Submitted:
21 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
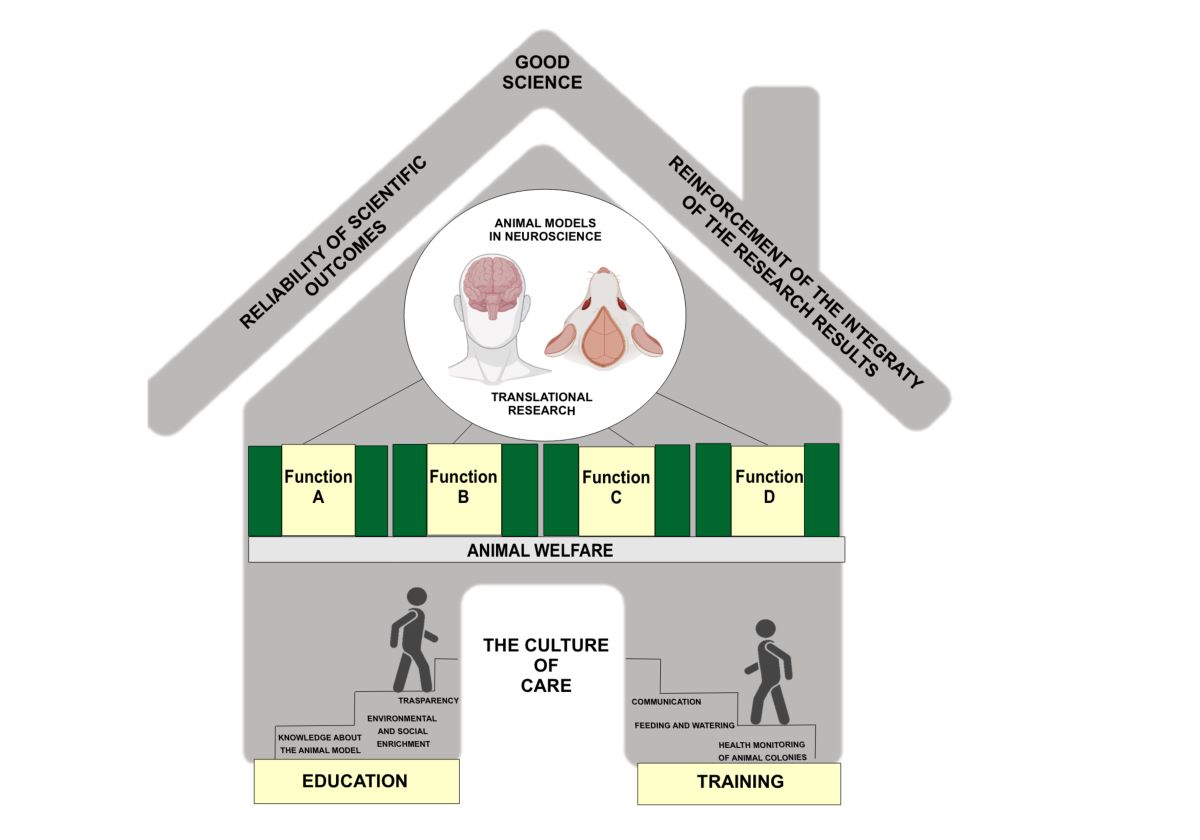
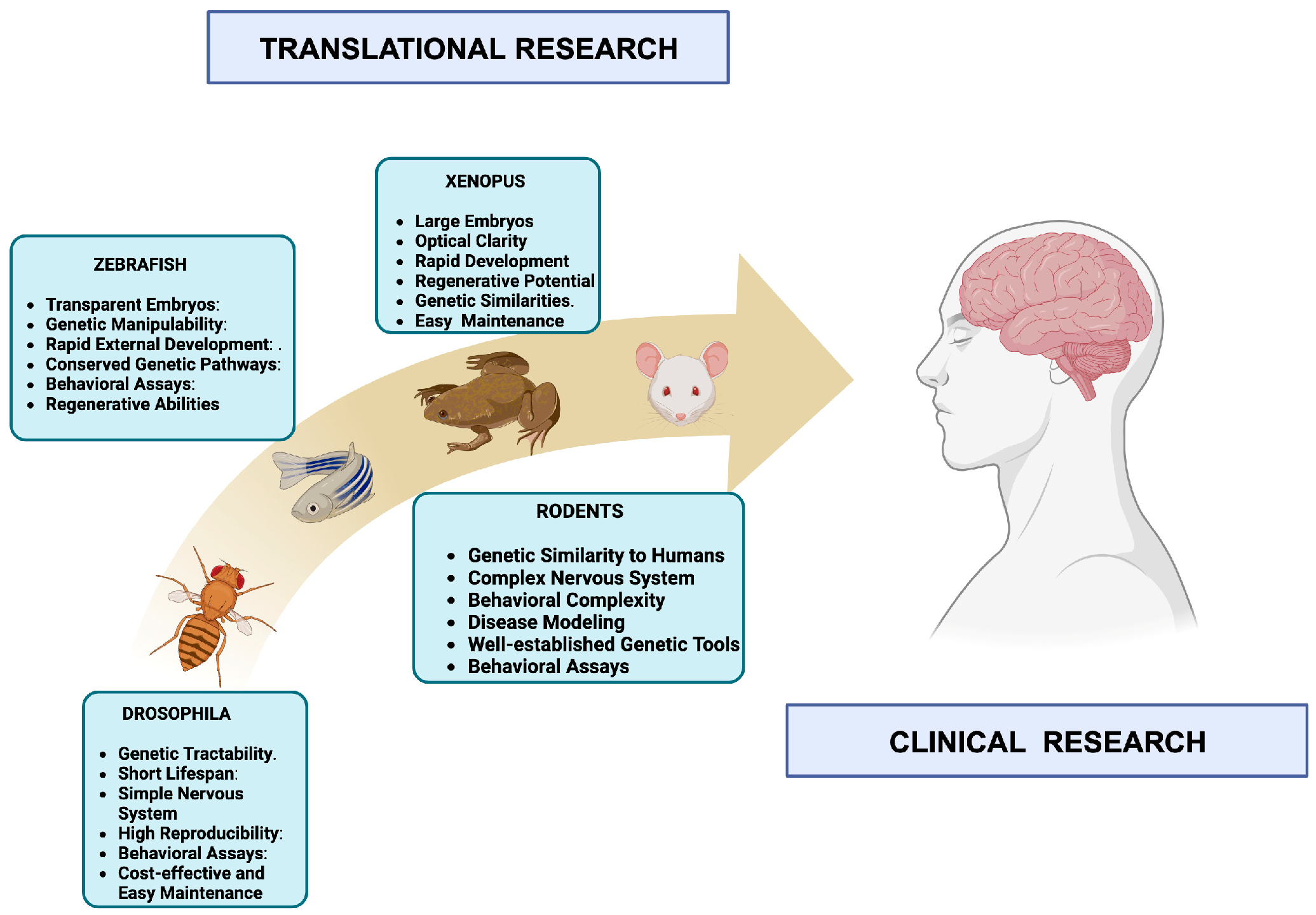
Keywords:
Introduction:
Tracing the Evolution: Animal Models in Unveiling Neuroscience's History:
Animal Models: Essential Tools in Unraveling the Mysteries of Neuroscience:
The Vital Role of Mice and Rats in the Advancement of Neuroscience:
Ethical Treatment in Research: The Culture of Care:
Embracing a 'Culture of Care': Defining and Advocating Ethical Practices:
Conclusion
Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Animal models (AMs) |
| Nervous System (NS) |
| Alternative Methods (AAs) |
| Replacement, Reduce, Refinement (3Rs) |
| Specific Pathogen-Free (SPF) |
| Laboratory Animal Allergies (LAA) |
| Germ-Free (GF) |
References
- Lambert, K. Wild brains: The value of neuroethological approaches in preclinical behavioral neuroscience animal models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 146, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanova, E.V.; Sweedler, J.V. Animal model systems in neuroscience. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1869–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenkerk, B.; Kaldewaij, F. The use of animal models in behavioral neuroscience research. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 19, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, M.M.; Krustev, E.; McDougall, J.J. Preclinical assessment of inflammatory pain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal, J.D. Elements of episodic-like memory in animal models. Behav. Processes 2009, 80, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanshree; Yu, W.S.; Fung, M.L.; Lee, C.W.; Lim, L.W.; Wong, K.H. The monkey head mushroom and memory enhancement in Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, C. New Insights into and Emerging Roles of Animal Models for Neurological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar, R. Animal testing and medicine. Heart Views 2011, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distelzweig, P. “mechanics” and Mechanism in William Harvey’s anatomy: varieties and limits. In Early modern medicine and natural philosophy; Distelzweig, P., Goldberg, B., Ragland, E.R., Eds.; History, philosophy, and theory of the life sciences; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2016; Vol. 14, pp. 117–140. ISBN 978-94-017-7352-2. [Google Scholar]
- van Helvoort, T. Bacteriological and physiological research styles in the early controversy on the nature of the bacteriophage phenomenon. Med. Hist. 1992, 36, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafkafi, N.; Agassi, J.; Chesler, E.J.; Crabbe, J.C.; Crusio, W.E.; Eilam, D.; Gerlai, R.; Golani, I.; Gomez-Marin, A.; Heller, R.; Iraqi, F.; Jaljuli, I.; Karp, N.A.; Morgan, H.; Nicholson, G.; Pfaff, D.W.; Richter, S.H.; Stark, P.B.; Stiedl, O.; Stodden, V.; Benjamini, Y. Reproducibility and replicability of rodent phenotyping in preclinical studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Jensen, F.E.; Greely, H.T.; Okano, H.; Treue, S.; Roberts, A.C.; Fox, J.G.; Caddick, S.; Poo, M.-M.; Newsome, W.T.; Morrison, J.H. Opportunities and limitations of genetically modified nonhuman primate models for neuroscience research. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020, 117, 24022–24031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.H.; Kandel, E.R. Synaptic remodeling, synaptic growth and long-term memory storage in Aplysia. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 169, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O. The human connectome: a complex network. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1224, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.D.; Shaevitz, J.W.; Murthy, M. Quantifying behavior to understand the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, R.J.; Aarestrup, K.; Cooke, S.J.; Cowley, P.D.; Deng, Z.D.; Fisk, A.T.; Harcourt, R.G.; Heupel, M.; Hinch, S.G.; Holland, K.N.; Hussey, N.E.; Iverson, S.J.; Kessel, S.T.; Kocik, J.F.; Lucas, M.C.; Flemming, J.M.; Nguyen, V.M.; Stokesbury, M.J.W.; Vagle, S.; VanderZwaag, D.L.; Young, N. Envisioning the future of aquatic animal tracking: technology, science, and application. Bioscience 2017, 67, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Anderson, R.J.; Ashbrook, D.G.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Park, Y.; Priebe, C.E.; Qi, Y.; Laoprasert, R.; Vogelstein, J.T.; Williams, R.W.; Johnson, G.A. Variability and heritability of mouse brain structure: Microscopic MRI atlases and connectomes for diverse strains. Neuroimage 2020, 222, 117274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, A.; Chiamulera, C.; Geyer, M.A.; Tricklebank, M.; Steckler, T. Removing obstacles in neuroscience drug discovery: the future path for animal models. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Yunta, E. Ethical issues concerning genetically modified animals for the study of human diseases. In Handbook of bioethical decisions. volume I: decisions at the bench; Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. A., Eds.; Collaborative Bioethics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; Vol. 2, pp. 513–525. ISBN 978-3-031-29450-1. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.L.; Thurm, A.; Ethridge, S.B.; Soller, M.M.; Petkova, S.P.; Abel, T.; Bauman, M.D.; Brodkin, E.S.; Harony-Nicolas, H.; Wöhr, M.; Halladay, A. Reconsidering animal models used to study autism spectrum disorder: Current state and optimizing future. Genes Brain Behav. 2022, 21, e12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, J.A.; Williams, H.E.; Eppler, R.M.; Steinhilb, M.L.; Khanna, M. Animal models of neurodegenerative disease: recent fly advances highlight innovative drug discovery approaches. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 883358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.S.; Horien, C.; Barson, D.; Scheinost, D.; Constable, R.T. Why is everyone talking about brain state? Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmüller, O.L.; Knoblich, J.A. Human cerebral organoids - a new tool for clinical neurology research. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panoutsopoulos, A.A. Organoids, Assembloids, and Novel Biotechnology: Steps Forward in Developmental and Disease-Related Neuroscience. Neuroscientist 2021, 27, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, R.R.; Rousselet, G.A. A guide to robust statistical methods in neuroscience. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2018, 82, 8.42.1–8.42.30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, M. The benefits and limitations of animal models for translational research in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenowitz, E.A.; Zakon, H.H. Emerging from the bottleneck: benefits of the comparative approach to modern neuroscience. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstmann, B.U.; Ratcliff, R.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: advantages, applications, and extensions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 641–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.C.; Smith, M.A. Animal models of resistance exercise and their application to neuroscience research. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 273, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sécher, T.; Bodier-Montagutelli, E.; Guillon, A.; Heuzé-Vourc’h, N. Correlation and clinical relevance of animal models for inhaled pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 167, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R.; Boelsterli, U.A. Healthy animals and animal models of human disease(s) in safety assessment of human pharmaceuticals, including therapeutic antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Liu, D.; Méndez-Olivos, E.E.; Muñoz, R.; Larraín, J. The African clawed frog Xenopus laevis: A model organism to study central nervous system regeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 652, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfie, M.; Jorgensen, E.M. C. elegans neuroscience: genetics to genome. Trends Genet. 1998, 14, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P.; Samuel, A.D.T. Caenorhabditis elegans: a model system for systems neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husson, S.J.; Gottschalk, A.; Leifer, A.M. Optogenetic manipulation of neural activity in C. elegans: from synapse to circuits and behaviour. Biol. Cell 2013, 105, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A newcomer with great promise in behavioral neuroscience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 144, 104978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.L. Learning and memory using Drosophila melanogaster: a focus on advances made in the fifth decade of research. Genetics 2023, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, F.; Pandey, U.B.; Digilio, F.A. Editorial: Drosophila as a model to study neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1275253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkwitz, S.; Mourrain, P.; Becker, T.S. Zebrafish: an integrative system for neurogenomics and neurosciences. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azkona, G.; Sanchez-Pernaute, R. Mice in translational neuroscience: What R we doing? Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 217, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenbroek, B.; Youn, J. Rodent models in neuroscience research: is it a rat race? Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. Model homes for model organisms: Intersections of animal welfare and behavioral neuroscience around the environment of the laboratory mouse. Biosocieties 2016, 11, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira de Castro, A.C.; Olsson, I.A.S. Does the goal justify the methods? Harm and benefit in neuroscience research using animals. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 19, 47–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, F.; Meijboom, F. Ethical issues associated with the use of animal experimentation in behavioral neuroscience research. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 19, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, M.J.; Lidster, K. Improving quality of science through better animal welfare: the NC3Rs strategy. Lab Anim (NY) 2017, 46, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murlanova, K.; Kirby, M.; Libergod, L.; Pletnikov, M.; Pinhasov, A. Multidimensional nature of dominant behavior: Insights from behavioral neuroscience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 603–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, P.R.; Cort, J.; Ebrahim, N.; Goodman, A.; Henning, J.; Karolia, M.; Rodrigues, S.-L.; Strkalj, G. Is 21st century neuroscience too focussed on the rat/mouse model of brain function and dysfunction? Front. Neuroanat. 2008, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, E.; Wisniewski, T. Alzheimer’s disease: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, J.; Buhidma, Y.; Fletcher, E.J.R.; Duty, S. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: a guide to selecting the optimal model for your research. Neuronal Signal. 2021, 5, NS20210026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Arregui, T.; Llorente, J.; Giménez Minguez, P.; Tønnesen, J.; Peñagarikano, O. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Epilepsy, Insights from Animal Models. Neuroscience 2020, 445, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.; Estevez, M.A.; Sarkar, A.A.; Banerjee-Basu, S. A multifaceted approach for analyzing complex phenotypic data in rodent models of autism. Mol. Autism 2019, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, E.A.; Swanberg, M. Animal models of parkinson’s disease. In Parkinson’s disease: pathogenesis and clinical aspects; Stoker, T. B., Greenland, J. C., Eds.; Codon Publications: Brisbane (AU), 2018; ISBN 9780994438164. [Google Scholar]
- Maple, T.L.; Bloomsmith, M.A. Introduction: The science and practice of optimal animal welfare. Behav. Processes 2018, 156, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, T.; Øvlisen, K. Assessment of the Culture of Care working with laboratory animals by using a comprehensive survey tool. Lab. Anim. 2021, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.S.; Goerlich, V.C.; van der Staay, F.J. A dynamic concept of animal welfare: The role of appetitive and adverse internal and external factors and the animal’s ability to adapt to them. Front. Anim. Sci. 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, F.; Hiebl, B.; Kunzmann, P.; Hutter, F.; Afkham, F.; LaFollette, M.; Gruber, C. Culture of care in animal research - Expanding the 3Rs to include people. Lab. Anim. 2022, 56, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheister, S.; Bleich, A. Health Monitoring of Laboratory Rodent Colonies-Talking about (R)evolution. Animals (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubrecht, R.C.; Carter, E. The 3rs and humane experimental technique: implementing change. Animals (Basel) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemanova, M.A. Crucial but neglected: Limited availability of animal welfare courses in education of wildlife researchers. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludolph, A.C.; Bendotti, C.; Blaugrund, E.; Chio, A.; Greensmith, L.; Loeffler, J.-P.; Mead, R.; Niessen, H.G.; Petri, S.; Pradat, P.-F.; Robberecht, W.; Ruegg, M.; Schwalenstöcker, B.; Stiller, D.; van den Berg, L.; Vieira, F.; von Horsten, S. Guidelines for preclinical animal research in ALS/MND: A consensus meeting. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velden, J.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Bakkers, J.; Batkai, S.; Bertrand, L.; Bezzina, C.R.; Bot, I.; Brundel, B.J.J.M.; Carrier, L.; Chamuleau, S.; Ciccarelli, M.; Dawson, D.; Davidson, S.M.; Dendorfer, A.; Duncker, D.J.; Eschenhagen, T.; Fabritz, L.; Falcão-Pires, I.; Ferdinandy, P.; Giacca, M.; Thum, T. Animal models and animal-free innovations for cardiovascular research: current status and routes to be explored. Consensus document of the ESC Working Group on Myocardial Function and the ESC Working Group on Cellular Biology of the Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3016–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, P.; Aboagye, E.O.; Balkwill, F.; Balmain, A.; Bruder, G.; Chaplin, D.J.; Double, J.A.; Everitt, J.; Farningham, D.A.H.; Glennie, M.J.; Kelland, L.R.; Robinson, V.; Stratford, I.J.; Tozer, G.M.; Watson, S.; Wedge, S.R.; Eccles, S.A.; Committee of the National Cancer Research Institute. Guidelines for the welfare and use of animals in cancer research. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1555–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklas, W. International harmonization of health monitoring. ILAR J. 2008, 49, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavizzi, F.; Galligioni, V.; Vasina, V.; Raspa, M. Animal health management and hygiene. In Practical handbook on the 3rs in the context of the directive 2010/63/EU; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 151–179. ISBN 9780128211809. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals Environment, Housing, and Management. 2011.
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition - National Research Council, Division on Earth and Life Studies, Institute for Laboratory Animal Research, Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals - Google Libri; National Academies Press, 2010; ISBN 9780309186636.
- de Azevedo, C.S.; Cipreste, C.F.; Pizzutto, C.S.; Young, R.J. Review of the effects of enclosure complexity and design on the behaviour and physiology of zoo animals. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumans, V. Environmental enrichment for laboratory rodents and rabbits: requirements of rodents, rabbits, and research. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health, 8th ed. National Academies Press (US): Washington (DC), 2011; ISBN 0309154006.
- Kurtz, D.M.; Feeney, W.P. The influence of feed and drinking water on terrestrial animal research and study replicability. ILAR J. 2020, 60, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Advantages | Rat Models | Mouse Models |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Larger brain size allows for easier surgical procedures and brain imaging. | Smaller size facilitates handling, breeding, and genetic modifications |
| Genetic Insights |
Helpful for genetic studies in complex physiological pathways |
Excellent for genetic research due to extensive genetic manipulation.. |
| Disease Modeling |
Used in various disease models, e.g., hypertension, Parkinson's Disease. Models’ various neurological disorders aiding in understanding disease progression and potential treatments. |
Widely used in disease modeling, offering diverse models for diseases. Models’ various neurological disorders aiding in understanding disease progression and potential treatments. |
| Behavioral Studies | Complex behaviors like humans enable diverse behavioral studies. Facilitates studies on learning, memory, addiction, and social behaviors, offering insights into neural mechanisms behind behavior. | Well-characterized behaviors make them useful for behavioral tests. Facilitates studies on learning, memory, addiction, and social behaviors, offering insights into neural mechanisms behind behavior. |
|
Pharmacological
Testing |
It is commonly used for drug testing, especially in behavioral tests. Primary models for testing potential therapeutics are crucial in assessing drug efficacy and safety before human trials. |
Excellent for genetic research due to extensive genetic manipulation. Effective for testing drug responses and toxicology in various settings. |
| Neural Plasticity | Insight into neural plasticity and brain development due to brain size | Valuable for studying neural plasticity. and developmental neuroscience. |
| Technological Advances |
Utilized in various technological advancements, including brain imaging. Propels the development of advanced technologies like optogenetics, brain imaging, and gene editing tools. |
Often used in pioneering technology advances in neuroscience research. Propels the development of advanced technologies like optogenetics, brain imaging, and gene editing tools. |
| Bridging Research |
Useful in translating findings from basic research to clinical applications. Provides critical connections between fundamental research and clinical applications, paving the way for novel therapies. |
Important for translating research. into clinical and translational areas. Provides critical connections between fundamental research and clinical applications, paving the way for novel therapies. |
| Accessibility: | Generally, less accessible due to size and cost considerations | More accessible, widely used due to their smaller size and cost. |
| Genetic Manipulation | Enables precise genetic manipulation, allowing the study of specific genes' roles in brain function and diseases. | Extensive genetic manipulation tools, including knockout, transgenic models |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





