automation in employee experience within the Manufacturing sector at Pune". Turk. Online J. Qual. Inq. 2021, 12, 10408–10413. [Google Scholar]
- Trziszka, M. Artificial intelligence in employee recruitment. Eur. Conf. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 24, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendra, P.; Satish, Y.; Singh, P. Changing Landscape of Recruitment Industry: A Study on the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Eliminating Hiring Bias from Recruitment and Selection Process. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2020, 17, 4404–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, M.H. Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Work: Human-AI Symbiosis in Organizational Decision Making. Bus. Horiz. 2018, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Pimdee, P. Innovative ideas: Thailand 4.0 and the fourth industrial revolution. Asian Int. J. Soc. Sci. 2017, 17, 4–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puriwat, W.; Tripopsakul, S. Preparing for Industry 4.0 – Will youths have enough essential skills?: An Evidence from Thailand. Int. J. Instr. 2020, 13, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanthuwongpakdee, N.; Intaprasert, P.; Gongkaew, C.; Bunnag, C.; Wichachai, S.; Soontornthum, T. Localizing SDGs in Thailand: Towards a More Inclusive National Science, Research, and Innovation (SRI) Plan. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, D.F. Economic Growth, Full Employment and Decent Work: The Means and Ends in SDG 8. Int. J. Hum. Rights 2017, 21, 1164–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küfeoğlu, S. SDG-9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure. In Emerging Technologies: Value Creation for Sustainable Development, Küfeoğlu, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 349–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wan Ibrahim, W.M.R.; Hassan, R. RECRUITMENT TRENDS IN THE ERA OF INDUSTRY 4.0 USING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: PRO AND CONS. 2019, 1, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hemalatha, A.; Kumari, P.B.; Nawaz, N.; Gajenderan, V. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Recruitment and Selection of Information Technology Companies. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS), 25-27 March 2021, 2021; pp. 60–66.
- Ore, O.; Sposato, M. Opportunities and risks of artificial intelligence in recruitment and selection. Int. J. Organ. Anal. [CrossRef]
- LEESA-NGUANSUK, S. Microsoft advises AI regulation under Personal Data Protection Act. Bangkok Post 16 May 2019 2019.
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byoung-Chol, L.; Bo-Young, K. A Decision-Making Model for Adopting an Al-Generated Recruitment Interview System. Int. J. Manag. 2021, 12, 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- Lisa, A.K.; Talla Simo, V.R. An in-depth study on the stages of AI in recruitment process of HRM and attitudes of recruiters and recruitees towards AI in Sweden. Student thesis, 2021.
- Mishra, S.; Kumar, S.P. E-recruitment and training comprehensiveness: untapped antecedents of employer branding. Ind. Commer. Train. 2019, 51, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, N.A.; Dean, D.; Cohen, D. Employee Job Search Motivation Factors: An evidence from Electricity Provider Company in Malaysia. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCenzo, D.A.; Robbins, S.P.; Verhulst, S.L. Human resource management, 11th ed. ed.; John Wiley & Sons Singapore: 2013.
- Yaseen, A. Recruitment and selection process of higher education sector and its impact on organizational outcomes. 2016 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzani, A.; Caputo, A.; Cortese, C.G. An analysis of the literature about the application of Artificial Intelligence to the Recruitment and Personnel Selection. BPA - Appl. Psychol. Bull. (Boll. Di Psicol. Appl. ) 2020, 68, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrin, M.; Kettley, P. e-Recruitment: Is it Delivering ? 2003.
- Oswal, N.; Ateeq, K.; Mathew, S. Trends in Recruitment Information and Communication System using Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business, 2021.
- Plessis, A.; Frederick, H. Effectiveness of e-recruiting: empirical evidence from the Rosebank business cluster in Auckland, New Zealand. 2012.
- Savola, H.; Troqe, B. Recruiters just wanna have...AI? : Implications of implementing AI in HR recruitment. Student thesis, 2019.
- Sekhri, A.; Cheema, J. The new era of HRM: AI reinventing HRM. Int. J. Sci. Res. Rev. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Anushree, S. How AI reinvented hiring practice at L’Oréal. Available online: https://www.peoplematters.in/article/technology/how-the-worlds-largest-cosmetic-company-transformed-its-hiring-practice-with-ai-19006 (accessed on.
- Vishwanadh, R. 30 AI-driven Tools to Optimize Your Talent Acquisition Process. Available online: https://www.aihr.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-talent-acquisition/ (accessed on.
- Fraij, J.; Várallyai, L. literature Review: Artificial Intelligence Impact on the Recruitment Process. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2021, 6, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- van Esch, P.; Black, J.S. Factors that influence new generation candidates to engage with and complete digital, AI-enabled recruiting. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Belief, attitude, intention and behaviour: An introduction to theory and research; 1975; Volume 27.
- Davis, F.D. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.L.; Higgins, C.A.; Howell, J.M. Personal Computing: Toward a Conceptual Model of Utilization. MIS Q. 1991, 15, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D.; Bagozzi, R.P.; Warshaw, P.R. Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivation to Use Computers in the Workplace1. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 22, 1111–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations: Modifications of a Model for Telecommunications. In Die Diffusion von Innovationen in der Telekommunikation, Stoetzer, M.-W., Mahler, A., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1995; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan, C.J. Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory, Albert Bandura Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1986, xiii + 617 pp. Hardback. US$39.50. Behav. Change 1988, 5, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compeau, D.; Higgins, C.A.; Huff, S. Social Cognitive Theory and Individual Reactions to Computing Technology: A Longitudinal Study. MIS Q. 1999, 23, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tűrkeș, M.C.; Căpușneanu, S.; Topor, D.I.; Staraș, A.I.; Hint, M.Ș.; Stoenica, L.F. Motivations for the Use of IoT Solutions by Company Managers in the Digital Age: A Romanian Case. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahreki, J.; Jamaluddin, H.; Lim, A.; Chin, L.; Hashemi, S.; Nakanishi, H. An Examination on the Effects of Technology Acceptance Model in Electronic Human Resource Management. 2020.
- Alam, M.Z.; Hoque, M.R.; Hu, W.; Barua, Z. Factors influencing the adoption of mHealth services in a developing country: A patient-centric study. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Uz-Zaman Khan, T.; Sutra Dhar, S.; Munira, K. HR Professionals’ Intention to Adopt and Use of Artificial Intelligence in Recruiting Talents. Bus. Perspect. Rev. 2020, 2, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.; Tai, H.-W.; Chang, C.-A. The willingness to adopt the Internet of Things (IoT) conception in Taiwan’s construction industry. JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT 2020, 26, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.A.; Alam, M.S.; Mamun, A.A.; Khan, T.-U.-Z.; Akter, A. A Study of the Adoption and Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Identification of Moderators and Mediator. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Bhardwaj, G.; Singh, S.V.; Kumar, V. Technology Acceptance Model to Assess Employee's Perception and Intention of Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Human Resource Management in IT Industry. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, volume 29.3, 11485–11490. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, G.; Singh, S.V.; Kumar, V. An Empirical Study of Artificial Intelligence and its Impact on Human Resource Functions. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computation, Automation and Knowledge Management (ICCAKM), 9-10 Jan. 2020, 2020; pp. 47–51.
- Khalilzadeh, J.; Ozturk, A.B.; Bilgihan, A. Security-related factors in extended UTAUT model for NFC based mobile payment in the restaurant industry. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 70, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.L.; Woolridge, R.W.; Wang, W.; Bell, J.R. The Impact of Perceived Privacy, Accuracy and Security on the Adoption of Mobile Self-Checkout Systems. J. Innov. Econ. Manag. 2020, 31, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.; Xu, X. Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochmann, J.; Laumer, S. AI Recruitment: Explaining job seekers' acceptance of automation in human resource management; 2020.
- Fatima, T.; Kashif, S.; Kamran, M.; Awan, T. Examining Factors Influencing Adoption of M-Payment: Extending UTAUT2 with Perceived Value. 2021.
- Alam, M.; Uddin, M. Adoption and Implementation of ERP Adoption and Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): An Empirical Study. J. Manag. Res. 2019, 6, 84–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kuberkar, S.; Singhal, T.K. Factors Influencing Adoption Intention of AI Powered Chatbot for Public Transport Services within a Smart City. 2020.
- Sombultawee, K. Antecedents and consequences of e-commerce adoption for SMEs. Kasetsart J. Soc. Sci. 2020, 41, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinaswamy, J.; Sengottaiyan, K.; Duraisamy, B. A QUALITATIVE APPROACH TOWARDS ADOPTION OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY BY MEDICAL DOCTORS APPLYING UTAUT MODEL. Xi'an Jianzhu Keji Daxue Xuebao/J. Xi'an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2020, 12, 4689–4703. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, D.; Soifer, E. AI Technologies, Privacy, and Security. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 826737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Chaudhuri, R.; Chaudhuri, S. Adoption of AI-integrated CRM system by Indian industry: from security and privacy perspective. Inf. Comput. Secur. 2021, 29, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisadikoon, K. A STUDY OF THE NECESSITY OF AND APPROACHES TO THE PREPARATION OF PERSONAL DATA PROTECTION GUIDELINES. TDRI Q. Rev. 2022, 37, 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- Trisadikoon, K. Personal Data at Risk in Govt Hands. Available online: https://tdri.or.th/en/2022/08/personal-data-at-risk-in-govt-hands/ (accessed on.
- Lee, J.D.; See, K.A. Trust in Automation: Designing for Appropriate Reliance. Hum. Factors 2004, 46, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, H.; David, P.; Ross, A. Trust in AI and Its Role in the Acceptance of AI Technologies; 2022; Volume 39.
- Söllner, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Leimeister, J.M. Why different trust relationships matter for information systems users. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2016, 25, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmoud, B.; Várallyai, L. Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Information Systems: Investigating its Trust and Adoption Determinants. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2020, 5, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavus, N.; Mohammed, Y.B.; Yakubu, M.N. An Artificial Intelligence-Based Model for Prediction of Parameters Affecting Sustainable Growth of Mobile Banking Apps. Sustainability 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, j.-h.; Song, C.-H. Effects of trust and perceived risk on user acceptance of a new technology service. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2013, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.B.; Monroe, K.B.; Grewal, D. Effects of Price, Brand, and Store Information on Buyers' Product Evaluations. J. Mark. Res. 1991, 28, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A. Consumer Perceptions of Price, Quality, and Value: A Means-End Model and Synthesis of Evidence. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-C. Analyzing Determinants for Adoption of Intelligent Personal Assistant: An Empirical Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.; Kwon, O. Technology Acceptance Theories and Factors Influencing Artificial Intelligence-based Intelligent Products; 2020; p. 101324.
- Sankaran, S.; Zhang, C.; Aarts, H.; Markopoulos, P. Exploring Peoples' Perception of Autonomy and Reactance in Everyday AI Interactions. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Gong, Y.; Yang, Z. Can AI artifacts influence human cognition? The effects of artificial autonomy in intelligent personal assistants. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, B.; Lis, M.; Chaiyasoonthorn, W.; Chaveesuk, S. Factors influencing behavioural intention to use MOOCs. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2021, 13, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5-Point Likert Scale. Handbook of Disease Burdens and Quality of Life Measures, Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2010; pp. 4288–4288. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.; Black, W.; Babin, B.; Anderson, R. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; 2010.
- Kline, R.; St, C. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; 2022.
- Ringle, C.M., Wende, Sven, & Becker, Jan-Michael. SmartPLS 4. Available online: https://www.smartpls.com (accessed on.
- Căpușneanu, S.; Mateș, D.; Tűrkeș, M.C.; Barbu, C.-M.; Staraș, A.-I.; Topor, D.I.; Stoenică, L.; Fűlöp, M.T. The Impact of Force Factors on the Benefits of Digital Transformation in Romania. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kiran, R.; Sharma, R.K. Embedding Technology Interface and Digital Payment Drivers in the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 Model: Transforming Behavioral Intention to Sustained Intention. Sustainability 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L. Starting at the Beginning: An Introduction to Coefficient Alpha and Internal Consistency. J. Personal. Assess. 2003, 80, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henseler, J.; Sarstedt, M. Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Comput. Stat. 2013, 28, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Straub, D.W. Editor's Comments: A Critical Look at the Use of PLS-SEM in "MIS Quarterly". MIS Q. 2012, 36, iii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M. A review of recent approaches for capturing heterogeneity in partial least squares path modelling. J. Model. Manag. 2008, 3, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J. On the convergence of the partial least squares path modeling algorithm. Comput. Stat. 2010, 25, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.t.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-K.; Wu, W.-Y.; Le, T.Q.; Phung, T.T. The Integration of the Technology Acceptance Model and Value-Based Adoption Model to Study the Adoption of E-Learning: The Moderating Role of e-WOM. Sustainability 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R. Factors Impacting Senior Citizens’ Adoption of E-Banking Post COVID-19 Pandemic: An Empirical Study from India. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrés-Sánchez, J.; Gené-Albesa, J. Explaining Policyholders’ Chatbot Acceptance with an Unified Technology Acceptance and Use of Technology-Based Model. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2023, 18, 1217–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaveesuk, S.; Chaiyasoonthorn, W.; Kamales, N.; Dacko-Pikiewicz, Z.; Liszewski, W.; Khalid, B. Evaluating the Determinants of Consumer Adoption of Autonomous Vehicles in Thailand—An Extended UTAUT Model. Energies 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, D.; Shilpa, K. “Chatting with ChatGPT”: Analyzing the factors influencing users' intention to Use the Open AI's ChatGPT using the UTAUT model. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Chuan-Chuan Lin, J.; Chiang, H.S. The effects of blogger recommendations on customers’ online shopping intentions. Internet Res. 2013, 23, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).