1. Introduction
Childhood immunization is globally celebrated as a cost-effective triumph in public health by preventing an estimated 3.5-5 million deaths annually from diseases like diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza, and measles [
1,
2]. Vaccines now play a pivot role against more than 20 infectious diseases thus protecting individuals across various age groups and contributing to longer, healthier lives [
2]. Despite this global success, achieving consistent and robust vaccination coverage remains a significant challenge for developing nations [
3]. This challenge is particularly acute in Pakistan, where socio-economic disparities and systemic barriers lead to suboptimal immunization rates as witnessed by recurrent measles outbreaks [
4,
5,
6].
The financial merits of immunization in low- and middle-income countries are clear, with every dollar spent generating
$52 in broader social and economic costs avoided [
7]. Yet, there persists a stagnation in immunization coverage mainly by recent global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic which has significantly strained health systems [
8]. As of 2021, an estimated 18.1 million zero-dose children had missed out on vaccinations, an increase of 5.9 million from 2019 [
8]. In 2022, 14.3 million children were not administered the initial DTP vaccine, indicating a concerning trend of limited immunization access [
8]. Consequently, Pakistan is one of the top 10 contributors in the list of countries harboring 60% of the partially or unimmunized children [
8].
The Shikarpur district in the Sindh province of Pakistan serves as a strategic representation of the challenges met by other rural and tribal regions in the developing world. With a population of 1,233,760 residents overall, the area struggles with health and educational inadequacies that may affect vaccination rates. These challenges are compounded by socioeconomic inequalities since children from economically disadvantaged homes have a much lower likelihood of receiving complete immunization [
9].
The historical landscape of tribal violence in Shikarpur, which includes tribes like the Jakhrani, Bhaya, and Teghani, has further complicated public health outreach [
10]. Between 2010 and 2014, there were 1,566 documented cases of tribal conflicts in the region. These clashes resulted in loss of life and caused disruptions to health services, leading to instability [
11]. The volatile nature of this environment highlights the need for innovative but quick methodologies to evaluate and enhance immunization rates.
While traditional expensive assessment tools such as household surveys and routine administrative reports provide insights into vaccination coverage, they often fall short in accuracy and reliability, especially in complex socio-political landscapes [
12,
13]. The Lot Quality Assurance Sampling (LQAS) method, historically utilized in industrial settings, offers a novel approach to public health surveillance. It allows for binary classification of coverage data, facilitating the rapid identification of areas with acceptable or unacceptable immunization rates [
14,
15].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first application of LQAS for the assessment of routine immunization coverage among children aged 12-23 months in this rural and tribal region. Moreover, our investigation delved deeper to uncover the reasons behind partially and un-immunized children of the same cohort. Thus, this research is pioneering in its approach to categorize the Union Councils—the foundational administrative level—into priority zones, providing crucial insights for future policy development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Rationale
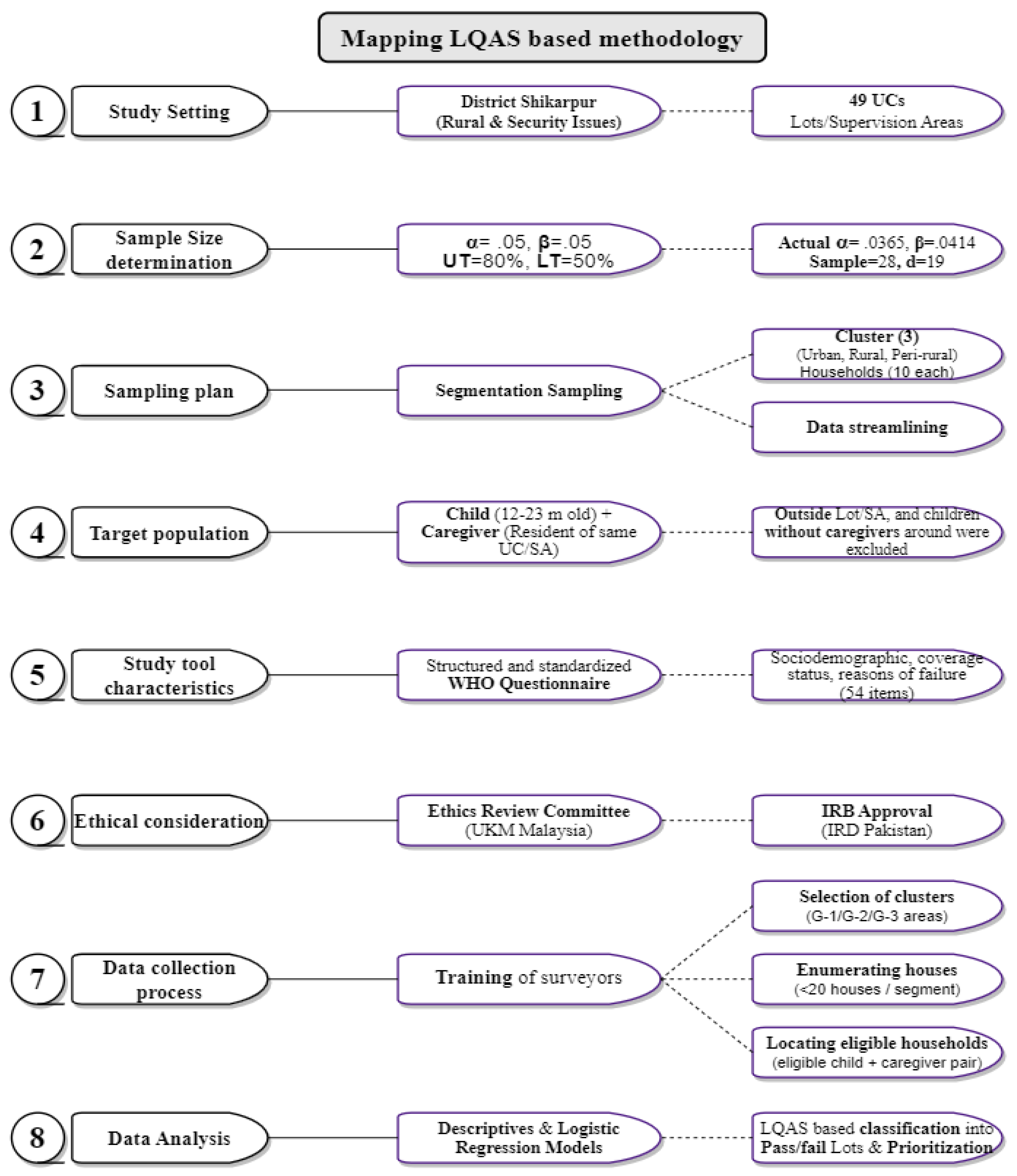
We designed a cross-sectional household survey using the clustered variant of Lot Quality Assurance Sampling (c-LQAS) methodology. It required the selection of Supervision Areas (SAs), identification of clusters, setting the upper and lower thresholds, and limiting errors, followed by robust analysis [
16].
2.2. Study Setting
The study was conducted in the Shikarpur district of the Sindh province, covering four talukas and 49 Union Councils, which span an area of 2,640 km2 and are located 29 km to the west of the Indus River. This district was selected due to its diverse socio-economic landscape and the unique public health challenges it presents.
2.3. Selection of Supervision Areas (SAs)
Each Union Council (UC) was designated as an individual Supervision Area (SA) to allow for a granular analysis of vaccination coverage. This approach enables targeted interventions at the UC level, where disparities in immunization rates may be most pronounced.
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
Sample sizes were determined using a combination of cumulative binomial probabilities and the hypergeometric distribution model through LQAS Sampling plan calculator; Brixton Health, London, UK. We set stringent tolerability levels for type I (α) and type II (β) errors at .05 based on the critical nature of vaccination coverage as a public health indicator. The sample size of 28 was determined for each SA, and the decision rule for the upper and lower thresholds of 80% (desired level) and 50% (lower benchmark) was computed to be 18 / 19. Therefore, in order for each lot to attain an acceptable status, a minimum of 19 out of 28 children must be fully vaccinated [
17]. The lots containing fewer than 19 immunized children were designated as "fail," indicating the inadequate level of vaccination coverage.
2.5. Sampling Method and Clustering
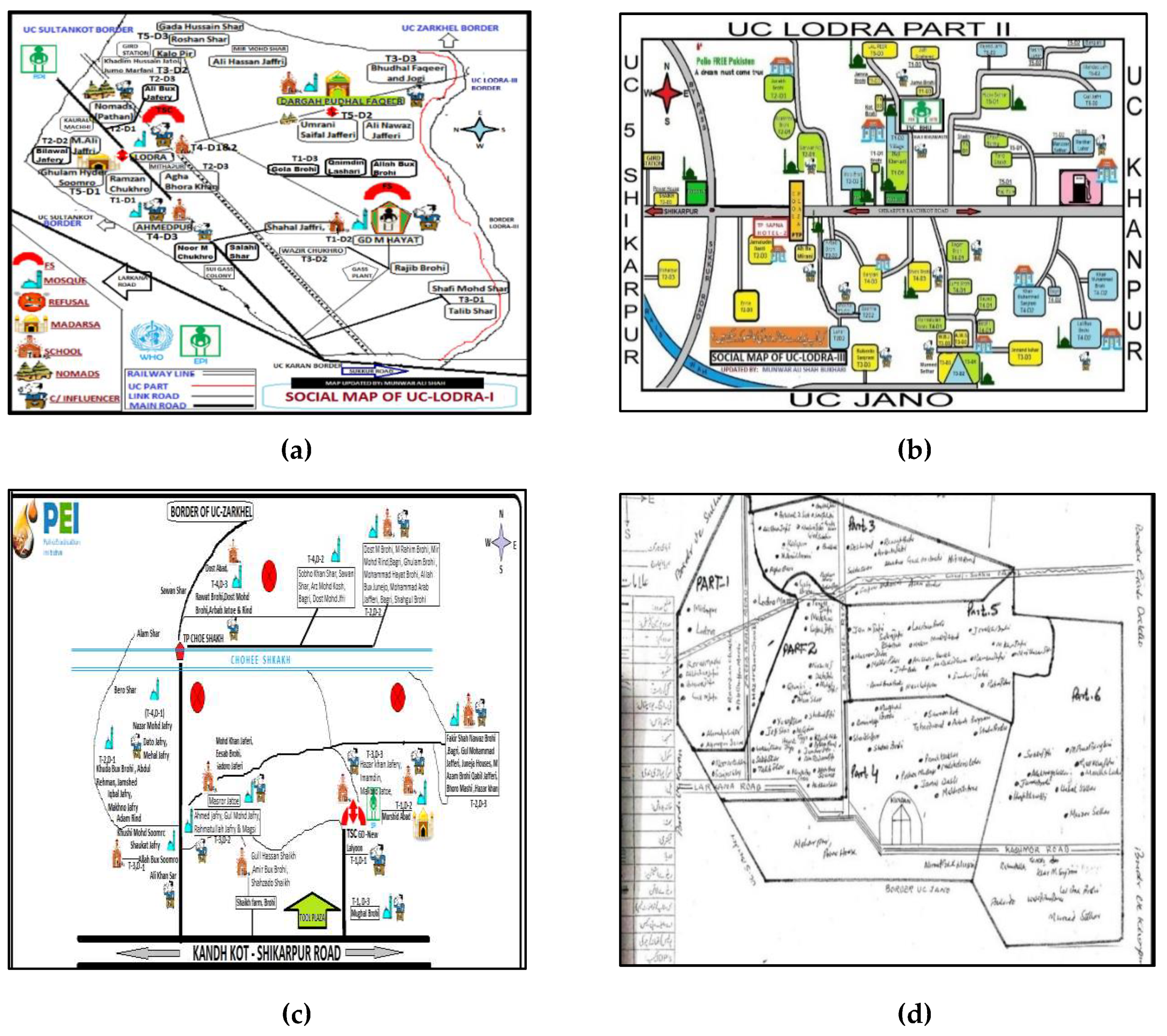
UC-level microplans (
Figure 1) from the Polio Eradication Initiative (PEI) were utilized to inform our segmentation sampling strategy. Each SA was divided into segments according to ease of access—categorized as G-1 (80-100 houses), G-2 (60-79 houses), and G-3 (<60 houses)—with a defined number of households. This categorization reflected the logistical time needed to access these areas from a public health service delivery perspective.
2.6. Study Population
Interviews with caregivers of children aged 12-23 months constituted the primary data source. We included one child per household to ensure data independence. Inclusion criteria required caregivers to provide a verifiable history of vaccination through recall or EPI card documentation. Caregivers who did not consent, could not communicate in a language understood by the study team, non-residents of Shikarpur, or did not volunteer for the interview were excluded from the study.
2.7. Key Definitions
Table 1.
Key definitions.
Table 1.
Key definitions.
| Terms |
Definitions |
| Fully Immunized Child*1
|
A child who has received the complete schedule of BCG, IPV, MCV, OPV (including OPV-0), and three doses each of Pentavalent and PCV vaccines before the age of 12 months |
| Cluster |
A limited subgroup consisting of at least seven eligible children (12-23 m) within the specified age range under evaluation |
| Primary vaccines |
BCG, Penta 1-3, MCV-1 |
| Zero Dose |
Any child who has not received any vaccine till the age of 12 months. |
*1 As per the National EPI childhood Immunization Schedule [18], which will be verified by the presence of a BCG scar and EPI card records
BCG: Bacillus Calmette–Gue´rin (BCG) is an antituberculosis vaccine.
Penta: Pentavalent vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, poliomyelitis, and Haemophilus influenzae type b
PCV: Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
*The schedule in 2019 included Hepatitis B0 too, but that is omitted from this table owing due to non-availability and limited supply from government side to EPI centers. |
2.8. Study Tool and Validation
A structured questionnaire endorsed by the WHO was employed, consisting of sociodemographic data, immunization coverage status, and factors influencing vaccination uptake [
19]. We ensured the content validity of the questionnaire through translation into Sindhi language, expert reviews, and a pilot study conducted with local participants. The pilot resulted in minor language adjustments to ensure cultural appropriateness and clarity.
2.9. Data Collection Duration and Process
We conducted this household survey in the month of August, 2019 as illustrated in
Figure 2. Four survey teams, each including a surveyor, a local guide, and a community influencer, were formed to ensure efficient data collection and community engagement. Team members received comprehensive training, including mock surveys to ensure familiarity with the study protocol and ethical considerations. Clusters were selected using a random number generator to avoid selection bias at all levels. Survey teams documented GPS coordinates upon reaching each cluster and conducted data collection as per our established methodology. Randomization was also applied at the level of household selection as per the predetermined criteria.
2.10. Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using STATA version 17.0. Descriptive statistics provided an overview of vaccination coverage, while QGIS mapping illuminated the geographical distribution of surveyed clusters. The LQAS principle guided the categorization of SAs, employing the Direct Adjustment Method and the calculation of confidence intervals to provide a detailed coverage estimate. Logistic Regression Model highlighted the risk factors contributing to the partial or unimmunized cohort.
While employing the Direct Adjustment Method to determine mini percentages, represented as “p” or "mini %", where “C” stood for the number of successes “ X”. The weighted averages were computed based on the total population estimates from the year 2020 provided by health department (Unpublished data). Once weights, denoted as “wt”, were assigned, the weighted average was derived using the formula “wt x p (mini %)”.
To determine confidence intervals, we followed the subsequent steps:
3. Results
3.1. LQAS Clustering
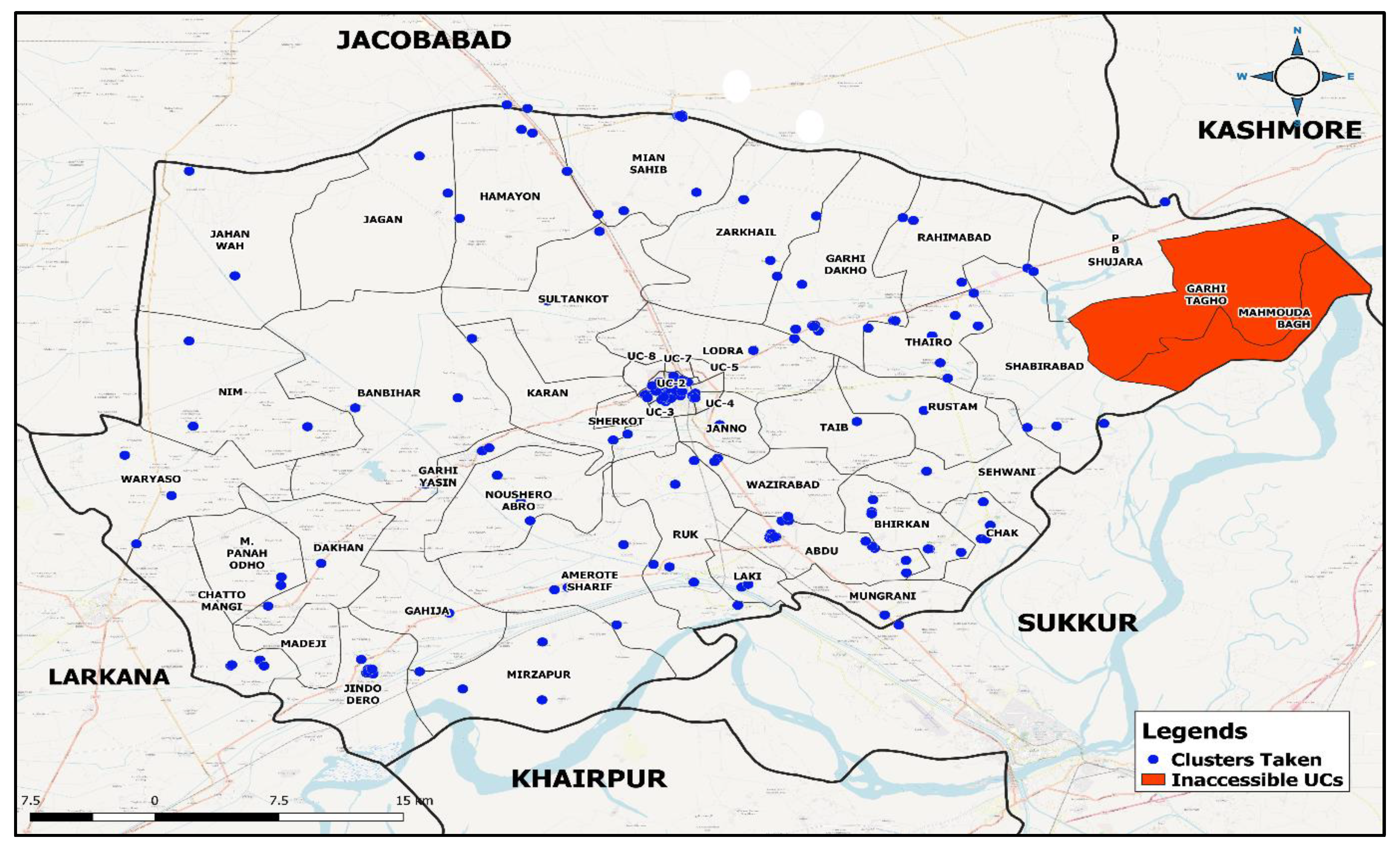
We selected 141 clusters from 47 Supervision Areas (SAs), commonly referred to as Lots or Union Councils. From these clusters, 1,402 children were surveyed. The final analysis excluded 86 children (6%) from this group. A total of 70 children (81%) were randomly removed from SAs where the sample size exceeded 28 child-caregiver pairings, while 16 children (19%) were dropped due to incomplete data.
Figure 3 shows that 2 SAs were inaccessible, and a police operation was unanticipated, preventing data collection.
3.2. Socio-demographic details
Table 2 shows the demographic characteristics of 1,316 caregiver-child couples included in our study. The mean age was 18.1 (SD = 3.6) months, with 411 (31.2%) aged 12–15 months, 300 (22.8%) aged 16–18 months, 245 (18.6%) aged 19–21 months, and 360 (27.4%) aged 22–24 months. Majority of the pairs were from Taluka Shikarpur 419 (31.8%), followed by Garhi Yasin 364 (27.6%), Lakhi 308 (23.5%), and Khanpur 225 (17.1%). The survey included 747 (56.7%) boys and 569 (43.3%) girls. Around 45.2% (n=595) reported that the childbirth took place at home. BCG scar was present in 930 (70.7%) children.
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of study participants children under 2 years of age and their caregivers (n=1,316) in district Shikarpur.
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of study participants children under 2 years of age and their caregivers (n=1,316) in district Shikarpur.
| Characteristics |
n |
% |
| Taluka |
|
|
| Shikarpur |
419 |
31.8 |
| Garhi Yasin |
364 |
27.6 |
| Lakhi |
308 |
23.4 |
| Khanpur |
225 |
17.1 |
| |
|
|
| Locality |
|
|
| Urban |
496 |
37.7 |
| Rural |
470 |
35.7 |
| Peri-urban |
350 |
26.6 |
| |
|
|
| Gender |
|
|
| Male |
747 |
56.7 |
| Female |
569 |
43.3 |
| |
|
|
| Child Age at Enrolment (months) (mean, SD) |
18.1 |
3.6 |
| 12 - 15 |
411 |
31.2 |
| 16 - 18 |
300 |
22.8 |
| 19 - 21 |
245 |
18.6 |
| 22 - 24 |
360 |
27.4 |
| |
|
|
| Birthplace |
|
|
| Home |
595 |
45.2 |
| Tertiary care facility |
554 |
42.1 |
| Primary care facility |
167 |
12.7 |
| |
|
|
| Father’s Occupation |
|
|
| Farmer |
439 |
33.4 |
| Daily wages |
349 |
26.5 |
| Houseman |
188 |
14.3 |
| Self-employed |
113 |
8.6 |
| Government employee |
66 |
5.0 |
| Private employee |
66 |
5.0 |
| Student |
2 |
0.1 |
| Unemployed |
62 |
4.7 |
| Retire |
3 |
0.2 |
| Other |
28 |
2.1 |
| |
|
|
| Mother’s Occupation |
|
|
| Housewife |
750 |
57.0 |
| Farmer |
372 |
28.3 |
| Government employee |
27 |
2.0 |
| Private employee |
25 |
1.9 |
| Daily wages |
52 |
4.0 |
| Self-employee |
12 |
0.9 |
| Student |
6 |
0.5 |
| Unemployed |
62 |
4.7 |
| Other |
10 |
0.8 |
| |
|
|
| Father’s Education (years) |
|
|
| No education (0) |
697 |
53.0 |
| Less than primary (1-4) |
135 |
10.3 |
| Primary (5) |
115 |
8.8 |
| Middle (6-8) |
68 |
5.2 |
| Matric (10) |
123 |
9.4 |
| Intermediate (12) |
103 |
7.8 |
| Graduate (16) |
50 |
3.8 |
| Higher than graduation (>16) |
25 |
1.9 |
| |
|
|
| Mother’s Education (years) |
|
|
| No education (0) |
749 |
56.9 |
| Less than primary (1-4) |
335 |
25.5 |
| Primary (5) |
100 |
7.6 |
| Secondary (6-8) |
43 |
3.3 |
| Matric (10) |
45 |
3.4 |
| Intermediate (12) |
30 |
2.3 |
| Graduate (16) |
8 |
0.6 |
| Higher than graduation (>16) |
6 |
0.5 |
| |
|
|
| Issues in accessing health facilities |
|
|
| Yes |
365 |
27.7 |
| No |
883 |
67.1 |
| |
|
|
| BCG scar (yes) |
930 |
70.7 |
| |
|
|
| Fully immunized children (FIC)** |
560 |
42.5 |
*Calculated using Principal Component Analysis
**Children who have received BCG, Penta1-3, PCV 1-3, OPV0-3, Measles-1 |
3.3. Immunization status
Among the children aged 12–23 months, 43% (n=560) were fully immunized, 38% (n=506) partially immunized, and 19% (n=250) were unimmunized as per crude coverage estimates.
3.4. Prioritization of areas
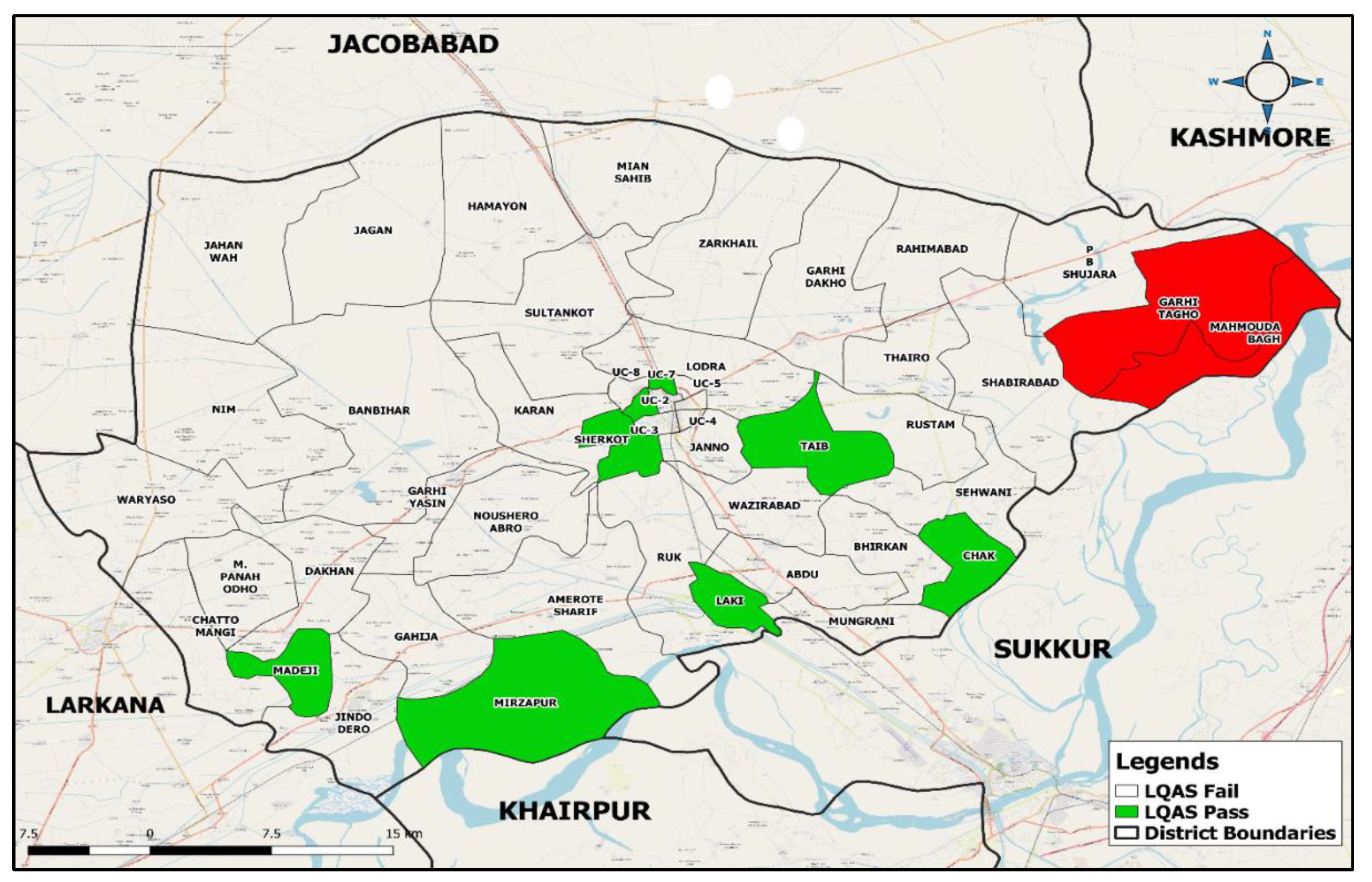
Figure 4 shows that only 17% (n=8/47) of the Sampling Areas (SAs) with 19 or more fully immunized children (FICs) met the passing criteria using Lot Quality Assurance Sampling (LQAS) with decision standards. Six of these successful SAs were "Low priority" due to having over 20 FICs. Two marginally passing SAs with FIC levels between 19 and 20 were labeled "Medium priority SAs". Table 3 lists the 39 "Fail and High priority SAs," which did not pass.
Table 3.
LQAS outcomes by Union Council (n=1,316)*.
Table 3.
LQAS outcomes by Union Council (n=1,316)*.
| Union Council |
Fully immunized |
Partially & Unimmunized |
LQAS |
Priority |
| (Pass/Fail)^ |
(Low/Medium/High)** |
| |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
| 1 |
16 |
57.1 |
12 |
42.9 |
Fail |
High |
| 2 |
22 |
78.6 |
6 |
21.4 |
Pass |
Low |
| 3 |
17 |
60.7 |
11 |
39.3 |
Fail |
High |
| 4 |
13 |
46.4 |
15 |
53.6 |
Fail |
High |
| 5 |
13 |
46.4 |
15 |
53.6 |
Fail |
High |
| 6 |
13 |
46.4 |
15 |
56.6 |
Fail |
High |
| 7 |
22 |
78.6 |
6 |
21.4 |
Pass |
Low |
| 8 |
15 |
53.6 |
13 |
46.4 |
Fail |
High |
| Abdu |
17 |
60.7 |
11 |
39.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Amrote Shareef |
11 |
39.3 |
17 |
60.7 |
Fail |
High |
| Bambhiarh |
7 |
25 |
21 |
75 |
Fail |
High |
| Bhirkan |
8 |
28.6 |
20 |
71.4 |
Fail |
High |
| Chak |
20 |
71.4 |
8 |
28.6 |
Pass |
Medium |
| Chatto Mangi |
10 |
35.7 |
18 |
64.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Dhakan |
15 |
53.6 |
13 |
46.4 |
Fail |
High |
| Gaheja |
12 |
42.9 |
16 |
57.1 |
Fail |
High |
| Garhi Dakho |
2 |
7.1 |
26 |
92.9 |
Fail |
High |
| Garhi Yaseen |
13 |
46.4 |
15 |
53.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Humayoon |
9 |
32.1 |
19 |
67.9 |
Fail |
High |
| Jagan |
15 |
53.6 |
13 |
46.4 |
Fail |
High |
| Jahan Wah |
- |
- |
28 |
100 |
Fail |
High |
| Jano |
12 |
42.9 |
16 |
57.1 |
Fail |
High |
| Jindo Dero |
6 |
21.4 |
22 |
78.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Karan |
4 |
14.3 |
24 |
85.7 |
Fail |
High |
| Khanpur |
16 |
57.1 |
12 |
42.9 |
Fail |
High |
| Lakhi |
25 |
89.3 |
3 |
10.7 |
Pass |
Low |
| Lodra |
9 |
32.1 |
19 |
67.8 |
Fail |
High |
| Madeji |
26 |
92.9 |
2 |
7.1 |
Pass |
Low |
| Mian Sahab |
2 |
7.1 |
26 |
92.9 |
Fail |
High |
| Mirzapur |
22 |
78.6 |
6 |
21.4 |
Pass |
Low |
| Mungrani |
8 |
28.6 |
20 |
71.4 |
Fail |
High |
| Naushero Abro |
7 |
25 |
21 |
75 |
Fail |
High |
| Nim |
6 |
21.4 |
22 |
78.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Panah Odho |
- |
- |
28 |
100 |
Fail |
High |
| Pir Bux Shujrah |
6 |
21.4 |
22 |
78.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Rahimabad |
5 |
17.9 |
23 |
82.1 |
Fail |
High |
| Ruk |
11 |
39.3 |
17 |
60.7 |
Fail |
High |
| Rustam |
17 |
60.7 |
11 |
39.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Sehwani |
13 |
46.4 |
15 |
53.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Shabirabad |
3 |
10.7 |
25 |
89.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Sherkot |
20 |
71.4 |
8 |
28.6 |
Pass |
Medium |
| Sultan Kot |
3 |
10.7 |
25 |
89.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Taib |
25 |
89.3 |
3 |
10.7 |
Pass |
Low |
| Thanhiro |
12 |
42.9 |
16 |
57.1 |
Fail |
High |
| Waryaso |
16 |
57.1 |
12 |
42.9 |
Fail |
High |
| Wazirabad |
10 |
35.7 |
18 |
64.3 |
Fail |
High |
| Zarkhail |
6 |
21.4 |
22 |
78.6 |
Fail |
High |
| Total |
560 |
43% |
756 |
57% |
8 |
|
| *28 children per union council |
| ^Criteria: Pass - ≥19 fully immunized children, Fail - <19 fully immunized children |
| **UCs having ‘Pass’ status are on low priority if above 20, medium priority if on 19 or 20 successes, while UCs having ‘Fail’ status are on high priority |
3.5. District coverage estimate analysis
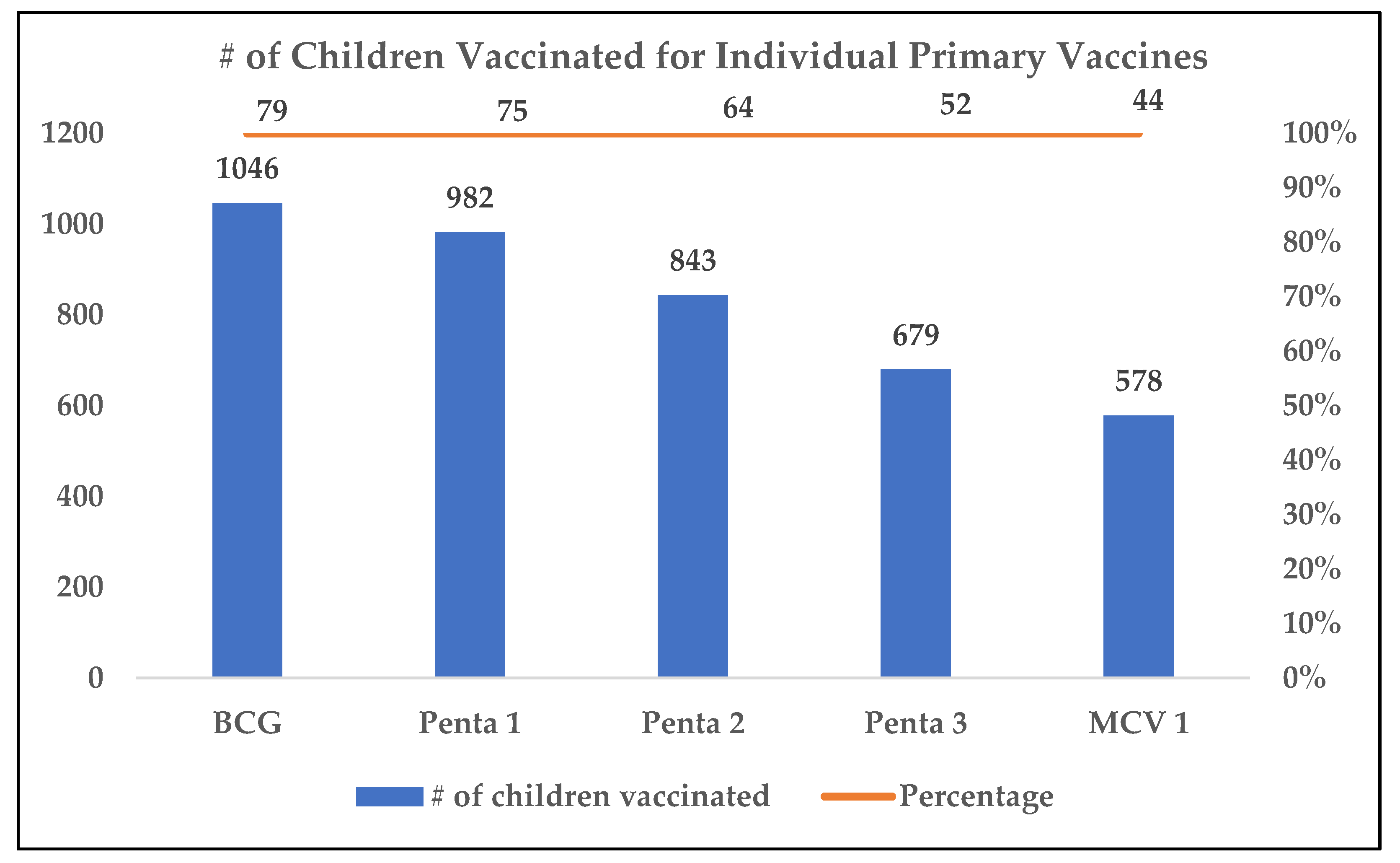
After applying the Direct Adjustment Method, the weighted average of District Shikarpur for FICs was found to be 42.4% (95% CI, 40.5% - 44.3%), as mentioned in Table 4. Coverage of individual primary vaccines (BCG, Penta1-3, MCV1) among children 12–23 months were as follows: BCG 79%, Penta-1 75%, Penta-2 64%, Penta-3 52%, and MCV-1 44%, as illustrated in
Figure 5.
Table 4.
Point estimate coverage with 95% confidence interval at district level (n=1,316)*.
Table 4.
Point estimate coverage with 95% confidence interval at district level (n=1,316)*.
|
Method applied: Direct Adjustment Method |
| Supervision Area (SA) |
SA Sample Size |
Number^1 Correct |
p= C/n^2 |
Relative Total Population (2020) |
Weights |
Weighted Average Coverage |
95 CI (1.96 x √Ʃwt2 x pq / n)
|
| n |
C |
mini % |
N |
wt = Ni/ƩN
|
wt x p (mini %) |
wt2
(Squared Weights)
|
p x q [1-p] |
(wt2 x pq)/n |
| 1 |
28 |
16 |
0.57 |
25,574 |
0.020 |
0.012 |
0.0004 |
0.245 |
0.000004 |
| 2 |
28 |
22 |
0.79 |
24,834 |
0.020 |
0.016 |
0.0004 |
0.168 |
0.000002 |
| 3 |
28 |
17 |
0.61 |
26,207 |
0.021 |
0.013 |
0.0004 |
0.239 |
0.000004 |
| 4 |
28 |
13 |
0.46 |
24,128 |
0.019 |
0.009 |
0.0004 |
0.249 |
0.000003 |
| 5 |
28 |
13 |
0.46 |
24,500 |
0.020 |
0.009 |
0.0004 |
0.249 |
0.000003 |
| 6 |
28 |
13 |
0.46 |
24,575 |
0.020 |
0.009 |
0.0004 |
0.249 |
0.000003 |
| 7 |
28 |
22 |
0.79 |
25,188 |
0.020 |
0.016 |
0.0004 |
0.168 |
0.000002 |
| 8 |
28 |
15 |
0.54 |
26,533 |
0.021 |
0.011 |
0.0005 |
0.249 |
0.000004 |
| Abdu |
28 |
17 |
0.61 |
29,994 |
0.024 |
0.015 |
0.0006 |
0.239 |
0.000005 |
| Amrote Shareef |
28 |
11 |
0.39 |
28,841 |
0.023 |
0.009 |
0.0005 |
0.239 |
0.000005 |
| Bambhiarh |
28 |
7 |
0.25 |
22,172 |
0.018 |
0.004 |
0.0003 |
0.188 |
0.000002 |
| Bhirkan |
28 |
8 |
0.29 |
28,269 |
0.023 |
0.006 |
0.0005 |
0.204 |
0.000004 |
| Chak |
28 |
20 |
0.71 |
28,997 |
0.023 |
0.017 |
0.0005 |
0.204 |
0.000004 |
| Chatto Mangi |
28 |
10 |
0.36 |
28,664 |
0.023 |
0.008 |
0.0005 |
0.230 |
0.000004 |
| Dhakan |
28 |
15 |
0.54 |
31,032 |
0.025 |
0.013 |
0.0006 |
0.249 |
0.000005 |
| Gaheja |
28 |
12 |
0.43 |
25,695 |
0.021 |
0.009 |
0.0004 |
0.245 |
0.000004 |
| Garhi Dakho |
28 |
2 |
0.07 |
31,661 |
0.025 |
0.002 |
0.0006 |
0.066 |
0.000002 |
| Garhi Yaseen |
28 |
13 |
0.46 |
22,212 |
0.018 |
0.008 |
0.0003 |
0.249 |
0.000003 |
| Humayoon |
28 |
9 |
0.32 |
30,404 |
0.024 |
0.008 |
0.0006 |
0.218 |
0.000005 |
| Jagan |
28 |
15 |
0.54 |
32,367 |
0.026 |
0.014 |
0.0007 |
0.249 |
0.000006 |
| Jahan Wah |
28 |
0 |
0.00 |
23,749 |
0.019 |
0.000 |
0.0004 |
0.000 |
0.000000 |
| Jano |
28 |
12 |
0.43 |
23,445 |
0.019 |
0.008 |
0.0004 |
0.245 |
0.000003 |
| Jindo Dero |
28 |
6 |
0.21 |
22,274 |
0.018 |
0.004 |
0.0003 |
0.168 |
0.000002 |
| Karan |
28 |
4 |
0.14 |
30,443 |
0.024 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
0.122 |
0.000003 |
| Khanpur |
28 |
16 |
0.57 |
27,784 |
0.022 |
0.013 |
0.0005 |
0.245 |
0.000004 |
| Lakhi |
28 |
25 |
0.89 |
16,645 |
0.013 |
0.012 |
0.0002 |
0.096 |
0.000001 |
| Lodra |
28 |
9 |
0.32 |
33,033 |
0.026 |
0.009 |
0.0007 |
0.218 |
0.000005 |
| Madeji |
28 |
26 |
0.93 |
31,667 |
0.025 |
0.024 |
0.0006 |
0.066 |
0.000002 |
| Mian Sahab |
28 |
2 |
0.07 |
26,910 |
0.022 |
0.002 |
0.0005 |
0.066 |
0.000001 |
| Mirzapur |
28 |
22 |
0.79 |
27,246 |
0.022 |
0.017 |
0.0005 |
0.168 |
0.000003 |
| Mungrani |
28 |
8 |
0.29 |
26,032 |
0.021 |
0.006 |
0.0004 |
0.204 |
0.000003 |
| Naushero Abro |
28 |
7 |
0.25 |
28,939 |
0.023 |
0.006 |
0.0005 |
0.188 |
0.000004 |
| Nim |
28 |
6 |
0.21 |
27,886 |
0.022 |
0.005 |
0.0005 |
0.168 |
0.000003 |
| Panah Odho |
28 |
0 |
0.00 |
13,974 |
0.011 |
0.000 |
0.0001 |
0.000 |
0.000000 |
| Pir Bux Shujrah |
28 |
6 |
0.21 |
30,053 |
0.024 |
0.005 |
0.0006 |
0.168 |
0.000003 |
| Rahimabad |
28 |
5 |
0.18 |
27,807 |
0.022 |
0.004 |
0.0005 |
0.147 |
0.000003 |
| Ruk |
28 |
11 |
0.39 |
24,812 |
0.020 |
0.008 |
0.0004 |
0.239 |
0.000003 |
| Rustam |
28 |
17 |
0.61 |
31,529 |
0.025 |
0.015 |
0.0006 |
0.239 |
0.000005 |
| Sehwani |
28 |
13 |
0.46 |
24,628 |
0.020 |
0.009 |
0.0004 |
0.249 |
0.000003 |
| Shabirabad |
28 |
3 |
0.11 |
29,325 |
0.023 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
0.096 |
0.000002 |
| Sherkot |
28 |
20 |
0.71 |
19,324 |
0.015 |
0.011 |
0.0002 |
0.204 |
0.000002 |
| Sultan Kot |
28 |
3 |
0.11 |
28,331 |
0.023 |
0.002 |
0.0005 |
0.096 |
0.000002 |
| Taib |
28 |
25 |
0.89 |
28,957 |
0.023 |
0.021 |
0.0005 |
0.096 |
0.000002 |
| Thanhiro |
28 |
12 |
0.43 |
26,585 |
0.021 |
0.009 |
0.0005 |
0.245 |
0.000004 |
| Waryaso |
28 |
16 |
0.57 |
21,980 |
0.018 |
0.010 |
0.0003 |
0.245 |
0.000003 |
| Wazirabad |
28 |
10 |
0.36 |
28,208 |
0.023 |
0.008 |
0.0005 |
0.230 |
0.000004 |
| Zarkhail |
28 |
6 |
0.21 |
25,530 |
0.020 |
0.004 |
0.0004 |
0.168 |
0.000003 |
| Total |
|
560 |
|
1,248,943 |
|
42.47% |
|
|
0.0001 |
| *28 children per union council |
| ^Criteria: Pass - ≥19 fully immunized children, Fail - <19 fully immunized children |
| ^1Number Correct is defined as the number of children found vaccinated through recall/EPI home based records |
|
95% CI: (1.96 x √0.0001)= ± 0.019, ± 0.019 X 100= ±1.9
|
| We are 95% confident that the true coverage lies within the range of 40.5% --------- 42.4%---------44.3% |
| **UCs having ‘Pass’ status are on low priority if above 20, medium priority if on 19 or 20 successes, while UCs having ‘Fail’ status are on high priority |
Out of 560 (42.5%) Fully immunized children (FIC), 26.3% had a preserved government immunization cards (EPI card) that confirmed their immunization status.
Table 5 presents the distribution of FICs across geographical regions. More than half (53.2%) of FICs resided in urban areas followed by 28.8% and 18% in rural and peri-rural areas. Among partially immunized children, 37% were in rural areas, 32.4% in urban, and 30% in peri-rural areas. For unimmunized children, 47.6% were in rural areas, 38.8% in peri-rural, and 13.6% in urban areas.
Table 5.
Immunization status of children (n= 1,316) according to the areas of their residence.
Table 5.
Immunization status of children (n= 1,316) according to the areas of their residence.
| Type of Areas |
Fully Immunized |
Partially Immunized |
Unimmunized |
| |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
| Urban Areas |
298 |
53.2 |
164 |
32.4 |
34 |
13.6 |
| Rural Areas |
161 |
28.8 |
190 |
37.5 |
119 |
47.6 |
| Peri-Rural Areas* |
101 |
18.0 |
152 |
30.0 |
97 |
38.8 |
| Grand Total |
560 |
42.6 |
506 |
38.4 |
250 |
19 |
| *Peri-rural areas are those areas which are considered as areas with the worst roads infrastructure (also known as Katcha Areas) |
3.5.1. Reasons of failure to immunize
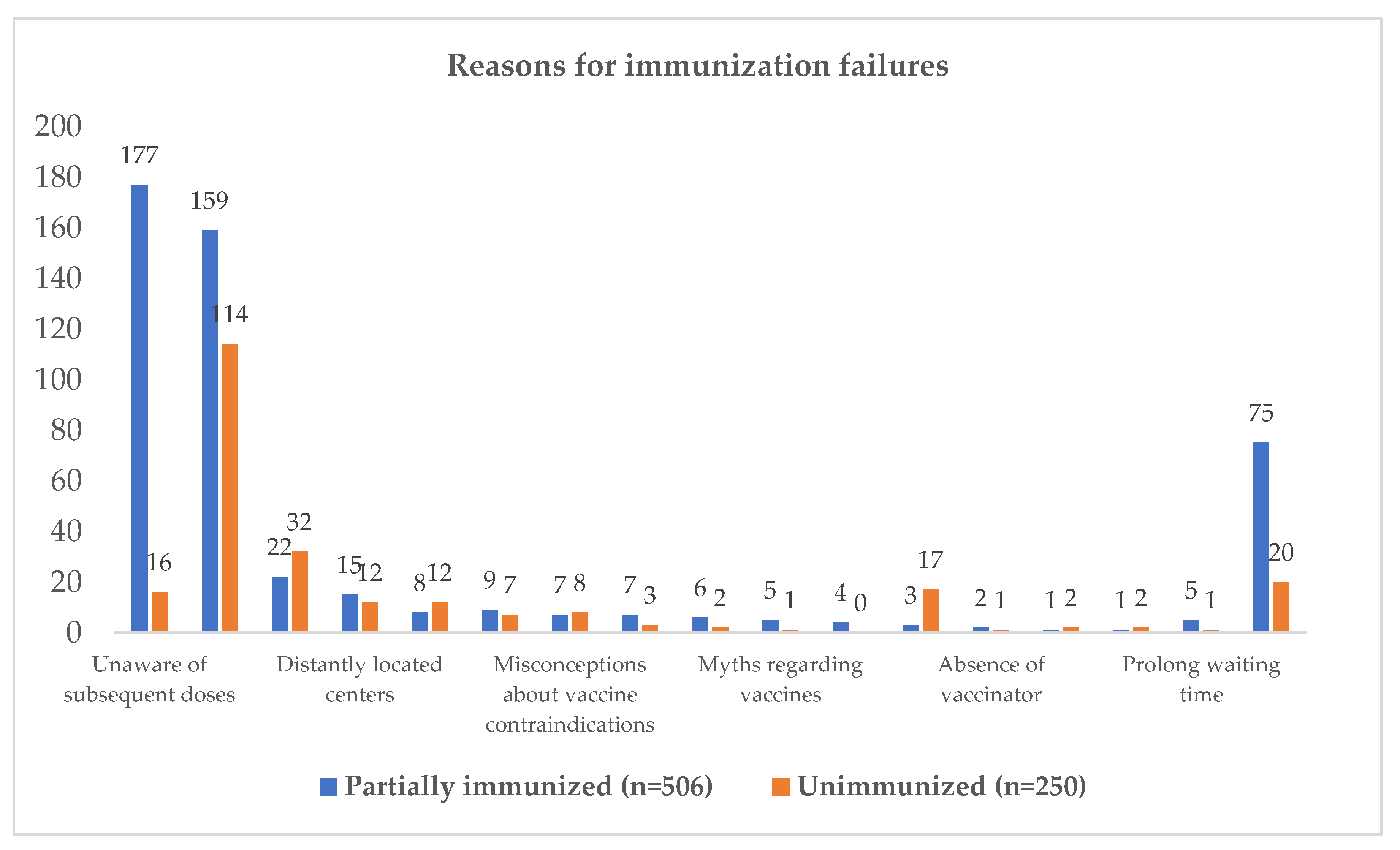
Figure 6 shows primary reasons of failure to complete immunization schedule, demonstrating 177 (35%) parents were unaware of subsequent doses, 159 (31.4%) lacked information, 22 (4.3%) feared side effects, 15 (3.0%) felt distantly located centers as main reason, and 8 (1.6%) were unsure of center timings/location. 114 (45.6%) unimmunized children (zero dose children) were uninformed, 32 (12.8%) feared side effects, 17 (6.8%) had inconvenient center timings, 16 (6.4%) were unaware of subsequent doses, 12 (4.8%) were unsure of center timings/location, and 12 (2.8%) felt that centers were distantly located.
Several key determinants were identified in a logistic regression analysis assessing factors affecting full immunization coverage among children under two years in Shikarpur district, as reflected in
Table 6. Geographical variation was significant, with children from Khanpur showing considerably lower odds of full immunization (OR: 0.38, 95% CI: 0.24 – 0.61, p<0.001) compared to Garhi Yasin, whereas Lakhi and Shikarpur exhibited varying odds. Urban-rural disparities were evident, as rural (OR: 0.64, 95% CI: 0.43 – 0.94, p=0.026) and peri-rural areas (OR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.36 – 0.85, p=0.007) had lower odds of full immunization compared to urban areas. Gender was not a significant factor. Higher paternal education significantly increased immunization likelihood (e.g., higher than graduation: OR: 21.5, 95% CI: 2.51 – 184.4, p=0.005), while access to health facilities and birthplace (primary care facility or tertiary care facility versus home birth) were not significant in the multivariable model. Socioeconomic status, as reflected in wealth quintiles, showed a positive gradient with immunization rates, with the upper quintile significantly more likely to be fully immunized (OR: 2.59, 95% CI: 1.22 – 5.50, p=0.013). The presence of a BCG scar was a robust predictor of full immunization (OR: 7.6, 95% CI: 5.13 – 11.22, p<0.001). These findings signifies the importance of addressing geographic, socioeconomic, and educational disparities to enhance childhood immunization coverage.
Table 6.
Univariable and multivariable analysis showing factors associated with full immunization coverage among children under 2 years of age in district Shikarpur.
Table 6.
Univariable and multivariable analysis showing factors associated with full immunization coverage among children under 2 years of age in district Shikarpur.
| Characteristics |
Univariable |
Multivariable |
| |
Odds
Ratio |
95%
Confidence Interval |
p-value |
Odds Ratio |
95% Confidence Interval |
p-value |
| Taluka |
| Garhi Yasin |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Lakhi |
1.83 |
1.34 – 2.48 |
<0.001 |
1.41 |
0.95 – 2.10 |
0.087 |
| Khanpur |
0.42 |
0.29 – 0.61 |
<0.001 |
0.38 |
0.24 – 0.61 |
<0.001 |
| Shikarpur |
1.09 |
0.82 – 1.45 |
0.536 |
0.51 |
0.33 – 0.79 |
0.003 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Locality |
| Urban |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Rural |
0.34 |
0.26 – 0.44 |
<0.001 |
0.64 |
0.43 – 0.94 |
0.026 |
| Peri-rural |
0.26 |
0.20 – 0.36 |
<0.001 |
0.56 |
0.36 – 0.85 |
0.007 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gender |
| Male |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Female |
0.94 |
0.76 – 1.18 |
0.642 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Child Age at Enrolment (months) |
| 12 – 15 |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 16 - 18 |
0.75 |
0.55 – 1.02 |
0.073 |
|
|
|
| 19 - 21 |
1.24 |
0.90 – 1.71 |
0.177 |
|
|
|
| 22 - 24 |
1.11 |
0.83 – 1.48 |
0.457 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Birthplace |
| Home |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Primary care facility |
1.99 |
1.40 – 2.82 |
<0.001 |
0.73 |
0.46 – 1.14 |
0.173 |
| Tertiary care facility |
2.29 |
1.80 – 2.91 |
<0.001 |
1.31 |
0.96 – 1.79 |
0.082 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Father’s Occupation |
| Unemployed |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Daily wages |
0.76 |
0.44 – 1.31 |
0.332 |
0.75 |
0.37 – 1.50 |
0.420 |
| Houseman |
0.78 |
0.44 – 1.40 |
0.421 |
1.09 |
0.49 – 2.46 |
0.820 |
| Self-employed |
1.39 |
0.74 – 2.61 |
0.303 |
0.80 |
0.36 – 1.78 |
0.586 |
| Government employee |
1.64 |
0.80 – 3.36 |
0.172 |
0.58 |
0.22 - 1.47 |
0.253 |
| Private employee |
1.05 |
0.52 – 2.11 |
0.889 |
0.68 |
0.27 – 1.66 |
0.400 |
| Student |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Farmer |
0.27 |
0.16 – 0.48 |
<0.001 |
0.61 |
0.29 – 1.28 |
0.195 |
| Retire |
0.41 |
0.03 – 4.78 |
0.478 |
0.13 |
0.00 – 2.06 |
0.152 |
| Other |
0.06 |
0.01 – 0.29 |
<0.001 |
0.22 |
0.03 – 1.34 |
0.102 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mother’s Occupation |
| Unemployed |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Farmer |
0.49 |
0.28 – 0.87 |
0.015 |
0.52 |
0.23 – 1.17 |
0.118 |
| Government employee |
3.16 |
1.22 – 8.18 |
0.017 |
0.99 |
0.30 – 3.31 |
0.999 |
| Private employee |
2.01 |
0.78 – 5.16 |
0.144 |
0.64 |
0.20 – 2.04 |
0.458 |
| Daily wages |
0.83 |
0.38 – 1.80 |
0.652 |
0.97 |
0.33 – 2.84 |
0.966 |
| Self-employee |
0.52 |
0.12 – 2.14 |
0.372 |
0.41 |
0.08 – 2.06 |
0.283 |
| Student |
0.31 |
0.03 – 2.87 |
0.307 |
0.08 |
0.00 – 0.86 |
0.037 |
| Housewife |
1.70 |
1.00 – 2.90 |
0.049 |
0.52 |
0.24 – 1.11 |
0.093 |
| Other |
1.05 |
0.26 – 4.13 |
0.938 |
1.66 |
0.28 – 9.74 |
0.574 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Father’s Education (years) |
| No education (0) |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Less than primary (1-4) |
1.79 |
1.22 – 2.61 |
0.003 |
1.13 |
0.68 – 1.87 |
0.625 |
| Primary (5) |
2.49 |
1.67 – 3.72 |
<0.001 |
1.30 |
0.78 – 2.16 |
0.312 |
| Middle (6-8) |
2.05 |
1.23 – 3.40 |
0.005 |
1.21 |
0.64 – 2.29 |
0.539 |
| Matric (10) |
4.72 |
3.14 – 7.09 |
<0.001 |
2.20 |
1.28 – 3.76 |
0.004 |
| Intermediate (12) |
5.19 |
3.33 – 8.11 |
<0.001 |
2.24 |
1.20 – 4.18 |
0.011 |
| Graduate (16) |
6.97 |
3.63 – 13.39 |
<0.001 |
2.63 |
1.14 – 6.04 |
0.023 |
| Higher than graduation (>16) |
58.8 |
7.90 – 437.6 |
<0.001 |
21.5 |
2.51 – 184.4 |
0.005 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mother’s Education (years) |
| No education (0) |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Less than primary (1-4) |
1.38 |
1.06 – 1.79 |
0.016 |
0.56 |
0.36 – 0.89 |
0.015 |
| Primary (5) |
1.52 |
1.00 – 2.32 |
0.048 |
0.69 |
0.38 – 1.25 |
0.225 |
| Secondary (6-8) |
1.80 |
0.97 – 3.34 |
0.060 |
0.50 |
0.22 – 1.14 |
0.101 |
| Matric (10) |
3.44 |
1.82 – 6.52 |
<0.001 |
1.23 |
0.50 – 3.02 |
0.640 |
| Intermediate (12) |
6.89 |
2.78 – 17.07 |
<0.001 |
1.79 |
0.59 – 5.40 |
0.298 |
| Graduate (16) |
12.06 |
1.47 – 98.58 |
0.020 |
1.15 |
0.11 – 11.8 |
0.900 |
| Higher than graduation (>16) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issues in accessing health facilities |
| No |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Yes |
0.45 |
0.35 – 0.58 |
<0.001 |
0.87 |
0.59 – 1.29 |
0.509 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Wealth quintiles |
| Lower |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Lower middle |
1.85 |
1.23 – 2.78 |
0.003 |
1.30 |
0.77 – 2.20 |
0.315 |
| Middle |
2.90 |
1.95 – 4.30 |
<0.001 |
1.34 |
0.75 – 2.39 |
0.310 |
| Upper middle |
5.36 |
3.62 – 7.94 |
<0.001 |
2.40 |
1.29 – 4.47 |
0.005 |
| Upper |
9.16 |
6.12 – 13.70 |
<0.001 |
2.59 |
1.22 – 5.50 |
0.013 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BCG scar |
| No |
1 (base) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Yes |
10.29 |
7.28 – 14.54 |
<0.001 |
7.6 |
5.13 – 11.22 |
<0.001 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
Pakistan initiated its Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) program in 1978 with the aim of shielding its children from diseases preventable by vaccination [
20]. However, by 2021, the country ranked third in terms of the number of under-vaccinated children [
20]. While previous data suggests that the national vaccination coverage is approximately 66% with the aim to reach 90% by 2022, such figures do not provide a clear insight into the performance at the grassroots administrative level [
21]. This lack of granularity in data complicates the task for management authorities when determining where resources need to be reallocated for optimal impact.
We addressed this gap by systematically assessing immunization coverage in Shikarpur for children aged 12-23 months using Lot Quality Assurance Sampling (LQAS), which also revealed priority areas. Our preliminary findings show that 42.4% of children in Shikarpur were vaccinated with all recommended vaccinations and 44% with MCV-1 alone on the scale of primary vaccines, placing it considerably below the district-level recommendation of 80%. Our methodology helped us identify significant factors for the inadequate vaccination rate. Lack of information and fear of side effects prevented caregivers of zero-dose children from starting the vaccination schedule, while caregivers of partially immunized children cited being unaware of the subsequent doses.
Additionally, LQAS approach indicated 39 priority sites for resource diversion. LQAS insights and the importance of vaccination coverage emphasize the need to resolve these challenges and ensure effective vaccination efforts for community children. One of the benefits of the Lot Quality Assurance Sampling (LQAS) method is rapid assessment, which is crucial in public health since prompt interventions can lead to swift results. We used 28 samples per UC to meet its needs, unlike other methods. Such cost and time savings, however, do not come at the expense of depth. Our analysis found that only 17% of surveyed regions meet criteria, while the rest need urgent attention from government bodies. LQAS's emphasis on localized evaluations at UC level encourages regional decisions and discourages a one-size-fits-all approach [
22]. However, this methodology comes up with certain limitations. LQAS inherently provides a binary outcome, often grouping results into 'acceptable' or 'unacceptable' categories [
23], potentially overlooking distinctions, especially in areas straddling the decision threshold. The reduced sample sizes, while cost-effective, might compromise precision specially when the sample size drops below 19 per SA/UC [
14]. We addressed this concern and created another category of medium priority to reduce the chances of misclassification. Furthermore, biases in respondents' reporting, driven perhaps by societal expectations or simple forgetfulness, might have skewed results. Future studies may also consider visiting EPI health centers to validate the claims and match the information from the health records. If the sampled lots were unrepresentative, the generalizability of the findings could also be questioned and this is the main reason why the sample size was increased from minimum 19 to 28 per UC.
Historically, numerous coverage assessments have been carried out throughout Pakistan with a significant majority focusing primarily on urban regions. And the reported vaccination coverage rates have fluctuated between 49% and 62.9% in these urban settings [
4,
24,
25]. However, a recent national survey estimated vaccination coverage in rural settings of Balochistan and FATA (KP-NMD) to be around 37.7% and 42.9%, respectively [
26]. So, despite Shikarpur’s better infrastructure when compared to many districts in those provinces such as Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, it exhibits vaccination coverage rates that align closely with these areas. This similarity may stem from prolonged tribal conflicts, which have deterred the health department from extending outreach services to more remote regions. The poor coverages are more pronounced in taluka Khanpur which has the highest security incident reported so far. We, adding up to this challenge, were also unable to collect our data from two Union Councils classified as no-go areas; both belonged to taluka Khanpur. Interestingly, one particular study highlighted as many as 47 interventions initiated by UNICEF and its partners to enhance these poor coverage rates within urban areas [
24] while only few, as carpool services, have been reported from rural areas [
27].
Our study revealed a striking finding for caregivers who either did not start the immunization schedule for their children or started it but missed vaccine doses. While the lack of immunization information is a major concern, caregivers' ignorance of follow-up doses highlighted another gap. This highlights the importance of service providers' communication channels, especially in low-literacy communities. Significantly, our findings replicate earlier findings about the lack of information affecting vaccine coverage in many Pakistani and international regions [
4,
28,
29]. The challenges faced by caregivers in maintaining consistent immunization practices seem to be a shared concern, highlighting the need for a comprehensive and unified approach to address these informational gaps. Fear of side effects was another frequently cited reason that restricted caregivers from initiating or adhering to the vaccination schedule. This concern is not unique but is prevalent in both developed and developing countries alike [
30]. Surprisingly, the challenges of long distances or infrastructure inadequacies were not the primary concerns given the ongoing tribal conflicts within the district. This can be attributed to the phenomenon that the initial phase of health-seeking behavior revolves around the willingness to begin immunization for their children. If parents or the community are unconvinced about the importance of vaccination, then logistical issues like reaching health facilities become secondary concerns. Therefore, this aspect of vaccine hesitancy offers a valuable opportunity for communication strategists to address and resolve the underlying issues. Busiest health facilities can serve as the sites for this kind of sensitization from the early points of Ante-Natal Care (ANC) visits when mothers are pregnant.
If these poor vaccination coverages persisted in Shikarpur without being intervened, it can have significant consequences in the form of increased risk of outbreaks from vaccine-preventable diseases as evident in the past [
31,
32]. Lower childhood vaccination coverages have other consequences as well which extend beyond the immediate health outcomes. Increased school attendance and achievement because of improved child health due to vaccination has been demonstrated to ultimately affect cognitive and educational outcomes in late adulthood [
33]. Hence, low vaccination rates may have long-term effects on cognitive function and educational performance as well. The associated reasons such as lack of information implies a potential need for health agencies to boost their awareness campaigns, ensuring they are widespread and easily accessible. Furthermore, healthcare professionals must be equipped with accurate and regularly updated information to relay to patients and their caregivers [
34]. Particularly, targeted information campaigns might be essential for populations in remote or underserved areas as Shikarpur [
35]. Another reason of unawareness of subsequent doses indicates possible lapses in the follow-up mechanisms integral to immunization programs. EPI Health systems, as a solution, might need to reevaluate and strengthen their reminder and follow-up systems. Leveraging technology, such as SMS reminders or mobile apps, could be a beneficial approach [
35]. Moreover, enhanced record-keeping and effective data sharing among health providers (vaccinators) can ensure that individuals are consistently reminded of upcoming doses. Training health workers to emphasize the necessity of completing the immunization schedule during the initial doses could further address this concern. And then the fear of side effects, both perceived and real, covers up health and socio-psychological domains [
36]. Myths and misinformation can exacerbate vaccine hesitancy, while genuine concerns demand attention and mitigation. So, transparent communication about potential side effects, their likelihood, and severity is crucial to building public trust. Implementing real-time monitoring and reporting systems for vaccine side effects can also reassure the public that concerns are promptly addressed. A past study has suggested that engaging with community peers, leaders and influencers can play a pivotal role in alleviating fears, fostering a community-wide trust in immunization [
37].
Overall, this study provides a roadmap for the policy developers signifying the need for multifaceted public health strategies in Shikarpur. Identifying 39 priority areas for intervention emphasizes the importance of targeted resource allocation and localized decision-making in improving vaccination coverage. These insights not only inform public health initiatives in Shikarpur but also offer valuable lessons for similar contexts globally, emphasizing a proactive approach in complex socio-political environments.
5. Conclusions
This study highlights the importance of using advanced methods like LQAS to understand the complex challenges in improving immunization coverage in areas like Shikarpur. It shows that combining detailed data analysis with approaches sensitive to local culture and geo-political situations is key to increasing vaccination rates. Additionally, it is essential for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community leaders to develop strategies that ensure all children have equitable access to vaccines by reallocating resources from LQAS-passed UCs to failed ones. This collaborative approach is crucial for protecting public health and achieving global vaccination goals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S., I.B., N.S., and K.S.; methodology, S.S., I.B., and K.S.; software, R.F. and R.H.; questionnaire review and pilot testing, S.S., I.B., and N.S.; formal analysis, S.S., I.B., N.S. and R.F.; resources, S.S.; data curation, R.F., R.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S., I.B., K.S., and N.S.; writing—review and editing, I.B., N.S., and R.H.; supervision, I.B., N.S., K.S., and R.H.; project administration, S.S., I.B., K.S., and N.S.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM PPI/111/8/JEP-590 and 28.04.2018); Institutional Review Board of Interactive Research & Development (IRD/IRB/2018/04/007) from Pakistan; and District Health Officer-Shikarpur letter No. (DHO/SHP/2347).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, prior to beginning data collection to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request after removing identifiers.
Acknowledgments
Our sincere thanks to Dr. Khurshid Ahmed Kazi, Dr. Asif Ali Zardari, and Dr. Zainul Abideen Khan for their critical guidance and technical expertise in finalizing this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Orenstein, W.A.; Ahmed, R. Simply put: Vaccination saves lives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 4031–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Vaccines and Immunization. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Audrey Rachlin, M.C.D.-H., Padraic Murphy, Samir V. Sodha, Aaron S. Wallace. Routine Vaccination Coverage—Worldwide, 2021. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/pdfs/mm7144a2-H.pdf.
- Yazdani, A.T.; Muhammad, A.; Nisar, M.I.; Khan, U.; Shafiq, Y. Unveiling and addressing implementation barriers to routine immunization in the peri-urban slums of Karachi, Pakistan: a mixed-methods study. Health Research Policy and Systems 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization – Eastern Mediterranean Regional Office. Expanded Programme on Immunization - Pakistan. https://www.emro.who.int/pak/programmes/expanded-programme-on-immunization.html. 2021. (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Ahmad, N.; Mhd Din, I.A.; Idris, I.B.; Zaini, N.e. Resurgence of measles infection among children: findings from a surveillance-based population study. Paediatrica Indonesiana 2023, 63, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Why CDC Is Involved in Global Immunization. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/immunization/why/index.html (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- World Health Organization. Immunization Coverage- Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/immunization-coverage (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Dimitrova, A.; Carrasco-Escobar, G.; Richardson, R.; Benmarhnia, T. Essential Childhood Immunization in 43 Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Analysis of Spatial Trends and Socioeconomic Inequalities in Vaccine Coverage. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, A. Challenges for the government school teachers during COVID-19 and tribal conflicts/feuds in Shikarpur district, Sindh, Pakistan. Education and Conflict Review 2023, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Idrees, M. Over 2,301 killed in 1,566 tribal clashes in Sindh during five years: report. Daily Pakistan, 10 Dec, 2018, 2018.
- Danovaro-Holliday, M.C.; Dansereau, E.; Rhoda, D.A.; Brown, D.W.; Cutts, F.T.; Gacic-Dobo, M. Collecting and using reliable vaccination coverage survey estimates: Summary and recommendations from the "Meeting to share lessons learnt from the roll-out of the updated WHO Vaccination Coverage Cluster Survey Reference Manual and to set an operational research agenda around vaccination coverage surveys", Geneva, 18-21 April 2017. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5150–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutts, F.T.; Claquin, P.; Danovaro-Holliday, M.C.; Rhoda, D.A. Monitoring vaccination coverage: Defining the role of surveys. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4103–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoda, D.A.; Fernandez, S.A.; Fitch, D.J.; Lemeshow, S. LQAS: User Beware. Int J Epidemiol 2010, 39, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hund, L. New tools for evaluating LQAS survey designs. Emerging Themes in Epidemiology 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, K.; Rondy, M.; Chevez, A.; Sadozai, N.; Gasasira, A.; Abanida, E.A.; Pate, M.A.; Ronveaux, O.; Okayasu, H.; Pedalino, B.; et al. Clustered lot quality assurance sampling: a pragmatic tool for timely assessment of vaccination coverage. Trop Med Int Health 2011, 16, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Valadez, W.W. Corey Leburg, Robb Davis. Assessing Community Health Programs- A Participant’s Manual and Workbook- Using LQAS for Baseline Surveys and Regular Monitoring. 2002.
- Razaq, S.; Batool, A.; Ali, U.; Khalid, M.S.; Saif, U.; Naseem, M. Iterative Design of an Immunization Information System in Pakistan. Proceedings of the 7th Annual Symposium on Computing for Development 2016. p. 1-10.
- World Health Organization. Training for Mid-Level Managers (MLM). Module 7: The EPI Coverage Survey, 2nd ed, republished 2020. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2008; ISSN1 978-92-4-001575-3. ISSN2 978-92-4-001576-0.
- Imran, H.; Raja, D.; Grassly, N.C.; Wadood, M.Z.; Safdar, R.M.; O'Reilly, K.M. Routine immunization in Pakistan: comparison of multiple data sources and identification of factors associated with vaccination. Int Health. 2018, 10, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, A.; Waseem, A.; Siddiqa, M.; Ijaz, M.; Shakeel, A.; Iftikhar, S. Contextual factors influencing incomplete immunization and investigation of its geospatial heterogeneity in Pakistan: a cross-sectional study based on PDHS (2017-18). BMC Public Health. 2023, 23, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group C. LQAS Frequently Asked Questions. 2008.
- Admon, A.J.; Bazile, J.; Makungwa, H.; Chingoli, M.A.; Hirschhorn, L.R.; Peckarsky, M.; et al. Assessing and improving data quality from community health workers: a successful intervention in Neno, Malawi. Public Health Action. 2013, 3, 56–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Ahmad, D.; Tariq, E.; Yunus, S.; Warsi, S.; Hasmat, L.; et al. Barriers to childhood vaccination in urban slums of Pakistan. East Mediterr Health J. 2023, 29, 371–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, S.; Ahmed, S.; Qazi, M.F.; Ali, R.; Ali, S.A.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; et al. Differential coverage for vaccines in the expanded program on immunization (EPI) among children in rural Pakistan. Vaccine 2023, 41, 2680–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Khan, A.; Rhoda, D.A.; Ahmed, I.; Umer, M.; Ansari, U.; et al. Routine Immunization Coverage and Immunization Card Retention in Pakistan: Results From a Cross-sectional National Survey. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2023, 42, 260–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.F.; Iftikhar, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, A.A.; Siddiqi, D.A.; Chandir, S. Feasibility assessment of immunization
carpool model for <2 years children in rural Pakistan . European Journal of Public Health. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Sahu, D.; Agrawal, A.; Vashi, M.D. Barriers and opportunities for improving childhood immunization coverage in slums: A qualitative study. Prev Med Rep. 2019, 14, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibanez, T.A.; Nguyen, K.H.; Greby, S.M.; Fisher, A.; Scanlon, P.; Bhatt, A.; et al. Parental Vaccine Hesitancy and Childhood Influenza Vaccination. Pediatrics 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.L. Recommended Solutions to the Barriers to Immunization in Children and Adults. SCIENCE OF MEDICINE. 2014, 111, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, H.; Deribew, A.; Woldie, M. Predictors of defaulting from completion of child immunization in south Ethiopia, May 2008: a case control study. BMC Public Health. 2009, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukusa, L.A.; Ndze, V.N.; Mbeye, N.M.; Wiysonge, C.S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of educating parents on the benefits and schedules of childhood vaccinations in low and middle-income countries. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018, 14, 2058–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, R. Oskorouchi AS-P, David E. Bloom. The Long-Term Cognitive and Schooling Effects of Childhood Vaccinations in China. National Bureau of Economic Research. 2020.
- Cataldi, J.R.; Kerns, M.E.; O'Leary, S.T. Evidence-based strategies to increase vaccination uptake: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020, 32, 151–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitaloka, C.P.; Handayani, S. Interventions to improve vaccination coverage of children in hard-to-reach population: A systematic review. International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS). 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Weinman, J.; Amlot, R.; Yiend, J.; Rubin, G.J. Parental Expectation of Side Effects Following Vaccination Is Self-fulfilling: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann Behav Med. 2019, 53, 267–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, J.; Overmars, I.; Leask, J.; Seale, H.; Chisholm, M.; Hart, J.; et al. Vaccine Champions Training Program: Empowering Community Leaders to Advocate for COVID-19 Vaccines. Vaccines (Basel). 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).