1. Introduction
Breast cancer is one of most common cancers in women. Aberrant estrogen receptor (ER) activity is the primary driver of tumor growth and progression in a majority of breast cancer patients. "Estrogen" refers to a family of female hormones, including estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), estriol (E3), and estetrol (E4) that can bind to ERs with different affinities, with E2 as the predominant circulating estrogen in humans [
1]. The two isoforms of estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ, are both members of nuclear receptors of transcriptional factors. The canonical cascade leading to ER transcriptional activity is initiated by the binding of estrogen, which results in a conformational change that induces receptor dimerization [
2], and translocation into the nuclei. Then the E2-ER complexes bind directly to the estrogen response elements (EREs) in the chromatin, the enhancer regions within or close to promoters, and/or 3’-untranlated regions of target genes [
3,
4]. Once bound to EREs, the E2-ER complexes can initiate gene expression by recruiting its specific co-regulatory proteins, known as co-activators and co-repressors [
5]. In addition, there are also indirect genomic activation of nuclear estrogen receptors and non-genomic signaling membrane receptor.
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) compete with estradiol to bind to the ligand-binding domain of ERα [
6]. Tamoxifen is one of the most used SERMs in the treatment of breast cancer, which works as an antagonist in breast tissues but an agonist in the uterus [
7]. It has been used as endocrine therapy for ER positive metastatic breast cancers over 40 years. However, about half of the ER positive breast cancer patients present resistance to tamoxifen, and further, nearly all initial responders eventually will acquire resistance. Therefore, it is important to elucidate how breast cancers acquire resistance to endocrine therapy and identify new therapeutic opportunities to improve the efficacy of endocrine therapy.
Sigma receptors, classified into sigma 1 (σ1) and sigma 2 (σ2) receptors [
8,
9], are found in a variety of tissues and organs. Sigma 2 receptor has been explored as a proliferation biomarker and imaging target for cancer diagnosis for years before transmembrane protein 97 (TMEM97, also known as MAC30) was identified as the
bona fide σ2 receptor [
10]. TMEM97 has been predominantly studied for its role in regulating cholesterol homeostasis [
11]. Elevated expression of TMEM97 or MAC30 has been linked with poor clinical parameters in gastric, colorectal [
12], breast [
13], and ovarian [
14] cancers, but the biological mechanism involved remains unknown. Herein we report that TMEM97/σ2 receptor modulate the growth of ER positive breast cancer cells via regulating ERα activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
17 β-Estradiol (E2), (Z)-4-Hydroxytamoxifen (OH-Tam), ICI 182,780 (Fulvestrant), and Rapamycin were purchased from AdooQ Bioscience. Cycloheximide and other common chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemical analysis on paraffin-embedded breast tissue array was carried out using commercial validated anti-TMEM97 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:100) (Thermo-Fisher Scientific). The breast cancer tissue microarray (BC081116b, US Biomax, Inc) contained 100 cases of breast invasive ductal carcinoma and 10 cases of adjacent breast tissue as control with single core per case. Each case had pathology information for ER, PR and HER2, TNM, clinical stage and grade. For IHC staining, the tissue microarray slides were deparaffinized, rehydrated and antigen retrieved by placing in Declere working solution (Cell Marque) in an electric pressure cooker for 30min. After a hot rinse with boiling Declere, slides were cooled for 5min. Then wash the slides with distilled water (3 changes), dehydrate through 95% and 100% alcohol (2 changes) and clear in xylene (2 changes). Slides were processed for immunohistochemical staining using the Histostain Plus Broad Spectrum kit (Zymed) following the manufacturer’s instructions. After mounting with DPX Mount (Sigma), slides were examined and photographed under microscopy (OLYMPUS DP73). The degree of staining is calculated by H-Score using the following formula: H-Score = 100*[(% at 0) * 0 + (% at 1+) * 1 + (% at 2+) * 2 + (% at 3+) * 3].
2.3. Cell culture and transfections
MCF7 and T47D, two estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cell lines, were purchased directly from ATCC and used within six months. MCF7 cells were grown and maintained in DMEM/High glucose with 4.0mM L-glutamine and sodium pyruvate medium (HyClone). T47D cells were grown and maintained in RPMI 1640 medium with L-glutamine (HyClone). All cell culture media were supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (ATCC) and Antibiotics-Antimycotics (100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin and 250μg/ml amphotericin B), and cultured in a humidified incubator under an atmosphere containing 5% CO2, at 37°C.
For estrogen and serum deprived conditions, cells were seeded in full culture medium (10% FBS) overnight and changed to phenol red free, DMEM/High glucose medium with L-glutamine and sodium pyruvate, supplemented with 0.5% charcoal-striped serum for 24 hours before indicated treatments.
2.4. Cloning and expression of TMEM97
The ORF for human TMEM97 gene (ENSG00000109084) was amplified from breast cancer MCF7 cells using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (Thermo Scientific) according to the manufacture's protocol and a nested PCR technique, and cloned into pCDH-myc vector. GFP gene was directly linked to the C-terminal end of TMEM97 and inserted into the same pCDH-myc vector (Supplemental Figure A). Meanwhile the CopGFP gene of the pCDH-myc vector was deleted at the same time. Correct insertion of the TMEM97-EGFP was confirmed by DNA sequencing.
For TMEM97-EGFP overexpression, 293T cells were infected with lentiviral vector and pCDH-TMEM97-EGFP along with packaging vectors (System Biosciences) by using DNAfectinTM liposome transfection reagent. Viral supernatants were collected 48 hours after transfection, diluted 1:1 in fresh medium in the presence of polybrene (4μg/ml) and added to MCF7 and T47D cells. The empty pCDH vector was used as a control. After 48 hours infection, cells with green fluoresces were sorted out by flow cytometry, and maintained in full culture conditions.
2.5. Knockdown of TMEM97 expression
For TMEM97 shRNA stable knockdown, TMEM97 shRNA constructs were purchased from Dharmacon (Supplemental Figure C). Three different constructs, 131 (Clone ID: V3LHS_333131), 835 (Clone ID: V2LHS_54836), 602 (Clone ID: V3LHS_404602), with different targeting regions. Sequencing primer 5' - GCATTAAAGCAGCGTATC - 3' for all three of the constructs. The empty vector pGIPZ was used as the control. The production of lentiviral particles and transduction were same as described above for lentiviral overexpression. The GFP positive transduced cells were selected by cell sorting and maintained in growth medium for expansion and characterizations.
2.6. Colony formation assay
100 MCF7 (TMEM97/PCDH) cells per well were seeded into tissue culture 12-well plates. They were cultured in 5% FBS DMEM or 0.5% Charcoal Stripped FBS phenol red free DMEM culture medium. Media was replaced weekly. Subsequently, the cells were washed with PBS then fixed in 4% formaldehyde. The fixed cells were stained with crystal violet (Fisher Scientific), washed with water, and allowed to air-dry. Colonies were counted and dishes were photographed.
2.7. Luciferase Assay
1×105 cells per well were seeded in 24-well culture plates with full culture medium overnight. Second day cells were transiently transfected with ERE-TATA-Luc reporter construct and Renilla construct in a 10:1 ratio for 24 hours. Then culture medium was changed to 0.5% CS-FBS phenol red free medium for another 24 hours prior to E2 treatment for 5 hours. Cells were harvested for dual luciferase assay afterwards. The luciferase activities were measured by dual luciferase assay kit (Promega) following the instructions described by manufacturer and normalized with the Renilla activities. Each experiment was performed with 4 repeats per sample.
2.8. MTS assay
1x104 cells were seeded into each well of 96-well plates overnight. Next day, cells were changed to desired culture media with or without compound treatment. After 4 days culturing, aspirated the culture medium and added 1 X PBS mixed with 20µl MTS reagent (Promega) for each well and incubated for 1 hour. Absorbance of 490nm light (OD490nm) was determined using a spectrophotometer. Each data point was represented as the mean of 4 repeats.
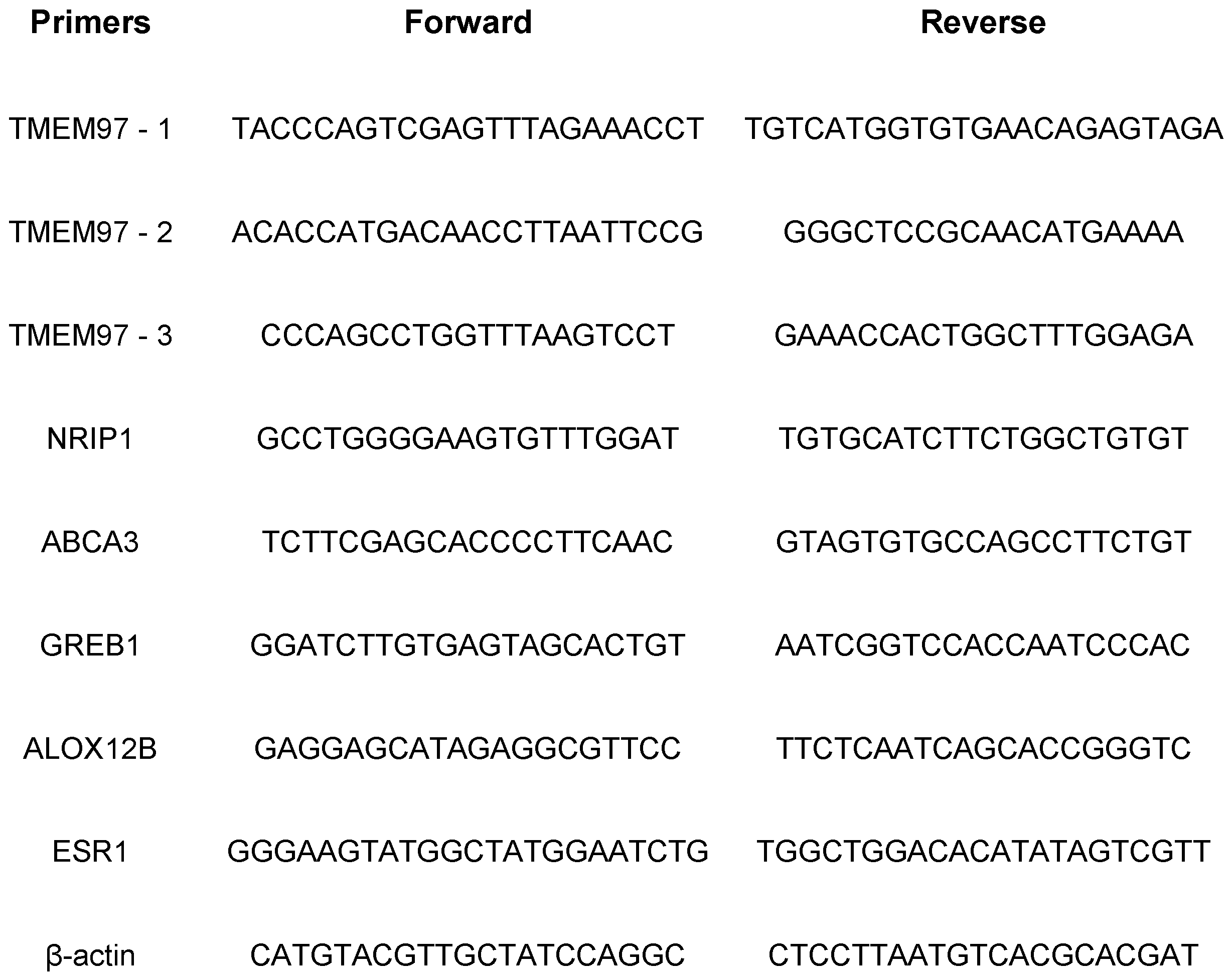
2.9. RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis
Total RNAs were isolated using GeneJET RNA Purification Kit (Thermos Scientific) following the manufacturer’s instructions. 1μg of RNA was used for reverse transcription done by ProtoScript
® II First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (New England Biolabs). The cDNA products were used as templates for real-time qRT-PCR with SYBR green qPCR mixture by AzuraQuant Green Fast qPCR Mix LoRox following the manufacturer's protocol. Reactions were run on the 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) and the reactions were performed in triplicate. Data were normalized to β-actin and relative mRNA expression was determined using the ΔΔCt. Gene-specific primer sequences are listed in
Table 1.
2.10. Immunoblots and antibodies
Cells were lysed with 2x SDS lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktail on ice. The cell lysate was sonicated for 10 seconds, and then followed by heating at 95°C for 5 minutes. All samples were loaded at the same amount and separated by SDS-PAGE gel in a Bio-Rad Protean II system. After transferring proteins to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane, the membrane was blocked with 5% BSA for 60 min at room temperature and incubated with the primary antibody at appropriate dilutions in 5% BSA at 4 °C. After overnight incubation with appropriate primary antibodies, the membrane was washed three times with Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 0.1% Tween for 5 min each time and probed with fluorescently labeled secondary anybody (1:10000) for 1 hour at room temperature. The membrane was then washed three more times with TBS-T for a total of 15 minutes. The immunoblots were visualized by Odyssey Infrared Imaging. Densitometry was performed using Odyssey 2.0 infrared imaging system.
The following antibodies used in this study were purchased from Cell Signaling. Rabbit monoclonal antibodies: anti-β-actin, anti-GAPDH, anti-p-ERα (Ser167), anti-ERα, anti-p-S6K1 (Thr389), anti-S6K1, anti-p-S6 (S236/S236), anti-p-S6 (S240/S244), anti-p-Erk1/2, anti-p-AKT, anti-p-c-Raf, anti-p-P38 MAPK, with the dilution of 1: 1000 for western blot. TMEM97 polyclonal antibody was purchased from Thermo-Fisher Scientific with the dilution of 1: 100-1: 250 for western blot.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed using spreadsheets with Microsoft Excel or GraphPad Prism V (GraphPad, USA). Data were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical comparisons were made using unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Differences were considered statistically significant if p≤0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Increased TMEM97 protein expression is associated with estrogen receptor status
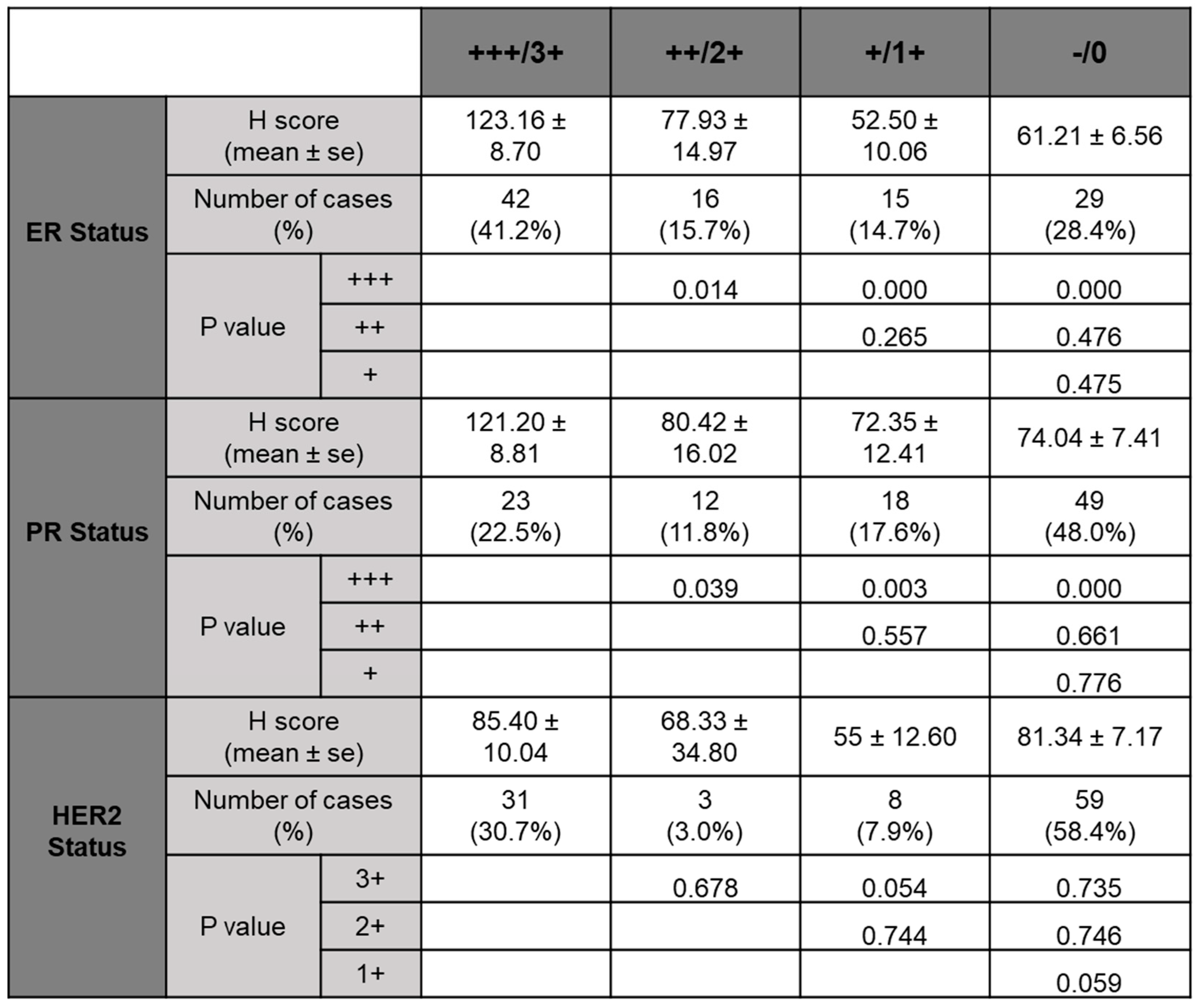
With TMEM97 identified as σ2R, we first determined the expression pattern of TMEM97 in human breast cancer tissues by immunohistochemical staining (IHC) with a validated TMEM97 antibody. The positive staining of TMEM97 was quantified under microscope using a double blinded approach and the H-scores calculated. It was found that the intensity of TMEM97 signaling was progressively higher with higher estrogen receptor (ER) status, with the most intensive staining in ER +++ tissues samples and reduced gradually in ER ++, ER + and ER negative samples (
Figure 1A)
. As shown in
Figure 1A and
Table 2, breast cancer patient tissue samples with the highest ER expression (ER+++) (n=42, 42%) exhibited the highest H-score of 123.16 ± 8.70, and the H-scores reduced as the ER positive status declined, with ER ++ samples (n=16, 15.7%) scored 77.93 ± 14.97, ER + samples (n=15, 14.7%) scored 52.50 ± 10.06. The differences between ER +++ group and all the others are statistically significant with p values less than 0.05.
Interestingly, we observed similar results linking TMEM97 with PR status similar to the ER status
. TMEM97 staining is predominantly strong in the PR positive tissue samples, with statistically significant expression in PR +++ tissue samples (H-score=119.89 ± 8.81, n=23, 22.5%) (
Figure 1B and Table 2). In contrast to ER or PR, HER2 status did not lead to any different expression pattern of TMEM97 (
Figure 1E and Table 2).
To further assess the clinical relevance of TMEM97/σ2 receptor in breast cancer, we queried TMEM97 using a public database, Kaplan–Meier plotter [
15]. This database uses aggregate microarray data to analyze the prognostic value of a specific gene by dividing the cohorts into two groups (High refers to the upper quartile and Low refers to the lower quartile) according to the gene expression. Multiple probes are available for a particular gene to make the database more vigorous. There are four different probes for TMEM97 gene. As shown in
Figure 1F, a high level of TMEM97, as detected by 3 out of the 4 probes, was significantly associated with low relapse free survival (RFS) in all types of breast cancers. The highest hazard ratio (HR) is 1.5 (p<0.001) as revealed by the probe set 212279_at, then followed by the probe 2122811_s_at and 212282_at with HR 1.4 (p<0.001) and 1.36 (p<0.001), respectively. Remarkably if we gated the two cohorts with estrogen receptor positive patients
(Figure 1G), all 4 probe sets exhibited significant correlation of high TMEM97 mRNA expression with poor relapse free survival. Among them the highest HR is 1.61 (p<0.001) as detected by probe 212281_s_at, and the lowest HR is 1.32 (p<0.01) by 214283_at. The bioinformatics data suggest that the survival of breast cancer patients is impacted by the TMEM97 mRNA level, especially for the ER positive patients.
3.2. Stimulation of ER positive breast cancer cell growth and survival under different culture conditions by TMEM97 overexpression
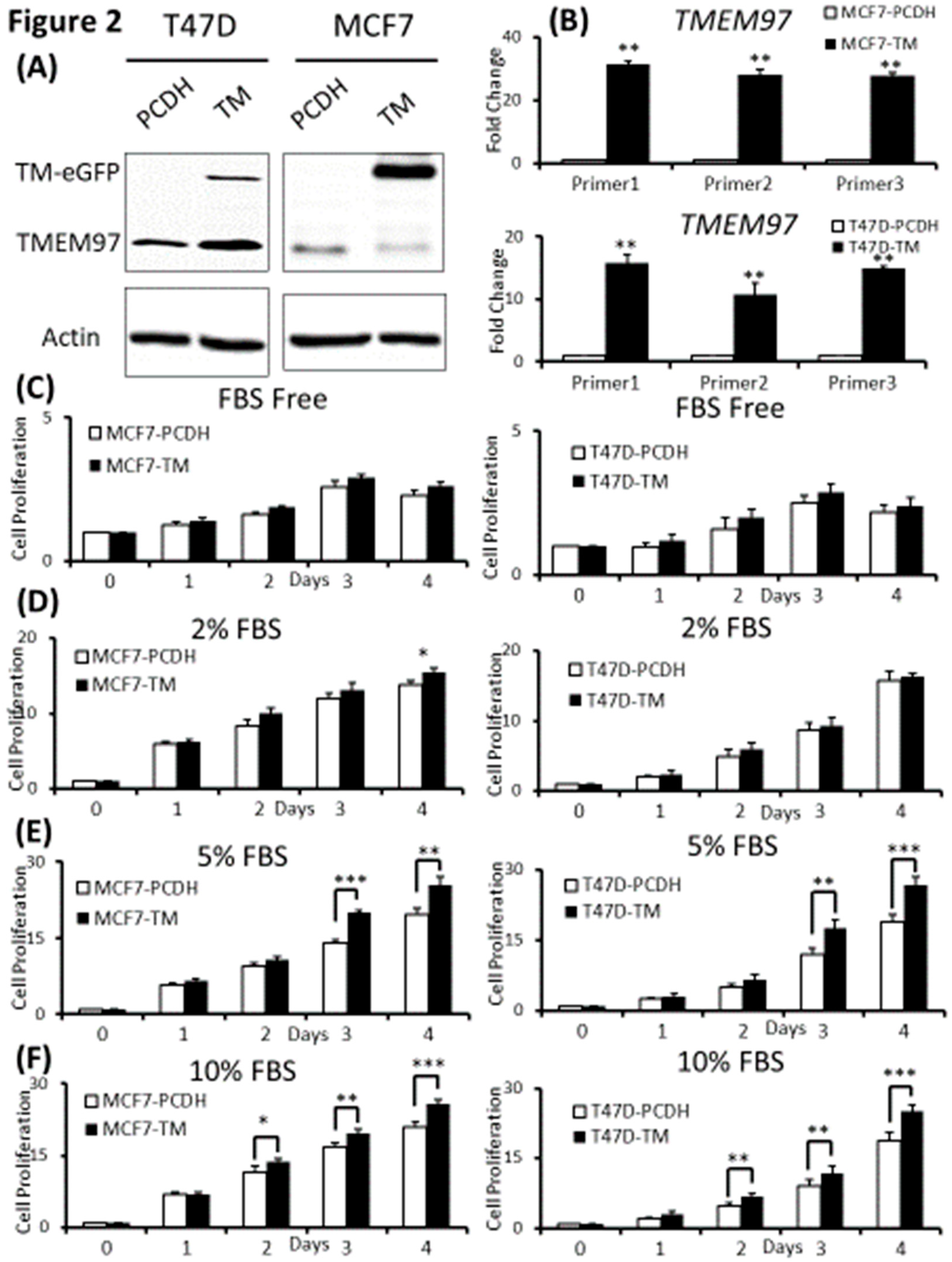
To determine the biological functions of TMEM97, we cloned and constructed the TMEM97 overexpression plasmid using pCDH-CMV lentivector (illustrated in Supplemental Figure A). Then we increased the expression of TMEM97 in MCF7 and T47D cells (ER positive breast cancer cells) by lentivirus infection, with GFP as indication of successful transductions and predominant localization of TMEM97 in the cytoplasm (Supplemental Figure B).
The overexpression of TMEM97 is confirmed at both protein (
Figure 2A) and mRNA levels (
Figure 2B). The molecular weight of TMEM97 protein itself is around 24kDa, and the molecular size of the fusion protein TMEM97-EGFP would be around 45kDa. As expected, there were two bands (~45KDa and ~24KDa) showing in the overexpression cells, while only one band in the PCDH control cells (
Figure 2A)
. Next, we performed quantitative PCR using 3 different sets of primers targeting 3 different positions of the TMEM97 gene from primer bank [
16] (
Figure 2B).
To determine whether increased expression of TMEM97 could promote and stimulate breast cancer cell growth and survival we performed the proliferation study by MTS assay under different culture conditions, and found that the overexpression cells (TM) tend to survive better than the control cells (PCDH) under serum depleted condition, though the differences were not significant in
Figure 2C. Then we gradually increased the serum levels in the culture media, the growth diverged at Day 4 for MCF7 cells cultured at 2% FBS (
Figure 2D), and became more significant under 5% FBS culture condition on Day 3 and Day 4 for both MCF7 and T47D cells (
Figure 2E). On Day 4 at 5%-FBS, the overexpression cells grew at 1.31 folds and 1.36 folds faster than the control cells in MCF7 and T47D, respectively (
Figure 2E). If cells were cultured under normal condition, 10% FBS, the growth advantage by TMEM97 overexpression even started at Day2, 1.2 folds for MCF7, 1.45 folds for T47D. And the trend kept the same to Day4, 1.24 folds for MCF7 and 1.33 folds for T47D (
Figure 2F).
3.3. TMEM97 supports ER positive breast tumor cell growth and colony formation under hormone depletion.
Phenol red, the widely used pH indicator in tissue culture medium, has been found structurally similar to some nonsteroidal estrogens and exhibits significantly estrogenic activities. The concentration of phenol red presented in culture medium is relatively high that it could stimulate the cell growth of some estrogen sensitive cells [
17,
18,
19], especially for the human breast cancer-derived MCF7 and T47D cells [
17]. In addition to the phenol red, another interference in the study of estrogen-responsive cell system is the estrogen that is already existed in FBS, since this hormone could pass through the placenta to the fetus’ circulation. To study the effects of steroid hormone
in vitro without the interference from the growth environment, a “hormone-free” condition is needed, so dextran-coated charcoal was utilized to deplete the hormone from the FBS. Charcoal stripped fetal bovine serum was produced by absorbing with activated carbon that removes non-polar material such as lipophilic (lipid-related) materials, like virus, certain growth factors, hormones and cytokines, but has little effect on salts, glucose, amino acids, etc. The phenol red free medium supplied with charcoal stripped FBS could keep the cell grow safely but maintain estrogen free for testing [
19].
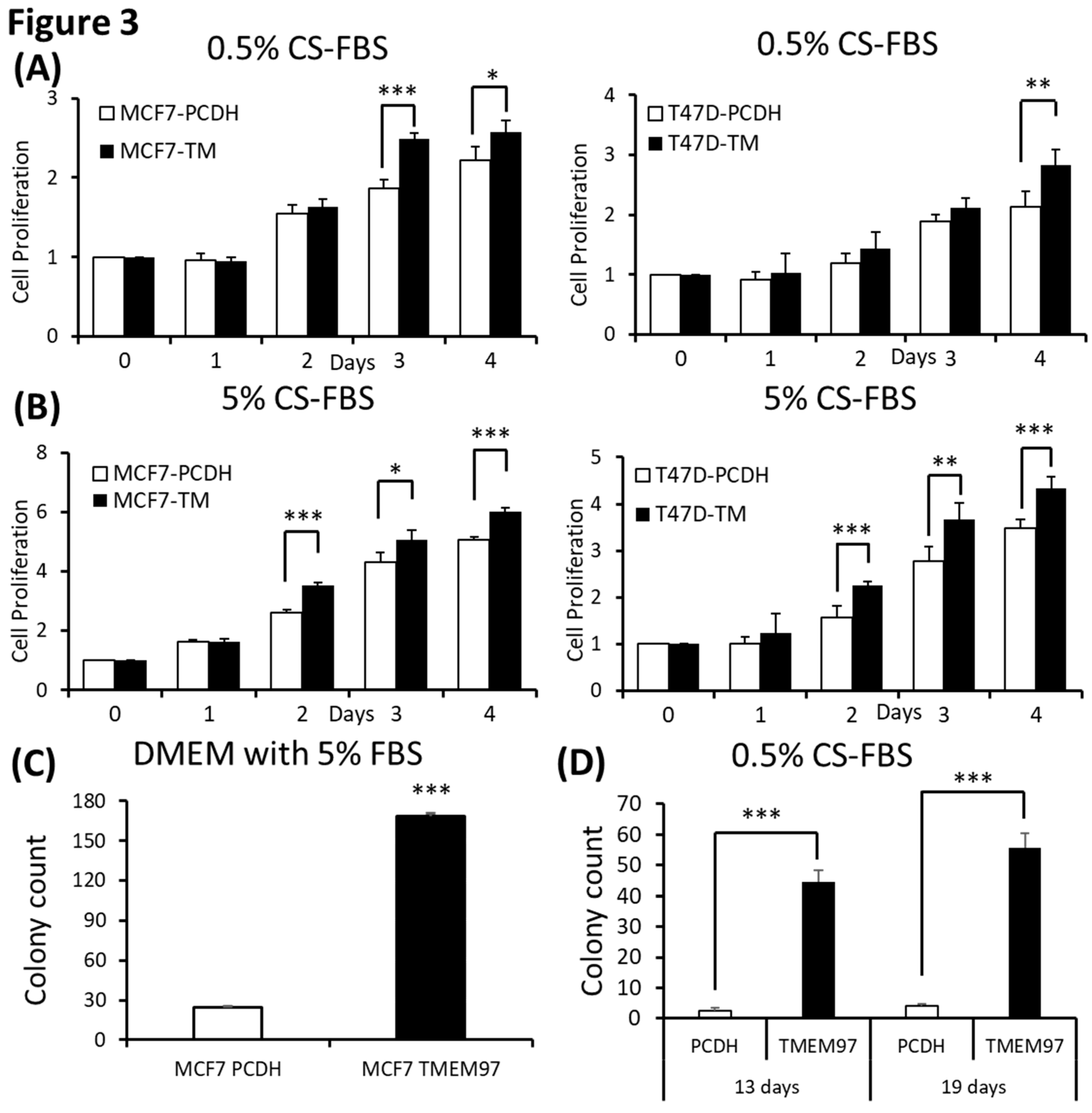
Since TMEM97 has been found positively associated with estrogen receptors, to understand their relationships without the interference of surrounding estrogen, we changed the culture medium to phenol red free medium supplied with charcoal stripped FBS (CS-FBS) at different concentrations. And we found that even supplied with very low concentration of CS-FBS (0.5%), TMEM97 overexpression cells still showed enhanced proliferation both in MCF7 and T47D cells (
Figure 3A). With increased concentration of CS-FBS (5%) as shown in
Figure 3B, the difference between the overexpression and the control started to show even at Day2. The data suggest that TMEM97 could also promote the cell growth under estrogen depleted condition for ER positive breast cancer cells.
Next, we determined whether TMEM97 promotes colony formation of breast tumor cells. 100 MCF7 (TMEM97/PCDH) cells were seeded into each well in a tissue culture plate and then cultured in 5% FBS DMEM or 0.5% Charcoal Stripped FBS phenol red free DMEM culture medium. After 13 days culturing in 5% FBS DMEM media, MCF7 TMEM97 showed increased colony formation when compared with pCDH cells (
Figure 3C). Under culture condition with 0.5% Charcoal Stripped FBS phenol red free DMEM culture media, pCDH cells hardly formed colonies after 13 days, but TMEM97 cells still showed a strong ability to form colonies (
Figure 3D). The result for group in 0.5% Charcoal Stripped FBS phenol red free DMEM culture media after 19 days showed a similar pattern (
Figure 3D). The results suggest that TMEM97 could promote cell growth and proliferation even under estrogen depleted condition for ER positive breast cancer cells.
3.4. Inhibition of ER positive breast cancer cell growth and survival by TMEM97 knockdown
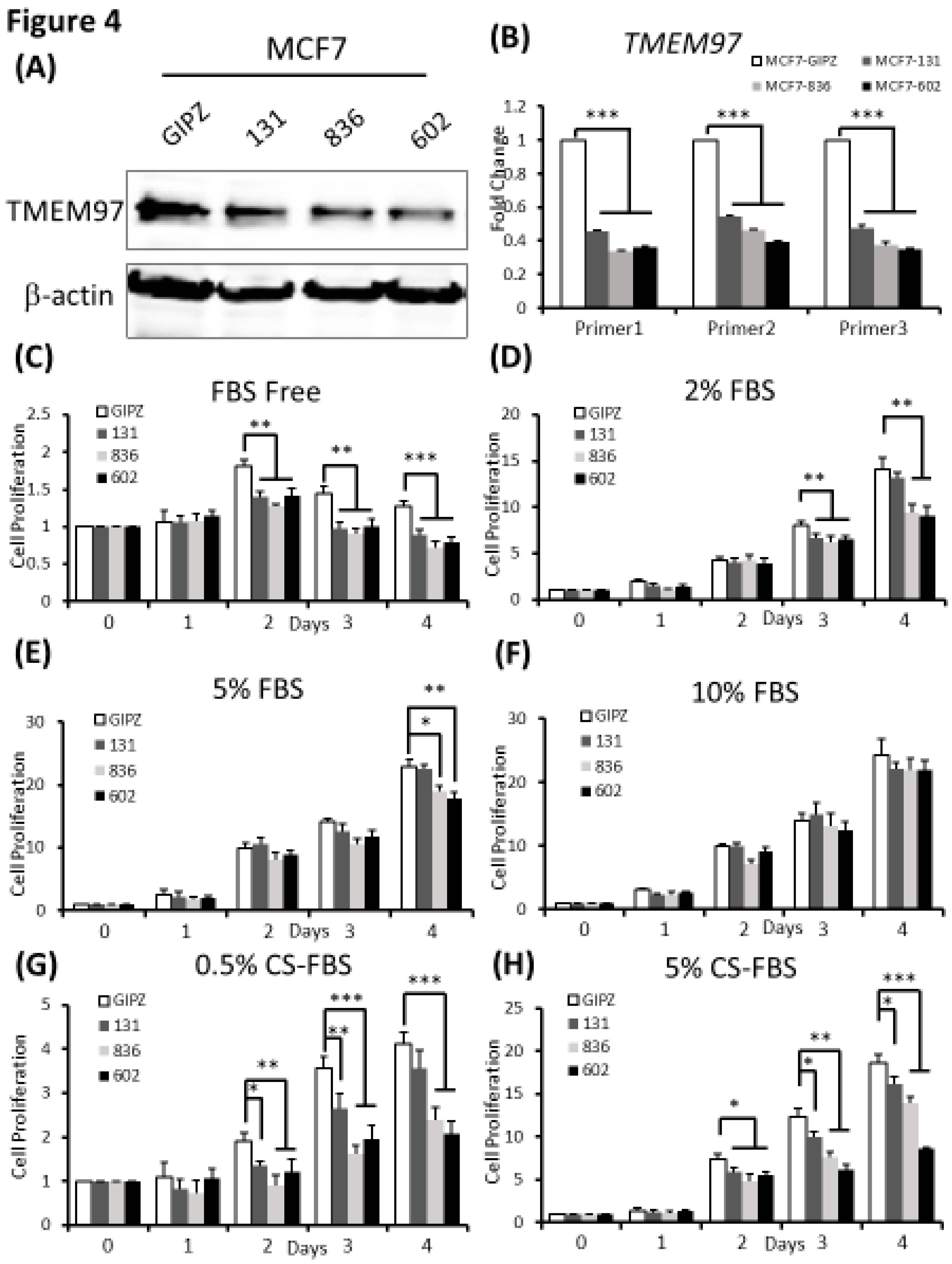
To determine whether TMEM97 is required for breast tumor growth, we performed shRNA-mediated TMEM97 knockdown experiments in MCF7 cells. Two of the three shRNA target the 3’ UTR of TMEM97 while one shRNA targets the ORF of TMEM97, as shown in
Supplemental Figure C. The efficiency of knockdown was tested at protein level (
Figure 4A). Then at the mRNA expression level, all three knockdown cell lines had reduced TMEM97 expression level to about 30% to 40% of the control, especially 836 and 602 cells, as confirmed by 3 different primers (same primers as used in overexpression confirmation) (
Figure 4B).
Next, we performed the cell growth assay for the shRNA-mediated knockdown cells under different culture conditions. As expected, the knockdown cells showed significant reduced cell growth, especially in the cells cultured under FBS free condition, which was around 80% reduction on Day 2, 60% on both Day 3 and Day 4 for all three knockdown cells (
Figure 4C). However, with continuously increased percentage of FBS supplement the growth disadvantage was finally eliminated (
Figure 4F). Notably, when cultured in 2% FBS, the decreased cell growth still existed for all the knockdown cells on Day 3. On Day 4 the difference only remained in 836 and 602 knockdown cells, but not for 131 cells (
Figure 4D). Similar results were observed in
Figure 4E after 4 days of 5% FBS cultivation. A different cell growth reduction between the 131, 836 and 602 cells could be due to different efficiency of TMEM97 knockdown. As indicated in
Figure 4B, 836 and 602 cells showed more reduced TMEM97 mRNA expression compared to 131 cells.
We also performed the proliferation assay for TMEM97 knockdown cells under estrogen depleted conditions. We found that knockdown cells presented reinforced growth suppression under estrogen depleted condition, regardless of what percentage of charcoal stripped FBS was provided (
Figure 4G,H). Consistent with previous data, the inhibition effects were more pronounced in 836 and 602 cells. As shown in
Figure 4G,H, the cell proliferation rate for 602 cells kept below 50% of the control cells after 4 days cultivation both in 0.5% CS-FBS and 5% CS-FBS.
These data suggested that knocking down of TMEM97 expression could suppress the breast cancer cell growth under starvation culture conditions, or estrogen deprivation conditions.
3.5. Estrogen receptor transcriptional activity is upregulated by the overexpression of TMEM97/σ2 receptor
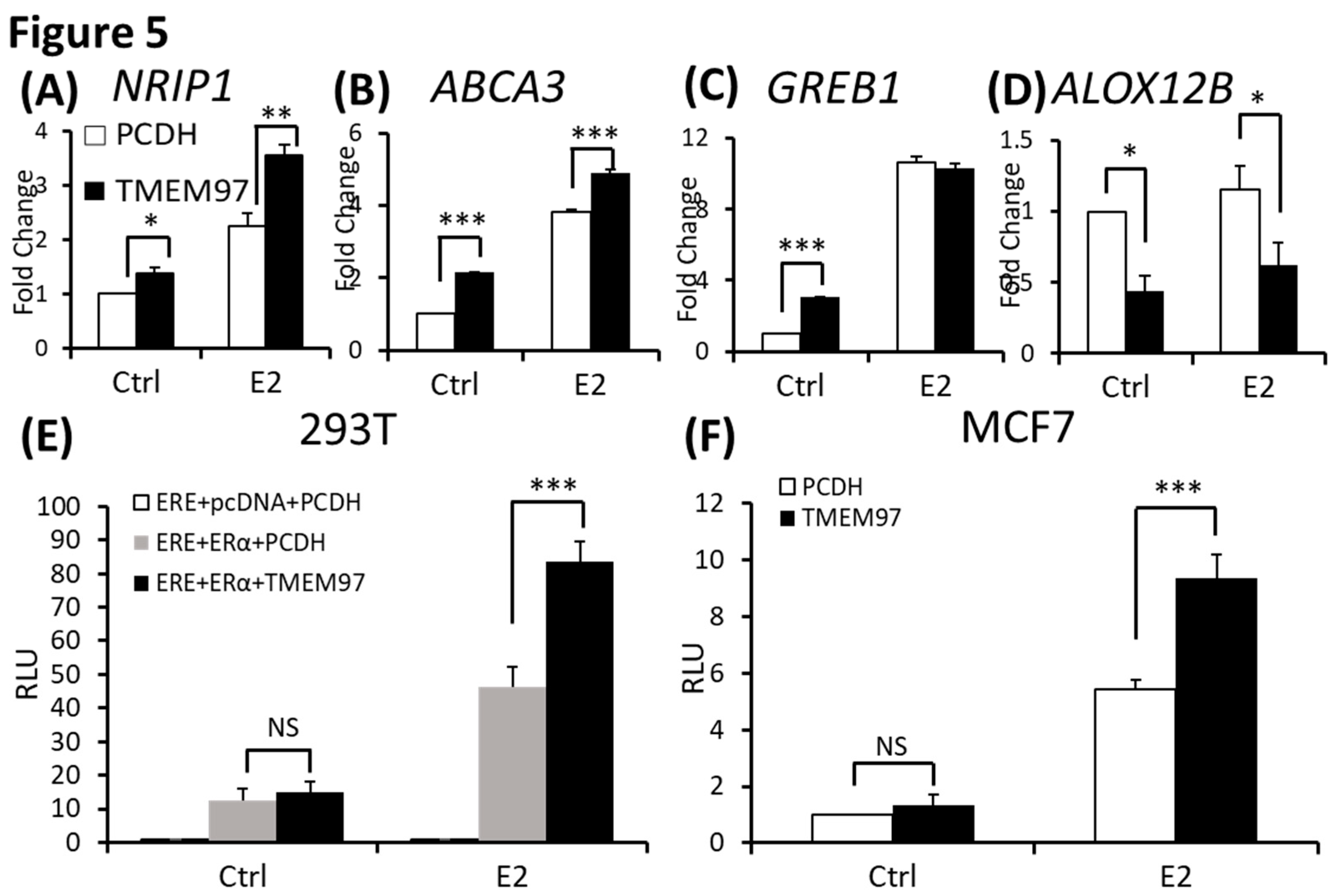
Based on the association of TMEM97 expression with estrogen receptor and the increased proliferation of ER positive breast cancer MCF7 cells, we determined whether TMEM97 regulates ER transcriptional activity. First we used qRT-PCR to evaluate changes at the transcript level of the ERα target genes
NRIP1 [
20],
ABCA3 [
21],
GREB1 [
22] and
ALOX12B. Among them,
NRIP1, ABCA3 and
GREB1 are ERα up-regulated genes, and
ALOX12B is an ERα downregulated gene. Cells were cultured at serum starved and estrogen depleted condition (0.5% CS-FBS phenol red free medium) for 24 hours before treatment with DMSO (Ctrl) and 17β-estradiol (E2) at 10µM for 5 hours.
We found significant induction of
NRIP1 and
ABCA3 in TMEM97 overexpression cells with or without E2 treatment (
Figure 5A,B). The significant induction of
GREB1 transcript level only existed without E2 treatment (
Figure 5C). For ERα down-regulated gene
ALOX12B, the transcript level was reduced in overexpression cells with or without E2 treatment (
Figure 5D). These data suggested that TMEM97 itself could modulate the expression of ERα target genes, with or without E2 stimulation. No differences were observed for GREB1 after E2 treatment may due to the super sensitive responses for this gene. Almost all (~95%) GREB1 binding region is shared by estrogen receptor binding, so that it is the most estrogen-enriched ER interactor [
22].
To measure the direct effect of TMEM97 on ERα transcriptional activity, we conducted a luciferase-based ERα reporter assay. As indicated in
Figure 5E, when transfected with ERα, E2 increased the ERE activity by around four folds after 5 hours treatment. When co-transfected with TMEM97-EGFP, the transcriptional activities after E2 treatment increased to six folds, and 1.8 folds relative to ERα vector alone. Next, we tested the ERα transcriptional activities in MCF7 stable TMEM97 overexpression cells under the same culture condition (
Figure 5F), and observed that after E2 treatment, the induced transcription in TMEM97 overexpression cells was significantly higher than in control cells (>1.7 folds). No transcriptional activity differences were observed in the absence of E2 in transiently transfected cells or in stable overexpression cells (
Figure 5E,F). The data suggest that increased TMEM97 expressions in MCF7 cells led to increased ERα activities in response to E2.
3.6. TMEM97/σ2 receptor activates ERα independent of estrogen and contributes to tamoxifen resistance
To determine the mechanism involved in TMEM97 regulating ER activities, we investigated the influence of TMEM97 overexpression on ERα protein. Serine 167 of the ERα has been identified as the major estrogen-induced phosphorylation site in breast cancer cells [
23]. We found that ERα p-S167 was markedly increased in an estrogen dependent manner in MCF7 cells (
Figure 6A). However, in TMEM97 overexpression cells the differences of p-S167 before and after E2 treatment was not obvious, because the basal level of p-S167 was extremely high in the overexpression cells even in the absence of E2 compared to control cells (
Figure 6A), suggesting that TMEM97 itself played a similar role to estrogen that could continuously activate ERα at its S167 site without the presence of estradiol.
Serine 167 of the ERα has been studied for many years. Phosphorylation of this site could activate and promote ERα-dependent transcription and cellular proliferation and is attributed to increased resistance to tamoxifen treatment [
24,
25,
26]. Various studies have shown that increased Ser167 phosphorylation correlates with poor prognosis in different cancer types [
27,
28]. Tamoxifen is widely used as a chemotherapeutic and preventative medicine for estrogen receptor positive tumors [
29].
To elucidate whether the sustained activated ERα S167 level in TMEM97 overexpression cells would lead to tamoxifen resistance, we performed proliferation assay with treatment of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (OH-Tam), a metabolite of tamoxifen with greater potency. MCF7 cells were deprived of E2 and then stimulated with E2 in the presence of different concentration of OH-Tam. After 4 days treatment, PCDH and TMEM97 showed significant differences of response to OH-Tam treatment as shown in
Figure 6B. The inhibition effects of OH-Tam in PCDH cells could be observed at 1nM. When increased to 1µM, the percentage of viable cells dropped to less than 50%. While in TMEM97 overexpression cells, OH-Tam exhibited weak agonist effect on cell proliferation at low concentration (0.1nM and 1nM). And when treated with 1µM for 4 days, the viable cells still remained around 70%, suggesting that TMEM97 overexpression cells are more resistant to tamoxifen treatment.
3.7. Activation of ERα by TMEM97 is through mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathway and can be blocked by mTOR inhibitor
To further investigate whether the endocrine resistance mechanism is due to the persistent stimulation of ERα Ser167, we examined the potential signaling pathway through which active p-ERα (S167) was increased in MCF7 TMEM97 overexpression cells. Ser167 can be phosphorylated by ERK1/2/MAPK [
30,
31], AKT [
32], p90 ribosome S6 kinase (p90RSK) [
24], CK2 [
23] and mTOR/p70S6K1 [
33,
34]. So, several western blots were performed from the signaling pathways mentioned above to reveal the possible cascades that participated in the TMEM97 mediated ERα phosphorylation. We found that mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathway was the only one that changed dramatically in overexpression cells, but not others (
Figure 6C). Similar to p-ERα S167, when cells were deprived of estrogen for 24 hours, the endogenous p70S6K1 protein remained active through TMEM97 overexpression compared to control cells, suggesting the involvement of 40S ribosome S6 kinase 1 [
35] (
Figure 6C).
The mTOR pathway has been identified as a key regulator of cell growth and proliferation in responses to extracellular stimuli, such as nutrition and growth factor availability. Rapamycin is a very well-known naturally derived mTOR inhibitor which can inhibit the tumor cell proliferation and has immunosuppressive properties [
36]. The 40S ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) is one of the best characterized downstream targets of mTOR, which can rapidly respond to the rapamycin treatment resulting in a dephosphorylation and inactivation [
37]. To test if the sustained activation of p-ERα S167 by TMEM97 was through the mTOR/S6K1 and could be regulated by this signaling pathway, we evaluated the effects of rapamycin on protein phosphorylation at different concentrations in the absence of estrogen. First, we could see the huge differences that both p-ERα S167 and p-S6K1 T389 were highly active in TMEM97 overexpression cells without treatment (
Figure 6D). But after the rapamycin treatment even at 1nM, the phosphorylation levels of p-ERα and p-S6K1 were reduced to the similar levels of control cells, especially for p-S6K1 (
Figure 6D), indicating that the mTOR inhibitor could block TMEM97 activation effect on S6K1.
3.8. TMEM97 knockdown reduces both ERα and mTOR/S6K1 signaling activity and increases the tamoxifen sensitivity
In parallel, we determined the effect of TMEM97 expression knockdown on ERα activity. First, we analyzed the ERα transcription activity in MCF7 cells with TMEM97 expression knocked down under the same culture conditions as above. As shown in
Figure 7A, TMEM97 knockdown did not alter the endogenous ERα transcriptional activity before E2 treatment. However, TMEM97 knockdown significantly reduced, but not abolished, the stimulation of ERE activities by E2, from 5.18 folds induction in vector control cells, to 4.3, 3.8 and 3.7 folds in 131, 836 and 602 cells, respectively (
Figure 7A).
Next, we determined whether knockdown of TMEM97 expression would affect the ERα and mTOR/S6K1 signaling. GIPZ, 131, 836 and 602 cells were serum and estrogen deprived for 24 hours and then stimulated with E2 for 5 hours, cells were then harvested for immunoblot for analyses of ERα phosphorylation. As shown in
Figure 7B, p-ERα S167 could be activated by E2 stimulation in all cells, while without the stimulation, the endogenous activity of p-ERα S167 were suppressed in TMEM97 knockdown cells, 836 and in particular, 602 cells. In addition to the reduction in p-ERα levels, the mTOR/S6K1 signaling was suppressed (
Figure 7C). The observations suggest that high expression of TMEM97 in ER positive breast cancer cells could enhance the ERα activity through the activation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway, while lacking TMEM97 expression would suppress the ERα activity together with the inhibition of mTOR/S6K1 signaling.
Since hyper-activation of p-ERα and p-S6K1 lead to tamoxifen resistance, we next determined the response of TMEM97 knockdown cells to tamoxifen. As shown in
Figure 7D, all TMEM97 knockdown cell lines showed significant tamoxifen sensitivity when compared to the vector control cells, under stimulation by E2. Apparently under very low concentrations, the growth capacity of TMEM97 knockdown cells were around 20%-30% less than the control cells. Taken together, knockdown of TMEM97 expression reduced ERα and mTOR/S6K1 signaling activities, rendering the cells with increased sensitivity to tamoxifen.
4. Discussion
In this study, we have made the following observations regarding TMEM97/σ2 receptor in breast cancer. First, TMEM97/σ2 receptor expression is notably elevated in breast tumors with high expression of ERα and PR, while no correlation with HER2 status is found. Second, TMEM97/σ2 receptor modulates tumor cell proliferation and growth, especially when cells are in a nutrition limited or estrogen depleted conditions. Third, TMEM97/σ2 receptor regulates ERα activities in breast cancer MCF7 and T47D cells. Fourth, TMEM97/σ2 receptor regulates mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathways, rendering ERα with increased level of active, phosphorylated ERα that can be blocked with a mTOR inhibitor. Fifth, increased TMEM97/σ2 receptor expression renders MCF7 cells with enhanced resistance to tamoxifen. These observations suggest that TMEM97/σ2 receptor participates in breast tumor cell growth driven by estrogen receptor signaling and further renders tumor cells with increased resistance toward endocrine therapeutics such as tamoxifen.
The clinical relevance of TMEM97/σ2 receptor in breast cancer is at first indicated by in silico analyses of a pubic database. In the database with tumor microarray data (Kaplan-Meier Plotter), breast cancer patients with high levels of TMEM97 mRNA had significantly reduced overall survival as revealed by three out of four probes mapped to TMEM97. In ER positive breast cancer, all four probes showed a significantly reduced survival in patients with high TMEM97 mRNA levels. While the in silico analyses suggest the potential involvement of TMEM97 in patient survival, cautions are warranted since the analyses only reveal a correlative, not causal, relationship between TMEM97 and patient survival.
A majority of breast cancers (70%) are ERα positive, in which tumor growth and progression requires continued ERα activity and signaling. We found that TMEM97 could promote MCF7 breast cancer cell proliferation especially under nutrition limited or estrogen depleted conditions when compared with the vector control cells. On the other hand, knockdown of TMEM97 reduced MCF7 cell growth. Similar results were observed in T47D cells, another ER positive breast cancer cell line. The data suggest that TMEM97 modulates the growth of ER positive breast cancer cells.
There are several lines of evidence suggesting the regulation of ER activities by TMEM97. First, TMEM97 overexpression increased ER transcriptional activities as revealed by the reporter gene analyses in MCF7 cells and co-transfection analyses. Second, TMEM97 knockdown reduced the ability of estrogen to enhance ER transcriptional activities. Third, TMEM97 overexpression can further increase the expression of ER target genes, and conversely, TMEM97 knockdown down-regulated the expression of ER target genes. Further, we found that TMEM97 could regulate the ERα activity through or partially through the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway. When subjected to the mTOR inhibitor, the enhanced ERα signaling activity by TMEM97 was abolished. Taken together, these data lead to a conclusion that TMEM97 can modulate ER activities through modulating mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway.
For patients with ERα positive breast cancer, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), such as tamoxifen, are the standard endocrine therapy, but resistance remains to be the major obstacle. About one-third of patients are resistant to tamoxifen at the beginning of treatment. Further, most patients who initially respond to tamoxifen will later develop resistance. In our study, we find overexpression of TMEM97 could lead to a sustained increase in the phosphorylation of ERα at Serine 167 and cells are more resistant to OH-Tamoxifen treatment. Co-treatment with rapamycin could re-sensitized the TMEM97 overexpression cells to OH-tamoxifen. When TMEM97 expression is knocked down, both ERα phosphorylation at Serine 167 and mTOR/S6K1 signaling activities are reduced. Tumor cells with TMEM97 knockdown were more sensitive to OH-tamoxifen than the vector control cells.
The mTOR itself as a core component of both complexes functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase regulates various cellular functions. The p70S6 kinase 1 is a downstream target of mTOR signaling, and phosphorylation of p70S6K1 at threonine 389 has been used as a hallmark of activation by mTOR [
38,
39], which then stimulates the initiation of protein synthesis through activation of S6 ribosomal protein [
40]. Studies have supported that hyperactivation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway contributes to endocrine resistance, which can be reversed by the mTORC1 inhibitor Everolimus
in vitro [
41,
42,
43]. And S6K1 could directly phosphorylate ERα specially at S167, leading to ligand-independent activation [
33,
34]. Subsequent studies showed that S6K1 and ERα constitute a positive feed-forward loop, the phosphorylated ERα by S6K1 which in turn promotes transcription of RPS6KB1 to further mediate breast cancer cell proliferation [
44]. In this study, increased S6K1 phosphorylation was consistently observed in TMEM97 overexpressing cells. However, in the mTOR signaling pathway upstream of S6K1, no significant differences in active Raf, Erk1/2, p38MAPK, or Akt were found between TMEM97 overexpressing cells and the pCDH vector controls, although estrogen can activate them. However, the increased pS6K1 in TMEM97 overexpressing cells is dependent on mTOR1 activities since rapamycin could abolish the observed increase in pS6K1.
The mTORC1 blockers (rapalogs) have been evaluated in clinical trials and been used as combination treatment with endocrine therapy for breast cancer and have achieved promising results [
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51]. In our study, we demonstrated that overexpression of TMEM97 in breast cancer cells contributed to tamoxifen treatment resistance, and the overexpressed cells continuously activated the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway and the ERα activity. The resistance and stimulation effects by TMEM97 could be blocked by the utilization of naturally derived mTOR inhibitor rapamycin, suggesting that TMEM97 may activate the ERα through or partly through mTOR signaling pathway independent of estrogen. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of more mTOR inhibitors especially mTORC1 inhibitors, like Everolimus, on TMEM97 overexpression cells both
in vitro and
in vivo.
5. Conclusions
In conclusions, TMEM97/σ2 receptor has been identified as a novel regulator of ERα in breast cancer cell growth and responses toward tamoxifen. As shown in the
Figure 7E, TMEM97 can regulate the activities of ERα through modulating ERα binding to estradiol and binding to responsive elements in the promoters of ER target genes. Another mechanism involved is the TMEM97 modulation of the cellular signaling, particularly, the mTOR/S6K1 signaling, in the activation of ERα. Further studies are needed to determine whether TMEM97 can be a valid target of intervention to modulate ER activities and to reduce resistance toward endocrine therapy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y. Zhang and D. Nie; methodology, experiments, and data acquisition, Y. Zhang, X. Fang, J. Wang; Data analysis and curation, Y. Zhang and D. Nie; writing—original draft preparation, Y. Zhang and X. Fang; writing—review and editing, D. Nie; funding acquisition, D. Nie. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
“Not applicable” for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
“Not applicable.” since the study did not involve humans.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request or deposited in public database once the manuscript is published.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Michael Crider in College of Pharmacy, Southern Illinois University Edwardsville in introducing the field of sigma receptors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The internal funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Watson CS, Jeng YJ, Kochukov MY. Nongenomic actions of estradiol compared with estrone and estriol in pituitary tumor cell signaling and proliferation. FASEB J. 2008;22(9):3328-36. Epub 2008/06/11. PubMed PMID: 18541692; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2518256. [CrossRef]
- Le Dily F, Beato M. Signaling by Steroid Hormones in the 3D Nuclear Space. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2). Epub 2018/01/23. PubMed PMID: 29360755; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5855546. [CrossRef]
- de Medina P, Payré BL, Bernad J, Bosser I, Pipy B, Silvente-Poirot S, et al. Tamoxifen is a potent inhibitor of cholesterol esterification and prevents the formation of foam cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;308(3):1165-73. Epub 2003/11/14. PubMed PMID: 14617686. [CrossRef]
- Klinge CM. Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(14):2905-19. PubMed PMID: 11452016; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC55815. [CrossRef]
- Shibata H, Spencer TE, Oñate SA, Jenster G, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, et al. Role of co-activators and co-repressors in the mechanism of steroid/thyroid receptor action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:141-64; discussion 64-5. PubMed PMID: 9238851.
- Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L, Kushner PJ, Agard DA, et al. The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 1998;95(7):927-37. PubMed PMID: 9875847. [CrossRef]
- Hu R, Hilakivi-Clarke L, Clarke R. Molecular mechanisms of tamoxifen-associated endometrial cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 2015;9(4):1495-501. Epub 2015/02/12. PubMed PMID: 25788989; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4356269. [CrossRef]
- Hellewell SB, Bowen WD. A sigma-like binding site in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: decreased affinity for (+)-benzomorphans and lower molecular weight suggest a different sigma receptor form from that of guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 1990;527(2):244-53. Epub 1990/09/17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellewell SB, Bruce A, Feinstein G, Orringer J, Williams W, Bowen WD. Rat liver and kidney contain high densities of sigma 1 and sigma 2 receptors: characterization by ligand binding and photoaffinity labeling. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;268(1):9-18. Epub 1994/06/15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon A, Schmidt HR, Wood MD, Sahn JJ, Martin SF, Kruse AC. Identification of the gene that codes for the sigma(2) receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(27):7160-5. Epub 20170530. PubMed PMID: 28559337; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5502638. [CrossRef]
- Wilcox CB, Feddes GO, Willett-Brozick JE, Hsu LC, DeLoia JA, Baysal BE. Coordinate up-regulation of TMEM97 and cholesterol biosynthesis genes in normal ovarian surface epithelial cells treated with progesterone: implications for pathogenesis of ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:223. Epub 2007/12/12. PubMed PMID: 18070364; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2241839. [CrossRef]
- Moparthi SB, Arbman G, Wallin A, Kayed H, Kleeff J, Zentgraf H, et al. Expression of MAC30 protein is related to survival and biological variables in primary and metastatic colorectal cancers. Int J Oncol. 2007;30(1):91-5. Epub 2006/12/05. [PubMed]
- Xiao M, Li H, Yang S, Huang Y, Jia S, Wang H, et al. Expression of MAC30 protein is related to survival and clinicopathological variables in breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2013;107(5):456-62. Epub 2012/09/22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang S, Li H, Liu Y, Ning X, Meng F, Xiao M, et al. Elevated expression of MAC30 predicts lymph node metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):324. Epub 2012/12/21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q, et al. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123(3):725-31. Epub 2009/12/19. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spandidos A, Wang X, Wang H, Seed B. PrimerBank: a resource of human and mouse PCR primer pairs for gene expression detection and quantification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Database issue):D792-9. Epub 2009/11/11. PubMed PMID: 19906719; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2808898. [CrossRef]
- Welshons WV, Wolf MF, Murphy CS, Jordan VC. Estrogenic activity of phenol red. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988;57(3):169-78. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu X, Chen B, Chen L, Ren WT, Liu J, Wang G, et al. U-shape suppressive effect of phenol red on the epileptiform burst activity via activation of estrogen receptors in primary hippocampal culture. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60189. Epub 2013/04/01. PubMed PMID: 23560076; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3613357. [CrossRef]
- de Faria AN, Zancanela DC, Ramos AP, Torqueti MR, Ciancaglini P. Estrogen and phenol red free medium for osteoblast culture: study of the mineralization ability. Cytotechnology. 2016;68(4):1623-32. Epub 2015/01/30. PubMed PMID: 25634598; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4960142. [CrossRef]
- Rosell M, Nevedomskaya E, Stelloo S, Nautiyal J, Poliandri A, Steel JH, et al. Complex formation and function of estrogen receptor α in transcription requires RIP140. Cancer Res. 2014;74(19):5469-79. Epub 2014/08/21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin CY, Ström A, Vega VB, Kong SL, Yeo AL, Thomsen JS, et al. Discovery of estrogen receptor alpha target genes and response elements in breast tumor cells. Genome Biol. 2004;5(9):R66. Epub 2004/08/12. PubMed PMID: 15345050; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC522873. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed H, D'Santos C, Serandour AA, Ali HR, Brown GD, Atkins A, et al. Endogenous purification reveals GREB1 as a key estrogen receptor regulatory factor. Cell Rep. 2013;3(2):342-9. Epub 2013/02/09. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold SF, Obourn JD, Jaffe H, Notides AC. Serine 167 is the major estradiol-induced phosphorylation site on the human estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8(9):1208-14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joel PB, Smith J, Sturgill TW, Fisher TL, Blenis J, Lannigan DA. pp90rsk1 regulates estrogen receptor-mediated transcription through phosphorylation of Ser-167. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(4):1978-84. PubMed PMID: 9528769; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC121427. [CrossRef]
- Zheng XQ, Guo JP, Yang H, Kanai M, He LL, Li YY, et al. Aurora-A is a determinant of tamoxifen sensitivity through phosphorylation of ERα in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(42):4985-96. Epub 2013/10/28. PubMed PMID: 24166501; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4002670. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Niu XL, Guo XQ, Yang J, Li L, Qu Y, et al. IL6 induces TAM resistance via kinase-specific phosphorylation of ERα in OVCA cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;54(3):351-61. Epub 2015/05/05. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Calderero I, Carnero A, Astudillo A, Palacios J, Chaves M, Benavent M, et al. Prognostic relevance of estrogen receptor-α Ser167 phosphorylation in stage II-III colon cancer patients. Hum Pathol. 2014;45(12):2437-46. Epub 2014/09/02. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato E, Orisaka M, Kurokawa T, Chino Y, Fujita Y, Shinagawa A, et al. Relation between outcomes and expression of estrogen receptor-α phosphorylated at Ser(167) in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(10):1307-12. Epub 2014/09/26. PubMed PMID: 25154549; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4462347. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, VC. Fourteenth Gaddum Memorial Lecture. A current view of tamoxifen for the treatment and prevention of breast cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 1993;110(2):507-17. PubMed PMID: 8242225; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2175926. [CrossRef]
- Riggins RB, Schrecengost RS, Guerrero MS, Bouton AH. Pathways to tamoxifen resistance. Cancer Lett. 2007;256(1):1-24. Epub 2007/05/01. PubMed PMID: 17475399; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2533271. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita H, Nishio M, Kobayashi S, Ando Y, Sugiura H, Zhang Z, et al. Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha serine 167 is predictive of response to endocrine therapy and increases postrelapse survival in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(5):R753-64. Epub 2005/07/27. PubMed PMID: 16168121; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1242143. [CrossRef]
- Martin MB, Franke TF, Stoica GE, Chambon P, Katzenellenbogen BS, Stoica BA, et al. A role for Akt in mediating the estrogenic functions of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 2000;141(12):4503-11. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamnik RL, Digilova A, Davis DC, Brodt ZN, Murphy CJ, Holz MK. S6 kinase 1 regulates estrogen receptor alpha in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(10):6361-9. Epub 2008/12/27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamnik RL, Holz MK. mTOR/S6K1 and MAPK/RSK signaling pathways coordinately regulate estrogen receptor alpha serine 167 phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(1):124-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenö P, Ballou LM, Novak-Hofer I, Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(2):406-10. PubMed PMID: 3257566; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC279557. [CrossRef]
- Yoo YJ, Kim H, Park SR, Yoon YJ. An overview of rapamycin: from discovery to future perspectives. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;44(4-5):537-53. Epub 2016/09/09. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson B, Ekim B, Fingar DC. Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J. 2012;441(1):1-21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh M, Pullen N, Brennan P, Cantrell D, Dennis PB, Thomas G. Regulation of an activated S6 kinase 1 variant reveals a novel mammalian target of rapamycin phosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(22):20104-12. Epub 2002/03/25. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen N, Thomas G. The modular phosphorylation and activation of p70s6k. FEBS Lett. 1997;410(1):78-82. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson RT, Schreiber SL. Translation control: connecting mitogens and the ribosome. Curr Biol. 1998;8(7):R248-50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghayad SE, Bieche I, Vendrell JA, Keime C, Lidereau R, Dumontet C, et al. mTOR inhibition reverses acquired endocrine therapy resistance of breast cancer cells at the cell proliferation and gene-expression levels. Cancer Sci. 2008;99(10):1992-2003. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeram M, Tan QT, Tekmal RR, Russell D, Middleton A, DeGraffenried LA. Akt-induced endocrine therapy resistance is reversed by inhibition of mTOR signaling. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(8):1323-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulay A, Rudloff J, Ye J, Zumstein-Mecker S, O'Reilly T, Evans DB, et al. Dual inhibition of mTOR and estrogen receptor signaling in vitro induces cell death in models of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(14):5319-28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruani DM, Spiegel TN, Harris EN, Shachter AS, Unger HA, Herrero-González S, et al. Estrogenic regulation of S6K1 expression creates a positive regulatory loop in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncogene. 2012;31(49):5073-80. Epub 2012/01/30. PubMed PMID: 22286763; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3342462. [CrossRef]
- Chan S, Scheulen ME, Johnston S, Mross K, Cardoso F, Dittrich C, et al. Phase II study of temsirolimus (CCI-779), a novel inhibitor of mTOR, in heavily pretreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(23):5314-22. Epub 2005/06/13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancey JE, Curiel R, Purvis J. Evaluating temsirolimus activity in multiple tumors: a review of clinical trials. Semin Oncol. 2009;36 Suppl 3:S46-58. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner JC, Forouzesh B, Erlichman C, Hidalgo M, Boni JP, Dukart G, et al. Phase I, pharmacokinetic study of temsirolimus administered orally to patients with advanced cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2010;28(3):334-42. Epub 2009/05/05. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, F. Clinical implications of recent studies using mTOR inhibitors to treat advanced hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2014;6:389-95. Epub 2014/10/06. PubMed PMID: 25336989; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4199833. [CrossRef]
- Fleming GF, Ma CX, Huo D, Sattar H, Tretiakova M, Lin L, et al. Phase II trial of temsirolimus in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136(2):355-63. Epub 2012/01/13. PubMed PMID: 22245973; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3658119. [CrossRef]
- Royce ME, Osman D. Everolimus in the Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015;9:73-9. Epub 2015/09/06. PubMed PMID: 26417203; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4571987. [CrossRef]
- Lumachi F, Santeufemia DA, Basso SM. Current medical treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2015;6(3):231-9. PubMed PMID: 26322178; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4549764. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
TMEM97/ σ2 receptor protein expression in breast cancer tumor tissues and its association with ER, PR, and patient survival. (A, B): IHC staining of TMEM97 in breast cancer tissue microarrays. Representative microscope images displayed as the ER status (A) or PR status (B) from strongest expression (+++) to negative. Bottom panel image at 10x with the medium panel image at 20x and the top panel image at 40x. (C, D, E): Double blinded estimated H-score base on different ER (C), PR (D) and HER2 status. Data are presented as graph mean ± SEM. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Statistical significance is calculated by unpaired Student’s t test. (F, G): The relapse free survival (RFS) of breast cancer patients, based on the RNA level of TMEM97 detected by four probe sets in microarray. The red line represents high expression of TMEM97, while the black line represents low expression. (F) The RFS in all types of breast cancer patients, and 3 out of 4 probes associate significantly with the poor survival. (G) The RFS in ER positive breast cancer patients, all 4 probes are significantly associated with the poor survival.
Figure 1.
TMEM97/ σ2 receptor protein expression in breast cancer tumor tissues and its association with ER, PR, and patient survival. (A, B): IHC staining of TMEM97 in breast cancer tissue microarrays. Representative microscope images displayed as the ER status (A) or PR status (B) from strongest expression (+++) to negative. Bottom panel image at 10x with the medium panel image at 20x and the top panel image at 40x. (C, D, E): Double blinded estimated H-score base on different ER (C), PR (D) and HER2 status. Data are presented as graph mean ± SEM. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Statistical significance is calculated by unpaired Student’s t test. (F, G): The relapse free survival (RFS) of breast cancer patients, based on the RNA level of TMEM97 detected by four probe sets in microarray. The red line represents high expression of TMEM97, while the black line represents low expression. (F) The RFS in all types of breast cancer patients, and 3 out of 4 probes associate significantly with the poor survival. (G) The RFS in ER positive breast cancer patients, all 4 probes are significantly associated with the poor survival.
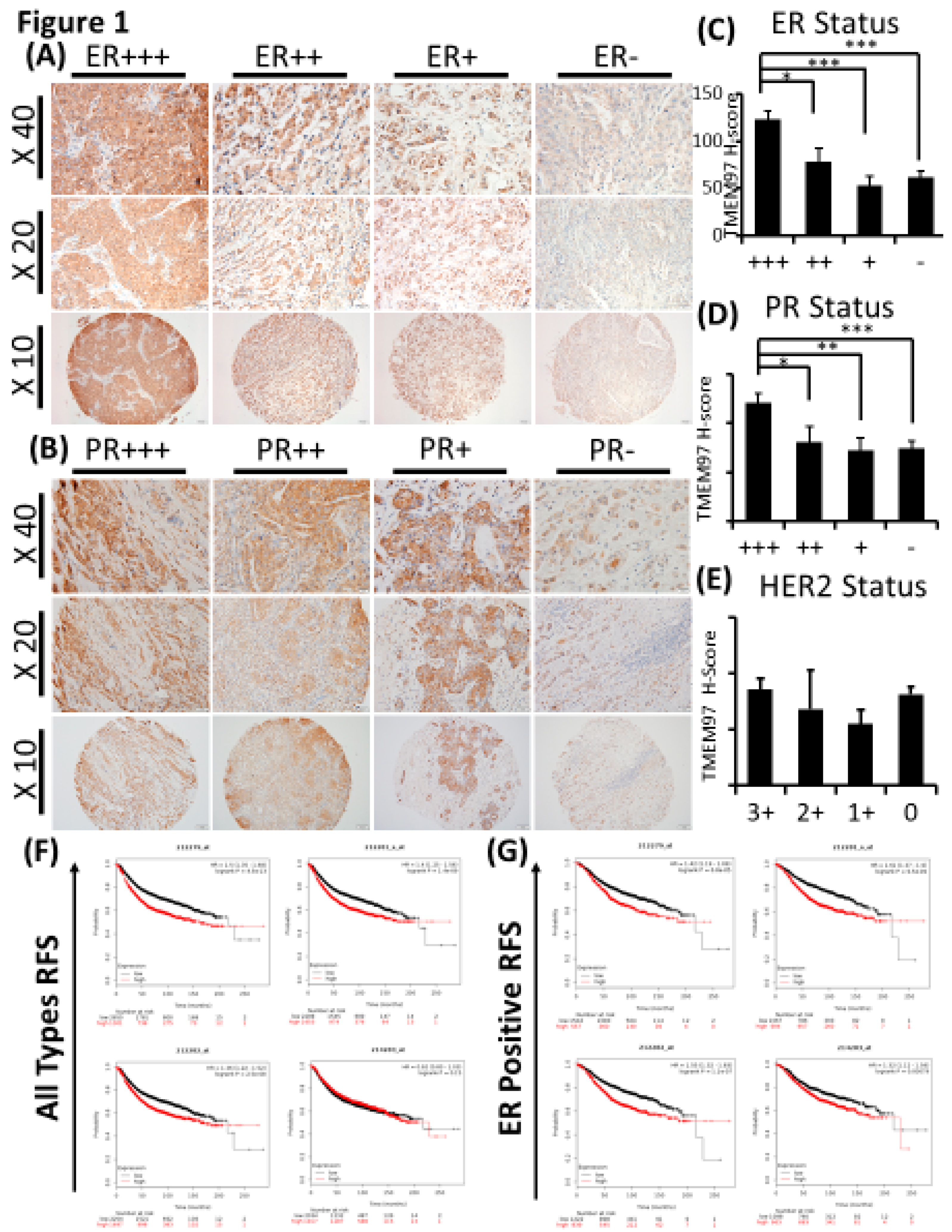
Figure 2.
Effects of increased expression of TMEM97 on breast cancer cell growth under different conditions. (A): Increased expression of TMEM97 at protein levels in breast cancer cells confirmed by Western blot. (B): Increased TMEM97 expression at RNA level confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. (C, D, E, F): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell growth under serum depleted culture condition (C), 2% FBS (D), 5% FBS (E), or 10% FBS (F). Left, MCF7 control compared with overexpression cells. Right, T47D control compared with overexpression cells. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and normalized with their respective numbers at Day 0. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 2.
Effects of increased expression of TMEM97 on breast cancer cell growth under different conditions. (A): Increased expression of TMEM97 at protein levels in breast cancer cells confirmed by Western blot. (B): Increased TMEM97 expression at RNA level confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. (C, D, E, F): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell growth under serum depleted culture condition (C), 2% FBS (D), 5% FBS (E), or 10% FBS (F). Left, MCF7 control compared with overexpression cells. Right, T47D control compared with overexpression cells. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and normalized with their respective numbers at Day 0. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 3.
Stimulation of ER positive breast cancer cell growth and colony formation by TMEM97 under different culture conditions. (A, B): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell growth cultured in phenol red free and 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS for 4 days (A), or in phenol red free and 5% charcoal stripped FBS (B). Left, MCF7 control compared with overexpression cells. Right, T47D control compared with overexpression cells. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and relative Day 0 respectively. (C, D): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell colony formation when cultured in DMEM with 5% FBS after 13 days (C) or in phenol red free DMEM with 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS after 13 days (D, left) and 19 days (D, right). The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 3.
Stimulation of ER positive breast cancer cell growth and colony formation by TMEM97 under different culture conditions. (A, B): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell growth cultured in phenol red free and 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS for 4 days (A), or in phenol red free and 5% charcoal stripped FBS (B). Left, MCF7 control compared with overexpression cells. Right, T47D control compared with overexpression cells. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and relative Day 0 respectively. (C, D): Effects of increased TMEM97 expression on breast cancer cell colony formation when cultured in DMEM with 5% FBS after 13 days (C) or in phenol red free DMEM with 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS after 13 days (D, left) and 19 days (D, right). The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 4.
Inhibition of ER positive breast cancer cell growth by TMEM97 knockdown.(A, B). Knockdown of TMEM expression by three different shRNAs, as evaluated by immunoblot (A), and RT-qPCR with three sets of primers (B). (C, D, E, F, G, H). Effects of TMEM97 knockdown on cell growth under different cell culture conditions, serum free media (C), media with 2% FBS (D), media with 5% FBS (E), media with 10% FBS (F), phenol red free media with 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS (G), or phenol red free media with 5% charcoal stripped FBS (H). The amounts of viable cells at different time points were measured by MTS assays and normalized with the readings at Day 0. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 4.
Inhibition of ER positive breast cancer cell growth by TMEM97 knockdown.(A, B). Knockdown of TMEM expression by three different shRNAs, as evaluated by immunoblot (A), and RT-qPCR with three sets of primers (B). (C, D, E, F, G, H). Effects of TMEM97 knockdown on cell growth under different cell culture conditions, serum free media (C), media with 2% FBS (D), media with 5% FBS (E), media with 10% FBS (F), phenol red free media with 0.5% charcoal stripped FBS (G), or phenol red free media with 5% charcoal stripped FBS (H). The amounts of viable cells at different time points were measured by MTS assays and normalized with the readings at Day 0. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 5.
Stimulation of ERα transcriptional activity by TMEM97. (A, B, C, D). Detection of NRIP1 (A), ABCA3 (B), GREB1 (C), ALOX12B (D) mRNA transcripts by RT- qPCR from MCF7 control and TMEM97 overexpression cells grown in phenol red free/ 0.5% charcoal-stripped FBS medium prior to 5 hours 10µM E2 treatment. (E). 293T cells were transit transfected with ERE reporter construct along with ERα, with or without TMEM97eGFP expression vector under full serum culture condition for 24hrs. After serum and estrogen depleted for another 24hrs, cells were subjected to 10µM E2 treatment for 5hrs and harvested for dual luciferase assay. Results show relative luciferase activities. (F). Dual luciferase assay for MCF7-TMEM97 overexpression and control cells. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 5.
Stimulation of ERα transcriptional activity by TMEM97. (A, B, C, D). Detection of NRIP1 (A), ABCA3 (B), GREB1 (C), ALOX12B (D) mRNA transcripts by RT- qPCR from MCF7 control and TMEM97 overexpression cells grown in phenol red free/ 0.5% charcoal-stripped FBS medium prior to 5 hours 10µM E2 treatment. (E). 293T cells were transit transfected with ERE reporter construct along with ERα, with or without TMEM97eGFP expression vector under full serum culture condition for 24hrs. After serum and estrogen depleted for another 24hrs, cells were subjected to 10µM E2 treatment for 5hrs and harvested for dual luciferase assay. Results show relative luciferase activities. (F). Dual luciferase assay for MCF7-TMEM97 overexpression and control cells. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 6.
TMEM97 stimulation of ERα activation and tamoxifen resistance can be blocked by mTOR signaling inhibitor. A. Immunoblot detection of p-ERα S167 in MCF7-PCDH/TMEM97 cells with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours. Cells were first cultured in phenol red free medium supplied with 0.5% CS-FBS for 24 hours and then proceeded to treatment. B. Responsiveness to tamoxifen treatment of PCDH and TMEM97. Cells were serum and estrogen deprived for 24 hours prior to 4 days of culture in E2 10µM and increasing concentrations of OH-Tam as indicated. C. Immunoblot for phosphorylation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway (left) and phosphorylation of other different signaling pathways in MCF7-PCDH and MCF7-TMEM97 cells. D. Effects of mTOR inhibitor rapamycin on PCDH and TMEM97 cell. Cells were cultured in phenol red free medium supplied with 0.5% CS-FBS for 24 hours then treated with rapamycin for 5 hours with indicated concentrations and examined the immunoblotted for p-ERα (S167) and p-S6K1 (T389). The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
Figure 6.
TMEM97 stimulation of ERα activation and tamoxifen resistance can be blocked by mTOR signaling inhibitor. A. Immunoblot detection of p-ERα S167 in MCF7-PCDH/TMEM97 cells with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours. Cells were first cultured in phenol red free medium supplied with 0.5% CS-FBS for 24 hours and then proceeded to treatment. B. Responsiveness to tamoxifen treatment of PCDH and TMEM97. Cells were serum and estrogen deprived for 24 hours prior to 4 days of culture in E2 10µM and increasing concentrations of OH-Tam as indicated. C. Immunoblot for phosphorylation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway (left) and phosphorylation of other different signaling pathways in MCF7-PCDH and MCF7-TMEM97 cells. D. Effects of mTOR inhibitor rapamycin on PCDH and TMEM97 cell. Cells were cultured in phenol red free medium supplied with 0.5% CS-FBS for 24 hours then treated with rapamycin for 5 hours with indicated concentrations and examined the immunoblotted for p-ERα (S167) and p-S6K1 (T389). The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test.
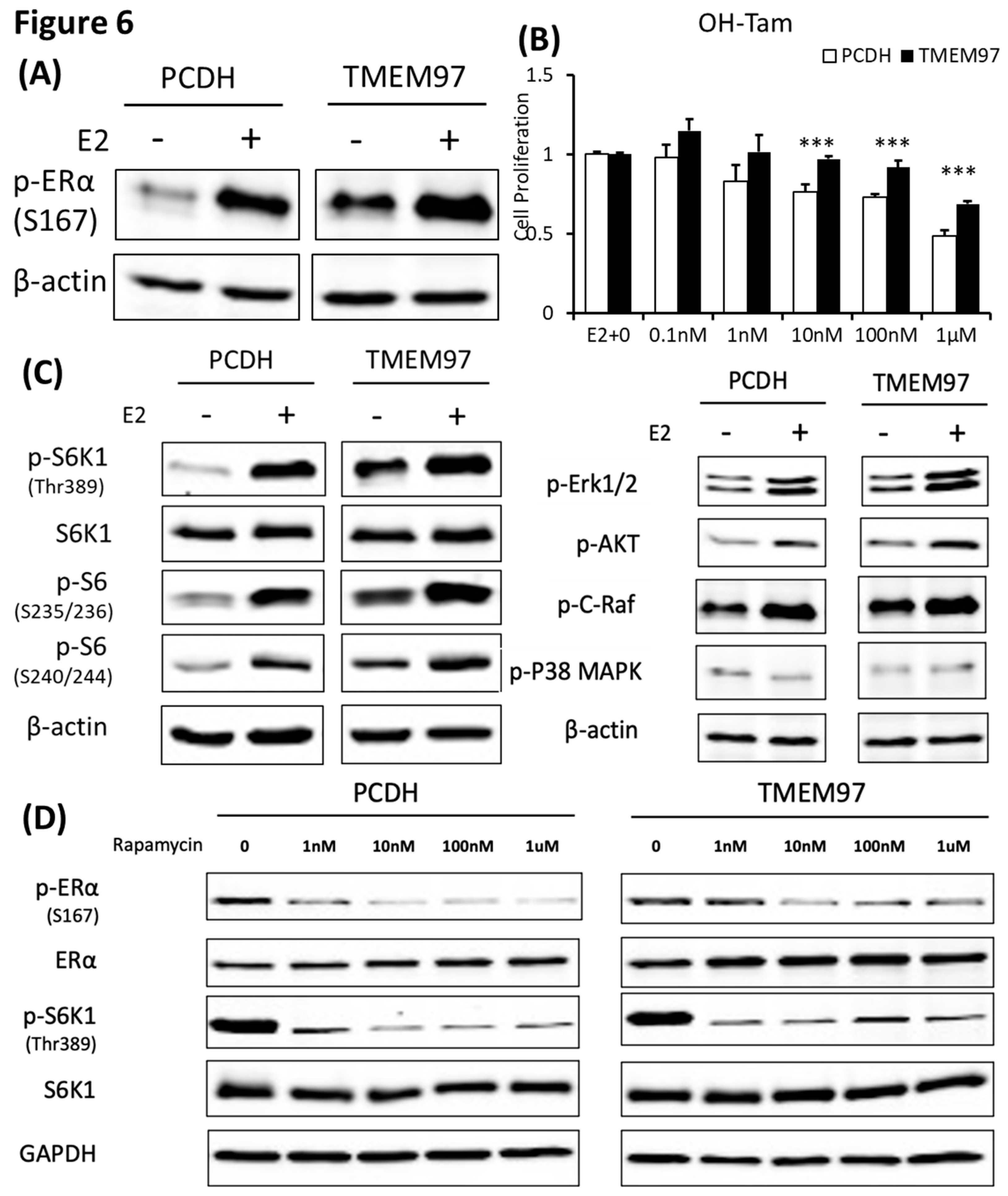
Figure 7.
TMEM97 knockdown reduces both ERα and mTOR/S6K1 signaling activity and increases the tamoxifen sensitivity: Two mechanisms for TMEM97 to regulate ERα activities. A. Dual luciferase assay for MCF7-GIPZ, 131, 836 and 602 cells. Cells were transiently transfected with ERE reporter construct under full serum culture condition for 24hrs. After serum and estrogen depleted for another 24hrs, cells were subjected to 10µM E2 treatment for 5hrs and harvested for dual luciferase assay. Results show relative luciferase activities. B. Immunoblot detection of p-ERα S167 with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours under serum and estrogen depleted condition. C. Immunoblot for phosphorylation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours under serum and estrogen depleted condition. D. Responsiveness to tamoxifen treatment of MCF7-TMEM97 knockdown cells. Cells were serum and estrogen deprived for 24 hours prior to 4 days of culture in E2 10µM and increasing concentrations of OH-Tam as indicated. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and relative to E2 stimulation alone respectively. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test. E. Regulation of ERα by TMEM97. TMEM97 can regulate the activities of ERα through modulating ERα binding to estradiol and binding to responsive elements in the promoters of ER target genes. Another mechanism involved is the TMEM97 modulation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling in the activation of ERα.
Figure 7.
TMEM97 knockdown reduces both ERα and mTOR/S6K1 signaling activity and increases the tamoxifen sensitivity: Two mechanisms for TMEM97 to regulate ERα activities. A. Dual luciferase assay for MCF7-GIPZ, 131, 836 and 602 cells. Cells were transiently transfected with ERE reporter construct under full serum culture condition for 24hrs. After serum and estrogen depleted for another 24hrs, cells were subjected to 10µM E2 treatment for 5hrs and harvested for dual luciferase assay. Results show relative luciferase activities. B. Immunoblot detection of p-ERα S167 with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours under serum and estrogen depleted condition. C. Immunoblot for phosphorylation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway with or without 10µM E2 treatment for 5 hours under serum and estrogen depleted condition. D. Responsiveness to tamoxifen treatment of MCF7-TMEM97 knockdown cells. Cells were serum and estrogen deprived for 24 hours prior to 4 days of culture in E2 10µM and increasing concentrations of OH-Tam as indicated. The proliferative capacity was measured by MTS assay and relative to E2 stimulation alone respectively. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of each experiment performed in quadruplicate. *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001 by two tailed paired Student’s T test. E. Regulation of ERα by TMEM97. TMEM97 can regulate the activities of ERα through modulating ERα binding to estradiol and binding to responsive elements in the promoters of ER target genes. Another mechanism involved is the TMEM97 modulation of mTOR/S6K1 signaling in the activation of ERα.
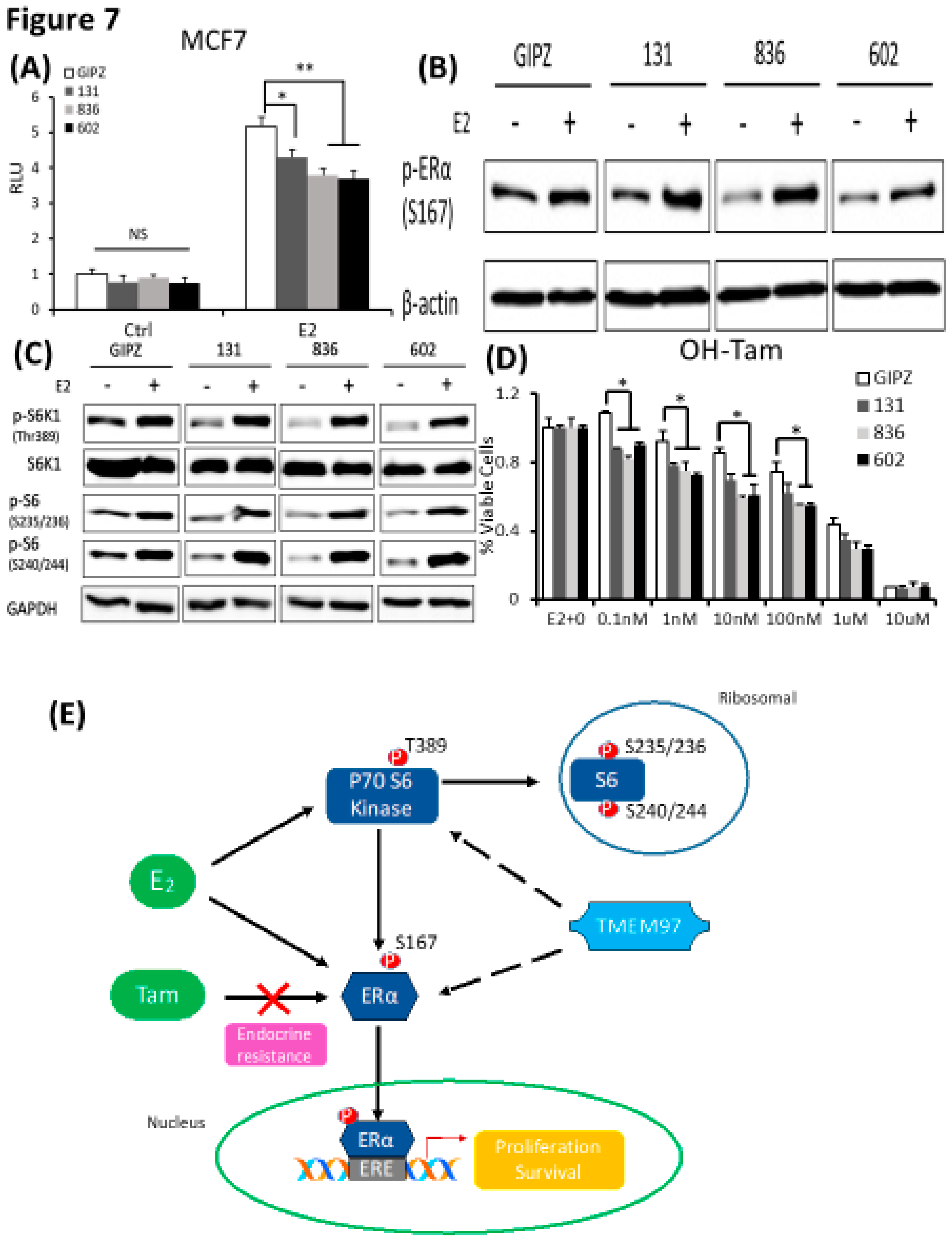
Table 1.
Primers used for gene expression in this study.
Table 1.
Primers used for gene expression in this study.
Table 2.
H-score and P value calculated for ER, PR and HER2 status.
Table 2.
H-score and P value calculated for ER, PR and HER2 status.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).