1. Introduction
The development of Reichardt`s dye 2,6-diphenyl-4-(2,4,6-triphenyl-1-pyridinium)-phenolate (
B30) (see
Scheme 1) was a milestone for the investigations of solvent properties [
1]. As a reminder, the original empirical solvent parameter
ET(30) is defined as the molar absorption energy of
B30 expressed in kcal/mol, measured in a given solvent[
1]:
There are numerous studies in the literature on the classification of the polarity of pure solvents and solvent mixtures as a function of their composition, measured with
B30 and other solvatochromic probe molecules [2-35]. For explanatory concepts of solvatochromism in solvent mixtures, see the insightful review at reference [34a]. An interim summary of treated solvent mixtures can be found in Table 3 of [
35]. In this context,
B30 and related solvatochromic probes have been used to create so-called HBD (hydrogen bond donating) strength scales of organic solvents [36-41]. In addition to HBD classification, there is a definition for hydrogen bonding accepting ability (HBA) for solvents [
42]. These classifications HBD and HBA reflect the molecular properties of the solvent molecule in terms of hydrogen bonds in the sense of the Kamlet-Taft approach and further similar concepts from Catalan and Laurence [36-41]. It was assumed that the interaction of the HBD groups of the solvent with the phenolate oxygen is crucial for the HBD-measurement for solvents and solvent mixtures [4, 40, 41]. But this approach is only partly justified as demonstrated by us recently [
43]. The concept of determining HBD parameters works quite well for ionic liquids (IL) and other salts due to the electrostatic interaction between the
B30 phenolate anion and the constituting cation of the IL [41, 44-46]. However, the problem is still under study due to some inconsistencies between theory and experimental results [
46].
Especially,
B30 has been used routinely as polarity indicator for binary solvent mixtures [2, 6-9, 13-21]. One of the most difficult problems in interpreting the solvatochromism of
B30 in solvent mixtures is the question of preferential solvation and its influence on the
ET(30) value, which has been studied over the last three decades [10, 15-21, 24]. However, the understanding of what is meant by preferential solvation is presented differently in the literature [9-12, 24]. The basic problem in defining two types of preferential solvation was correctly identified by Ghoneim [
24]. There are two basic scenarios to distinguish in this question for
B30:
- i.
the solvent mixture (true micelles are a different matter) is intrinsically inhomogeneous and solute B30 is therefore preferentially confined by a fraction mixture, or
- i.
ii. the dissolved probe such as B30 preferably forms a specific complex with one of the two solvent components.
A complementary good definition for preferential solvation is given by Morisue and Ueno regarding case ii. “Preferential solvation is a phenomenon, whereby solvent proportion of binary mixed solvent in the vicinity of a solute molecule differentiates from the statistic proportion in bulk” [
30]. It must therefore be clearly distinguished whether the probe molecule is specifically solvated by the solvent molecule or is in a partial volume enriched with a mixture component. Scenario i. assumes that the physical structure of the solvent mixture is not affected by solute
B30. In the case of scenario ii, the type of probe itself determines the extent to which preferential solvation takes place. Thus, if scenario ii. is relevant, different solvatochromic probes should show different dependencies as a function of quantitative solvent composition. Langhals showed as early as 1981 that different solvatochromic probes for the same mixture as for ethanol/water show the same dependencies as function of solvent composition [
5]. That crucial finding would rule out scenario ii. But the situation is not that simple.
Despite ambitious work on this topic, the problem of solvatochromism in solvent mixtures has not really been adequately addressed in the literature. Therefore, it is necessary to go into more detail on the chronological development of the concepts for the interpretation of UV/Vis spectroscopic absorption energy data from probe molecules in solvent mixtures.
In the first works on
B30 [1, 2], the
ET(30) values of various binary solvent mixtures were determined and it was shown that
ET(30) depends in a complex way on the quantitative composition of the mixture. Later, Langhals recognized that solvatochromism of
B30 in terms of
ET(30) can be empirically described as a logarithmic function with respect to the concentration of the components [
6]. Already in 1982, Langhals also showed that
ET(30) of primary alcohols is a linear function of their total molar concentration (
N ) [
7]. The core problem was that no theoretically sound justification for this linkage was presented in the past. Possibly for this reason, this very important discovery was not properly understood by many scientists and its importance was not fully appreciated. These seemingly empirical findings have a significant physical background based on the Lorentz-Lorenz relation (LLR) [
47].
Later in 1986, Haak and Engberts presented a valuable work on the influence of temperature (
T) on the solvatochromic properties of
B30 in aqueous solvent mixtures [
8]. It is worth analysing this study in detail, as the authors have correctly identified the effects of hydrophobic alcoholic components such as 2-n-butoxyethanol (BE) in water on
ET(30). However, several interpretations require re-evaluation in the light of new physical research on specific solvent mixtures, as will be shown in the course of this study.
Since 1982, the general topic of preferential solvation in solvent-water mixtures has been studied in detail by Marcus on the basis of thermodynamics using the Kirkwood-Buff theory for fully miscible aqueous solvent mixtures in many papers [48-51]. Marcus was aware of various inconsistencies between thermodynamic results and solvatochromic measurements [
12]. He stated: “A single probe, such as the betaine used for the
ET(30) polarity parameter, cannot provide an answer”. Already in 1988, Dorsey [
9] concluded that
B30 does sense the hydrogen bond network rather than direct hydrogen bonds: “Therefore, it could be that a change in the hydrogen-bonding network of the solution is being sensed by the ET-30 probe in the dilute alcohol concentration as well”. This thesis gets to the heart of the problem.
Since the year 1992, O. Connor and Rosés developed the preferential solvation model (PSM) independently of each other [11, 15-17]. The PSM suggests the formation of stoichiometrically defined complexes between the solvatochromic probe (solute) and the two solvents as well as of solvent molecules with each other. It was assumed that the measured UV/Vis shift is caused by the formation of a complex between the
B30 or related probes probe and the solvent molecule [1, 36, 37]. This scenario belongs to case ii. In these models, the strength of H-bridge binding is assumed to correlate linearly with the extent of the UV/Vis shift. In a meaningful paper by Kipkemboi from 1994 that has not received further attention [
13], the solvatochromism of
B30 in 2-methyl-2-propanol/water and 2-amino-2-methylpropane/ water mixtures was studied in detail. The authors correctly concluded that preferential solvation cannot be the main reason for the observed effect. The inclusion of the refractive index and the partial molar concentration of the components in the qualitative interpretation showed that both the polarizability and the number of water dipoles have an influence on the solvatochromic shifts of
B30.
In 2004, Bentley, however, took up Langhals' discovery [
7] and showed the dependence of
ET(30) on global polarity of alcohols in terms of
N. Furthermore,
ET(30) values of alcohol-water mixtures were alternatively investigated as a function of volume and the molar fraction of the mixture composition [
27]. From this, Bentley concluded that preferential solvation may be overestimated.
True preferential solvation could be demonstrated for
B30 in the system phenol/acetone and phenol/acetonitrile [
43,
44]. Here, stoichiometric 1:1 complex of
B30 with phenol can be clearly identified. In phenol/1,2-dichloroethane, depending on the quantitative composition, both effects i. and ii. can be observed simultaneously with different proportions depending on the phenol concentration [43,52-54]. Importantly, these UV/Vis-studies have convincingly demonstrated that the effect of the formation of specific hydrogen bonds on
ET(30) is much smaller than that of the volume solvent phenol [
43]. Recent studies show that preferential solvation can be demonstrated, but the solute/solvent complexes need to be clearly identified by independent spectroscopic measurements due to the apparent acid-base interaction [55, 56].
As mentioned, the PSM models are based in particular on the assumption that the UV/Vis shift of
B30 and related solvent-HBD sensitive dyes such as 1-ethyl-4-(methoxycarbonyl) pyridinium iodide (
K),
cis-dicyano-bis(1,10-phenanthroline) iron II (
Fe), or Brookers Merocyanine (
BM), is caused by the formation of specific interactions (hydrogen bonds) between the solvent and the probe. This is a fundamental misunderstanding. This fact can be clearly demonstrated independently on three different derivatives of the Reichardt dye family from literature [57-59]. C. Reichardt himself passed over the statement of the solvatochromic results of the thiolate-betaine derivative of
B30, which did not show the desired difference to
B30 when measured in HBD solvents [
57]. It was an unpleasant experience for us that H-bridge binding patterns at the barbiturate anion substituent of
B30 derivative cause only a negligible UV/Vis shift compared to bulk HBD solvents [
58]. At that time, however, we had not yet properly appreciated the consequences of this finding for understanding the UV/Vis shift. Unfortunately, we had to abandon the concept of molar detection with UV/Vis shift of solvatochromic probes. Recently, the Sander-group showed that the [2,6-di-
tert.-butyl-4-(pyridinium-1-yl] phenolate forms a defined 1:1 complex with water, leads to small shifts of the π–π* transition only compared to the influence of the global polarity of the volumetric water [
59]. Thus,
B30 and other related probes do not fulfil this alleged property as an indicator of HBD strength of the solvent molecule when the bulk solvent is measured [
36,
37,
40,
41]. The total UV/Vis shift of
B30 in pure HBD solvents is mainly due to the effect of the global polarity of the hydrogen bonding network of the solvent and not to a direct hydrogen bonding with the dissolved probe [7,28,43,60-62]. Sander and coworker also showed that the stoichiometric
B30/HBD-solvent complex is the actual solvatochromic species and not the pristine
B30. This result was the missing link to understanding the discrepancies between the different interpretations, because it was known that steric shielding of the phenolate oxygen of
B30 derivatives leads to a change in the solvatochromic properties [
1].
The misinterpretation that the total UV/Vis shift is preferentially due to the direct formation of hydrogen bonds at
B30 must be fundamentally corrected, even though many papers have taken this as a defined basis. Accepting this fact will be difficult for many scientists working in this field, as it overturns entrenched thought patterns. In accordance to Bentley [
27] we question the classical preferential solvation approach of special solvatochromic probes for particular alcohol/water and related aqueous binary solvent systems regarding scenario ii. as reported [4,19-21,25-27,31-34].
Furthermore, Suppan correctly concluded that the process of hydrogen bonding between solute and solvent in water may endergonic, using the preferential solvation index for interpretation [
63]. Later, Rezende recognised that the concept of preferential solvation had some weaknesses and the index of preferential solvation was also recommended to circumvent some problems in explaining difficult results [
64,
65].
However, the actual physical problem in evaluating UV/Vis absorption energy data from solvatochromic probes in solvent mixtures is much more serious. Most authors used routinely the mole fraction
x of a component of the solvent mixtures to record the quantity composition in physical relations. It was assumed that a strictly linear dependence of the UV/Vis absorption energy of the dissolved solvatochromic dye on
x would indicate an ideal mixing behavior [10,14-31]. This thesis must be fundamentally questioned, since only the change in the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) of a solvent mixture can be linearly linked to the mole fraction of the components involved [
10,
66]. Gibbs free energy is a composite variable [
66]. For the UV/Vis absorption energy of a dissolved probe molecules in a solvent mixture, however, the situation is somewhat different. The number of transition moments, i.e. the atoms and molecules that are affected by both the light and solvent in a given volume, depends on the average molar concentration (
Nav,x) of solvent dipoles with respect to
x, but not directly on
x [
47,
67,
68]. Therefore, the experimentally found curvilinear relationship
ET(30) as a function of
x(water) can prescribe a preferred solvation [10,14-21], since
Nav,x is reciprocal to
x(water); see later
Figure 1b. We suspect that the real reason for the curved shape of the function
ET(30) or
EPHBD (empirical polarity parameter for HBD strength) as a function of
x(water) is not always the preferential solvation, but the influence of both the inhomogeneity due to the mass difference of the two different solvents and the associated physical structuring of the solvent mixture depending on its composition. This aspect is especially relevant for aqueous mixture due to the low molar mass of water. There are hardly any well-founded studies on the subject of the various quantities of mixture composition, as the mole fraction
x has apparently become established as the routine basis for calculation. There are only a few papers that briefly mention the influence of the different composition variables on
ET(30) and qualitatively illustrate it with some examples [
9,
27,
43,
50]. Significantly, Marcus already suspected that this topic would raise a number of unanswered questions; he mentioned timidly “the different measures of composition of a binary solvent mixture should be borne in mind” [
50].
Furthermore, it has been empirically found that
EPHBD of pure solvents is linearly correlated to
N (total molar concentration) of the solvent under solvent variation for special solvent families [
6,
27,
43,
61,
62].
EPHBD is usually the UV/Vis absorption energy (ν
max in cm
-1) or in kcal/mol [
ET(30)] of the solvatochromic probe like
B30 measured at λ
max, Equations (1) and (2).
N refers to the molar concentration, according to Equation (3a), of the solvent dipoles or the polarised solvent molecules according to the Debye-, Clausius-Mosotti- or Lorentz-Lorenz relation [
47]. σ is the physical density and
M the molar mass of the pure solvent substance.
Furthermore, there is a basic relationship of
N with the spectroscopic measurands
νmax and
εmax (Lmol/cm = 10
3 cm
2/mol) as the molar absorption coefficient as shown by Equation (3b).
Equation (3b) has been completely overlooked in the past. This relationship is not artificial. The physical relationship between the absorption energy, the molar absorption coefficient
εmax and
N is theoretically determined by Beer`s approximation and the LLR [
67,
68]. The fundamental LLR is shown by Equation (4a).
With the refractive index measured at 589 nm; Rm molar refractivity and f() = [()2 -1]/[()2 +2].
It is a matter of identifying the physically correct amount of
N in the solvent system [
69]. The general factor
N in the original LLR, Equation (4a), refers to the molar concentration of the total number of solvent molecules [
47]. It has been shown recently, within homologous series of n-alkane derivatives, the correlation of the refractive index as a function of
N result in a negative slope which is theoretically not in line with the original LLR [
47]. Since
N is empirically linked with ν
max Equation (2), many correlations of ν
max with
from literature are not meaningful. Only if the actual molar concentration of the “chromophore” of the solvent molecule, the C-H bond concentration
NCH, is taken into account, the applicability of LLE for correlation analyses is fulfilled. The reason for this is simple, because
N ~ -
NCH. [
69]. Therefore, instead of
N, the respective concentration of the corresponding functional fractions of the solvent is actually required that is
NCH for special solvent families. Accordingly,
N should be replaced by
NCH when structure-property relationships are investigated regarding refraction index, Equation (4b):
For solvents containing hydroxyl- and/or -CO-NH-groups, the situation is straightforward as the HBD-groups are the dominant dipoles in the solvent volume. Thus, Equation (2) essentially holds when solvent families are treated individually, but is convincingly applicable to HBD solvents [
6,
27,
61]. Indeed, many
EPHBD correlate linearly with the physically determined hydroxyl group density, which is proportional to the molar concentration
N [Equation (2)], and not with the acidity in terms of the p
Ka of the solvent [
43]. For non-HBD solvents one only finds straight line relationships between
EP and
N if one stays within the series of a particular solvent family [
61]. One reason for the clear result of Equation (2) is that ε
max of the solvatochromic probe
, Equation (3b), changes inversely linearly to ν
max for most negative solvatochromic dyes under solvent variation [
1,
70,
71]. Equation (2) does work moderately good for positive solvatochromic dyes as preliminary evaluations on 4-nitroaniline or Nile Red suggest [unpublished results]. A supplementary explanation would be, that the molar absorption coefficient ε of the probe changes systematically linearly with
N, because ε also correlates with the refractive index due to the Kramer-Kronig relation [
72]. In these cases, ε
max behaves substantially unchanged within structurally similar solvent series. This observation is in agreement with older studies by Suppan [
73,
74].
There are several reasons for the motivation of this review and re-evaluation of
ET(30) parameters of organic co-solvent/ water mixtures. The field of aqueous solvent mixtures has become enormous progress in both experimental-methodological and theoretical terms. Many new insights into their microstructure and dynamics structure and properties have been gained the recent years for alcohol/water mixtures [75-95] and other co-solvent/water mixtures (see refrences in main text). In particular, these new findings on the microstructure of alcohol-water mixtures require a re-evaluation of many older results on the solvatochromism of probes in these mixtures. A crucial argument for testing the solvatochromism of
B30 in aqueous mixtures is that water is not a strongly acidic solvent in the sense of the HBD property, but one of the most polar solvents due to its exceptionally high molar concentration
N and the polarisation of the volumetric OH bonds [
60]. Note, you have to differentiate very clearly whether you are talking about volumetric water or smaller amounts of water as solute in a mixture [
75]. From x(water) < 0.2, the situation of aqueous mixtures behaves differently compared to the water-rich section, as water behaves more like a solute than a solvent [75-77].
Another argument concerns the appropriate use of the different measures of mixture composition [
50]. As a preview of this work, we demonstrated for selected binary alcohol/water and methanol/chloroform mixtures that
ET(30) is an approximately linear function of the average molar concentration (
Nav) of the solvent mixture with exceptionally high correlation quality for certain concentration ranges; correlation coefficient for linear relationship r (reggresion coefficient) ~ 0.99 [
43]. Probably, linear dependencies
ET(30) as function of
Nav only result when the thermal motion of the solvent molecules overcomes the micro-structuring of the solvent mixture and thus the solvatochromic probe measures an averaged number of various solvent dipoles as a snapshot in certain composition ranges ? To answer such questions, one has to take a closer look at the dynamics of the solvent mixture. Pure solvents and alcohol/water mixtures fit in one relationship when the dielectric relaxation time and the number of OH-dipoles, relating to
N with respect to mole fraction, are correlated (see
Figure 4 of [
85]). The relaxation time increases with decreasing number of OH dipoles due to increasing alcohol content. Reminder, the dielectric relaxation time τ is defined as the time it takes 63% of the molecules in the sample to return to disorder [
86]. Thus, the degree of ordering of binary alcohol/water mixtures containing two different types of OH-dipoles probably increases with increasing structuring i.e. concentration of C-C bonds originating from the alcohol molecules. It is important to note that ethanol/water mixtures fit well into this linear relationship of pure alcohols when the average molar concentration of the OH groups is taken into account [
85].
The question arises whether (binary) solvent mixtures can be treated in the same way as pure solvents in terms of the average molar concentration (
Nav) of relevant solvent dipoles resp. polarizable solvent molecules and which approach is appropriate for this methodology. The situation regarding the appropriate measure of composition is rather intricate. For the correlation of the results of UV/Vis spectroscopy or dielectric spectroscopy, different composition variables such as the molar and volume fraction of the mixture are sometimes used alternately [
9,
28,
87,
88]. The fundamental aspect of composition quantities is dealt with in the methods chapter of this paper.
2. Methods
The average molar concentration
Nav is a crucial physical property of all non-homogeneous substances. It must be clearly defined which atoms and molecules are being considered. In this study binary solvent mixtures are treated.
Nav of any homogeneous binary solvent mixture can be simply calculated by the quantity of composition of the two components, their molar masses and the actual physical density of the solvent mixture according to Equation (5) [
63].
ρm(1,2) is the actual density (after mixing) of the mixture at given Z.
M1 and M2 are the molar masses (g/mol) of solvent1 and 2, respectively;
Mav,z is the average molar mass of the solvent components.
The Z1 and Z2 factors are either
the mole fraction (Z = x; →Nav,x),
mass fraction (Z = w; →Nav,w), or
volume fraction (Z = φ; →Nav,v) of solvent1 and solvent2 before mxing.
The average molar concentrations
Nav.z in terms of different
Mav,z have not yet been fully considered as quantitative composition size in evaluating physical measurands of solvent mixtures. We had underestimated this point in an earlier work [
62]. The linearity of a relationship of a measurand on the composition size is not necessarily a criterion for physical correctness, as the various mixing rules for explaining the refractive index of solvent mixtures show [96-98]. It must be emphasised that the decisive quantity is the average molar mass
Mav,z which can be calculated either by x, w or φ [
99]; see Equation (6a):
Therefore, the numerical differences between
Nav,x,
Nav,w and
Nav,v are due to the differences in
M1 and
M2 as well as the quantitative ratio of the two solvents and less to the density changes, as shown for various alcohol/water mixtures when
Nav,x is plotted as function of x(water) (see
Figure S1).
The problem of the average molar mass is a central issue in polymer chemistry because, depending on the molar mass distribution (MWD) or inhomogeneity of the polymer mixture so synthesized, different physical measurement methods (end group analysis by NMR or acid-base titration, viscosity, osmotic pressure of the polymer solution, light scattering, ultracentrifugation) detect different numerical values of the average molar mass for the same polymer sample [
100]. The numerical value of the average molecular mass not only depends on the respective measuring method but also on the shape of the MWD
. [
100]. Note, colligative physical methods measure the number average (
Mn) of the polymer sample. This would correspond to the
Mav,x of solvent mixtures. Non-colligative physical methods (preferably) measure data related to the weight average (
Mw). The result of the non-colligative method depends on the type of solvent or polymer solute. For example, the refractive index is a non-colligative measurement. It is therefore not surprising that the determination of the mixture composition by refractive index measurements always gives rise to discussions [96-98].
The non-uniformity of a polymer is defined by the ratio
Mw/
Mn [
100,
101]. According to the teachings of polymer chemistry [
101], the ratio of
Mav,w/
Mav,x =
DI has been defined as the dispersion index of a binary solvent mixture in this work. Accordingly, Equation (6b) is used in practice as an indicator of the non-uniformity of the solvent mixture.
DI is an artificially constructed variable, but the approach is borrowed from polymer chemistry.
For a binary mixture this approach is straightforward.
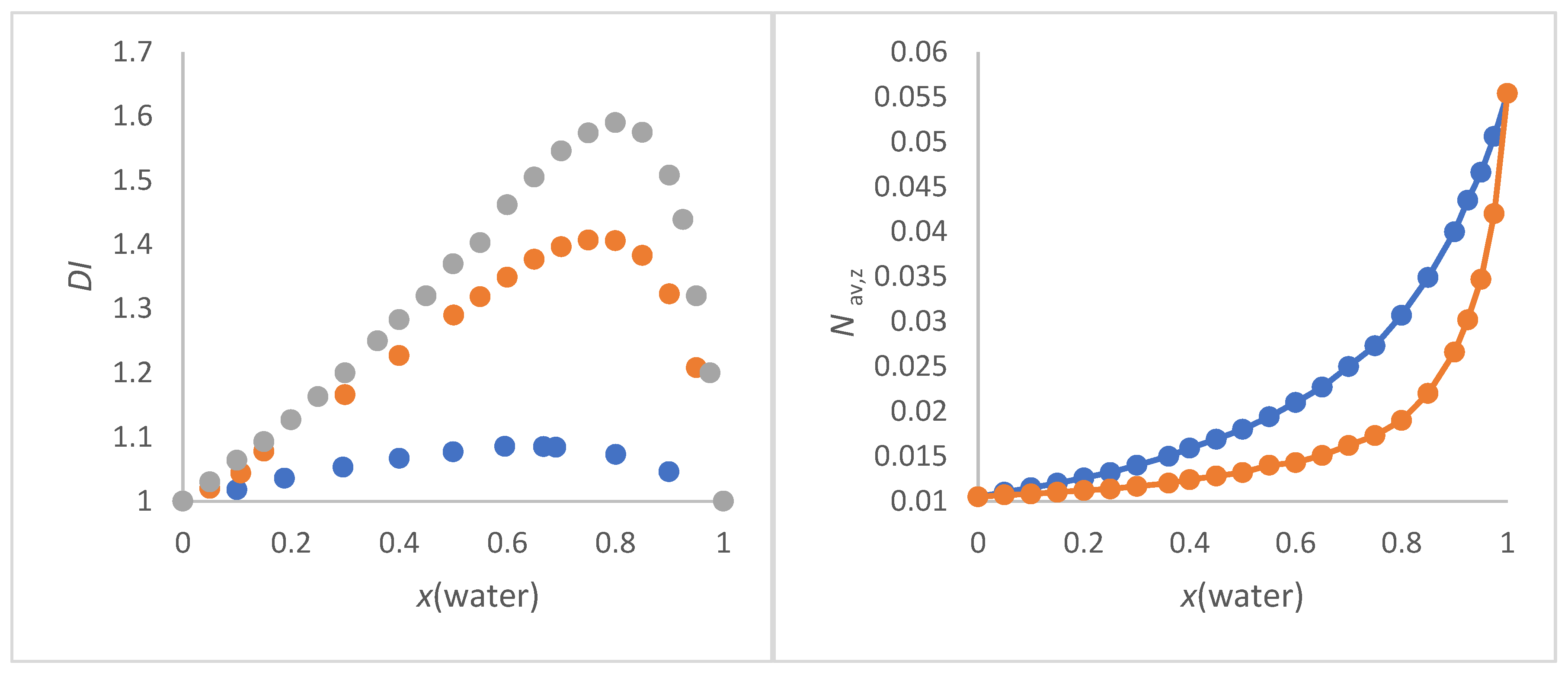
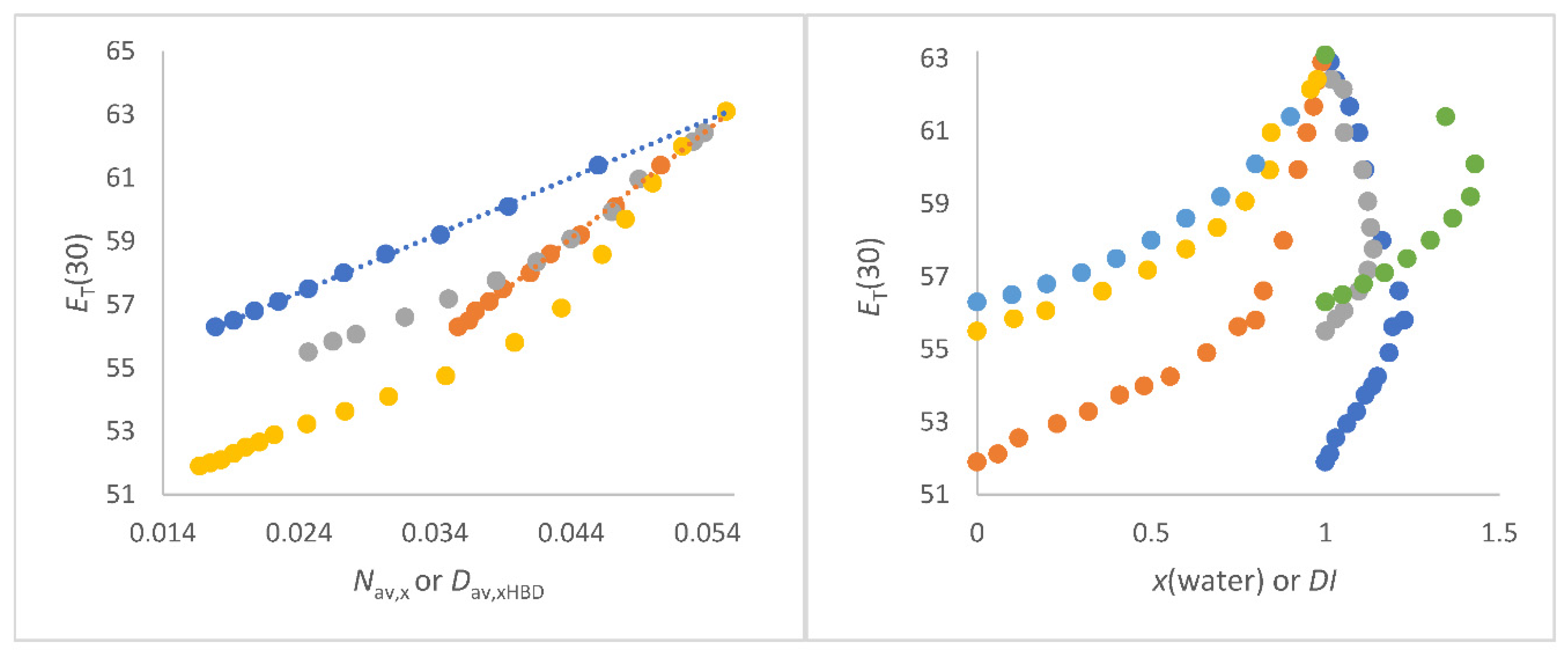
Figure 1a shows the dependence of
DI as function of x(water) for methanol/water, 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water.
Mav,x and
Mav,w are calculated by Equations (7a) and (7b), respectively.
Figure 1.
a (left panel). Dependence of
DI as function of x(water) for methanol/water (blue), 2-propanol/water (red) and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water (grey);
Figure 1b (right panel).
Nav,z (in mol/cm
3) of 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixture as a function of x(water).
Nav,x (blue) and
Nav,w (red).
Figure 1.
a (left panel). Dependence of
DI as function of x(water) for methanol/water (blue), 2-propanol/water (red) and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water (grey);
Figure 1b (right panel).
Nav,z (in mol/cm
3) of 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixture as a function of x(water).
Nav,x (blue) and
Nav,w (red).
The 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixture shows the greatest inhomogeneity at x(water) = 0.8 (strongest curvature of the graph in
Figure 1b), since the quotient
Mav,w/
Mav,x has its maximum at this position as a function of x(water). At this x (water) = 0.8,
Nav,x = 0.25 mol/cm
3 and
Nav,w = 0.15 mol/cm
3. As can be expected arithmetically, the greater the mass difference, the greater the
DI for given x. The smaller the mass difference, the wider the
DI is distributed at
DImax. It cannot be overlooked that the position of the highest
DI (
DImax.) with respect to x(water) corresponds to both the order of the molar excess molar volume of water and excess thermodynamic properties for these alcohol/water mixtures [77-79,82,94]. This is remarkable because the
DI only takes into account the masses and their proportions and does not contain any other physical data. It can be assumed that this correspondence is rather coincidental for alcohol-water mixtures. Hence, the suitability of
DI for supporting the interpretation
ET(30) as function of solvent composition in alcohol/water mixtures will be demonstrated as part of this work.
As explained in the introduction, for the evaluation of UV/Vis spectroscopic absorption data) [
67,
68], the mole fraction (x) is theoretically appropriate for determination the average nolar mass
. Thus,
Nav,x determined by Equation (7a) will be preferentially applied in this work for correlation with
ET(30).
The weight fraction
w1 is calculated by the mass portions
m1 and
m2 of the two components according to
w1 =
m1 /(
m1 +
m2). Then
Nav,w results from from Equation (7b).
Due to
Mav,w is inherently greater than
Mav,x [
100,
101],
Nav,x is always greater than
Nav,w.
Figure 1b, for example, shows the relationships between the composition quantities
Nav,x and
Nav,w, respectively, with x (water) for the binary solvent mixture 2-methyl-2-propanol/water.
Figure 1b clearly shows that
Nav,w reflects the inhomogeneity of the mixture as function of quantitative composition to a greater extent than
Nav,x because of the stronger deviation from linearity
Nav,x versus x(water) (see also
Figure S1).
The volume fraction to determine
Nav,v can also be used, Equation (7c). But there are still some open questions regarding the physical meaning of this quantity despite the IUPAC definition [
102].
This consideration relates to the solvent volume of the individual solvent constituents before mixing according to the IUPAC definition of the volume fraction: “Volume of a constituent of a mixture divided by the sum of volumes of all constituents prior to mixing” [
102]. This definition assumes ideal mixing behavior, which is not the case for most aqueous and non-aqueous solvent mixtures [
103]. When certain quantities of two liquids are mixed, neither the total number nor the total mass of the molecules change, but the sum of the volumes can change compared to the volumes before mixing. Therefore, the use of the volume fraction in the determination of
Nav,v is questionable in terms of actual physical meaningfulness. The use of
Nav,v (average molar concentration related to volume fraction) can only serve as an empirical guide. It represents the apparent influence of the volume change after mixing compared to the initial volumes.
Due to these well known problems regarding the volume changes after mixing, the issue is thermodynamically treated in terms of excess molar volume (
VE) by Equation (8) and described by several sophisticated concepts and approaches semi-empirically [ 66,77,104]. Equation (8) is established textbook knowledge.
With ρm(1) and ρm(2) density of the pure solvent 1 and 2, respectively. x1 and x2 is the mole fraction of solvent 1 and solvent 2, respectively. The analyses of VE as function of x(solvent1) and x(solvent2) can provide valuable information on the partial excess partial molar volumes of solvent 1 and 2 as a function of composition.
If the mole fraction of OH groups of one component on
Nav is considered, i.e. that of the HBD-solvent (
M1) content on
Nav, then Equation (7a) can be modified to Equation (9).
The approach of Equation (9) is useful to determine whether the influence of the portion of HBD-solvents mixed with non-HBD solvents is due to the overall polarity or to the preference of the HBD component, as shown for chloroform/methanol, with methanol acting as the preferred solvating agent, based on its partial concentration [
43]. Equation (9) can also be used to consider the average number of OH groups (
DHBD,av) of a multifunctional OH component in the mixture, e.g. for dihydric alcohols like 1,2-ethanediol [
62]. For pure 1,2-ethanediol, then, 2
N =
DHBD. See later the treatment of 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures in relation to
ET(30).
The problem with the average molar concentration is that the sum of the two dipoles is considered, e.g. for methanol and water. This is correct if the sum of the dipoles of the solvent and their effect are proportional to the measurand. Recently, we have demonstrated that the total molar concentration
N of pure solvents is not appropriate to describe the changes in refractive index
as a function of structural variation within homologous series of n-alkane derivatives [
68]. Instead, the molar concentration of the C-H bonds (or N-H) is crucial to adequately reflect the theoretically required linear relationship between
and
N according to the Lorentz-Lorenz Equation (4b). Equation (10) is especially convinient for co-solvent/water mixtures to calculate the average molar concentration of C-H and/or N-H bonds of the co-solvent [
69].
with m- number of C-H and N-H bonds per co-solvent molecule; x-is the mole fraction of the CH-group-containing co-solvent. For instance, m = 8 for 1,4-dioxane [
69]. Due to the atomic refraction of the C-H and N-H (amide) bond are nearly the same [
105], an additional correction is not necessary for formamide (FA),
N-methylformamide (NMF) and
N.N-dimethylformamide (DMF). For mixtures of organic solvents, the situation is more complicated because additional chemical bonds contribute to the molar refraction of the individual solvent molecules. This is especially crucial for halogenated and aromatic solvents. Therefore, only the situation for co-solvent/water mixtures is straightforward because water is a weak (negligible) chromophore.
Basically, the general statement of this chapter shows that the absorption energy (EP) of a dissolved dye in a mixture is inversely proportional to the mole fraction due to Mav ~ x(co-solvent) ~ 1/EP according to equations (6a) and (3b). These basic relationships apply independently of a physical law such as LLR.
3. Results
3.1. Selection of the Solvent Mixtures
Due to the enormous flood of data, we looked for a common thread in order to be able to make statements that are as representative as possible. Marcus distinguishes two groups of aqueous solvent mixtures that co-solvent either enhance the water structure or not. The evaluation is derived from the excess partial molar volume or excess partial molar heat capacity of the water [
106,
107]. Note, the Marcus classification only holds for the water rich section [
x(water) >0.7,
xco-solvent <0.3] [
106,
107]. Marcus stated “Some solutes such as ethylene glycol, 1,4-dioxane, acetonitrile, N-methylformamide(NMF), formamide (FA) (and urea), ethanolamine, and dimethylsulfoxide, many of which hydrogen-bond very strongly with water, do not enhance the water structure” [
107]. The selection was made according to this scientifically justified criterion. However, the Marcus evaluation can only serve as a rough guide, because depending on whether the excess partial molar volume or the corresponding heat capacity is used, some co-solvents can be assigned differently. For some co-solvents such as DMF, acetone and THF, the classification is borderline [
106] to [
107], which shows how difficult the issue is. The binary mixtures acetonitrile/water, acetone/water and THF/water each have a special character and will be treated together later in a separate publication. The situation regarding non-enhancement of water structure is definitely clear for FA/water, 1,2-ethanediol/water and glycerol/water mixtures [
106].
The enhanceemnt of the water structure is special relevant for ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures [
106,
107]. However, the term "enhancement of the water structure" sounds mysterious. [
77,
78]. The problem is that there are qualitatively different microdomains of water in alcohol/water mixtures in terms of structure and size [89-92,108]. Marcus [
107] stated: “Enhancement of the water structure then consists of the changing of some of the dense (water) domains to bulky ones”. This phenomenon would inevitably lead to an increase in the average alcohol concentration in the remaining mixed phase compared to the co-existing microdomain water phase or the hypothetical phase resulting from the initial mixing ratio for each composition. Therefore, the overall polarity of the actual ethanol/water mixed phase should be lower than the phase that would result if ethanol and water were fully mixed statistically at a given composition. This consideration should be keeped in mind.
The ethanol-water mixture seems to be one of the most difficult solvent mixtures to understand when considering simple systems; see [
108] and references cited. The temperature increase associated with volume shrinkage when mixing ethanol and water seems a thermodynamic anomaly [
78]. The strongly negative entropy of the mixing process suggests complicated structure formation as function of composition as suggested by dielectric spectroscopy and special microscopic techniques [85-88,108].
The curves of the solvatochromic parameters as a function of
x(water) in [
18,
19] correspond remarkably well with those of the partial molar volume as function of
x(water) of methanol/water, ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water [
94,
95]. Therefore, the physics of alcohol /water mixtures deserve special attention in this study. If microstructuring of the solvent mixture has an influence on the dissolved
B30 has not yet been discussed in detail.
3.2. Refractive Index of Aqueous Solvent Mixtures
The suitability of equation (10) is exemplified for several amide derivative/water, DMSO/water and 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures for which
ET(30) values are reported and discussed below. These solvent mixtures belong to the class where no enhancement of the water structure is evident [
107]. The literature references for
data are listed in the Tables of the supporting information section. For NMF/water, no usable refractive index data could be found in the literature.
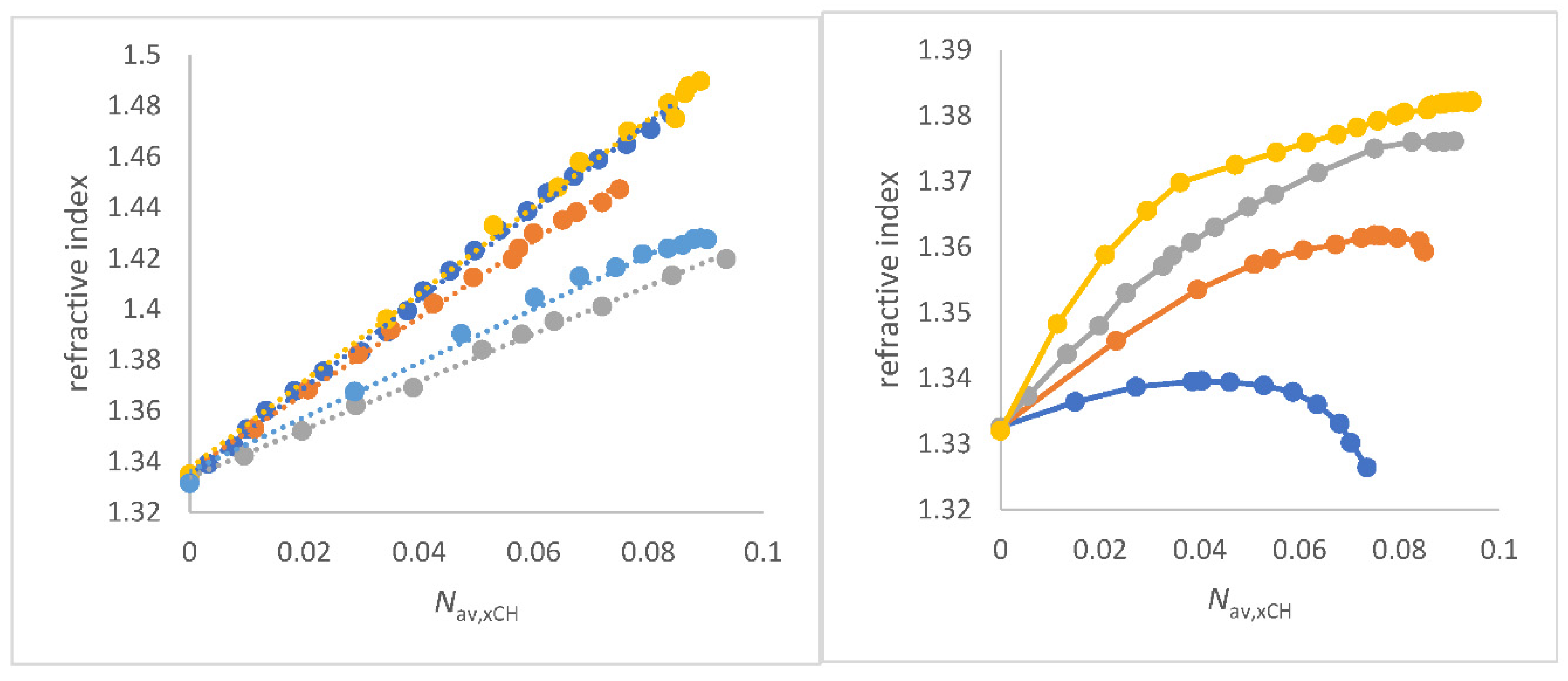
The representation of the refractive index measured at 589 nm wavelength (
) as a function of
Nav,x,CH results in a straight line as seen in
Figure 2a and from Equation (11) to Equation (15). 1,2-ethanediol/water and glycerol/water mixtures, which both show excellent linearity of
as a function of
Nav,x,CH , are outlined in chapter 3.4.6.
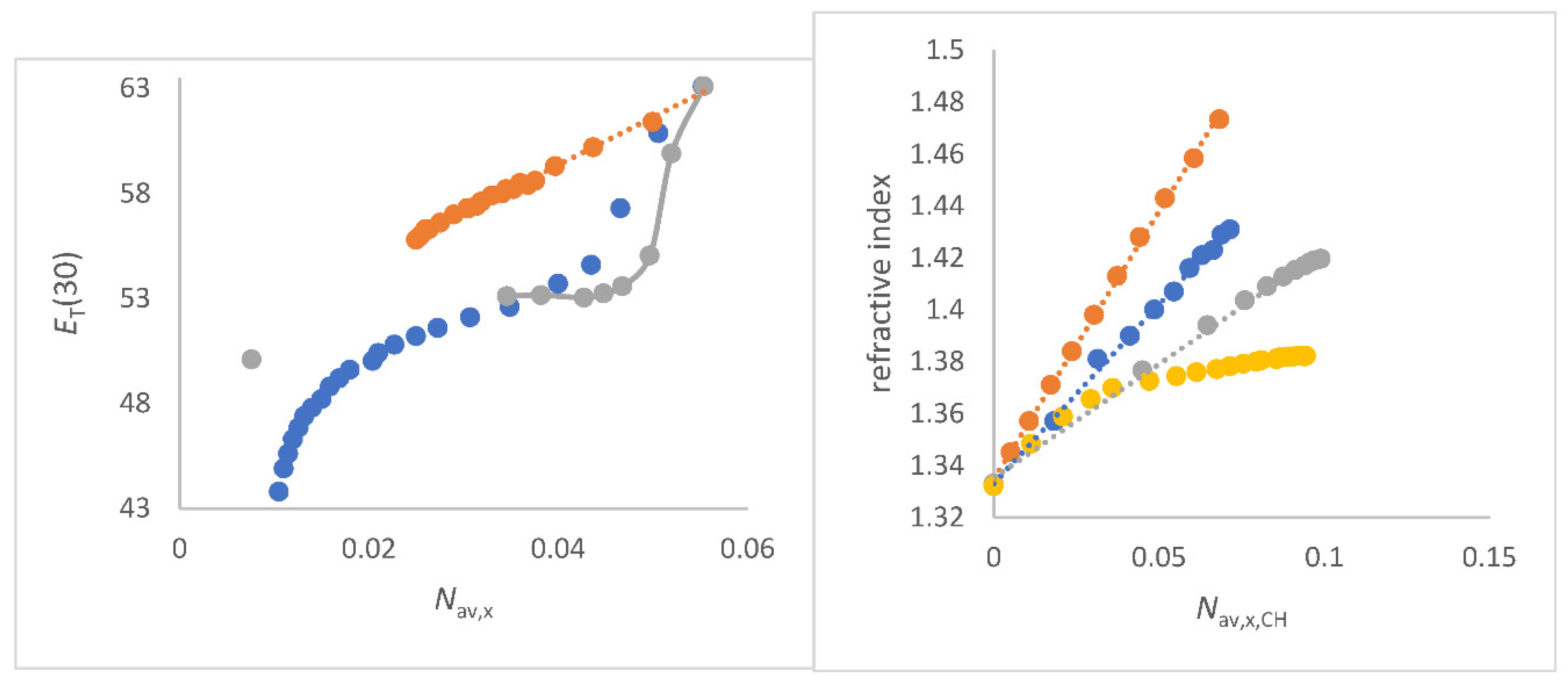
Figure 2.
a (left panel) Correlations of refractive index
as function of
Nav,x,CH (mol/cm
3) for co-solvents that do not enhance the water structure of co-solvent/water mixtures;
Figure 2b (right). Plots of refractive index
as function of
Nav,x,CH (mol/cm
3) for co-solvents that enhance the water structure of co-solvent/water mixtures; to a) FA/water (red), water/N-formylmorpholine (NFM) (yellow), DMF/water (grey), 1,4-dioxane/water (light blue) and DMSO/water (deep blue); to b) methanol/water (blue), ethanol/water (red), 2-propanol/water (grey), and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water (yellow).
Figure 2.
a (left panel) Correlations of refractive index
as function of
Nav,x,CH (mol/cm
3) for co-solvents that do not enhance the water structure of co-solvent/water mixtures;
Figure 2b (right). Plots of refractive index
as function of
Nav,x,CH (mol/cm
3) for co-solvents that enhance the water structure of co-solvent/water mixtures; to a) FA/water (red), water/N-formylmorpholine (NFM) (yellow), DMF/water (grey), 1,4-dioxane/water (light blue) and DMSO/water (deep blue); to b) methanol/water (blue), ethanol/water (red), 2-propanol/water (grey), and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water (yellow).
The positive slopes Δ
/Δ
Nav,x,CH and the excellent quality of the correlations
as a function of
Nav,x,CH for several co-solvent/water mixtures are a clear proof of the physical sense of this approach for solvent mixtures because it fulfills the theoretical requirement of Beer`s approximation and the LLR [
47,
67,
69]. The
ET(30) parameter of aqueous solvent mixtures decreases with increasing
for these co-solvent/water mixtures that do no show an enhancement of the water structure. For each specific solvent mixture, a separate correlation is found. These results are seen in
Figure S2 and explained at the appropriate place in the following text where the special mixture is discussed.
The convincing linear relationships in
Figure 2a are clear evidence for both the correctness of the quantity
Nav,x,CH and the approach of Equation (4b) and Equation (10) in the analysis of the refractive index of aqueous solvent mixtures as long as alcohol/water mixtures are not taken into account. Remarkably, the linearity
as a function of
Nav,x,CH does not apply to alcohol/water mixtures in which there is an anhancement of the water structure [106,107,109-112]. In particular, the methanol/water and ethanol/water systems give a maximum curve of
as a function of composition amount; see
Figure 2b. For the other alcohol/water mixtures an asymptotic curve is obtained, but still with positive slope along the curve;
Figure 2b. In the past, there are empirical concepts to circumvent the non-linearity
as function of composition for methanol/water; i.e. by using the quotient
/density instead
alone [
109]. But the physical background is more complicated and still under study. Recent studies have shown that microdomains of water and ethanol/water are present at the mesoscale, consisting of different refractive indices [
108]. Depending on the balance of segregation and aggregation of these areas [
109], the non-linearity of
as a function of composition is due to the coexistence of two different microdomains with different compositions and thus different refractive index. The ratio of the two ranges is a function of the original solvent proportions before mixing. The polarization effects and dipolar dispersion forces, which are relevant for methanol/water mixtures, can have an additional influence [
60,
92,
93].
Figure 2b clearly supports the hypothesis of the coexistence of different microdomains of water/alcohol mixtures [
89,
90,
108]. Basically, the alcohol/water mixtures that show an enhancement of the water structure according to Marcus do not show a linear dependency
on
Nav,x,CH.
Alcohol/water mixtures are further discussed in this paper under the aspect of co-existence of different microdomains.
3.3. Temperature Influence on ET(30) in Terms of Density Impact
The
ET(30) data of ethanol measured at different
T are from the original work of Dimroth/ Reichardt and Linert to his subject [
1,
113]. The data used are given in
Table S1 in the SI part. Both data sets show nearly perfect linear correlation of
ET(30) versus
N as expected; see Equation 16a and 16b; diagram is shown in the
Figure S3. With increasing
T,
ET(30) decreases due to the decrease in density and thus decreasing the number of dipoles per volume.
The
T-influence of the solutions of
B30 in ethanol and methanol was also investigated by Zhao [
114]. The authors claimed a
B30/methanol complexation with decreasing
T due to the appearance of an apparent isosbestic point in the UV/Vis spectra series in contrast to
B30 in ethanol. This conclusion is still not clear because the increase in the intensity of the UV/vis absorption band is likely due to volume shrinkage by cooling, the correction for which was not included in the reference. The increase in intensity and the associated hypsochromic shift of the UV/Vis absorption band of
B30 with decreasing
T thus can feign this isosbestic point. The presence of alcohol/
B30 complexes was also suspected by
T-dependent UV/vis-studies carried out by El Soud [
115]. However, complex formation of
B30 with ethanol was not directly proven by direct spectroscopic measurements. Sanders suggested that the
B30/HBD solvent complex would be the actual solvatochromic species as derived from theoretical considerations [
59]. However, the specific influence of the dye/solvent complex on
ET(30) is much smaller than the volume effect of the global hydrogen bond network. For these reasons, these few results are only a snapshot, as there is still much to be done to understand the
T influence on
ET(30) in terms of density fluctuation associated with structure alteration as a function of temperature [
115,
116]. However, this first inventory shows that the increase in
ET(30) with decreasing
T is mainly due to an increase in density and thus in
N.
3.4. Solvatochromism of B30 in Aqueous Solvent Mixtures
This part of the manuscript is the central concern. It is about correcting many misinterpretations in the literature. The most ET(30) data of the solvent mixtures for evaluation were taken from the numerous publications in ref [1-4,11-20] and others. Some special comments are required on the data sets used, as several aspects have to be taken into account. You have to check which ET(30) value corresponds exactly to the indicated concentration because molar fraction, weight fraction and volume content are used alternately [1,2,8,11-20].
For the evaluation, the densities of the mixture are needed for each specific composition and temperature of the mixture. This was the most difficult task to accomplish. Fortunately, the densities of alcohol/water mixtures often correlate significantly with the mole fraction (x) within certain sections of composition. Thus, unknown densities for special compositions can be calculated by correlation equations using precise data from literature. References are given in the captions of Figures and Tables in the supplementary materials, SI, section.
Advantageously, many of the measured
ET(30) values from literature agree very well between different authors for series of measurements. We have compared the data of Reichardt [
2] and Rosés [
18,
19,
20] and found that an almost perfect agreement of the measured
ET(30) values as a function of
Nav,x is found. As example see
Figure S4a for ethanol/water mixture. For this task it was necessary to convert the volume percentages from [
1,
2] to mole fraction. Despite the very good agreement, a data set from the same source was mostly used for the investigation if sufficient measured values were available. For the FA/water mixture, data from two different references were mixed because the authors' measurements covered different composition ranges [
21,
117]. There are only very small deviations. If one remains within one data series, regression coefficient r approach one for FA/water. For the NMF/water mixtures, there is no great variation obove x(water) >0.02, see suppoting information of [
21].
The high quality of the whole data set from Rosés should be emphasized. Rosés also used the carboxylate substituted betaine dye of
B30; the
B30-COONa to investigate alcohol water mixtures due to the weak solubility of
B30 in pure water and highly water concentrated mixtures [
19]. There is an almost perfect agreement betweeen
ET(30) and
ET(30-COONa) over the whole composition range. This aspect is taken up again in the discussion section.
The perfect complementarity of the different
ET(30) values for DMSO/water from several references [
7,
12,
14,
118,
119] should be noted (see Figures S4b). All data sets fit exactly in one relationship (see later). However, there are very small differences [ΔE
T(30) ~1 kcal) between the authors result.
Since the
ET(30) data sets for 1,2-ethanediol/water show some not tolerable differences in the low water concentration range between the data from [
12] and [
15], we used only the data set from [
12] which fit well (see
Figure S5).
The perfect complementary alignment of the
ET(30) data from [
13] and [
19] for the 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixture at high water concentration is also particularly noteworthy.
An unfortunately frequent problem was that many measured UV/Vis data of several solvatochromic dyes were neither given accurately in tables nor in supporting information [
6,
10]. Either only the evaluated results of the coefficients of the applied solvation models were given, or artificially modified parameters instead of the original spectroscopic data. Also, often only the diagrams were shown without the data being additionally given in tabular form. Unfortunately, this data could hardly be used. All secure data used for the correlation analyses are compiled in tables in the supplement materials section together with the physical data on properties of the solvent mixtures from the literature.
To support the correlations of
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x, , Kosower's
Z-scale was deemed appropriate [120-122], because of the linear correlation of
Z with the
ET(30) parameter [
1,
34,
35]. However, this turned out not to be the case. It is essential to clarify the situation of the different Z-values for DMSO/water and ethanol/water mixtures from the literature, because only the Z-values given by Kosower were determined directly with
K [120, 121]. The Z-values used by
Marcus for correlations were calculated by himself indirectly using
Brownstein's S-values [
123] (see note in citation 23 of marcus paper) [
12]. The same applies to Gowland's Z-values, which were also determined indirectly by 4-pyridine-
N-oxide via a correlation equation [
123,
124]. We are convinced the main problem is the reproducible measurement of Z values with
Kosower`s dye, because in [
124] it was mentioned that Z value is dependent on concentration of
K in ethanol/water.
To test whether case ii. of preferential solvation is significant, literature data of other negatively solvatochromic probes such as
B1 [(2,4,6-triphenyl-1-pyridinium)-phenolate] [
1], Brooker`s Merocyanine (
BM) [
125] or
Fe [
126] were taken into account, although fewer data points per correlation are available. For this purpose the qualitative results
EP or the UV/Vis absorption energy at peak maximum ν
max(
Fe) as a function of
Nav,x are examined.
3.4.1. 1,2-Ethanediol/Water, Methanol/Water and Ethanol/Water Mixtures
The reason for consideration 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures compared to methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures is the following. In all three systems, the enthalpy of mixing is exothermic over the entire composition range [
81,
82,
127]. While 1,2-ethanediol as co-solvent does not enhance the water structure, methanol and ethanol do [
106,
107].
As mentioned, the relation
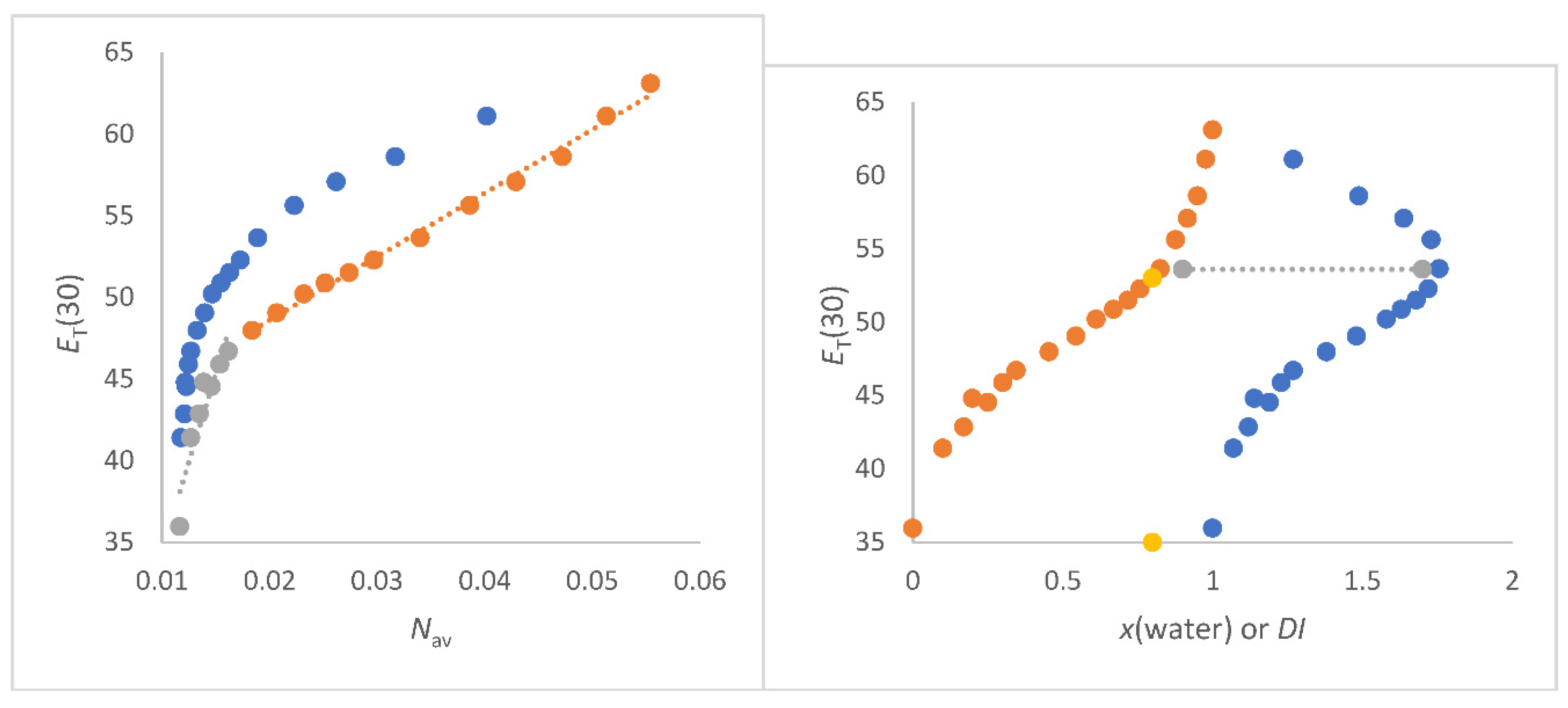
ET(30) as function of x(water) result in a curved line regardless whether methanol/water, ethanol/water or 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures are considered as seen in
Figure 3b. This has been discussed in the introduction and is sufficiently described in the literature [2,8,10-20]. The greater the molar mass difference, the more non-uniform the mixture, the greater the
DImax ethanediol/water mixtures (green) > ethanol/water mixtures (blue) > methanol/water mixtures (grey). This in turn depends on x(water) in the mixture. It can be clearly stated that the strongest curvature along a line of
ET(30) as a function of x(water) for each specific co-solvent/water mixtures occurs when
DI is highest. This is a purely physical effect that has nothing to do with specific solvation.
The situation is different if
ET(30) is theoretically correctly correlated with
Nav,x (see
Figure 3a, left hand panel). Then one obtains an excellent linear correlation for the 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures [Equation (17) and (18)]. This overall result is of great significance. The 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures shows no abrupt structural changes over the entire composition range [
74,
107,
127]. Despite the curved form of
ET(30) as a function of x(water), an excellent linear correlation of
ET(30) with
Nav,x is obtained for 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures. The interpretation of the
ET(30) course as function of
Nav,x for the 1,2-ethenediol/water mixtures requires an essential comment, because each 1,2-ethanediol molecule contains two OH groups. Therefore, the number of OH dipoles per 1,2-ethanediol is doubled [
62]. For the ethanediol/water mixtures, the hydroxyl group density regarding the number of total OH dipoles is taken into account by use of the
DHBD (density of OH groups) quantity and calculated by means of Equation (9) using the partial OH concentration of the 1,2-ethanediol component in the mixture (see
Table S2). The determined function
ET(30) versus
DHBD for 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures according to Equation (9) is the red-dot line in
Figure 3b. This curve is completely congruent with the relationship
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x for methanol/water mixtures in the water rich section (
Nav,x > 0.04 mol/cm
3). However, it is remarkable that the correlation
ET(30) versus
Nav,x methanol/water mixtures from
Nav,x <0.04 mol/cm
3 runs parallel to the correlation
ET(30) versus
Nav,x (deep blue) for 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures indicating the variation of OH-dipoles influence on
ET(30). This result shows convincingly the strong impact of the total number of OH groups of binary aqueous mixtures in terms of
DHBD,av,x or
Nav,x on
ET(30) [
62]. These unambiguous results completely rule out a preferential solvation of
B30 in methanol/water, ethanol/water as well as 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures relating to scenario ii. The results for the methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures do also not really correspond to the scenario i. It is always the total number of dipoles per volume that determines the
ET(30) value within certain composition ranges, independent of structural variations.
A kink can be seen in the correlation line
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x for methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures in
Figure 3a.The kink of this line is attributed to structure variation at
Nav,x = 0.038 mol/cm
3 of the methanol/water mixtures. At
Nav,x = 0.0384 mol/cm
3 , the methanol/water mixtures shows the largest refractive index and largest volume contraction. However, the linear plots of
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x for each solvent mixture section are of excellent quality as seen by Equations (17) – (20).
In the literature there are various physical data on the properties of methanol/water mixtures indicating structure variation in the range between x(water) = 0.5 to 0.6; corresponding to
Nav,x = 0.035 and 0.04 mol/cm
3 [85-94]. This wide distribution is also confirmed by the heat of interaction as a function of composition, with the largest measured heat of about -850 kJ/mol in a range from x(water)~06 to 0.75 [
80,
81]. The refractive index of methanol/water mixtures reaches its maximum at x(water) = 0.6 [109-111]. The highest heat of the exothermic interaction is at x(water) = 0.6 [81, 82] (
Nav,x = 0.038 mol/cm
3) which is completely reflected by the
DImax of the methanol/water mixtures that is the highest at x(water) = 0.6 (see
Figure 1b).
However, the overall situation with these two monohydric alcohol-water mixtures is not entirely clear. For ethanol/water mixtures, the function
ET(30) versus
Nav,x shows a clear kink at exactly
Nav,x = 0.04 mol/cm
3 of the total number of dipoles corresponding to x(water) = 0.8. The excess molar volume for ethanol/water mixtures is at x(water) = 0.6, but the heat of interaction is highest at x(water) = 0.82 to 0.845 [81, 82]. Hence, the refractive index maximum of ethanol/water mixtures does not correpond to the thermodynamics as apparently found for methanol/water mixtures. The different courses of the methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures composition with regard to the refractive index were also noted by Langhals [
109]. For the ethanol/water mixtures, the plots
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x or
x(water) are clearly determined by the thermodynamics. Exactly at this composition where the greatest heat of inteaction is measured, the graphs show a kink in the line indicating the strucure alteration [
5,
80,
81,
83,
88]. These correspondences between the curves in
Figure 3a and the thermodynamics or refractive index show the influence of the physical properties of the mixture on
ET(30).
But there are several additional aspects to consider. Bentley [
28] has shown that the volume fraction correlates better with the static dielectric constant or
ET(30) of alcohol-water mixtures compared to the mole fraction as a composition parameter of alcohol-water mixtures. The volume fraction was also recommended in a recent publication to explain the
ET(30) as a function of solvent composition more accurately than using the mole fraction [
128]. Accordingly, for ethanol/water and methanol/water mixtures, the
Nav,w and
Nav,v quantities were calculated and empirically tested as variables for correlation with
ET(30) [
62]. It seems surprising that the
Nav,w and
Nav,v quantities give a much better linear relationship with
ET(30) than using
Nav,x when the entire composition range is considered. The methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures fit smoothly into the series of primary alcohols if the overall data set
ET(30) of primary alcohols are considered; see Equation (21) and Equation (22) and Figure .S6 in the supplement materials part. The overall correlations including 42 data points are convincing.
There is no qualitative difference whether the function ET(30) versus Nav,v or ET(30) versus Nav,w is considered.
Therefore, the motivation for use the volume fraction given in [
128] should be reconsidered. The mass fraction would give related results. Regardless of which alcohol/water mixture is used, the actual curve
ET(30) versus
Nav,w or
Nav,v is not really strictly linear, although a very good regression coefficient can be calculated for linearity. The data dots along the relationship showed a significant pattern like a string of pearls as seen in
Figure S6 in the supporting materials part. This is an important detail. Thus, the subtleties observed in the correlation of
ET(30) with
Nav,x do not vanish, but are merely diminished in the plots
ET(30) as function of either
Nav,w or
Nav,v. The approximate linearity of
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,w and
Nav,v is due to the stronger algorithmic consideration of the inhomogeneity of the solvent components in
Nav,w or
Nav,v (see
Figure 1b).
These results clearly show that the discussed preferential solvation of
B30 by water is meaningless for methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures. This is also an indication that polarizablity forces and dipolar effects of the molecules of the solvent mixture act collectively upon
B30. In 1963, in the first paper on phenolate betaine dyes, Dimroth and Reichardt also studied the better water soluble
B1 probe in ethanol/water mixtures [
1]. Data see
Table S4. There is also a very good correlation of
ET(1) as function of
Nav,v, as seen by Equation (23). The correlation of
ET(1) as function of
Nav,x is equivalent to that of
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x .
If pure water is omitted from Equation (23), the correlation quality is significantly improved to r = 0.999. This is also a strong indication that B1 is preferentially enriched in ethanol/water rich domains when the mixture is investigated.
The
xb values of
BM (
xb is the shift of the UV/Vis peak of
BM in methanol/water) [
125]) do correlate with
Nav,x very well; see Equation (24).
Consequently, the preferential solvation of
BM in methanol/water as assumed by Machado [
26] or Tanaka [
129] is not applicable when
Nav,x is used instead of x(water) to evaluate solvatochromism. The methanol/water mixtures were also investigated by
Taha using the
Fe probe [
126]. There is also a linear correlation and no bended curve for ν
max(
Fe) as function of
Nav,x , Equation (25).
It should be mentioned that for methanol/water mixtures the correlation of EP as a function of Nav,x or N av,v are quite similar from an arithmetic point of view (unpublished).
For ethanol/water mixtures, the ν
max(
Fe) shows a similar correlation with excellent quality as reported previously [
43]. The correlations of ν
max(
Fe) with x(water) in place with
Nav,x is worse. These results clearly show that several types of negatively solvatochromic dyes such as
B30,
B1,
BM and
Fe do not indicate preferential solvation in the methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures. Thus the linear correlations of
EP parameters as function of
Nav,x according to Equation (2) are clearly confirmed by other solvatochromic dyes despite the fewer data set compared to
ET(30). Since different solvatochromic probes show the same dependencies of
EP as a function of
N av,x, it is quite clear that the solvent structure determines the solvatochromism and not preferential solvation of scenario ii. This is in complete agreement with older results from Langhals [
5].
3.4.2. FA/Water and Related Amide/Water Mixtures
FA/water is the only binary aqueous mixing system considered in this study that fulfils the thermodynamics of ideal mixing [
66,
106,
107]. The heat of mixing is endothermic and the entropy is positive over the entire composition range. The mixing entropy is highest at
x = 0.5 [130-133]. The best linear correlations ( r approach one) of
ET(30) as function of
Navx over the entire composition range of the solvent mixture are found for FA/water, NMF/water and 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures (see
Figure 3b and
Figure 4a).
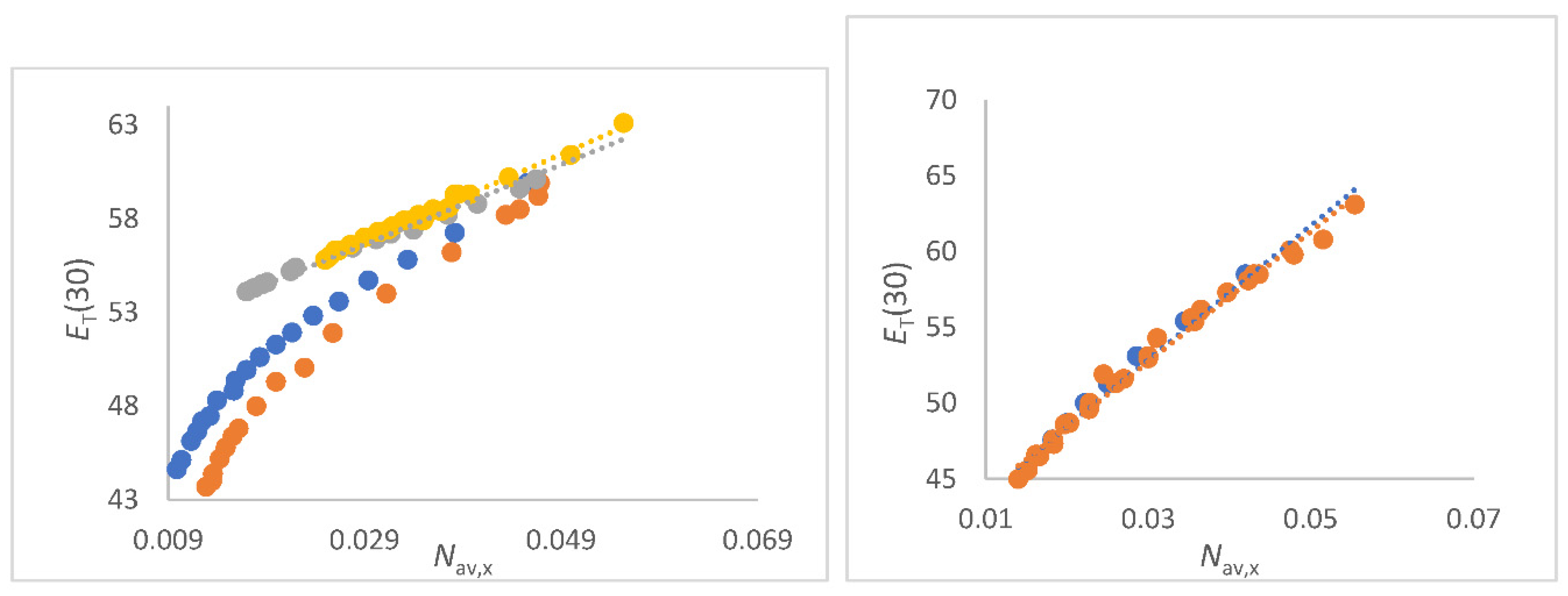
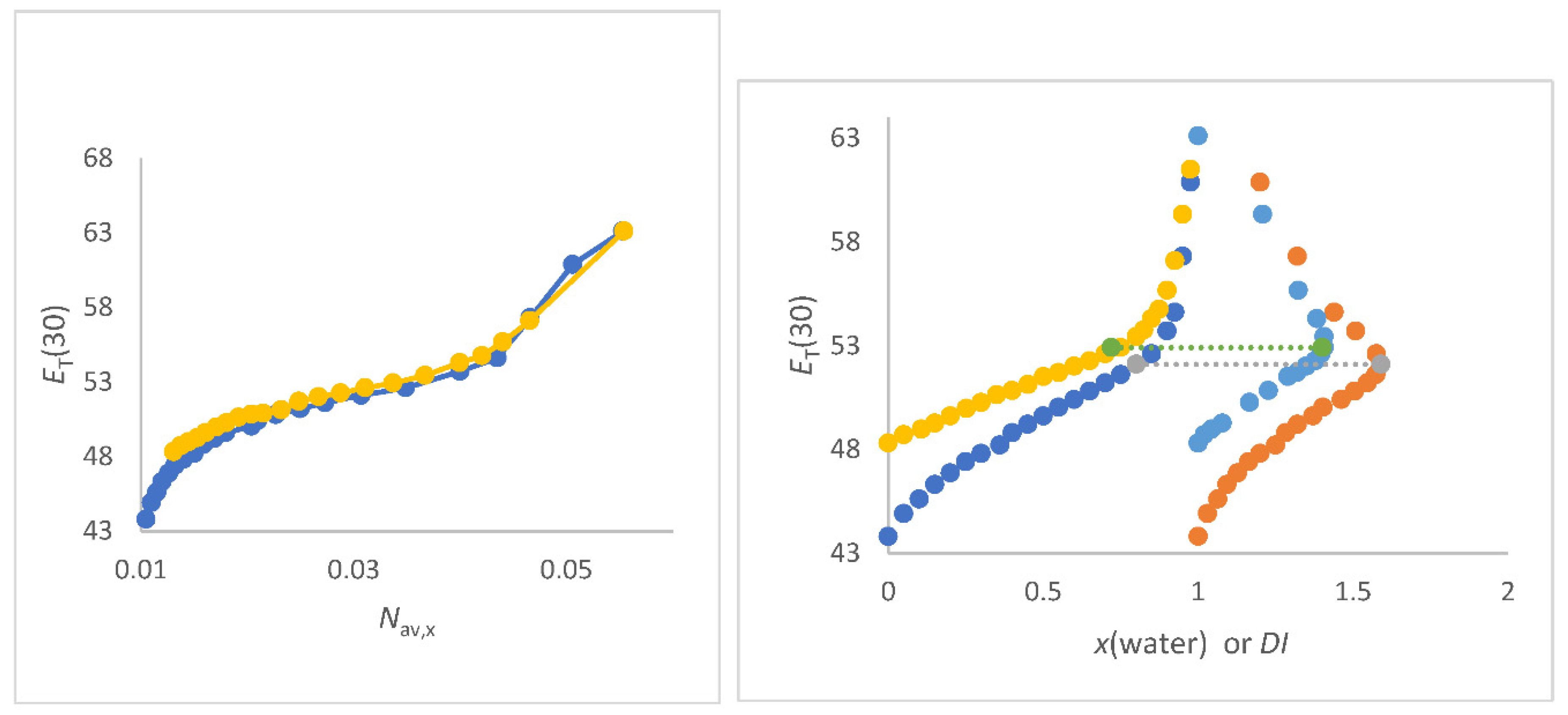
Figure 4.
a (left panel). Correlations of
ET(30) (kcal/mol) as function of
Nav,x (mol/cm
3) FA/water (yellow), NMF/water (grey),
N-formylmorpholine/water (blue) and DMF/water(red) mixtures. Data see
Table S2 to S5;
Figure 4b (right panel). Correlations of
ET(30) (kcal/mol) as function of
Nav,x (mol/cm
3) for DMSO/water mixtures (red, all data); Blue dots are data from [
15] (O Connor).
Figure 4.
a (left panel). Correlations of
ET(30) (kcal/mol) as function of
Nav,x (mol/cm
3) FA/water (yellow), NMF/water (grey),
N-formylmorpholine/water (blue) and DMF/water(red) mixtures. Data see
Table S2 to S5;
Figure 4b (right panel). Correlations of
ET(30) (kcal/mol) as function of
Nav,x (mol/cm
3) for DMSO/water mixtures (red, all data); Blue dots are data from [
15] (O Connor).
For FA/water mixtures the linear correlations
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x is of excellent quality; see
Figure 4a as well as Equation (26).
The perfect linearity can be explained by the outstanding physical properties of the FA/water mixing system [106,107,133-134]. The water like structure of FA is due to the fact that water and FA molecules can exchange positions without changing the solvent structure [
134], only the
VE [Equation (8)] is hardly changed [
133]. Thus, no segregation occurs and the average number of dipoles per volume determines the
ET(30) at ambient temperature perfectly. Furthermore, for NMF/water, NFM/water and DMF/water mixtures there are also excellent linear correlations of
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x in the section of higher water content; x
co-solvent < 0.35 due to similar physical properties of these mixtures [107,135-137]. The physical data of the solvent mixtures NMF/water, DMF/water and NFM/water mixtures are given in Tables S2 to S5 in the supporting materials section [130-137].
The slight bend in the curve of lower water content is due to the nonlinear change in density as function of composition [135-137]. Thus, water is more seen as a solute rather than solvent in accordance to [
75] when
Nav,x < 0.035 mol/cm
3. However, an excellent linear correlation of the refractive index as a function of
Nav,x,CH is seen for all mixtures (see
Figure 2a) over the entire composition range, including the range of low water concentrations.
3.4.3. DMSO/Water Mixture
The DMSO-water mixtures are a challenge in terms of physics among binary aqueous solvent systems due to the unclear themodynamics at higher DMSO content [138-146]. It was therefore chosen for this fundamental work as educational illustration. There is a great deal of physical studies on this mixtures, so only those that are relevant to explaining solvatochromism in relation to
Nav,x will be referred to. The following analysis will show where the problems lie. There results a very good linear correlation of
ET(30) with
Nav,x including
ET(30) data from several references, Equation (28) and
Figure 4b.
Despite the overall correlation
ET(30) with
Nav,x seems convincing due to the clear linearity, there is a small kink in the linear plot at
Nav,x ≈ 0.025 to 0.03 mol/cm
3. If only the data from [
14] were considered, see equations (29a) and (29b).
This small effect has a significant physical background because the density of the system changes significantly at this composition [
138,
140]. However, the density measurements in the DMSO-rich region reported in literature are not consistent. In the water-rich section from
Nav,x < 0.05541 mol/cm
3 (pure water) to
Nav,x = 0.03 mol/cm
3 the density of water/DMSO mixtures decreases linearly with increasing water content. The density behaves nearly constant in the section of high DMSO content from
Navx = 0.03 (60% weight DMSO) to 0.014 mol/cm
3 (pure DMSO) (see
Table S9). In [
140] was reported that density even slightly decreases; but this has no real influence on the data evaluation regarding the interpretation of the
ET(30) values in terms of
Nav,x . Note, exactly at this mixture composition
Nav,x = 0.028 mol/cm
3 the plot
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x has a slight, imperceptible kink.
However, the correlation of the UV/Vis absorption energy of
cis-dicyano-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-iron II (
Fe) [ ν
max10
-3 cm
-1 (
Fe)] [
126] as function of
Nav,x for DMSO/water mixtures clearly shows a linear dependence, see Equation (30).
In the literature, there are several investigations on the DMSO/water mixtures using different solvatochromic probes [12,15,147-149]. Regardless of the type of probe used, it can be clearly stated that at
Nav,x ≈ 0.03 mol/cm
3 a slight change in the course of the parameters as function of composition is observed. Thus, the physical structural change of the DMSO/water system determines the empirical parameter and not artificially constructed acid-base properties of the solvent system [
147,
149]. This result is in complete agreement with the prediction in the introduction that no differences should occur in case ii. when different probes are used. For reasons of space, the analyses of the Kamlet-Taft (KAT) parameters of DMSO/water [
147] are presented in the
Figure S6 in the supporting information part. As consequence of this result, the determination of individual empirical polarity parameters in terms of the KAT or Catalán scale is meaningless for DMSO/water mixtures. Furthermore, a curved function of the
ET(30) value of the solvatochromic probe on x(water) of DMSO/water mixtures is found [see (
Figure 5) of [
12]] that would become linear if the
x(water) would be replaced by
Nav,x.
The change in the course of solvatochromic parameter after KAT at
Nav,x about 0.03 mol/cm
3 is clearly attributed to physical changes in the solvent structure. Furthermore, if one plot the static dielectric constant (ε
r ) as function of
Nav,x the kink at
Nav,x at 0.03 mol/cm
3 becomes also obvious (see
Figure S7). The ε
r data are from [
143]. This feature is also shown in the plot of
ET(30) as a function of ε
r (
Figure S8) or
(
Figure 2b). While the correlation of
as a function of
Nav,CH is nearly linear (
Figure 2a), the correlation of
ET(30) as function of
shows a slight kink corresponding to
Nav,x = 0.03 (see
Figure S2).
As resume to the DMSO/water mixtures, the overall comcentration of dipoles (water + DMSO) of the system determines the solvatochromic property and not preferential solvation. This is a clear result. Surprising is actually only the quite good linearity of the function ET(30) against Nav,x when many data from the literature are used together. This shows that B30 is not very sensitive to physical changes in the DMSO/water system at RT. Therefore, the solvatochromic method is not well suited to detect the physical change in the liquid structure of DMSO/water at distinct composition.
What is the reason for the good linearity of
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x although larger structural changes of the mixture occur at
Nav,x = 0.03 mol/cm
3? The complexity of water dynamics of DMSO/water mixtures was profoundly studied by ultrafast IR-experiments and dielectric spectroscopy [141-143]. These results are very important to partly explain the results of the correlations in this study. The average lifetime of the water bonded DMSO is changed (decreases) nearly linearly with the mole fraction of water which is consistent that
ET(30) nearly linearly increases with water content (see also
Figure 5 in [
141]). This explains why the barely perceptible kink in the correlation may negligible, because the water dynamics overcome the local structuring around the dye solute. Thus, the water−water component lifetime is independent of water concentration in the section of high DMSO content
Nav,x < 0.03 mol/cm
3. Obviously, there are neither water/DMSO nor
B30/water complexes relevant for the determination of
ET(30) as the solvent mixture has a high dynamic at 298 K [
142,
143]. Thus, despite DMSO/water or
B30/water complexes are present, they cannot be recognized by
B30 because of the fast dynamics of the binary solvent system. The situation is similar to other solvatochromic dyes as seen in
Figure S9.
Therefore, other physical measurements such as dielectric spectroscopy are more suitable than solvatochromic probe molecules for analysing the structure of DMSO/water mixtures. The outstanding behavior of the DMSO/water mixtures at higher DMSO content
Nav,x < 0.028 mol/cm
3 was the subject of numerous simulation experiments [144-146]. Obviously, the behavior at
Nav,x < 0.03 mol/cm
3 is attributed to the entropy increase of the system, which can still hardly be understood theoretically [
146], because the experimentally determined heat of interaction is exothermic over the entire composition range. In a further work we want to take up the DMSO/water system again, because it provides some very concise method-dependent result series, which are to be evaluated in depth with regard to composition quantities (see also discussion).
3.4.4. 1,4-Dioxane/Water Mixtures
The 1,4-dioxane-water mixtures were also subjected to numerous physical investigations [150-161]. Dependencies of UV/Vis-absorption energy maxima of solvatochromic dyes such as B30, Fe, different 7-N,N-diethylaminocoumarins, M540 or harmaline as function of dioxane-water composition were extensively studied in literature [2,5,69,126,157-161].
The thermodynamics of the binary system 1,4-dioxane/water is characterised by the transition from exothermic heat of mixing to endothermic heat of mixing with increasing 1,4-dioxane content [
150]. This is the decisive contrast to the DMSO/water system. Heat of interaction
ΔrH is exothermic and has its mostly exothermic heat at about x(water) = 0.8 (yellow dot in
Figure 5b) corresponding to
Nav,x = 0.032 mol/cm
3;
Nav,v = 0.018 mol/cm
3.. The largest partial molar volume of water in 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures is at x = 0.8 [
151].
ΔrH is zero at x(water) = 0.52 (
Nav,x = 0.02 mol/cm
3). With this composition, the mixture has the highest density and the lowest -TΔS value. At x(water) < 0.52, the heat of interaction becomes endothermic.
For the evaluation in this work, the volume fractions of the 1,4-dioxane/water solvent mixtures given in [
2] were re-converted to the average molar concentration of the solvent dipoles. Unfortunately, the extensive data set from [
6] could not be used because the specific
ET(30) data were not documented in tabular form. Fortunately, there is an excellent agreement between the
ET(30) data of four different literature sources as shown in
Table S7. The
ET(30) data from these four different sources fit perfectly in one relationship. To evaluate the influence of the inhomogeneity of the mixture in terms of composition, we have plotted
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x and
Nav,v as well as x(water) (
Figure 5a and 5b).
The correlation of
ET(30)as function of
Nav,x results in two consecutive linear lines with a kink at
Nav,x = 0.015 [x(water) = 0.3] mol/cm
3; see Equation (31a) and (31b) and
Figure 5a. At this composition, there is also the strongest curvature (at E
T(30) ~ 46 kcal/mol) in the curve
ET(30) as function of x(water) in the 1,4-dioxane-rich section (see
Figure 5b).
The kink in the grey/red-dot curve (
Figure 5a) approach approximately that composition
Nav,x = 0.02 mol/cm
3 at which the mixture behaves athermic
ΔrHmixing = 0. A similar result is found for the correlation of ν
max10
-3 cm
-1 (
Fe) as function of
Nav,x . There is a bend in the curve. However, there are too few data in the dioxane-rich section to make a clear statement. The correlation of
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,v (blue dots in
Figure 5a) gives an asymptotic curve without linearity of special sections.
Water and 1,4-dioxane are subject to fine structuring over the entire composition range, in which both types of molecule are always involved [153-156]. The volumetric structure of 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures changes significantly in the section from
Nav,x < 0.02 mol/cm
3. Acccordingly, the strongest bend in the graph correponds to that composition where the significant change in the volumetric structure of the 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures takes place. Exactly at
ET(30) = 47 kcal/mol (
Nav,x = 0.018 mol/cm
3) the dielectric relaxation time τ1 passes through a mximum ( τ1 ≈ 25 ps) for 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures [
154]. The use of
Nav,X(water) after Equation (9) as a mixture composition parameter gives a similar diagram pattern as when
Nav,x is used, indicating that 1,4-dioxane and water are always involved together in the volumetric structure and thus in the solvation of dissolved
B30. Thus, 1,4-dioxane does not enhance the water structure in any way, which is in complete agreement with the Marcus classification [
107].
It is worth analysing the correlations of
ET(30) as a function of x(water) from the point of view of thermodynamics and the structural change of the dioxane-water mixture, as shown in
Figure 5b.At x(water) = 0.52 (
Nav,x = 0.02 mol/cm
3 ) the curve
ET(30) as a function of x(water) shows an inflection point (not marked in
Figure 5b). Exactly at this composition this binary solvent system behaves a-thermal, i.e.
ΔrHmixing = 0 and has the largest excess molar volume [
150,
151]. The strong curvature
ET(30) as function of x(water) = 0.8, (yellow marked) (
Nav,v = 0.015 mol/cm
3 ) is clearly due to the inherent mass inhomogeneity of the mixture, as shown in the simultaneous graph for the
DI (
Figure 5b). At this composition the mixture has the highest exothermic heat. This result is consistent to the results from the thermodynamics of methanol/water and ethanol/water mixture. These results are good indications that
x(water) reflects the thermodynamics of the mixture in relation to other measurands more comprehensive than the
Nav,x quantity, which is physically reasonable. Thus, the S-shaped function
ET(30) versus
x(water) (
Figure 5b, red dots) is attributed to the change in interaction heat as function of composition. This feature is only partly recognized when
Nav,x is used as composition size as seen in
Figure 5a. There is no bend or kink in the plot
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x at
Nav,x ~ 0.032 mol/cm
3 (largest exothermic heat) but at
Nav,x = 0.02 mol/cm
3 (zero heat).
The linear function of
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x in the water-rich section
Nav,x > 0.02 mol/cm
3 is due to the fact that the average concentration of both the water dipoles and 1,4-dioxane molecules determines the
ET(30) value. Both fractions are permanently intermixed and show no segregation [
154,
155]. Somewhat below this threshold at
Nav,x = 0.018 mol/cm
3 , a clear kink in the curve
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x can be seen. The larger
ET(30) in the dioxane rich fraction, compared to an hypothetical linear plot
ET(30) versus
Nav,x, , can be readily explained by results of Buchner: “This indicates a largely microheterogeneous structure for such mixtures, with the presence of water-rich domains of significant size in the dioxane-rich fraction”[
155]. Thus,
B30 preferentially measures the water-enriched sections of 1,4-dioxane/water domains within the composition spectrum. Obviously, the water clusters are solvated by 1,4-dioxane excess and the
B30 is enriched in the 1,4-dioxane clusters below
Nav,x <0.015 mol/cm
3.
The refractive index as function of composition of the 1,4-dioxane/mixture with respect to
Nav,xCH (see
Figure 2a, red dots) and Equation (15) results in a linear plot. This is in line with the fact that the static dielectric constant εr is also a linear function of
Nav,x including the pure 1,4-dioxane (see
Figure S8b). For this examination the composition data
x(water) from [
154] were converted to
Nav,x. However, in contrast, the correlation of
ET(30) as function of ε
r or
is not linear over the entire composition range due to the pure 1,4-dioxane or the 1,4-dioxane-rich fraction does not linearly fit; see
Figure S8a. As consequence the
B30 probe reflects the volumetric structure of 1,4-dioxane/water differently compared to volumetric physical polarity-related measurements as dielectric spectroscopy or refraction index.
In summary, the 1,4-dioxane/water system presents a challenge with regard to the formation of solvent structures as a function of the quantitative composition, since different physical methods (UV/vis spectroscopy of B30, dielectric spectroscopy, refractive index, calorimetry) register different dependencies of the measurand on the different composition sizes. Note that only x and Nav,x are physically reasoned quantities that relate to thermodynamic and UV/Vis-spectroscopic quantities, respectively. Despite this concern, in summary, the complex dependence of ET(30) on the 1,4-dioxane/water composition in terms of Nav,x, Nav,xv or x(water) can be interpreted readily using the results of binary solvent system physics and mixture inhomogeneity, in which thermodynamics, concentration of dipoles and solvent dynamics play a role. Despite this reluctance, it can be clearly stated that the specific solvation of B30 by HBD solvent molecules is not responsible for that UV/Vis shift. The ET(30) value is mainly determined by the concentration of the water dipoles, which are permanently intermixt by 1,4-dioxane molecules.
3.4.5. 2-Propanol/Water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/Water Mixtures
In this chapter, the mixtures 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures are considered, which show a change in the heat with increasing alcohol content in the sense of a reversal from exothermic to endothermic heat [
81,
82] similar to the 1,4-dioxane/water system [
150]. Especially, the 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures have been the subject of research and speculative interpretations during the last decades [162-171]. A mystical character was attributed to this special mixture because of the method-dependent results of the mixture [
171].
At first the correlations of ET(30) as function of Nav,x and x(water) will be discussed; Figure (6a) and (6b).
The representation of
ET(30) as a function of mole fraction
x(water) shows qualitatively similar courses for all mixtures. These graphics are presented in the
Figure S10 in the supporting information section. Comparing the curves
ET(30) with that of the inhomogeneity (
DI) of the solvent mixture both as a function of x(water), see
Figure 3b and
Figure 6b, the same result is recognized for 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol mixtures compared to methanol/water, ethanol/water, and 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures. The strongest bending of the plot
ET(30) versus x(water) always occurs immediately after the greatest inhomogeneity. This "immediately after" corresponds to about 1.5 kcal/mol with respect to
ET(30) which is illustrated by the horizontal lines (grey and green dots) between the two curves as seen in
Figure 6b. This scenario holds for all
Mav,w/
Mav,x, plots regardless of the type of alcohol/water mixture. Only with methanol/water mixtures is the composition range not so sharply defined.
The curves
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x for methanol/water, ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures differ qualitatively for both methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures compared to 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol /water mixtures in the section of low water content. Hence, the graphs
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x show an inflection points; at about 0.031 mol/cm
3 and 0.0273 mol/cm
3, for 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures, respectively. At lower water concentration, the binary solvent systems 2-propanol/water (x(water) < 0.5;
Nav,x = 0.02 mol/cm
3) and 2-methyl-2-propanol mixtures (x (water) < 0.55;
Navx = 0.018 mol/cm
3) are endothermic in terms of mixing interaction heat. At about x = 0.65 to x = 0.5 (water) (
Nav,x ≈ 0.03, see
Figure 6a) both systems behave a-thermic; i.e
ΔHmixing = 0. Exactly at this composition, the curve
ET(30) as a function of
Nav,x (see
Figure 6a) shows an inflection point. Same result is found for the 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures (see
Figure 5b). This indicates the change in water structure and its influence in the solvation mechanism of the
B30 probe. In the endothermic range, both curves
ET(30) versus
Nav,x show higher
ET(30) than expected from linearity. In this section, the mixing entropy is positive and the water portion in the mixture obviously determines the
ET(30) more than in the water-rich section. The dielectric relaxation time clearly decreases from lower to higher water content, i.e. in the water-poor section a more temporally stable structure is present than in the water-rich section. This is an important detail that is also observed for other related solvent systems which show endothermic mixing heat in the composition section of the non-aqueous component at x(co-solvent) > 0.5 such as acetone/water or acetonitrile/water mixtures to be published later.
The
Fe complex was also studied in 2-propanol/water mixtures. In accordance with the correlations of
ET(30) versus
Nav,x, the plot ν
max (
Fe) as function of
Nav,x (see
Figure S11) also shows a related pattern as that of
Figure 6a indicating the influence of the physical structure of the solvent as function of composition similar as for
B30.
Furthermore, there are numerous studies using positive solvatochromic probes such as Nile red [
7], 4-nitroaniline, [
18], 4-nitroanisole, [
18] 4-(1-azetidinyl) benzonitrile [
170] or coumarin 343 and 480 [
171] in various alcohol/water mixtures. The profound analyses of the results of positive solvatochroomic dyes in methanol/water, ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water, and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures will be reported in a later publication.. As preview, these analyses support the conclusions of this study but underline that the solvation thermodynamics is dependent on the probe used especially in the water rich section [172-174].
While 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures show similar pattern ET(30) as function of Nav,x, the 2-butoxyethanol/water mixtures behaves differently due to hydrophobic solvation which will be discussed in the final chapter..
3.4.6. 2-Butoxyethanol/Water Mixtures
As a final example, the solvatochromism of
B30 in 2-butoxyethanol (BE)/water mixtures will be re-analysed; the
ET(30) data are from reference [
7]. BE itself is partially hydrophobic, but mixes completely with water at room temperature [
175]. At higher temperatures, however, segregation occurs. The BE-water mixtures have been the subject of numerous physical investigations due to its self-structuring properties [176-185]. The self-propelled agglomeration of the BE molecules in water has been proven by various scattering methods [
176,
177]. At x(BE) > 0.02 agglomeration begins to occur resulting in an inhomogeneous solvent mixture at the level at about 1 nm [
176]. However, other studies showed that 130 nm aggregates are present [
177]. The inhomogeneity of the BE/water mixing system is complicated by the fact that this feature can be observed on different length and time scales [180-183,185].
The BE/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures are often compared with regard to their similarity [
185]. We will demonstrate that the two solvent mixtures are completely different in spite of the discussion in literature. The microstructures of both solvent mixtures are very subtle and are strongly influenced by the composition in the water rich section. However, the heat of mixing is exothermic nearly over the entire composition range for BE/water mixtures, but weakly endothermic at high BE (ca 95 wt %) concentration [
179,
180]. Furthermore, photo-switchable spiro compounds were measured in BE/water mixtures [
184]. It was suspected that the solvent structure of BE/water is affected by this type of photo-switching. Thus, one cannot exclude the possibility that the dissolved probe molecule co-determines the fine structure of BE/water mixtures which make the whole situation complicated. Therefore, only the analysis of the
ET(30) values is discussed here. Unfortunately, the interesting solvatochromic results of El Seoud on this solvent system were not given as original data [
22]. If one plots
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x , for BE/water mixtures an asymmetric course results as seen in
Figure 7a (grey dots).
The crucial section of low BE content serves special attention, (
Nav,x = 0,0497 mol/cm
3) (grey dot line); x(BE) ≈ 0.02) or
Nav,xCH = 0,015 mol/cm
3, as aggregate formation of the BE molecules takes place at this composition [
176] and
B30 dye is obviously absorbed by these BE-rich agglomerates leading to an abrupt decrease in
ET(30) at
Nav,x ≈ 0.05 mol/cm
3. This is consistent with the fact that
ET(30) decreases abruptly with increasing C-H concentration due to the BE component at
Nav,CH = 0.017 mol/cm
3 (not shown). There is only a narrow transition.
This result exactly fulfils scenario i. mentioned in the introduction. The agglomeration of BE is driven by hydrophobic interaction, as additionally suggested by the analysis of the fluorescence of coumarin and related probe molecules in BE/water mixtures [
185,
186]. Obviously, the trapping of probes is also determined by the solvent cage proerty of the BE/water mixtures. This is in contrast to 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures, where strong thermal fluctuations in partial concentration occur [
187]. Thus, a true hydrophobic solvation of
B30 does not take place in 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures, instead the partial water structures are changed depending on the composition as discussed in the previous chapter [
187,
188].
The two binary solvent mixtures glycerol/water and ethanediol/water show a perfect mixing behaviour in the sense of the Marcus classification, so that there is no enhancement of the water structure in any way [
88,
106]. These two mixtures are documented in
Figure 7b as references. For glycerol/water and 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures perfect linear correlations of
as function of
Navx,CH result; see Equation (32) and (33) [
88,
189]. The same holds for the correlation of the static dielectric constant as function of
Nav,x for glycerol/water (unpublished).
The larger slopes of Δ
/ Δ
Navx,CH for glycerol/water and 1,2-ethanediol/water mixtures compared to BE/water mixtures are attributed to the influence of the polarizability of the hydrogen bond network and the higher refraction of the C-O bond compared to C-H [
60,
62,
105]. This aspect is important for sugars and polyhydric alcohols, as will be documented in a later article.
The change in the overall bulck solvent structure of 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures as function of composition is also clearly visible in the plot of the refractive index as function of
Nav,CH (yellow dot line in
Figure 2b and
Figure 7b) that shows a kink at about 0.035 to 0.04 mol/cm
3. Remarkably, the kink in the graph
ET(30) as function of
Nav,x is also obsevved at this composition; see
Figure 6a. In this concentration range the thermodynamic changes from exothermic to endothermic with increasing
Nav,CH for 2-methy-2-propanol/water mixtures. This thermodynamic scenario does not apply to BE/water mixtures [
179,
180].
Remarkably, the correlation of
as function of
Na
v,CH for BE/water mixtures is linear over the whole composition range; see Equation (34) and
Figure 7b (grey dot line).
Obviously, BE as a co-solvent does not enhance the water structure, but water enhances the BE structure. That is the special thing. According to the Marcus classification, this is the inverse scenario regarding enhancement of solvent structures. These considerations convincingly show the qualitative differences between BE/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures. The different solvation behavior of B30 in BE/water mixtures compared to 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures can also be supported by considering the DI from Equation (6b). The BE/water mixtures show the greatest inhomogeneity with respect to DI at x(water) = 0.85 (Nav,x = 0.029 mol/cm3), while the kink in the curve ET(30) as a function of Nav,x occurs well away from this at ≈ 0.045 mol/cm3. This is the crucial difference of BE/water mixtures compared to all other (monohydric) alcohol/water mixtures investigated in this work. Therefore, this result could be used as criterion to define preferential solvation scenario of case i. However, the results do not exclude that the B30 dye itself has an influence on the solvent cage of the BE/water mixture at low BE content, as mentioned in the references [184 ,185] for other solutes.
4. Discussion
The relationship of ET(30) as a function of Nav,x for co-solvent/water mixtures shows different pattern depending on the co-solvent of the mixture. The scenario of each specific co-solvent/water mixture can be clearly assigned according to the Marcus classification. Four different scenarios can be recognised:
The
ET(30) increases significantly and linearly with
Nav,x (1,2-ethanediol/water, FA/water, NMF/ water, and DMSO/water mixtures) (see
Figure 3a,
Figure 4a and b). These co-solvents belong to the group of solvents that do not at all enhance the water structure and form strong hydrogen bonds with water. In these cases, the
ET(30) of the pure co-solvent fits into the linear representation.
The ET(30) increases asymptotically with increasing Nav,x where the ET(30) value is always higher than with a linear dependency (1,4-dioxane/water, DMF/water, NFM/water, and NFM/water mixtures) (see Fig. 4a and 5a). In these cases, the co-solvent-rich fraction shows nonlinearity ET(30) as function of Nav,x. These co-solvents do not enhance the water structure but form weaker hydrogen bonds with water than those belonging to scenario A).
The
ET(30) increases with increasing
Nav,x where the
ET(30) value is always lower than with a linear dependency (methanol/water and ethanol/water mixtures) (see
Figure 3a). This scenario holds for co-solvents that enhance the water structure.
ET(30) shows an S-shaped progression as a function of
Nav,x (see
Figure 6a). With increasing
Nav,x the
ET(30) value is always higher than with a linear dependence in the co-solvent-rich section, but the
ET(30) is lower than with a linear dependence in the water-rich section (2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water, and 2-butoxyethanol/water mixtures). This scenario applies to mixing systems that mutually enhance either the water structure or the structure of the co-solvent strongly.
In particular, these binary co-solvent/water mixtures of scenario A), to which glycerol/water mixtures also belongs, have proven themselves as robust reference liquids for contact angle measurements due to no segregation aoccurs when in contact to various types of surfaces [
190]. This is an important result in support of the Marcus theory for classification of aqueous mixtures.
When a fast solvent dynamic occurs of special solvent system, thermal motion overcomes local structuring effects which lead to a nearly perfect linear relationship of ET(30) as function of Nav,x for the FA/water, DMSO/water, 1,2-ethanediol/water, urea/water (unpublished), and NMF/water mixtures, as demonstrated. This interpretation is strongly supported considering the results of dielectric spectroscopy and ultra-fast IR experiments.
The heat of the interaction of 1,2-ethanediol/water, DMSO/water and NMF/water mixtures on the one hand is exothermic over the entire composition range, the heat of the interaction of the FA/water mixtures, on the other hand, is always weakly endothermic. The best fits ET(30) as function of Nav,x are for 1,2-ethanediol/water, NMF/water mixtures (exothermicity over the entire composition range) and FA/water mixtures (weak endothermicity over the entire composition range). For alle co-solvent/water mixture regarding A), the qualitative heat of interaction is not altered as function of composition.
For scenario B), the co-solvents also belong to the Marcus classification, which do not enhance the water structure. There is a linear dependence of ET(30) as a function of Nav,x up to Nav,x > 0.02 mol/cm3. However, the water portion obviously has a greater impact on ET(30) than concluded from the average number of dipoles over the entire composition range. A linear correlation of ET(30) as function of Nav,x is always found in the section of higher water content. Thus, the acting average molar concentration of the dipoles (water and co-solvent) upon the probe is the dominant factor in the section of higher water content. Only from Nav,x > 0.0135 onwards is there a bend in the curve indicating that water as a co-component loses its influence on ET(30). These co-solvents form weaker hydrogen bonds with water compared to scenario A), indicating that the water structure changes non-linearly with composition [191-193]. These co-solvents can be assigned differently depending on the criteria used by Marcus for the assessment.
Also, for the 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures, the ET(30) is always larger than expected from the sum of water and 1,4-dioxane dipoles. The curves are congruent for 1,4-dioxane/water and DMF/water mixtures up to Nav,x = 0.0135 mol/cm3. However, whereas the heat of mixing of DMF with water is exothermic over the entire compostion range, the situation for 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures is different as discussed. Thus, the thermodynamic changes in the mixtures DMF/water and dioxane/water are not always registered by the correlation of ET(30) with Nav,x.
The correlation of
ET(30) with
x(water) provides better indications of thermodynamic changes at distinct composiions of 1,4-dioxane/water mixture, but does not indicate preferential solvation. This detailed result is very meaningful because it shows the linkage of
x(water) with thermodynamics but not directly with the UV/Vis shift. In summary, the scenario B) requires more detailed studies using related binary solvent mixtures. Further studies will consider the complexity of THF/water, acetone/water, and acetonitrile/water mixtures [
192,
193] and other binary solvent mixtures such as pyridine/water or piperidine/water mixtures [
2] with regard to solvatochromism in order to clarify or complement some of the conclusions on scenario B) of this study. As Marcus demonstrates, each specific mixture actually requires special treatment and evaluation in order to understand the many physical effects. Therefore, this review only provides a rough overview of the overall problem using selected examples.
For scenario C) and D) the co-solvents belong to the Marcus classification, which enhance the water structure. But why is the
ET(30) value for methanol/water, ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures lower at high water concentrations than would be expected for a linear dependence such as observed for 1,2-ethanediol/water as seen in
Figure 3a? The answer is quite pragmatic: the hydrophobic dye
B30 is difficult to dissolve in pure water [
1].Thus it dissolves much better in the alcohol/water rich domains where the partial alcohol concentration is larger than the total alcohol concentration in the initial mixture. Therefore, a lower
ET(30) is measured logically than would be expected based on the total average molar concentration (
Nav,x), as the average water concentration in the partial alcohol/water fraction must be lower outside the areas with enhanced water structure. The mole fraction
x(water) as a measure of solvent composition in solvatochromism analysis fakes preferential solvation since
x is inversely proportional to
Nav,x. The curved functions of
ET(30) as a function of
x(water) determined so far are due to the inhomogeneity (
DI) of the solvent mixture.
This result is a significant contribution to the identification of enhanced water structures in alcohol-water mixtures. The enhanced microdomain water structure ranges of alcohol/water mixtures are obviously not covered by B30 for two reasons; first: B30 dissolves poorly in pure water, and second: the molar absorption coefficient of B30 in water is rather low [1, 70].
The first argument is supported by the fact that different solvatochromic dyes such as 4-nitroaniline, 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitroanisole or
B30 show qualitatively different dependencies of the UV/Vis absorption energy as a function of alcohol/water composition, especially in the water-rich range x(water) > 0.8 [
18,
19]. This observation applies regardless of whether methanol/water, ethanol/water, 2-propanol/water or 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures are considered. Obviously, hydrophilic dyes are distributed in both areas and hydrophobic dyes are preferentially dissolved in the alcohol/water fraction. Since
B30 itself is a hydrophobic molecule, this scenario is likely.
This explanation is also consistent with the results of the BE/water mixtures, which captures the hydrophobic B30 particularly well, as an abrupt decrease in ET(30) with increasing BE content occurs when agglomeration of n-butoxyethanol takes place.
However, it looks that
B30 and
B30-COONa measure the water rich section in the same sense [
19].
B30-COONa is much more soluble in alcohol/water than in pure water, as our own measurements show (not published). Note that the half-width of the UV/Vis absorption band of
B30 measured in alcohol/water mixtures is quite broad. These very broad UV/Vis spectra with large half-value widths are often measured in water-salt mixtures [
194]. They indicate the presence of different, very similar solvation structures, which are detected by the dye. Unfortunately, the UV/Vis spectra are not given in [
19]. It is therefore not possible to tell whether there are superpositions of several UV/Vis bands. A final statement is therefore not yet possible.
The 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures belong to scenario D). In the co-solvent rich section the B30 is preferentially influenced by the partial water concentration of the mixture due to larger ET(30) is measured as expected from linearity. This observation holds for the endothermic section of mixing the alcohols with water. The situation is quite delicate when the thermodynamics of the mixture changes from exothermic to endothermic depending on the composition. Then, at ΔrHmixing = 0, the plot ET(30) as function of Nav,x shows an inflection point as clearly recognized for 2-propanol/water, 2-methyl-2-propanol/water and 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures. However, this is only an interim result that needs to be confirmed by further studies.
As a conclusion from these considerations, it is assumed that the thermodynamics of the interaction between solvatochromic probe and solvent mixture is crucial. Unfortunately, the dissolution thermodynamics of
B30 is still not systematically studied in various solvents. There are only two papers with calorimetric results on the thermodynamic of solvation
B30 [195, 196]. The results from the two references do not match the theory of exothermic solvation leading to lowering the ground state energy [34b,35]. The dissolution process of
B30 in acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, and higher alcohols is found to be endothermic which is difficult to explain and may be attributed to entropic effects and not to re-association of
B30 as discussed [
196]. Thus, the thermodynamics of the
B30/HBD solvent interaction is not trivially explainable in terms of specific hydrogen bond formation. This is in line with the results of present study that hydrogen bond formation has no remarkable effect on the
ET(30) value. As consequence, the influence of the thermodynamic of solvation of
B30 in terms of the real ground state energy is difficult to judge because the calorimetric studies on several
B30/solvent systems are hard to interpret. There are different approaches to correlate the polarity data with calorimetric data, which is partly successful, but also gives very strange results. Therefore, this approach has often not been pursued further [
197].
The complicated situation regarding solvation thermodynamics is similar for positive solvatochromic dyes such as 4-nitroaniline (
NA). The dissolution process of
NA in co-solvent/water mixtures is endothermic in terms of the heat of mixing in the high water content region [
172,
173]. Thus, a reinterpretation of the solvatochromic results of
NA in co-solvent/eater mixtures from the literature [
18,
19,
174] is imperative. The effect of endothermic solvation and its effect on the UV/Vis absorption energy requires a more detailed analyses in future work [63,172-174]. The idea that the solvation of an electronic state leads to an energetic lowering should be abandoned.
There is an additional aspect to consider. Dissolved
B30 probes are statistically influenced by the dynamically moving solvent molecules. Due to the high dynamics of the binary mixtures at 298 K, both dipoles water and co-solvent are strongly influenced by the thermal motion. For this reason, only one snapshot of various solvation states is ever measured by the UV/vis spectrum. A superposition of many solvation states is registered. Thus, discrimination of domain formation in solvent mixtures by solvatochromic probes is only possible if the dynamics of the solvent is much lower than that of the optical excitation of
B30. This argument applies precisely to such mixtures where the co-solvent enhances the water structure. This can be explained if the relaxation time τ1 measured by dielectric spectroscopy is taken into account. The larger the τ1 values, the more structural subtleties of the mixture are detected by the solvatochromic probe at ambient temperature as shown for 2-propanol/water and 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures [
85,
87,
88]. Therefore, the results of dielectric spectroscopy in terms of relaxation time are a useful accompanying guide to explain the results of UV/Vis measurements.
The two groups of co-solvents that either improve the water structure or not can probably be distinguished on the basis of the refractive index if
is correlated as function of
Nav,x,CH as demonstrated in
Figure 2. If there is no linear correlation of
with
Nav,x over the entire composition range, microdomains of water have formed in the mixture in the form of enhanced water structures. However, this characteristics is less pronounced for the static dielectric constant and only detectable by means of excess ε
r [Spange, unpublished; see also Fig. S7 and S8b)]. For example, this rule does not apply to the correlation of the dielectric constant as a function of
Nav,x for DMSO/water mixtures, where a curved line is found instead of a linear course for
Nav,x [
198,
199,
200]. For this, ε
r correlates linearly with x(water), but not linearly with
[
200]. This particular behaviour of DMSO/water mixtures is due to the recently recognised unusual microheterogeneity of these special mixtures [
201]. This important detail supports the thesis that the local mass inhomogeneity in terms of
DI has an influence on the result of the physical measurement. Therefore, nothing is riskier than relying on routine evaluations of measurement results as function of composition of co-solvent/water mixtures. This aspect will be discussed for the acetone/water and acetonitrile/water mixtures in more detail in a later publication.
Due to the complex structure of aqueous solvent mixtures, ever better knowledge is emerging on the basis of conventional and modern measurement methods taking into account density, refractive index, heat of interaction and other properties (dielectric relaxation) of the individual solvent mixture systems. Linking UV/Vis spectroscopic data as ET(30) with physical properties of the solvent mixture (molar concentration of dipoles, dielectric dynamics, thermodynamics, domain size formation) has proven to be necessary but very complex.
There is always new work on the structure of ethanol/water or the 2-methyl-2-propanol/water mixtures, which shows a refined picture of these unusual solvent systems [108, 202, 203]. However, the results of recent studies clearly confirm the presence of co-existing microdomains of water and alcohol/water.
The considerations of this study also apply to organic solvent mixtures. Thus Langhals showed as early as 1981 that the same relationships that apply to aqueous mixtures can also be used for binary organic solvent mixtures [
204]. This motivates to re-evaluate and classify binary organic solvent mixtures as well. This requires extensive literature work to record the density data. However, the formation of hydrogen bonds upon the probe may have a stronger effect in specical systems, but the use of
Nav,x instead of
x is necessary for a correct evaluation of solvatochromic data [
205].
5. Conclusions
The Marcus classification of aqueous solvent mixtures has proved very useful and explains the qualitatively different correlations of ET(30) with Nav,x for different co-solvent/water mixtures. This should easily solve many puzzles from the literature, because all previous evaluations of solvatochromic data with the mole fraction x(water or co-solvent) as the composition variable are physically incorrect. Signigicant linear and curvilinear relationships of ET(30) as a function of solvent composition in terms of Nav,x were detected. With increasing both the OH dipole and co-solvent dipole concentration, ET(30) increases linearly for those mixtures where the co-solvent does not enhance the water structure. This feature holds for FA/water, 1,2-ethandiol/water, NMF/water, and DMSO/water. Co-solvents which enhance the water structure of aqueous mixtures (Marcus) show S-shaped or bended curve of ET(30) as function of Nav,x depending on the thermodynamics of the mixing process and solvent dynamics in terms of relaxation time. Even if preferential solvation of a solute occurs, this cannot always be observed by solvatochromic probes if the dynamics in the binary solvent micture are too high. Then an average number of solvation states is recorded. The complexity of the structure of alcohol-water mixtures is reflected by the correlation of the refractive index or ET(30)as function of different composition quantities as x(water), Nav,x, Nav,x,CH or Nav,v.
The
Nav,x quantity of the mixture is physically reasoned as appropriate measure of composition to analyse UV/Vis results of solvatochromic probes because of the linear relationship with the UV/Vis absorption energy according to the LLR [
68]. The refined interpretations of
ET(30) as function of solvent composition in this work were only possible on the basis of many new and modern insights into the structure of solvent mixtures [
85,
108,
155,
156,
199,
200] and the true significance of optical measurements [67-69]. Fundamentally, the significance of the various measures of the average molar mass of solvent mixtures requires further research into their relationship to physical methods of investigation and their informative value. The use of the solvent mixtures inhomogeneity in terms of the
Mav,w/
Mav,x quantity should be considered for other solvent systemes to support the conclusions of this study in future work.
Finally, it is incomprehensible why hardly anyone has used the average molar concentration Nav,z as a measure of the composition of solvent mixtures. The mole fraction x is needed for thermodynamics, but not for spectroscopic concerns. However, both quantities are crucial for understanding the physics of the system. Regardless of the theoretically justified relationships of the Debye-, Clausius-Mosotti- or Lorentz-Lorenz-equations, the use of the molar concentration is actually necessary for the evaluation of UV/vis spectroscopic data and refractive index.
Despite the correlations found, it must be clearly stated that solvatochromism is only conditionally suitable for analysing solvent mixtures, unless one only wants to quickly measure the composition by means of calibration lines [6, 204]. To understand the complex dependence of the absorption energy of a solvatochromic probe on solvent composition, the structure of the solvent mixture must be analysed, but solvatochromy cannot analyse structures as Marcus correctly stated for acetonitile/water mixtures [
206].