Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
27 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Effects of RIC on the hippocampus
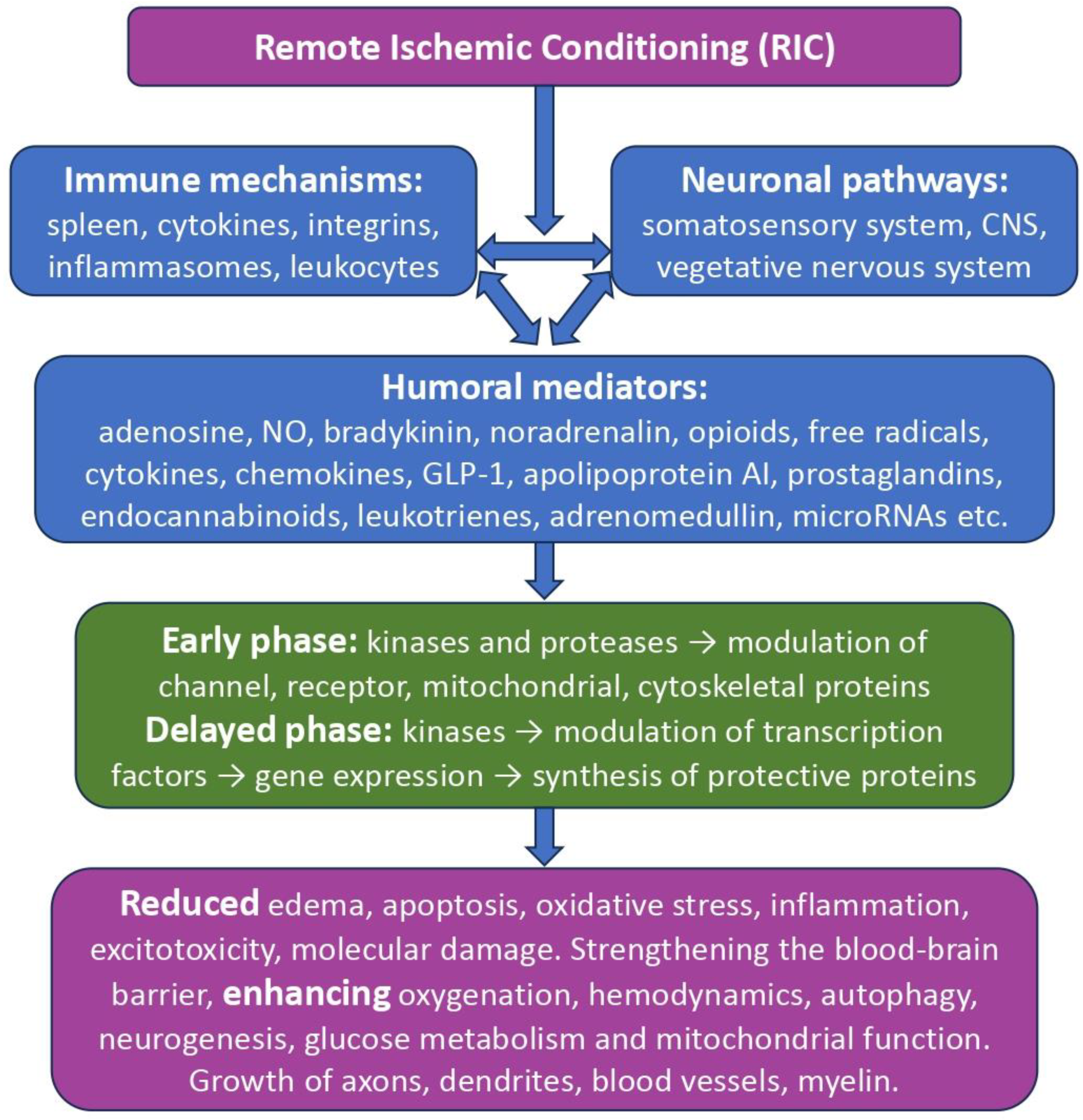
3. Neuro-immuno-humoral pathway
4. Early phase of neuroprotection
5. Delayed anti-apoptotic mechanisms
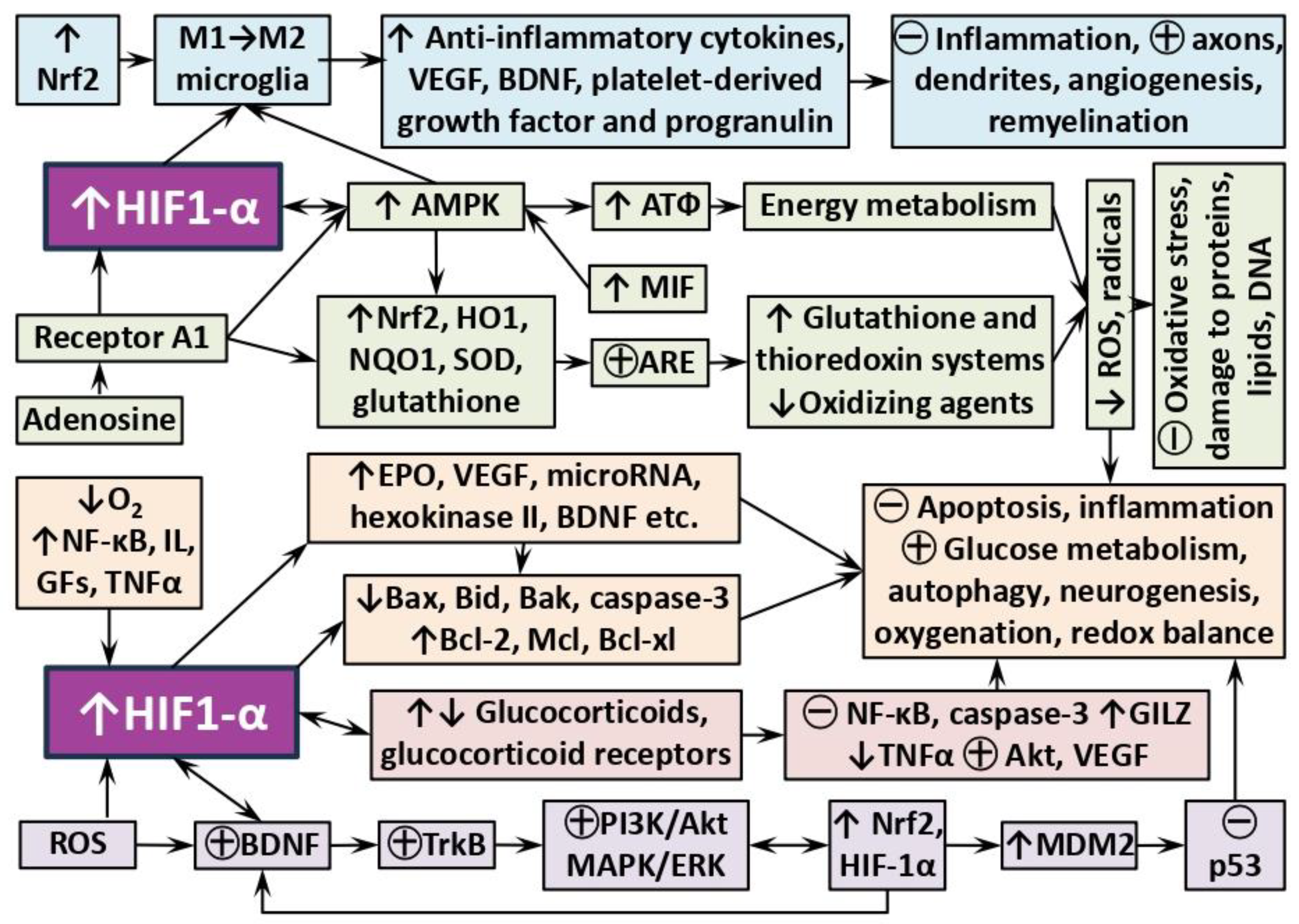
6. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms
6. Role of HIF-1α and steroid hormones
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murry, C.E.; Jennings, R.B.; Reimer, K. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986, 74, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przyklenk, K.; Bauer, B.; Ovize, M.; Kloner, R.A.; Whittaker, P. Regional ischemic 'preconditioning' protects remote virgin myocardium from subsequent sustained coronary occlusion. Circulation 1983, 87, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Naggar, I.; Stewart, M.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Neurogenic pathway mediated remote preconditioning protects the brain from transient focal ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2011, 1386, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candilio, L.; Malik, A.; Hausenloy, D.J. Protection of organs other than the heart by remote ischemic conditioning, J. Cardiovasc. Med. (Hagerstown) 2013, 14, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharbanda, R.K.; Mortensen, U.M.; White, P.A.; Kristiansen, S.B.; Schmidt, M.R.; Hoschtitzky, J.A.; Vogel, M.; Sorensen, K.; Redington, A.N.; MacAllister, R. Transient limb ischemia induces remote ischemic preconditioning in vivo. Circulation 2002, 106, 2881–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreka, G.; Vertesaljai, M.; Szantho, G.; Font, G.; Piroth, Z.; Fontos, G.; Juhasz, E.D.; Szekely, L.; Szelid, Z.; Turner, M.S.; Ashrafian, H.; Frenneaux, M.P.; Andreka, P. Remote ischaemic postconditioning protects the heart during acute myocardial infarction in pigs. Heart 2007, 93, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.R.; Saul, I.; Prado, R.; Busto, R.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Remote organ ischemic preconditioning protect brain from ischemic damage following asphyxial cardiac arrest. Neurosci. Let. 2006, 404, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodaee, M.; Seifi, B.; Najafi, A.; Sedaghat, Z. First report of the protective effects of remote per- and postconditioning on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury. Transplantation 2011, 92, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, R.; Grąt, M. Direct, remote and combined ischemic conditioning in liver surgery. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kim, W.H. Perioperative Cardioprotection by Remote Ischemic Conditioning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogorski, A.; Harati, K.; Kapalschinski, N.; Daigeler, A.; Hirsch, T.; Lehnhardt, M.; Goertz, O.; Kolbenschlag, J. Remote Ischemic Conditioning - Endogenous Tissue Protection and its Possible Applications in Surgery. 2018. Zentralbl. Chir. 2018, 143, 42–49, (article in German). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Querol, C.; Quintana-Luque, M.; Arque, G.; Purroy, F. Preclinical evidence of remote ischemic conditioning in ischemic stroke, a metanalysis update. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet, I.; Marto, J.P.; Mendonça, M.; Baptista, M.V.; Vieira, H.L.A. Remote but not Distant: a Review on Experimental Models and Clinical Trials in Remote Ischemic Conditioning as Potential Therapy in Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 294–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet, I.; Martins, C.; Ângelo-Dias, M.; Carvalho, A.S.; Aloria, K.; Matthiesen, R.; Viana-Baptista, M.; Borrego, L.M.; Vieira, H.L.A. Pilot study in human healthy volunteers on the mechanisms underlying remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) - Targeting circulating immune cells and immune-related proteins. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 367, 577847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Hoda, M.N.; Vaibhav, K.; Giri, S.; Wang, P.; Waller, J.L.; Ergul, A.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Fagan, S.C.; Hess, D.C. Remote ischemic postconditioning: harnessing endogenous protection in a murine model of vascular cognitive impairment. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Q. Remote Limb Ischemic Preconditioning Protects Rats Against Cerebral Ischemia via HIF-1α/AMPK/HSP70 Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, T.; Wieloch, T.; Smith, M.L. Brain damage in a mouse model of global cerebral ischemia. Effect of NMDA receptor blockade. Brain Res. 2003, 982, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.G.; Li, W.B.; Li, Q.J.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Feng, R.F.; Ai, J. Limb ischemic preconditioning attenuates apoptosis of pyramidal neurons in the CA1 hippocampus induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao [Acta physiologica Sinica] 2004, 55, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Burda, R.; Danielisova, V.; Gottlieb, M.; Nemethova, M.; Bonova, P.; Matiasova, M.; Morochovic, R.; Burda, J. (2014). Delayed remote ischemic postconditioning protects against transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion as well as kainate-induced injury in rats. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyaeva, N.V. Biochemical Mechanisms and Translational Relevance of Hippocampal Vulnerability to Distant Focal Brain Injury: The Price of Stress Response. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2019, 84, 1306–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onufriev, M.V.; Moiseeva, Y.V.; Zhanina, M.Y.; Lazareva, N.A.; Gulyaeva, N.V. A Comparative Study of Koizumi and Longa Methods of Intraluminal Filament Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats: Early Corticosterone and Inflammatory Response in the Hippocampus and Frontal Cortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkina, G.T.; Kalinina, T.S.; Gulyaeva, N.V.; Lanshakov, D.A.; Dygalo, N.N. Changes in Gene Expression and Neuroinflammation in the Hippocampus after Focal Brain Ischemia: Involvement in the Long-Term Cognitive and Mental Disorders. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2021, 86, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyaeva, N.V.; Onufriev, M.V.; Moiseeva, Y.V. Ischemic Stroke, Glucocorticoids, and Remote Hippocampal Damage: A Translational Outlook and Implications for Modeling. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 781964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, V.; Khan, M.; Zakaria, E.R.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Hamidi, M.; O'Keeffe, T.; Vanderah, T.W.; Joseph, B. Continuous remote ischemic conditioning attenuates cognitive and motor deficits from moderate traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 85, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandweiss, A.J.; Azim, A.; Ibraheem, K.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Rhee, P.; Vanderah, T.W.; Joseph, B. Remote ischemic conditioning preserves cognition and motor coordination in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 83, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drunalini Perera, P.N.; Hu, Q.; Tang, J.; Li, L.; Barnhart, M.; Doycheva, D.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Delayed remote ischemic postconditioning improves long term sensory motor deficits in a neonatal hypoxic ischemic rat model. PloS One 2014, 9, e90258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Remote ischemic preconditioning improves spatial learning and memory ability after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Perfusion 2013, 28, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Yan, Z.; Wei, D.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H. Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2009, 1288, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasdekis, S.N.; Athanasiadis, D.; Lazaris, A.; Martikos, G.; Katsanos, A.H.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Machairas, A.; Liakakos, T. The role of remote ischemic preconditioning in the treatment of atherosclerotic diseases. Brain Behav. 2009, 3, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, K.A.; Zenko, M.Y. Applying remote ischemic pre- and postconditioning for the correction of experimental depression. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova, 2019, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, K.A.; Zenko, M.Y. Anxiolytic effect of remote ischemic pre- and post-conditioning in the model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. Im I.P. Pavlova. 2018, 68, 663–672, (article in Russian). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, K.A.; Pivina, S.G.; Rybnikova, E.A. The Anxiolytic Effects of Moderate Hypoxia and Remote Ischemia in the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Model Are Accompanied by Modification of Functioning of the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis. Neurochem. J. 2018, 12, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molano Franco, D.; Nieto Estrada, V.H.; Gonzalez Garay, A.G.; Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I. Interventions for preventing high altitude illness: Part 3. Miscellaneous and non-pharmacological interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD013315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensrud, T.; Li, J.; Dai, X.; Manlhiot, C.; Kharbanda, R.K.; Tropak, M.; Redington, A. Pretreatment with the nitric oxide donor SNAP or nerve transection blocks humoral preconditioning by remote limb ischemia or intra-arterial adenosine. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H1598–H1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalay, M.; Barsukevich, V.; Mastitskaya, S.; Mrochek, A.; Pernow, J.; Sjöquist, P.-O.; Ackland, G.L.; Gourine, A.V.; Gourine, A. Remote ischaemic pre- and delayed postconditioning—similar degree of cardioprotection but distinct mechanisms. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, M.; Buchholz, B.; Rodríguez, M.; Pérez, V.; Inserte, J.; García-Dorado, D.; Gelpi, R.J. Role of the parasympathetic nervous system in cardioprotection by remote hind limb ischaemic preconditioning. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.T.; Lu, Y.; Mei, B.; Xia, Z.; Irwin, M.G. Cardioprotection from remote preconditioning involves spinal opioid receptor activation. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, X.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Gao, C.; Sun, X. α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Mediates the Neuroprotection of Remote Ischemic Postconditioning in a Rat Model of Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 246, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastitskaya, S.; Marina, N.; Gourine, A.; Gilbey, M.P.; Spyer, K.M.; Teschemacher, A.G.; Kasparov, S.; Trapp, S.; Ackland, G.L.; Gourine, A.V. Cardioprotection evoked by remote ischaemic preconditioning is critically dependent on the activity of vagal pre-ganglionic neurones. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, B.; Kelly, J.; Muñoz, M.C.; Bernatené, E.A.; Méndez Diodati, N.; González Maglio, D.H.; Dominici, F.P.; Gelpi, R.J. Vagal stimulation mimics preconditioning and postconditioning of ischemic myocardium in mice by activating different protection mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 97, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Shiva, S.; Heusch, G.; Kelm, M. Circulating nitrite contributes to cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalay, M.V.; Mastitskaya, S.; Mrochek, A.; Ackland, G.L.; Gutierrez del Arroyo, A.; Sanchez, J.; Sjoquist, P.O.; Pernow, J.; Gourine, A.V.; Gourine, A. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mediates cardioprotection by remote ischaemic conditioning. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 112, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, H.; Cao, C.; Lee, C. TRPV1 activation is involved in the cardioprotection of remote limb ischemic postconditioning in ischemia-reperfusion injury rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, S.M.; Chiang, E.; Reyes, A.; Martir, G.; Patel, A.; Karmali, S.; Patel, S.; West, S.; Del Arroyo, A.G.; Gourine, A.V.; Ackland, G.L. Neuromodulation of innate immunity by remote ischaemic conditioning in humans: Experimental cross-over study, Brain Behav. Immun. Health. 2021, 16, 100299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokudina, E.S.; Maslov, L.N.; Tsibulnikov, S.Y.; Singh, N.; Klim, V.S.; Skryabina, A.А. The role of humoral factors in the remote preconditioning of the heart. Russ. Fiziol. Zh. Im. I.M. Sechenova. 2019, 105, 416–436, (article in Russian). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehni, A.K.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Possible involvement of insulin, endogenous opioids and calcitonin gene-related peptide in remote ischaemic preconditioning of the brain. Yakugaku zasshi: J. Pharm. Society. 2007, 127, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.M.; Riquelme, J.A.; Zheng, Y.; Vicencio, J.M.; Lavandero, S.; Yellon, D.M. Endothelial cells release cardioprotective exosomes that may contribute to ischaemic preconditioning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, L.; Davidson, S.M.; Yellon, D.M. Does remote ischaemic conditioning reduce inflammation? A focus on innate immunity and cytokine response. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, X. Exosomes isolated from the plasma of remote ischemic conditioning rats improved cardiac function and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction through targeting Hsp70. Aging (Albany NY). 2020, 12, 3682–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao de la Barca, J.M.; Bakhta, O.; Kalakech, H.; Simard, G.; Tamareille, S.; Catros, V.; Callebert, J.; Gadras, C.; Tessier, L.; Reynier, P.; Prunier, F.; Mirebeau-Prunier, D. Metabolic Signature of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Involving a Cocktail of Amino Acids and Biogenic Amines. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2016, 5, e003891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ran, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ji, X.; Geng, X.; Du, H.; Hu, X. Splenic responses play an important role in remote ischemic preconditioning-mediated neuroprotection against stroke. J. Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Naggar, I.; Stewart, M.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Neurogenic pathway mediated remote preconditioning protects the brain from transient focal ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2011, 1386, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Ren, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H. The chronic protective effects of limb remote preconditioning and the underlying mechanisms involved in inflammatory factors in rat stroke. PloS One 2012, 7, e30892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, M.H.; Tudor, G.; Lu, H.T.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D. Remote Ischemic Conditioning in Cerebral Diseases and Neurointerventional Procedures: Recent Research Progress. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Maslov, L.N.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Remote ischemic preconditioning-induced neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Preclinical evidence and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Thakkar, M.; Robinson, C.; Doré, S. Limb Remote Ischemic Conditioning: Mechanisms, Anesthetics, and the Potential for Expanding Therapeutic Options. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprick, J.D.; Mallet, R.T.; Przyklenk, K.; Rickards, C.A. Ischaemic and hypoxic conditioning: potential for protection of vital organs. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Takahashi, T.; Hsieh, J.; Liao, J.; Steinberg, G.K.; Zhao, H. The Akt signaling pathway contributes to postconditioning's protection against stroke; the protection is associated with the MAPK and PKC pathways. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fathali, N.; Lekic, T.; Ostrowski, R.P.; Chen, C.; Martin, R.D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Remote limb ischemic postconditioning protects against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rat pups by the opioid receptor/Akt pathway. Stroke. 2011, 42, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Q. Remote Limb Ischemic Preconditioning Protects Rats Against Cerebral Ischemia via HIF-1α/AMPK/HSP70 Pathway, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zuo, B.; Wu, X. The Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Remote Ischemic Postconditioning. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, A.; Wick, W.; Waltenberger, J.; Weller, M.; Dichgans, J.; Schulz, J.B. Neuroprotection by hypoxic preconditioning requires sequential activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and Akt. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6401–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Shiva, S.; Heusch, G.; Kelm, M. Circulating nitrite contributes to cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, F.; Lin, N.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, W.; Zong, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, T. Remote ischemic post-conditioning improves neurological function by AQP4 down-regulation in astrocytes. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 289, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.; Luo, Y.; Ge, P. Ischemic postconditioning decreases cerebral edema and brain blood barrier disruption caused by relief of carotid stenosis in a rat model of cerebral hypoperfusion. PloS One. 2013, 8, e57869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wills, M.; Li, F.; Geng, X.; Ding, Y. Remote ischemic conditioning with exercise (RICE) promotes functional rehabilitation following ischemic stroke. Neurol. Res. 2021, 43, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comità, S.; Femmino, S.; Thairi, C.; Alloatti, G.; Boengler, K.; Pagliaro, P.; Penna, C. (2021) Regulation of STAT3 and its role in cardioprotection by conditioning: focus on non-genomic roles targeting mitochondrial function. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Lin, C.; Yuan, L.; Chen, L.; Guo, P.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Preactivation of Notch1 in remote ischemic preconditioning reduces cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through crosstalk with the NF-κB pathway. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Mo, X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Non-invasive remote limb ischemic postconditioning protects rats against focal cerebral ischemia by upregulating STAT3 and reducing apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, K.P.; Yang, J.W.; Wang, X.B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, J.J.; Guo, J.H.; Li, L.Y. Advances in intervention methods and brain protection mechanisms of in situ and remote ischemic postconditioning. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2021, 36, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, B.A.; Restuccia, D.F. PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.C.; Xian, X.H.; Li, W.B.; Li, L.; Yan, C.Z.; Li, Q.J.; Zhang, M. Activation of p38 MAPK participates in brain ischemic tolerance induced by limb ischemic preconditioning by up-regulating HSP 70. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 224, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Yan, W.; Zhou, J.; Pei, H.; Zhao, R. Per- and post-remote ischemic conditioning attenuates ischemic brain injury via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in aged rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, L.; Ren, C. Remote limb preconditioning protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death through ameliorating neuronal oxidative DNA damage and parthanatos. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 366, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, G.C.; Schaan, A.P.; Cabral, G.F.; Santana-da-Silva, M.N.; Pinto, P.; Vidal, A.F.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, Â. A Cell's Fate: An Overview of the Molecular Biology and Genetics of Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Jin, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Ren, C. Remote Limb Preconditioning Generates a Neuroprotective Effect by Modulating the Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway and TRAIL-Receptors Expression. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jha, M.K.; Suk, K. Lipocalin-2 in the Inflammatory Activation of Brain Astrocytes. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 35, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C. Downregulation of lipocalin-2 and Bim expression after remote limb preconditioning in the ischemic rat brain. Brain Res. 2018, 1679, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Lin, S.; Su, J.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hashimoto, K.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, J.C. Activation of BDNF by transcription factor Nrf2 contributes to antidepressant-like actions in rodents. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, E.; Vecino, R.; Sánchez-Morán, I.; Rodríguez, C.; Suárez-Pindado, A.; Bolaños, J.P.; Almeida, A.; Delgado-Esteban, M. Preconditioning-Activated AKT Controls Neuronal Tolerance to Ischemia through the MDM2-p53 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, D.; Sun, M.; Feng, J. A Combination of Remote Ischemic Perconditioning and Cerebral Ischemic Postconditioning Inhibits Autophagy to Attenuate Plasma HMGB1 and Induce Neuroprotection Against Stroke in Rat. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 58, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Cao, J.; Song, D.; Tian, L.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Yin, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C. Autophagy is involved in the cardioprotection effect of remote limb ischemic postconditioning on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in normal mice, but not diabetic mice. PloS One. 2014, 9, e86838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Dong, W.; Shi, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, K.J.; Luo, Y. Bcl-2 phosphorylation triggers autophagy switch and reduces mitochondrial damage in limb remote ischemic conditioned rats after ischemic stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Xiong, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Tian, Y.; Jiao, C.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Remote ischemic preconditioning protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via heme oxygenase-1-induced autophagy. PloS One 2014, 9, e98834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohailla, S.; Clarizia, N.; Sourour, M.; Sourour, W.; Gelber, N.; Wei, C.; Li, J.; Redington, A.N. Acute, delayed and chronic remote ischemic conditioning is associated with downregulation of mTOR and enhanced autophagy signaling. PloS One 2014, 9, e111291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, J. Remote limb ischemic post-conditioning attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat skin flapby limiting oxidative stress. Acta Cir. Bras. 2016, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Du, L.; Ding, X.; Liu, C. Remote ischemic conditioning protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, C.H. Effect of remote ischemic post-conditioning on systemic inflammatory response and survival rate in lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation model. J. Inflamm. (Lond). 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Su, L.; Li, X.; Di, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; He, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Remote limb ischemic postconditioning protects mouse brain against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via upregulating expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO-1 in mice. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Lu, G.; Guo, J.; Dou, Y. Limb remote ischemic post-conditioning reduces brain reperfusion injury by reversing eNOS uncoupling. Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 52, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- He, N.; Jia, J.J.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Lin, B.Y.; Peng, Y.F.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, T.C.; Tong, R.L.; Jiang, L.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.S. Remote ischemic perconditioning prevents liver transplantation-induced ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats: Role of ROS/RNS and eNOS. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Hou, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, L. Noninvasive limb remote ischemic preconditioning contributes neuroprotective effects via activation of adenosine A1 receptor and redox status after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1459, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, S.E.; and O'Neill, L.A. HIF1α and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y. Microglia Polarization From M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 815347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Saavedra, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; and Pang, T. A Dual AMPK/Nrf2 Activator Reduces Brain Inflammation After Stroke by Enhancing Microglia M2 Polarization. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendedel, A.; Johann, S.; Mehrabi, S.; Joghataei, M.T.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Kipp, M.; and Beyer, C. Activation and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Intrathecal Application of SDF-1a in a Spinal Cord Injury Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in ischaemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Moon, S.K.; Maruyama, T.; Narumiya, S.; Doré, S. Prostaglandin FP receptor inhibitor reduces ischemic brain damage and neurotoxicity. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 48, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, T.; Schützhold, V.; Fandrey, J.; Ferenz, K.B. When the Brain Yearns for Oxygen. Neurosignals 2019, 27, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrica, L.; Li, L.; Newville, J.; Kenton, J.; Gustus, K.; Brigman, J.; Cunningham, L.A. Genetic inactivation of hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) in adult hippocampal progenitors impairs neurogenesis and pattern discrimination learning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2019, 157, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroshina, E.V.; Savyuk, M.O.; Ponimaskin, E.; Vedunova, M.V. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) in Ischemic Stroke and Neurodegenerative Disease. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 703084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barteczek, P.; Li, L.; Ernst, A.S.; Böhler, L.I.; Marti, H.H.; Kunze, R. Neuronal HIF-1α and HIF-2α deficiency improves neuronal survival and sensorimotor function in the early acute phase after ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Kuang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, T.; He, Y.; Di, C.; Kang, J.; Yuan, L.; Yu, B.; Li, Q. A positive feedback circuit comprising p21 and HIF-1α aggravates hypoxia-induced radioresistance of glioblastoma by promoting Glut1/LDHA-mediated glycolysis. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Du, S.; Fu, Z.; Chen, T.; Qin, Y.; Sui, F.; Jiang, Y. HIF-1α/microRNA-128-3p axis protects hippocampal neurons from apoptosis via the Axin1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in Parkinson's disease models. Aging 2020, 12, 4067–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasabe, E.; Tatemoto, Y.; Li, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Osaki, T. Mechanism of HIF-1alpha-dependent suppression of hypoxia-induced apoptosis in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.M.; Roy, M.; Robitaille, G.A.; Richard, D.E.; Bonnet, S. HIF-1 inhibition decreases systemic vascular remodelling diseases by promoting apoptosis through a hexokinase 2-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 88, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrovska, Z.O.; Chong, E.Y.; Serebrovska, T.V.; Tumanovska, L.V.; Xi, L. ; Hypoxia, HIF-1α, and COVID-19: from pathogenic factors to potential therapeutic targets. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Sarieva, K.; Lomert, E.; Nimiritsky, P.; Eschenko, N.; Galkina, O.; Lyanguzov, A.; Tyulkova, E.; Rybnikova, E. Pharmacological HIF1 Inhibition Eliminates Downregulation of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Prevents Neuronal Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampus Caused by Severe Hypoxia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, J.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.T.; Cho, E.J.; Youn, H.D. p53 stabilization and transactivation by a von Hippel-Lindau protein. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Tomida, A.; Tsuruo, T. Dephosphorylated hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha as a mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis during hypoxia. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5779–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liao, X.Y.; Pan, M.X.; Tang, J.C.; Chen, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, P.X.; Lu, L.J.; Zou, Y.Y.; Qin, X.P.; Bu, L.H.; Wan, Q. Glycine Exhibits Neuroprotective Effects in Ischemic Stroke in Rats through the Inhibition of M1 Microglial Polarization via the NF-κB p65/Hif-1α Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannahill, G.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Adamik, J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; McGettrick, A.F.; Goel, G.; Frezza, C.; Bernard, N.J.; Kelly, B.; Foley, N.H.; Zheng, L.; Gardet, A.; Tong, Z.; Jany, S.S.; Corr, S.C.; Haneklaus, M.; Caffrey, B.E.; Pierce, K.; Walmsley, S.; Beasley, F.C.; Cummins, E.; Nizet, V.; Whyte, M.; Taylor, C.T.; Lin, H.; Masters, S.L.; Gottlieb, E.; Kelly, V.P.; Clish, C.; Auron, P.E.; Xavier, R.J.; O'Neill, L.A. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature 2013, 496, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGettrick, A.F.; O'Neill, L.A.J. The Role of HIF in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.; Stein, J.; Meneses, A.; Bechmann, N.; Neuwirth, A.; Kaden, D.; Krüger, A.; Sinha, A.; Alexaki, V.I.; Luis Gustavo Perez-Rivas, Kircher, S.; Martinez, A.; Theodoropoulou, M.; Eisenhofer, G.; Peitzsch, M.; El-Armouche, A.; Chavakis, T.; Wielockx, B. HIF1α is a direct regulator of steroidogenesis in the adrenal gland. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3577–3590. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaeghen, T.; Beyaert, R.; Libert, C. Bidirectional Crosstalk Between Hypoxia Inducible Factors and Glucocorticoid Signalling in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, K.A.; Mironova, V.I.; Rybnikova, E.A.; Samoilov, M.O. Characteristics of the transcription factor HIF-1α expression in the rat brain during the development of a depressive state and the antidepressive effects of hypoxic preconditioning. Neurochem. J. 2010, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, D.; Santhakumar, K.; Markham, E.; Li, N.; Storbeck, K.H.; Krone, N.; Cunliffe, V.T.; van Eeden, F. Bidirectional crosstalk between Hypoxia-Inducible Factor and glucocorticoid signalling in zebrafish larvae. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova, E.; Nalivaeva, N. Glucocorticoid-Dependent Mechanisms of Brain Tolerance to Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.O.; Godson, C.; Brady, H.R.; Taylor, C.T. Potentiation of glucocorticoid activity in hypoxia through induction of the glucocorticoid receptor. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, C.E.; Chou, P.C.; Coutts, D.; Kumar, V.; To, M.; Akashi, K.; Pinhu, L.; Griffiths, M.; Adcock, I.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha induces corticosteroid-insensitive inflammation via reduction of histone deacetylase-2 transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36047–36054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Song, X.L.; Cai, H.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Song, L.N.; Yang, R.; Lu, J. Upregulations of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper by hypoxia and glucocorticoid inhibit proinflammatory cytokines under hypoxic conditions in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.E.; Huck, G.; Stiehl, D.P.; Jelkmann, W.; Hellwig-Bürgel, T. Dexamethasone impairs hypoxia-inducible factor-1 function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybnikova, E.A.; Baranova, K.A.; Zenko, M.Y.; Churilova, A.V.; Stupin, K.V. Comparative analysis of various modes of preconditioning to increase high altitude tolerance. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 3, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, K.A. Preconditioning by Moderate Hypoxia Increases the Amount of Corticosteroid Receptors in the Rat Brain in a Model of Depression. Neurochem. J. 2020, 14, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, M.; Boycott, H.E.; Atkinson, L.; Miller, A.; Boyle, J.P.; Pearson, H.A.; Peers, C. Hypoxia suppresses glutamate transport in astrocytes. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2007, 27, 3946–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




