1. Introduction
Portland cement has been used as construction material for nearly two centuries, where the cement is used as binder material in concrete and mortar. However, production of Portland cement represents about 6-8 % of global anthropogenic CO
2 emissions. Therefore, there is a strong interest in finding alternative binder materials that have a significantly lower CO
2 footprint [
1,
2,
3]. One potential alternative to Portland cement is alkali-activated materials (AAM) or “geopolymers”, which have already been used as construction material in several applications [
2,
3,
4].
Alkali-activated materials are completely devoid of Portland cement, resulting in a considerably lower CO
2 footprint, but also having different reaction mechanisms and subsequent strength development. Where Portland cement develops strength during a hydration reaction when cement powder reacts with water and forms C-S-H gel as the main strength providing binder phase, the aluminosilicate precursors of AAM react with an alkaline activator (usually NaOH, KOH, or their silicates) thereby forming other types of strength providing reaction products. The calcium content of the precursors determines in large part which binder phases are formed, where low Ca content leads to the formation of N-A-S-H or K-A-S-H phases and high Ca content leads to the formation of C-A-S-H phases [
5,
6]. Low-calcium alkali-activated materials are often referred to as “geopolymers”. It should be noted that regardless of the Ca content, the precursors of AAMs dissolve into monomeric or small oligomeric Si- and Al-species in the activator solution before the aluminosilicate binder phases precipitate. Therefore, the reactivity of the precursors (i.e., their dissolution potential) is of considerable importance for the subsequent strength development.
In addition to applications as construction material, Portland cement is also commonly used as barrier material during cementing operations of wells for oil & gas production, CO
2 storage, and geothermal energy production [
7,
8,
9,
10]. During well construction, cement is pumped into the annulus outside the steel casing, both to provide support to the steel casing and to ensure zonal isolation in the well. Furthermore, cement is also pumped into wells during plug & abandonment (P&A) operations, to ensure that hydrocarbons and other downhole fluids do not leak into the environment after well abandonment [
7,
11,
12]. There is currently a drive in the research community to find alternative well cementing materials as well, where geopolymers have been suggested as potential candidates [
11,
12,
13]. Several different types of precursor materials have been used to prepare geopolymer well cements, such as fly ash [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19], rock waste [
20,
21,
22], and volcanic ash [
23].
Metakaolin as precursor material during alkali-activation has so far not been widely studied for well cement applications, which could be due to the relatively large water consumption of the platelike metakaolin particles [
24,
25], thereby causing potential slurry viscosity and pumpability issues. However, it has been shown that metakaolin-based geopolymers can have good potential as well cement during steam injection operations, due to their improved mechanical properties [
26], and consequently, there is a need for further studies of mechanical properties and strength development of these materials.
In this study, we have prepared metakaolin-based alkali-activated cements with different Si/Al ratios and different activator concentrations, to determine the resulting effects on compressive strength over time. Furthermore, it is known that minor additions of other, more reactive aluminosilicate precursors that act as a “co-binder” in the slurry can also improve the reactivity and subsequent strength development [
27,
28]. Consequently, two different co-binders were included in the mix design as well.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Two different sources of metakaolin (MK) were used in this study, one type provided by Metacaulim do Brasil and the other type provided by Imerys, denoted “MKB” and “MKF”, respectively.
Table 1 lists the chemical composition of these two metakaolin materials, as provided by their suppliers, as well as appearance and some physical properties. Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBFS) was provided by Swecem, and MicroSilica (MS) was provided by Elkem.
Table 2 lists the chemical composition of GGBFS and MS, as provided by their suppliers. Potassium silicate solution of 1.6 molar ratio and 52 % dry content was provided by Woellner, and a 12 M KOH solution was provided by Solberg. Distilled water was used to dilute the activator solutions to selected concentrations.
2.1. Characterization techniques
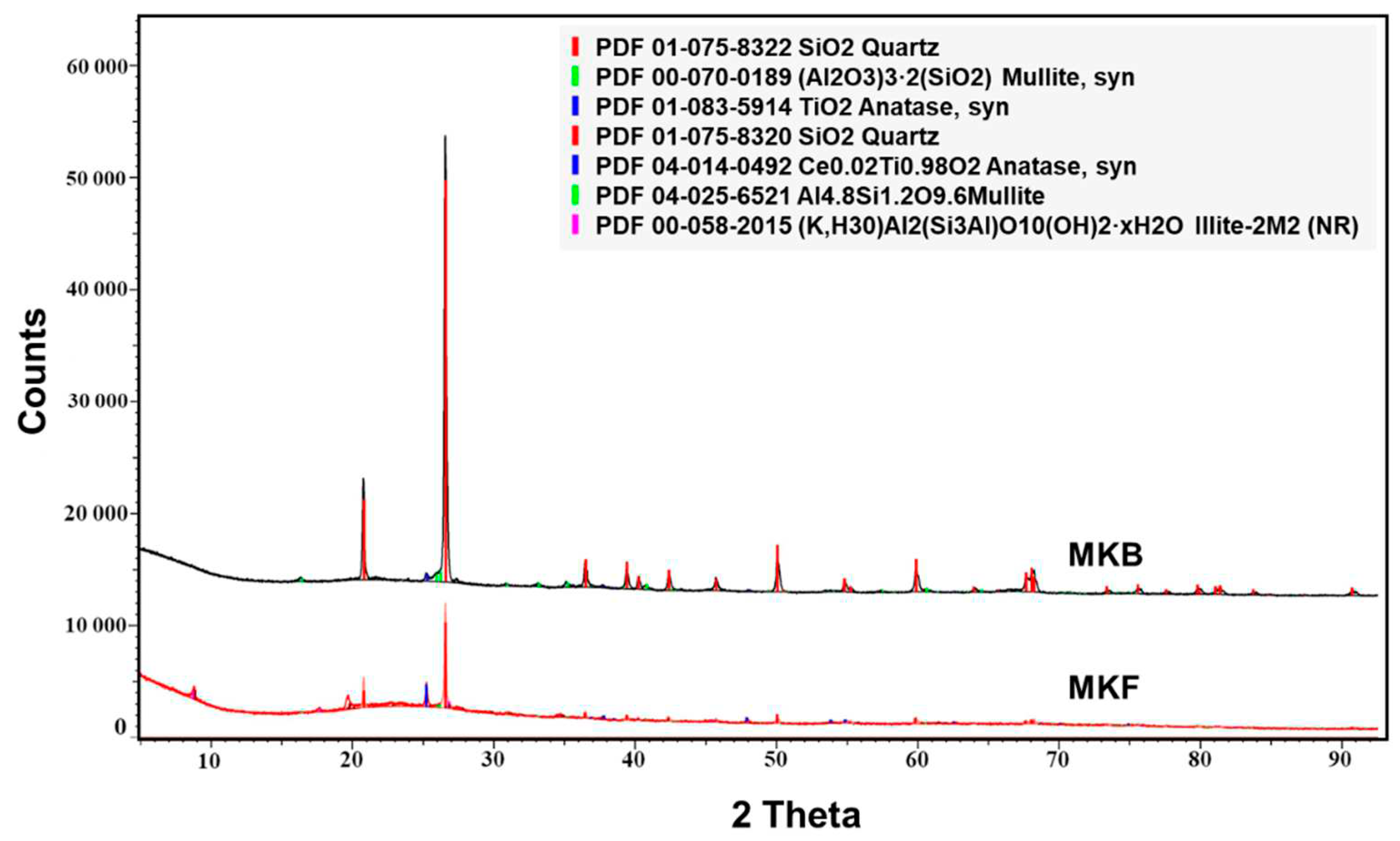
X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) was performed using a Bruker D8 Advance Eco diffractometer equipped with a Lynxeye detector (Cu-Kα radiation, 40 kV voltage, 25 mA current). The X-ray patterns were obtained in the 2Θ range of 5°-90° using a 0.6 mm divergence slit during continuous rotation. Afterwards, the software Diffrac. Eva, implementing the PDF-4+ database from the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD), was employed to identify mineral phases and visualize the data.
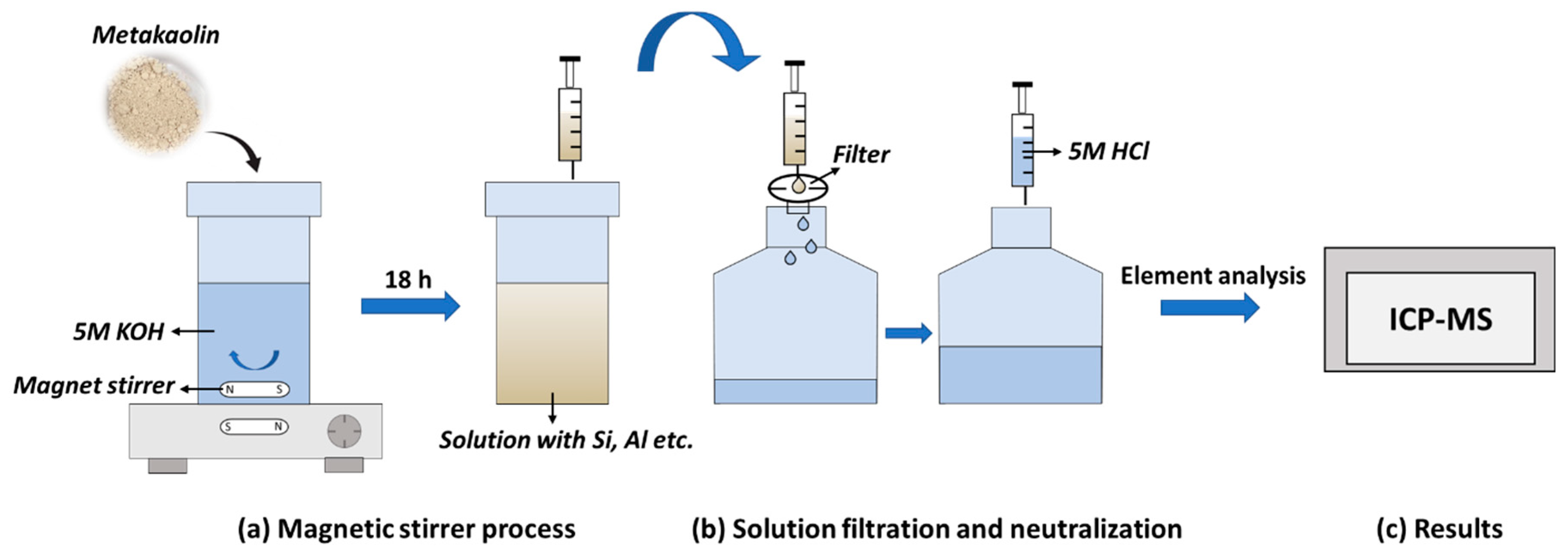
Solubility of Si and Al of metakaolin samples at alkaline conditions was determined by performing dissolution tests based on the following procedure [
29,
30]: 2 g of sample was added to 80 ml of 5 M KOH and stirred for 18 h at room temperature (20 ºC). Subsequently, a suitable amount of the resulting solution was filtrated and neutralized with 5 M HCl, before being sent to elemental analysis (ICP-MS) performed by external provider Eurofins.
Figure 1 illustrates the solubility test procedure.
Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) was measured with a MATEST 300 kN compression machine, with a loading rate of 4000 psi/min according to API guidelines [
31]. Particle size distributions (PSD) were performed at a Mastersizer 3000 instrument from Malvern Panalytical, and rheological properties such as shear stress and shear rate were measured using an OFITE model 900 viscometer. Setting time of cement slurries was determined by the Vicat method [
32].
2.3. Sample preparation
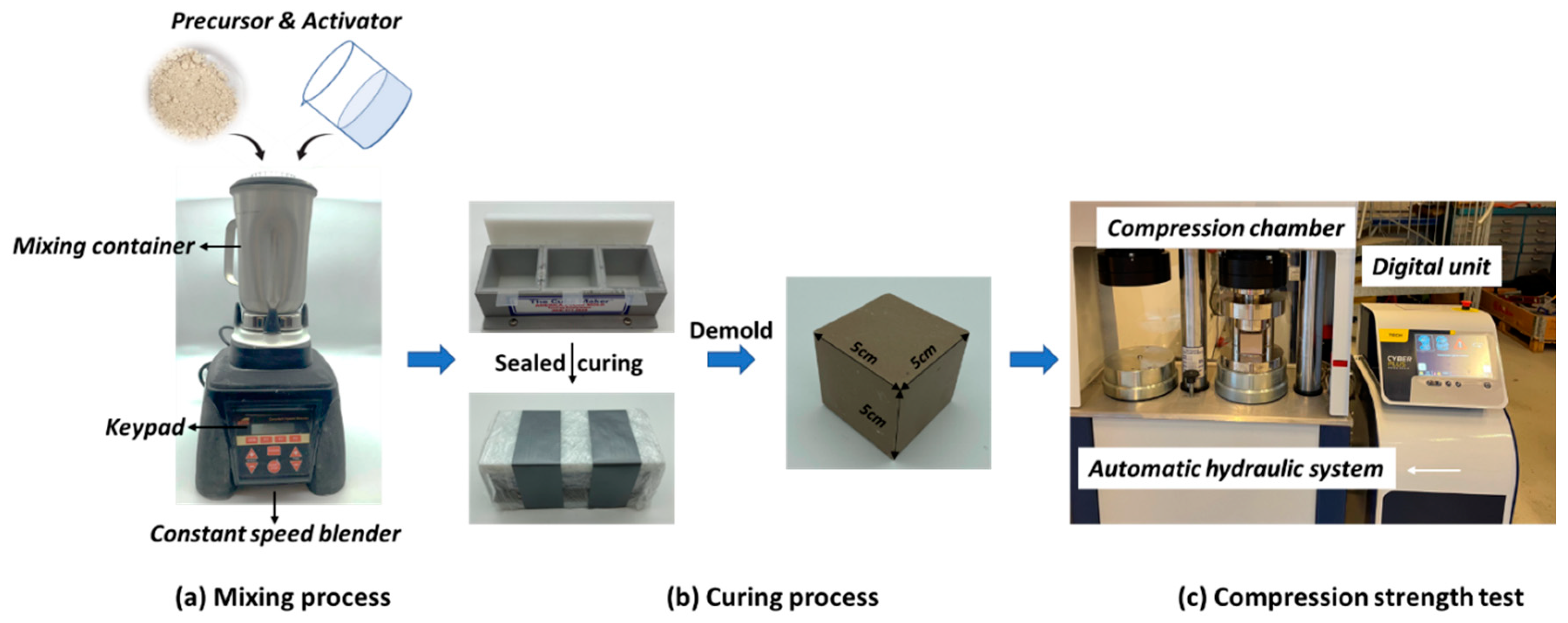
Cement slurries were prepared by mixing suitable amounts of solid precursors with liquid activators, where metakaolin type MKB was used as the main precursor in all experiments, however, MKF and GGBFS were also investigated as co-binders. Samples consisting of both MKB and MKF have been denoted as “Bx Fy”, where x and y is the percentage of MKB and MKF, respectively. Several samples of varying Si/Al ratios were prepared with increasing Si amounts obtained by addition of MicroSilica as well as adjusting the ratio of potassium silicate vs KOH in the activator. Furthermore, several samples of varying KOH concentrations were prepared, where the increased KOH concentration was obtained by adjusting the amount of 12 M KOH vs distilled water in the mixture. All samples were prepared with a solid/water ratio of 0.55.
The cement slurries were mixed in an OFITE’s model 25 constant speed blender according to the mixing procedure described in API 10B-2 [
31], where the solid precursors were added to the liquid activator solution during 15 seconds at 4000 rpm, and the slurry was subsequently mixed at 12 000 rpm for 35 seconds. After mixing, the slurry was poured into 5 cm cubic molds, and cured in sealed conditions at room temperature (20 ºC). It should be noted that 20 ºC is a quite low temperature for most downhole applications, but this temperature was selected as it is relevant for tophole well sections. Room temperature is also relevant for civil engineering applications. The samples were de-molded after 1 day and the cubes were placed in sealed plastic bags and left to cure until designated time for UCS testing. Two parallels were tested for each sample, where the reported results are the average of these two measurements.
Figure 2 illustrates the sample preparation procedure.
3. Results and discussion
3.2. Slurry properties and setting time
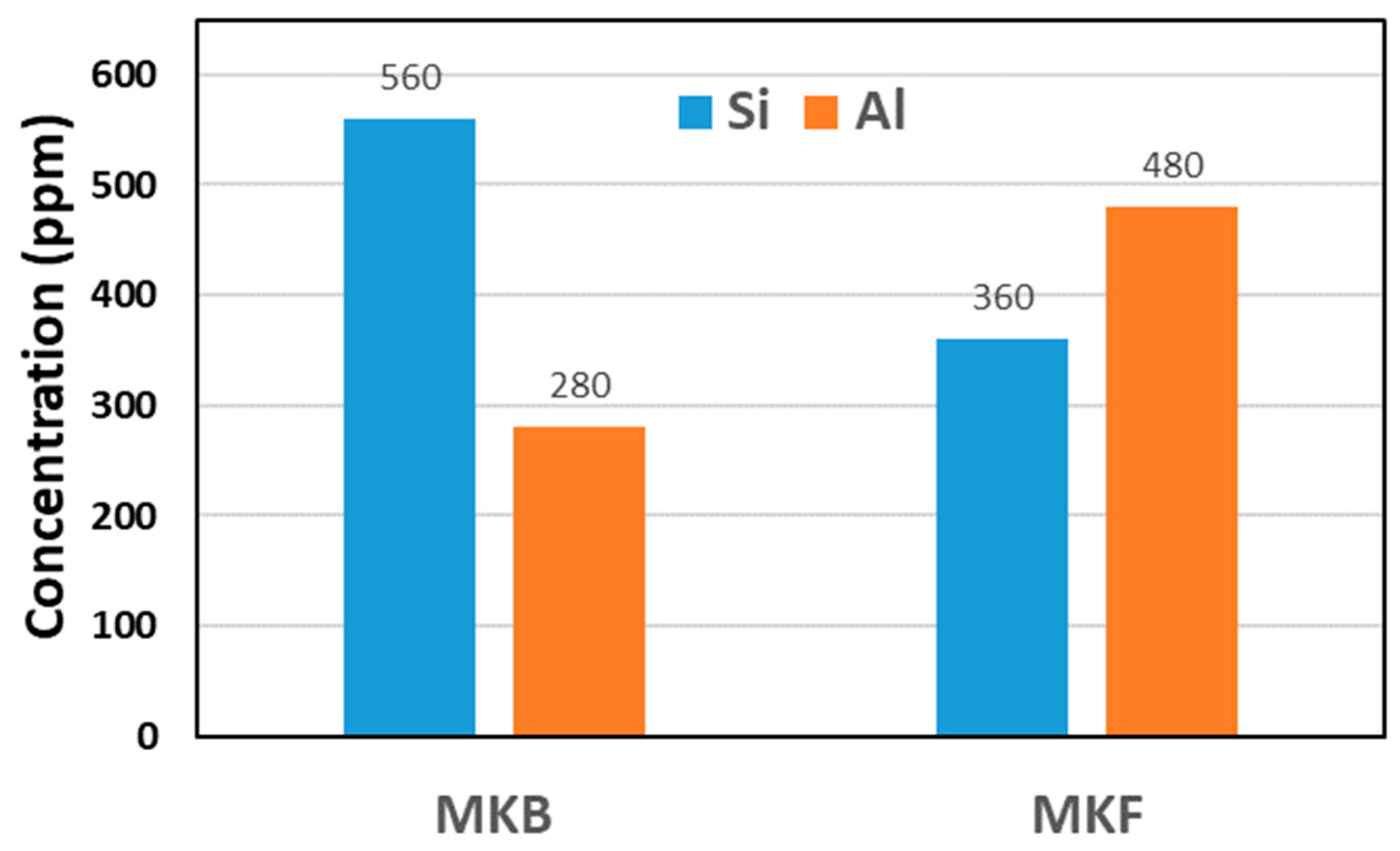
During initial experiments, MKB was found to have a low reactivity towards alkali-activation, i.e., the samples did not set within reasonable time at room temperature when activators were added to MKB as the sole precursor. This low reactivity could be due to the relatively low Al solubility (
Figure 5), as sufficient amounts of dissolved Al and Si are required for geopolymerization reactions to occur [
5,
33]. It has been found for other low-reactive aluminosilicate precursors, such as mine tailings, that the reactivity can be improved by the addition of minor amounts of another, more reactive aluminosilicate precursor that acts as a “co-binder” in the slurry [
27,
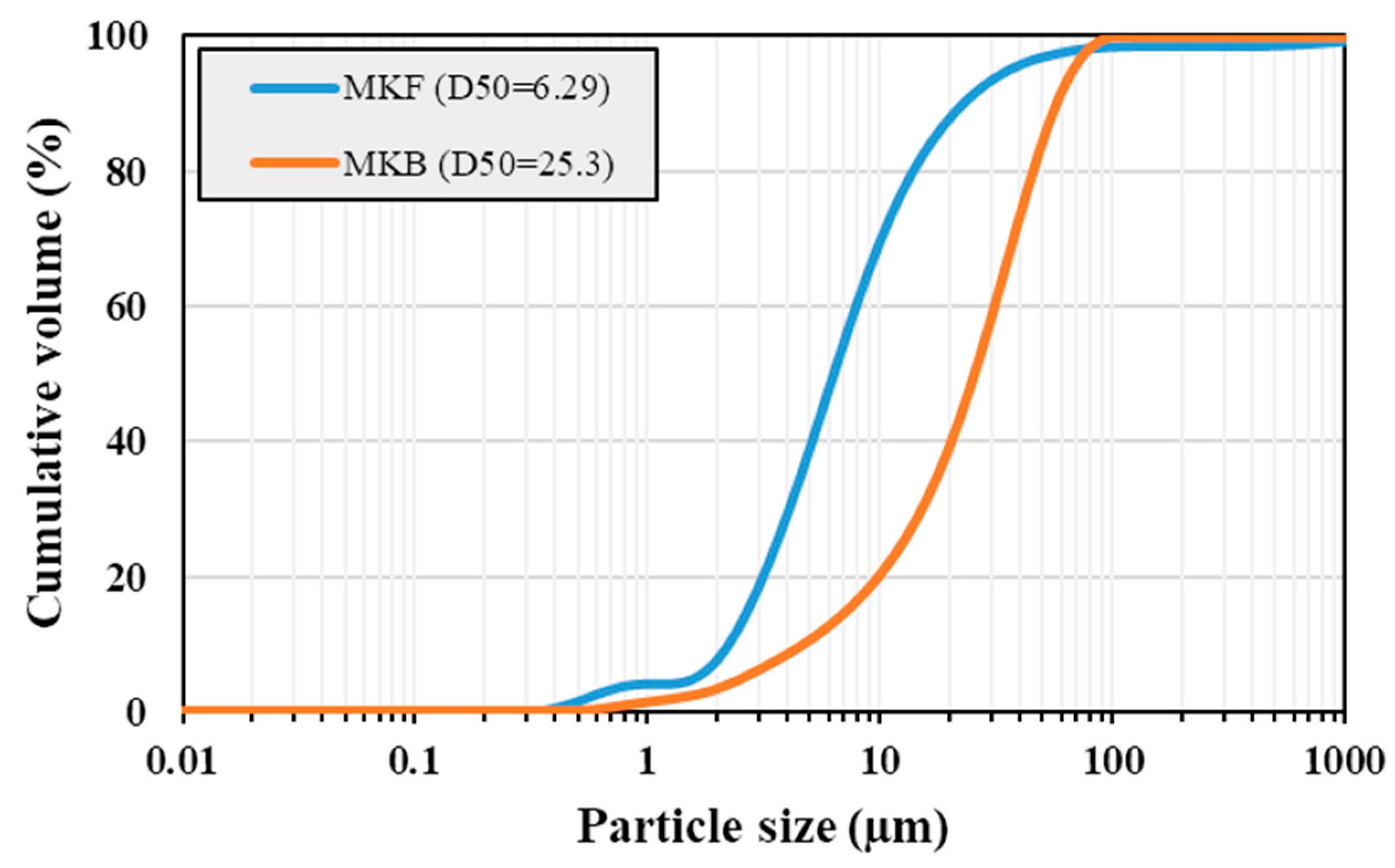
28]. In other words, the co-binder helps to start the geopolymerization reaction, thereby enabling the low-reactive precursor to react as well. Consequently, another metakaolin sample (MKF) was included in the mixture as a co-binder to ensure proper setting of the cement slurry. The MKF sample was expected to be considerably more reactive than MKB, due to its lower particle size (
Figure 4) and higher Al solubility (
Figure 5).
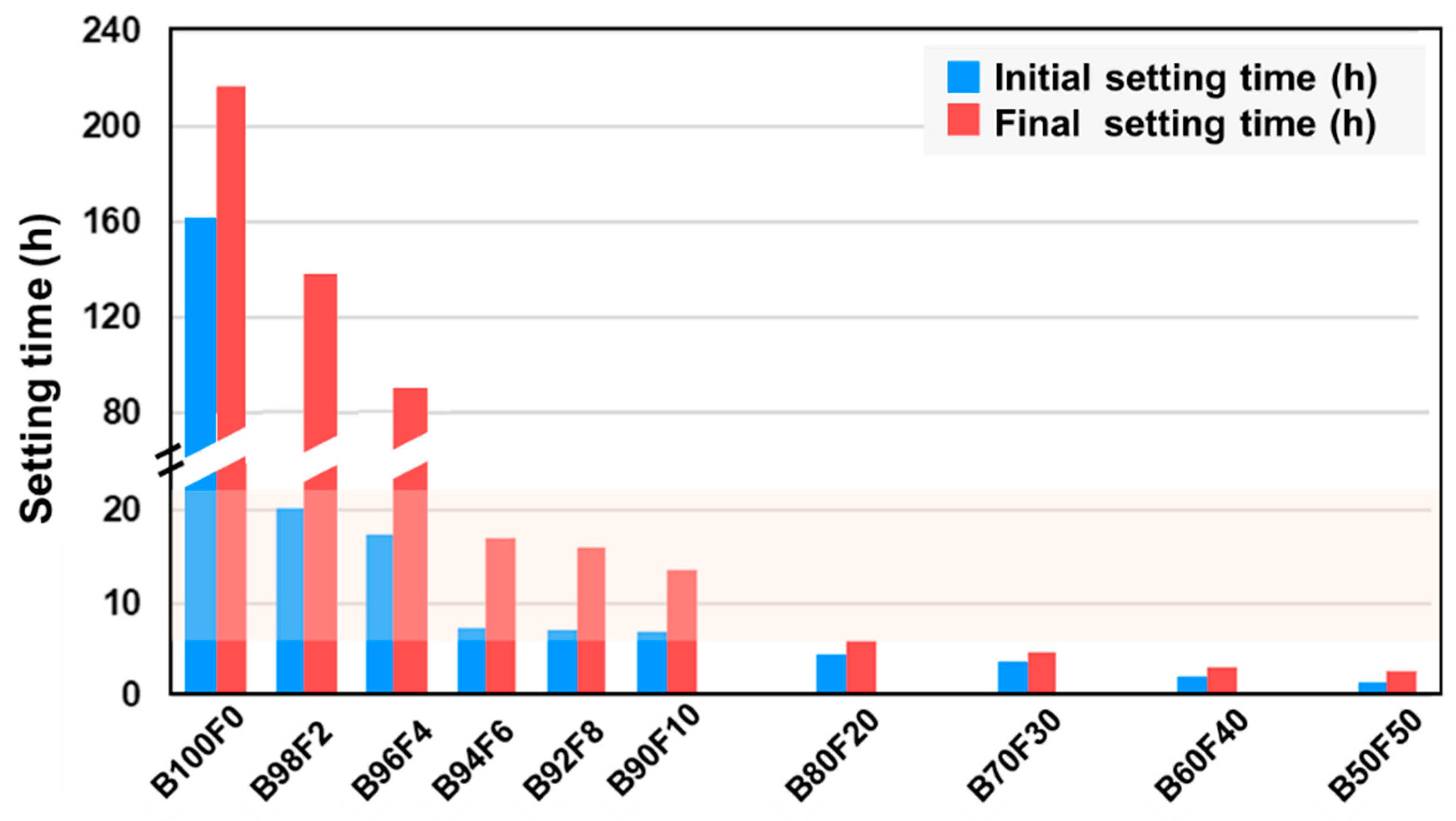
Figure 6 shows the setting times of metakaolin-based cement samples with varying amounts of MKF as co-binder. While it is observed that neat MKB samples set after about a week, the setting time decreases significantly with increasing amounts of MKF as co-binder. Indeed, the addition of at least 6% MKF is needed to ensure a setting time below 24 hours, which is required in order to ensure proper cement placement [
7]. However, although the addition of MKF lead to decreased setting time, the fineness of the MKF particles (
Figure 4) also generated a considerable increase in slurry viscosity.
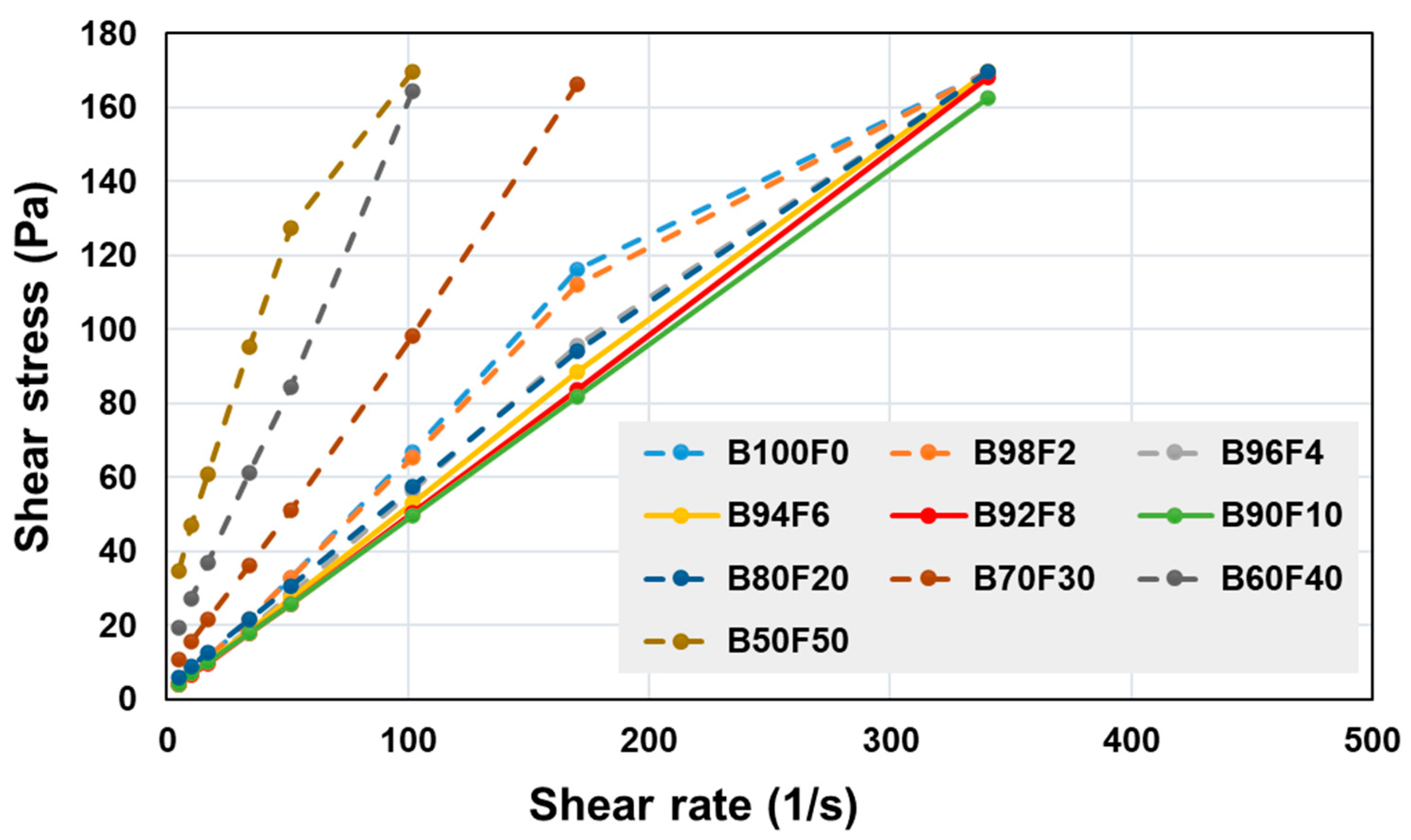
Figure 7 shows the rheology flow curves (shear rate vs. shear stress) for MKB-based slurries with varying amounts of MKF. It is beyond the scope of the present paper to perform a thorough rheological analysis of these slurries, however, a simplified, qualitative assessment can be performed: From the shapes of the flow curves, it can be assumed that the slurries follow a Bingham rheology model [
7]. Consequently, the viscosity of the slurry is determined by slope of the flow curve, where steeper slopes mean higher viscosity. Therefore, it can be seen from
Figure 7 that increasing amounts of MKF in the slurry leads to steeper curves and thereby higher viscosity, which may result in slurry pumpability problems. Nonetheless, at 10% MKF and below, the viscosity is at its lowest for this mix design. Therefore, combined with its sufficiently low setting time (
Figure 6), 10% MKF was added as co-binder in the subsequent strength development tests.
3.3. Strength development with MKF as co-binder
Strength development is perhaps the most important property of cementitious materials, both for well cementing applications and within civil engineering. For geopolymer cements, the strength development of the aluminosilicate gel binder is dependent upon the Si/Al ratio in the mixture [
34,
35,
36], where Si/Al ratios of about 2 is optimal with respect to the obtained compressive strength. As noted above, all samples were based upon MKB as the main precursor, with MKF as a co-binder. The intention of using the more reactive MKF as a co-binder was that it would dissolve quickly and react with the activator to form an initial K-A-S-H gel in the slurry, thereby ensuring setting and sufficient early strength. Furthermore, this initially precipitated K-A-S-H gel should act as nucleation sites for subsequent K-A-S-H gel formation when the less reactive MKB precursor also dissolves.
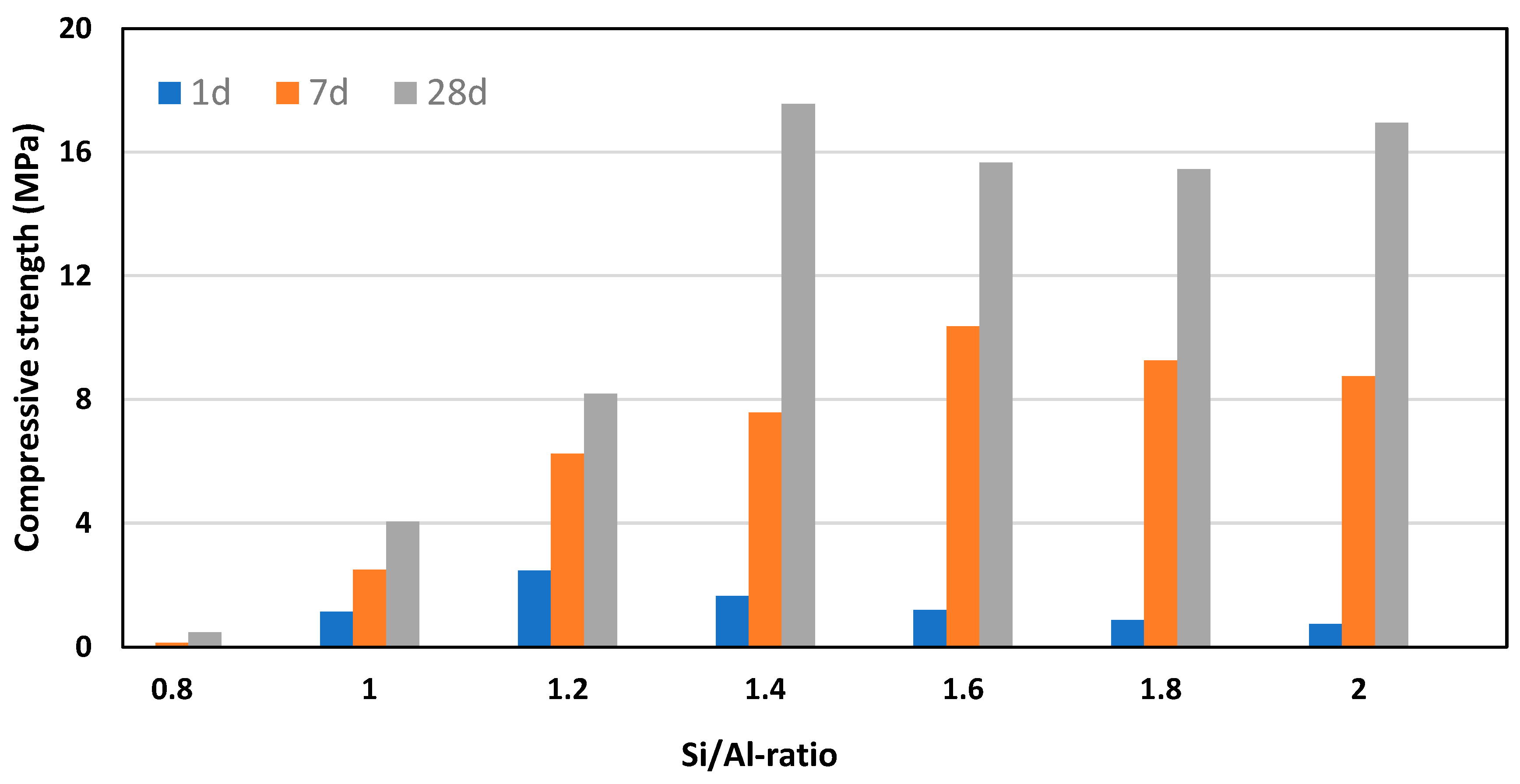
Figure 8 shows the obtained compressive strength after 1, 7, and 28 days curing time for metakaolin-based cement samples with 10 % MKF (B90F10) and varying Si/Al ratios in the mix design. (The KOH concentration was 6.5 M.) It is seen from the figure that although the early strength (1 day) is relatively low, there is a significant increase in strength from 1 day to 7 days, and also from 7 days to 28 days for most of the samples. The early strength is probably caused by K-A-S-H gel precipitation from the co-binder MKF, whereas the delayed strength increase strongly indicates that MKB also reacts and participates in the strength development. This could indicate that the initial K-A-S-H gel acts as nucleation sites for the subsequent geopolymerization of the less reactive MKB precursor.
Moreover, the measured compressive strengths are significantly dependent upon the Si/Al ratio in the slurry. The highest strengths are obtained at Si/Al ratios of 1.4 and above, which is considerably lower than the predicted optimum of 2. However, it should be noted that the calculated Si/Al ratios of the mixtures were based upon the assumption that only the kaolinite parts of the metakaolin samples dissolved, and that the quartz parts remained inert. Whereas the Si solubility results for MKB (
Figure 5) indicate that this assumption is at least partly incorrect. It is likely that the high quartz content in MKB dissolve at least partly over time, thereby increasing the actual Si/Al ratio in the slurry above the simplified, calculated ratios. The actual Si/Al ratio of the samples may therefore be closer to 2 than their denoted values.
In addition to the Si/Al ratio, the activator concentration is also important in influencing the strength development of aluminosilicate cements [
6,
33].
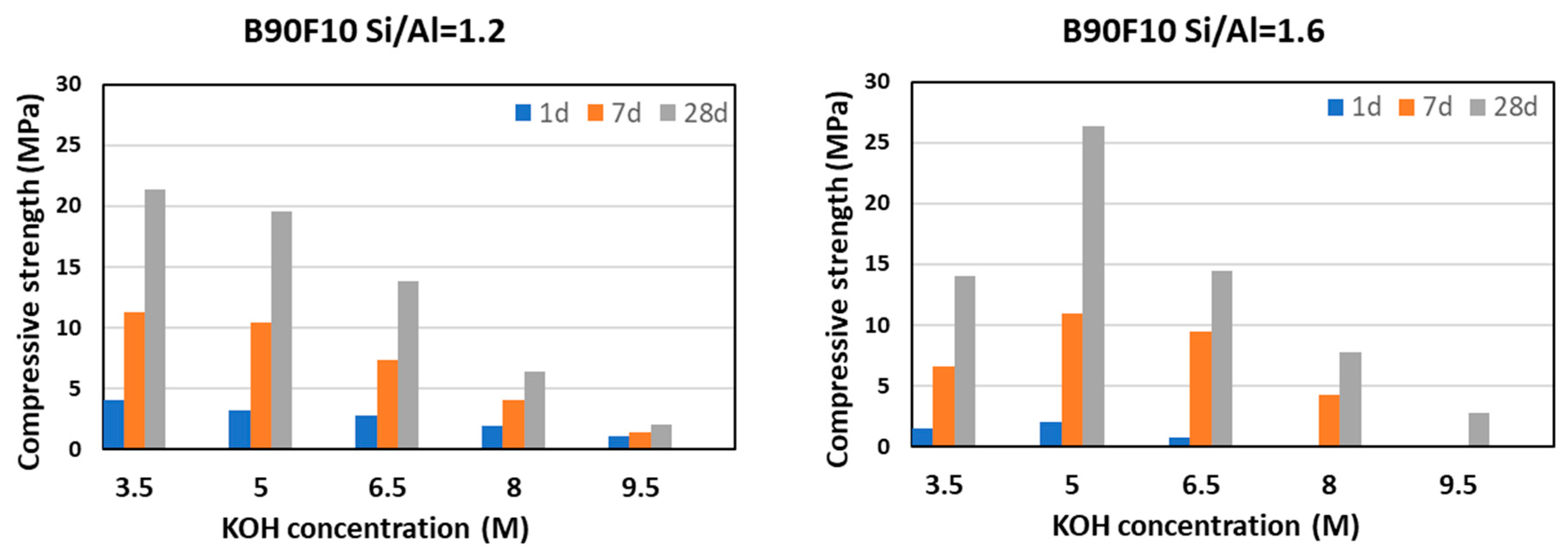
Figure 9 shows the obtained compressive strength after 1, 7, and 28 days curing time for B90F10 cement samples with varying KOH concentrations and Si/Al ratios of both 1.2 and 1.6. The resulting compressive strength is heavily dependent upon the KOH concentration of the activator, where concentrations above 5-6 M leads to lower compressive strengths, possibly due to an increased solubility of the K-A-S-H gel.
Therefore, from these findings it can be concluded that the obtained compressive strength is dependent upon both the Si/Al ratio and the KOH concentration, which leaves considerable room for slurry composition optimization to find the targeted strength.
3.3. Strength development with BFS as co-binder
For comparison, some samples were also prepared with 10% GGBFS as co-binder instead of MKF using otherwise the exact same slurry compositions. Several studies with low-reactive fly ash as a precursor during alkali-activation have shown that the addition of increasing amounts of BFS as co-binder can both decrease setting time and increase compressive strength [
37,
38,
39]. BFS is a high-calcium aluminosilicate precursor that forms C-A-S-H gel during alkali-activation [
5,
6], and it has been shown that this initial C-A-S-H gel can act as nucleation sites for subsequent N-A-S-H gel formation [
38,
39]. Consequently, BFS should function as a co-binder for the low-reactive MKB as well.
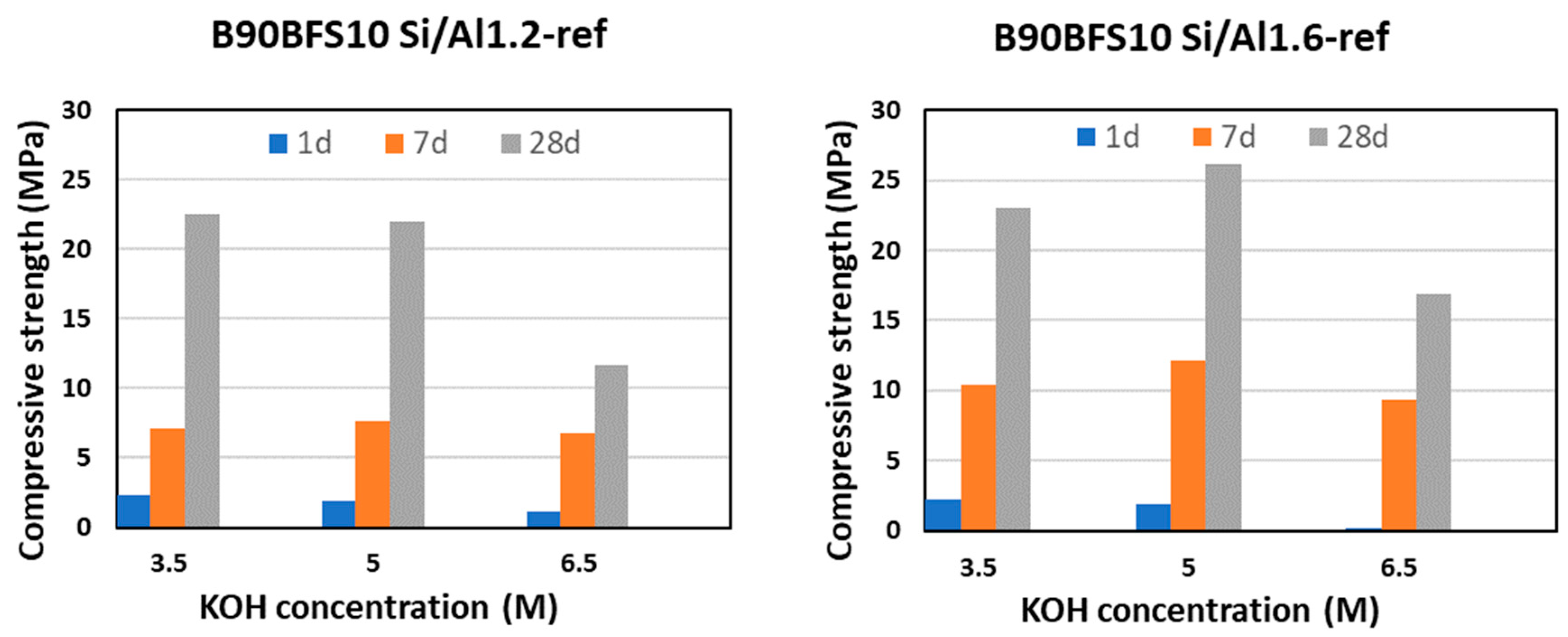
Figure 10 shows the obtained compressive strength after 1, 7, and 28 days curing time for MKB-based cement samples with 10% GGBFS of varying KOH concentrations and Si/Al ratios of 1.2 and 1.6. Here GGBFS also acts well as a co-binder providing some early strength within 1 day due to C-A-S-H gel formation, and then significant subsequent strength increases due to potential K-A-S-H gel formation by the later MKB dissolution. Moreover, although the highest obtained strength with GGBFS as a co-binder is similar to what was observed with MKF as a co-binder, a general trend of somewhat higher compressive strengths at 28 days with BFS as co-binder can be seen for most of the samples. This slightly increased strength may be caused by the presence of Ca
2+ ions in the slurry, as it has been shown that Ca
2+ ions in solution can improve the dissolution of quartz [
40], thereby increasing the amount of dissolved Si from MKB that can contribute to the C-A-S-H or K-A-S-H formation. Consequently, the addition of BFS as co-binder results in both early strength development and increased later strength development as well.
5. Conclusions
The compressive strength of metakaolin-based geopolymer cement depends upon both the Si/Al ratio of the mix design as well as the activator concentration. By varying both of these parameters in a systematic way, it would be possible to optimize the obtained strength. Furthermore, it has also been found in this study that when an initially low reactive metakaolin material is used as precursor, the final reactivity and resulting strength development can be improved by using co-binders. The co-binders ensure early strength development via precipitation of K-A-S-H and C-A-S-H gels, and also by enabling subsequent strength development due to improved dissolution of the low-reactive metakaolin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, TV.; Methodology, BL and TV.; Formal Analysis, BL.; Investigation, BL; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, TV and BL.; Writing – Review & Editing, TV and BL; Visualization, BL and TV; Project Administration, TV.; Funding Acquisition, TV
Funding
This work was performed as a part of the project Development of Environmentally Friendly Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers for Oil Well Cementing and Well Abandonment (MGeo), funded by the Research Council of Norway (grant number: 328733).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank our project partners in Brazil, TECCIM and UFRN, for fruitful discussions throughout the project period
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UN Environment; Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-efficient cements: Potential economically viable solutions for a low-CO2 cement-based materials industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018. 114. 2-26. [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P.; Brice, D.G. Chemical Research and Climate Change as Drivers in the Commercial Adoption of Alkali Activated Materials. Waste Biomass Valor. 2010. 1:145–155. [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P. Technical and commercial progress in the adoption of geopolymer cement. Minerals Eng. 2012. 29, 89–104. [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandian, S.; Chaliasou, A.; Kanellopoulos, A. Recycling mine tailings as precursors for cementitious binders – Methods, challenges and future outlook. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021. 312. 125333. [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Bernal, S.A. Geopolymers and Related Alkali-Activated Materials. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2014. Vol. 44:299-327. 2. [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.; Krivenko, P.; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Kavalerova, E.; Maltseva, O.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. A review on alkaline activation: new analytical perspectives. Mater. Construcc. 2014. 64 [315]. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.B.; Guillot, D. Well Cementing, 2nd ed.; Schlumberger: Sugarland, TX, USA, 2006.
- Carrol, S., Carey, J.W., Dzombak, D., Huerta, N.J., Li, L., Richard, T., Um, W., Walsh, S.D.C., Zhang, L. Review: Role of chemistry, mechanics, and transport on well integrity in CO2 storage environments. Int. J. Green. Gas Contr. 2016. 49, 149-160. [CrossRef]
- Kiran, R., Teodoriu, C., Dadmohammadi, Y., Nygaard, R., Wood, D., Mokhtari, M., Salehi, S. Identification and evaluation of well integrity and causes of failure of well integrity barriers (A review). J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017. 45, 511-526. [CrossRef]
- Vrålstad, T.; Skorpa, R.; Todorovic, J.; Agofack, N.; Hoang, N-H. Cement Sheath Integrity During High Temperature Geothermal Well Operations. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2022 41st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, OMAE2021, June 21-30, 2021, Virtual, Online. 21 June. [CrossRef]
- Vrålstad, T.; Saasen, A.; Fjær, E.; Øia, T.; Ytrehus, J.D.; Khalifeh, M. Plug & abandonment of offshore wells: Ensuring long-term well integrity and cost-efficiency. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 478–491. [CrossRef]
- Chukwuemeka, A.O.; Oluyemi, G.; Mohammed, A.I.; Njuguna, J. Plug and abandonment of oil and gas wells – A comprehensive review of regulations, practices, and related impact of materials selection. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023. 226, 211718. [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Saasen, A.; Hodne, H.; Godøy, R.; Vrålstad, T. Geopolymers as an Alternative for Oil Well Cementing Applications: A Review of Advantages and Concerns. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2018, 140, 092801. [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Saasen, A.; Vralstad, T.; Hodne, H. Potential utilization of class C fly ash-based geopolymer in oil well cementing operations. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014. vol. 53, pp. 10-17. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Khattak, M.J.; Rizvi, H.; Karbalaei, S.F.; Kiran, R. Sensitivity analysis of fly ash geopolymer cement slurries: Implications for oil and gas wells cementing applications. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 37, 116–125. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Khattak, J.; Saleh, F.K.; Igbojekwe, S. Investigation of mix design and properties of geopolymers for application as wellbore cement. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 178, 133–139. [CrossRef]
- van Oort, E.; Juenger, M.; Liu, X.; McDonald, M. Silicate-Activated Geopolymer Alternatives to Portland Cement for Thermal Well Integrity. Society of Petroleum Engineers. In Proceedings of the SPE Thermal Well Integrity and Design Symposium, Banff, AB, Canada, 17 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.H.A.; Medvedev, A.; Yakovlev, A.; Sazali, Y.A; Jain, B.; Hassan, N.; Thompson, C. Development of New Geopolymer-Based System for Challenging Well Conditions. In: Proceedings of International Petroleum Technology Conference held virtually on 23 March - 1 April 2021. [CrossRef]
- Horan, C.; Genedy, M.; Juenger, M.; van Oort, E. Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers as Lower Carbon Footprint Alternatives to Portland Cement for Well Cementing Applications. Energies. 2022, 15, 8819. [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Saasen, A.; Hodne, H.; Motra, H.B. Laboratory evaluation of rock-based geopolymers for zonal isolation and permanent P&A applications. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 352–362. [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Khalifeh, M.; Saasen, A.; Godøy, R.; Delabroy, L. Alternative setting materials for primary cementing and zonal isolation – Laboratory evaluation of rheological and mechanical properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021. 201, 108455. [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Hjelm, S.; Khalifeh, M.; Salehi, S. Synthesis of sustainable one-part geopolymers for well cementing applications. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023. 227. 211822. [CrossRef]
- Alanqari, K.; Al-Yami, A.; Wagle, V. Development of a Geopolymer Cement for Primary Well Cementing: Method, Preparation and Particle Size Effect on Reaction Reactivity. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2022 41st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, OMAE2022, June 5-10, 2022, Hamburg, Germany. [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The role of particle technology in developing sustainable construction materials. Adv. Powder Technol. 2010. 21, 2-7. [CrossRef]
- Derkani, M.H., Bartlett, N.J., Koma, G., Carter, L.A., Geddes, D.A., Provis, J.L., Walkley, B. Mechanisms of dispersion of metakaolin particles via adsorption of sodium naphthalene sulfonate formaldehyde polymer. J.Colliod.Inter.Sci. 2023. 628, 745-757. [CrossRef]
- Paiva, M.D.M., Silva, E.C.C.M., Melo, D.M.A., Martinelli, A.E., Schneider, J.F. A geopolymer cementing system for oil wells subject to steam injection. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018. 748-759. [CrossRef]
- Tchadjie, L.N., Ekolu, S.O. Enhancing the reactivity of aluminosilicate materials toward geopolymer synthesis. J Mater Sci. 2018. 53:4709–4733. [CrossRef]
- Kiventerä, J., Perumal, P., Yliniemi, J., Illikainen, M. Mine tailings as a raw material in alkali activation: A review. Int. J. Miner, Metallur. Mater. 2020. 28 (8), 1009-1020. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H., van Deventer, J.S.J. The geopolymerisation of alumino-silicate minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000. 59, 247–266. [CrossRef]
- Wei, B., Zhang, Y., Bao, S. Preparation of geopolymers from vanadium tailings by mechanical activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017. 145. 236-242. [CrossRef]
- API 10B-2. Recommended Practice for Testing Well Cements. 2018.
- EN-196-3:2016. Methods for testing cement. Part 3: Determination of setting times and soundness.
- Duxson, P., Fernández-Jiménez, A., Provis, J. L., Lukey, G. C., Palomo, A., van Deventer, J. S. J. Geopolymer Technology: The Current State of the Art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007. 42(9), 2917–2933. [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties Colloids Surf. A. 2005, 269, 47-58. [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Lukey, G.C; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The effect of alkali and Si/Al ratio on the development of mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A. 2007. 292, 8-20. [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, M.; Fu, S.; Jia, D.; Yan, S.; Yuan, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou. Y. Effects of Si/Al ratio on the structure and properties of metakaolin based geopolymer. Ceramics International. 2016. 42, 14416–14422. [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Alonso, S.; Vázquez, T. Alkali-activated fly ash/slag cement - Strength behaviour and hydration products. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000. 30. 1625-1632. [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.K.; Lukey, G.C.; Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Effect of calcium silicate sources on geopolymerisation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008. 38. 554-564. [CrossRef]
- Puligilla, S.; Mondal, P. Role of slag in microstructural development and hardening of fly ash-slag geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013. 43. 70-80. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Lothenbach, B.; Shakoorioskooie, M.; Scrivener, K. Effect of different ions on dissolution rates of silica and feldspars at high pH. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022. 152. 106644. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).