Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
14 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Kinematics and Dynamic Model of Mobile Robots Non-Holonomic
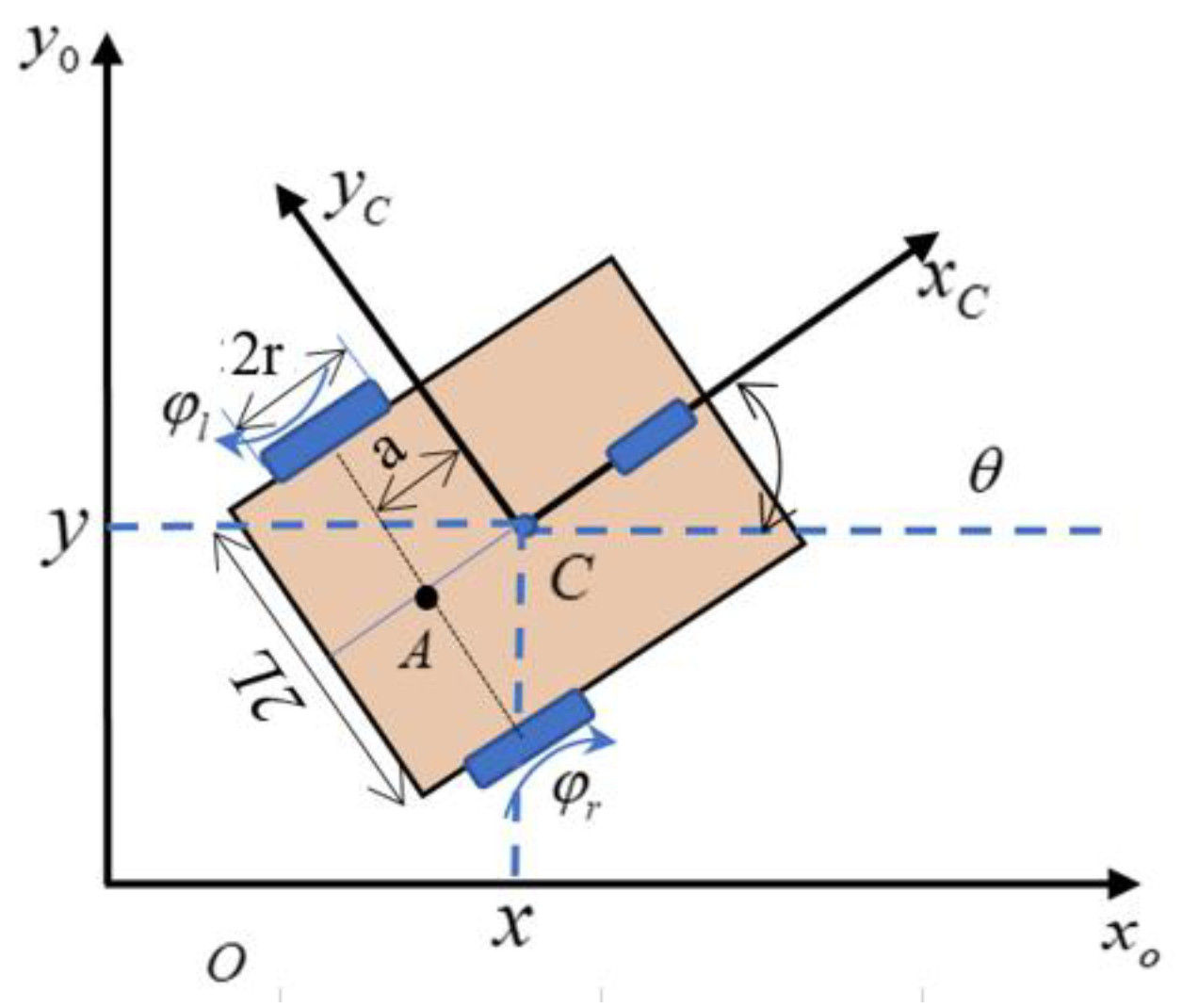
2.1. The Kinematics of the Non-Holonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot (WMR)
2.2. Dynamics of Non–Holonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot (WMR)
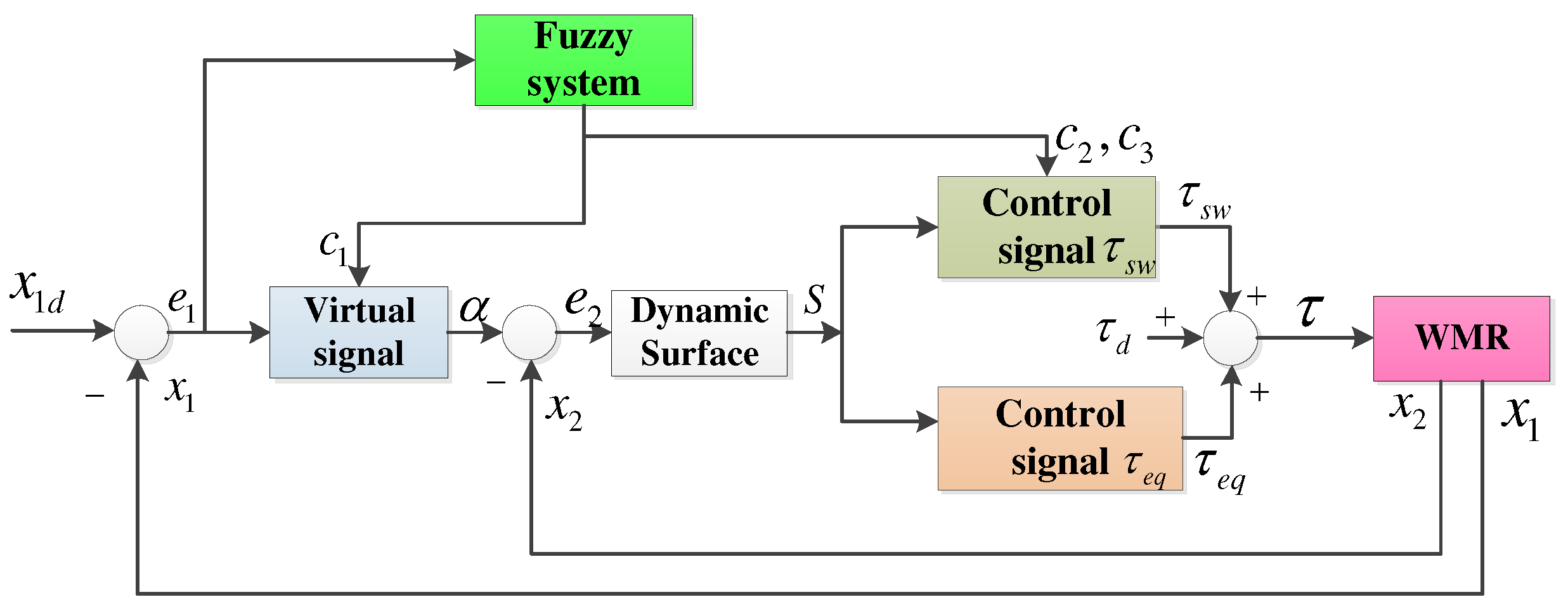
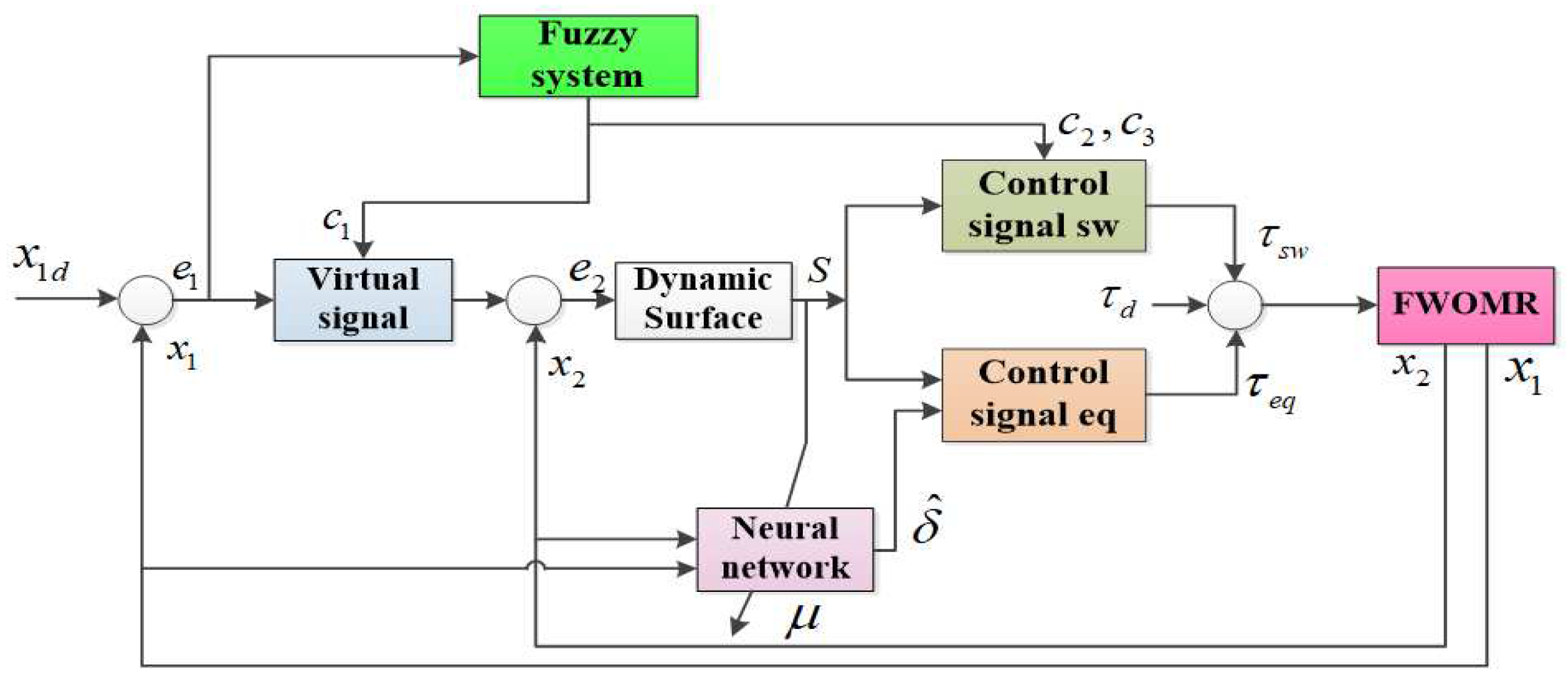
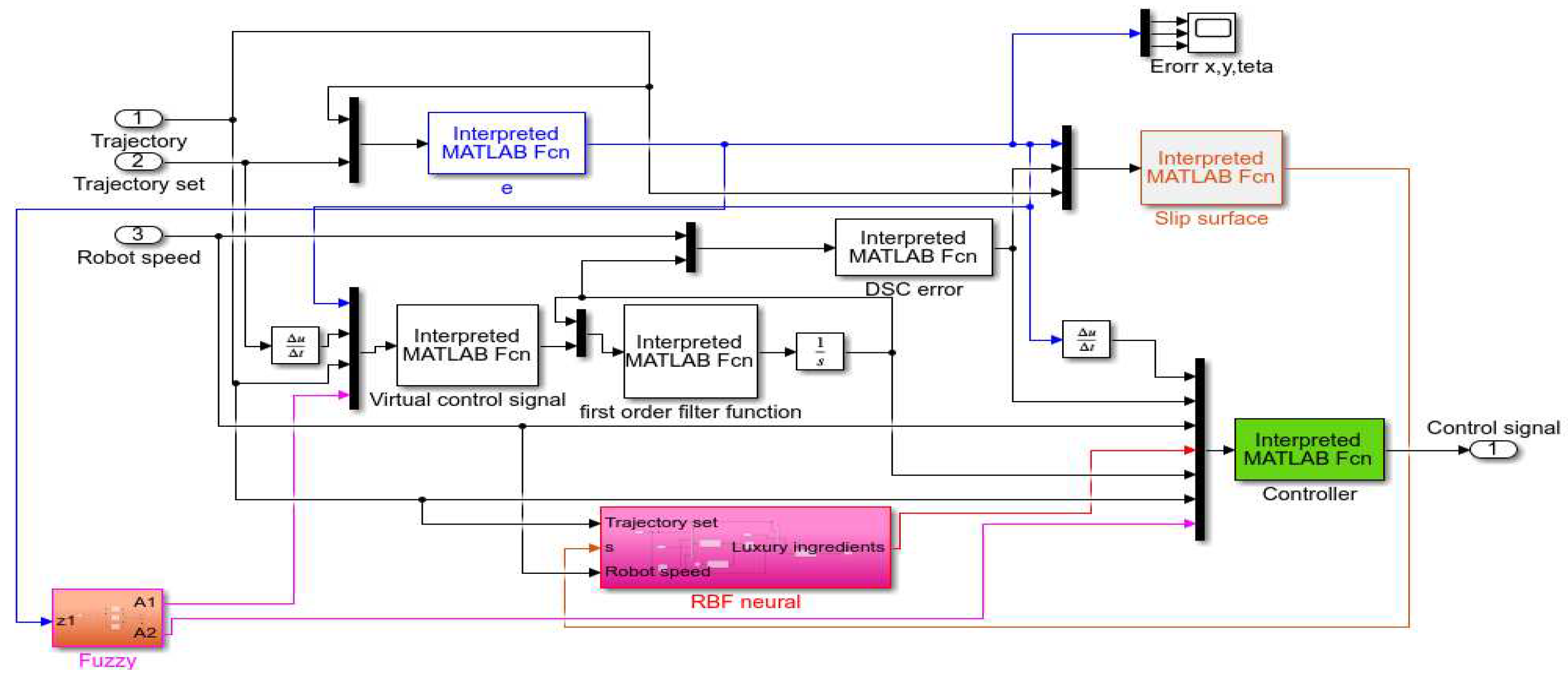
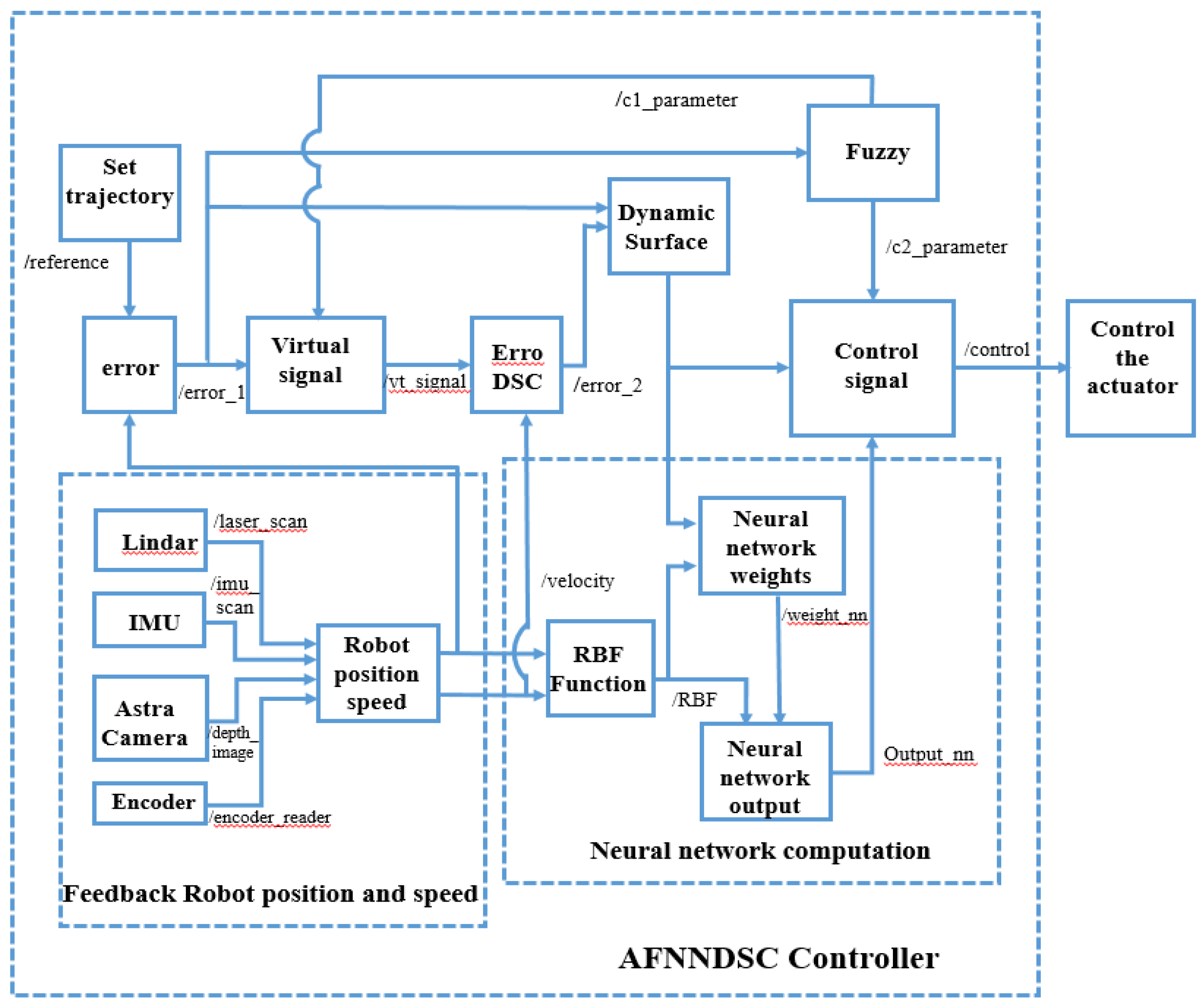
3. Design the Adaptive Fuzzy Neural Network Dynamic Surface Controller (AFNNDSC)
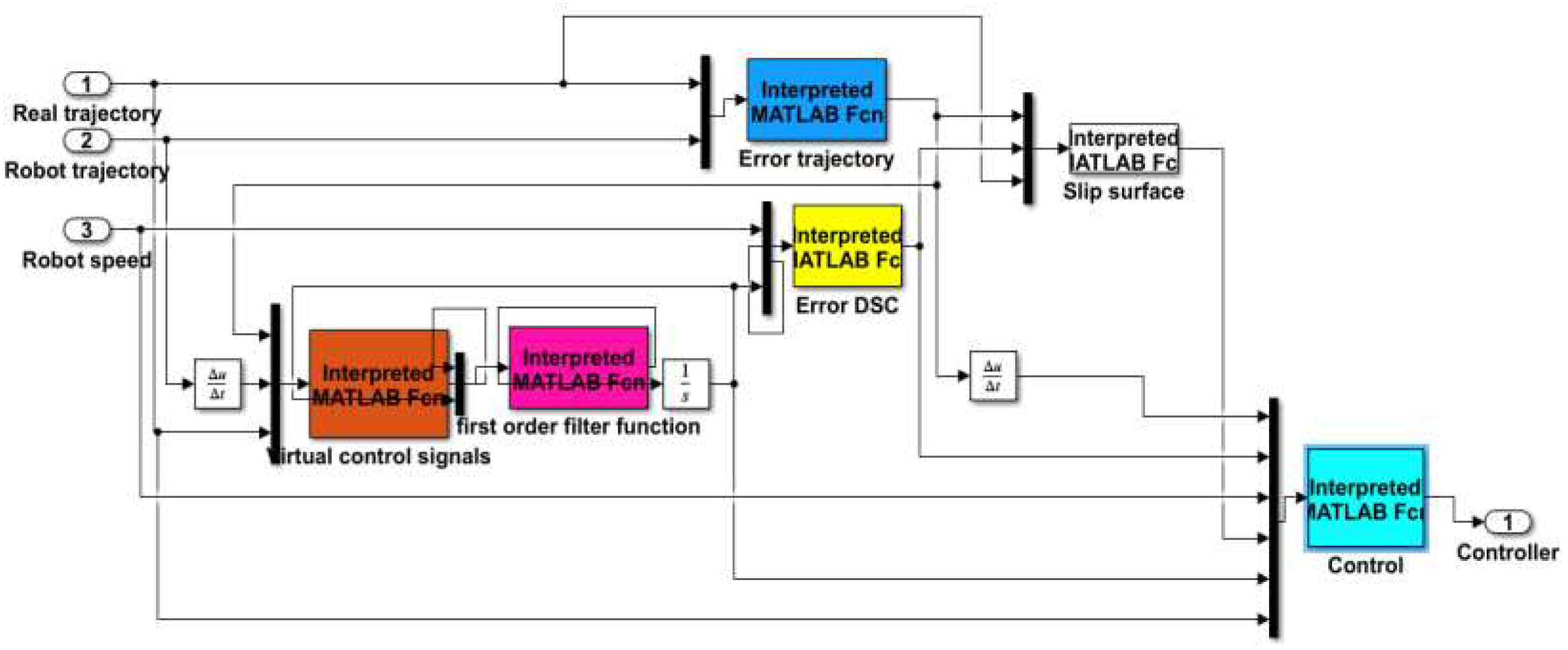
3.1. Dynamic Sliding Control Algorithm
3.1.1. WMR Building a Dynamic Sliding Surface Trajectory Control Algorithm for WMR
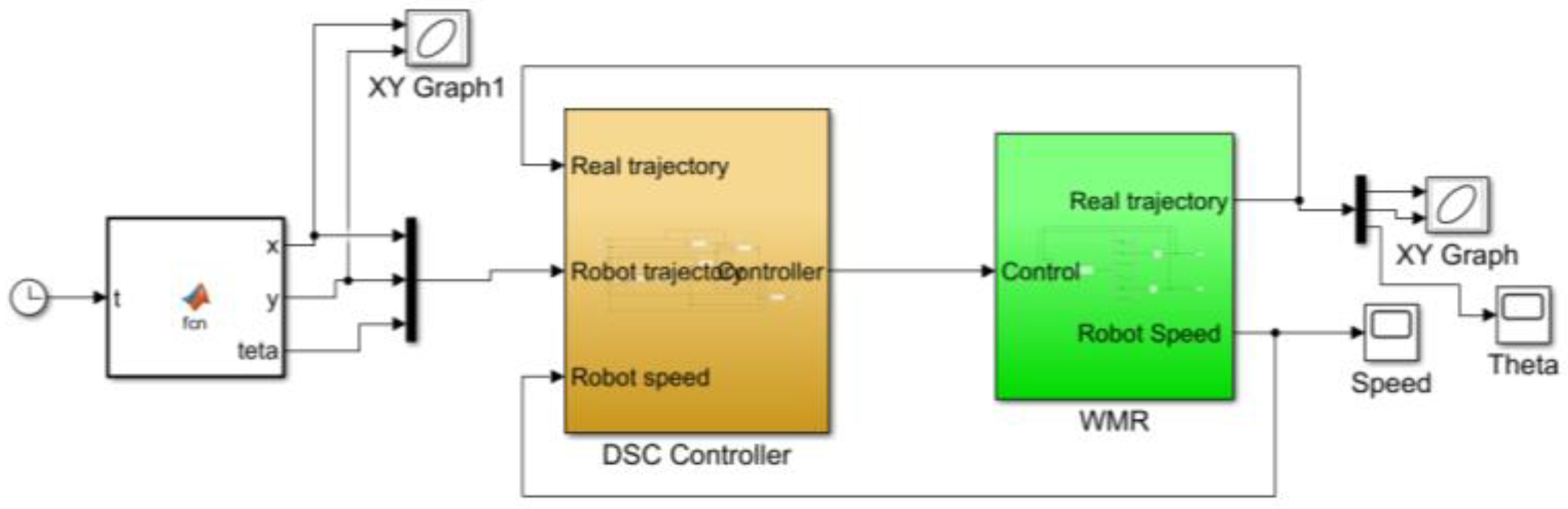
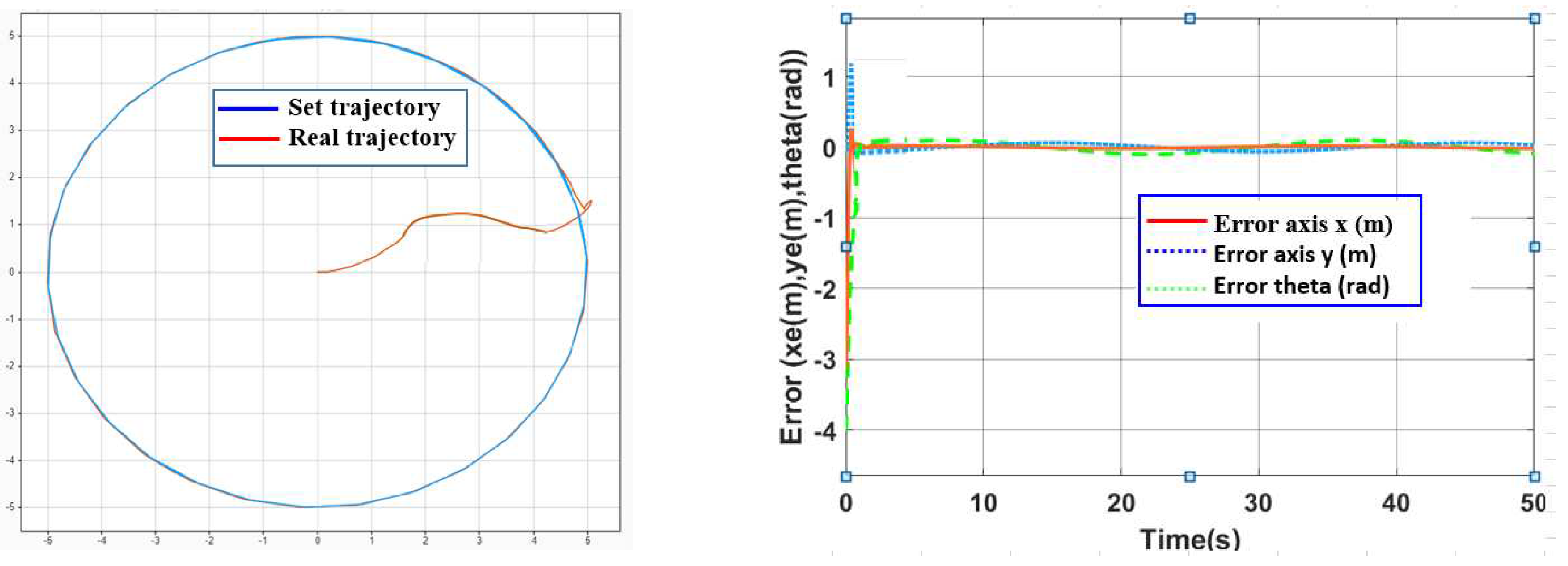
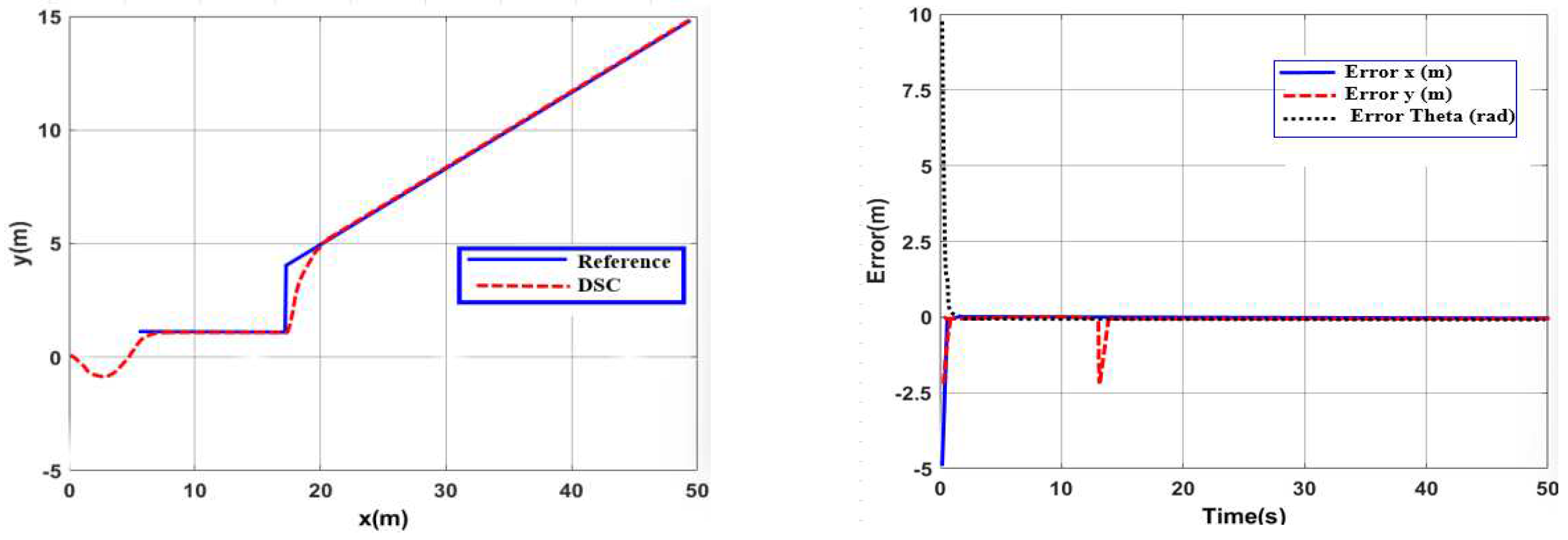
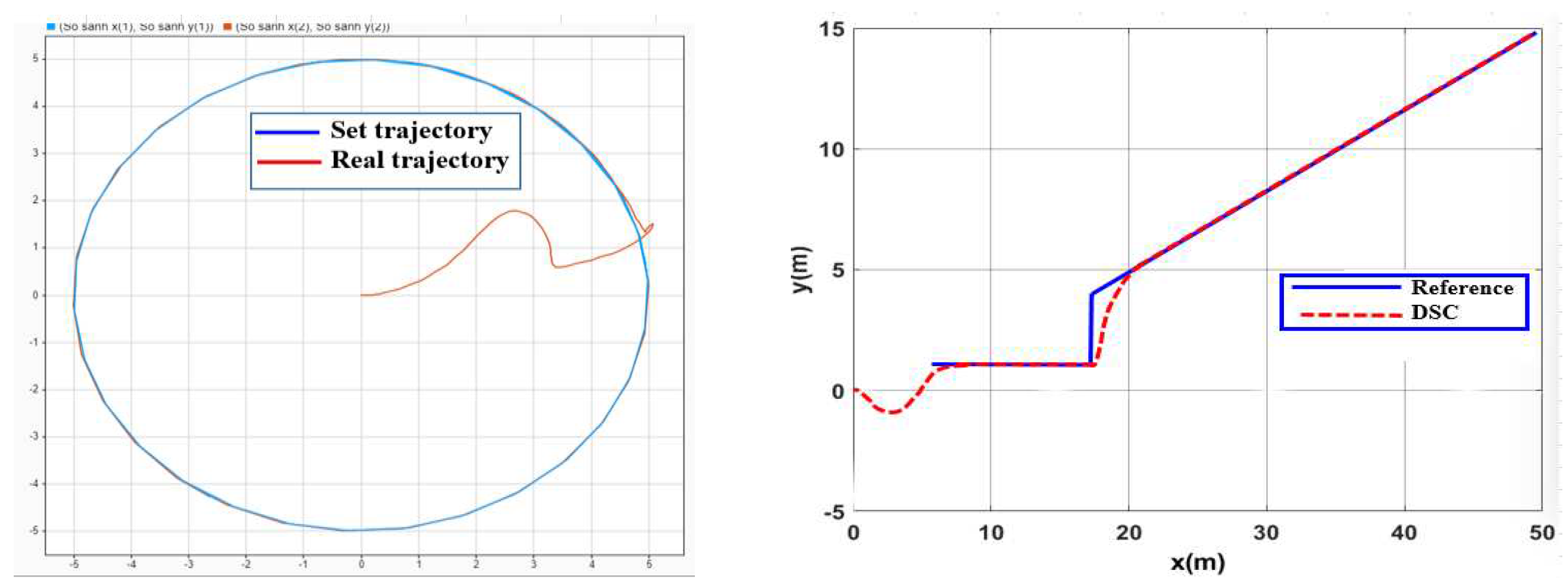
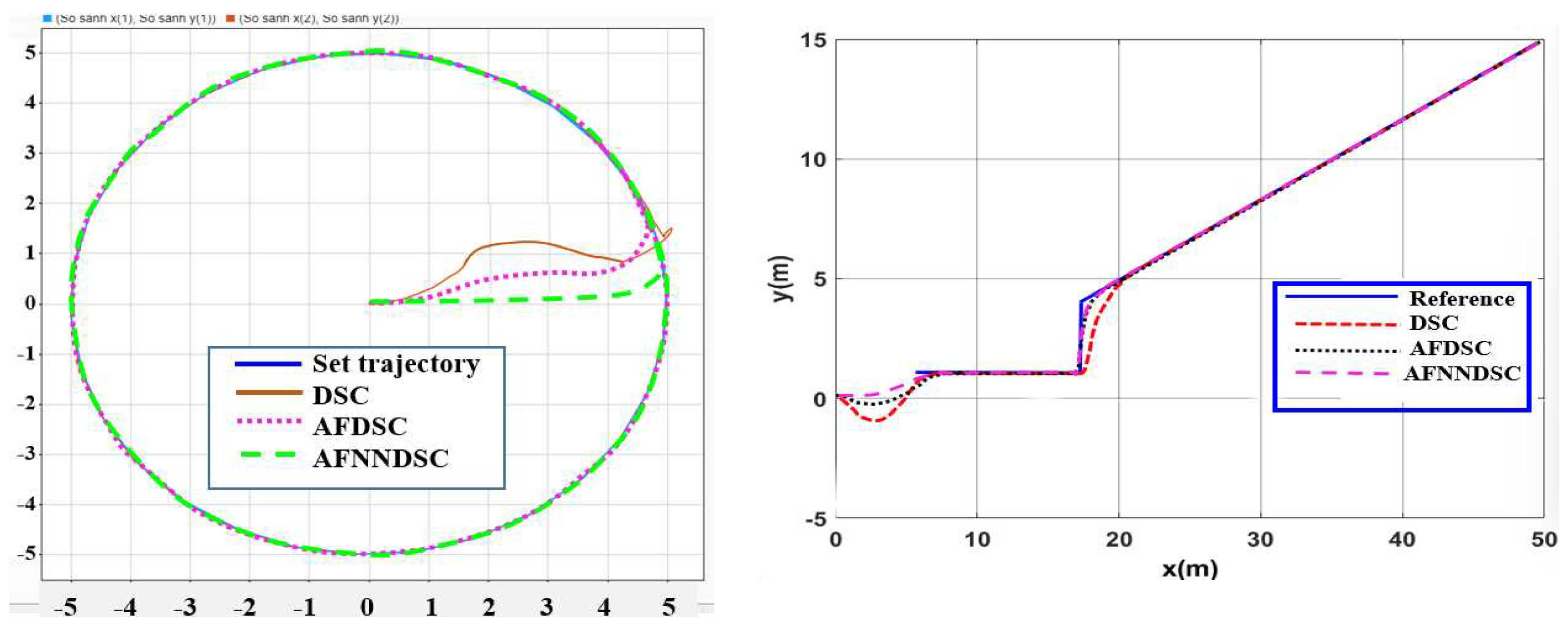
3.1.2. Simulation to Verify the Algorithm
- a. In case there is no interference
- b. In case of interference
3.2. Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Dynamic Surface Controller for (AFDSC)
3.2.1. The Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Dynamic Surface Controller
- Variable language of
- : NB, NS, Z, PS, PB
- Variable language of
- : NB, NS, Z, PS, PB
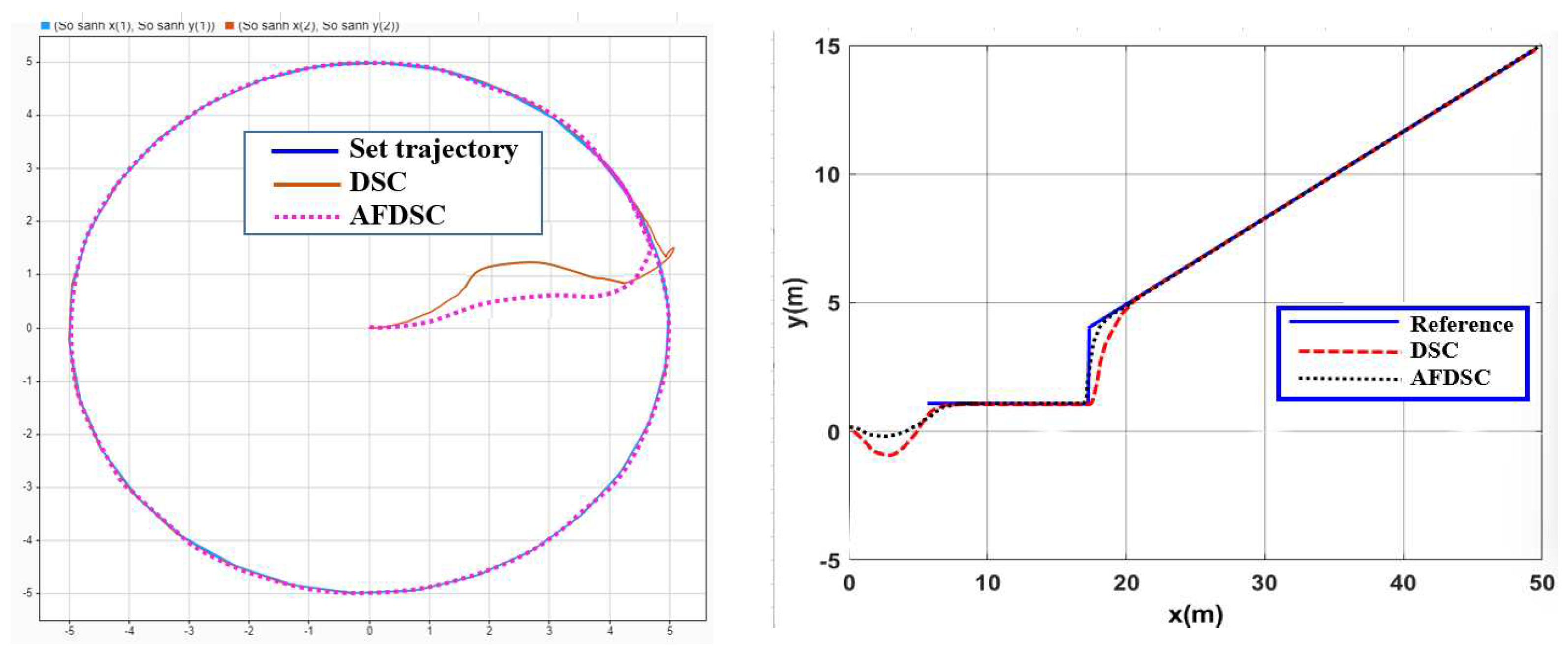
3.2.2. Simulation to Verify the Controller AFDSC
3.3. Adaptive Fuzzy Neural Network Dynamic Surface Controller for (AFNNDSC)
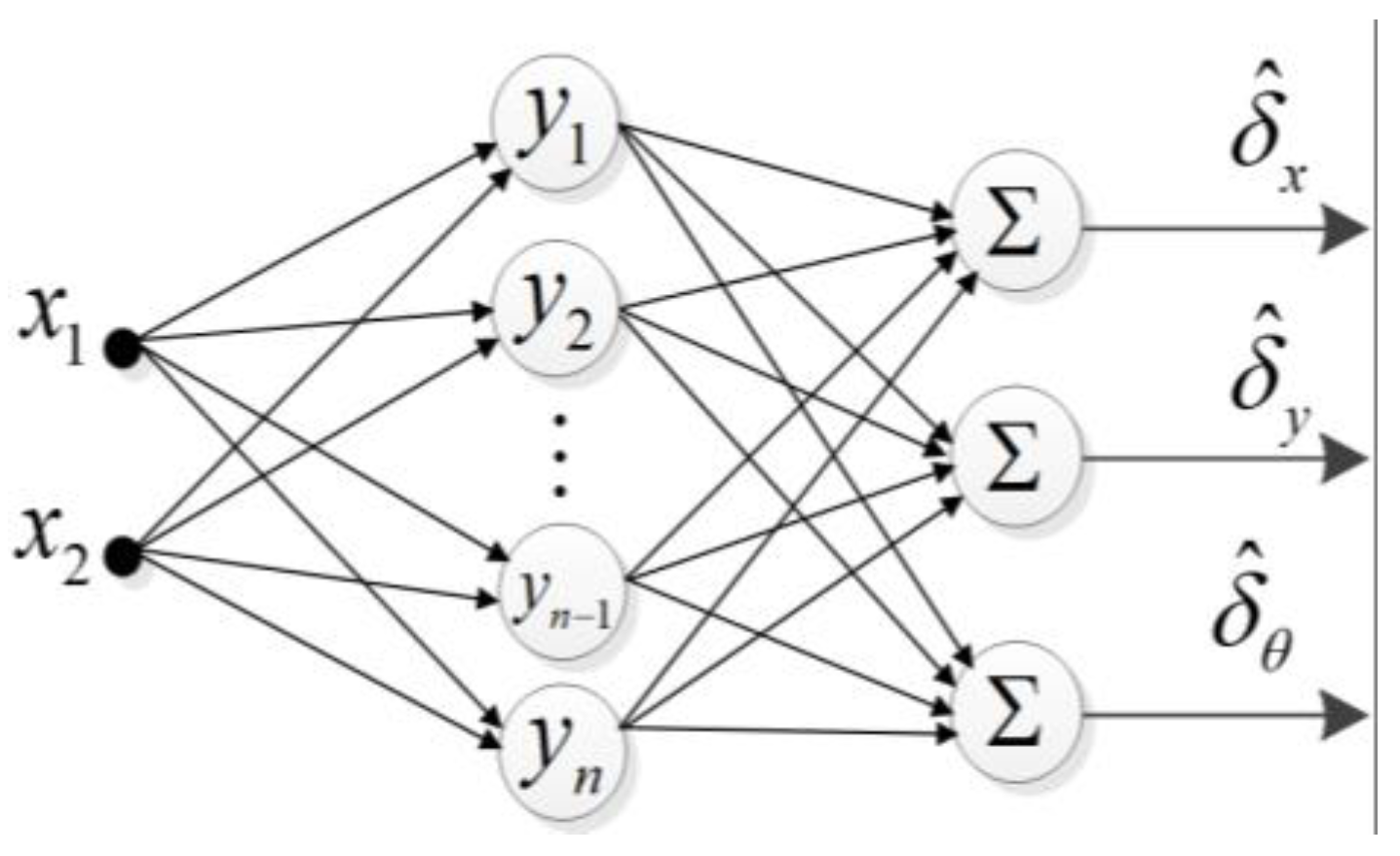
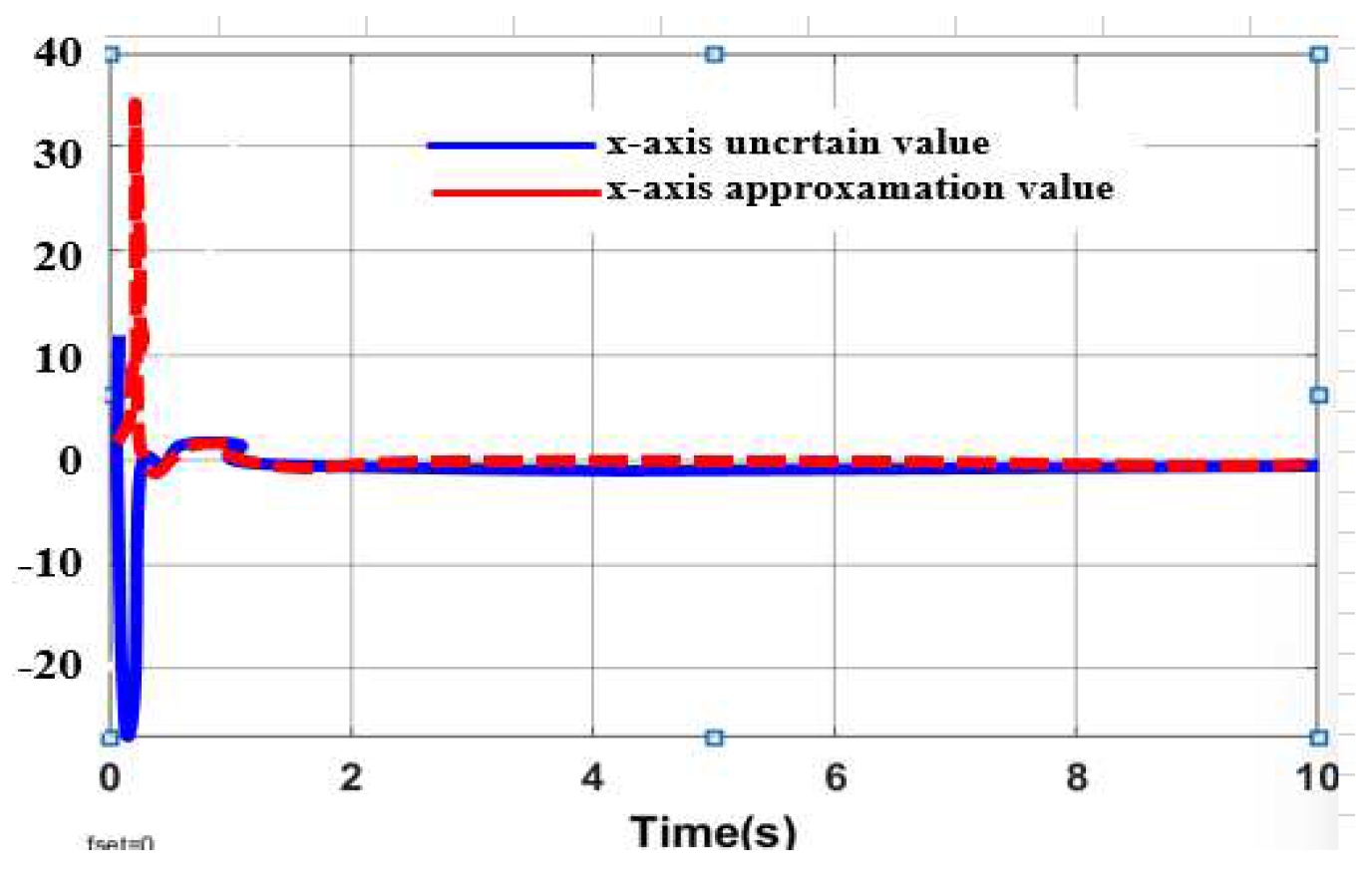
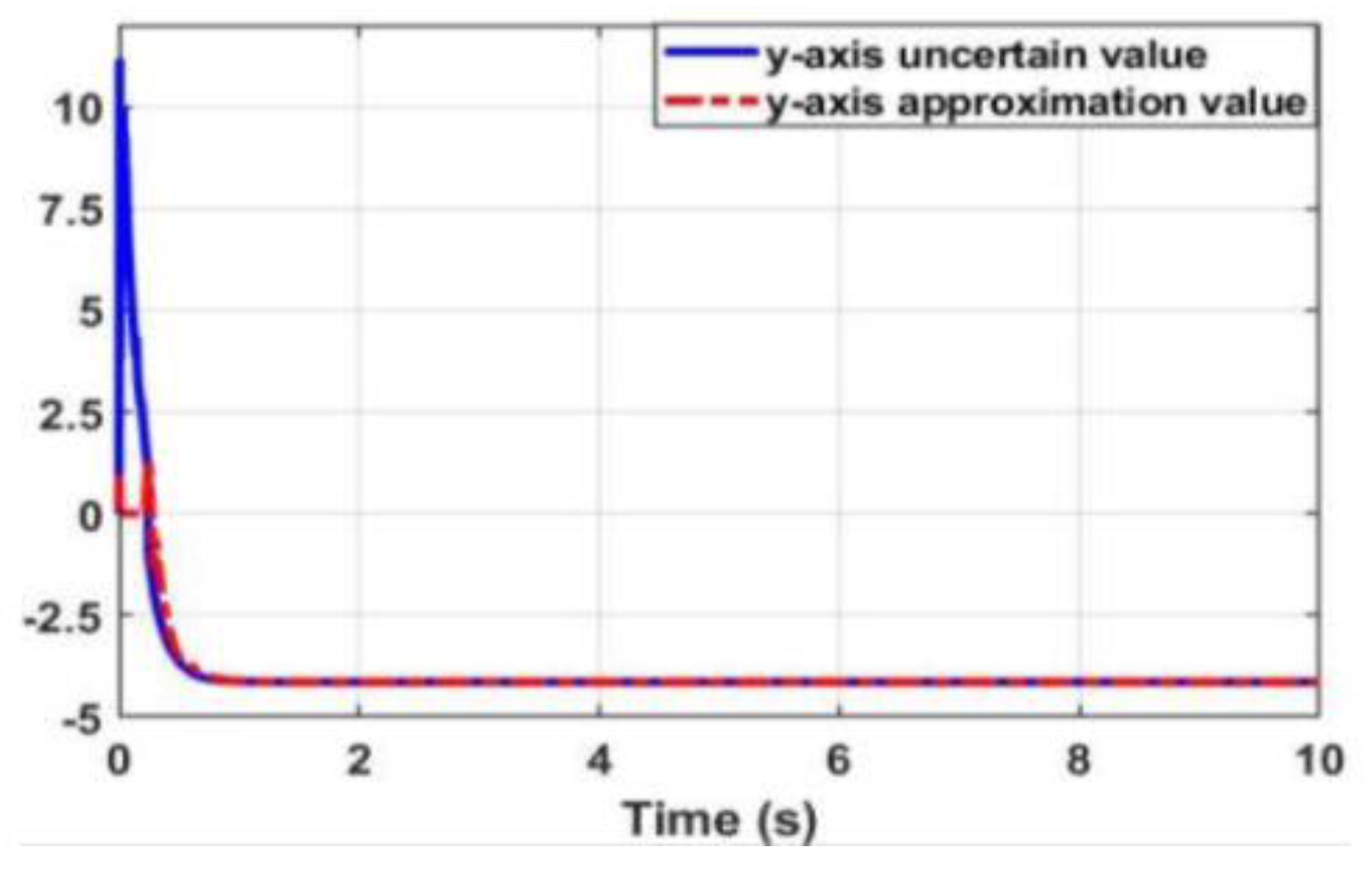
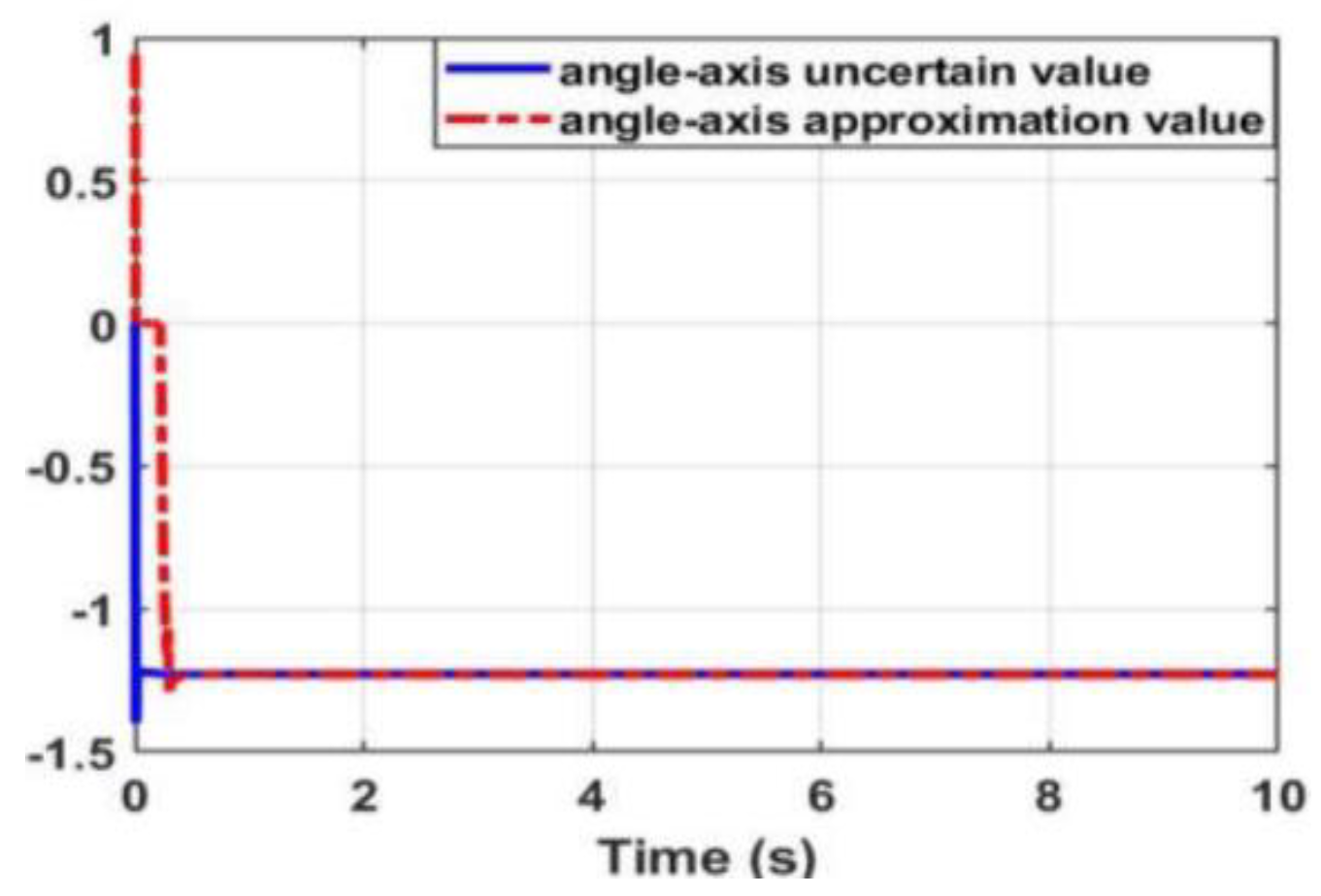
3.3.1. Approximation of WMR Model Uncertainty Component Using Radial Neural Network
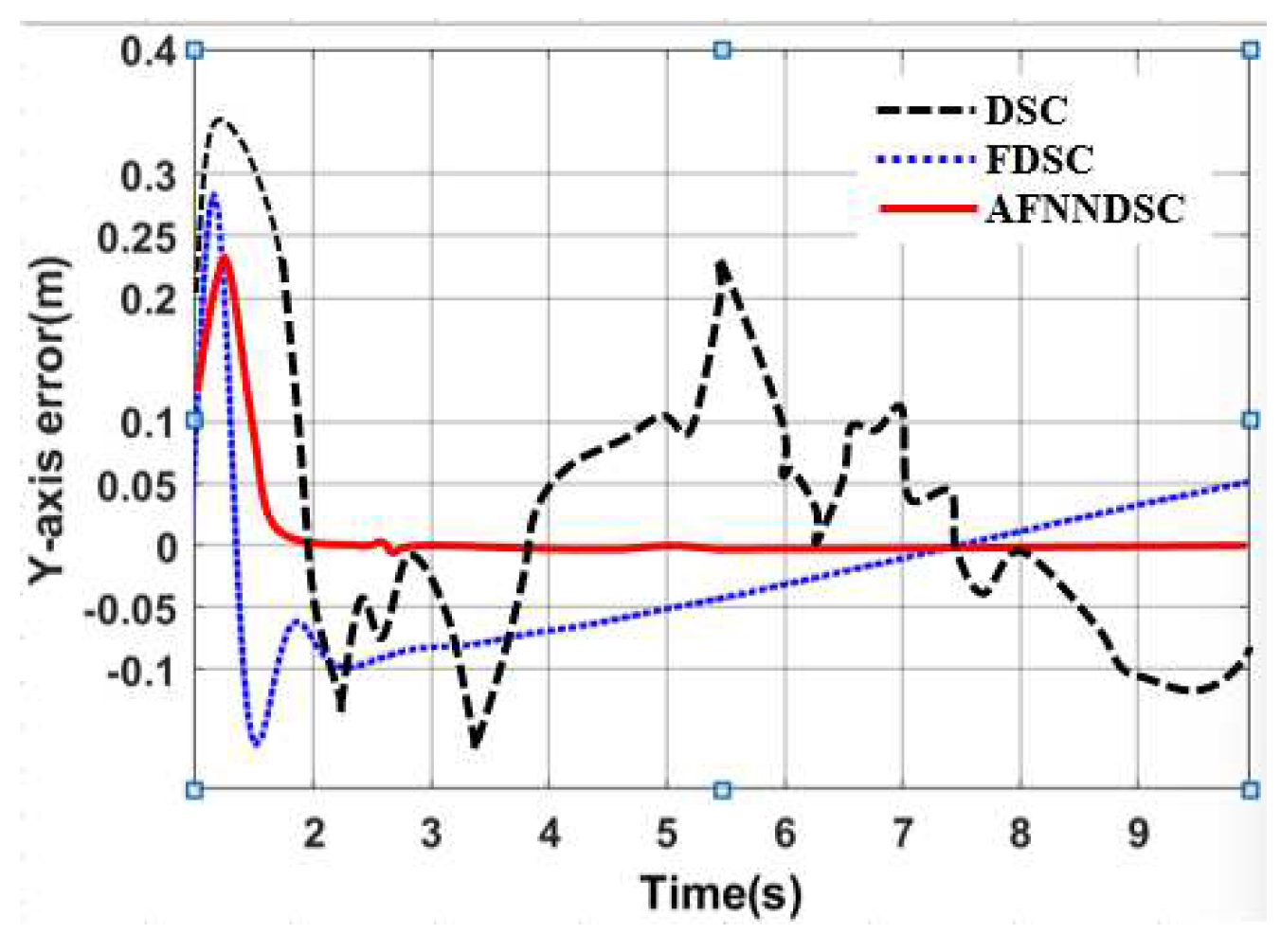
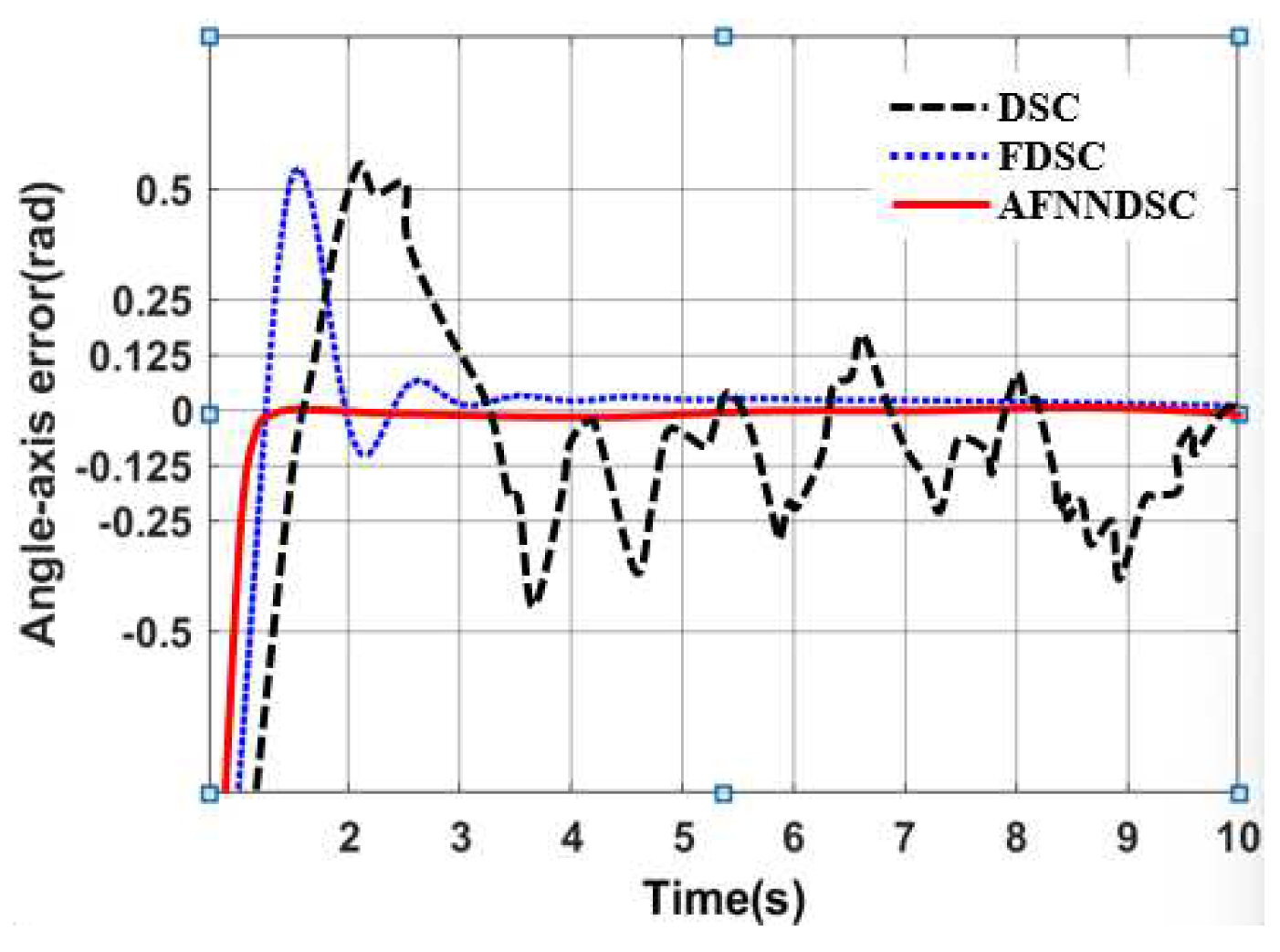
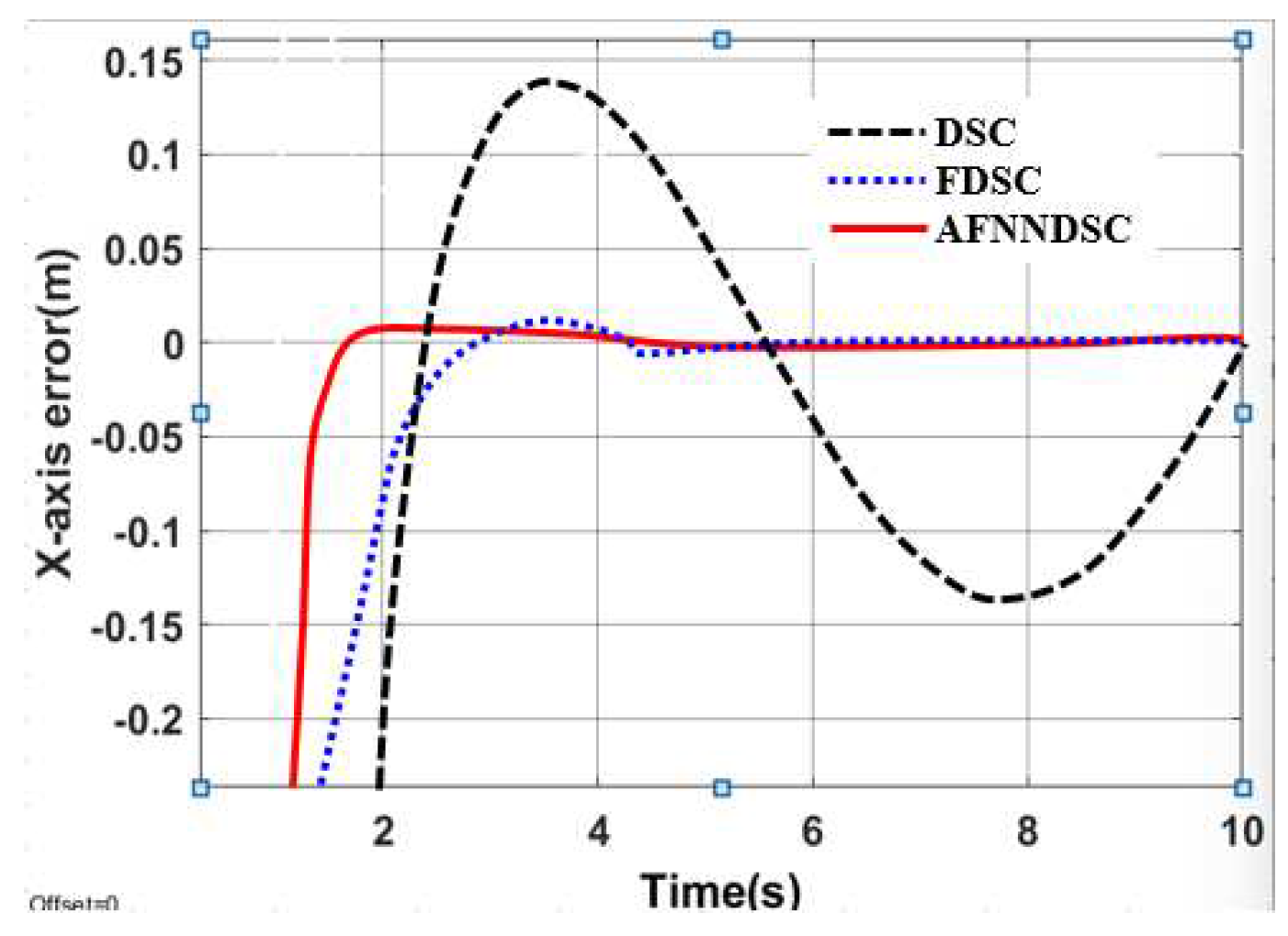
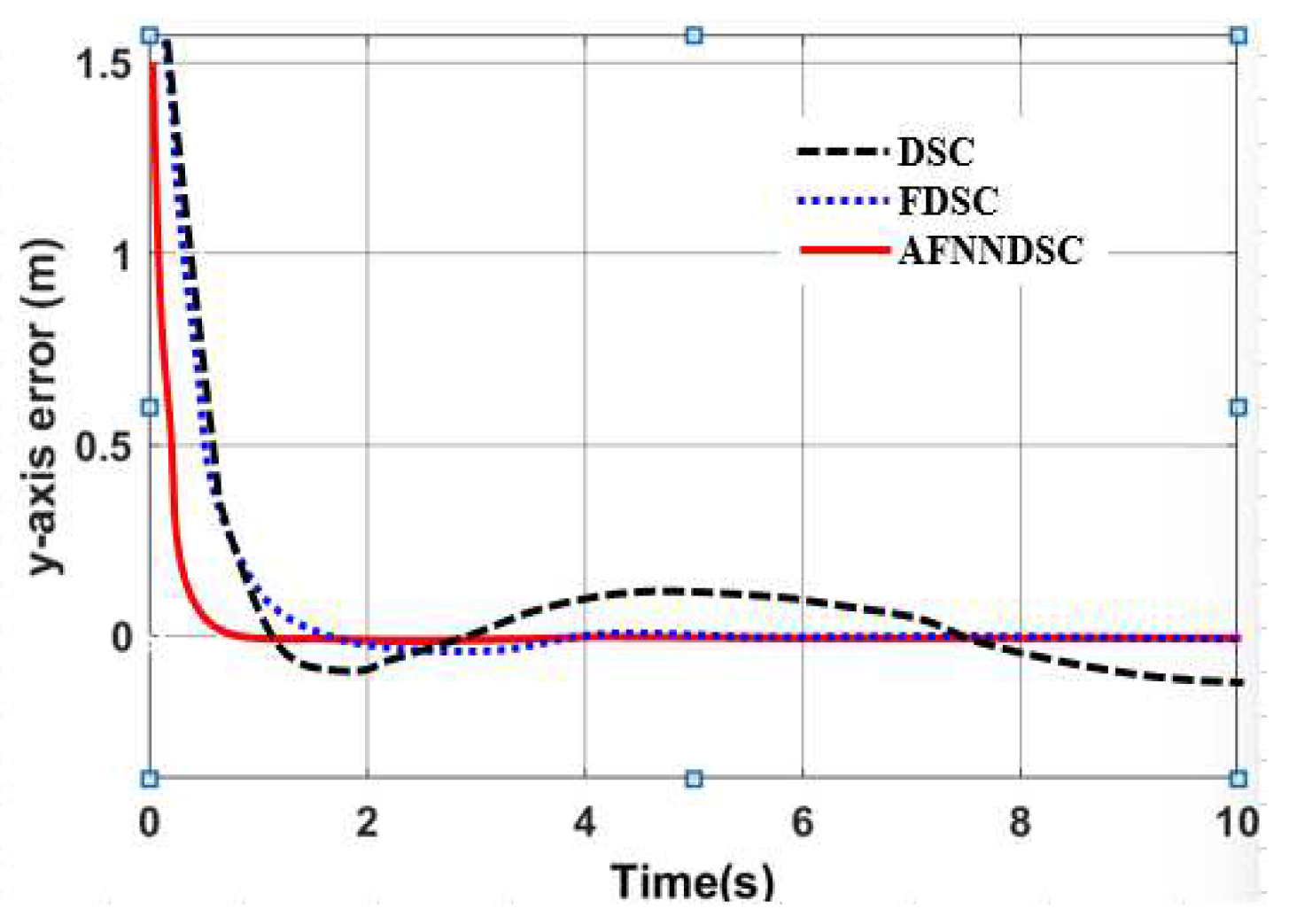
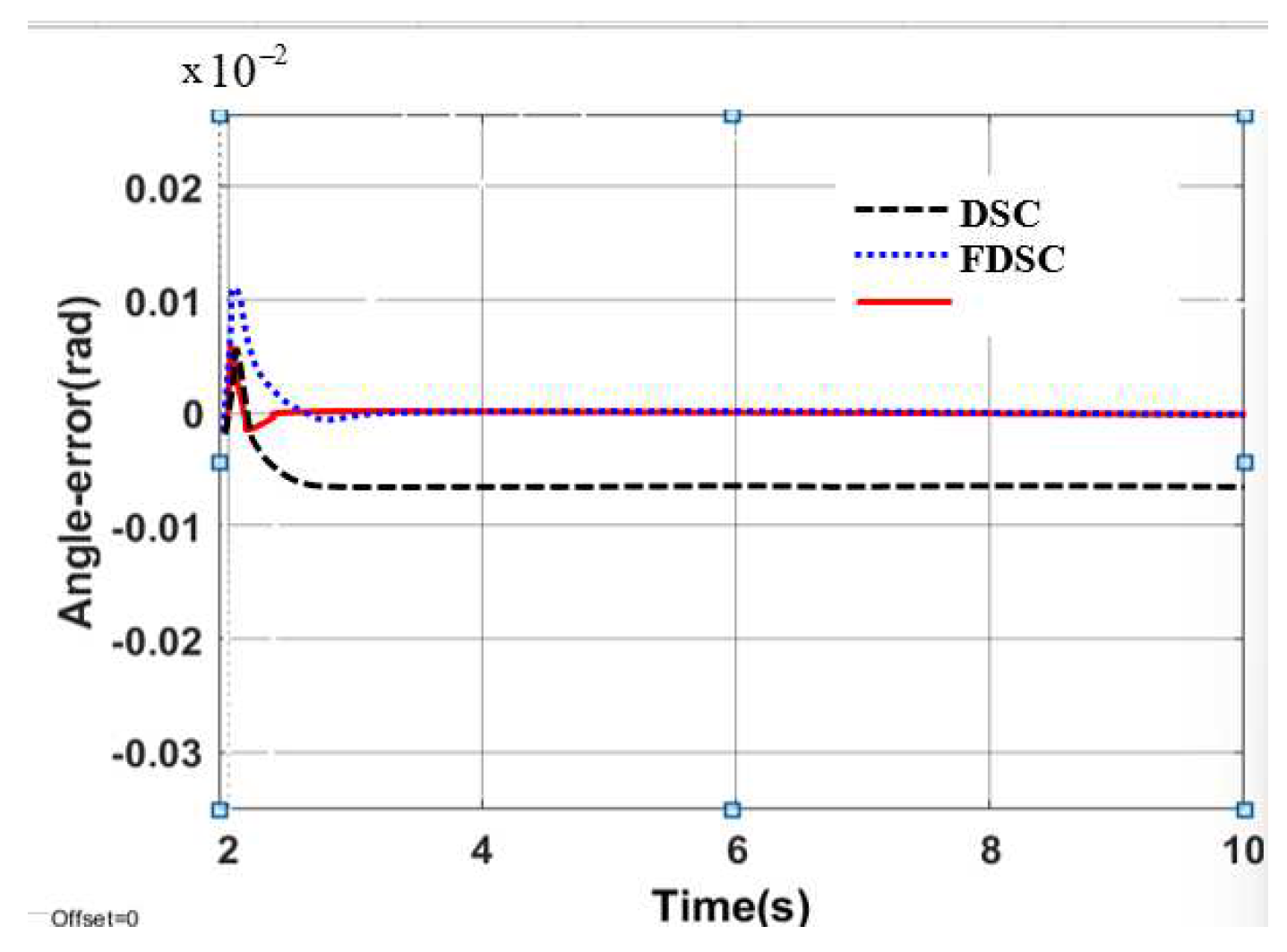
3.3.2. Result Simulation of Adaptive Fuzzy Neural Netwok Dynamic Surface controller.
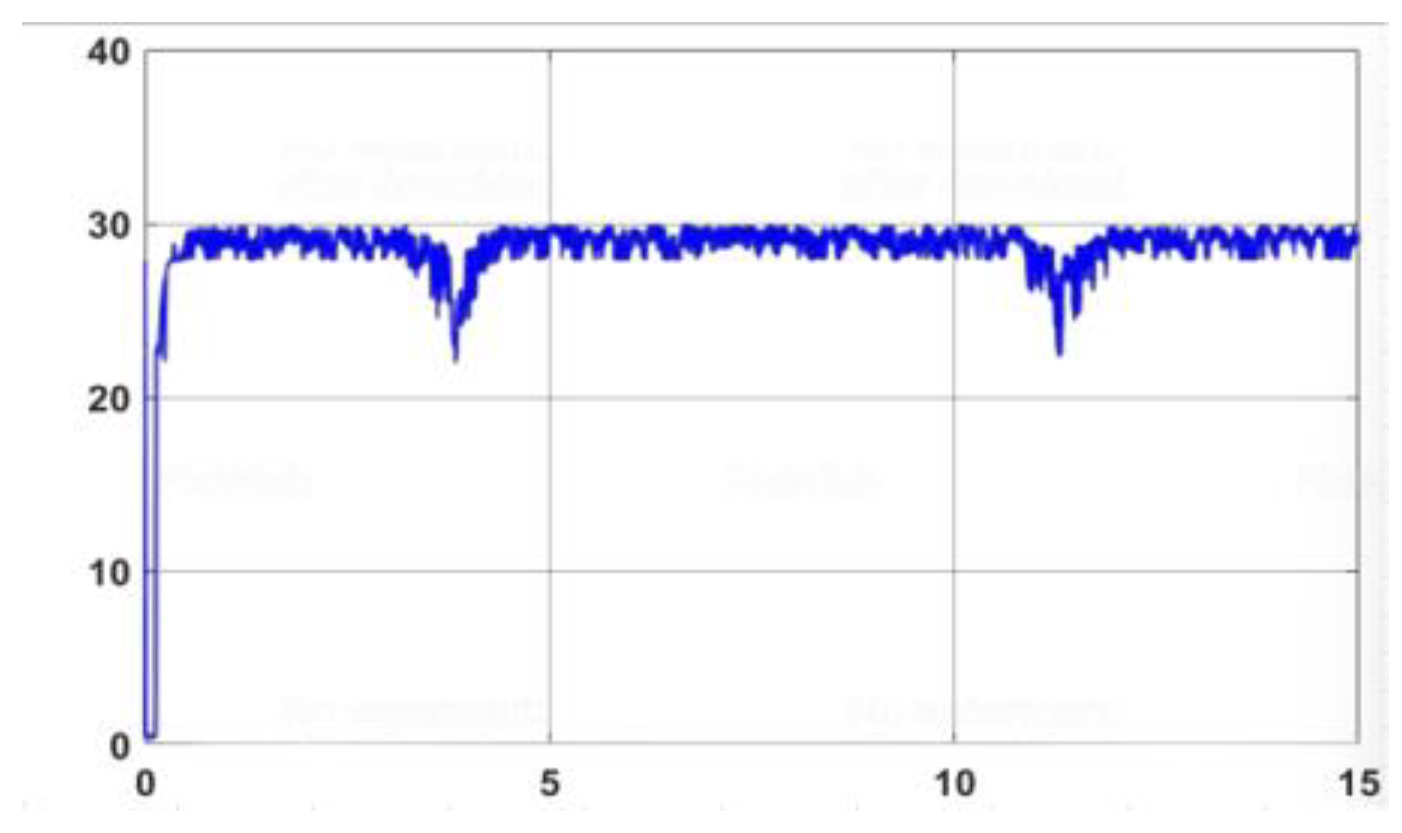
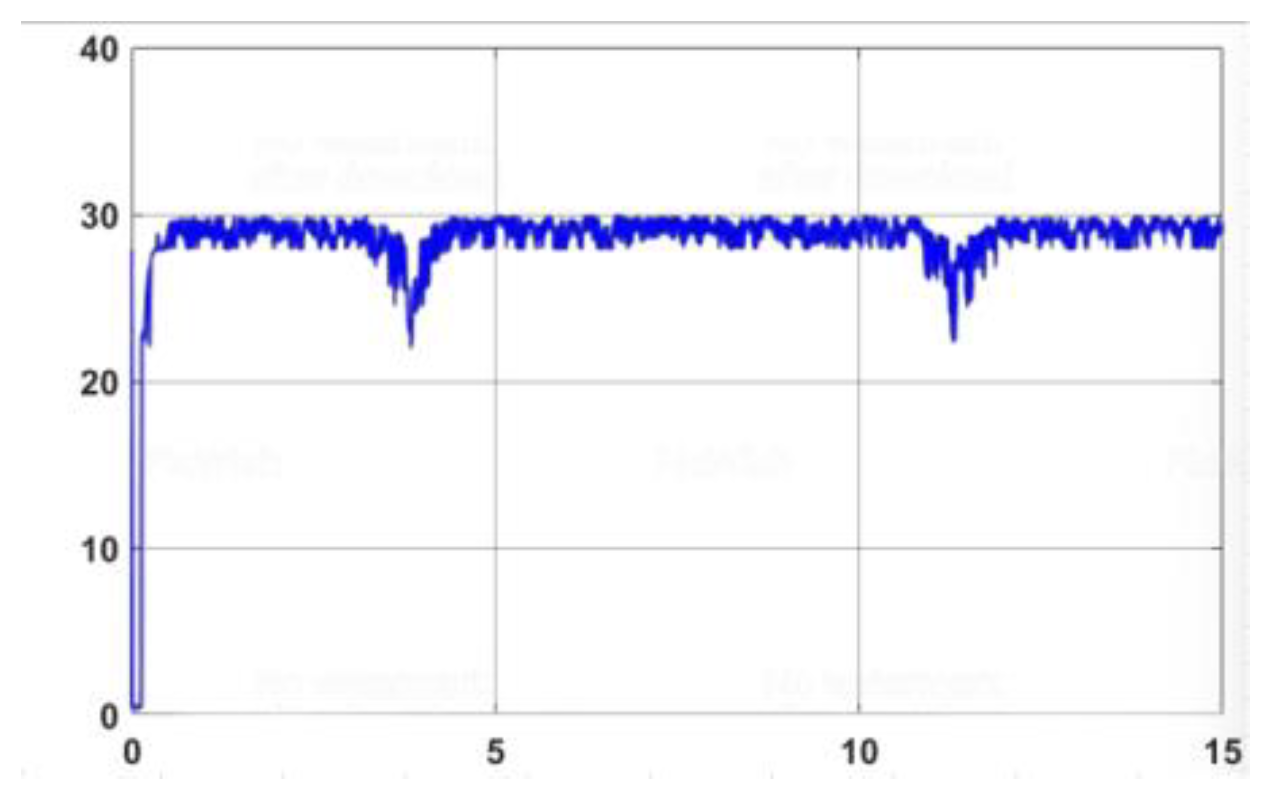
3.3.3.1. The robot model is affected by external disturbances
3.3.3.2. Impact of Variation in Friction Coefficient from The environment
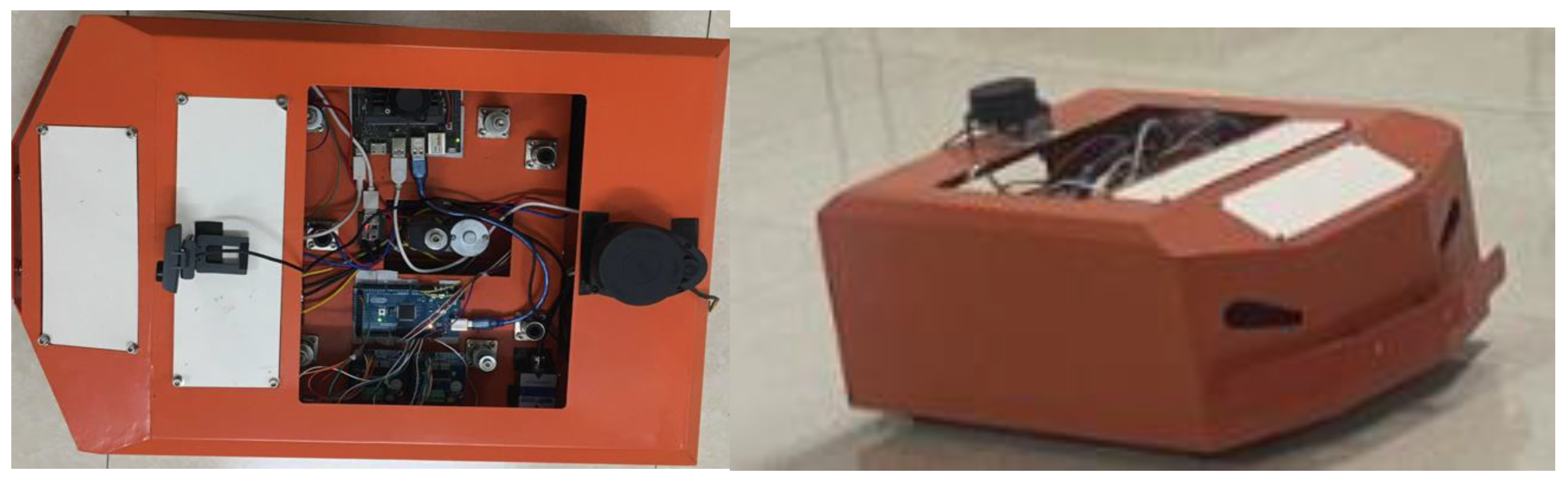
4. Fabrication and Experimental Operation of WMR with the Proposed Controller
4.1. Manufacturing WMR Model
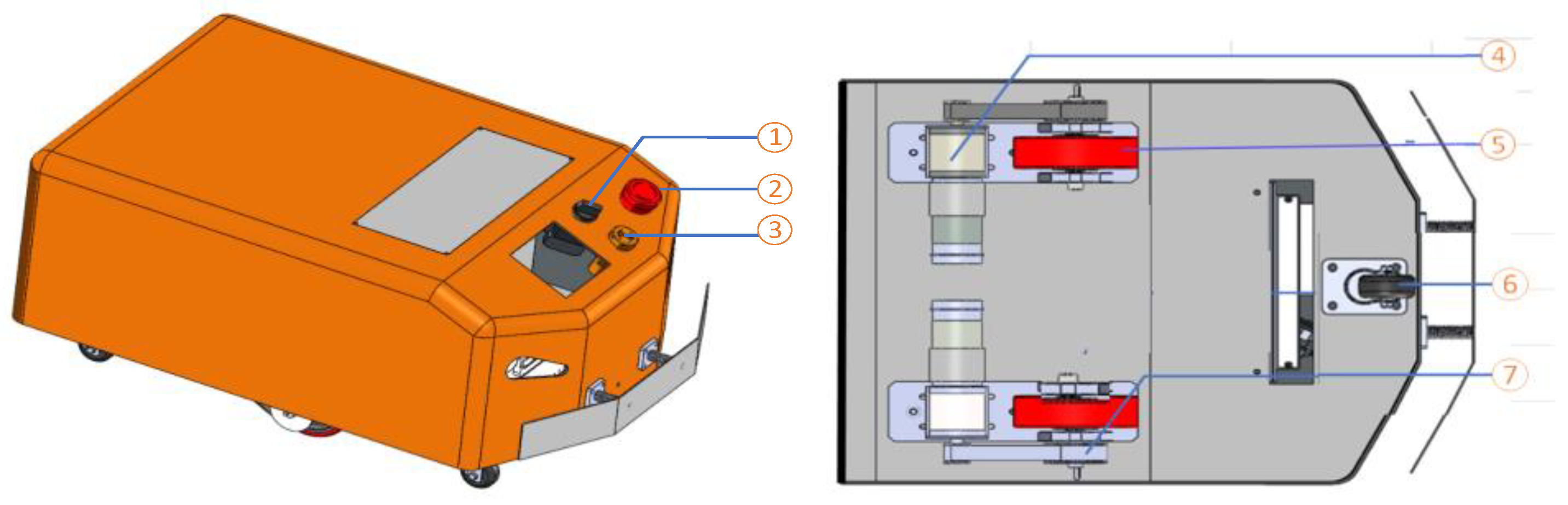
4.1.1. Mechanical Design of WMR
| 1: Switch On/Off 2: Emergency stop button |
3: Sirens 4: DC |
5: Active wheel 6: Passive wheel |
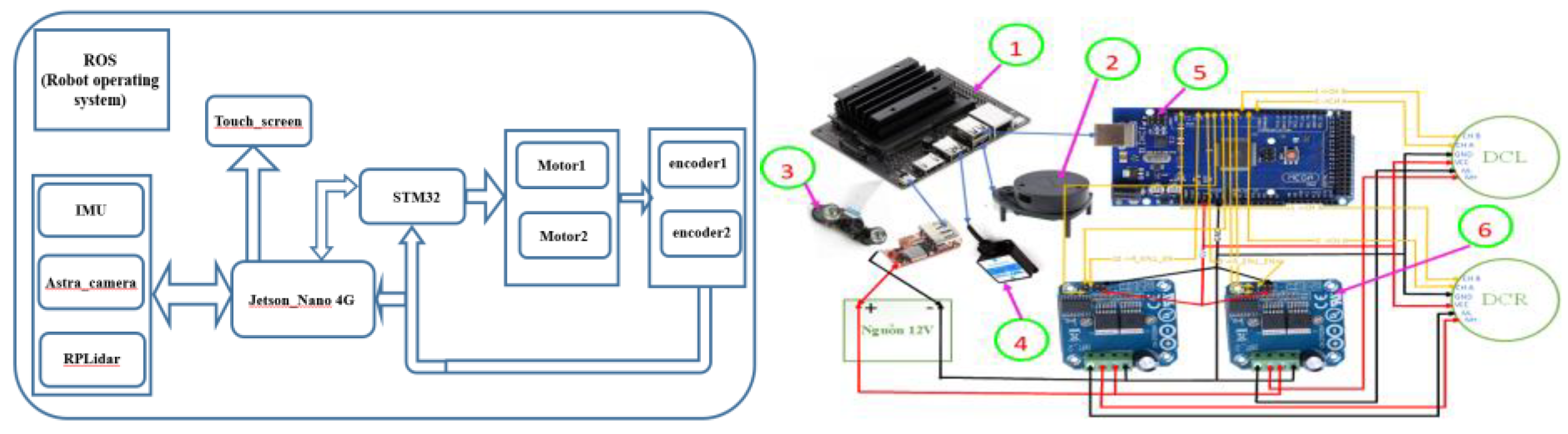
4.1.2. Design the Control Circuit Hardware Structure for the Robot
| 1: Jetson Nano 4G 2: Lidar RPLIDAR A1M8 360° |
3:Camera AI 4: IMU HWT901B |
5: STM32 F407 6: Driver DC BTS7960 43A |
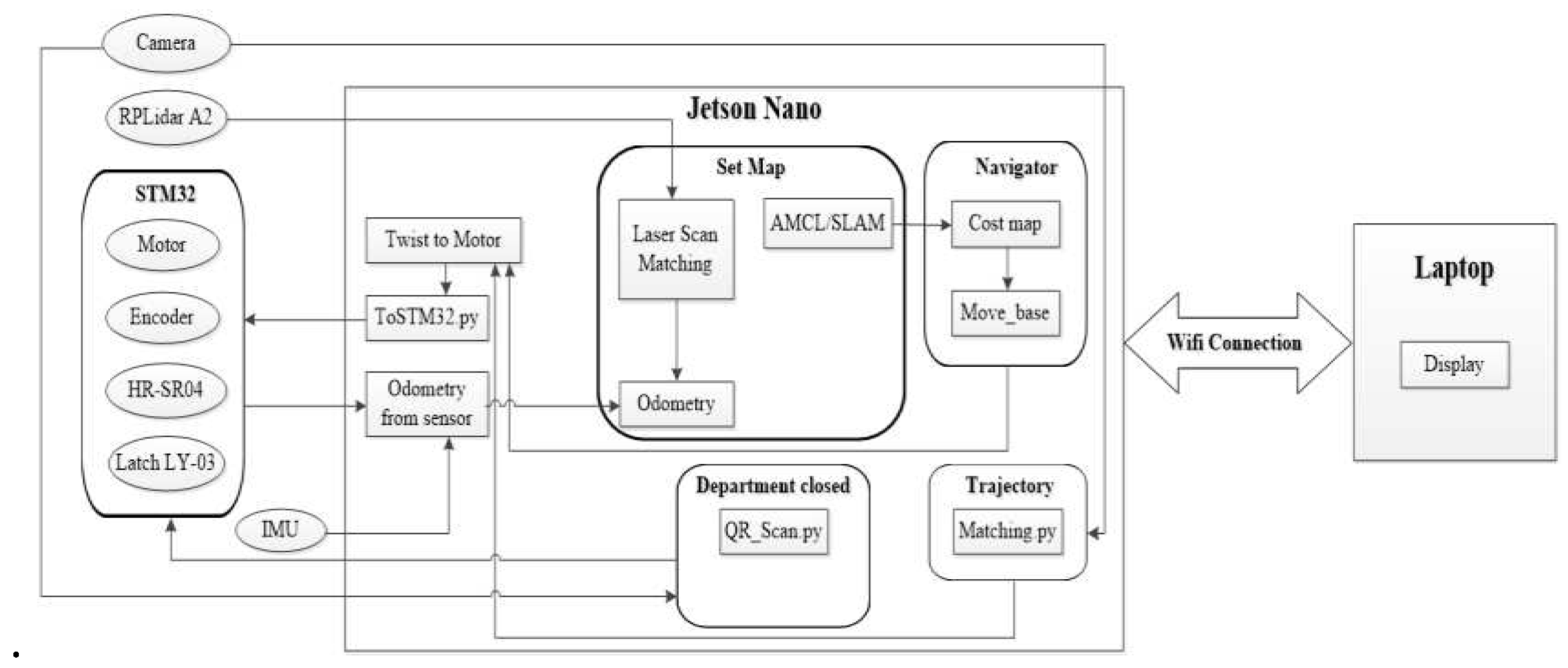
4.1.3. Robot Control Software
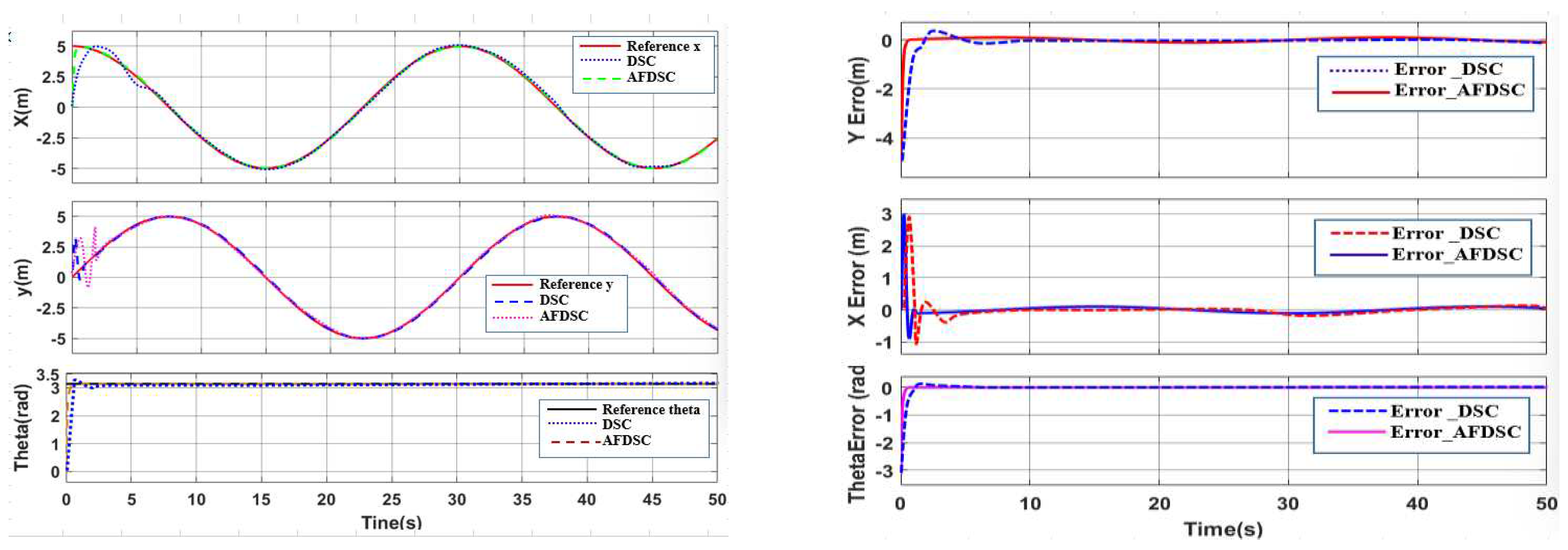
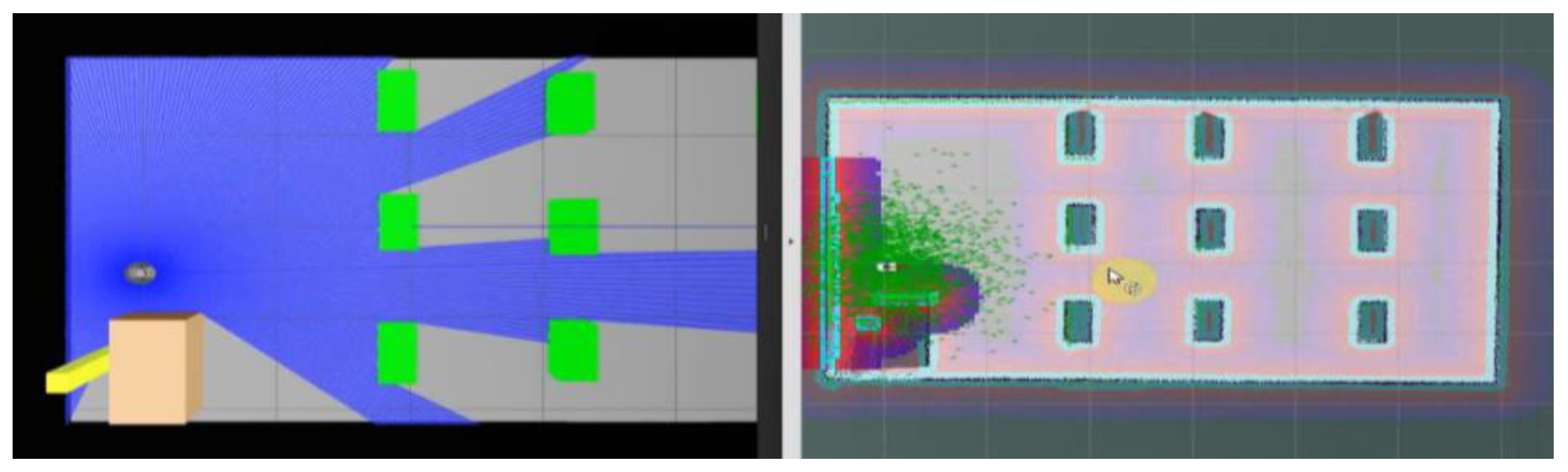
4.2. Simulate the Controller Tracking the Planned Trajectory on Gazebo
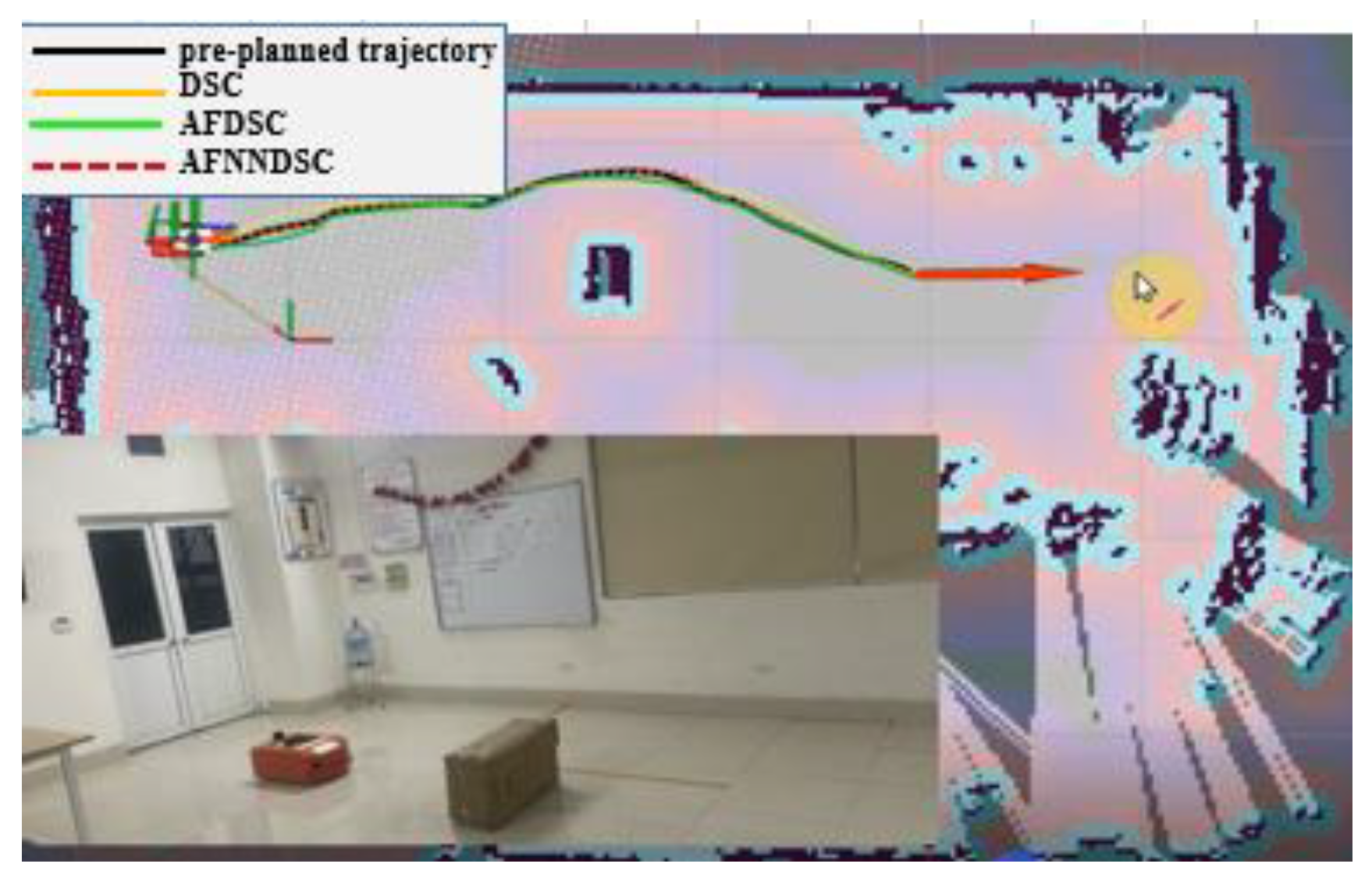
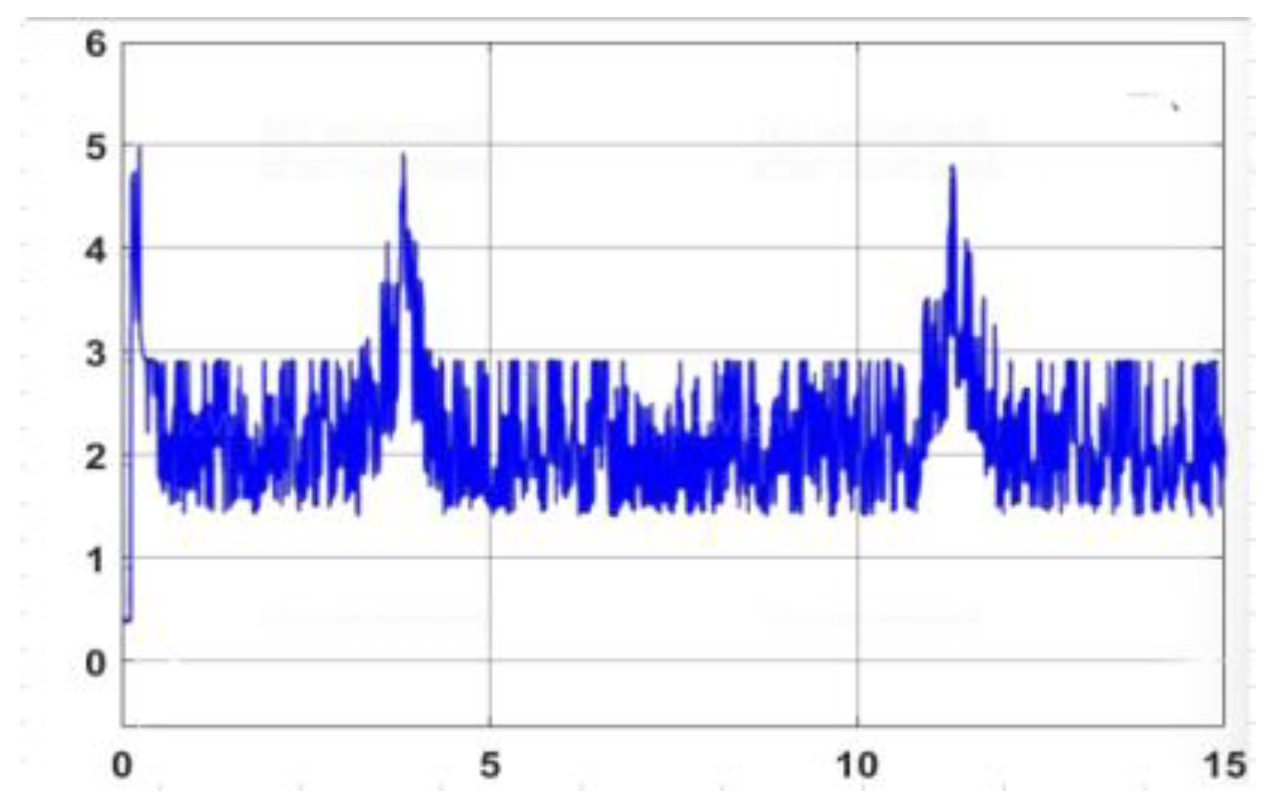
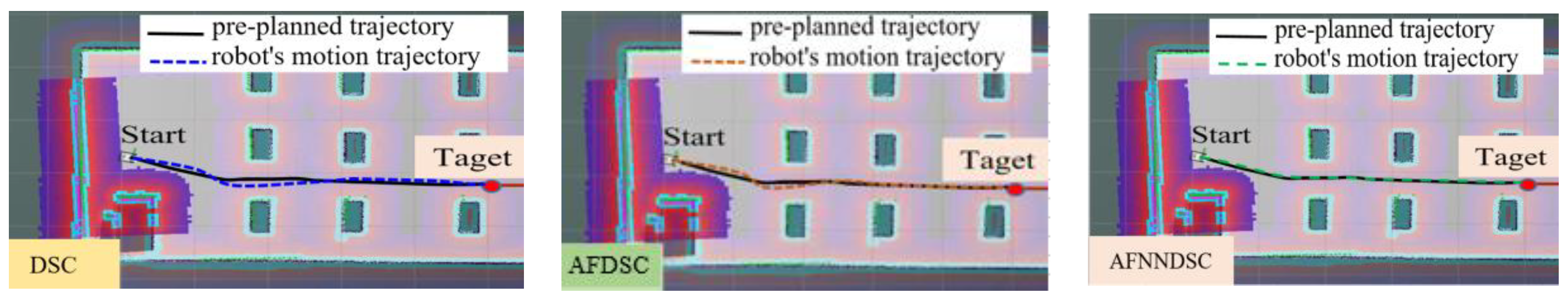
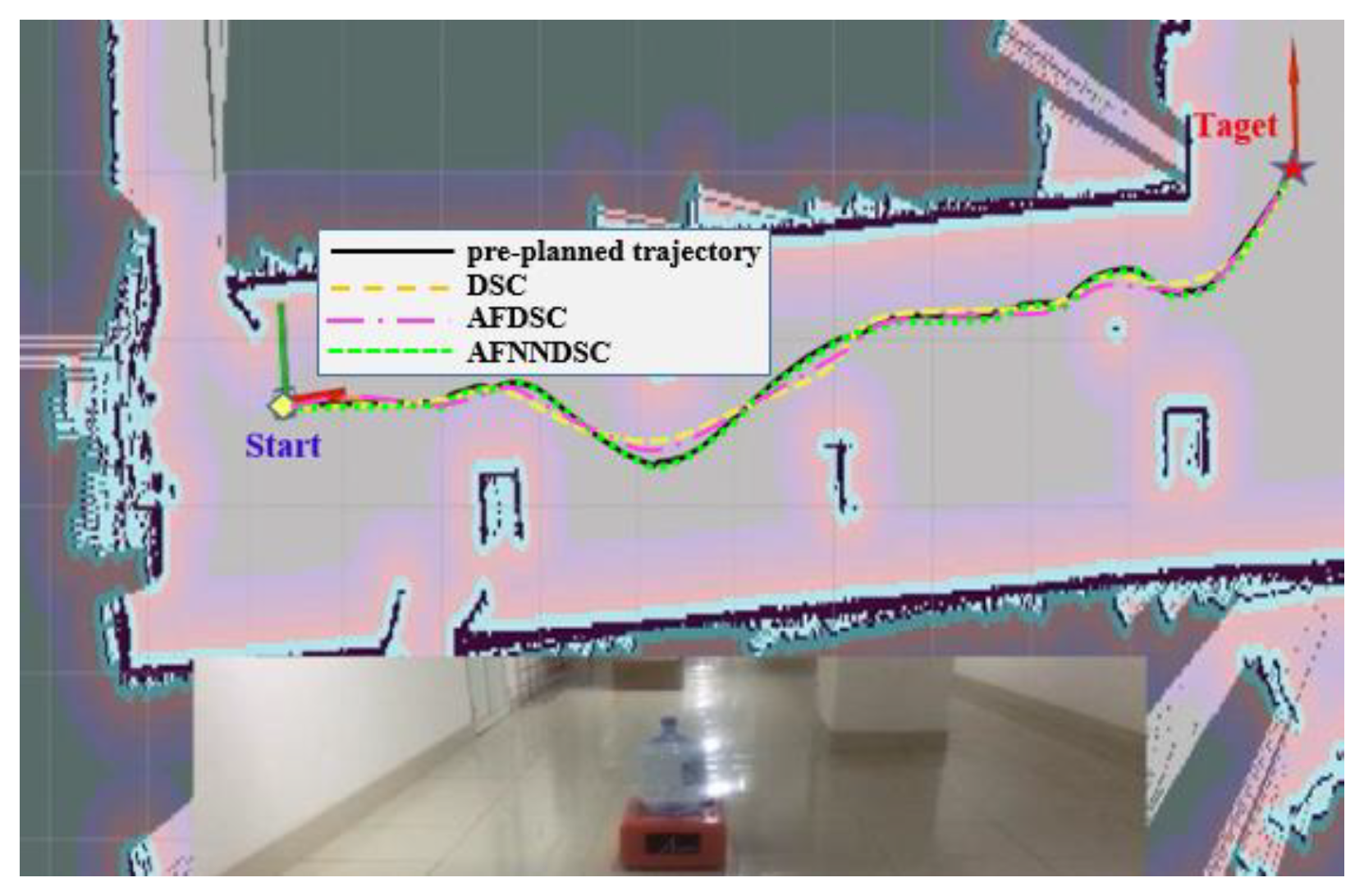
4.3. Experimental Model to Verify Results
5. Conclusion
References
- Y. Z. ,. S. D. ,. G. X. ,. R. G. ,. S. L. Hongwei Fang, "Robust tracking control for magnetic wheeled mobile robots using adaptive dynamic programming," ISA Transactions, vol. 128, pp. 123-132, 2022.
- T. V. T. N. N. S. &. M. T. L. Vo Ba Viet Nghia, "Adaptive neural sliding mode control for two wheel self-balancing robot," International Journal of Dynamics and Control volume, vol. 10, p. 771–784, 2022.
- H. Y. &. S. Wang, "Trajectory Tracking Control for Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robots with External Disturbances and Parameter Uncertainties," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 18, p. 3015–3022, 2020.
- K. N. T. H. D. T. P. N. T. K. Nguyen Van Tinh, "Neural Network-based Adaptive Sliding Mode Control Method for Tracking of a Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot with Unknown Wheel Slips, Model Uncertainties, and Unknown Bounded External Disturbances," Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 103-123, 2018.
- P. Z. M. W. &. Z.-P. J. Tengfei Liu, "New Results in Stabilization of Uncertain Nonholonomic Systems: An Event-Triggered Control Approach," Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, vol. 34, p. 1953–1972, 2021.
- X. F. &. C. Wang, "Robust Adaptive Terminal Sliding Mode Control of an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot for Aircraft Skin Inspection," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 19, p. 1078–1088, 2021.
- V. P.-V. A. S.-O. &. J. D. S.-T. Aldo Jonathan Muñoz-Vázquez, "Adaptive Fuzzy Velocity Field Control for Navigation of Nonholonomic Mobile Robots," Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, vol. 101, no. 38, 2021.
- Y. Liu, W. He, H. Qiao, and H. Ji, "Adaptive-Neural-Network-Based Trajectory Tracking Control for a Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot With Velocity Constraints," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 68, no. 6, pp. 5057 - 5067, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z.-L. F. Z.-Q. Z. R.-Z. G. &. S.-B. Z. Jing-Jun Zhang, "Trajectory Tracking Control of Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robots Using Model Predictive Control Subjected to Lyapunov-based Input Constraints," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems , vol. 20, p. 1640–1651, 2022.
- X. B. S. Z. &. G. S. Sunxin Wang, "Trajectory Tracking Control of Wheeled Mobile Robots Using Backstepping," Lecture Notes in Computer Science book series , Vols. (LNAI,volume 11744), pp. 1393-1399, 2019.
- M. J. R. a. A. Y. Memon, "Trajectory Tracking and Stabilization of Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Recursive Integral Backstepping Control," Electronics , pp. 1-22, 2021.
- M. Cui, "Observer-Based Adaptive Tracking Control of Wheeled Mobile Robots With Unknown Slipping Parameters," IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 169646 - 169655, 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. J. S. M. W. N. B. Payam Nourizadeh, "In situ slip estimation for mobile robots in outdoor environments," Journal of Field Robotics, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 467-482, 2022.
- N. S. Y. W. Y. F. Dingkun Liang, "Differential Flatness-Based Robust Control of Self-balanced Robots," The International Journal of Robotics Research, vol. 51, no. 31, pp. 949-954, 2018.
- S. L. W. L. &. K. W. Zhenjie Ma, "Backstepping sliding mode-based anti-skid braking control for a civil aircraft," Aerospace Systems , vol. 6, p. 187–197, 2023.
- S. f. d. Narges Ghobadi, "Dynamic modeling and sliding mode control of a wheeled mobile robot assuming lateral and longitudinal slip of wheels," International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), 2019.
- G. C. I. Motte, "Slow manifold approach for the control of mobile robots not satisfying the kinematic constraints," IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 875-880, 2000.
- S. D. X. W. &. K. M. Chen Ding, "Output feedback sliding mode control for path-tracking of autonomous agricultural vehicles," Nonlinear Dynamics, vol. 110, p. 2429–2445, 2022.
- H. G. ,. L. D. W. L. H. Y. Z. D. Chao Chen, "Trajectory tracking control of WMRs with lateral and longitudinal slippage based on active disturbance rejection control," Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 107, pp. 236-245, 2018.
- J. J. F. C. M. N. L. César Peña, "Control of wheeled mobile robots singularly perturbed by using the slipping and skidding variations: curvilinear coordinates approach (Part I)," ResearchGate Logo, 2020.
- J. Sasiadek, "Space Robotics and its Challenges," ResearchGate Logo, 2019.
- A. T. &. N. Cordo, "Evaluation of the Vehicle Sideslip Angle According to Different Road Conditions," Proceedings of the 4th International Congress of Automotive and Transport Engineering , p. 814–819, 2018.
- H. C. Y. H. H. G. H. S. H. D. N. W. Lin Zhang, "Model predictive control for integrated longitudinal and lateral stability of electric vehicles with in-wheel motors," Emerging Trends in LPV-Based Control of Intelligent Automotive System, vol. 20, pp. 1-19., 2020.
- J. G. I. a. J. F. C. Thiago B. Burghia, "Kinematic control design for wheeled mobile robots with," ARTICLE HISTORY, 2021.
- L. Y. a. C. G. Xiaoshan Gao, "Modeling and Analysis in Trajectory Tracking Control for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Wheel Skidding and Slipping: Disturbance Rejection Perspective," Actuators, vol. 10, no. 2, 2021.
- S. Yoo, "Approximation-based adaptive control for a class of mobile robots with unknown skidding and slipping," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 85, no. 10, p. 703–710, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Z. R. C. H. T. N. Hao Xie, "Robust tracking control of a differential drive wheeled mobile robot using fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode," Computers & Electrical Engineering, vol. 96, p. 107488, 2021.
- L. Y. a. C. G. Xiaoshan Gao, "Modeling and Analysis in Trajectory Tracking Control for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Wheel Skidding and Slipping: Disturbance Rejection Perspective," Actuators, vol. 10, 2021.
- D. W. C. B. Low, "GPS-based tracking control for a car-like wheeled mobile robot with skidding and slipping," IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 13, p. 480–484, 2008.
- B. T. C. C. P. M. R. Lenain, "Mixed kinematic and dynamic sideslip angle observer for accurate control of fast off-road mobile robots," Journal of Field Robotics, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 181-196, 2010.
- Z. W. L. Z. P. W. Jizheng Liu, "Sideslip angle estimation of ground vehicles: a comparative study," IET Control Theory & Applications, vol. 14, no. 20, pp. 3490-3505, 2021.
- M. B. E. K. A. K. G. Bayar, "Improving the trajectory tracking performance of autonomous orchard vehicles using wheel slip compensation," Biosystems Engineering, vol. 146, pp. 149-164, 2016.
- S. F. G. R. M. C. S. M. S. Valentina Breschi, "Vehicle sideslip estimation via kernel-based LPV identification: Theory and experiments," Automatica, vol. 122, 2020.
- G. R. a. J.-L. B.-C. Antonio Leanza, "A Factor Graph-based approach to vehicle sideslip angle estimation," Arxiv, pp. 4597- 4602., 2021.
- S. D. H. V. T. Y. &. P. V. C. La Van Truong, "Adaptive Trajectory Neural Network Tracking Control for Industrial Robot Manipulators with Deadzone Robust Compensator," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 18, p. 2423–2434, 2020.
- X. Fu, S. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Wang and Z. Liu, "Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Omnidirectional Mobile Robot Based on a New Friction Modeling," International Conference on Computer Technology, Electronics and Communication, 2019.
- J. K. H. P. P. Y. a. J. C. G. Swaroop, " “Dynamic surface control for a class of nonlinearsystems ”,," IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 1893-1899., 2000.
- A.K. S. ,. M. A. S. ,. A. M. L. Edalati, "Adaptive fuzzy dynamic surface control of nonlinear systems with input saturation and time-varying output constraints," Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, vol. 100, pp. 311-329, 2018.
- D. W. &. Y. H. Changshun Wang, "Neural Network Based Adaptive Dynamic Surface Control for Omnidirectional Mobile Robots Tracking Control with Full-state Constraints and Input Saturation," International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems , vol. 19, p. s4067–4077, 2021.
- T. Z. L. ,. M. a. Y. Peng Qin, "Predefined-Time Fuzzy Neural Network Control for Omnidirectional Mobile Robot," Prosesses, vol. 11, no. 1, 2022.
- N. M. +. a. N. F. N. Rosillo, "A Generalized Matlab/ROS/Robotic Platform Framework for Teaching Robotics," Robotics in Education , vol. 25, no. 6, 2019.
- D. P. M. S. C. R. P. R. André Araújo, "Integrating Arduino-Based Educational Mobile Robots in ROS," Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, vol. 77, no. 2, 2017.
- C. R. T. S. S. A. R. Rajesh Kannan Megalingam, "“ROS based Autonomous Indoor Navigation Simulation Using SLAM Algorithm”,," International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, vol. 7, pp. 199-205, 2018.
- D. W. C. B. Low, "GPS-based path following control for a car-like wheeled mobile robot with skidding of mobile robots in the presence of wheel slip and external disturbance force," Neurocomputing, vol. 188, pp. 12-22, 2016.
- S. Qi, D. Zhang, L. Guo, and L. Wu, “Adaptive Dynamic Surface Control of Nonlinear Switched Systems with Prescribed Performance” J. Dyn. Control Syst., vol. 24, no. 2, 2018, 269–286.
- P. Petrehuş, Z. Lendek, and P. Raica, “Fuzzy modeling and design for a 3D crane”, IFAC Proc. Vol., vol. 46, no. 20 PART 1, 2013, 479–484. [CrossRef]
- M. Galli, R. Barber, S. Garrido, and L. Moreno, “Path planning using MatlabROS integration applied to mobile robots” 2017 IEEE Int. Conf. Auton. Robot Syst. Compet. ICARSC 2017, 98–103 85.
- A. Araújo, D. Portugal, M. S. Couceiro, and R. P. Rocha, “Integrating Arduino-Based Educational Mobile Robots in ROS” J. Intell. Robot. Syst. Theory Appl., vol. 77, no. 2, 2014, 281–298.
- Rajesh Kannan Megalingam, Chinta Ravi Teja, Sarath Sreekanth, Akhil Raj: “ROS based Autonomous Indoor Navigation Simulation Using SLAM Algorithm”, International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Volume 118 No. 7 2018, 199-205.
- Ahmed F. Amer, Elsayed A. Sallam, and Ibrahim A. Sultan Adaptive Sliding-Mode Dynamic Controller for Nonholonomic Mobile Robots, In 2016 12th International Computer Engineering Conference (ICENCO), IEEE (2015), pp. 230-235.
- S. Rudra, R. K. Barai, and M. Maitra, “Design and implementation of a block backstepping based tracking control for nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot” , Int. J. Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2016, vol. 26, pp. 3018-3035. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Rabbani and A. Y. Memon, “Trajectory Tracking and Stabilization of Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Recursive Integral Backstepping Control,” Electronics, vol. 10, pp. 1-22, August 2021. [CrossRef]
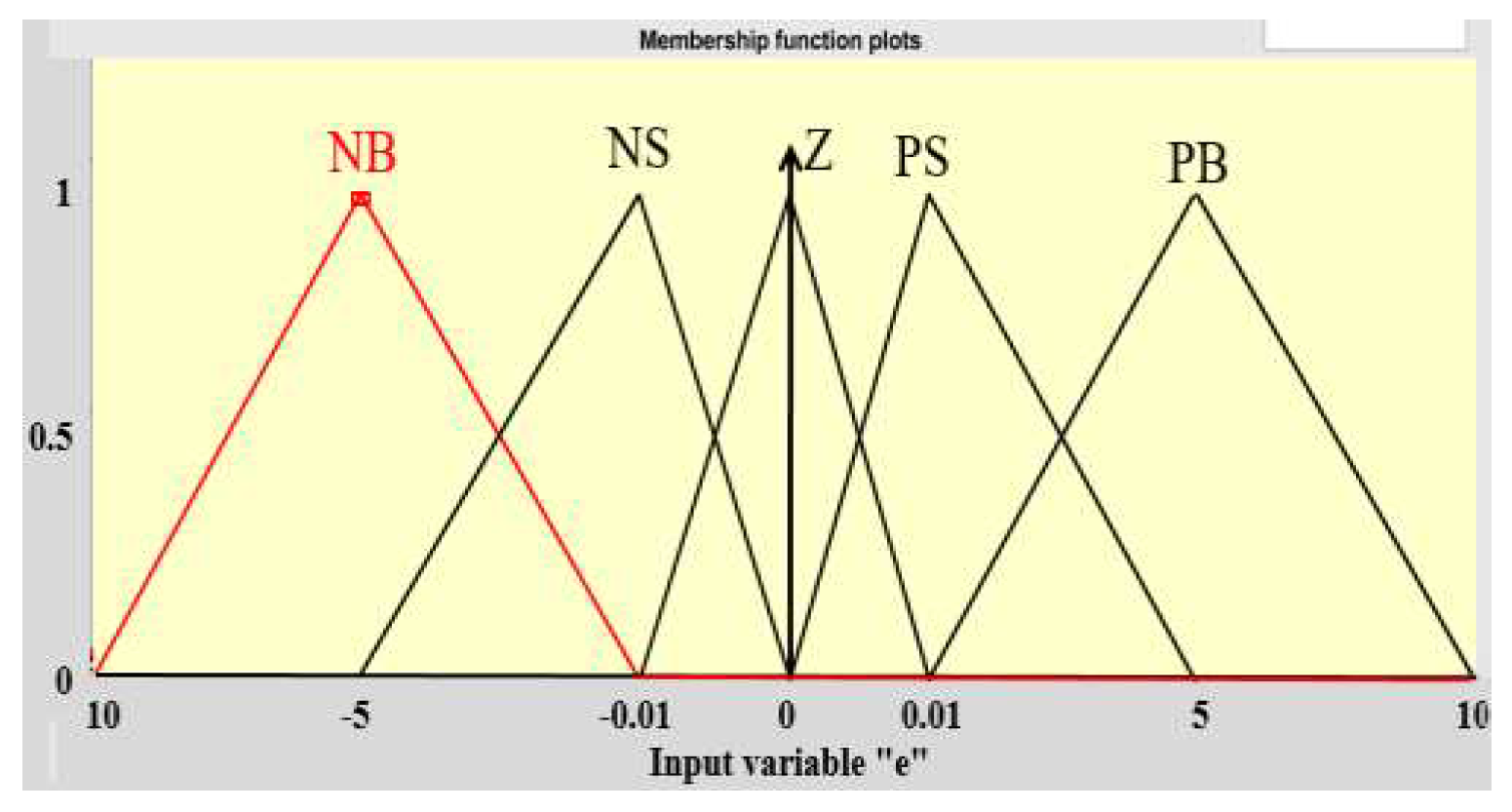
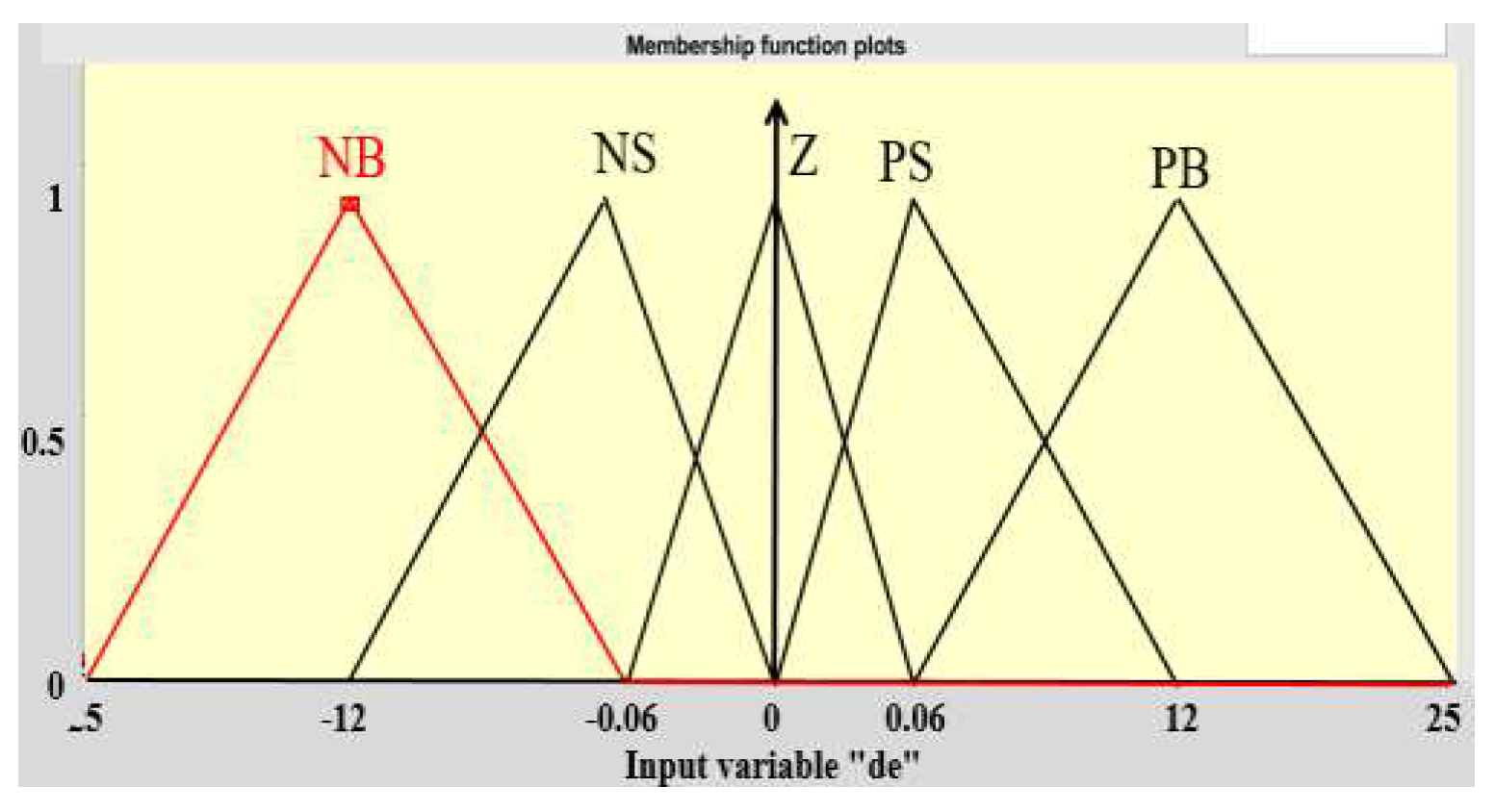
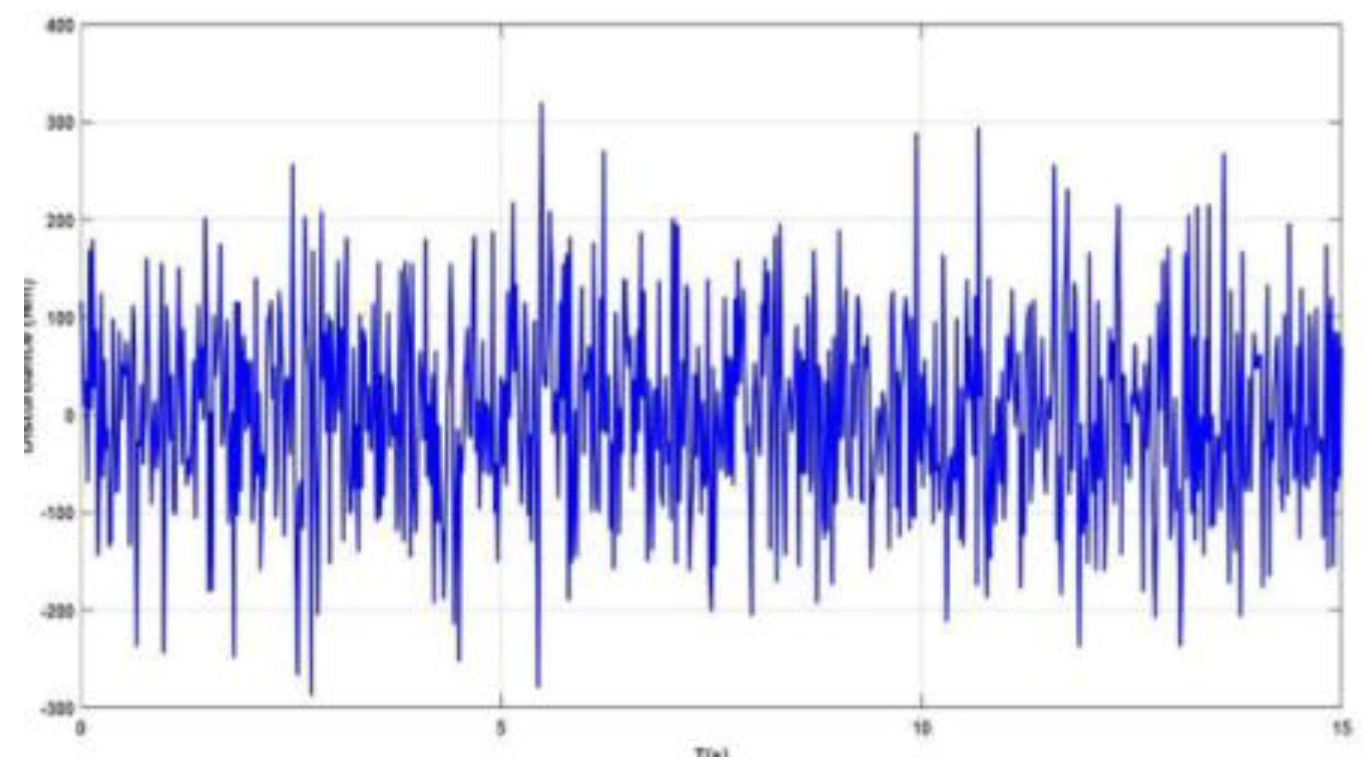



| Language variation e | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
| NB | NB | Negative big |
| NS | NS | Negative small |
| Z | Z | Zezo |
| PS | PS | Positive small |
| PB | PB | Positive big |
|
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NS | Z | PS | PB | |
| NB | M(M) | S(B) | VS(VB) | S(B) | M(M) |
| NS | B(S) | M(M) | S(B) | M(M) | B(S) |
| Z | VS(VB) | B(S) | M(M) | B(S) | VS(VB) |
| PS | B(S) | M(M) | S(B) | M(M) | B(S) |
| PB | M(M) | S(B) | VS(VB) | S(B) | M(M) |
| Variable output language | Meaning | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| VS | Verry small | 1.5 | 20 |
| S | Small | 4,25 | 25 |
| M | medium | 6.5 | 30 |
| B | Big | 8 | 35 |
| VB | Verry big | 10 | 40 |
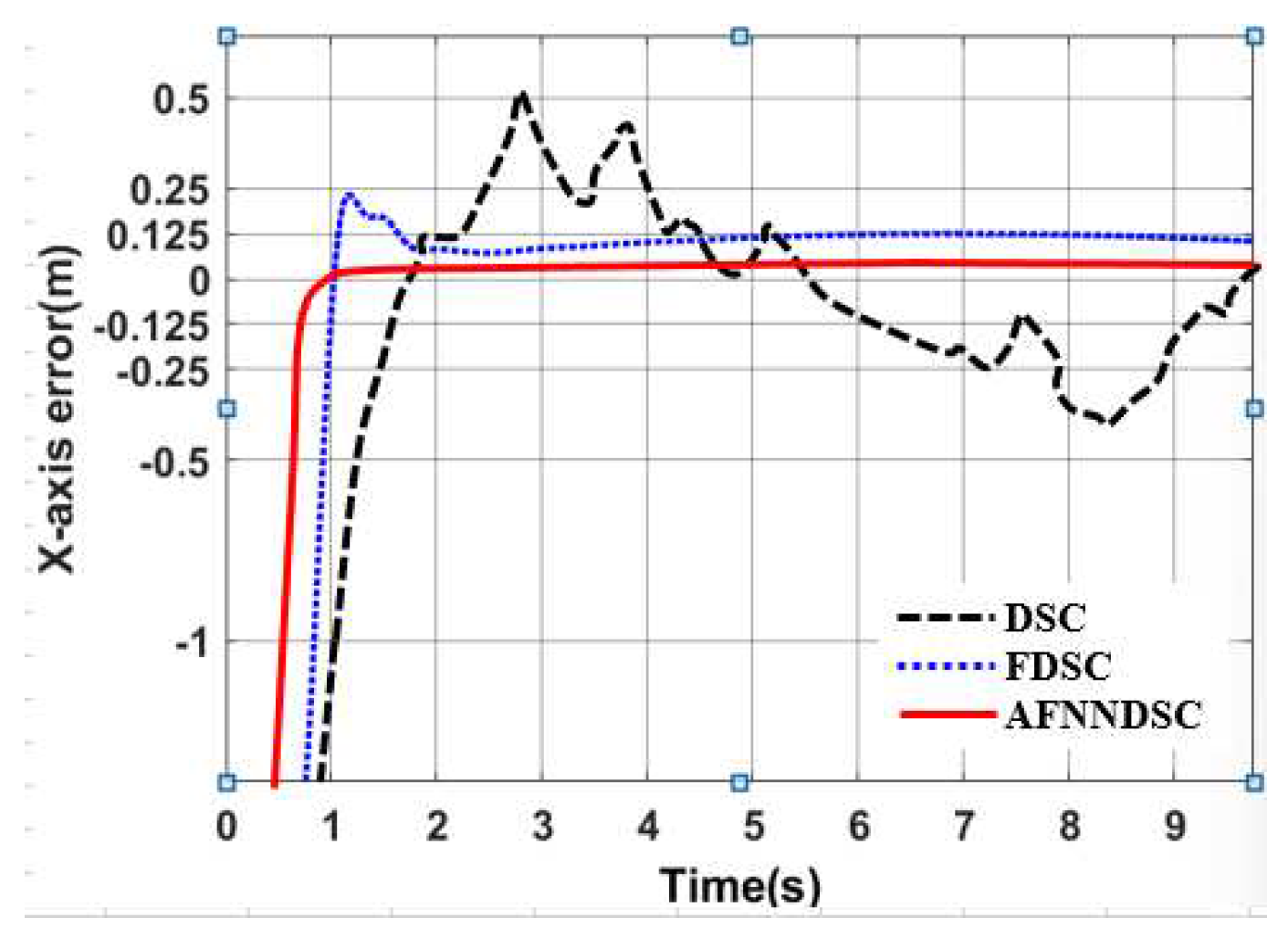
| Controller | The largest deviation value is when the robot follows the trajectory | ||
| X-axis(m) | Y-axis(m) | Angle (rad) | |
| DSC | 0.1452 | 0.1683 | 0.00652 |
| AFDSC | 0.00136 | 0.00415 | 0.000452 |
| AFNNDSC | 0.000572 | 0.000523 | 0.000394 |
| Experimental environment | DSC Controller | AFDSC Controller | AFDSC Controller | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Around the room | 0.04163(m) | 0.00968(m) | 0.000934(m) |
| 2 | Along the corridor | 0.02431(m) | 0.007217(m) | 0.000763(m) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





