Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
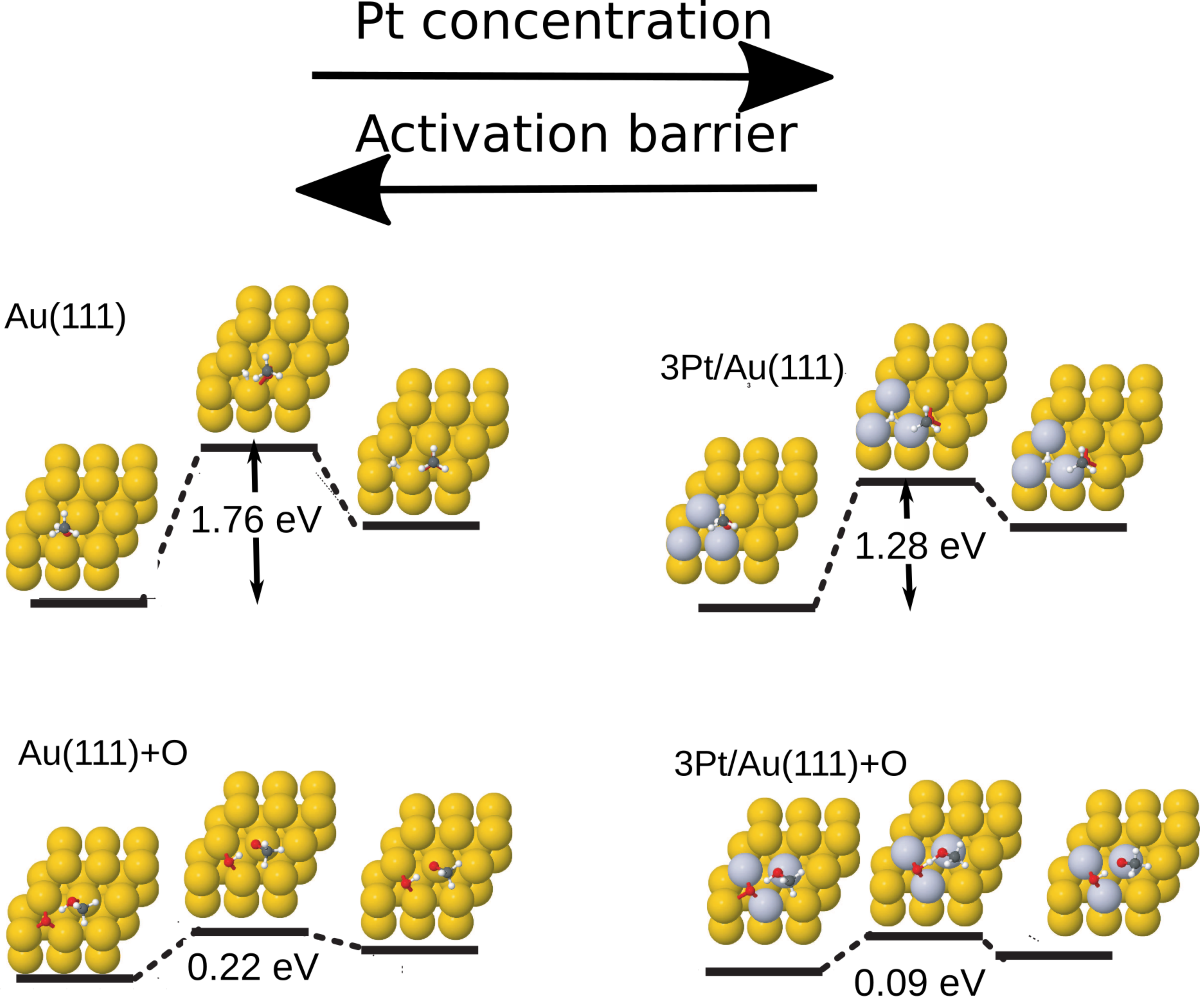
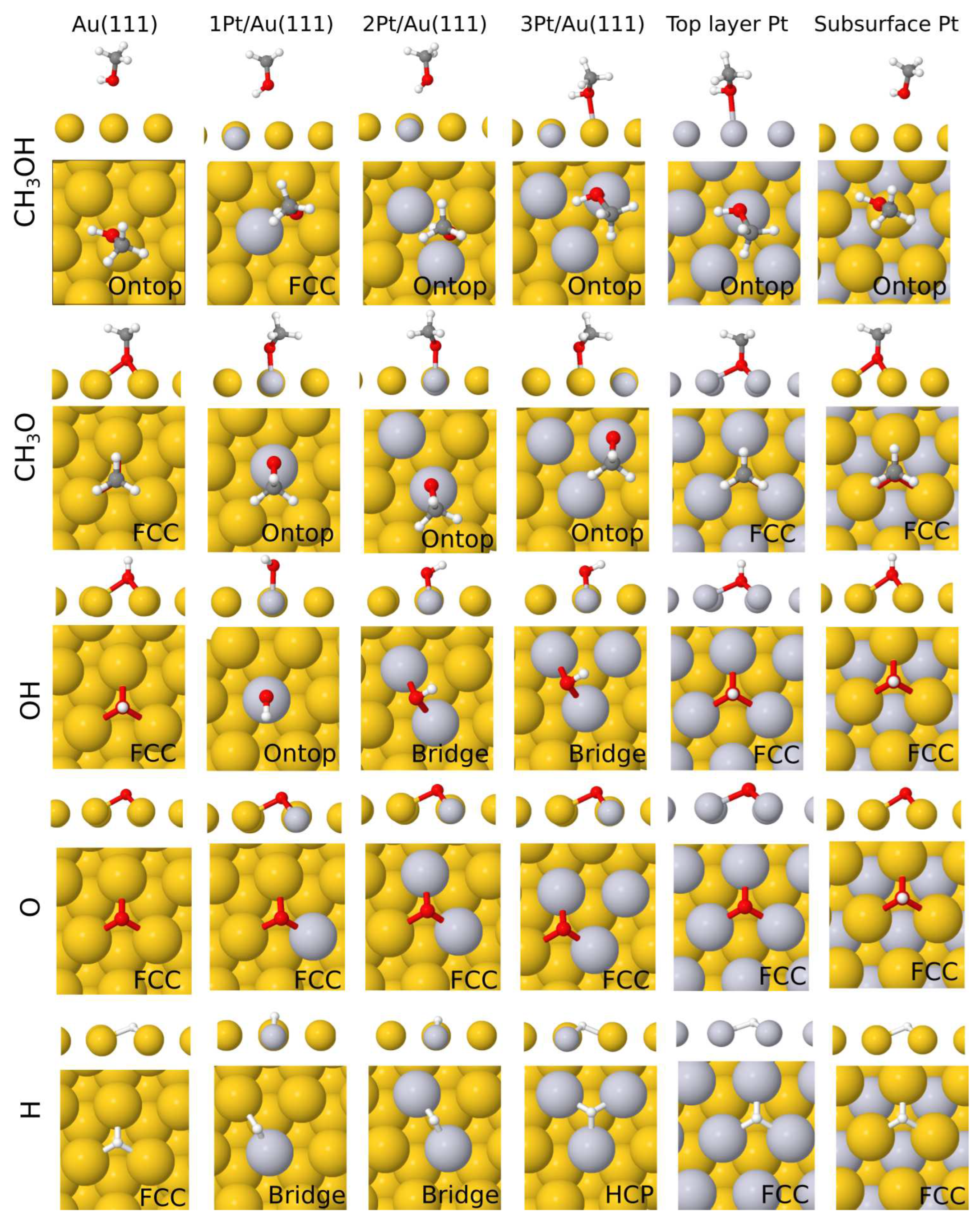
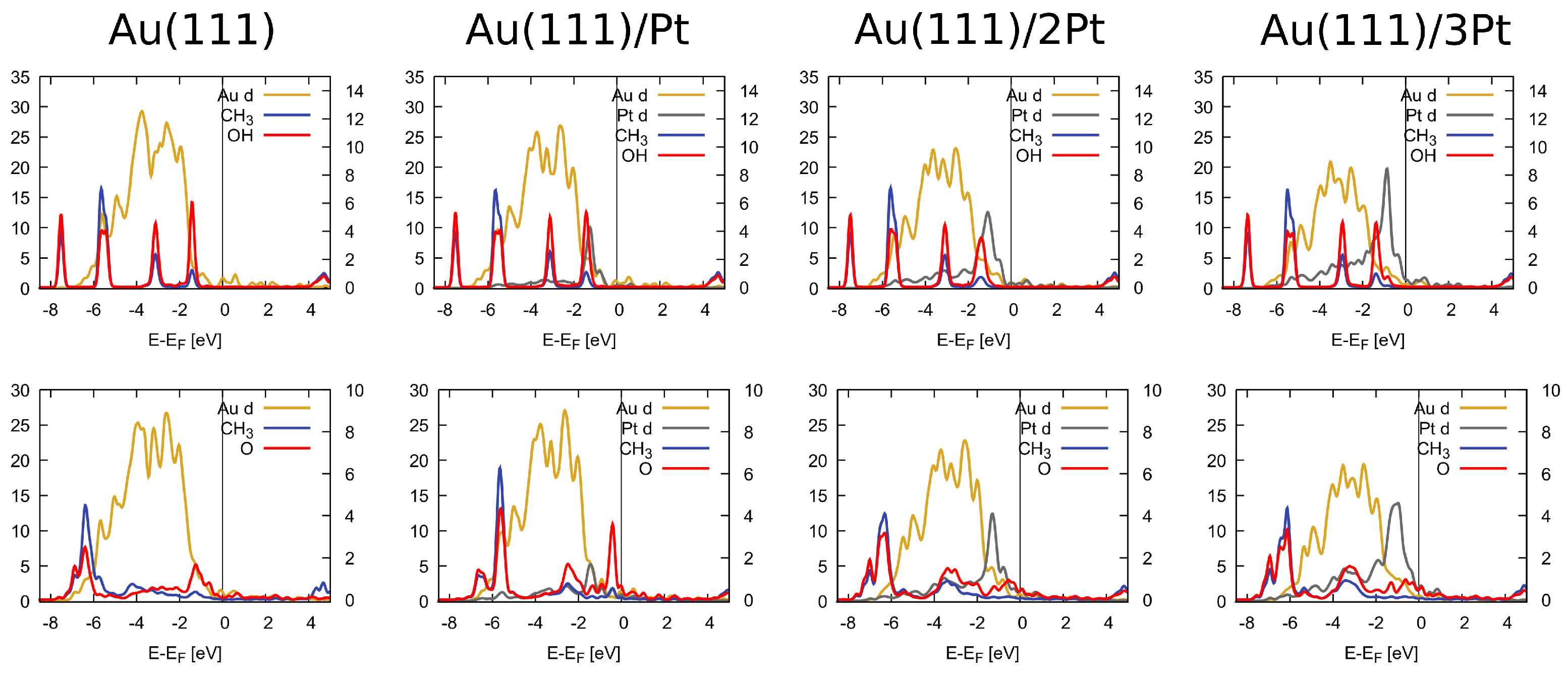
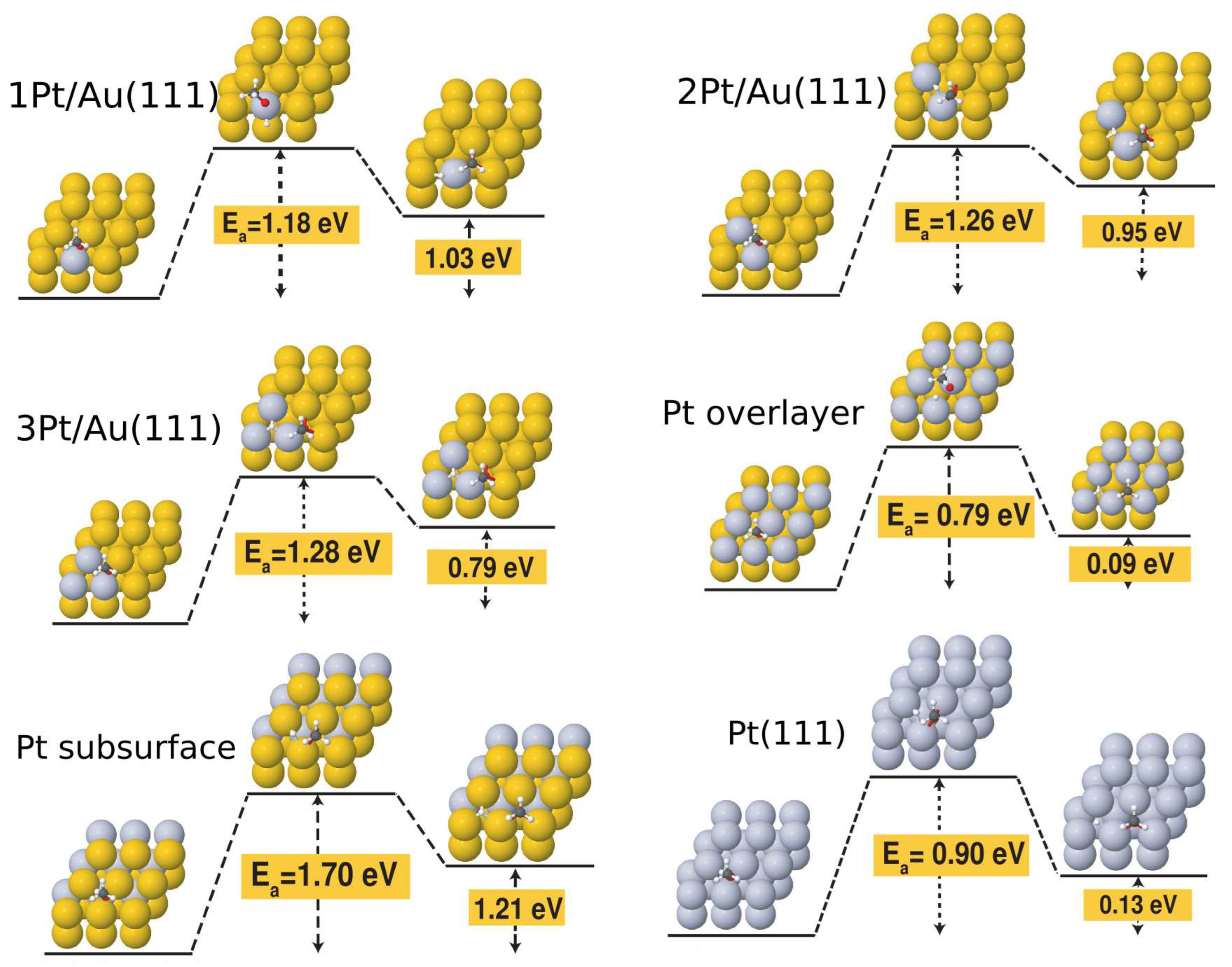
3. Results

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| GGA | Generalized Gradient Approximation |
| PW-91 | Perdew-Wang exchange Correlation potential |
| BFGS | Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno |
| CI-NEB | Climbing Image Nudged Elastic Band method |
| PDOS | Partial Density of States |
| SM | Supplementary Material |
References
- Dijksman, A.; Marino-González, A.; Mairata i Payeras, A.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Sheldon, R.A. Efficient and Selective Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols into Aldehydes and Ketones Using Ruthenium/TEMPO as the Catalytic System. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2001, 123, 6826–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Song, L.; Li, X. An Overview of Selective Oxidation of Alcohols: Catalysts, Oxidants and Reaction Mechanisms. Catalysis Surveys from Asia 2016, 20, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tao, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Small Molecule Alcohols over Pt, Pd, and Au Catalysts: The Effect of Alcohol’s Hydrogen Bond Donation Ability and Molecular Structure Properties. Catalysts 2019, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Fine, N.a.; Lo, C.S. Platinum Nanoclusters Exhibit Enhanced Catalytic Activity for Methane Dehydrogenation. Topics in Catalysis 2012, 55, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; She, Y. Mechanism of methanol decomposition on the Pd/WC(0001) surface unveiled by first-principles calculations. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering 2020, pp. 1–13.
- Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y. Selective Gas-Phase Oxidation of Alcohols over Nanoporous Silver. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y. The mechanism of methanol dehydrogenation on the PdAu(1 0 0) surface: A DFT study. Applied Surface Science 2020, 510, 145434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, Q.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.Q.; Wu, M.; Fu, W.; Tang, Y.; Duan, X.; Chen, D.; Wan, Y. Optimising surface d charge of AuPd nanoalloy catalysts for enhanced catalytic activity. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel Gold Catalysts for the Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide at a Temperature far Below 0 °C. Chemistry Letters 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, O.; Dolcet, P.; Nefedov, A.; Huang, X.; Saraçi, E.; Wöll, C.; Grunwaldt, J.D. The influence of the gold particle size on the catalytic oxidation of 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furfural. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucinska, E.; Pattisson, S.; Miedziak, P.J.; Brett, G.L.; Morgan, D.J.; Sankar, M.; Hutchings, G.J. Cinnamyl Alcohol Oxidation Using Supported Bimetallic Au–Pd Nanoparticles: An Optimization of Metal Ratio and Investigation of the Deactivation Mechanism Under Autoxidation Conditions. Topics in Catalysis 2020, 63, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Chu, Q.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Diao, T.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, M. Double Catalyst-Catalyzed: An Environmentally Friendly Sustainable Process to Produce Methallyl Alcohol. Catalysis Letters 2020, 150, 2660–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, M.T.; Sykes, E.C.H.; Michaelides, A.; Stamatakis, M. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Resistance and Structural Stability of Single Atom Alloys. Topics in Catalysis 2018, 61, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.R.; Yang, X.F.; Long, B.; Li, J. A water-promoted mechanism of alcohol oxidation on a Au(111) surface: Understanding the catalytic behavior of bulk gold. ACS Catalysis 2013, 3, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Yuan, W.; Meng, Y.; Zou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hong, W.; Che, J.; Hao, M.; Ye, B.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Fan, J. A Rational Solid-State Synthesis of Supported Au–Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles with Enhanced Activity for Gas-Phase Selective Oxidation of Alcohols. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2017, 9, 31853–31860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravesh, E.; Melander, M.M.; Wärnå, J.; Salmi, T.; Honkala, K.; Murzin, D.Y. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethanol on gold: Combination of kinetic experiments and computation approach to unravel the reaction mechanism. Journal of Catalysis 2021, 394, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaciara, I.E.; de Sousa, S.A.; Laíse, L.N.; Oliveira, J.M.; Castro, K.P.; Costa, J.C.; de Moura, E.M.; de Moura, C.V.; Garcia, M.A. Au-Pd Selectivity-switchable Alcohol-oxidation Catalyst: Controlling the Duality of the Mechanism using a Multivariate Approach. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 3022–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Akdim, O.; Huang, X.; Wang, K.; Douthwaite, M.; Pattisson, S.; Lewis, R.J.; Lin, R.; Yao, B.; Morgan, D.J.; Shaw, G.; He, Q.; Bethell, D.; McIntosh, S.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Insights into the Effect of Metal Ratio on Cooperative Redox Enhancement Effects over Au- and Pd-Mediated Alcohol Oxidation. ACS Catalysis 2023, 13, 2892–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Henkelman, G. Dehydrogenation Selectivity of Ethanol on Close-Packed Transition Metal Surfaces: A Computational Study of Monometallic, Pd/Au, and Rh/Au Catalysts. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2017, 121, 27504–27510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Veith, G.M.; Prati, L. Bismuth as a modifier of Au–Pd catalyst: Enhancing selectivity in alcohol oxidation by suppressing parallel reaction. Journal of Catalysis 2012, 292, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Liang, J.; Hu, W.; Cao, X.; Jia, C.; Jiang, J. The O, OH and OOH-assisted selective coupling of methanol on Au-Ag(111). Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2016, 18, 9969–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Gál, T.; Srankó, D.; Sáfrán, G.; Maróti, B.; Sajó, I.; Schmidt, F.P.; Beck, A. Selective aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol on alumina supported Au-Ru and Au-Ir catalysts. Molecular Catalysis 2020, 492, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salciccioli, M.; Yu, W.; Barteau, M.A.; Chen, J.G.; Vlachos, D.G. Differentiation of O-H and C-H bond scission mechanisms of ethylene glycol on Pt and Ni/Pt using theory and isotopic labeling experiments. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2011, 133, 7996–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- a Tenney, S.; Shah, S.I.; Yan, H.; a Cagg, B.; Levine, M.S.; Rahman, T.S.; a Chen, D. Methanol Reaction on Pt-Au Clusters on TiO2(110): Methoxy- Induced Diffusion of Pt. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 26998–27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, L.N.; Belskaya, O.B.; Trenikhin, M.V.; Leont’eva, N.N.; Gulyaeva, T.I.; Likholobov, V.A. Effect of Pt(Au)/MgAlOx catalysts composition on their properties in the propane dehydrogenation. Catalysis Today 2021, 378, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Voss, M.R.; Busse, H.; Koel, B.E. Chemisorbed Oxygen on Au(111) Produced by a Novel Route: Reaction in Condensed Films of NO2+H2O. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 1998, 102, 4693–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sha, J.; Sabbe, M.; Sautet, P.; Pera-Titus, M.; Michel, C. Identification of active catalysts for the acceptorless dehydrogenation of alcohols to carbonyls. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Wang, L. Vinyl alcohol formation via catalytic β-dehydrogenation of ethanol on Ir(100). Chemical Physics Impact 2021, 3, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Haubrich, J.; Baker, T.A.; Kaxiras, E.; Friend, C.M. Theoretical Study of O-Assisted Selective Coupling of Methanol on Au(111). The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2011, 115, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Shah, S. MMENT>Computational study of complete methanol dehydrogenation on Au(100) and Au(310) surfaces: Dominant role of atomic oxygen. Surface Science 2014, 620, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; others. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. Journal of physics: Condensed matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Wang, Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy. Physical review B 1992, 45, 13244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokalj, A. Computer graphics and graphical user interfaces as tools in simulations of matter at the atomic scale. Computational Materials Science 2003, 28, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, W.P. Precision Measurements of the Lattice Constants of Twelve Common Metals. Phys. Rev. 1925, 25, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkelman, G.; Uberuaga, B.P.; Jónsson, H. A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths. The Journal of chemical physics 2000, 113, 9901–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2009, 21, 084204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Wu, Z.P.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Role of Ni in Bimetallic PdNi Catalysts for Ethanol Oxidation Reaction. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018, 122, 22448–22459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Haubrich, J.; Baker, T.A.; Kaxiras, E.; Friend, C.M. Theoretical study of O-assisted selective coupling of methanol on Au(111). Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2011, 115, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Au(111) | 1Pt/Au | 2Pt/Au | 3Pt/Au | Pt overlayer | Pt sublayer | |
| CH3OH | -0.11 (o) | -0.12 (fcc) | -0.13 (o) | -0.27 (o) | -0.38 (o) | -0.12 (o) |
| CH3O | -1.75 (fcc) | -1.88 (o) | -1.87 (o) | -1.92 (o) | -2.24 (fcc) | -1.77(fcc) |
| OH | -2.66 (fcc) | -2.73 (o) | -2.80 (b) | -2.82 (b) | -2.65 (fcc) | -2.19(fcc) |
| O | -5.07 (fcc) | -5.24 (fcc) | -5.43 (fcc) | -5.40 (fcc) | -4.67 (fcc) | -3.46(fcc) |
| H | -3.18 (fcc) | -3.46 (b) | -3.74 (b) | -3.84 (hcp) | -3.04 (fcc) | -2.26(fcc) |
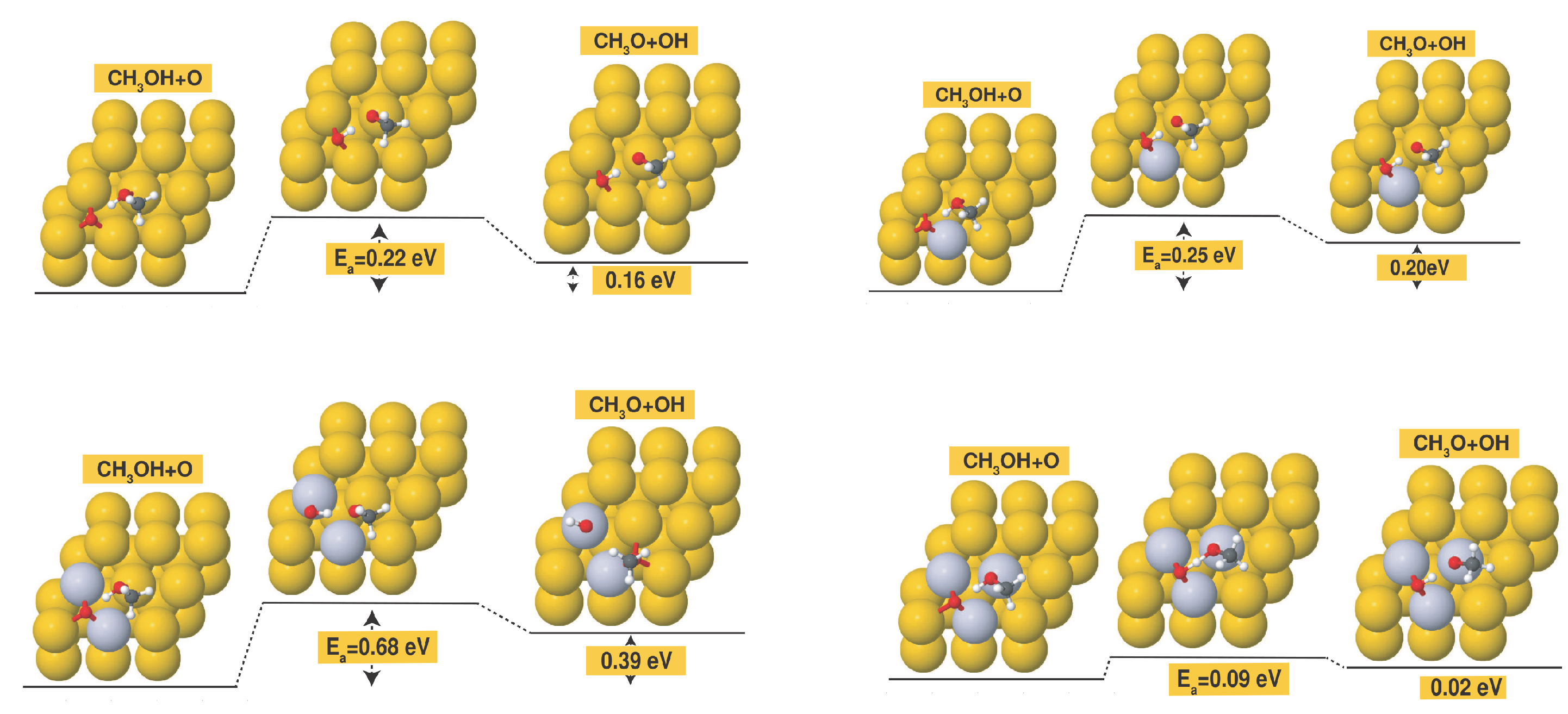
| surface | ||
| Au(111) | 1.76 | 1.34 |
| 1Pt/Au | 1.18 | 1.03 |
| 2Pt/Au | 1.26 | 0.95 |
| 3Pt/Au | 1.28 | 0.79 |
| Pt overlayer | 0.79 | 0.08 |
| Pt sublayer | 1.70 | 1.21 |
| Pt(111)a | 0.90 | 0.13 |
| aat the Au lattice constant. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





