Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
27 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Related works
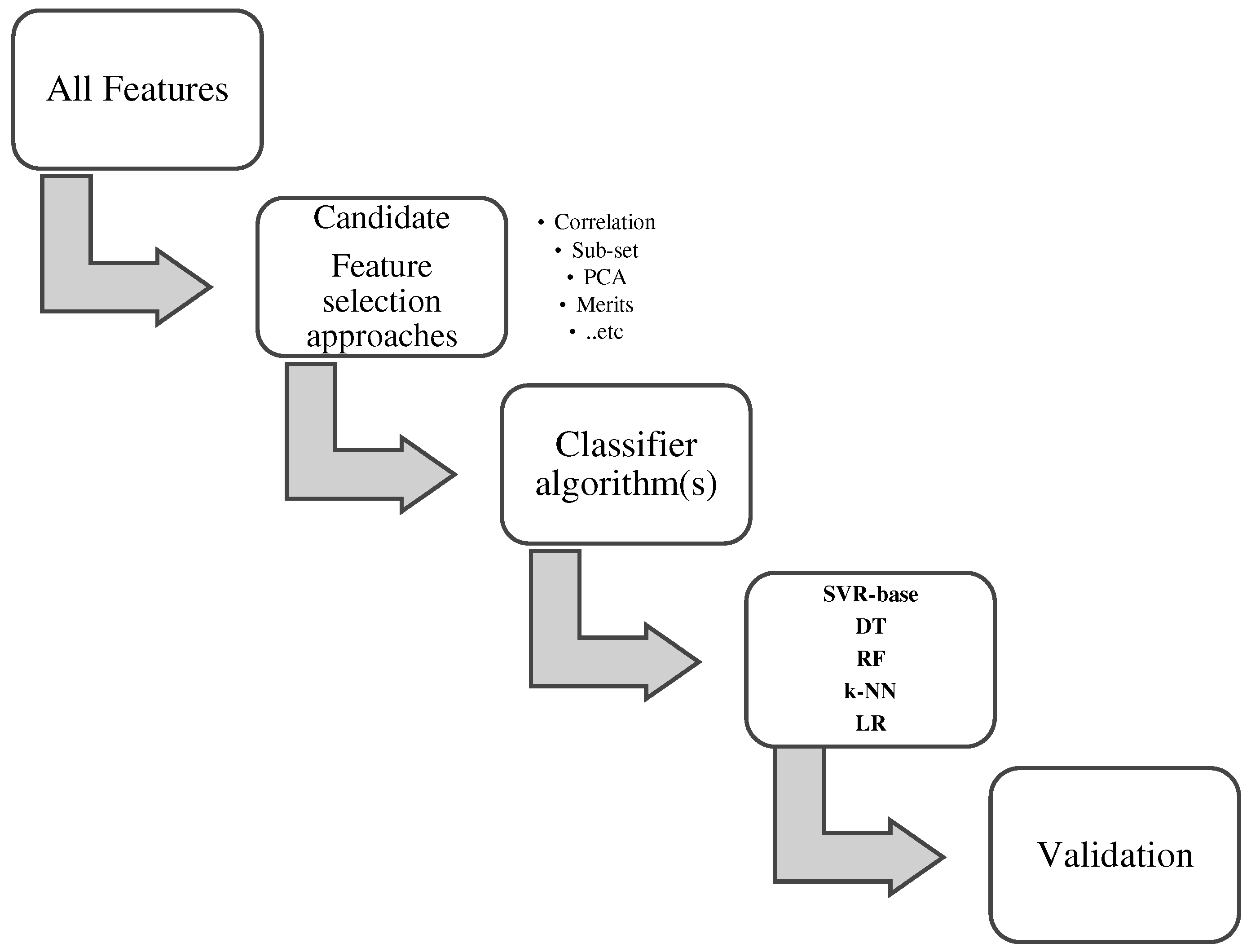
Materials and methods
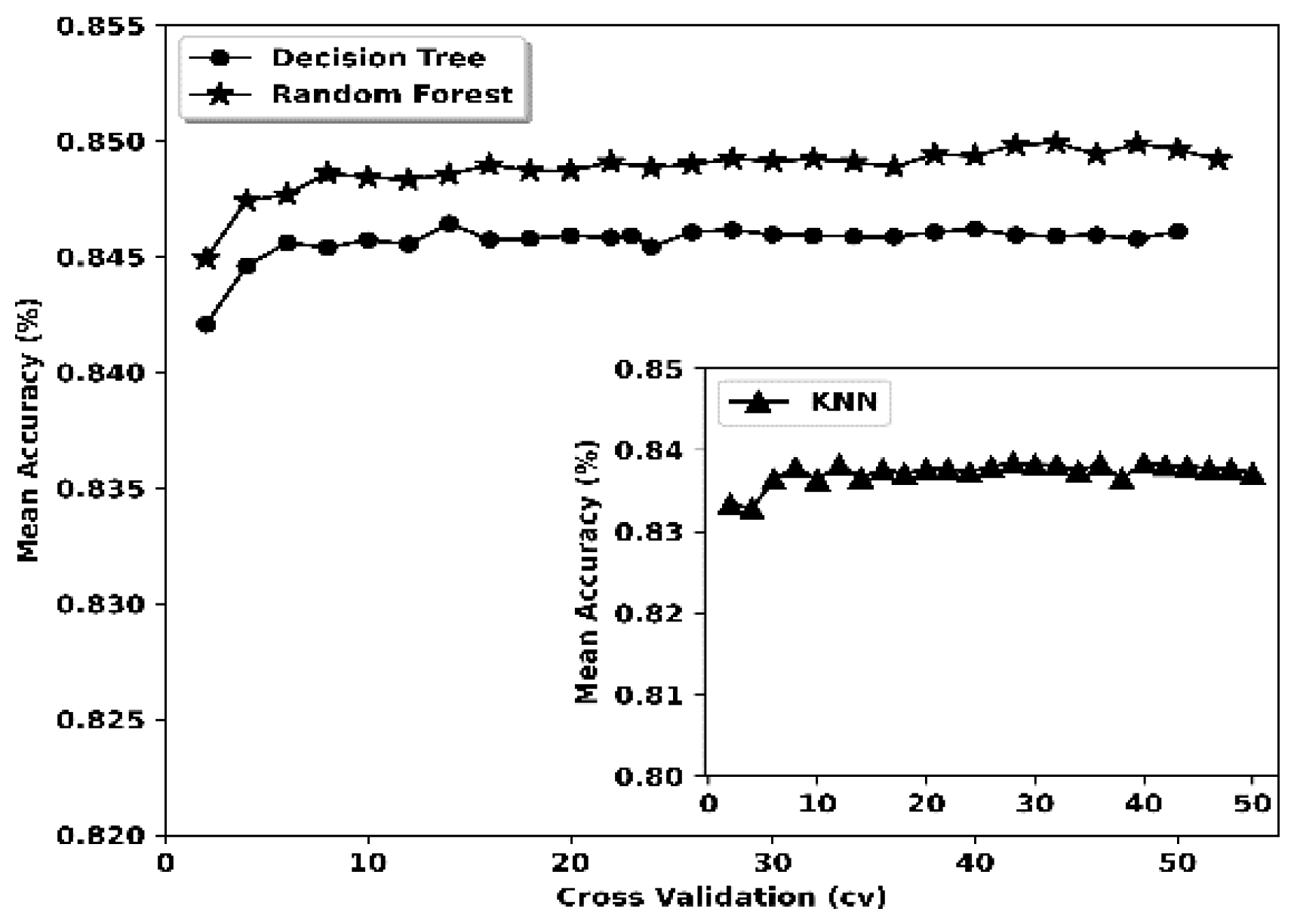
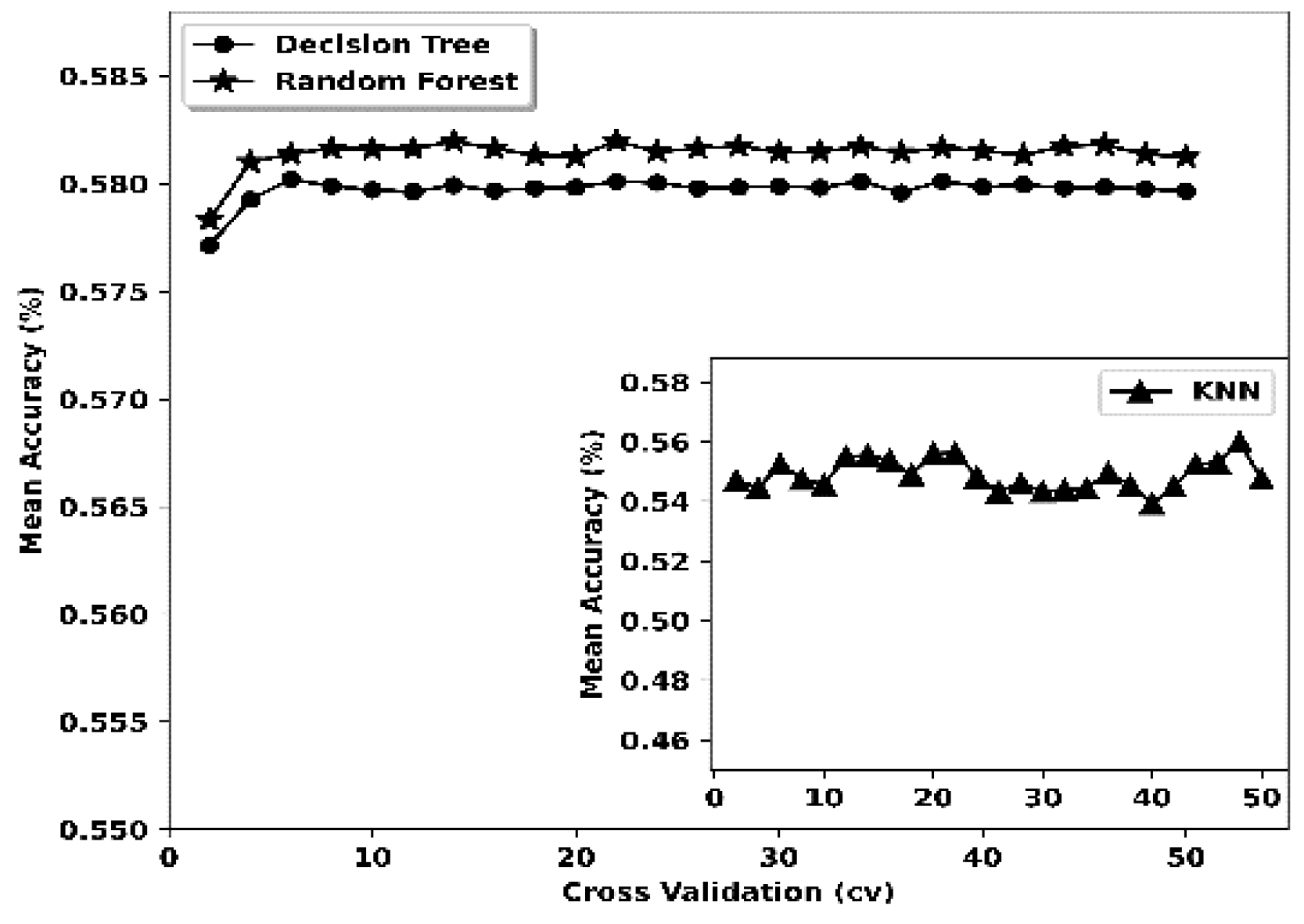
Results and discussion
Conclusion
References
- Romagna, M.; van den Hout, N. J (October 2017) Hacktivism and Website Defacement: Motivations, Capabilities and potential Threats. Proceedings of the 27th Virus Bulletin International Conference: 41–50. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
- Aslan, Çağrı Burak; Li, Shujun; Çelebi, Fatih V.; Tian, Hao (9 November 2020) The World of Defacers: Looking Through the Lens of Their Activities on Twitter. IEEE Access. 8: 204132–204143. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, Xuan Dau (2018) A Website Defacement Detection Method Based on Machine Learning Techniques. Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology - SoICT 2018. Danang City, Viet Nam: ACM Press: 443–448. ISBN 978-1-4503-6539-0. [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, A.; Davanzo, G.; Medvet, E(2010) A Framework for Large-Scale Detection of Web Site Defacements. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2010, 10, 10.
- Zone-H. (2022) News. www.zone-h.org/listingnews. Accessed (9th June 2021).
- Burruss, G. W., Howell, C. J., Maimon, D., & Wang, F (2021) Website defacer classification: A finite mixture model approach. Social Science Computer Review.
- Davanzo, G.; Medvet, E.; Bartoli, A(2011) Anomaly detection techniques for a web defacement monitoring service. J. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 12521–12530.
- Banerjee, S., Swearingen, T., Shillair, R., Bauer, T. J., & Ross, A (2021) Using machine learning to examine cyberattack motivations on web defacement data. Social Science, Computer Review.
- Zhang, X., Tsang, A., Yue, W. T., & Chau, M (2015) The classification of hackers by knowledge exchange behaviors. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(6), 1239–1251.
- Maimon, David, Andrew Fukuda, Steve Hinton, Olga Babko-Malaya, and Rebecca Cathey (2017) On the Relevance of Social Media Platforms in Predicting the Volume and Patterns of Web Defacement Attacks. in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), 4668-4673. IEEE.
- Andress, J., & Winterfeld, S (2013) Cyber warfare: Techniques, tactics and tools for security practitioners. Elsevier.
- Howell, C. J., Burruss, B. W., Maimon, D., & Sahani, S (2019) Website defacement and routine activities: Considering the importance of hackers’ valuations of potential targets. Journal of Crime and Justice, 42, 536.
- Maggi, F., Balduzzi, M., Flores, R., Gu, L., & Ciancaglini, V (2018) Investigating web defacement campaigns at large. In Proceedings of the 2018 on asia conference on computer and communications security (pp. 443–456).
- Ooi, Kok Wei, Seung-Hyun Kim, Qiu-Hong Wang, and Kai Lung Hui (2012) Do Hackers Seek Variety? An Empirical Analysis of Website Defacements. AIS.
- Borgolte, K.; Kruegel, C.; Vigna, G. Meerkat (2015) Detecting Website Defacements through Image-based Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the 24th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security), Washington, DC, USA, 12–14 August 2015.
- Yury Zhauniarovich, Issa Khalil, Ting Yu, Marc Dacier ((2018)) A Survey on Malicious Domains Detection through DNS Data Analysis, ACM Computing Survev, 1 (1), pp. 35.
- Rajesh Gupta, Sudeep Tanwar, Sudhanshu Tyagi, Neeraj Kumar (2020) Machine Learning Models for Secure Data Analytics: A taxonomy and threat model, Computer Communications, Volume 153, pp. 406-440. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Amine Ferrag, Leandros Maglaras, Sotiris Moschoyiannis, Helge Janicke (2020) Deep learning for cyber security intrusion detection: Approaches, datasets, and comparative study, Journal of Information Security and Applications, Vol. 50, 2020, 102419. [CrossRef]
- News, (2003)Web defacing contest stirs up conflict, Computer Fraud & Security, Vol. 2003, 8, 2003, pp.2-3. [CrossRef]
- Samaneh Mahdavifar, Ali A. Ghorbani (2019) Application of deep learning to cybersecurity: A survey, Neurocomputing, Vol. 347, Pages 149-176. [CrossRef]
- Defacer.ID(2022). Available online: https://defacer.id (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Burruss et al., (2021) Website defacer classification: a finite mixture model approach, Social Science Computer Review 1-13.
- Aslan, C¸ B., Li, S., C¸ elebi, F. V., & Tian, H (2020) The world of defacers: Looking through the lens of their activities on Twitter. IEEE Access, 8, 204132–204143.
- Fox, B. H., & Farrington, D. P (2015) An experimental evaluation on the utility of burglary profiles applied in active police investigations. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 42(2), 156–175.
- Braga, A. A., Turchan, B., Papachristos, A. V., & Hureau, D. M (2019) Hot spots policing of small geographic areas effects on crime. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 15(3). [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, G. J. N., & Johnson, S. D. (Eds.)(2018) The oxford handbook of environmental criminology. Oxford University Press. [CrossRef]
- A. Moneva et al., (2022) Repeat victimization by website defacement: An empirical test of premises from an environmental criminology perspective, Computers in Human Behavior, 126 (2022), 106984.
- Gurjwar R.K, Sahu D.R., and Tomar D.S., (2013) An approach to reveal website defacement, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security (IJCSIS), Vol. 11, No. 6, June 2013.
- Hoang, X.D (2018) A Website Defacement Detection Method based on Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Research and Applications (ICERA 2018), Thai-Nguyen, Vietnam, 1–2 December 2018.
- Banff Cyber Technologies (2022) Best Practices to Address the Issue of Web Defacement. Available online: https://www.banffcyber.com/knowledge-base/articles/best-practices-address-issue-web-defacement/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- H. Hassani, X. Huang, E. S. Silva, and M. Ghodsi (2016) A review of data mining applications in crime, Statistical Analysis and Data Mining: 9e ASA Data Science Journal, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 139–154.
- Y.-H. Tseng, Z.-P. Ho, K.-S. Yang, and C.-C. Chen (2012) Mining term networks from text collections for crime investigation, Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 39, no. 11, pp. 10082– 10090.
- A. Malathi and S. S. Baboo, (2011) An enhanced algorithm to predict a future crime using data mining, International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 21, no. 1, 2011.
- Hoang X. D. and Nguyen N. T., (2019) Detecting website defacements based on machine learning techniques and attack signatures, Computers 2019, 8, 35.
- S.G.A. van de Weijer et al., (2021) Heterogeneity in trajectories of cybercriminals: a longitudinal analyses of web defacements, Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 4 (2021), 100113.
- Holt et al., (2021) Examining the characteristics that differentiate jihadi-associated cyberattacks using routine activities theory, Social Science Computer Review, pp.1-17.
- Berton, B., & Pawlak, P. (2015) Cyber jihadists and their web. European Union Institute for Security Studies.
- Central Intelligence Agency (2018) The CIA world factbook 2018. Skyhorse Publishing Inc.
- Heickero¨, R (2014) Cyber terrorism: Electronic jihad. Strategic Analysis, 38(4), 554–565.
- Carson, J. V., & Suppenbach, M. (2018) The Global Jihadist Movement: The most lethal ideology? Homicide Studies, 22(1), 8–44.
- Mee Lan Han et al., (2019) CBR-based decision support methodology for cybercrime investigation: focused on the data-driven website defacement analysis, Hindawi, Security and Communication Networks, Vol. 2019, (1901548), pp.21.
- Howell, Jordan C., George W. Burruss, David Maimon & Shradha Sahani (2019) Website defacement and routine activities: considering the importance of hackers’ valuations of potential targets, Journal of Crime and Justice, 42, 2019, pp.536-550.
- Bernasco, W (2008) Them again?: Same-offender involvement in repeat and near repeat burglaries. European Journal of Criminology, 5(4), 411–431. [CrossRef]
- E. ALPAYDIN (2010) Introduction to Machine Learning, 2nd ed., London: MIT press, 2010, pp. 67-97.
- V. N. Vapnik, (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory, 2nd ed., New York: Springer, 2000, pp. 112-235.
- V. CHERKASSKY and Y. MA, (2004) Practical selection of SVM parameters and noise estimation for SVM regression, Neural Networks, 17, 2004, pp.113–126.
- Holt, T. J., Leukfeldt, R., & van de Weijer, S (2020) An examination of motivation and routine activity theory to account for cyberattacks against Dutch web sites. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 47(4), 487–505.
- Holt, T. J., Stonhouse, M., Freilich, J., & Chermak, S. M (2019) Examining ideologically motivated cyber-attacks performed by far-left groups. Terrorism and Political Violence, 33, 1–22.
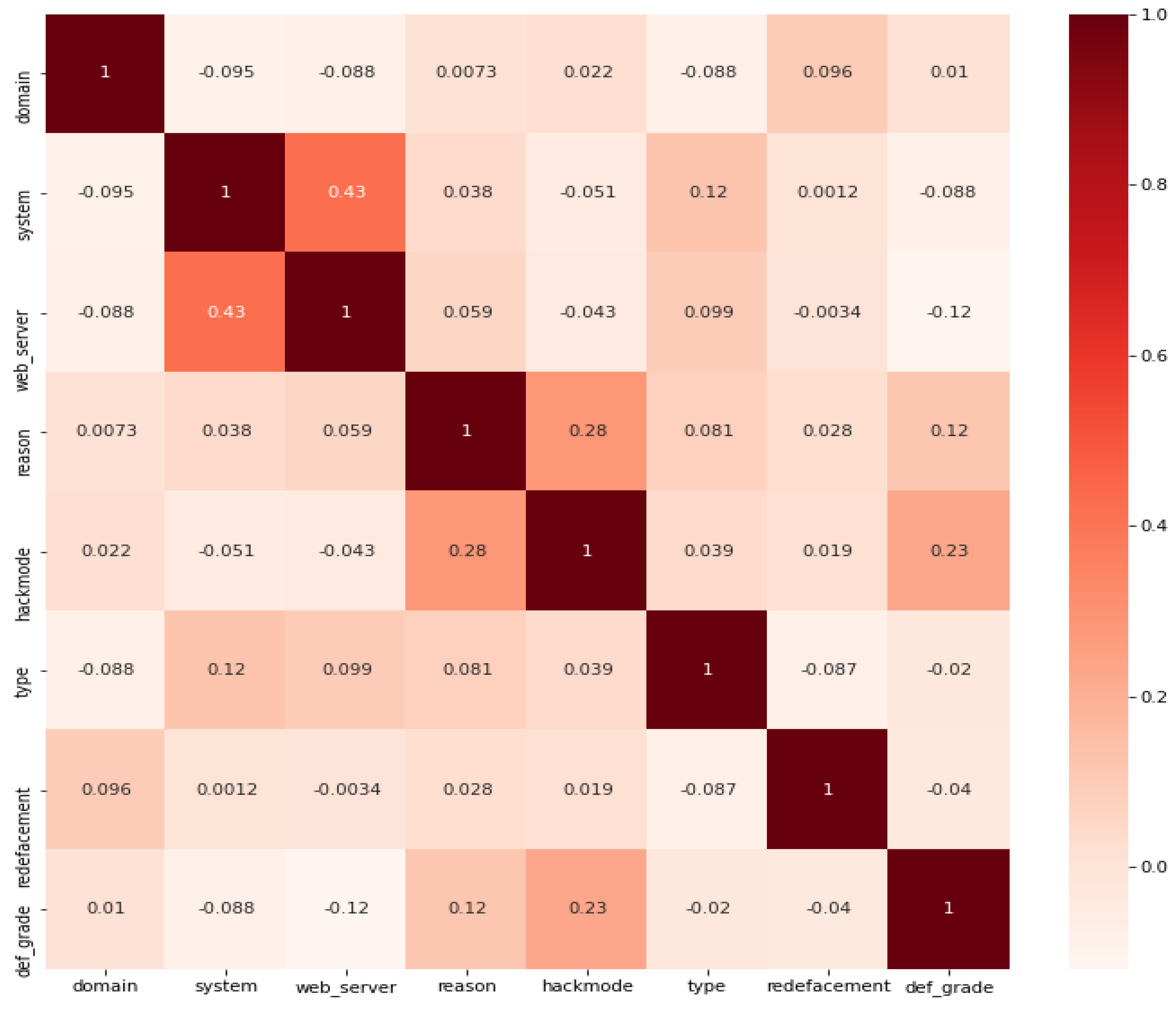
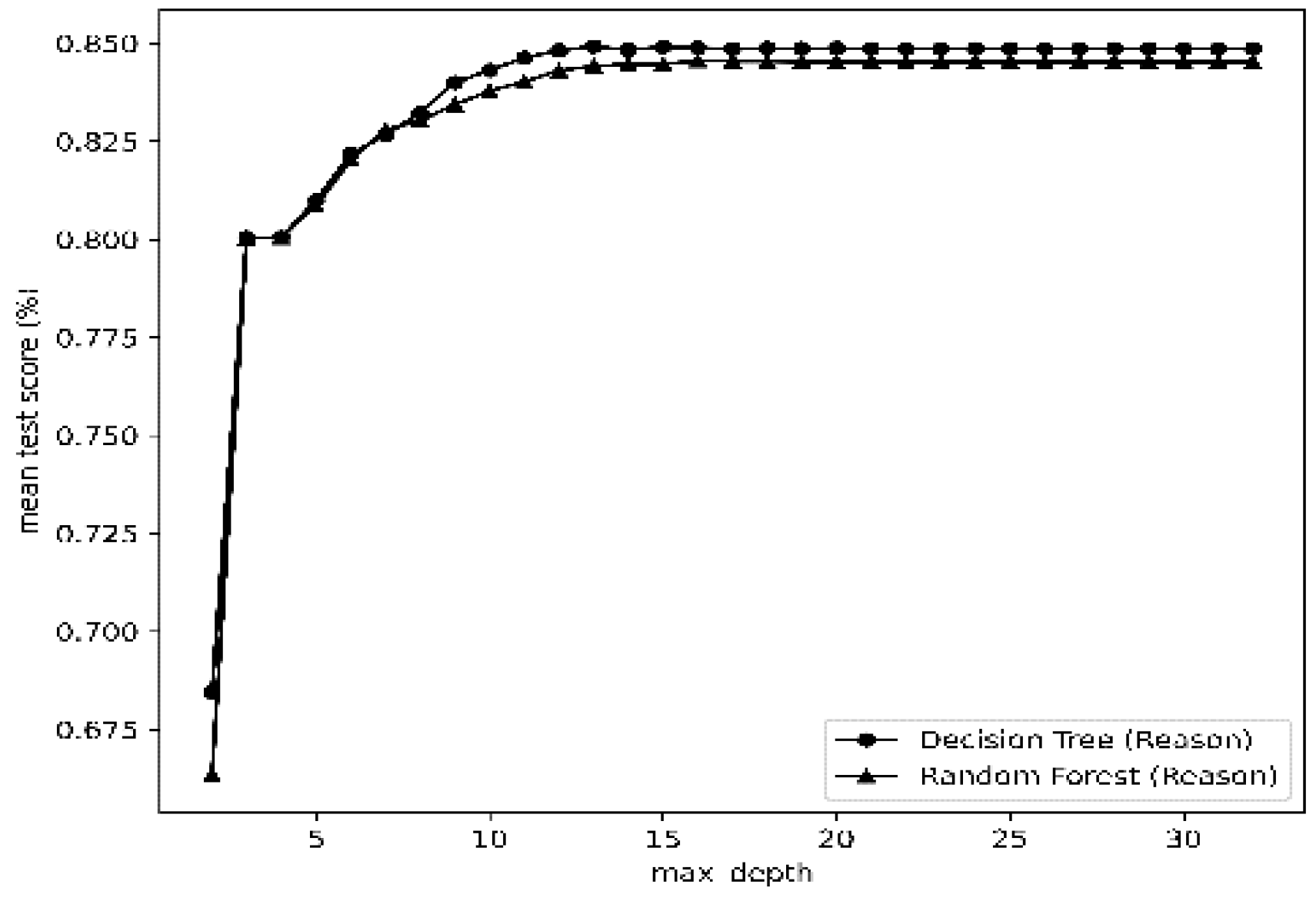
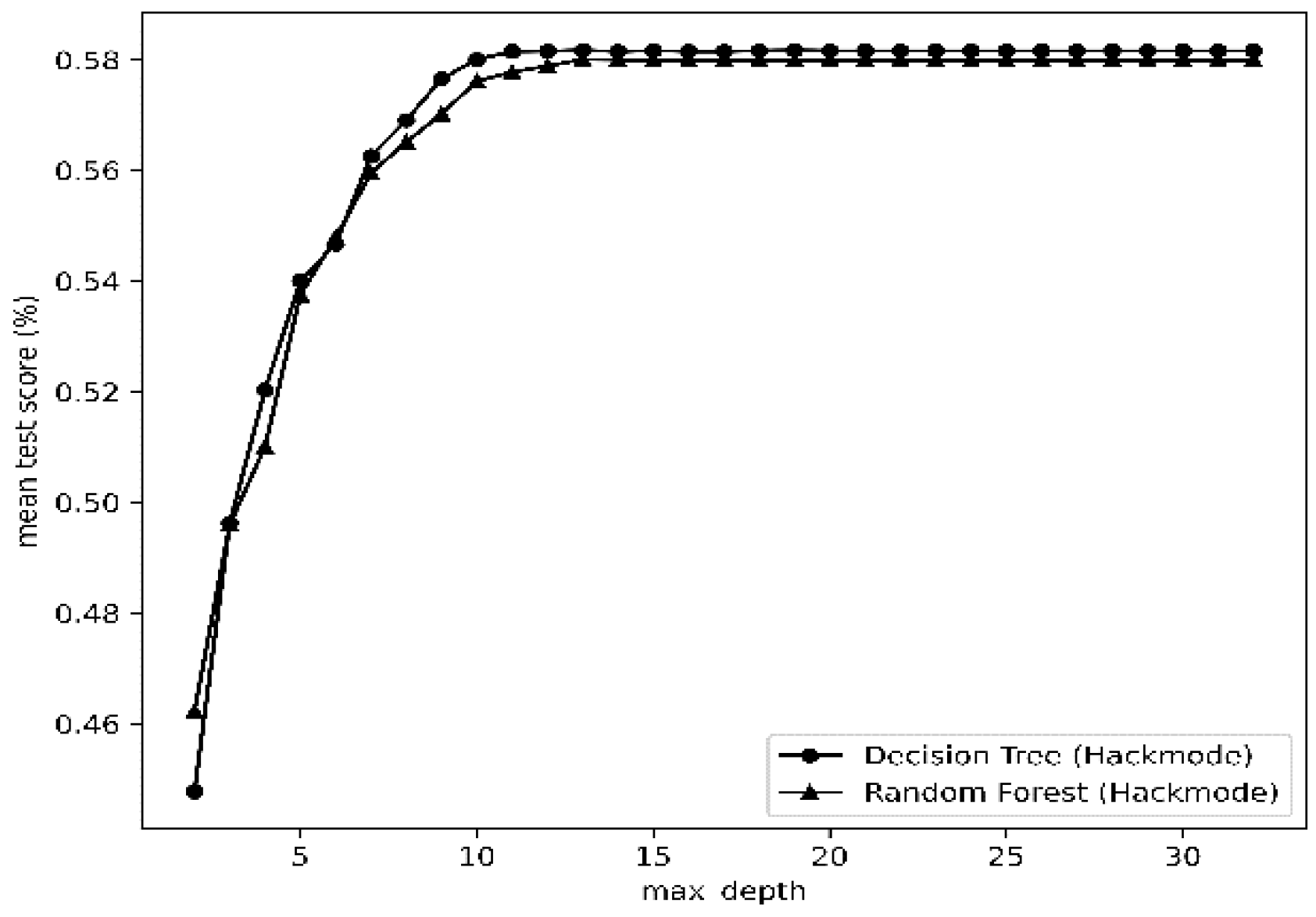
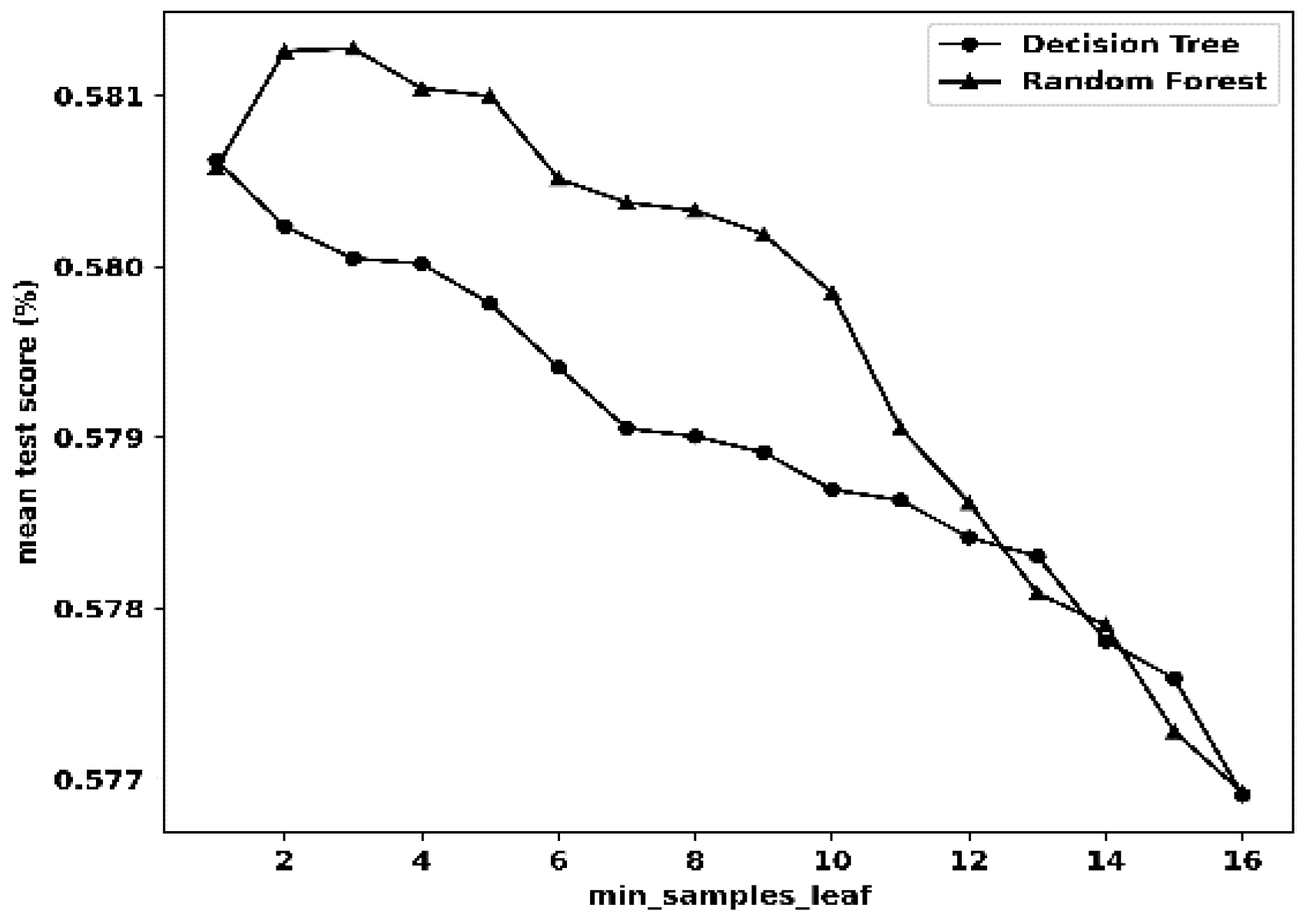
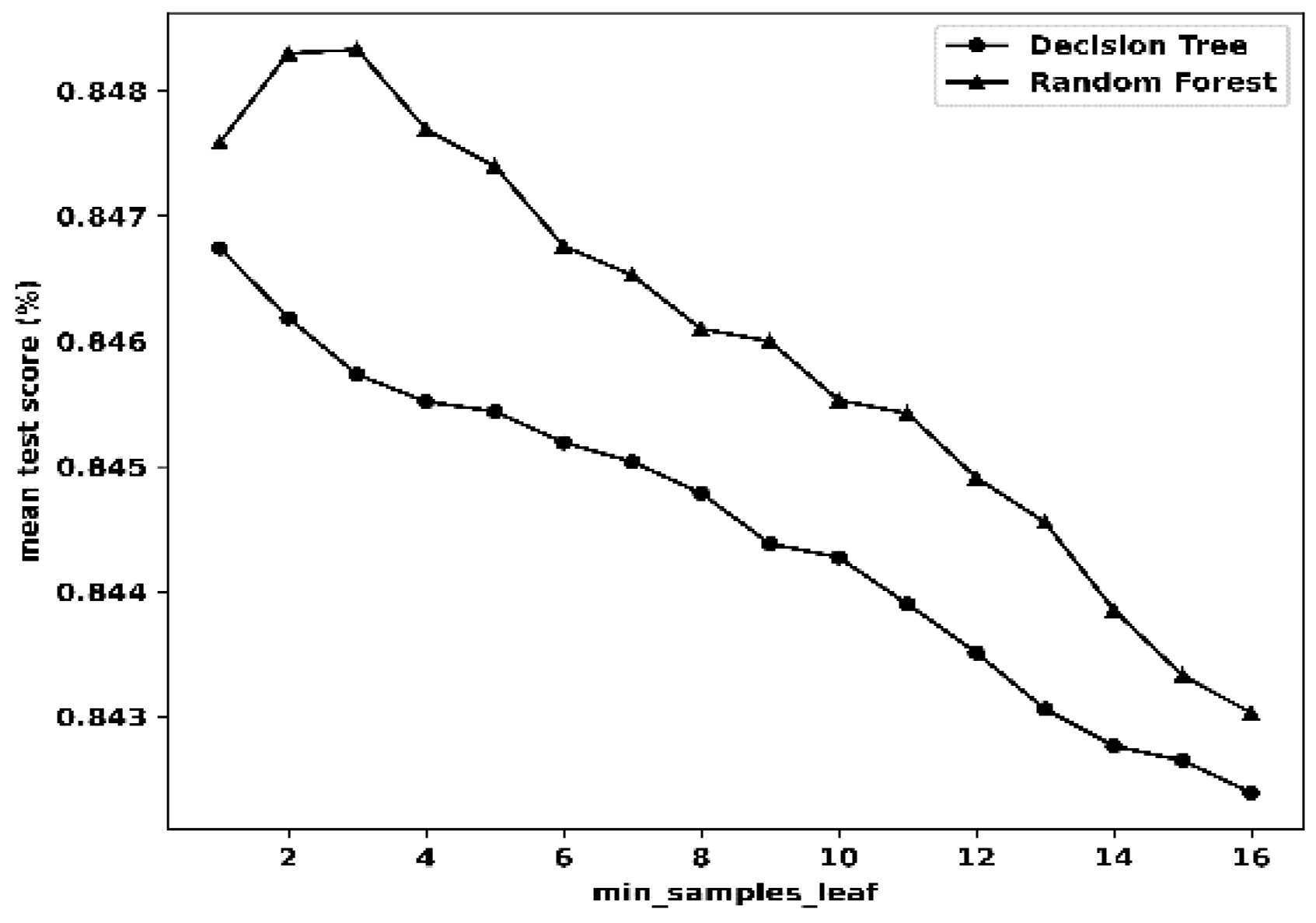
| Statistical Metric |
Dataset Features | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | System | Web_Server | Reason | Hackmode | Type | Redefacement | Def_Grade | Domain | System | |
| Mean | 2.8 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 1.26 | 3.93 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 2.8 | 0.85 |
| Stdv. | 2.89 | 1.72 | 1.13 | 2.25 | 5.14 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 2.89 | 1.72 |
| Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25% | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 50% | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 75% | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Max | 16 | 17 | 17 | 10 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| Count | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 | 80382 |
| Model | Hyperparameter(s) | Target | Hyperparameter(s) | Target | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter(s) | Value(s) | Parameter(s) | Value(s) | |||
| Decision Tree (DT) | CVa | 16 | Reason | CV | 14 | Hackmode |
| max_depth | 16 | max_depth | 14 | |||
| min_sample_leaf | 1 | min_sample_leaf | 1 | |||
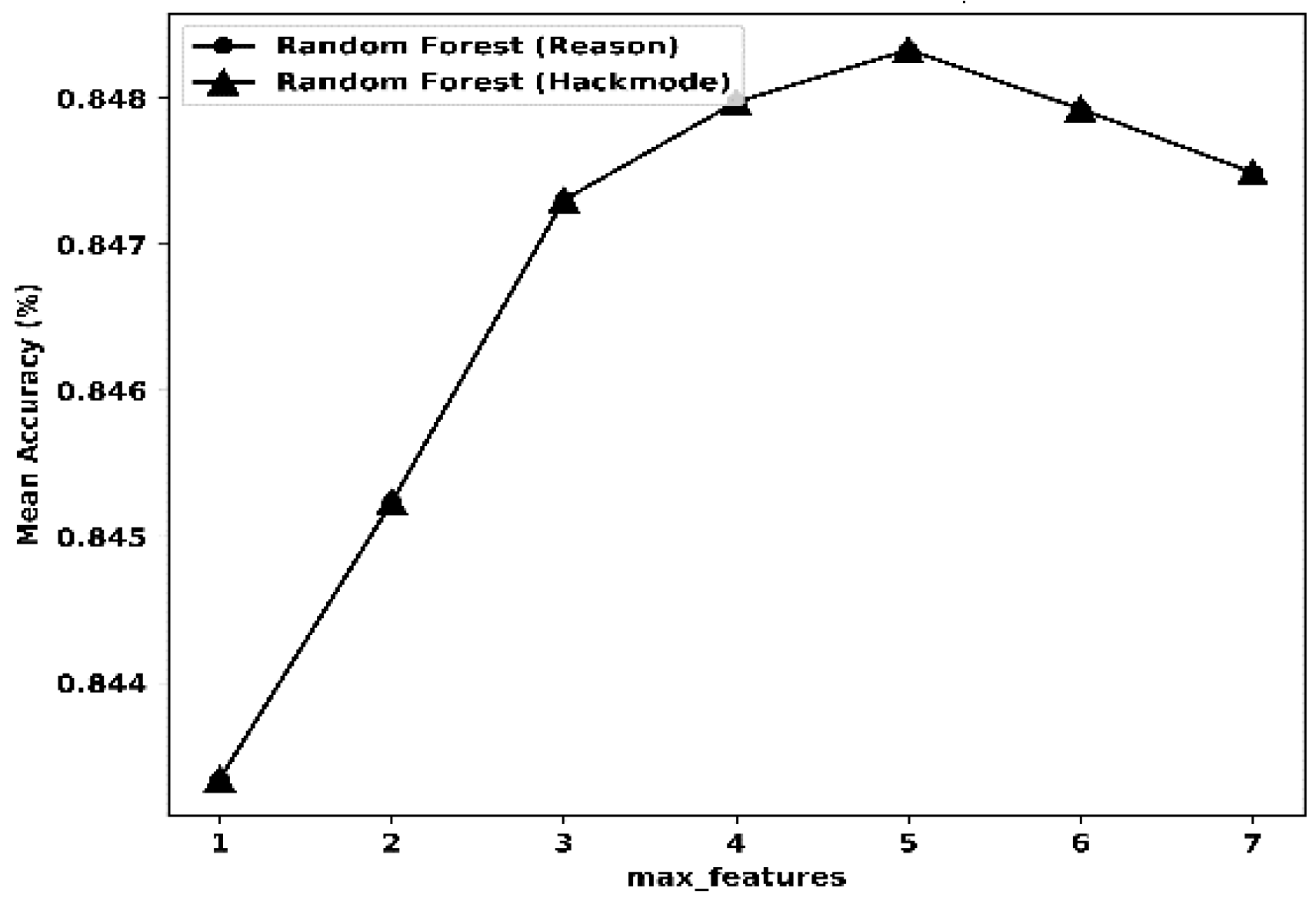
| Random Forest (RF) | CV | 15 | Reason | CV | 16 | Hackmode |
| max_depth | 16 | max_depth | 16 | |||
| max_features | 5 | max_features | 5 | |||
| min_sample_leaf | 3 | min_sample_leaf | 3 | |||
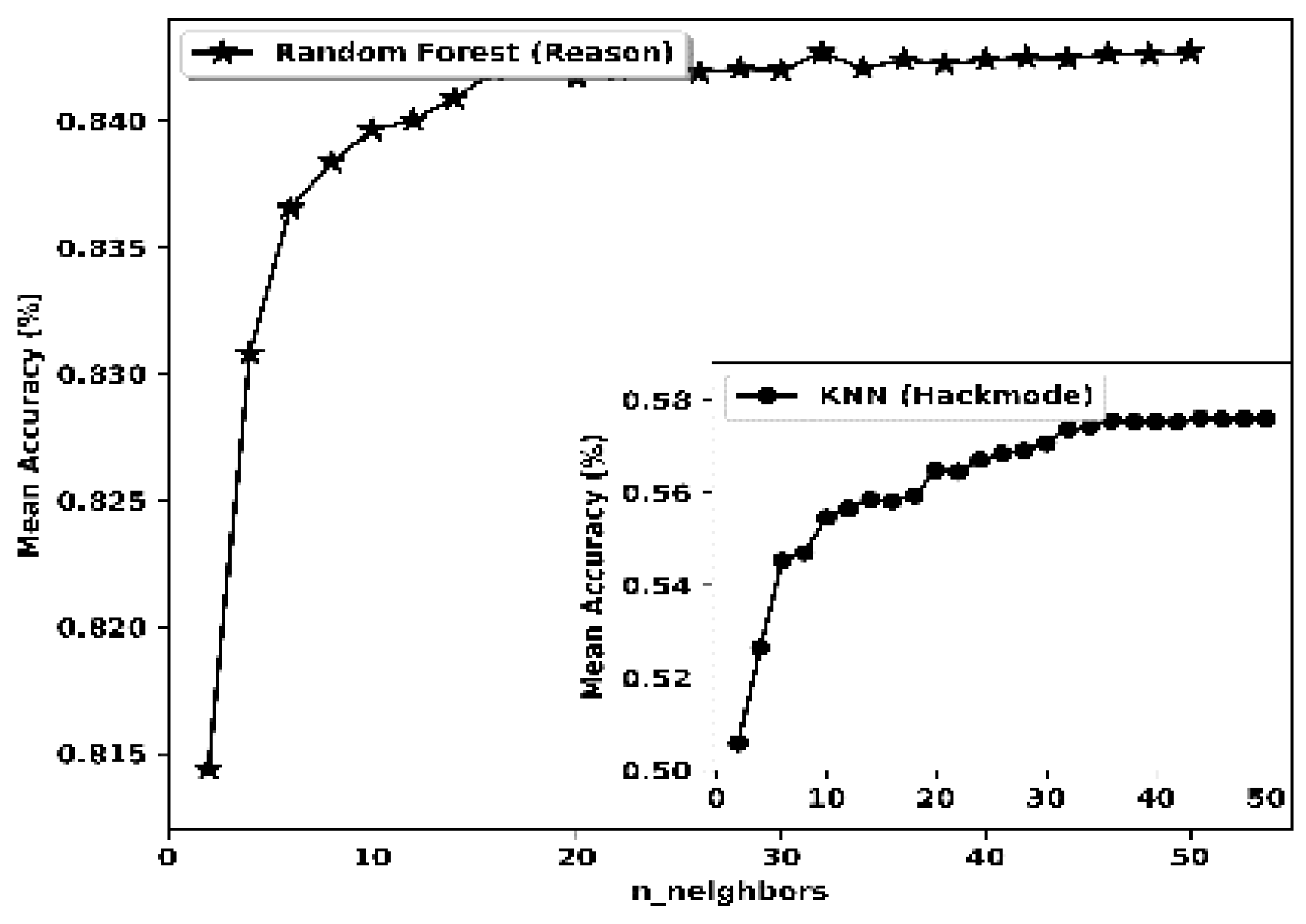
| K-nearest Neighbour (k-NN) | CV | 8 | Reason | CV | 14 | Hackmode |
| algorithm | ball_tree | Algorithm | ball_tree | |||
| n_neighbours | 18 | n_neighbours | 7 | |||
| leaf_size | 9 | leaf_size | 9 | |||
| weights | distance | weights | distance | |||
| Model | Training Time (s) | Evaluation Time (s) | Mean Error (%) | Target | Training Time (s) | Evaluation Time (s) | Mean Error (%) | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
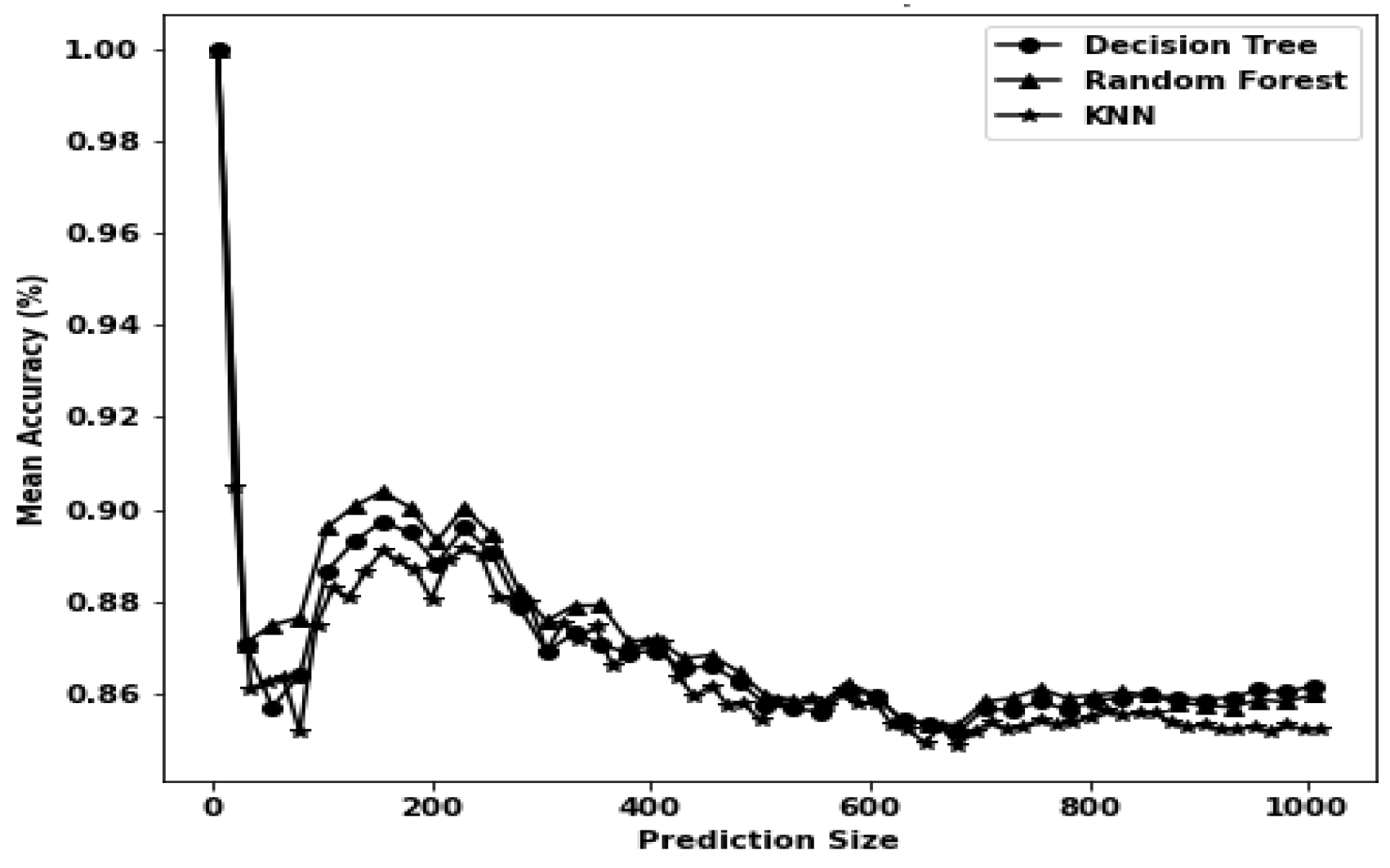
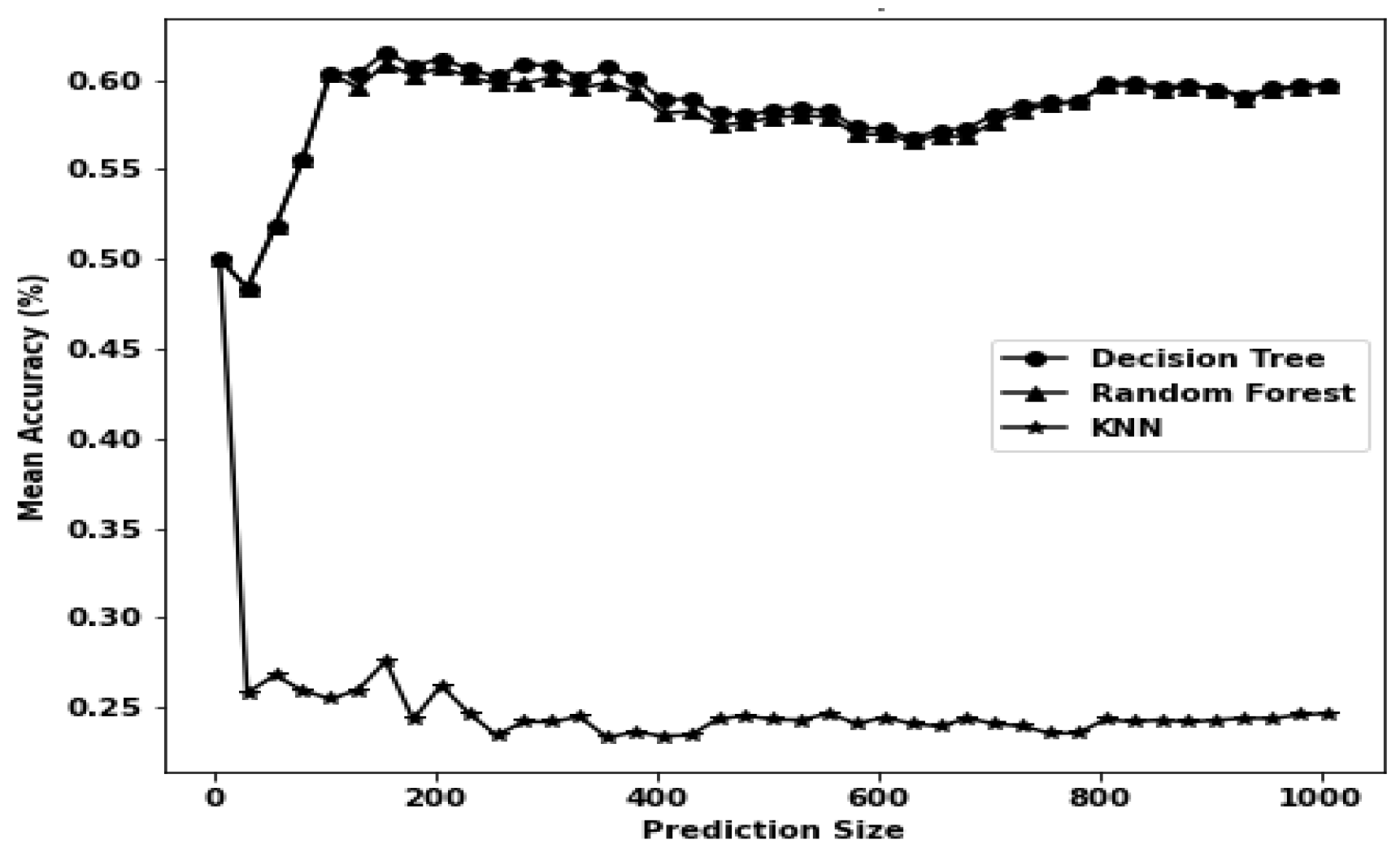
| DT | 0.342 | 0.018 | 0.1488 | Reason | 0.228 | 0.018 | 0.4131 | Hackmode |
| RF | 17.832 | 1.17 | 0.1479 | Reason | 14.712 | 2.13 | 0.4135 | Hackmode |
| k-NN | 39.678 | 68.34 | 0.156 | Reason | 37.86 | 73.692 | 0.4372 | Hackmode |
| Reason(s) | Attack reason selected by attacker | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Heh...just for fun! 57046 | 6.277% |
| 1 | Political reasons3619 | 4.500% |
| 2 | I just want to be the best defacer21782 | 27.098% |
| 3 | Revenge against the website2151 | 2.675% |
| 4 | As a challenge2540 | 3.156% |
| 5 | Patriotism2247 | 2.795% |
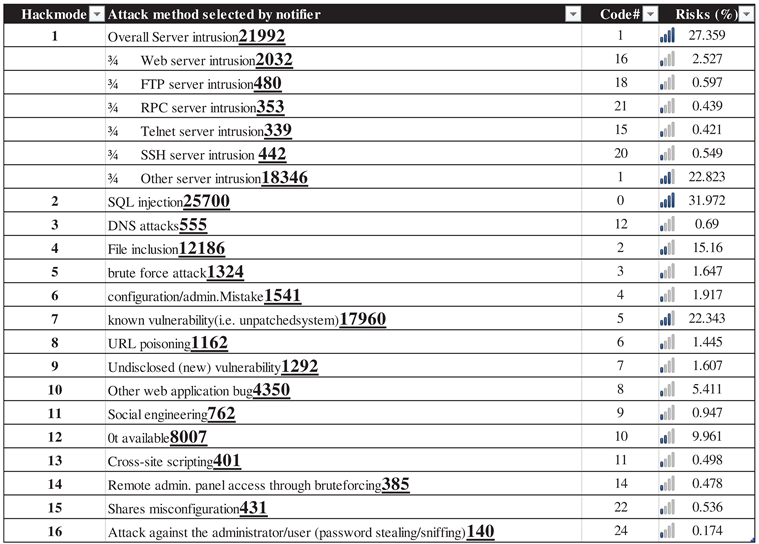
| Author(s), year(s) | Dataset SRC, Size | #Objects | Duration, Type | Software tool | Algorithm(s) | Metrics | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | Zone-H 93644 defacements |
80382 objects | 2015-2016, standard | Python 3.10 (64-bit) | - DT - RF -k-NN |
max_depth, min_sample_leaf, n_neighbours timing AVG errors accuracy |
Classifier prediction |
| Burruss et al., 2021 | Zone-H 1292 defacements 119->questionnaire |
119 questionnaires | June-August 2017, 1062->Standard 119->Questionnaire |
Stata v 16.1, gsem command(StataCrop,2017) | AIC = 657.653, BIC = 668.769, Log likelihood | - IRR% - SE |
Classifier prediction |
| A. Moneva et al., 2022 | Zone-H 9117268 defacements |
23.6%-single attack 76.4%-mass attack |
2010-2017, standard | R-package3.6.1&R-Studio1.2.5001 | Statistical means | - Bar charts - Histograms - Log10 - Percentage% - Frequency |
Regression assessment. |
| Gurjwar R.K, Sahu D.R., and Tomar D.S., 2013 | Monitoring 250 image MANIT, Bhopal (M.P.), INDIA |
100 webpage | 2013, Monitoring | CentOS Linux 5.9 C#.Net |
CRC32, MD5, SHA 512, PSNR and SSIM techniques. | -Accuracy | Pre-processed/data clean. |
| Hoang X. D. and Nguyen N. T., 2019 | 1200 English 217 Vietnamese 1200 DefacedPages |
50 attack signatures | 2019, standard | Python Sklearn machine learning library | Multinominal Naïve Bayes Random Forest |
- Accuracy - F1 score - Detection rate% |
Raw data conducted. |
| S.G.A. van de Weijer et al., 2021 | Zone-H 2,745,311 defacements |
66,553 hackers | 2010-2017, standard | PL(i.e.,C++/Java) | Logistic regression | Hackers’ AVGs for: - Timing - Length - frequency |
Regression |
| Holt et al., 2021 | Zone-H 2285172 defacements 2012-2016 @USA |
29,035 attackers | 2012-2016, standard | STATA 13 using the cluster command | Routine activity theory(RAT) Binary logistic regression |
-SE - b - # multicollinearity - Tolerance - Variance inflation |
Classifier prediction |
| Mee Lan Han et al., 2019 | Zone-H 212,093 defacements |
k-hacker@DB randomly selected 100 hackers | 2004-2019, standards | data driven and evidence driven decision tools | CBR-based | - similarity measure - clustering |
Data drive. |
| Howell Jordan C., et al., 2019 | 13 M@Zone-H United States’ Central Intelligence Agency Freedom House Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams(FIRST.org) Kaspersky Lab |
114 countries | 2017, standard | Statistical Analysis tools | Negative binominal regression | -IRR - SD, AVGs - b |
Classifier prediction. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





