1. Introduction
1.1. Burnout Syndrome
Burnout is one of the most studied psychosocial syndromes in the workplace in recent years, typically shouldered by service professionals. Its best known and most studied definition includes three degenerative dimensions. The first is that of Psychophysical Exhaustion of the operator. The second is that of Depersonalization (or Cynicism) towards users and colleagues. The third and final stage is the reduction of Professional Effectiveness [
1,
2].
Originally, burnout was defined as a form of work overload that can afflict so-called helping professionals, in which the main source of stress is dealing with people either in distress or in need of help [
2,
3,
4]. Over the past 2 decades, burnout has been framed as an organizational pathology in the broader field of services (thus relating not only to the helping professions), within the Job Demands-Resources (JD-R) model of stress [
2,
5]. According to this definition of the syndrome, which is more appropriately named Job burnout, job demands (e.g., time pressure, an inadequate physical environment, or excessive workload) and job resources (e.g., having control over one’s work, being able to participate in decisions, perceiving support from the organization) are present in organizational contexts. According to the JD-R model, job burnout is the outcome of the unfavourable combination of excessive demands and insufficient job resources. This dynamic results in the attrition and depletion of mental and physical resources, job disengagement, and negative symptoms and consequences to mental health (cognitive and emotional), physical health, work motivation, the quality of workers’ interpersonal relationships, business performance, and productivity [
4].
In the broader framework of the JD-R Theory of organizational well-being [
6,
7], Job burnout is the “dark side” of Work engagement. The latter can be defined as a positive and fulfilling work-related state of mind (cognitive and affective) [
8,
9], characterized by three dimensions [
10,
11,
12]. Vigor consists of high mental energy and resilience during work. Dedication is connoted by attribution of meaning, inspiration, and pride in one’s work. Finally, Absorption concerns being completely and happily focused on one’s work. Work engagement and Job burnout, in the JD-R Theory, are considered opposing constructs, as these counter-polarities are identifiable: Vigor vs Exhaustion, Dedication vs Cynicism, and Absorption vs Professional ineffectiveness [
10,
12,
13,
14,
15].
Recently, Burnout syndrome has been included – as a nonmedical condition – in the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) [
3,
16], and its definition basically adheres to that of a three-dimensional model originally formulated by Maslach and colleagues [
1,
2,
5]. The symptoms and consequences of Burnout syndrome most frequently found in the literature can also be traced back to the three stages previously described. Psychophysical exhaustion involves a collapse of personal energy and resources, with symptoms related to anxious-depressive states: resistance to engage in work activity, apathy, demoralization, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, mood alterations, feelings of inadequacy, guilt, and a sense of frustration and failure [
17]. In depersonalization (or cynicism), there is a drastic decrease in work motivation and commitment. In addition, emotional detachment from work, hostility toward colleagues and patients, and pessimism are found [
18]. Finally, professional ineffectiveness is marked by a sharp decline in self-esteem, distrust in one’s abilities and resources, and feelings of inadequacy toward work [
19].
1.2. Burnout in Healthcare
Regarding the healthcare context specifically, several studies [
20,
21,
22] have highlighted the importance of Job burnout in organizational processes in which healthcare workers are called upon to manage work commitments and demands. For example, in a study of physicians and nurses in intensive care units [
23], mental and physical exhaustion due to excessive work demands was highlighted, with the ability of work engagement to counteract it and promote job satisfaction. Another study, a longitudinal design conducted on dentists [
13], found the depressive symptoms associated with burnout and the ability of work engagement to counteract burnout and promote the life satisfaction of healthcare workers.
Studies conducted during the recent Covid-19 pandemic, which is known to have put considerable strain on healthcare workers worldwide, have highlighted several facets of burnout. For example, Poelmann et al. [
24] found a significant increase in burnout in a sample of healthcare workers in a surgical setting due to the pandemic. Conversely, Liu and colleagues [
25] showed that the work engagement of medical staff in an intensive care unit, who had to care for Covid-19 patients in critical situations, was negatively affected by their perception of the strength of the virus. In a recent meta-analysis involving 29 studies (including a total of more than 16,000 subjects) on the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on healthcare professionals in emergency departments [
26], higher levels of burnout emerged in all investigated dimensions (Emotional exhaustion, Depersonalization, and Professional inefficiency) than those recorded before the pandemic. In particular, a higher level of burnout was shown among nurses than among physicians.
Other systematic reviews of empirical studies on burnout have documented a high prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression among frontline health workers who cared for Covid-19 patients, particularly among physicians. For example, Salari et al. [
27] indicated the need for regular mental health monitoring, interventions, and preventive education on the topic of burnout, in order to avoid delayed diagnoses and long-term impacts on the well-being of healthcare workers. In addition, the stigma associated with Covid-19 patient care can significantly increase physicians’ burnout compared to other groups of healthcare workers [
28]. Another study [
29] of U.S. healthcare workers (nurses, physicians, and social workers with a sample size of more than 20,000), revealed considerable stress and burnout, especially among women and racial/ethnic minority employees. Anxiety, depression, and work overload correlated with higher rates of stress and burnout. This study also found that workers who felt valued reported lower levels of stress. Similar findings have emerged from other studies [
30] that highlighted the positive role of social support and Psychological Capital [
31] in counteracting worker burnout.
In the Italian context, too, the pandemic placed exceptional demands on healthcare workers. During the first outbreaks, these triggered elevated levels of work-related stress and emotional exhaustion, markedly higher than the values found in pre-pandemic studies. For example, Barello and colleagues [
32] (with a sample of about 1,200 Italian healthcare professionals), highlighted that emotional distress led to worse patient care and to long-term health consequences for professionals. However, Italian healthcare professionals who derived gratification from their service during the pandemic crisis experienced a smaller negative impact on their own mental health.
1.3. Fulfilment, Disillusion, and Burnout in Healthcare
Several authors [
33,
34,
35] have taken up and reiterated the importance of the self-actualizing, values, and vocational aspects of work with respect to burnout. Specifically, on the negative side of distress, a failure to fulfil one’s expectation of one’s work motivations and values can lead workers into a condition of disillusion. This dimension of burnout was originally present in the defining models of Edelwich and Brodsky [
36] and Pines et al. [
37] and has been operationalized (and made measurable) by Santinello and colleagues [
33] and taken up in some recent studies [
35,
38,
39,
40]. On the positive side of job well-being, at the opposite end of the spectrum, fulfilment is an important dimension of work engagement, distinct from job satisfaction. According to several authors [
41,
42], the term fulfilment describes the sense of engagement and eudemonic gratification. In fact, while the term satisfaction refers to a condition of sufficiency, fulfilment implies completion and the full realization of a worker’s potential, in reference to and consistent with the person’s expectations, values, and personal existential motivations. The two considered dimensions, therefore – disillusion (in the negative sense) and fulfilment (in the positive sense) – emphasize the importance of the meaning that work has for the person in society and for their very existence.
In healthcare, several scholars have emphasized the importance of values, motivations, and satisfaction of job expectations in relation to Burnout syndrome [
43,
44]. Some of the most well-known vocational motivational drivers for fulfilment of healthcare workers found in the literature include: being able to help others, contributing to the betterment of society, empathy for the suffering of others, having the opportunity to do useful work for others, having had other healthcare workers in the family, or other people to look up to as role models [
45,
46,
47,
48].
Nonnis et al. [
35], in a study conducted with a sample of Italian nurses, pointed out that working excessively (one of the two defining dimensions of workaholism [
49]), in addition to exhausting their psychophysical resources, forced the nurses to focus on the more contingent, urgent, and practical matters of their work, and deteriorated and could undermine the vocational ideals that drove them to the healthcare profession, leading them to experience disillusion.
Concerning the Covid-19 period, Martínez-López and colleagues [
50], studying healthcare workers in Spain in facilities for the elderly, highlighted the importance of fulfilment for counteracting burnout and for the sustainability of the work environment. Jung et al. [
51] highlighted the relationship between workload and burnout on the one hand, and work engagement and fulfilment on the other hand, in a sample of (approximately 1,000) Danish healthcare workers. Lyubarova and colleagues [
52], through a literature review, highlighted the gender differences present in the relationship between fulfilment and burnout, workload, and organizational task complexity. In healthcare, therefore, disillusion and its “bright side” – represented by fulfilment – are important motivational, vocational, and value dimensions related to the job satisfaction of healthcare workers. However, the literature on this issue, in such a sensitive and socially relevant work domain, is scarce.
1.4. Satisfaction With a Career in Healthcare
According to a classic definition, Job satisfaction is related to the dimension of pleasure that arises from the accomplishment of something coveted [
53]. Even in healthcare settings, job satisfaction involves two components: expectations and perceived performance. Expectations are based on declarations from peers, colleagues, and the organization to which one belongs [
54]. Thus, job satisfaction is a condition in which expectations have been met with respect to the perceptions that healthcare professionals have of their work context, and it implies a positive attitude of the working professional and the sincerity and credibility of their healthcare organization.
More specifically, a healthcare worker’s satisfaction with their career is one component of job satisfaction that refers to their career trajectory and their overall satisfaction with the quality of their chosen career path and its relationship to the quality of their overall life [
55]. Career satisfaction represents the health worker’s attitude toward their chosen profession, which is derived from their long-term sedimented work experiences related to their career choices.
Several studies have investigated the job satisfaction of health workers in relation to burnout before the pandemic [
56,
57] and during and after [
58,
59], but few have investigated the relationship between burnout and career satisfaction among healthcare workers. Kuhn et al. [
60] found that among physicians in emergency medicine, those who self-reported high scores on the emotional exhaustion dimension were also less satisfied with their career choice. To the best of our knowledge, however, there were no studies in the literature on the effects of disillusion (and its opposite, fulfilment) on the relationship between burnout and the career satisfaction of healthcare workers.
1.5. Aim and Hypotheses
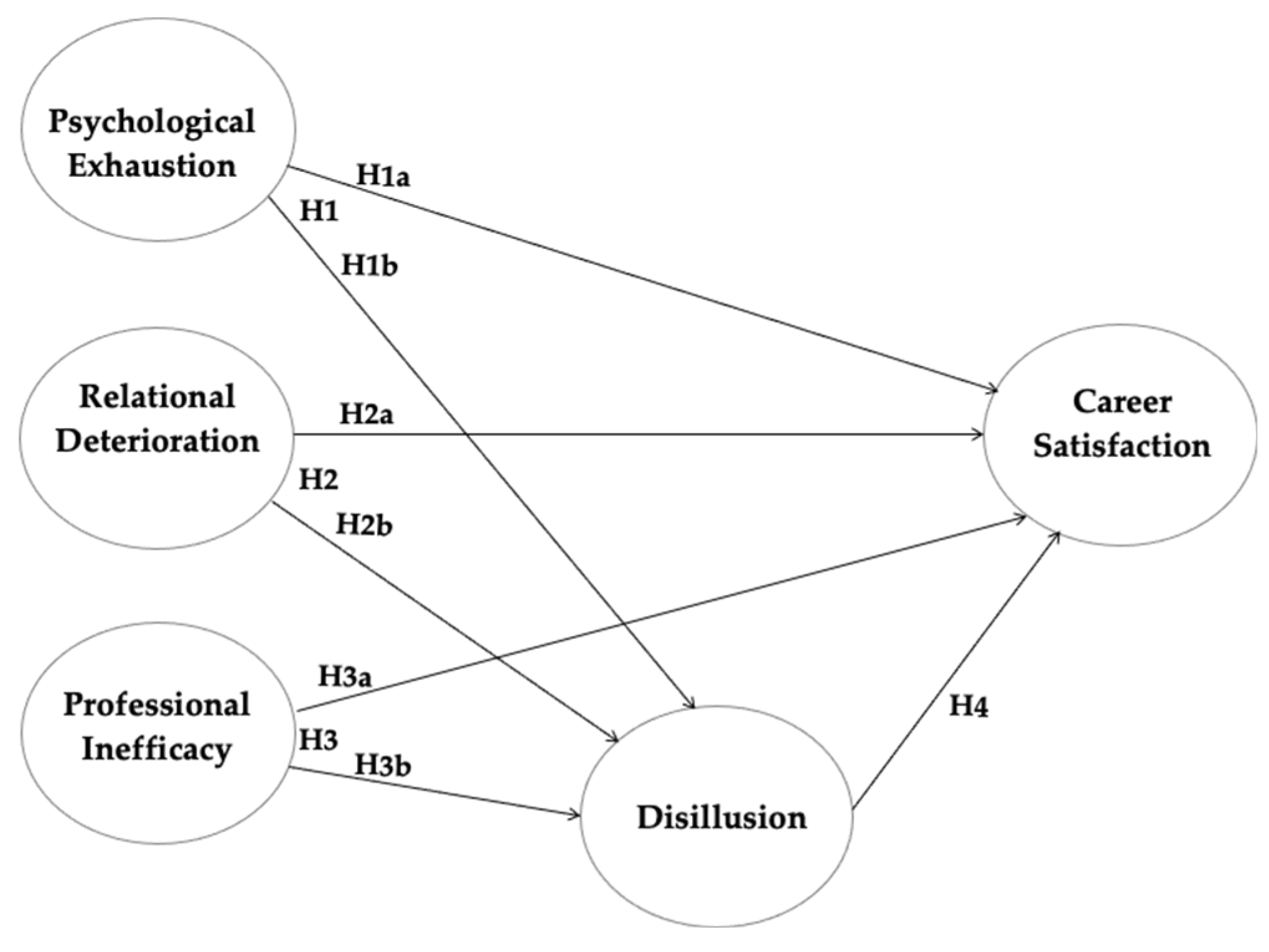
Based on the studies conducted in this field, the aim of the present study is to evaluate the effects of different dimensions of burnout (specifically Psychophysical exhaustion, Relational deterioration, Professional inefficacy) related to the Career satisfaction of healthcare workers. These relationships are evaluated by considering the direct and mediated effects of Disillusion. We hypothesize (H):
H1. Psychophysical exhaustion negatively affects Career satisfaction. Specifically: (H1a) Psychophysical exhaustion directly affects Career satisfaction; moreover (H1b), this effect might be mediated by Disillusion.
H2. Relational deterioration negatively affects Career satisfaction. Particularly: (H2a) Relational deterioration directly affects Career satisfaction; also (H2b), this effect might be mediated by Disillusion.
H3. Professional inefficacy negatively affects Career satisfaction. Definitely: (H3a) Professional inefficacy directly affects Career satisfaction; additionally (H3b), this effect might be mediated by Disillusion.
H4. Disillusion negatively affects Career satisfaction.
Figure 1 illustrates our study hypotheses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
The proposed study was carried out with a cross-sectional design, collecting quantitative data (standardized questionnaires). A total of 295 questionnaires were administered in paper-and-pencil format in three public hospitals in the province of Cagliari (Italy), as part of a program of training and assessment activities for health workers. The respondents were selected according to their willingness to participate in this study; thus we recruited a non-probabilistic, convenience sample. The data were collected between June 2022 and May 2023, in the final phase of the pandemic (i.e., following the second lockdown in Italy). In this regard, it is important to point out that in the Italian hospital wards in which the research protocol was facilitated, some mandatory anti-Covid safety measures were still in place: FFP2 masks, hand sanitization, temperature measurement at ward access, interpersonal spacing, and wearing protective single-use gowns.
2.2. Assessment Instruments
The administered research protocol was organized into different sections. The first included a measure of social, professional, and demographic questions (inquiring about age, gender, job role, professional level, seniority of service). The subsequent sections included the following two psychological validated instruments. For Job burnout, The Link Burnout Questionnaire (LBQ) [
61] was administered to evaluate the participants’ Job burnout and Work engagement. This instrument is a self-assessment of 24 items, with all statements assessed with a 6-point scale (from 1 = never to 6 = always). The four bipolar dimensions (each defined by six questions, three positive and three negative) were: Psychophysical Exhaustion-engagement (α = 0.77, e.g., “I feel physically exhausted by my work”, “Work makes me feel active and vital”); Relational Deterioration-involvement (α = 0.79, e.g., “I have the impression that most of my users do not follow my directions”, “I feel gratified by the relationship with my users”); Professional Inefficacy-efficacy (α = 0.78, e.g., “I feel inadequate to deal with my users’ problems”, “In work, I seem to deal effectively with most of the problems”); Disillusion-fulfilment (α = 0.85, e.g., “My expectations of this work have been disappointed”, “I still feel motivated by my professional ideals”).
The dimension of Career satisfaction was assessed by a specific sub-scale of the Italian version of the Occupational Stress Indicator (OSI) [
62]. The six items that make up the scale are preceded by the opening sentence, “Rate your level of satisfaction,” and were evaluated by a Likert scale, from 1 = completely false, to 6 = absolutely true (e.g., “The current possibilities for career development,” “The possibility of maturation or personal development that your job allows you”). This dimension showed a good index of reliability (α = 0.77).
2.3. Participants
Participants in this study included 295 health workers, aged from 25 to 66 years (age M = 49, SD = 10). Specifically, 227 (76.9%) participants were females; 68 (23.1%) were males. They reported the following organizational roles: executive physician (n = 55, 18.8%), nursing coordinator (n = 13, 4.5%), nurse (n = 115, 39.4%), obstetrician (n = 25, 8.6%), healthcare technician (n = 7, 2.4%), or socio-healthcare worker (n = 77, 26.4%). They were then divided into different occupational levels: Direction (n = 56, 19.0%), Coordination (n = 21, 7.1%), or Subordinates (n = 218, 73.9%). They reported an average seniority of 18 years (SD = 11.5).
2.4. Method and Data Analysis
For the description of the sample with respect to Job burnout, Career satisfaction, and particularly with respect to the Disillusion-fulfilment dimension, we carried out the statistical procedure identified by authors of the standardized instruments [
61,
62].
Partial Least Squares-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) was carried out to estimate the paths among the latent (unobserved) constructs, assessed by specific observed indicator items [
63]. Specifically, PLS-SEM was preferred over the classical variance-based SEM to both take an explorative approach and evaluate complex relationships among latent constructs [
64,
65,
66]. Moreover, with it we sought to increase the variance explicated between the latent constructs. Furthermore, PLS-SEM is also considered appropriate when there are non-normal raw data and/or small samples [
65,
67].
In the application of PLS-SEM analysis, a typical two-stage approach was taken [
67]. In the first stage the measurement model was estimated, calculating the reliability and validity, to assess the measurement integrity and the quality of the latent constructs. Specifically, the following indices were computed: Cronbach’s alpha, Dijkstra-Henseler’s rho A, Average Variance Extracted (AVE), Adjusted R2 [
65] (the rules of thumb regarding these indices are described in our Results section).
Besides, to assess the discriminant validity we computed the Heterotrait–Monotrait (HTMT) ratio of correlation [
68], and to consider the potential problems of multicollinearity, we evaluated the Variance Inflation Factors (VIF) (also for these coefficients, the rules of thumb were described in our Results) [
66]. In the measurement model, to evaluate the latent constructs of burnout dimensions, the items belonging to each scale of the LBQ were counted as observed variables [
61]; furthermore, to assess the latent variable of Career satisfaction, the OSI items were used as observed variables [
62].
The next step in PLS-SEM was established by the structural model to evaluate the relationship connecting the latent constructs. This part of the analysis considered all pathways among constructs; a resampling bootstrapping technique (5,000 resamples) was applied to evaluate the path coefficients and their statistical significance regarding direct and indirect effects (alpha < 0.05) [
65].
The literature had a few studies that investigated the effect of burnout on career satisfaction. In addition, to the best of our knowledge, there were no studies on the mediating role of Disillusion-fulfilment on this relationship, particularly in healthcare workers. Therefore, in our study we focused our attention on the investigation of relationships among these latent variables. The data were analysed with the open-source software Jamovi, version 2.3.28 [
69], and with SmartPLS software, version 4.0.9.6 [
70].
2.5. Ethical Issues
This research project was authorized by the Ethics Committee of the University of Cagliari (approval number 0166737 dated July 10, 2023) and was thus conducted in full compliance with the Ethical Principles of Psychologists and the Code of Conduct of the American Psychological Association (APA), integrated into the Associazione Italiana Psicologia’s (AIP) Code of Ethics. The project did not address any sensitive topics and was carried out with informed and consenting adults. Last, in accordance with Italian privacy law, the project guaranteed anonymity and privacy to all participants.
3. Results
3.1. Burnout, Engagement, Satisfaction, Disillusion, and Fulfilment of Healthcare Professionals
A profiling of the sample showed that 4.41% (n = 13 healthcare workers) assessed themselves to be in a condition of overt burnout (with high distress scores on all four dimensions that make up the LBQ); 36.9% (n = 109) were at risk, and three (about 1%) reported a condition that can be defined as work engagement (i.e., they provided low scores on all four dimensions of the questionnaire). In detail, among workers at risk of burnout, 23 health workers (7.8%) reported, on three out of the four LBQ dimensions, high distress values, and 45 (15.25%) had two out of four dimensions in this configuration.
Regarding the specific bipolarity Disillusion-fulfilment, 68 practitioners (about 23%) reported a condition of complete disillusion, 199 (about 67.5%) a risk condition, and 28 healthcare workers (about 9.5%), indicated a state of fulfilment.
Career satisfaction saw about 46.5% of healthcare workers (n = 137) completely dissatisfied, about 37.5% (n = 111) in a condition of risk of dissatisfaction, and finally about 16% (n= 47) completely satisfied with their career.
3.2. The PLS-SEM Method
The validity and reliability of the measurement model were appraised by the Dijkstra-Henseler’s rho A and Cronbach’s alpha (which must be greater than the threshold of 0.70) [
65]. We assessed the indicator loadings, and we computed the AVE to assess discriminant and convergent validity (a good convergent validity is detected once indicators’ loadings and AVE are greater than 0.70 and 0.50, respectively) [
65] (see
Table 1). We computed the R squared (R2) values in order to quantify the explained variance of endogenous latent variables in the model (the R
2 ranged from 0.570 for the latent variable of Career satisfaction to 0.741 for the latent variable of Disillusion) [
65].
The discriminant validity of this outer model was assessed by the HTMT ratio of correlation (specifically, in the literature it is stated that if the value is greater than 0.90 [
66], there is weak discriminant validity). In our data, only the HTMT index regarding the relation between LBQ Psychophysical exhaustion and LBQ Disillusion displayed values a little above the threshold; this fact might be related to the specific likeness and features of the dimensions measured in these subscales of the LBQ (
Table 2).
Moreover, to assess potential multicollinearity issues, the VIFs for analysed relationships were observed (per the literature, their estimates must not be above the limit value of 5.0) [
65]. See
Table 3.
In summary, the above reported indices (see
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3) indicate that our model met the quality criteria expected in the literature [
66].
3.3. The PLS-SEM Method
In the structural model, the paths between latent constructs were assessed by a resampling bootstrapping procedure (5,000 resamples) that disclosed the significance of each direct and indirect path coefficient [
71,
72]. The hypotheses and the findings of the model are displayed in
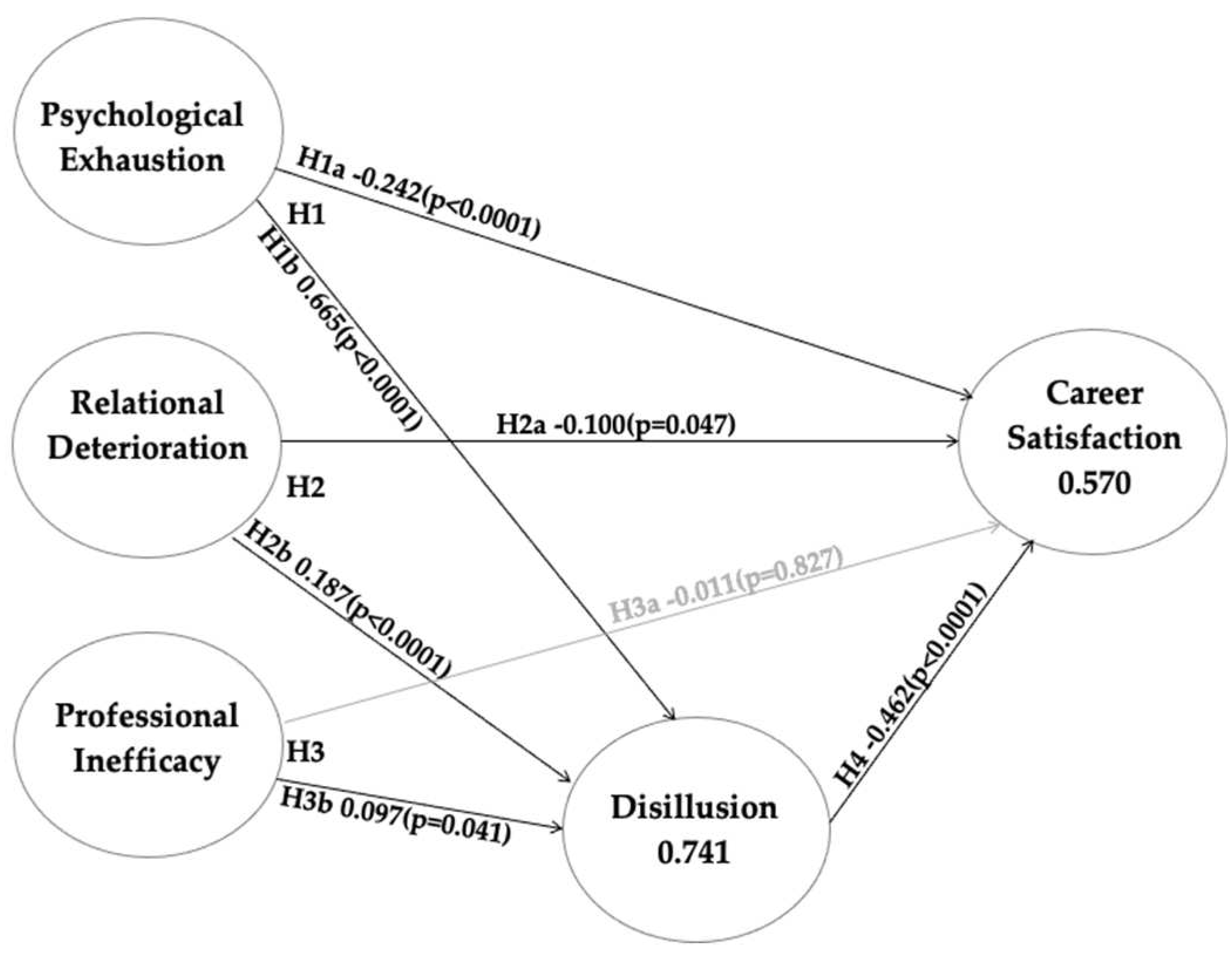
Table 4 and in
Figure 2, presenting the connections between latent constructs, the reported values, the established effects, and their beta coefficients, with their statistical significance.
The F2 index was computed to mark the effect size, specifically the influence of an independent latent dimension on a dependent latent dimension; this index is considered good if higher than 0.015. The data (
Table 5) showed a relatively higher effect size for the relationship from LBQ Psychophysical exhaustion to LBQ Disillusion (0.812); furthermore, of note was a low effect size for the relationship between LBQ Relational deterioration to OSI Career satisfaction (0.013), and from LBQ Professional inefficacy to OSI Career satisfaction (0.0001).
With PLS-SEM we estimated the direct, indirect, and total effects among constructs, verifying our hypotheses (see
Figure 2 and
Table 5).
Regarding H1, we detected that Psychophysical exhaustion had a significant negative direct effect on Career satisfaction (H1a; β = -0.242, p = 0.003) and a significant positive direct effect on Disillusion (H1b; β = 0.665, p < 0.001). Furthermore, we observed a significant indirect and negative effect of Psychophysical exhaustion on Career satisfaction, defined as the effect through the mediator Disillusion (β = -0.307, p < 0.001). The total effect of Psychophysical exhaustion on Career satisfaction (demarcated as the effect of one variable on another variable, without any mediator) was identified with a negative and statistically significant beta coefficient (β = -0.549, p < 0.001).
Referring to H2, the results show that Relational deterioration had a direct negative and significant direct effect on Career satisfaction (H2a; β = -0.100, p = 0.047) and a significant direct positive effect on Disillusion (H2b; β = 0.187, p < 0.001). Moreover, we observed a significant indirect effect of Relational deterioration on Career satisfaction, mediated by Disillusion (β = -0.086, p < 0.001). The total effect of Relational deterioration on Career satisfaction (without the mediator Disillusion) was negative and statistically significant (β = -0.187, p < 0.001).
Per H3, the results show that the direct effect of Professional inefficacy on Career satisfaction was not significant (H3a; β = -0.011, p = 0.827), but there was a significant positive direct effect of Professional inefficacy on Disillusion (H3b; β = 0.097, p = 0.041). Moreover, the examination of the indirect effects did not highlight a significant effect of Professional inefficacy on Career satisfaction, mediated by Disillusion (β = -0.045, p = 0.058). Also, the total effect of Professional inefficacy on Career satisfaction (without the mediator) was not statistically significant (β = -0.056, p = 0.325).
Finally, regarding H4, there was a significant positive direct path from Disillusion to Career satisfaction (H4; β = -0.462, p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Our assessment of the psychological variables measured in a sample of Italian healthcare workers point to a condition of work and organizational distress. In fact, just under 5% of the sample reported an overt burnout condition, and nearly 37% fell into a burnout risk condition. In addition, nearly 8% were in a particularly high-risk condition, in that on three out of four dimensions they reported high scores, and about 16% reported high scores on two out of four dimensions. Only 1% of the sample was in an engagement condition, connoted by energy, relational involvement, professional efficacy, and fulfilment [
61]. This sample profile is consistent with the historical period in which the data were collected (the final phase of the pandemic in Italy). Moreover, it is congruent with other studies conducted in several countries (e.g. [
24,
26,
29]) and in Italy (e.g., [
32]) on the psychosocial health status of healthcare workers in the pandemic period. The results that emerged appear far removed from a condition of occupational well-being, in which those who deal daily with such a delicate, complex, and sensitive object as the care and health of people should be.
Data on the specific focus of the Disillusion-fulfilment dimension showed that about 23% reported a state of complete disillusion, 67.5% a condition of risk of compromising their work motivations and ideals, and just under 10% a state of fulfilment. This result is also in line with previous studies that analysed the importance of the Fulfilment dimension in healthcare in the pandemic period (e.g., [
50,
51]). A new element revealed by this study is the assessment of the “dark side” of Fulfilment, represented by Disillusion in healthcare workers.
Regarding participants’ career satisfaction, the sample provided critical scores. In fact, almost half of the sample (46.5%) self-reported a level of complete dissatisfaction, about 33% were at risk of dissatisfaction, and only 16% considered themselves completely satisfied with their career path. Again, the profile that emerged is far from ideal for healthcare workers. This result may help build on the few empirical studies available on this dimension in healthcare, with reference to the Covid-19 pandemic period.
Regarding the effect of burnout on career satisfaction among health workers, our hypotheses were confirmed. We observed a direct negative effect of the burnout dimensions Psychophysical exhaustion (H1a), Relational deterioration (H2a), and Disillusion (H4) on the Career satisfaction of health workers. This finding is consistent with the (few) studies conducted on the topic, both before the pandemic period (e.g., [
60]) and during Covid-19 (e.g., [
55]). A novel aspect of this finding, which has been little emphasized in the literature, is the effect that burnout has not only on a condition of contingent and temporary job dissatisfaction (documented in several studies; e.g., before the pandemic, [
56,
57], and during Covid-19 [
58,
59]), but also on a more structured, sedimented, and stable experience, such as career dissatisfaction. This aspect implies the overall balance over a longer time span (in some cases decades) and is in some ways more insidious. In fact, given the already described self-fulfilling and existential nature inherent in the choice of the health profession (see, for example [
47,
48]), severe career dissatisfaction (due to burnout) implies an experience of perceived failure in healthcare workers (connoted by stability or even finality) not only professionally, but also existentially.
Additional investigation will be needed on the non-significance of the direct relationship (H3a) of Professional inefficacy on Career satisfaction. Given the few previous studies on this relationship, we can only provide a few speculative explanations.
The first is related to the possible semantic similarity of the items of the two constructs: both use an evaluation in terms of gratification of healthcare professionals with respect to work, and this may have resulted in an insufficiently clear distinction between the two dimensions, per the self-reports of the sample.
Another possible explanation could be the different nature of the two constructs from a temporal point of view. While professional inefficacy is oriented toward a contingent and temporary state evaluation of the practitioner, career satisfaction implies a more thoughtful, structured, and stabilized balance of a working-life trajectory that can also be over a long period. Thus, it is possible that although a health worker may feel that they are in a contingent state of job ineffectiveness (exacerbated by the post-pandemic situation), this does not necessarily imply that they have arrived at a stable (and sometimes definitive) failed “balance sheet” regarding their career.
The results provide empirical evidence for the negative mediating role played by Disillusion (or failed fulfilment) in the relationship between the individual dimensions of burnout, Psychophysical exhaustion (H1b), and Relational deterioration (H2b), with respect to Career satisfaction. In both cases, a condition of disillusion exacerbated the incidence of these two dimensions of burnout on this type of satisfaction. This finding has unique elements to it, that, although Disillusion has been defined for several decades [
36,
37] and has recently been revived [
61] and reconsidered in some empirical contributions [
14,
35,
39,
40], its role with respect to career satisfaction has not yet been adequately defined. In fact, this result points to the importance of self-actualization and fulfilment of work values and ideals, and how deleterious, conversely, their non-achievement (Disillusion) can be on a dimension of satisfaction that impacts a professional and existential balance sheet in a significant and sensitive field such as healthcare.
Ultimately, the negative impact of Professional inefficacy on Disillusion (H3b) was confirmed. This finding is in line with early models that described burnout in the helping professions as a staged and degenerative syndrome [
36,
37], and more recently [
14,
39,
61]. Indeed, in these models, the prolongation of a state of professional inefficacy leads to attrition and eventually to the undermining of work ideals and values. Finally, this novel finding contributes to empirical evidence of the negative influence of Professional inefficacy on Disillusion, on which the scientific literature is still scarce.
5. Conclusions
The scientific literature has extensively documented how dangerous Burnout syndrome is, particularly in healthcare [
20,
21,
22]. The unsustainability of healthcare staff’s escape from stress and burnout caused by Covid-19 [
24,
26,
27,
32] and the promotion of their satisfaction and work engagement imply the requirement of a synergistic implementation of several courses of action whose effectiveness in healthcare settings has been widely documented (e.g., [
13,
23,
25]). The results of the present study imply that the ideal, vocational, value, and self-actualizing aspects of healthcare work should also be considered. Indeed, these appear to be important in sustaining motivation, well-being, performance, work engagement, and ultimately satisfaction (in this case, career satisfaction) in this key profession.
In the context of the JD-R model [
4,
7], regarding the opposition between Job burnout and Work engagement and the ability of the latter to prevent and counteract the syndrome, it might therefore be useful to consider – in addition to the already identified job demands and job resources of a subjective nature present in healthcare settings [
2,
5] – the dimension of Fulfilment [
41,
42] and its opposite, Disillusion [
14,
39,
61]. This dimension seems to have the capacity to significantly impact the vocational, existential, and value aspects of work, which are of fundamental importance for the work engagement and satisfaction of healthcare workers, especially in this post-pandemic period [
50,
51,
52].
This study has some limitations. The first is the nature of the data collected. These were exclusively subjective, self-report, and cross-sectional. However, both burnout and satisfaction can also be assessed through objective indicators (e.g., for burnout sick days or medical prescriptions; for satisfaction performance indicators). It will therefore be appropriate for future studies to consider these types of indicators, as well.
The second limitation is the nature of the sample – a convenience, non-random, and non-stratified sample with respect to different job profiles and some socio-demographic variables (such as gender, age, length of service, or territorial area of affiliation). This means we could not generalize the validity of our results.
The third limitation is our small sample size which did not allow us to explore in detail the impact of our assessed socio-demographic variables on the relationships among the psychological variables in focus. This limitation, and the previous one, would be overcome with an enlarged, diversified, and stratified study sample.
Despite these limitations, our study provides some interesting empirical evidence for the importance of the occupational psychological dimension of Fulfilment and its “dark side” Disillusion, in the relationship between burnout and career satisfaction in healthcare workers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N. and A.U..; methodology, M.N. and M.A.; validation, M.N., M.A., N.A. and F.C.; formal analysis, M.A., F.C. and N.A.; investigation, M.N. F.C. and N.A.; resources, A.U. and C.G.C.; data curation, F.C. and N.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N., M.A., F.C. and N.A.; writing—review and editing, C.G.C.; supervision, C.G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Cagliari (approval number 0166737 dated July 10, 2023) and was thus conducted in full compliance with the Ethical Principles of Psychologists and the Code of Conduct of the American Psychological Association (APA), integrated into the Associazione Italiana Psicologia’s (AIP) Code of Ethics; for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data available within the article. For more information, please contact the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maslach, C.; Leiter, M.P.; Schaufeli, W.B. Measuring burnout. In The Oxford Handbook of Organizational Well-Being; Cooper, C. L., Cartwright, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2009; pp. 86–108.
- Schaufeli, W.B. Burnout: A short socio-cultural history. In Burnout, Fatigue, Exhaustion; Neckel, S., Schaffner, A., Wagner, G., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 105–127.
- Nadon, L.; De Beer, L.T.; Morin, A.J.S. Should Burnout Be Conceptualized as a Mental Disorder? Behav. Sci. 2022, 12(3), 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufeli, W.B. Burnout: A Critical Overview. In Organizational stress and well-being; Lapierre, L.M., Cooper, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2023; pp. 214-259.
- Schaufeli, W.B. Applying the Job Demands-Resources model: A ‘how to’ guide to measuring and tackling work engagement and burnout. Organ. Dyn. 2017, 46, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Schaufeli, W.B.; Taris, T.W. How are changes in exposure to job demands and job resources related to burnout and engagement? A longitudinal study among Chinese nurses and police officers. Stress and Health 2017, 33(5), 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattrie, L.T.; Kittler, M.G.; Paul, K.I. Culture, burnout, and engagement: A meta-analysis on national cultural values as moderators in JD-R theory. Appl. Psychol. 2020, 69(1), 176–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B. Work Engagement. What Do We Know and Where Do We Go? Rom. J. Appl. Psychol. 2012, 14(1), 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B. Defining and measuring work engagement: Bringing clarity to the concept. In Work engagement: A handbook of essential theory and research; Bakker, A.B.; Leiter, M.P., Eds.; Psychology Press, London, United Kingdom, 2010, pp. 10–24. [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, J.J.; Ropponen, A.; Schaufeli, W.B.; De Witte, H. Who is engaged at work? A large-scale study in 30 European countries. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 61(5), 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B. Engaging leadership: How to promote work engagement? Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B.; van Rhenen, W. How changes in job demands and resources predict burnout, work engagement, and sickness absenteeism. J. Organ. Behav. 2009, 30(7), 893–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, J.J.; Schaufeli, W.B. Do burnout and work engagement predict depressive symptoms and life satisfaction? A three-wave seven-year prospective study. J. Affect. Disord. [CrossRef]
- Nonnis, M.; Pirrone, M.P.; Cuccu, S.; Agus, M.; Pedditzi, M.L.; Cortese, C.G. Burnout syndrome in reception systems for illegal immigrants in the Mediterranean. A quantitative and qualitative study of Italian practitioners. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2071–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B. Work Engagement: A Critical Assessment of the Concept and Its Measurement. In Handbook of Positive Psychology Assessment; Tuch, W. R., Bakker, A. B., Tay, L., Gander, F., Eds.; Göttingen, Hogrefe, 2022; pp. 273-295.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http%3a%2f%2fid.who.int%2ficd%2fentity%2f129180281 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Rožman, M.; Grinkevich, A.; Tominc, P. Occupational stress, symptoms of burnout in the workplace and work satisfaction of the age-diverse employees. Organizacija. [CrossRef]
- Quiceno, J.M.; Alpi, S.V. Burnout: "Syndrome of burning oneself out at work (SBW)". Acta Colomb. de Psicol. 2007, 10(2), 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Trigo, T.R.; Teng, C.T.; Hallak, J.E.C. Burnout syndrome and psychiatric disorders. Archives of Clinical Psychiatry (São Paulo), 2007; 34, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, S.A.; Bubenek-Turconi, Ş.I.; Droc, G.; Marinescu, E.; Nita, E.; Popa, M.C.; Popescu-Spineni, D.; Tomescu, D. Burnout syndrome in the Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Unit. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care 2019, 26(1), 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, K.; Zborowska, A.; Młynarska, A. Rationing Care, Job Satisfaction, Fatigue and the Level of Professional Burnout of Nurses in Urology Departments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak-Błoszyk, K.; Krysińska, K.; Andriessen, K.; Stańdo, J.; Czabański, A. Work-Related Suicide Exposure, Occupational Burnout, and Coping in Emergency Medical Services Personnel in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mol, M.M.C.; Nijkamp, M.D.; Bakker, A.B.; Schaufeli, W.B.; Kompanje, E.J.O. Counterbalancing work-related stress? Work engagement among intensive care professionals. Austr Crit Care 2018, 31(4), 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelmann, F.B.; Koëter, T.; Steinkamp, P.J.; Vriens, M.R.; Verhoeven, B.; Kruijff, S. The immediate impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on burn-out, work-engagement, and surgical training in The Netherlands. Surgery 2021, 170(3), 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, N. Tackling the negative impact of COVID-19 on work engagement and taking charge: A multi-study investigation of frontline health workers. J. Appl. Psychol. 2021, 106(2), 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazy, A.R.M.; Alruwaili, A. The Global Prevalence and Associated Factors of Burnout among Emergency Department Healthcare Workers and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Khazaie, H.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Khaledi-Paveh, B.; Kazeminia, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Shohaimi, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Eskandari, S. The prevalence of stress, anxiety and depression within front-line healthcare workers caring for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-regression. Hum Resour Health 2020, 18(1), 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, C.; Chen, W.T.; Hung, C.C.; Huang, E.P.C.; Lee, T.S.H. COVID-19 stigma associates with burnout among healthcare providers: Evidence from Taiwanese physicians and nurses. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121(8), 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; McLoughlin, C.; Stillman, M.; Poplau, S.; Goelz, E.; Taylor, S.; Nankivil, N.; Brown, R.; Linzer, M.; Cappelucci, K.; Barbouche, M.; Sinsky, C. A. Prevalence and correlates of stress and burnout among U.S. healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A national cross-sectional survey study. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 35, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafei, S.E.C.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sambou, M.L.; Walker, A.N.; Li, W.; Liu, S. The Association between Burnout, Social Support, and Psychological Capital among Primary Care Providers in Togo: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2023, 59(1), 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthans, F.; Youssef-Morgan, C.M. Psychological Capital: An Evidence-Based Positive Approach. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2017, 4, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barello, S.; Palamenghi, L.; Graffigna, G. Burnout and somatic symptoms among frontline healthcare professionals at the peak of the Italian COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 290, 113129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santinello, M.; Negrisolo, A. Quando ogni passione è spenta. La sindrome del burnout nelle professioni sanitarie; Mc Graw Hill: Milan, Italy, 2009; pp. 5–34. [Google Scholar]
- Borgogni, L.; Consiglio, C.; Alessandri, G.; Schaufeli, W.B. "Don’t throw the baby out with the bathwater!" Interpersonal strain at work and burnout. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol 2012, 21, 875–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnis, M.; Massidda, D.; Cuccu, S.; Cortese, C.G. The impact of workaholism on nurses’ burnout and disillusion. Open Psychol. J. 2018; 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelwich, J.; Brodsky, A. Burnout: Stages of disillusionment in the helping professions. Human Sciences Press, New York, USA, 1981.
- Pines, A.; Aronson, E.; Kafry, D. Burnout: From tedium to personal growth. The free Press: New York, USA, 1981.
- Pedditzi, M.L.; Nonnis, M. Psycho-social sources of stress and burnout in schools: Research on a sample of Italian teachers. Med. Lav. 2014, 105, 48–62. [Google Scholar]
- Nonnis, M.; Agus, M.; Frau, G.; Urban, A.; Cortese, C.G. Job Seekers’ Burnout and Engagement: A Qualitative Study of Long-Term Unemployment in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnis, M.; Frau, G.; Agus, M.; Urban, A.; Cortese, C.G. Burnout without a job: An explorative study on a sample of Italian unemployed jobseekers. J. Public Health Res. 2023; 12, ISSN 2279-9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Gunderman, R.B. Enhancing the Professional Fulfillment of Physicians. Acad Med 2006, 81(6), 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, G.; Baldwin, D.S. A critical review of the definition of ‘wellbeing’ for doctors and their patients in a post Covid-19 era. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2021, 67(8), 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellieni, C.V.; Righetti, P.; Ciampa, R.; Iacoponi, F.; Coviello, C.; Buonocore, G. Assessing burnout among neonatologists. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, V.; Zeppegno, P.; Gramaglia, C.; Gili, S.; Deantonio, L.; Krengli, M. A survey of Italian radiation oncologists: Job satisfaction and burnout. Tumori 2014, 100(3), 307–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- While, A.; Blackman, C. Reflections on nursing as a career choice. J Nurs Manag 1998, 6(4), 231–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognstad, M.K.; Aasland, O. Change in career aspirations and job values from study time to working life. J Nurs Manag 2007, 15(4), 424–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.M.; Kelly, C.M.; Kremser, A.K.; Jolly, B.; Billett, S. The motivations to nurse: an exploration of factors amongst undergraduate students, registered nurses and nurse managers. J Nurs Manag, 2009; 17, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, I.; Brady, K.J.; Trockel, M. An exploration of key issues and potential solutions that impact physician wellbeing and professional fulfillment at an academic center. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B.; van der Heijden, F.M.M.A.; Prins, J.T. Workaholism, burnout and well-being among junior doctors: The mediating role of role conflict. Work Stress, 2009; 23, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, J.A.; Lázaro-Pérez, C.; Gómez-Galán, J. Burnout among Direct-Care Workers in Nursing Homes during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Spain: A Preventive and Educational Focus for Sustainable Workplaces. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, F.U.; Bodendieck, E.; Bleckwenn, M.; Hussenoeder, F.S.; Luppa, M.; Riedel-Heller, S.G. Burnout, work engagement and work hours – how physicians’ decision to work less is associated with work-related factors. BMC Health Serv Res 2023, 23(1), 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyubarova, R.; Salman, L.; Rittenberg, E. Gender Differences in Physician Burnout: Driving Factors and Potential Solutions. Perm J 2023, 27(2), 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, P.E. Job satisfaction: Application, assessment, causes, and consequences. SAGE Publications Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA., 1997.
- Arifin, J.; Raharjo, T.J. Analysis of the Organizational Climate Factors on the Service Quality and Work Satisfaction Towards Lecturer’s Work Commitments in the Specialist’s Medical Education Program at Universitas Diponegoro Semarang. In 6th International Conference on Science, Education and Technology (ISET 2020), Atlantis Press, 2021; pp. 545-548. [CrossRef]
- Meilianti, S.; Matuluko, A.; Ibrahim, N.; Uzman, N.; Bates, I. A global study on job and career satisfaction of early-career pharmacists and pharmaceutical scientists. Explor. Res. Clin. Soc. Pharm. 2022, 5, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, S.; Vargas, M.; Servillo, G. Organizational strategies to reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res 2019, 33, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Misra, R.; Madan, R. The Saviors Are Also Humans’: Understanding the Role of Quality of Work Life on Job Burnout and Job Satisfaction Relationship of Indian Doctors. J Health Manag 2019, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, E.; Widestrom, M.; Gould, J.; Fang, R.; Davis, K.G.; Gillespie, G.L. Examining the Impact of Stressors during COVID-19 on Emergency Department Healthcare Workers: An International Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selič-Zupančič, P.; Klemenc-Ketiš, Z.; Onuk Tement, S. The Impact of Psychological Interventions with Elements of Mindfulness on Burnout and Well-Being in Healthcare Professionals: A Systematic Review. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, G.; Goldberg, R.; Compton, S. Tolerance for uncertainty, burnout, and satisfaction with the career of emergency medicine. Ann Emerg Med 2009, 54(1), 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santinello, M. Link Burnout Questionnaire—LBQ. Giunti O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze, Italia, 2007.
- Sirigatti, S.; Stefanile, C. OSI: Occupational Stress Indicator. Giunti O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze, Italia, 2002.
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Guilford Publications, 2023.
- Hair, J.; Tatham, R.L.; Anderson, R.E.; Black, W. Multivariate data analysis. Pearson Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006; Vol. 6.
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31(1), 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.; Hair, J. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling, Springer Nature Switzerland, AG, 2021; pp. 1-47. [CrossRef]
- Esposito Vinzi, V.; Chin, W.W.; Henseler, J.; Wang, H. Handbook of Partial Least Squares: Concepts, Methods and Applications. Springer Handbooks of Computational Statistics, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Hair Jr, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. Evaluation of reflective measurement models. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Springer, 2021; pp. 75-90.
- The jamovi project. Jamovi (Version 2.3). 2023 [Software]. https://www.jamovi.org.
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Becker, J.M. SmartPLS 4. Oststeinbek: SmartPLS. (Versione 4). 2022 [Software]. https://www.smartpls.com.
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Pieper, T.M.; Ringle, C.M. The Use of Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling in Strategic Management Research: A Review of Past Practices and Recommendations for Future Applications. Long Range Plann. 2012, 45(5), 320–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair Jr, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced issues in partial least squares structural equation modeling. SAGE Publications Inc., 2023.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).