Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
20 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Ethnomedicinal Uses
3. Geographical Distribution
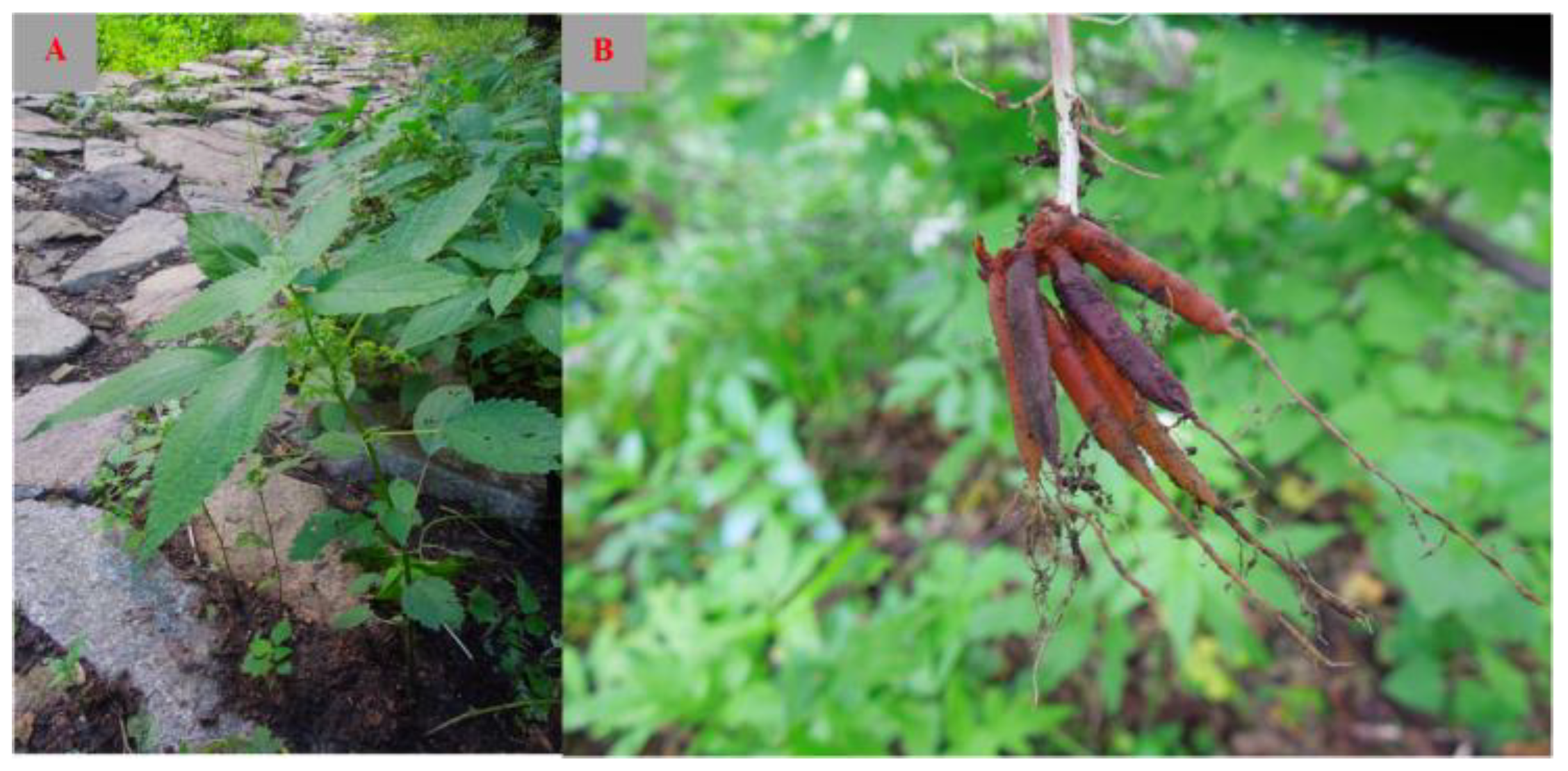
4. Botanical Description
5. Phytochemistry
5.1. Flavonoids
5.2. Phenolics
5.3. Nitrogen Compounds
5.4. Steroids
5.5. Terpenoids
5.6. Coumarins
5.7. Phenylpropanoids
5.8. Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives
5.9. Others
6. Quality Control
7. Pharmacological Effects
7.1. Antioxidant Activity
7.2. Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
7.3. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Activity
7.4. Other Pharmacological Effects
7.5. Toxicity
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, M.M.; Li, Y.N.; Ming, W.K.; Wu, P.F.; Yi, P.; Gong, Z.P.; Hao, X.J.; Yuan, C.M. Bioassay-guided isolation of human carboxylesterase 2 inhibitory and antioxidant constituents from Laportea bulbifera: Inhibition interactions and molecular mechanism. Arabian J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, B.; Yu, D.Y.; Feng, B.M. Flavonoids from Laportea bulbifera and their anti-N1 neuraminidase activities. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2018, 35, 931–935, 942. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.C.; Choi, S.Z.; Lee, S.O.; Chung, A.K.; Nam, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.R. Flavonoid constituents and their antioxidant activity of Laportea bulbifera Weddell. Korean J. Pharmacogn 2003, 34, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.R.; Su, Z.Q.; Pi, H.F.; Yao, G.M.; Zhang, P.; Luo, X.; Xie, S. N.; Xiang, M. Immunosuppressive constituents from Urtica dentata Hand. J. Asian Nat. Prod. 2010, 12, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.X. Study on the mechanism of anti-hyperlipidemia effects and its pharmacodynamics substantial foundation of Laportea bulbifera. Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Wen, H.C.; Dou, D.Q. Chemical constituents from Laportea bulbifera, a Zhuang medicine. Chin. Pharm. J. 2019, 54, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, Z.P.; Li, W.W.; Lan, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.L. Identification of chemical compositions in Laportea bulbifera by UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 2018, 24, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Y. Study on the anti-inflammatory material basis and preliminary metabolism in vivo of the ethnic medicine Laportea bulbifera. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yang, X.S.; Hao, X.J. Studies on the chemical constituents of Laportea bulbifera. Chin. Med. Mat. 2011, 34, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.J. Study on chemical constituents and bioactivities of two national medicinal plants. Master’s Thesis, China State Institute of Pharmaceutical Industry, Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Feng, W.; Qi, J.; Feng, B. Phytochemical, chemotaxonomic and bioinformatics study on Laportea bulbifera (Urticaceae). Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, 202200070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.L.; Li, W.J.; Hou, W.R.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yi, L.J.; Zeng, Y.; Xiang, M. Study on effect of total coumarins from Urtica dentata on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med 2012, 37, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Zou, S.H.; Xu, W.F.; Sun, Q.W.; Yun, L. Spectrum–effect relationship of antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of Laportea bulbifera based on multivariate statistical analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 34, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Hou, W.R.; Xie, S.N.; Zhang, W.D.; Wang, X. Immunosuppressive effects of an ethyl acetate extract from Urtica dentata Hand on skin allograft rejection. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Xie, S.N.; Hou, W.R.; Tao, E.; Xiang, M. Effects of analgesia, anti-inflammation and immunosuppression of acetic ether extract of Chinese medicine honghuoma. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2009, 25, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, S.S.; Lu, J.L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiang, M. Therapeutic effects of total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand on collagen-induced arthritis in Balb/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.J.; Tang, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, D.; Xiao, H.Q.; Lan, Y.Y.; Wang, A.M.; Xi, X.L.; Gong, Z.P. Study on quality control of Miao medicine Laportea bulbifera based on fingerprint analysis and quantitative analysis of multi-components. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2020, 51, 4325–4330. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.J.; Li, G. Report on the scientific and technological competitiveness of large varieties of traditional Chinese Medicine. The People’s Medical Publishing House. 2019.
- Flora of China Editorial Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Flora of China. Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995, Volume 23, pp. 31–32.
- Editorial Committee of Chinese Materia Medica, State Administration of TCM. Chinese Materia Medica (Zhonghua Bencao): In Miao’s Material Medica. Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 2005.
- Fu, L.G.; Chen, T.Q.; Lang, K.Y.; Hong, T.; Lin, Q. Higher Plants of China; Qingdao Publishing House: Qingdao, China, 2000; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Iconographia Cormophytorum Sinicorum; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1972; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Lu, X.; Feng, B.M.; Yu, D.Y.; Wang, H.G.; Shi, L.Y.; Yu, Z.X.; Qin, H.H. Flavonoids isolated from Laportea bulbifera. Chinese Chemical Society. Proceedings of the 11th National Conference on Natural Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Chemical Society, volume 3. 2016.
- Wang, S.L. Material basis for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Laportea bulbifera and its quality control. Master’s Thesis, Guiyang Medical College, Guiyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.H. Preliminary study on quality control and spectral effect relationship of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of medicinal materials of Miao medicine honghema. Guiyang College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang, China, 2017.
- Feng, J.X.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Z.B.; Sun, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Xia, G.Q.; Zang, H. Screening the extract of Laportea bulbifera (Sieb. et Zucc.) Wedd. based on active component content, its antioxidant capacity and exploration of hepatoprotective activity in rats. Molecules. 2023, 28, 6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as potential anti-inflammatory molecules: A review. Molecules. 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.Y.; Suo, Y.R.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.Q.; Dai, Y.H.; Ni, Y.Y.; Yang, R.R.; Qiao, Y.H.; Ma, Z.Q.; Lin, R.C. Screening of active components of Urtica dentata Hand by RAW264.7 anti-inflammatory cell model and chemical constituents. Global Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 11, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Cherubim, D.J.; Buzanello Martins, C.V.; Oliveira Fariña, L.; da Silva de Lucca, R.A. Polyphenols as natural antioxidants in cosmetics applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finamore, A.; Palmery, M.; Bensehaila, S.; Peluso, I. Antioxidant, immunomodulating, and microbial-modulating activities of the sustainable and ecofriendly spirulina. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 3247528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Jayaraman, S. An update on β-sitosterol: A potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antika, L.D.; Tasfiyati, A.N.; Hikmat, H.; Septama, A.W. Scopoletin: A review of its source, biosynthesis, methods of extraction, and pharmacological activities. Z. Naturforsch. C. J. Biosci. 2022, 77, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Fan, X.; Cui, B.; Zhao, T.; Mao, L.; Feng, H.; Lin, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C. Scoparone as a therapeutic drug in liver diseases: Pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and molecular mechanisms of action. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; WenHua, L.; XiaoHui, Z. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad Abdul Kadar, N.N.; Ahmad, F.; Teoh, S.L.; Yahaya, M.F. Caffeic acid on metabolic syndrome: A review. Molecules. 2021, 26, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, N. Therapeutic potentials and mechanisms of the Chinese traditional medicine danshensu. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 864, 172710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Functional roles of fatty acids and their effects on human health. JPEN, J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2015, 39, 18S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Willemsen, L.E.M. Immunopharmacology of fatty acids. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, F.; Agostoni, C.; Borghi, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cena, H.; Ghiselli, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Lercker, G.; Manzato, E.; Pirillo, A.; Riccardi, G.; Risé, P.; Visioli, F.; Poli, A. Dietary linoleic acid and human health: Focus on cardiovascular and cardiometabolic effects. Atherosclerosis. 2020, 292, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Xie, F.; Huang, W.; Hu, M.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L. The review of alpha-linolenic acid: Sources, metabolism, and pharmacology. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 164–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizhou Medical Products Administration. Quality standards for traditional Chinese medicine and ethnomedicine in Guizhou Province (2019 edition) volume 2. Beijing: China Medical Science Press. 2022.
- Wan, D.R.; Feng, S.Q.; Li, A.J. Pharmacognostic identification of ethnic medicine honghuoma and huoma. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 1989, 20, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.W.; Xu, W.F.; Qi, W.N.; Bai, C.H.; Wei, S.H. Study on the pharmacognostic identification of Miao herbs honghema and confusion varieties aima. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2015, 38, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L. Material basis for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Laportea bulbifera and its quality control. Master’s Thesis, Guiyang Medical College, Guiyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Gong, Z.P.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, A.M.; Li, W.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Lan, Y.Y. Simultaneous determination of 11 constituents in Laportea bulbifera of Miao medicine by UPLC-ESI-MS. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 39, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Wen, D.; Chen, Y.R.; Xu, W.F.; Wei, S.H. Correlation analysis on polysaccharide content of medicinal material of Miao National Herbs Laportea bulbifera germplasm with environmental factors. Seed. 2016, 35, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Peng, W. Identification and quantification of total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand and its roles in promoting immune tolerance via TLR4-mediated dendritic cell immaturation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, S.S.; Lu, J.L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiang, M. Therapeutic effects of total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand on collagen-induced arthritis in Balb/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Du, B.; Xu, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of phytochemicals from fruits, vegetables, and food legumes: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Zheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Lan, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Z.P. Potential pharmacodynamic substances of Laportea bulbifera in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on serum pharmacochemistry and pharmacology. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2022, 47, 4755–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Xie, S.N.; Hou, W.R.; Tao, E.; Xiang, M. Effects of analgesia, anti-inflammation and immunosuppression of ethyl acetate extract of Chinese medicine honghuoma. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2009, 25, 559–560. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Gong, Z.P.; Kang, N.F.; Wu, D.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.T.; Pan, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lan, Y.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y.L. Differences in intestinal absorption characteristics of Laportea bulbifera extract in normal and rheumatoid arthritis model rats by isolated everted intestine model. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Study on effects and mechanism of the active fraction of honghuoma in rheumatoid arthritis. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.L.; Li, W.J.; Hou, W.R.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yin, L.J.; Zeng, Y.; Xiang, M. Study on effect of total coumarins from Urtica dentata on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Xiang, M. Total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression of the TLR4-signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Y. Preparation and anti-T2DM-IR effects of flavonoid rich extract from Urtica dentata Hand. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hubei Provincial Revolutionary Committee Health Bureau. Hubei Chinese Herbal Medicine Record (II). Wuhan: Hubei People's Press. 1982.
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Du, K.; Liang, C.; Wang, S.; Owusu Boadi, E.; Li, J.; Pang, X.; He, J.; Chang, Y.X. Traditional herbal medicine: Therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W. Exploration of the effects of N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the prevention and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and related mechanisms. Master’s Thesis, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

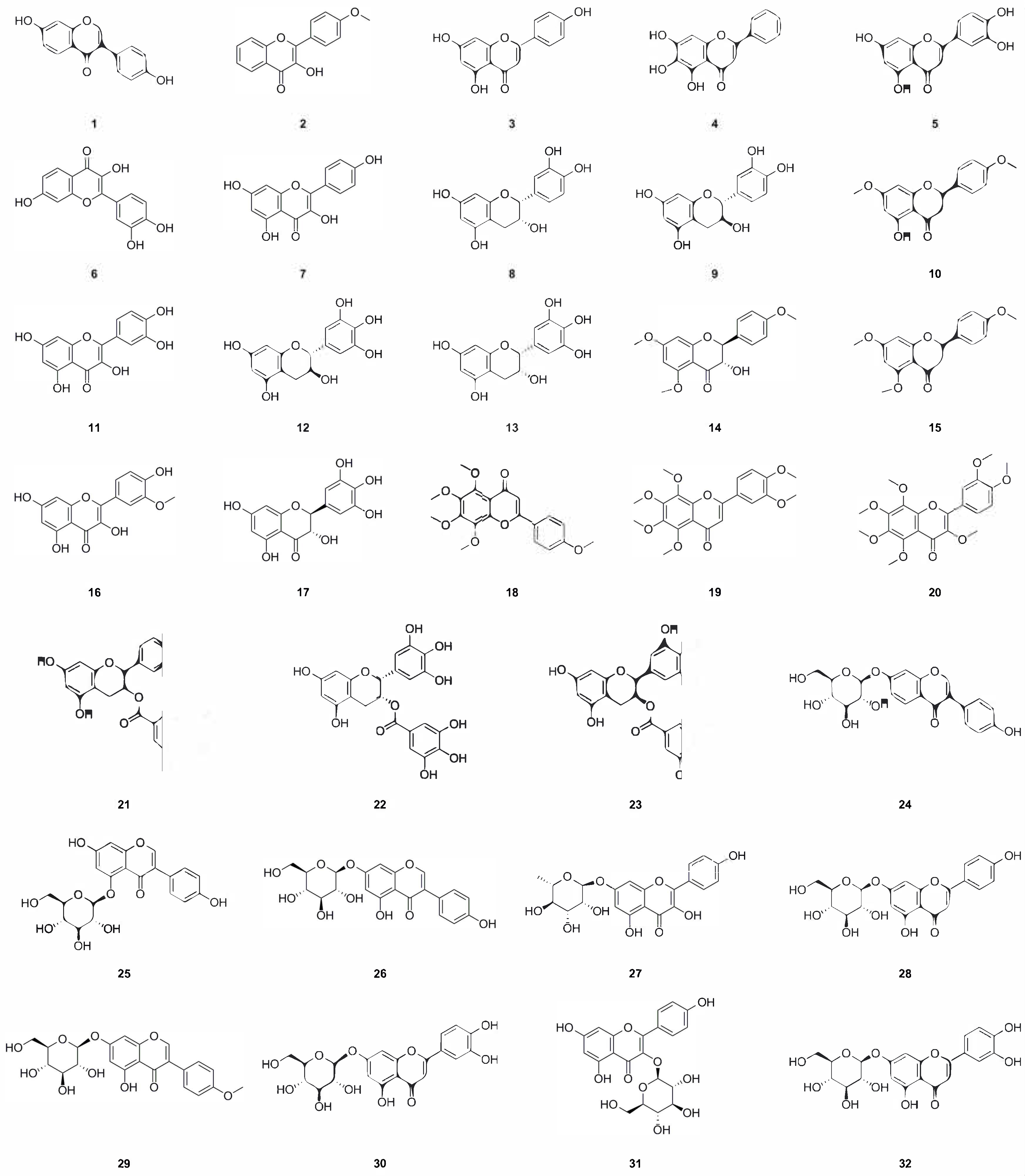
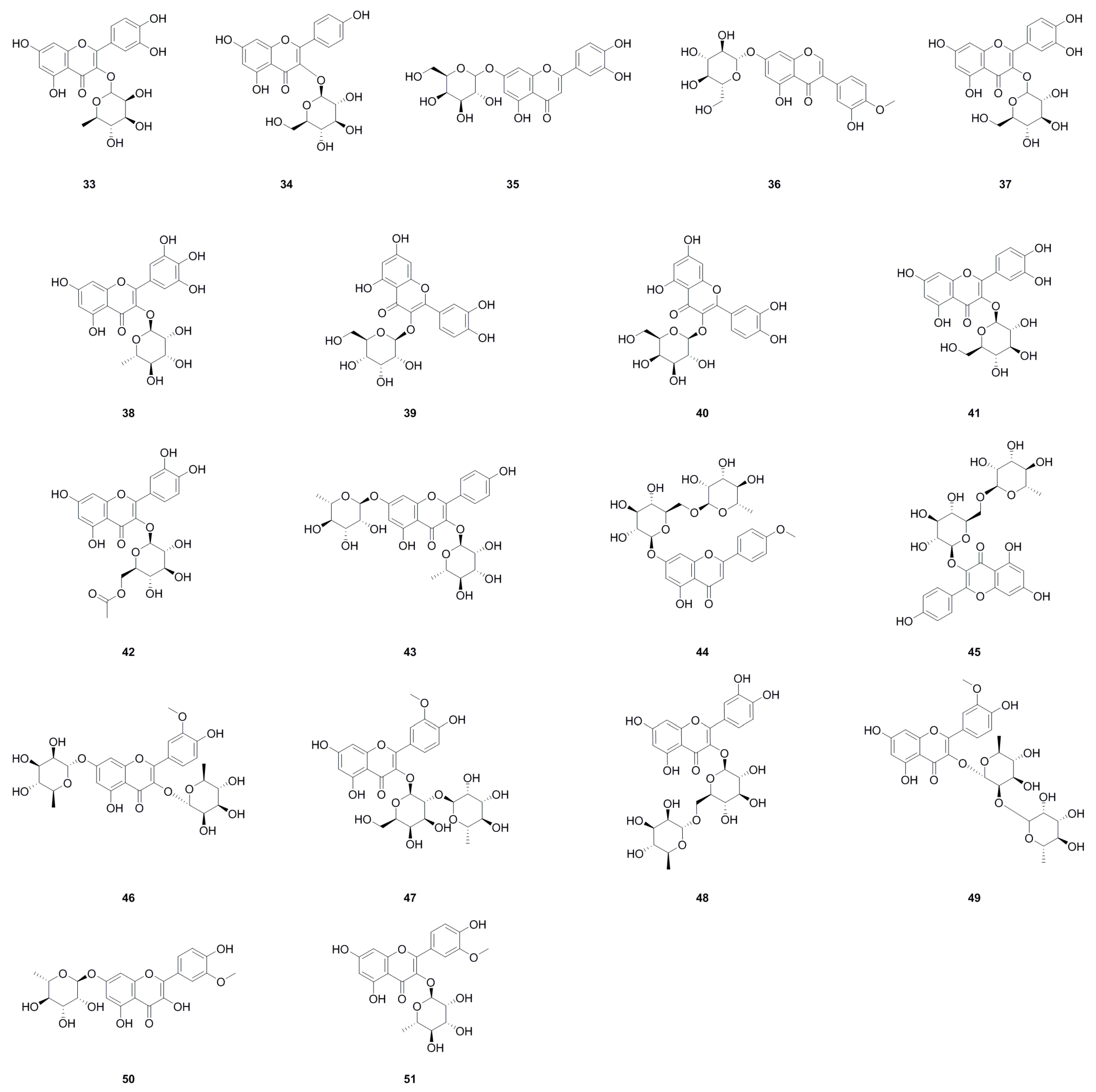
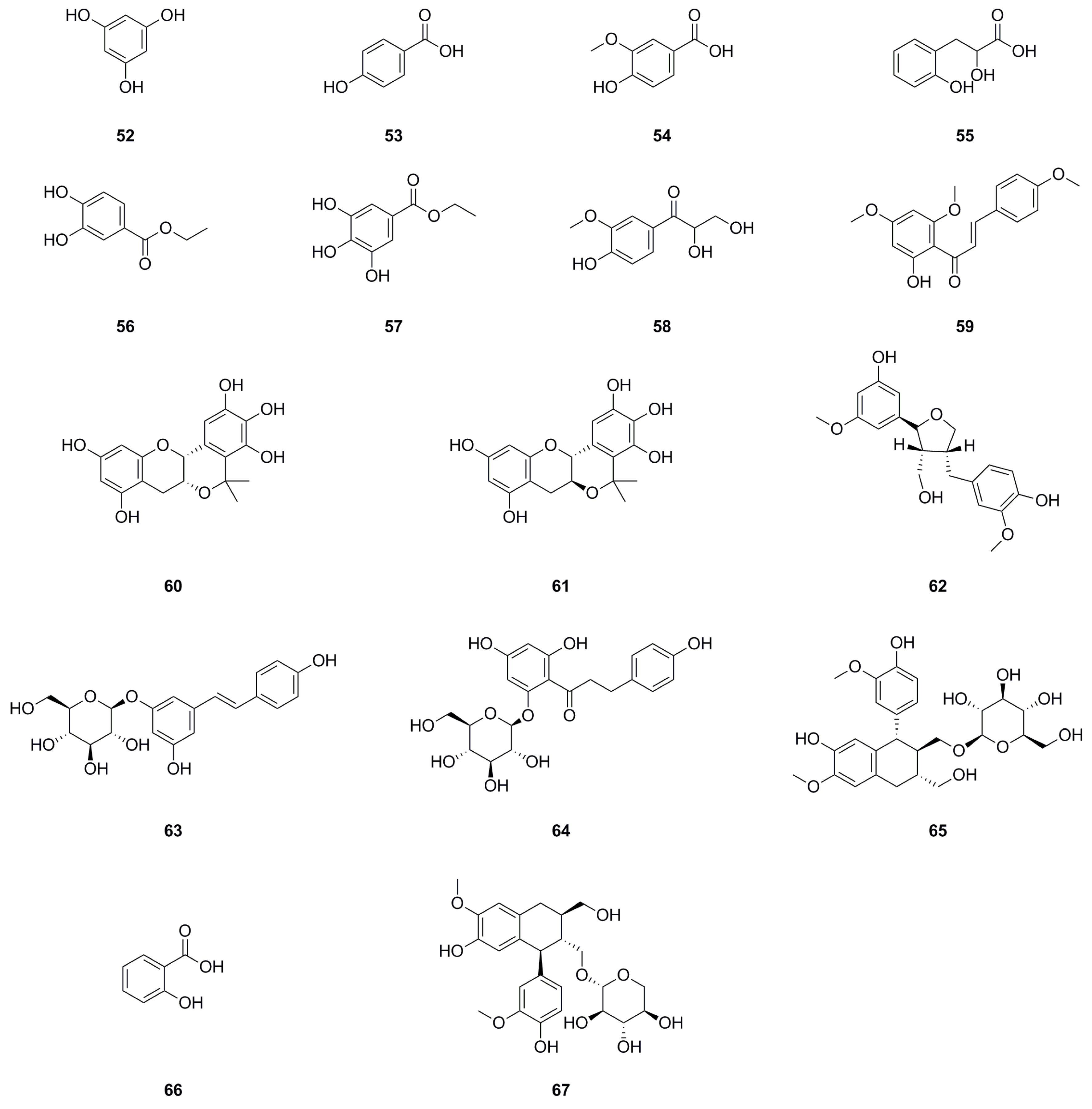
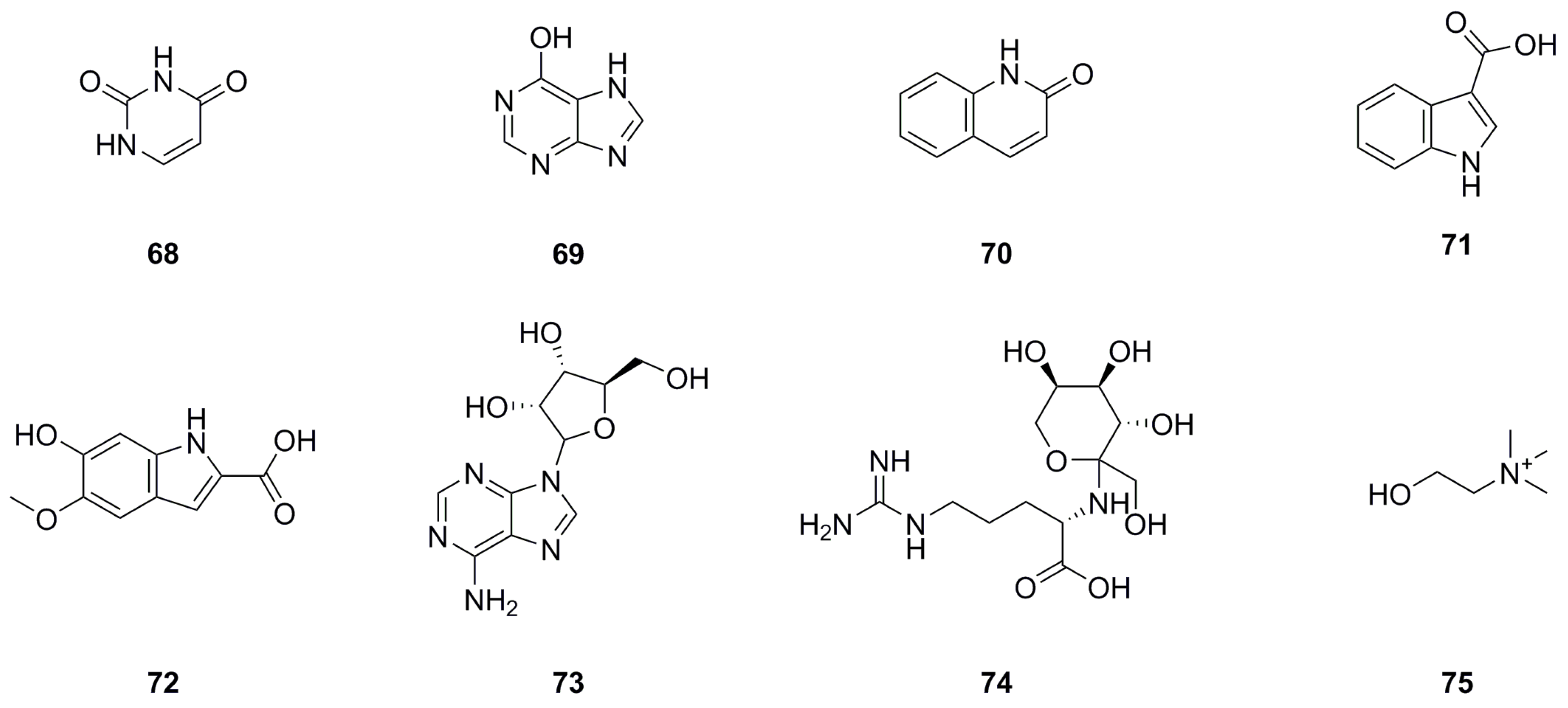
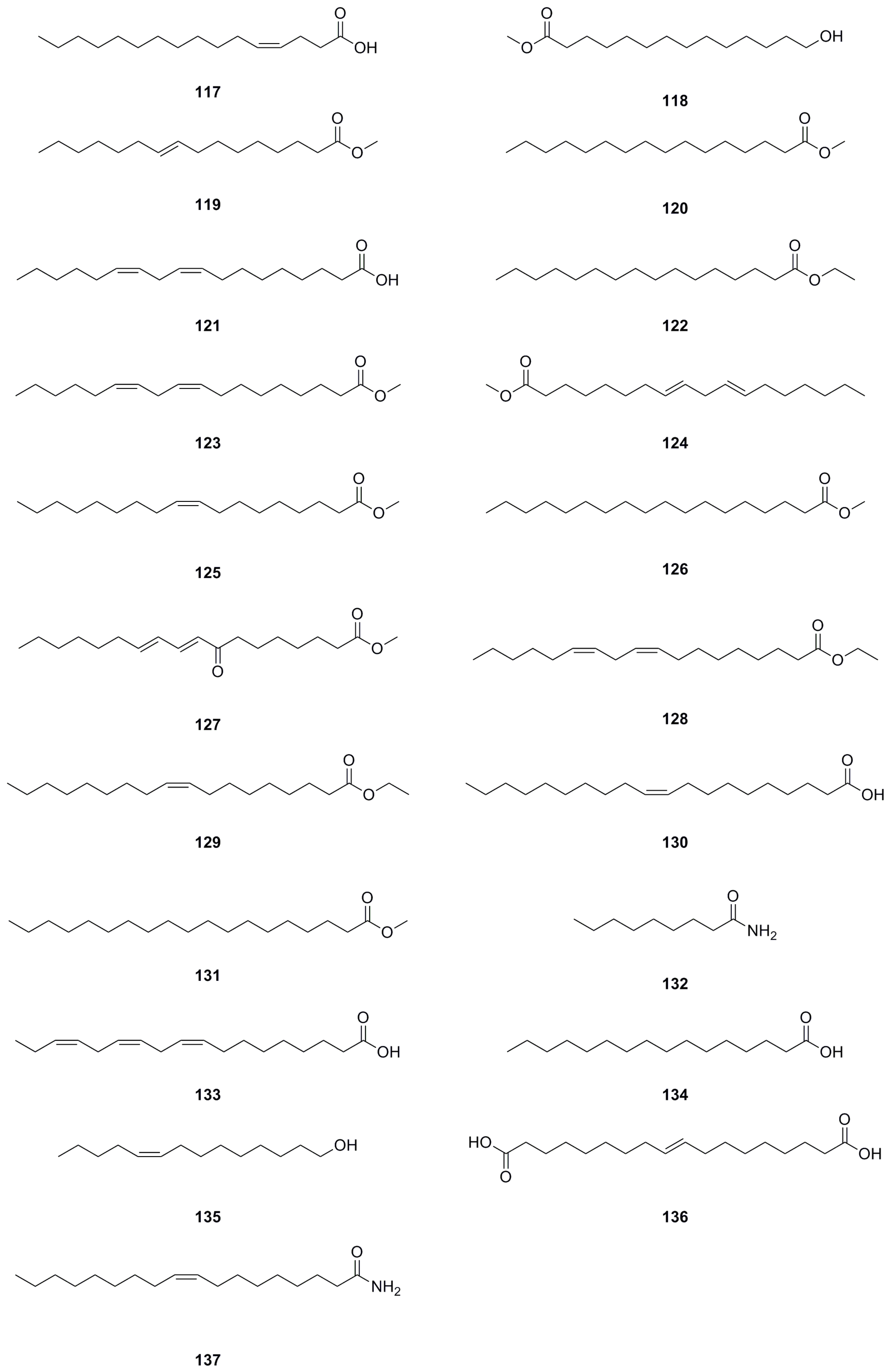
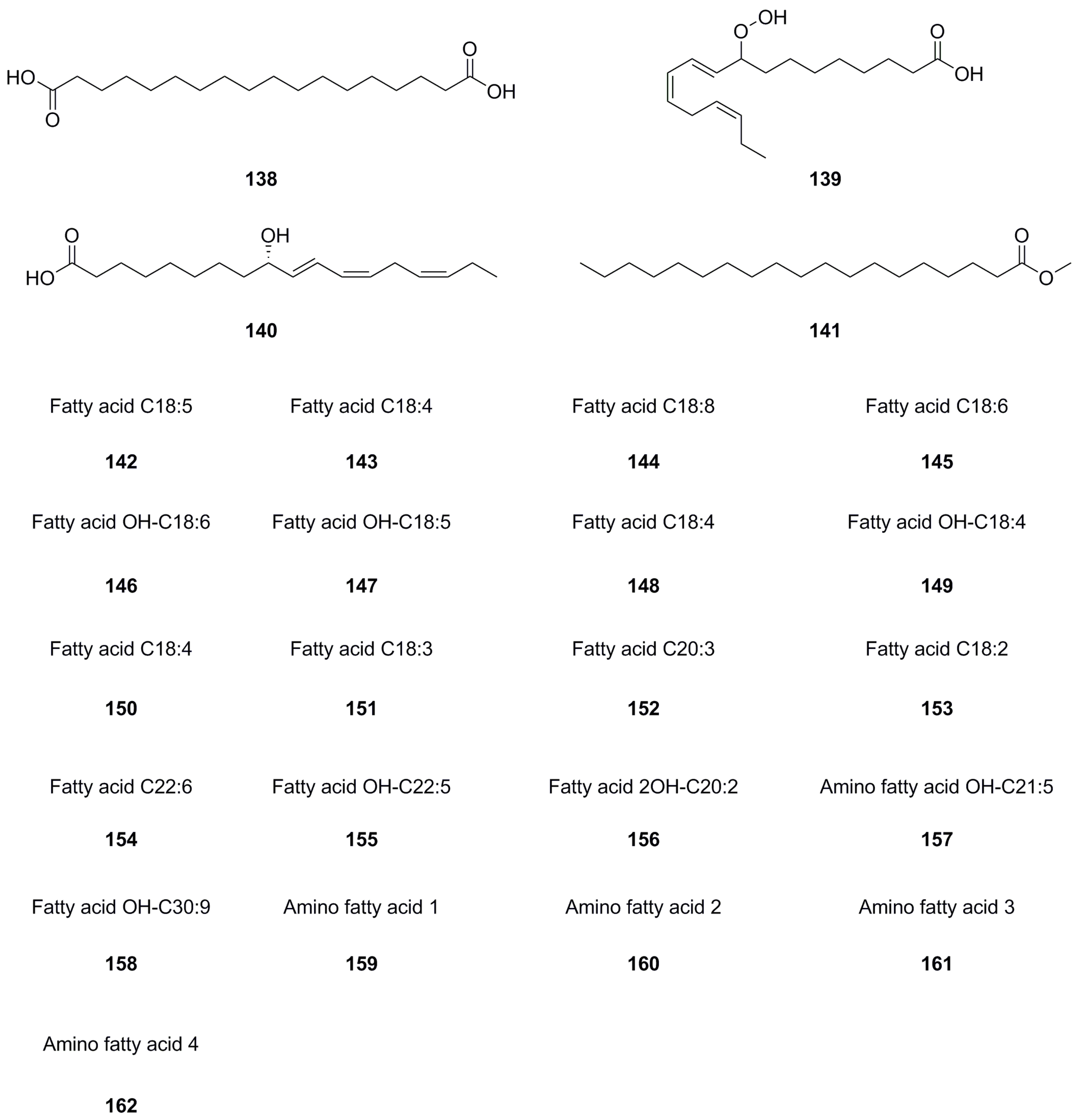
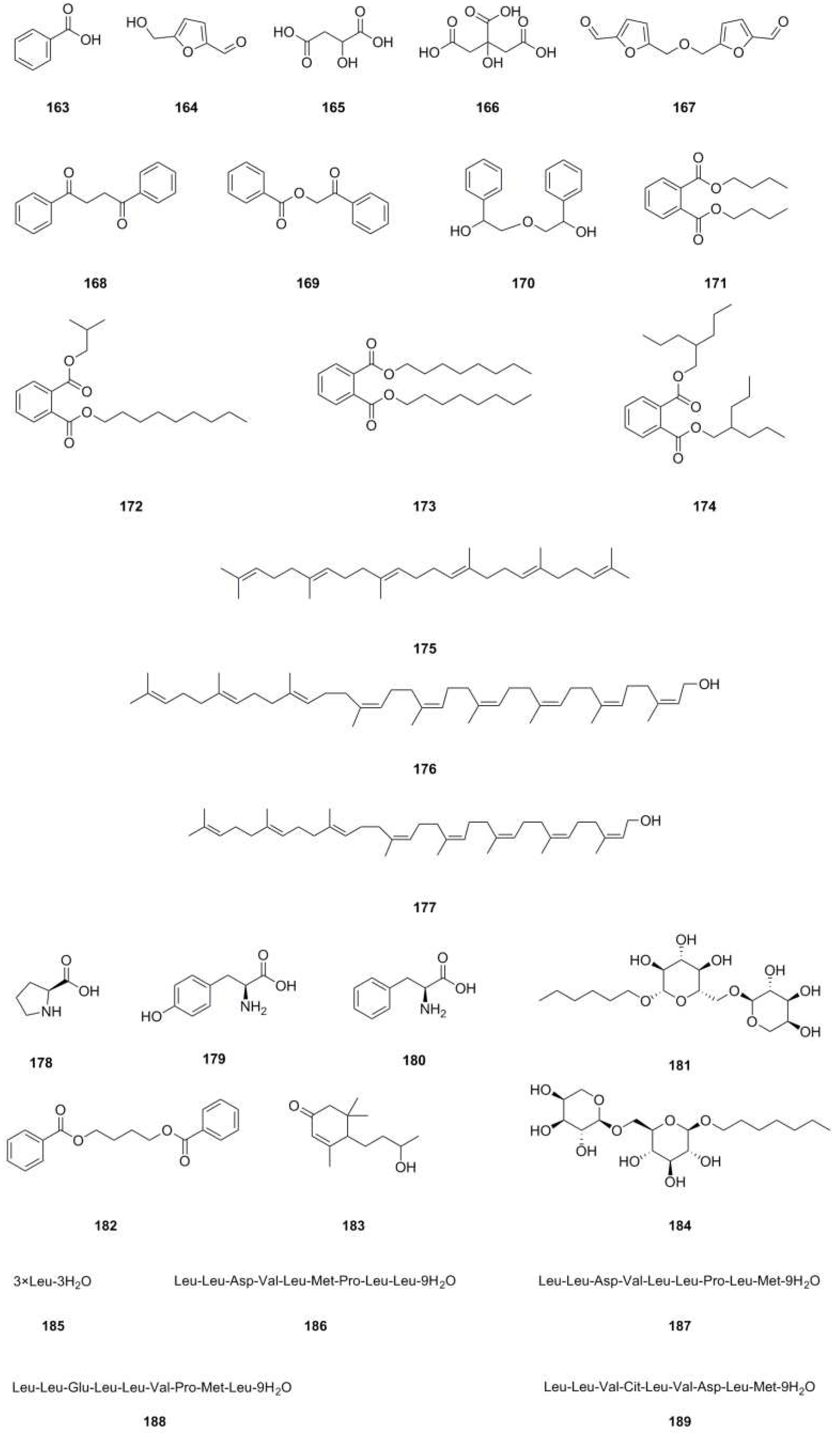
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Daidzein | C15H10O4 | 254.0579 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 2 | 4’-Methoxyflavonol | C16H12O4 | 268.0736 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 3 | Apigenin | C15H10O5 | 270.0528 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1,11] | aerial parts, roots |
| 4 | 5,6,7-Trihydroxyflavone | C15H10O5 | 270.0528 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 5 | Luteolin | C15H10O6 | 286.0477 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp | [1,6] | roots, whole herb |
| 6 | Fisetin | C15H10O6 | 286.0477 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 7 | Kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 286.0477 |
1H NMR, 13C NMR, HPLC-MS |
[1,8] | roots |
| 8 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | 290.0790 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 9 | Catechin | C15H14O6 | 290.0790 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 10 | 5-Hydroxy-7,4’-dimethoxyflavone | C17H16O5 | 300.0998 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 11 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | 302.0427 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [1,7] | roots, whole herb |
| 12 | (–)-Gallocatechin | C15H14O7 | 306.0740 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 13 | Epigallocatechin | C15H14O7 | 306.0740 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UV, mp, ESI-MS | [1,24] | roots, whole herb |
| 14 | (+)-4’,5,7-Trimethoxydihydroflavonol | C18H18O6 | 330.1103 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS | [1] | roots |
| 15 | Naringenin trimethyl ether | C18H18O5 | 314.1154 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 16 | Isorhamnetin | C16H12O7 | 316.0583 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 17 | (+)-Dihydromyricetin | C15H12O8 | 320.0532 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 18 | Tangeretin | C20H20O7 | 372.1209 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 19 | Nobiletin | C21H22O8 | 402.1315 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 20 | 3,5,6,7,8,3’,4’-Heptamethoxyflavone | C22H24O9 | 432.1420 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 21 | (–)-Epicatechin-3-O-gallate | C22H18O10 | 442.0900 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 22 | (–)-Epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate | C22H18O11 | 458.0849 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 23 | (–)-Gallocatechin 3-O-gallate | C22H18O11 | 458.0849 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 24 | Daidzin | C21H20O9 | 416.1107 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [1,2,23] | roots, aerial parts, whole herb |
| 25 | 5,7,4-Trihydroxy-isoflavone-5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O10 | 432.1056 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 26 | Genistin | C21H20O10 | 432.1056 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 27 | Kaempferol-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside | C21H20O10 | 432.1056 | mp, HR-MS, 13C NMR | [6] | whole herb |
| 28 | Apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O10 | 432.1056 | 1H NMR, HR-MS, 13C NMR | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 29 | 5,7,3’-Trihydroxy-4-methoxyisoflavone-7-O-β-lucopyranoside | C22H22O10 | 446.1213 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 30 | Luteoloside | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 31 | Kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 32 | Luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 33 | Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 34 | Astragalin | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 35 | Luteolin-7-galactoside | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | UHPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 36 | Pratensein-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C22H22O11 | 462.1162 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 37 | Isoquercitrin | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [7] | whole herb, roots |
| 38 | Myricetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 39 | Quercetin-3-alloside | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 40 | Hyperoside | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [1,2,23] | roots, aerial parts, whole herb |
| 41 | Quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [23] | whole herb |
| 42 | Quercetin-3-O-β-D-6″-acetylglucopyranoside | C23H22O13 | 506.1060 | 1H NMR | [2] | aerial parts |
| 43 | Kaemferitrin | C27H30O14 |
578.1636 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, HR-MS | [2,6,11] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 44 | Acaetin-7-O-rutinoside | C28H32O14 | 592.1792 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-MS | [2,23] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 45 | Nicotiflorin | C27H30O15 | 594.1585 | UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [7] | whole herb, roots |
| 46 | Isorhamnetin-3,7-O-α-L-dirhamnoside | C28H32O15 | 608.1741 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 47 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-2)-β-galactopyranoside | C28H32O16 | 624.1690 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 48 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 610.1534 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [1,7,25] | roots, whole herb |
| 49 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-α-rhamnosyl-(1-2)-rhamnoside | C28H32O15 | 608.1741 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 50 | Isorhamnetin-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside | C22H22O11 | 462.1162 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 51 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside | C22H22O11 | 462.1162 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52 | Phloroglucinol | C6H6O3 | 126.0317 | mp, UV, ESI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [24] | whole herb |
| 53 | p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | C7H6O3 | 138.0317 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1,11] | roots, aerial parts |
| 54 | Vanillic acid | C8H8O4 | 168.0423 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, mp, HR-ESI-MS, UV, HR-EI-MS, HMBC | [1,4,29] | roots, whole herb |
| 55 | 2-Hydroxy-3-(O-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid | C9H10O4 | 182.0579 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 56 | Ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate | C9H10O4 | 182.0579 | mp, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [6] | whole herb |
| 57 | Ethyl gallate | C9H10O5 | 198.0528 | mp, HR-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [6] | whole herb |
| 58 | C-Veratroylglycol | C10H12O5 | 212.0685 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 59 | Flavokawain A | C18H18O5 | 314.1154 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 60 | (+)-5,5-Dimethyl-5,6a,7,12a-tetrahydroisochromeno[4,3-b]chromene-2,3,4,8,10-pentaol | C18H18O7 | 346.1053 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS | [1] | roots |
| 61 | (–)-5,5-Dimethyl-5,6a,7,12a-tetrahydroisochromeno[4,3-b]chromene-2,3,4,8,10-pentaol | C18H18O7 | 346.1053 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS | [1] | roots |
| 62 | (+)-Vibruresinol | C20H24O6 | 360.1573 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 63 | Piceid | C20H22O8 | 390.1315 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 64 | Phloridzin | C21H24O10 | 436.1369 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 65 | (+)-Isolariciresinol 9'-O-glucoside | C26H34O11 | 522.2101 | mp, HR-MS, 13C NMR | [6] | whole herb |
| 66 | Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 138.0317 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 67 | Schizandriside | C25H32O10 | 492.1995 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68 | Uracil | C4H4N2O2 | 112.0273 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 69 | 6-Hydroxypurine | C5H4N4O | 136.0385 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 70 | Quinolin-2(1H)-one | C9H7NO | 145.0528 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 71 | 1H-Indole-3-carboxylic acid | C9H7NO2 | 161.0477 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 72 | 6-Hydroxy-5-methoxy-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid | C10H9NO4 | 207.0532 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 73 | 9-Ribofuranosyladenine | C10H13N5O4 | 267.0968 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 74 | N2-Fructopyranosylarginine | C12H24N4O7 | 336.1645 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 75 | Choline | C5H14NO+ | 104.1070 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
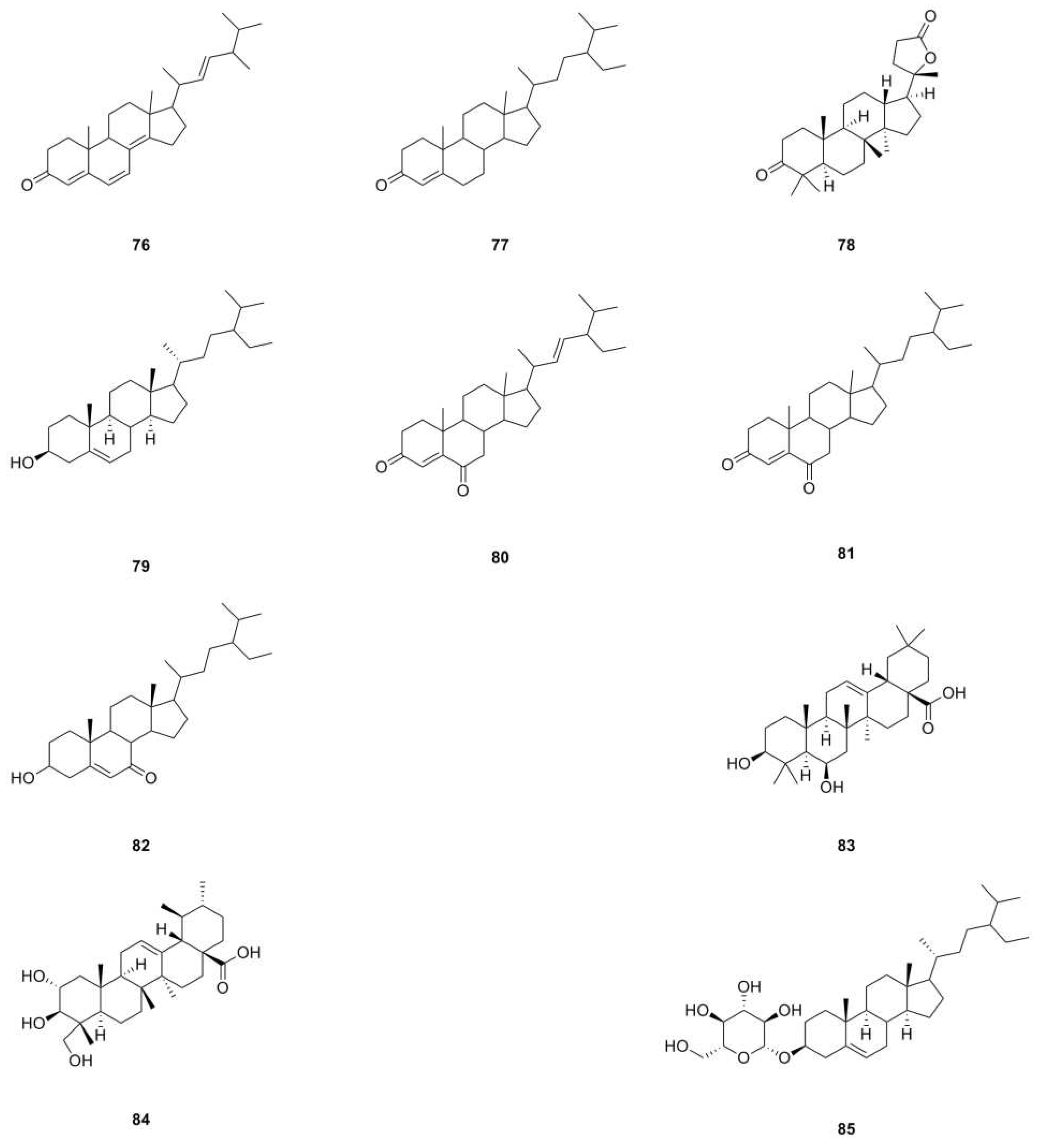
| 76 | Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one | C28H40O | 392.3079 | EI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 77 | Sitostenone | C29H48O | 412.3705 | EI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 78 | (+)-Cabralealactone | C27H42O3 | 414.3134 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 79 | β-Sitosterol | C29H50O | 414.3862 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, EI-MS | [9,11] | aerial parts, roots |
| 80 | Stigmasta-4,22-diene-3,6-dione | C29H44O2 | 424.3341 | EI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 81 | Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-dione | C29H46O2 | 426.3498 | EI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 82 | 7-Keto-β-Sitosterol | C29H48O2 | 428.3654 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 83 | Sumaresinolic acid | C30H48O4 | 472.3553 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 84 | Asiatic acid | C30H48O5 | 488.3502 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 85 | β-Daucosterol | C35H60O6 | 576.4390 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, EI-MS | [9,11,24] | aerial parts, roots, whole herb |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
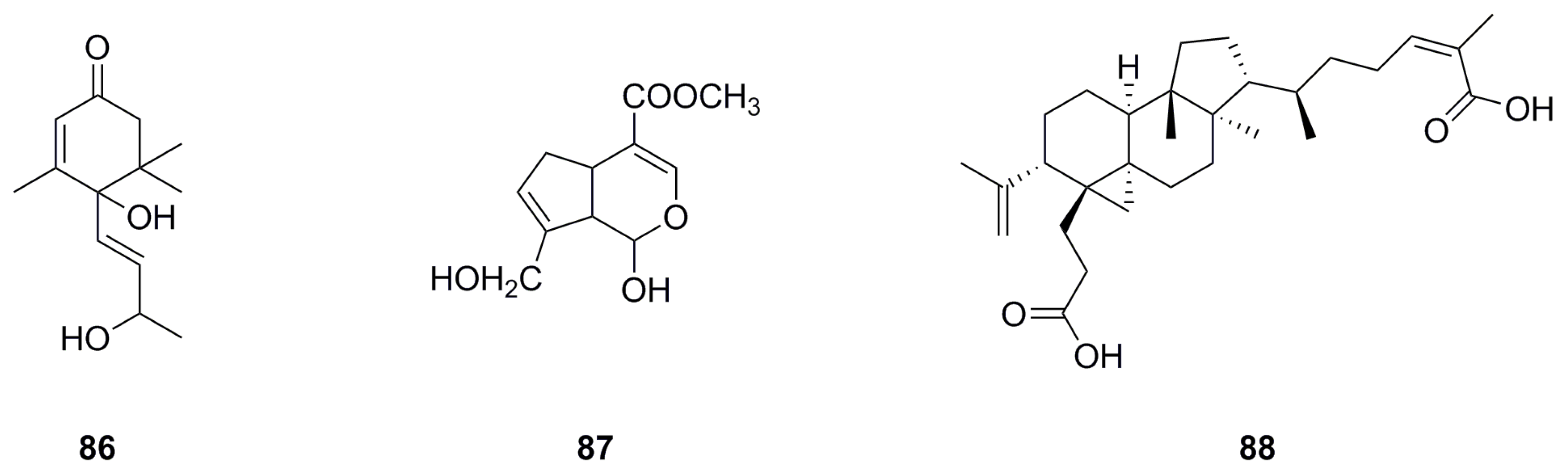
| 86 | α-Ionol | C13H20O3 | 224.1412 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 87 | Genipin | C11H14O5 | 226.0841 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 88 | Nigranoic acid | C30H46O4 | 470.3396 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
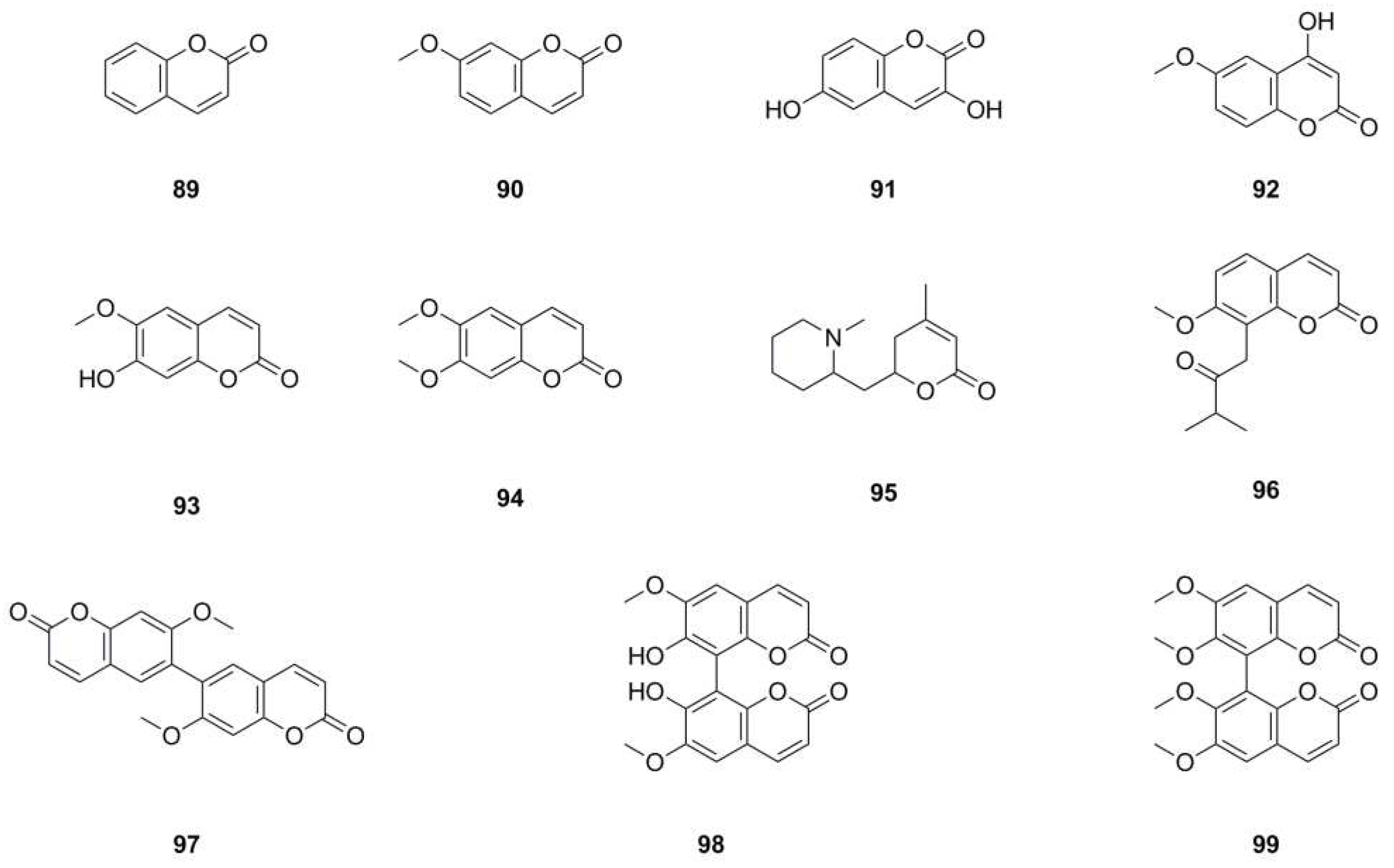
| 89 | Coumarin | C9H6O2 | 146.0368 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 90 | 7-Methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one | C10H8O3 | 176.0473 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1,5] | whole herb, roots |
| 91 | 3,6-Dihydroxycoumarin | C9H6O4 | 178.0266 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 92 | 4-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one | C10H8O4 | 192.0423 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 93 | Scopoletin | C10H8O4 | 192.0423 | mp, 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [6,11] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 94 | Scoparone | C11H10O4 | 206.0579 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, mp, HR-ESI-MS, UV | [1,4] | roots |
| 95 | Dumetorine | C13H21NO2 | 223.1572 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 96 | Isomeranzin | C15H16O4 | 260.1049 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [29] | whole herb |
| 97 | 7,7’-Dimethoxy-6,6’-biscoumarin | C20H14O6 | 350.0790 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, mp, HR-ESI-MS, UV | [4] | roots |
| 98 | 7,7’-Dihydroxy-6,6’ -dimethoxy-8,8’-biscoumarin | C20H14O8 | 382.0689 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, mp, HR-ESI-MS, UV | [4] | roots |
| 99 | 6,6’,7,7’-Tetramethoxyl-8,8’-biscoumarin | C22H18O8 | 410.1002 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, mp, HR-ESI-MS, UV | [4] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
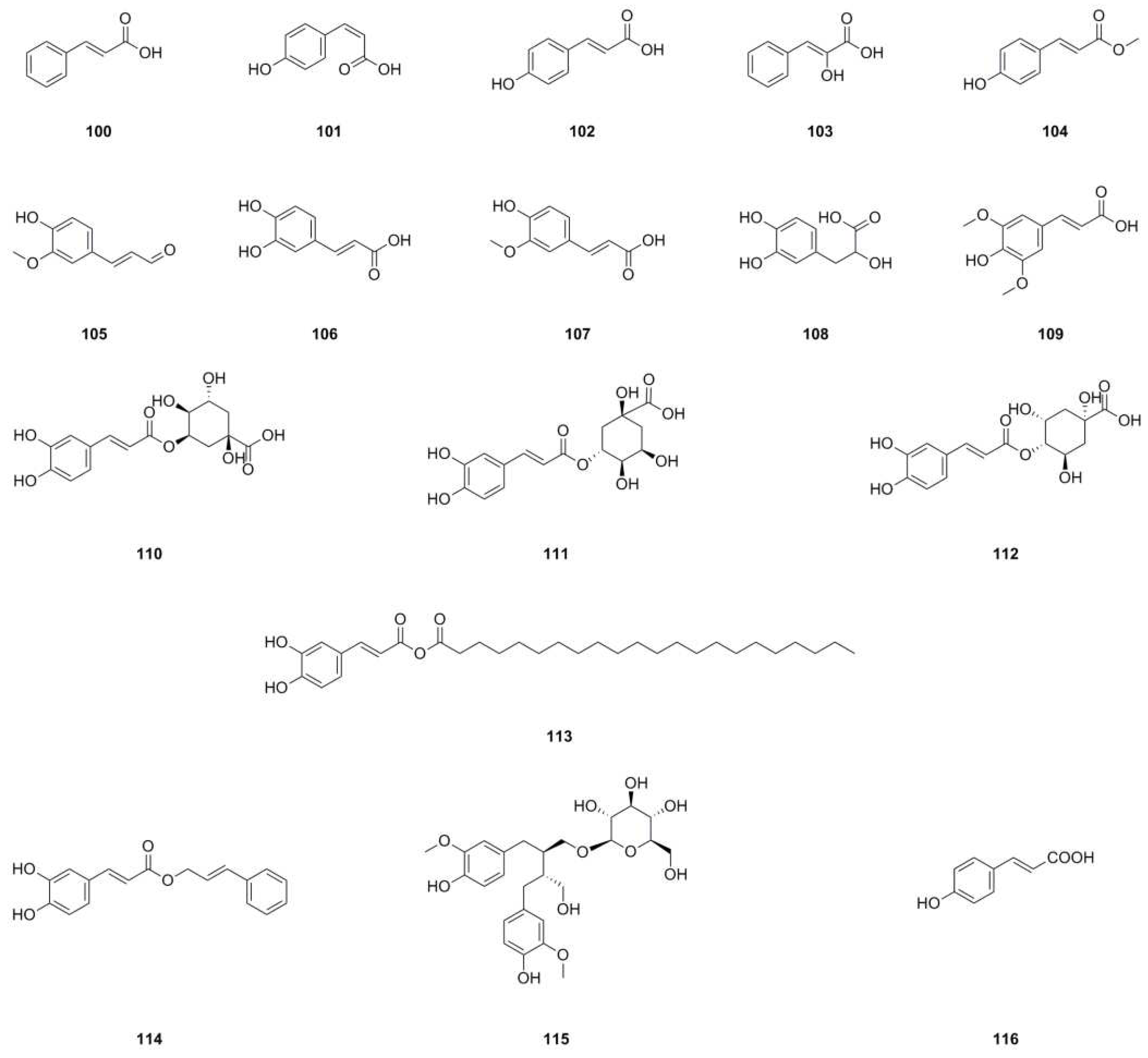
| 100 | trans-Cinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 101 | Z-p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 102 | trans-p-Hydroxycinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 |
1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, HR-MS |
[6,11] | aerial parts, whole herb |
| 103 | cis-Hydroxycinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 104 | Methyl- trans-4-hydroxycinnamate | C10H10O3 | 178.0630 | 1H NMR | [11] | aerial parts |
| 105 | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamaldehyde | C10H10O3 | 178.0630 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 106 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 180.0423 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [29] | roots |
| 107 | Ferulic acid | C10H10O4 | 194.0579 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 108 | Danshensu | C9H10O5 | 198.0528 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 109 | Sinapic acid | C11H12O5 | 224.0685 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 110 | Neochlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [7,25] | whole herb, roots |
| 111 | Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [7,25] | whole herb, roots |
| 112 | 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [7,25] | whole herb, roots |
| 113 | Caffeic acid docosanoyl ester | C31H50O5 | 502.3658 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 114 | Caffeic acid cinnamyl ester | C18H16O4 | 296.1049 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 115 | Secoisolariciresinol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C26H36O11 | 524.2258 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 116 | (E)-4-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 117 | Hexadec-(4Z)-enoic acid | C16H30O2 | 254.2246 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 118 | 12-Hydroxypentanoic acid methyl ester | C15H30O3 | 258.2195 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 119 | Methyl hexadec-9-enoate | C17H32O2 | 268.2402 | GC-MS | [24] | whole herb |
| 120 | Methyl hexadecanoate | C17H34O2 | 270.2559 | GC-MS | [24] | whole herb |
| 121 | Linoleic acid | C18H32O2 | 280.2402 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 122 | Ethyl palmitate | C18H36O2 | 284.2715 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 123 | Methyl linoleate | C19H34O2 | 294.2559 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 124 | 11-Octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester | C19H34O2 | 294.2559 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 125 | Methyl oleate | C19H36O2 | 296.2715 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 126 | Methyl stearate | C19H38O2 | 298.2872 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 127 | Methyl (9E,11E)-8-oxooctadeca-9,11- dienoate | C19H32O3 | 308.2351 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 128 | Ethyl linoleate | C20H36O2 | 308.2715 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [10] | whole herb |
| 129 | Ethyl Oleate | C20H38O2 | 310.2872 | GC-MS | [24] | whole herb |
| 130 | (Z)-10-Eicosenoic acid | C20H38O2 | 310.2872 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 131 | Methyl nonadecanoate | C20H40O2 | 312.3028 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 132 | Nonanamide | C9H19NO | 157.1467 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 133 | Linolenic acid | C18H30O2 | 278.2246 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 134 | Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 256.2402 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 135 | (Z)-9-Tetradecen-1-ol | C14H28O | 212.2140 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 136 | 1,18-Octadec-9-enedioic acid | C18H32O4 | 312.2301 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 137 | 9(Z)-Octadecenamide | C18H35NO | 281.2719 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 138 | Octadecanedioic acid | C18H34O4 | 314.2457 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 139 | 9-HpOTrE | C18H30O4 | 310.2144 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 140 | 9-HOTrE | C18H30O3 | 294.2195 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 141 | Methyl nonadecanoate | C20H40O2 | 312.3028 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 142 | Fatty acid C18:5 | C18H28O2 | 276.2089 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 143 | Fatty acid C18:4 | C18H30O2 | 278.2246 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 144 | Fatty acid C18:8 | C18H22O3 | 286.1569 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 145 | Fatty acid C18:6 | C18H26O3 | 290.1882 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 146 | Fatty acid OH-C18:6 | C18H26O3 | 290.1882 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 147 | Atty acid OH-C18:5 | C18H28O3 | 292.2038 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 148 | Fatty acid C18:4 | C18H30O3 | 294.2195 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 149 | Fatty acid OH-C18:4 | C18H30O3 | 294.2195 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 150 | Fatty acid C18:4 | C18H30O3 | 294.2195 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 151 | Fatty acid C18:3 | C18H32O3 | 296.2351 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 152 | Fatty acid C20:3 | C20H38O2 | 310.2872 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 153 | Fatty acid C18:2 | C18H34O5 | 330.2406 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 154 | Fatty acid C22:6 | C22H36O3 | 348.2664 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 155 | Fatty acid OH-C22:5 | C22H36O3 | 348.2664 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 156 | Fatty acid 2OH-C20:2 | C20H39NO4 | 357.2879 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 157 | Amino fatty acid OH-C21:5 | C21H35NO5 | 381.2515 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 158 | Fatty acid OH-C30:9 | C30H44O3 | 452.3290 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 159 | Amino fatty acid 1 | C18H37NO3 | 315.2773 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 160 | Amino fatty acid 2 | C18H39NO3 | 317.2930 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 161 | Amino fatty acid 3 | C19H37NO3 | 327.2773 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 162 | Amino fatty acid 4 | C20H43NO2 | 329.3294 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| No. | Name | Formula | Exact Theoretical Molecular Weight | Characterization Method | Refs. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 163 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | 122.0368 | UHPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 164 | 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxaldehyde | C6H6O3 | 126.0317 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [8] | roots |
| 165 | Malic acid | C4H6O5 | 134.0215 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 166 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | 192.0270 | HPLC-MS | [8] | roots |
| 167 | Bis(5-formylfurfuryl) ether | C12H10O5 | 234.0528 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [29] | whole herb |
| 168 | 1’4-Diphenyl-1’4-butanedione | C16H14O2 | 238.0994 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, EI-MS | [9] | roots |
| 169 | 1-(2-Phenylcarbonyloxyacetyl) benzene | C15H12O3 | 240.0786 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, EI-MS | [9] | roots |
| 170 | 2,2’-Oxy-bis(1-phenylethanol) | C16H18O3 | 258.1256 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mp, EI-MS | [9] | roots |
| 171 | Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 278.1518 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, GC-MS | [24,29] | whole herb |
| 172 | Phthalic acid, isobutyl nonyl ester | C21H32O4 | 348.2301 | GC-MS | [24] | whole herb |
| 173 | Dioctyl phthalate | C24H38O4 | 390.2770 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [29] | whole herb |
| 174 | Bis(2-propylpentyl) phthalate | C24H38O4 | 390.2770 | GC-MS | [24] | whole herb |
| 175 | Squalene | C30H50 | 410.3913 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR | [1] | roots |
| 176 | Betulaprenol 9 | C45H74O | 630.5740 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, EI-MS | [10] | whole herb |
| 177 | Betulaprenol 8 | C40H66O | 562.5114 | 1H NMR, 13C NMR, EI-MS | [10] | whole herb |
| 178 | L-Proline | C5H9NO2 | 115.0633 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 179 | L-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | 181.0739 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 180 | Phenylalanine | C9H11NO2 | 165.0790 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 181 | Creoside IV | C17H32O10 | 396.1995 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 182 | 1,4-Bis(benzoyloxy)butane | C18H18O4 | 298.1205 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 183 | 4-(3-Hydroxy-1-butyl) -3,5,5-trimethyl-2-cyclohexenone | C13H22O2 | 210.1620 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 184 | Heptyl 6-O-α-L -arabinopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | C18H34O10 | 410.2152 | UHPLC–ESI–Q–TOF–MS | [26] | roots |
| 185 | 3×Leu-3H2O | C18H33N3O3 | 339.2522 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 186 | Leu-Leu-Asp-Val-Leu-Met-Pro-Leu-Leu-9H2O | C49H85N9O11S | 1007.6089 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 187 | Leu-Leu-Asp-Val-Leu-Leu-Pro-Leu-Met-9H2O | C49H85N9O11S | 1007.6089 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 188 | Leu-Leu-Glu-Leu-Leu-Val-Pro-Met-Leu-9H2O | C50H87N9O11S | 1021.6246 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
| 189 | Leu-Leu-Val-Cit-Leu-Val-Asp-Leu-Met-9H2O | C49H87N11O12S | 1053.6256 | UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS | [5] | whole herb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




