Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
14 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Subjects involved in the statistical analysis
2.2. Phenotype severity
2.3. Variant evaluation
2.4. Facial gestalt analysis
2.5. Statistical analysis in genotype-phenotype correlations
3. Results
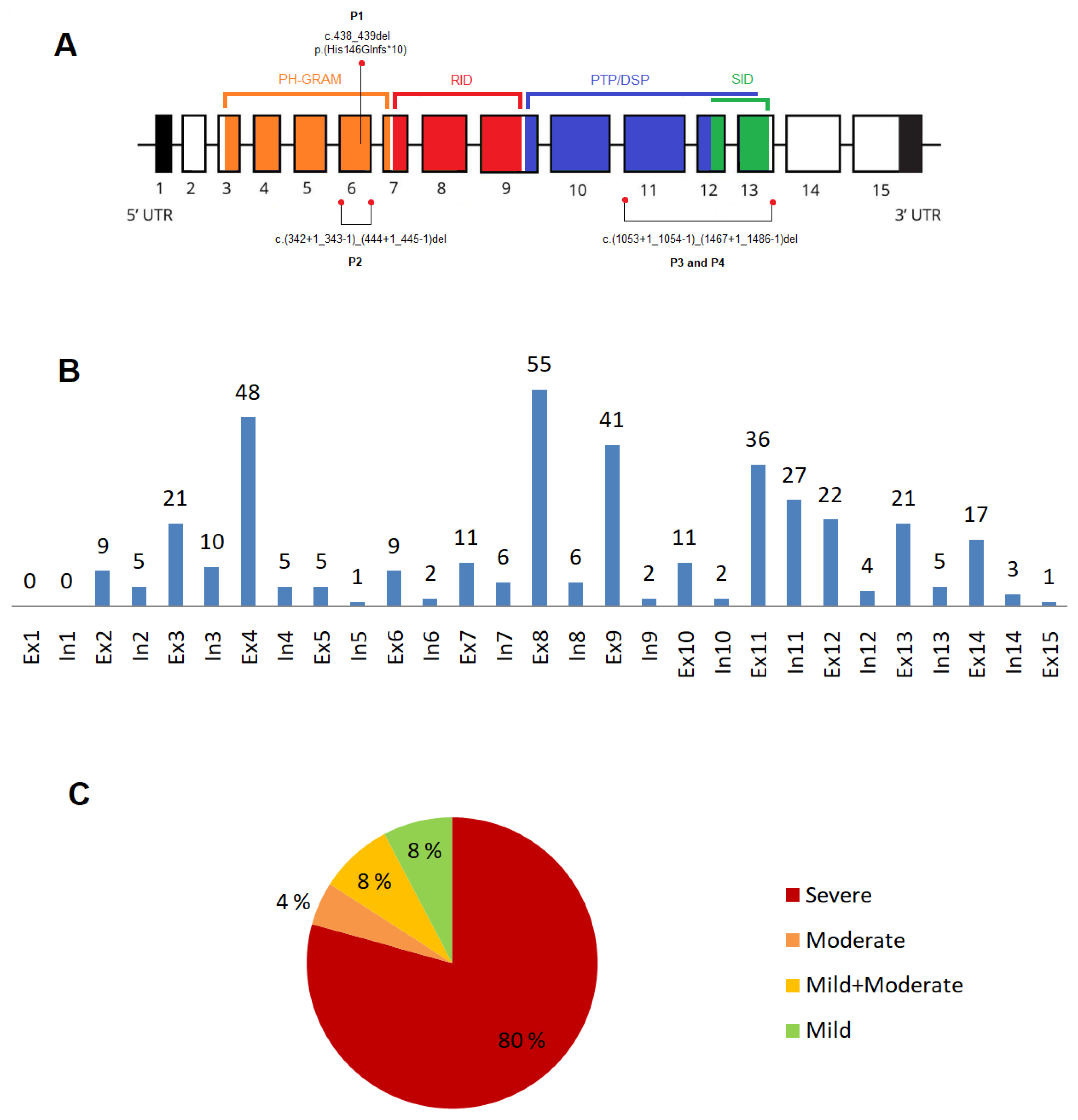
3.1. Novel variants in the MTM1gene
3.2. XLMTM cohort: variants type and their distribution
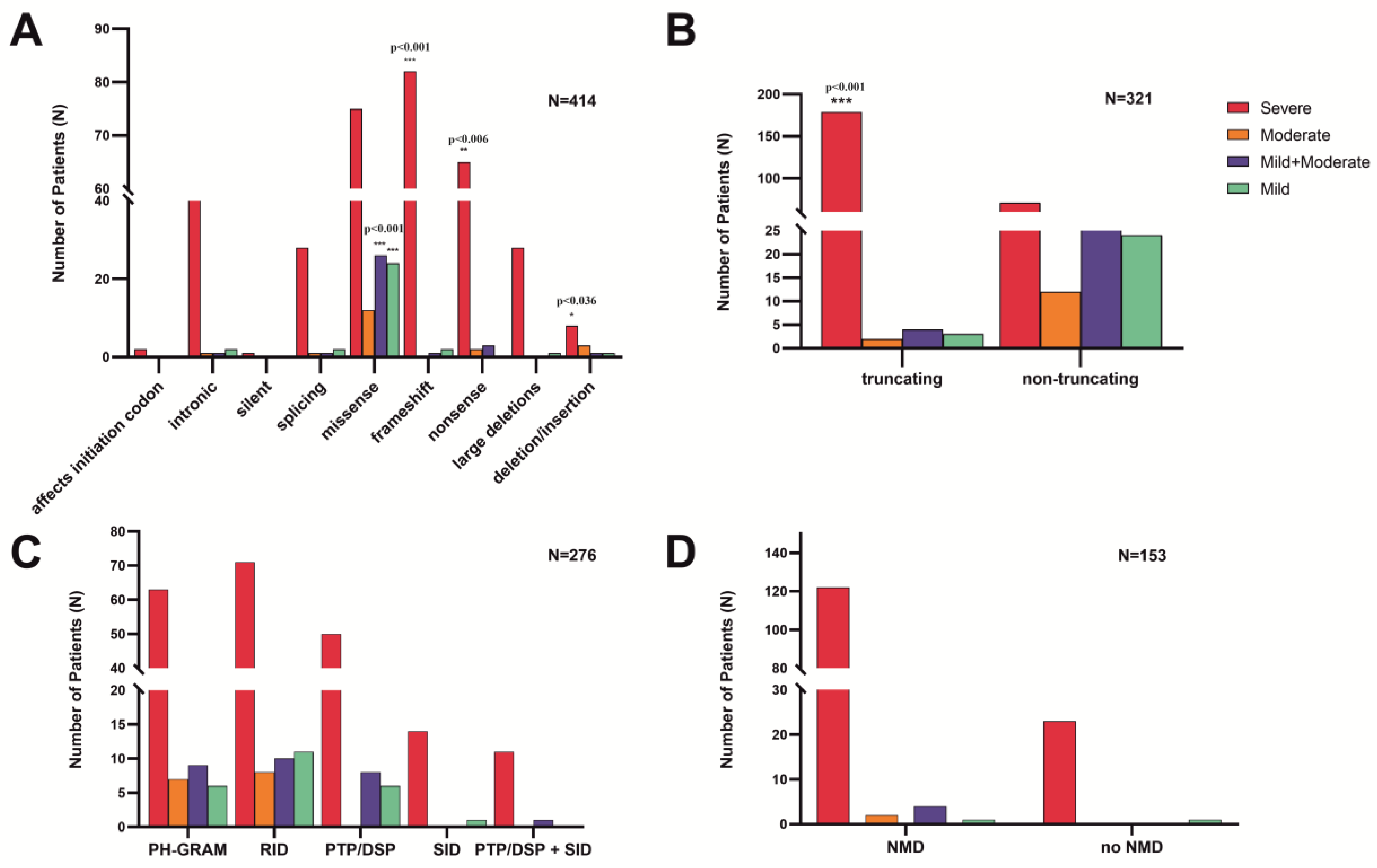
3.2.1. Exonic and intronic variants
3.2.2. Variants in the MTM1-specific functional domain
3.2.3. Truncating effect and non-sense mediated mRNA decay
3.2.4. Phenotype severity and variant types
3.2.5. Recurrent variants in the MTM1 gene
3.2.6. Inter-individual phenotype variability
3.3. Genotype-phenotype correlations
3.4. Facial gestalt analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, G. S., Maehama, T., & Dixon, J. E. (2000). Myotubularin, a protein tyrosine phosphatase mutated in myotubular myopathy, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(16), 8910–8915. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, F. L., & Dixon, J. E. (2006). Myotubularin phosphatases: policing 3-phosphoinositides. Trends in cell biology, 16(8), 403–412. [CrossRef]
- Bertazzi, Dimitri & De Craene, Johan-Owen & Friant, Sylvie. (2014). Myotubularin MTM1 Involved in Centronuclear Myopathy and its Roles in Human and Yeast Cells. Journal of molecular and genetic medicine: an international journal of biomedical research. [CrossRef]
- Laporte, J., Guiraud-Chaumeil, C., Tanner, S. M., Blondeau, F., Hu, L. J., Vicaire, S., Liechti-Gallati, S., & Mandel, J. L. (1998). Genomic organization of the MTM1 gene implicated in X-linked myotubular myopathy. European journal of human genetics : EJHG, 6(4), 325–330. [CrossRef]
- Spiro, A. J., Shy, G. M., & Gonatas, N. K. (1966). Myotubular myopathy. Persistence of fetal muscle in an adolescent boy. Archives of neurology, 14(1), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Laporte, J., Blondeau, F., Buj-Bello, A., & Mandel, J. L. (2001). The myotubularin family: from genetic disease to phosphoinositide metabolism. Trends in genetics : TIG, 17(4), 221–228. [CrossRef]
- Herman, G. E., Finegold, M., Zhao, W., de Gouyon, B., & Metzenberg, A. (1999). Medical complications in long-term survivors with X-linked myotubular myopathy. The Journal of Pediatrics, 134(2), 206–214. [CrossRef]
- McEntagart, M., Parsons, G., Buj-Bello, A., Biancalana, V., Fenton, I., Little, M., Krawczak, M., Thomas, N., Herman, G., Clarke, A., & Wallgren-Pettersson, C. (2002). Genotype-phenotype correlations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 12(10), 939–946. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J., Oliveira, M. E., Kress, W., Taipa, R., Pires, M. M., Hilbert, P., Baxter, P., Santos, M., Buermans, H., den Dunnen, J. T., & Santos, R. (2013). Expanding the MTM1 mutational spectrum: novel variants including the first multi-exonic duplication and development of a locus-specific database. European journal of human genetics : EJHG, 21(5), 540–549. [CrossRef]
- Dowling JJ, Lawlor MW, Das S. X-Linked Myotubular Myopathy. 2002 Feb 25 [Updated 2018 Aug 23]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1432/.
- Lawlor, M. W., & Dowling, J. J. (2021). X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 31(10), 1004–1012. [CrossRef]
- Motoki, T., Fukuda, M., Nakano, T., Matsukage, S., Fukui, A., Akiyoshi, S., Hayashi, Y. K., Ishii, E., & Nishino, I. (2013). Fatal hepatic hemorrhage by peliosis hepatis in X-linked myotubular myopathy: a case report. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 23(11), 917–921. [CrossRef]
- Amburgey, K., Tsuchiya, E., de Chastonay, S., Glueck, M., Alverez, R., Nguyen, C. T., Rutkowski, A., Hornyak, J., Beggs, A. H., & Dowling, J. J. (2017). A natural history study of X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neurology, 89(13), 1355–1364. [CrossRef]
- Beggs, A. H., Byrne, B. J., De Chastonay, S., Haselkorn, T., Hughes, I., James, E. S., Kuntz, N. L., Simon, J., Swanson, L. C., Yang, M. L., Yu, Z. F., Yum, S. W., & Prasad, S. (2018). A multicenter, retrospective medical record review of X-linked myotubular myopathy: The recensus study. Muscle & nerve, 57(4), 550–560. [CrossRef]
- Gurovich, Y., Hanani, Y., Bar, O. et al. Identifying facial phenotypes of genetic disorders using deep learning. Nat Med 25, 60–64 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Laporte, J., Biancalana, V., Tanner, S. M., Kress, W., Schneider, V., Wallgren-Pettersson, C., Herger, F., Buj-Bello, A., Blondeau, F., Liechti-Gallati, S., & Mandel, J. L. (2000). MTM1 mutations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Human mutation, 15(5), 393–409. [CrossRef]
- Bendl, J., Stourac, J., Salanda, O., Pavelka, A., Wieben, E. D., Zendulka, J., Brezovsky, J., & Damborsky, J. (2014). PredictSNP: robust and accurate consensus classifier for prediction of disease-related mutations. PLoS computational biology, 10(1), e1003440. [CrossRef]
- Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S. et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17, 405–423 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Savarese, M., Musumeci, O., Giugliano, T., Rubegni, A., Fiorillo, C., Fattori, F., Torella, A., Battini, R., Rodolico, C., Pugliese, A., Piluso, G., Maggi, L., D’Amico, A., Bruno, C., Bertini, E., Santorelli, F. M., Mora, M., Toscano, A., Minetti, C., & Nigro, V. (2016). Novel findings associated with MTM1 suggest a higher number of female symptomatic carriers. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 26(4-5), 292–299. [CrossRef]
- Biancalana, V., Scheidecker, S., Miguet, M., Laquerrière, A., Romero, N. B., Stojkovic, T., Abath Neto, O., Mercier, S., Voermans, N., Tanner, L., Rogers, C., Ollagnon-Roman, E., Roper, H., Boutte, C., Ben-Shachar, S., Lornage, X., Vasli, N., Schaefer, E., Laforet, P., Pouget, J., … Laporte, J. (2017). Affected female carriers of MTM1 mutations display a wide spectrum of clinical and pathological involvement: delineating diagnostic clues. Acta neuropathologica, 134(6), 889–904. [CrossRef]
- Tanner, S. M., Schneider, V., Thomas, N. S., Clarke, A., Lazarou, L., & Liechti-Gallati, S. (1999). Characterization of 34 novel and six known MTM1 gene mutations in 47 unrelated X-linked myotubular myopathy patients. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 9(1), 41–49. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T. C., Horinouchi, H., Noguchi, S., Minami, N., Murayama, K., Hayashi, Y. K., Nonaka, I., & Nishino, I. (2005). Characterization of MTM1 mutations in 31 Japanese families with myotubular myopathy, including a patient carrying 240 kb deletion in Xq28 without male hypogenitalism. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 15(3), 245–252. [CrossRef]
- Barth, P. G., & Dubowitz, V. (1998). X-linked myotubular myopathy--a long-term follow-up study. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society, 2(1), 49–56. [CrossRef]
- Biancalana, V., Caron, O., Gallati, S., Baas, F., Kress, W., Novelli, G., D’Apice, M. R., Lagier-Tourenne, C., Buj-Bello, A., Romero, N. B., & Mandel, J. L. (2003). Characterisation of mutations in 77 patients with X-linked myotubular myopathy, including a family with a very mild phenotype. Human genetics, 112(2), 135–142. [CrossRef]
- Hoffjan, S., Thiels, C., Vorgerd, M., Neuen-Jacob, E., Epplen, J. T., & Kress, W. (2006). Extreme phenotypic variability in a German family with X-linked myotubular myopathy associated with E404K mutation in MTM1. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 16(11), 749–753. [CrossRef]
- Amoasii, L., Bertazzi, D. L., Tronchère, H., Hnia, K., Chicanne, G., Rinaldi, B., Cowling, B. S., Ferry, A., Klaholz, B., Payrastre, B., Laporte, J., & Friant, S. (2012). Phosphatase-dead myotubularin ameliorates X-linked centronuclear myopathy phenotypes in mice. PLoS genetics, 8(10), e1002965. [CrossRef]
- Herman, G. E., Kopacz, K., Zhao, W., Mills, P. L., Metzenberg, A., & Das, S. (2002). Characterization of mutations in fifty North American patients with X-linked myotubular myopathy. Human mutation, 19(2), 114–121. [CrossRef]
- Pierson, C. R., Agrawal, P. B., Blasko, J., & Beggs, A. H. (2007). Myofiber size correlates with MTM1 mutation type and outcome in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 17(7), 562–568. [CrossRef]
- Bryen, S. J., Oates, E. C., Evesson, F. J., Lu, J. K., Waddell, L. B., Joshi, H., Ryan, M. M., Cummings, B. B., McLean, C. A., MacArthur, D. G., Kornberg, A. J., & Cooper, S. T. (2021). Pathogenic deep intronic MTM1 variant activates a pseudo-exon encoding a nonsense codon resulting in severe X-linked myotubular myopathy. European journal of human genetics : EJHG, 29(1), 61–66. [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T. C., Bar-Haim, A., Moosa, S., Ehmke, N., Gripp, K. W., Pantel, J. T., Danyel, M., Mensah, M. A., Horn, D., Rosnev, S., Fleischer, N., Bonini, G., Hustinx, A., Schmid, A., Knaus, A., Javanmardi, B., Klinkhammer, H., Lesmann, H., Sivalingam, S., Kamphans, T., … Krawitz, P. M. (2022). GestaltMatcher facilitates rare disease matching using facial phenotype descriptors. Nature genetics, 54(3), 349–357. [CrossRef]
- Annoussamy, M., Lilien, C., Gidaro, T., Gargaun, E., Chê, V., Schara, U., Gangfuß, A., D’Amico, A., Dowling, J. J., Darras, B. T., Daron, A., Hernandez, A., de Lattre, C., Arnal, J. M., Mayer, M., Cuisset, J. M., Vuillerot, C., Fontaine, S., Bellance, R., Biancalana, V., … Servais, L. (2019). X-linked myotubular myopathy: A prospective international natural history study. Neurology, 92(16), e1852–e1867. [CrossRef]
- Fattori, F., Maggi, L., Bruno, C., Cassandrini, D., Codemo, V., Catteruccia, M., Tasca, G., Berardinelli, A., Magri, F., Pane, M., Rubegni, A., Santoro, L., Ruggiero, L., Fiorini, P., Pini, A., Mongini, T., Messina, S., Brisca, G., Colombo, I., Astrea, G., … D’Amico, A. (2015). Centronuclear myopathies: genotype-phenotype correlation and frequency of defined genetic forms in an Italian cohort. Journal of neurology, 262(7), 1728–1740. [CrossRef]
- Laporte, J., Guiraud-Chaumeil, C., Vincent, M. C., Mandel, J. L., Tanner, S. M., Liechti-Gallati, S., Wallgren-Pettersson, C., Dahl, N., Kress, W., Bolhuis, P. A., Fardeau, M., Samson, F., & Bertini, E. (1997). Mutations in the MTM1 gene implicated in X-linked myotubular myopathy. ENMC International Consortium on Myotubular Myopathy. European Neuro-Muscular Center. Human molecular genetics, 6(9), 1505–1511. [CrossRef]
- Buj-Bello, A., Biancalana, V., Moutou, C., Laporte, J., & Mandel, J. L. (1999). Identification of novel mutations in the MTM1 gene causing severe and mild forms of X-linked myotubular myopathy. Human mutation, 14(4), 320–325. [CrossRef]
- Liechti-Gallati, S., Müller, B., Grimm, T., Kress, W., Müller, C., Boltshauser, E., Moser, H., & Braga, S. (1991). X-linked centronuclear myopathy: mapping the gene to Xq28. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 1(4), 239–245. [CrossRef]
- de Gouyon, B. M., Zhao, W., Laporte, J., Mandel, J. L., Metzenberg, A., & Herman, G. E. (1997). Characterization of mutations in the myotubularin gene in twenty six patients with X-linked myotubular myopathy. Human molecular genetics, 6(9), 1499–1504. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashim, A., Gonorazky, H. D., Amburgey, K., Das, S., & Dowling, J. J. (2017). A novel intronic mutation in MTM1 detected by RNA analysis in a case of X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neurology. Genetics, 3(5), e182. [CrossRef]
- Paila, U., Chapman, B. A., Kirchner, R., & Quinlan, A. R. (2013). GEMINI: integrative exploration of genetic variation and genome annotations. PLoS computational biology, 9(7), e1003153. [CrossRef]
- Bonne, G., Rivier, F., & Hamroun, D. (2017). The 2018 version of the gene table of monogenic neuromuscular disorders (nuclear genome). Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 27(12), 1152–1183. [CrossRef]
- Plon, S. E., Eccles, D. M., Easton, D., Foulkes, W. D., Genuardi, M., Greenblatt, M. S., Hogervorst, F. B., Hoogerbrugge, N., Spurdle, A. B., Tavtigian, S. V., & IARC Unclassified Genetic Variants Working Group (2008). Sequence variant classification and reporting: recommendations for improving the interpretation of cancer susceptibility genetic test results. Human mutation, 29(11), 1282–1291. [CrossRef]
- den Dunnen, J. T., & Antonarakis, S. E. (2000). Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Human mutation, 15(1), 7–12. [CrossRef]
- Dubowitz V, Sewry C.A, Oldfors A: Muscle Biopsy. A practical approach, 2021, 5th edition, Elsevier.

| Patient ID | Ancestry (Ethnicity) |
MTM1 variant | Type | Exon | Domain | ACMG classification | Origin | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
P1/F1 M |
Slovakia (Caucasian) |
c.438_439delCA (p.His146Glnfs*10) | frameshift | ex 6 | PH-GRAM | pathogenic | maternal | Severe |
|
P2/F2 M |
Austria (Caucasian) |
c.(342+1_343-1)_(444+1_445-1)del p.(Asp115_Leu148del) |
in-frame deletion | ex 6 | PH-GRAM | likely pathogenic | maternal | Severe |
|
P3/F3 M |
Austria (Caucasian) |
c.(1053+1_1054-1)_(1467+1_1468-1)del; p.(Leu352_Gln489)del | in-frame deletion | ex 11-13 | PTP/DSP-SID | likely pathogenic | maternal | Severe |
|
P4/F3 M |
Austria (Caucasian) |
c.(1053+1_1054-1)_(1467+1_1468-1)del; p.(Leu352_Gln489)del | in-frame deletion | ex 11-13 | PTP/DSP-SID | likely pathogenic | maternal | Severe |
| Variant | Type | Exon/intron | Domain | Count | Phenotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.98_103del, p.(Glu33_Ala34del) | deletion | ex 3 | PH-GRAM | 2 | 1S/1Mi | [31,32] |
| c.109C>T, p.(Arg37*) | nonsense | ex3 | PH-GRAM | 9 | 8S/1Mo | [20,22,24,27,33,34] |
| c.139_141del, p.(Lys47del) | deletion | ex4 | PH-GRAM | 5 | 4S/1Mo | [24,30,33,35] |
| c.142G>T, p.(Glu48*) | nonsense | ex 4 | PH-GRAM | 2 | 1S/1Mo | [7,21] |
| c.205C>T, p.(Arg69Cys) | missense | ex 4 | PH-GRAM | 12 | 2S/1Mo/6M/3Mi | [16,27,31,32,36] |
| c.232-26_232-23del | intronic | in4 | - | 2 | 1S/1Mo | [31,37] |
| c.590C>T, p.(Thr197Ile) | missense | ex8 | RID | 3 | 1S/1Mo/1Mi | [16,32] |
| c.614C>T, p.(Pro205Leu) | missense | ex8 | RID | 9 | 8S/1Mi | [21,22,24,27,31] |
| c.679G>A, p.(Val227Met) | missense | ex9 | RID | 3 | 1S/1M/1Mi | [16,27,31] |
| c.695A>G, p.(His232Arg) | missense | ex9 | RID | 2 | 1S/1Mo | [21,31] |
| c.721C>T, p.(Arg241Cys) | missense | ex9 | RID | 13 | 3S/1Mo/5M/4Mi | [16,21,31,33,34,35] |
| c.1262G>A, p.(Arg421Gln) | missense | ex12 | PTP/DSP | 8 | 7S/1M | [16,24,27,33,36] |
| c.1558C>T,p.(Arg520*) | nonsense | ex 14 | - | 3 | 1S/2M | [16,18] |
| Binary comparison | No. of cases | Mean AUC | AUC SD | p value for AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XLMTM vs. Unaffected | 14 vs. 11 | 1.00 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| XLMTM vs. MD1 | 14 vs. 10 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.074 |
| XLMTM vs. NMDs | 14 vs. 11 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 0.229 |
| Unaffected vs. NMDs | 11 vs. 11 | 0.99 | 0.02 | 0.023 |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





