Submitted:
25 October 2023
Posted:
27 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Austenite-martensite incompatibility problem in NiTi
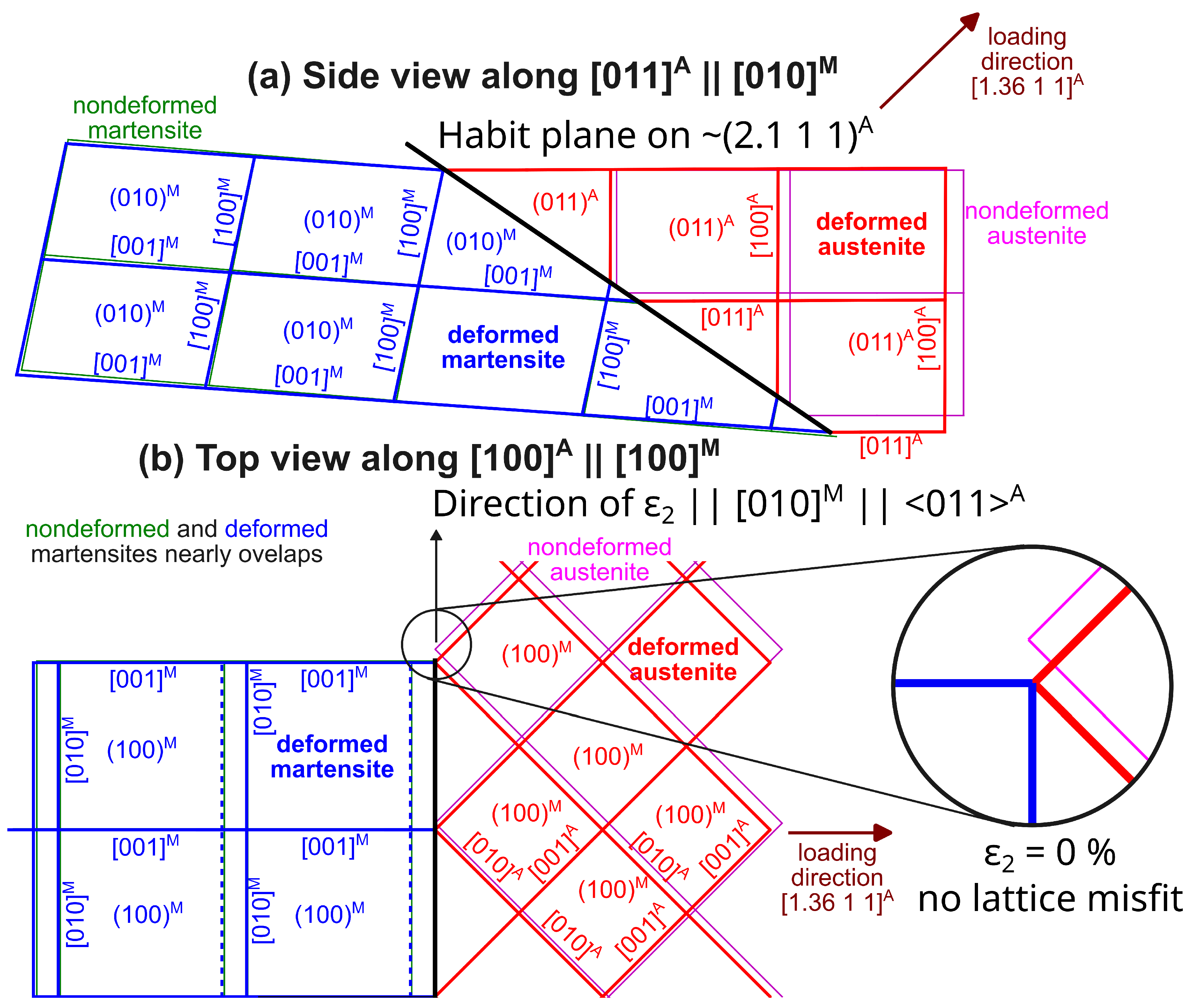
3. Preliminary Insight into Elastic Deformation Effects on Austenite-Martensite Incompatibility
4. Methods
4.1. Equation of Compatibility between Austenite and Martensite under Stress
4.2. Considered stress state and lattice correspondence
4.3. Numerical implementation
4.4. Lattice parameters and elastic properties
4.4.1. Austenite
4.4.2. Simulation of Elastic Softening of Austenite
4.4.3. Martensite
5. Results
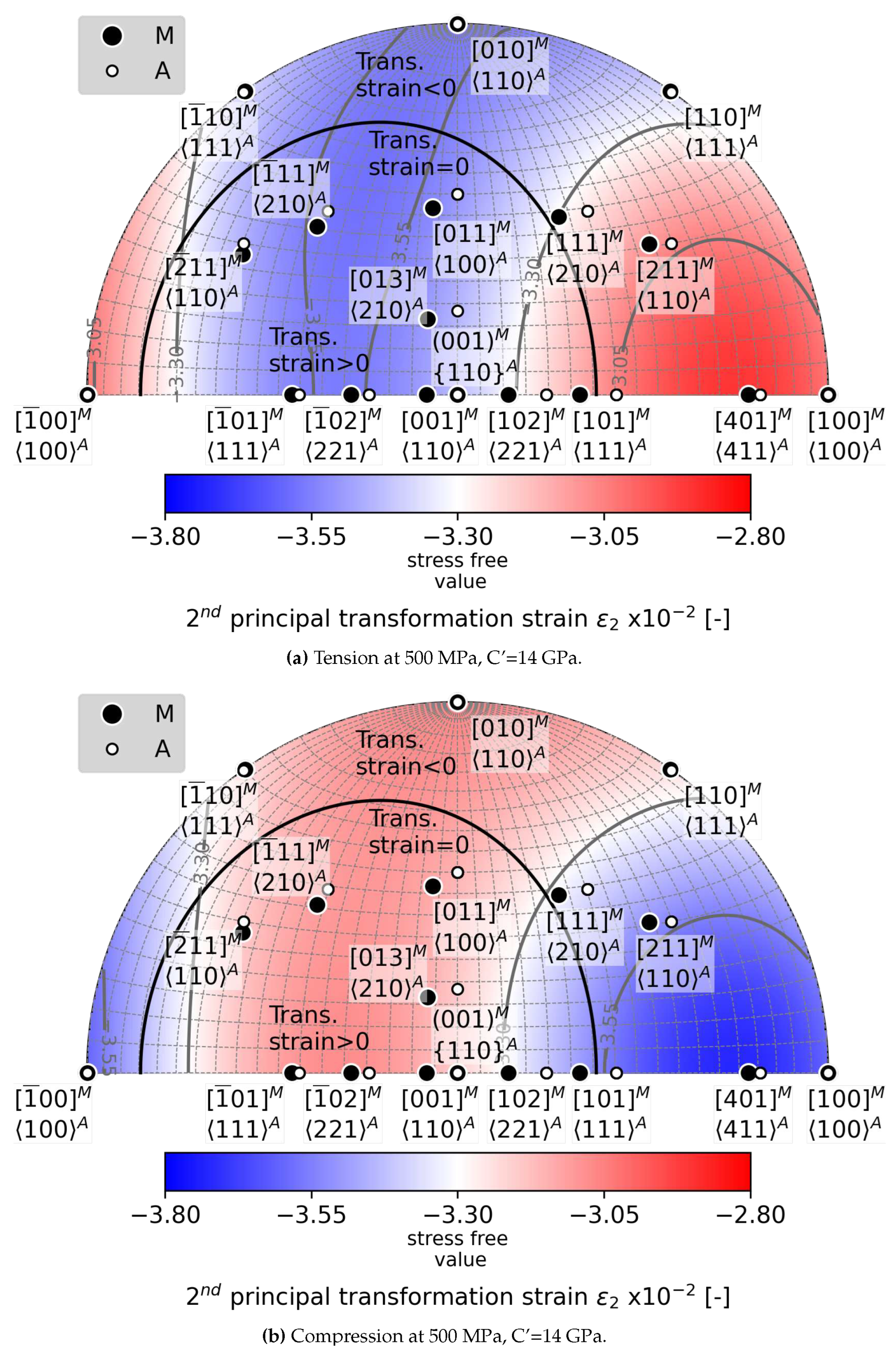
5.1. Loading direction dependent effects of tension and compression on
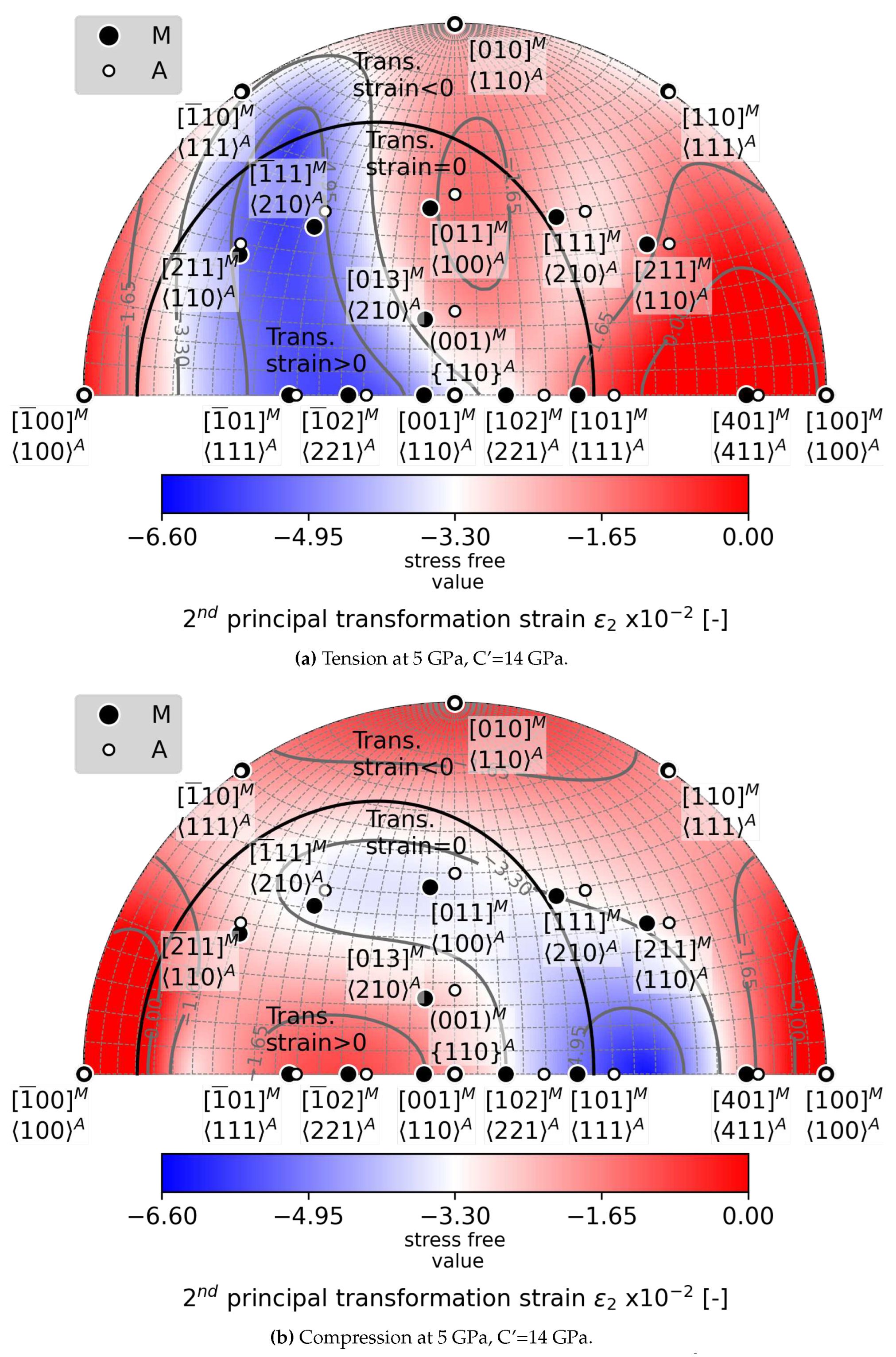
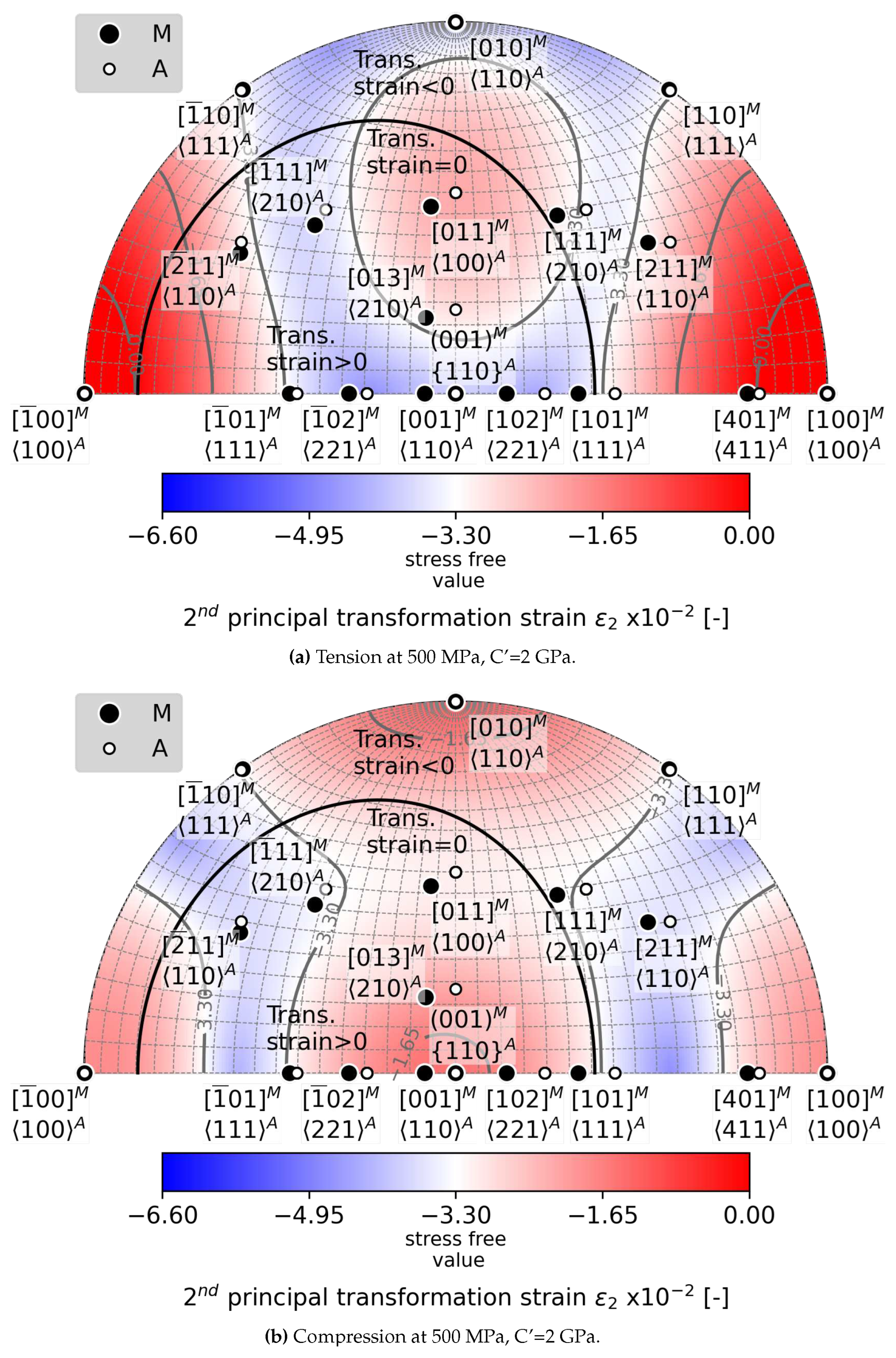
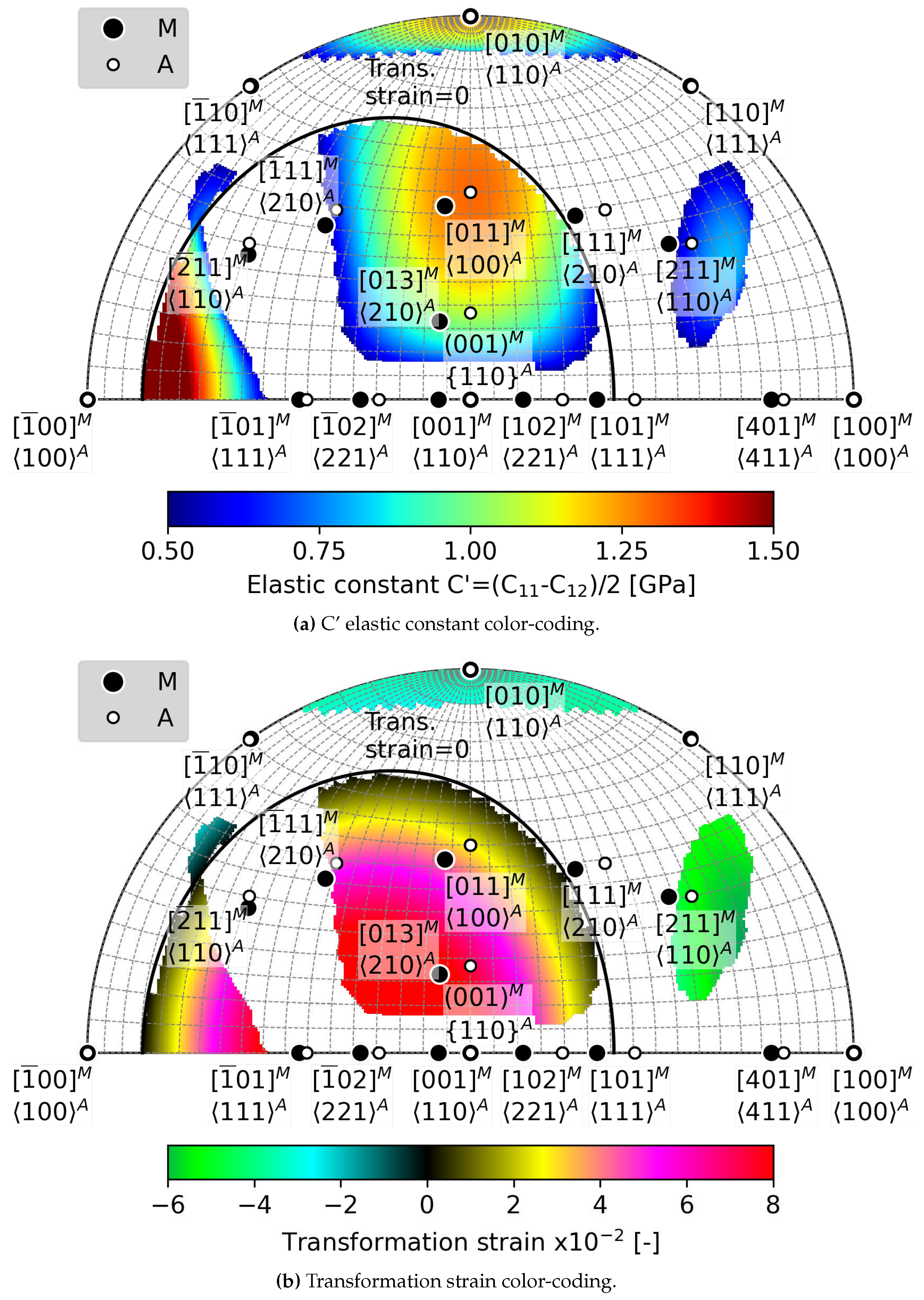
5.2. Loading Direction Dependent Effects of C’ Softening of austenite on
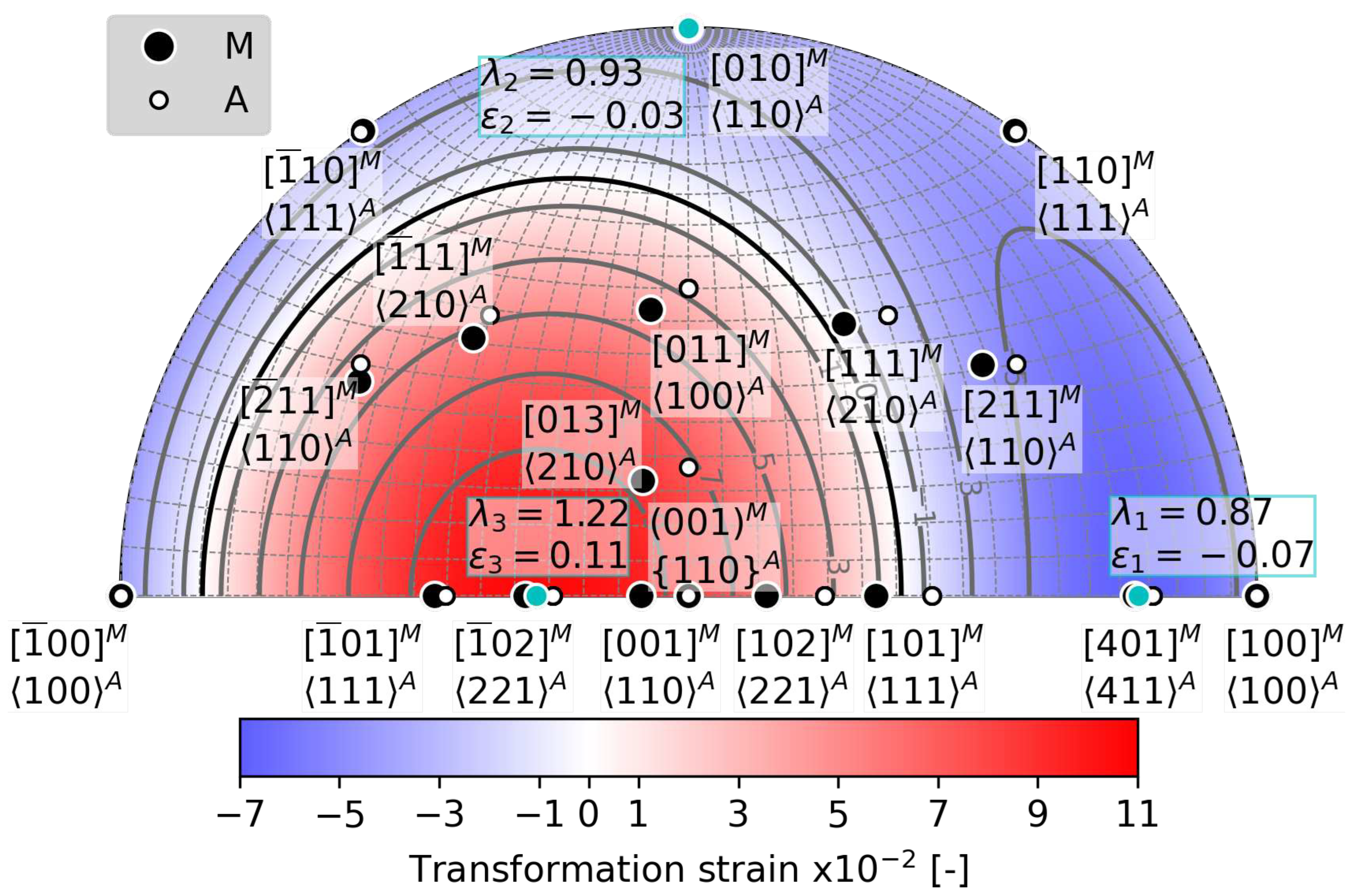
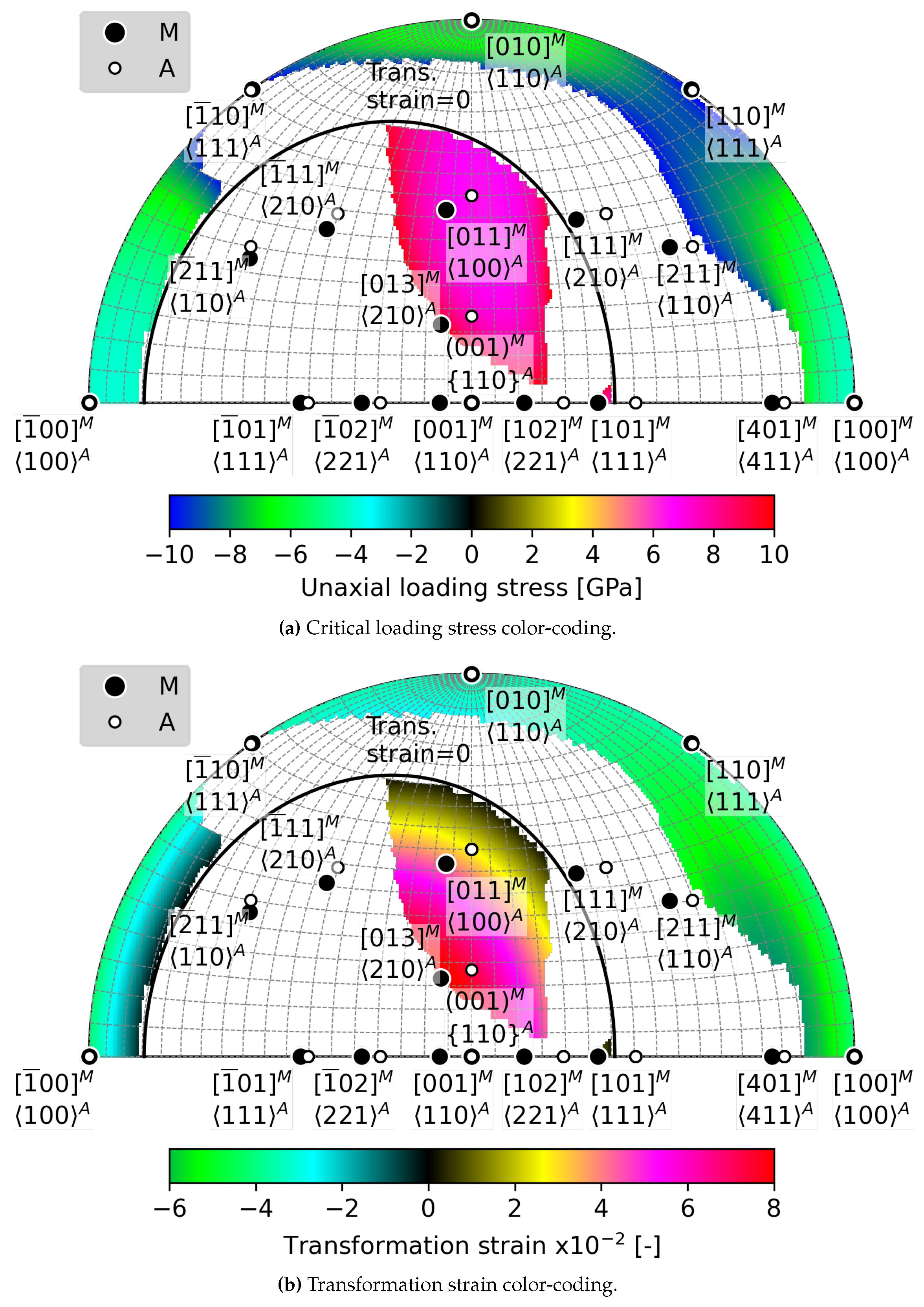
5.3. Critical Uniaxial Loading Ensuring Austenite-Martensite Compatibility
5.4. Compatibility of austenite and martensite under uniaxial loading and austenite softening
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
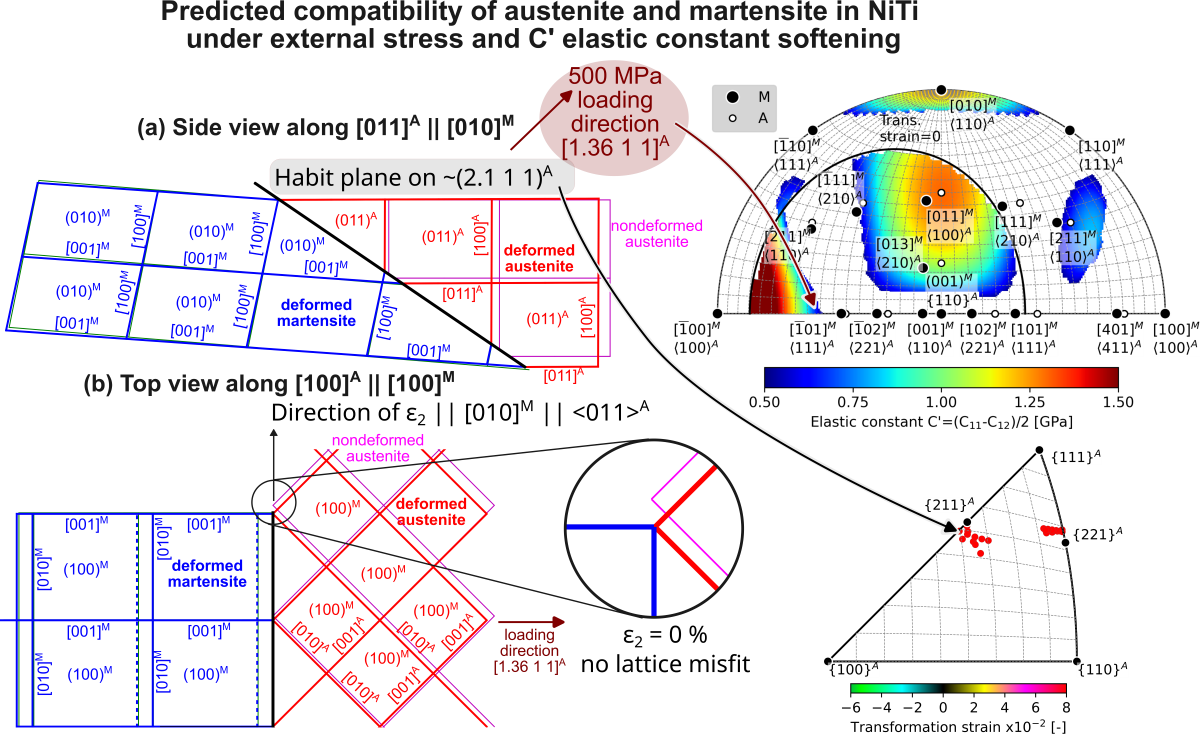
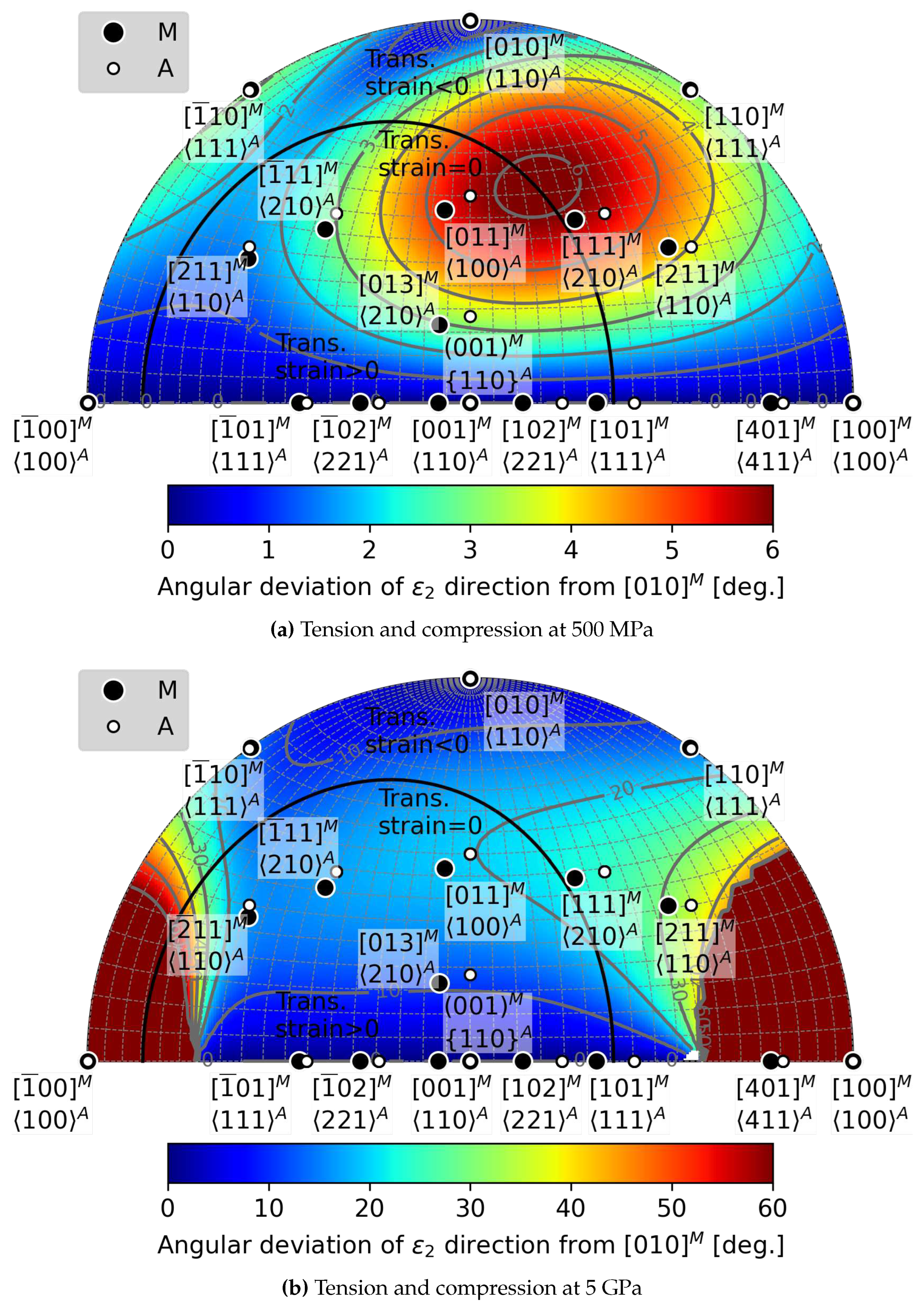
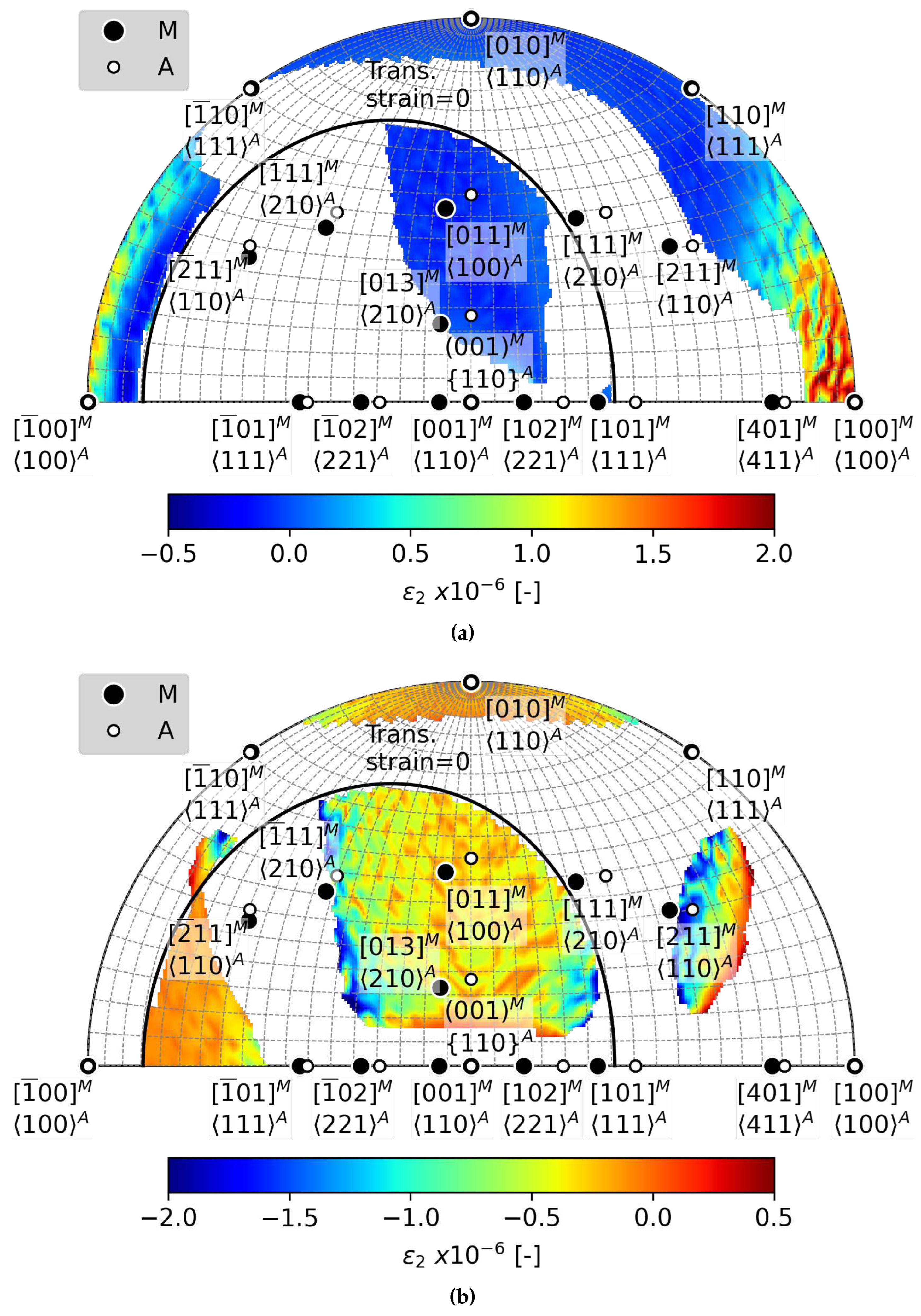
- The elastic strain impacts the second principal transformation strain, , and the corresponding eigenvalue , in both magnitude and direction. Considering a moderate stress of 500 MPa, the magnitude of decreases from -3.3 % to -3 %, and simultaneously, its direction moves away from by as much as 6 degrees. Therefore, it is likely that elastic strains affect the location of habit planes observed in situ on samples subjected to external stress.
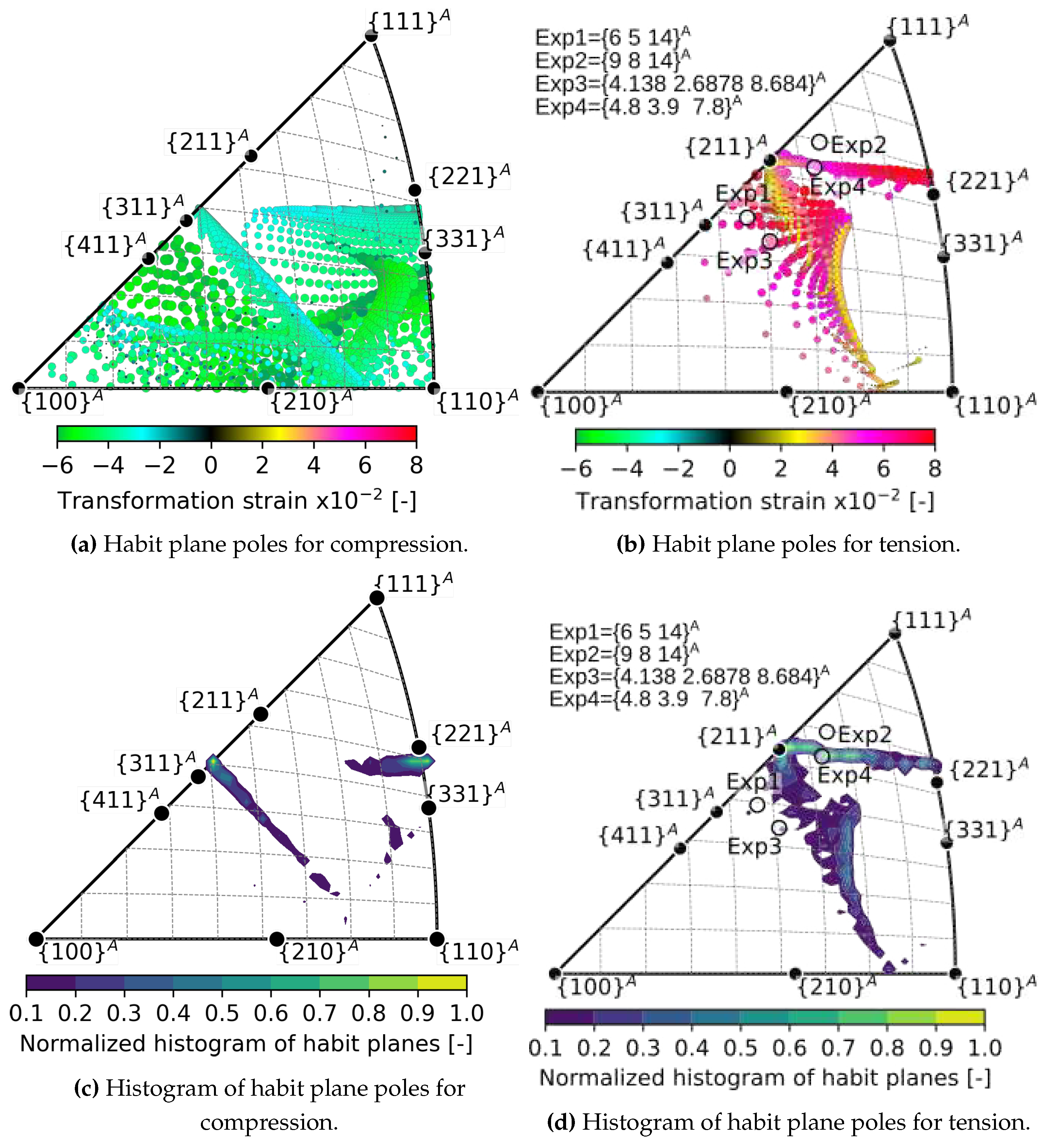
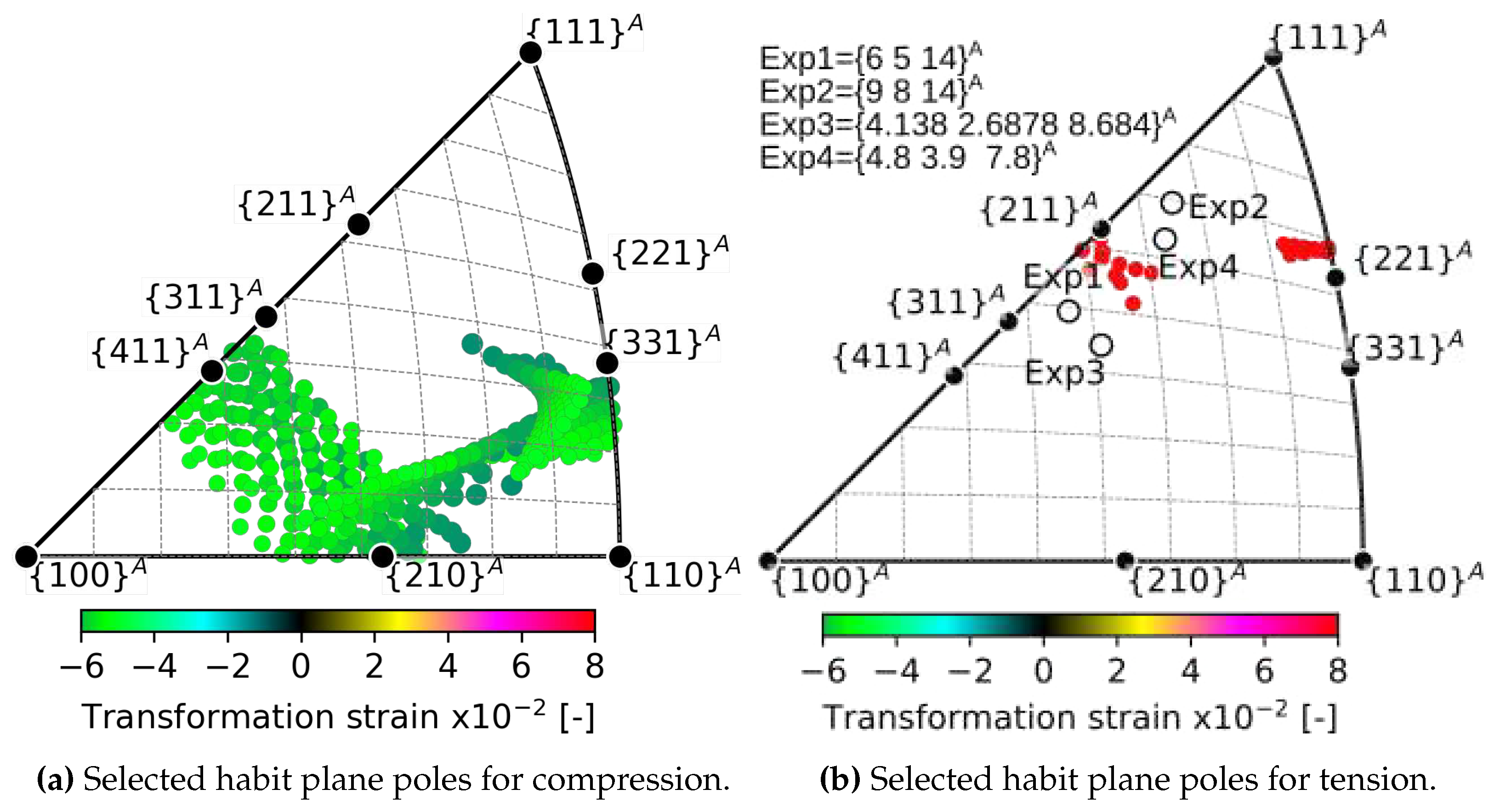
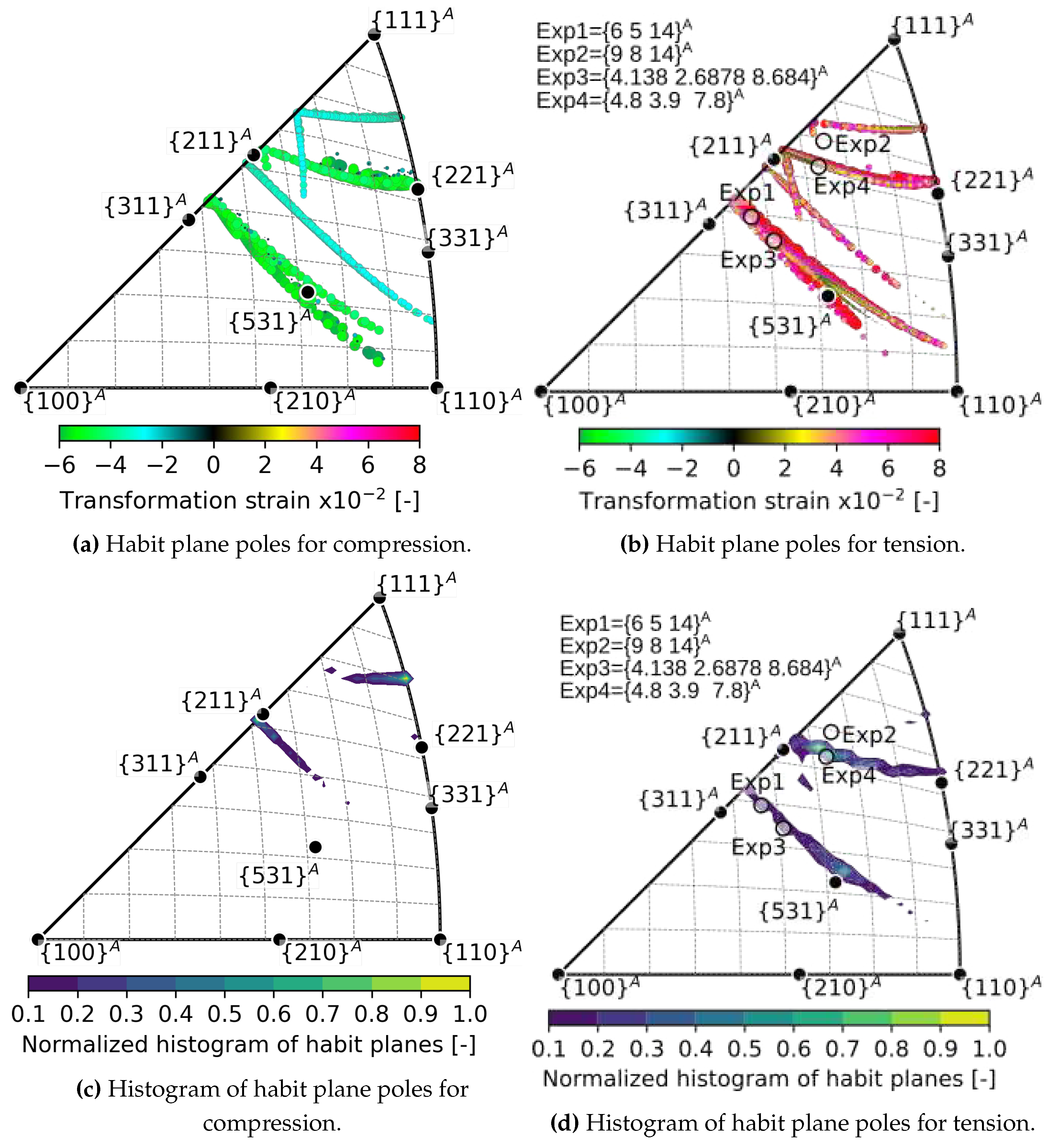
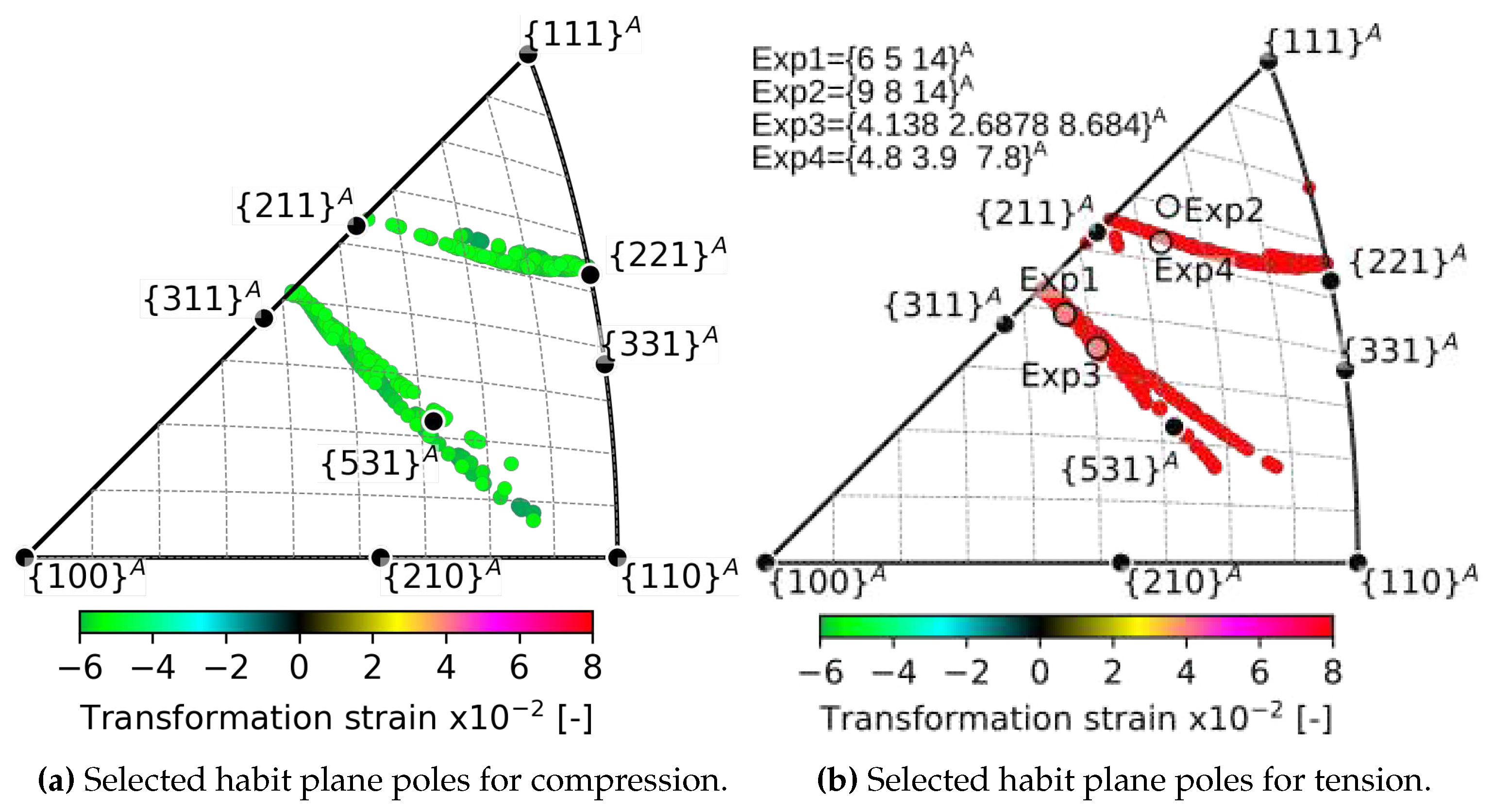
- Above a critical uniaxial stress, strain compatible habit plane interfaces between austenite and single variant of martensite exists within a limited region of orientation space. There is a larger orientation spread of habit planes in compression than in tension and magnitudes of critical stresses tend to be lower in compression.
- When the C’ elastic constant softens below 2 GPa, the critical loading stress for formation of habit planes between austenite and a single variant of martensite decreases to 500 MPa.
- Softening of the C’ elastic constant has more favorable impact on habit plane formation in tension than in compression. There is a larger orientation space available for critical loading in tension compared to compression.
- The predicted habit plane normals lie in two narrow bands within the austenite orientation space near the low-index poles - , and -. These theoretical predictions were compared with experimentally determined orientations of habit planes of tensile stress induced B2-B19’ transformation in NiTi single crystals in the literature - , [7], [8], [35].
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Deformation gradients between elastically distorted cubic B2 austenite and monoclinic B19’ martensite
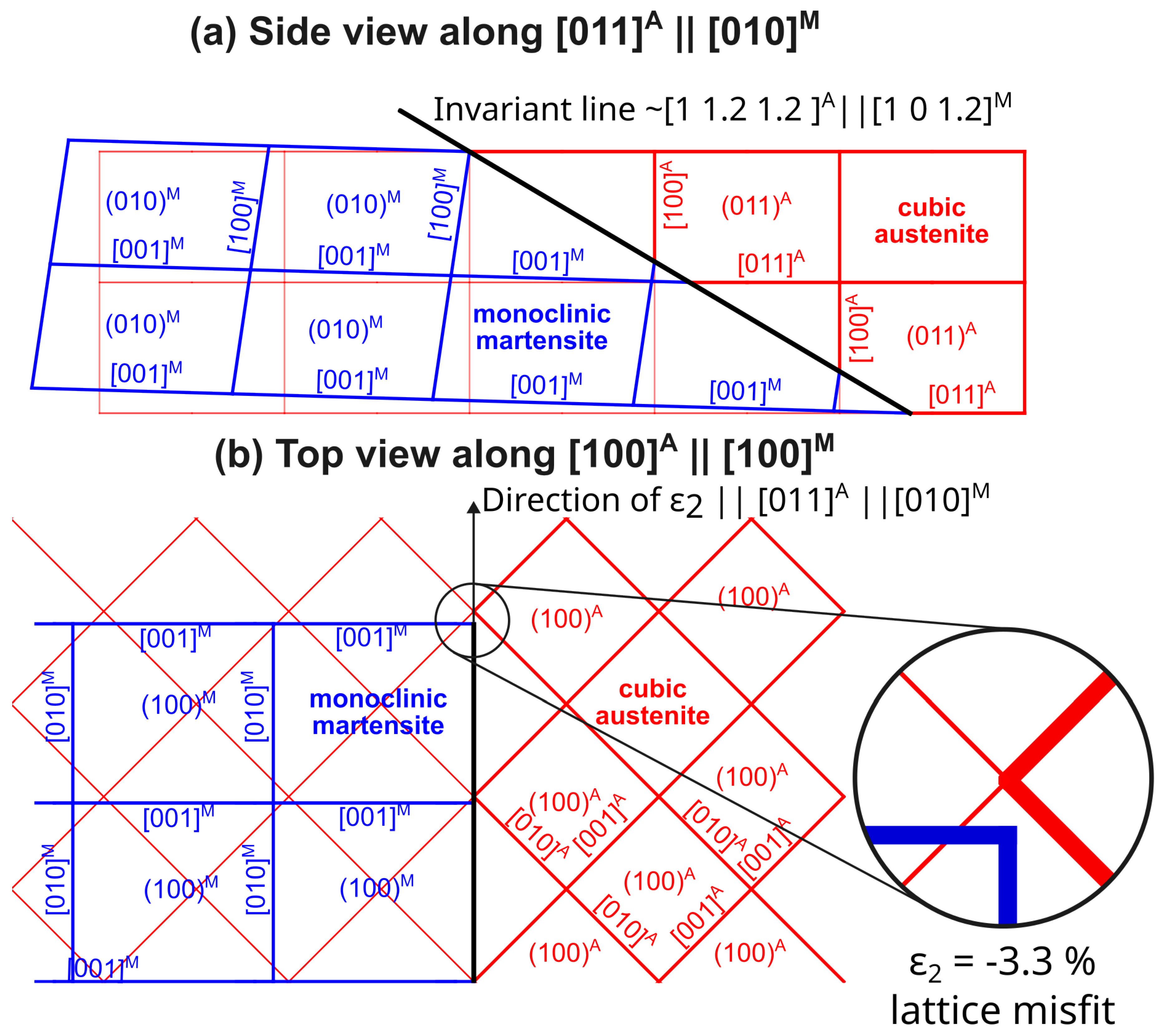
Appendix A.1. Relationships between stress-free austenite and martensite lattices
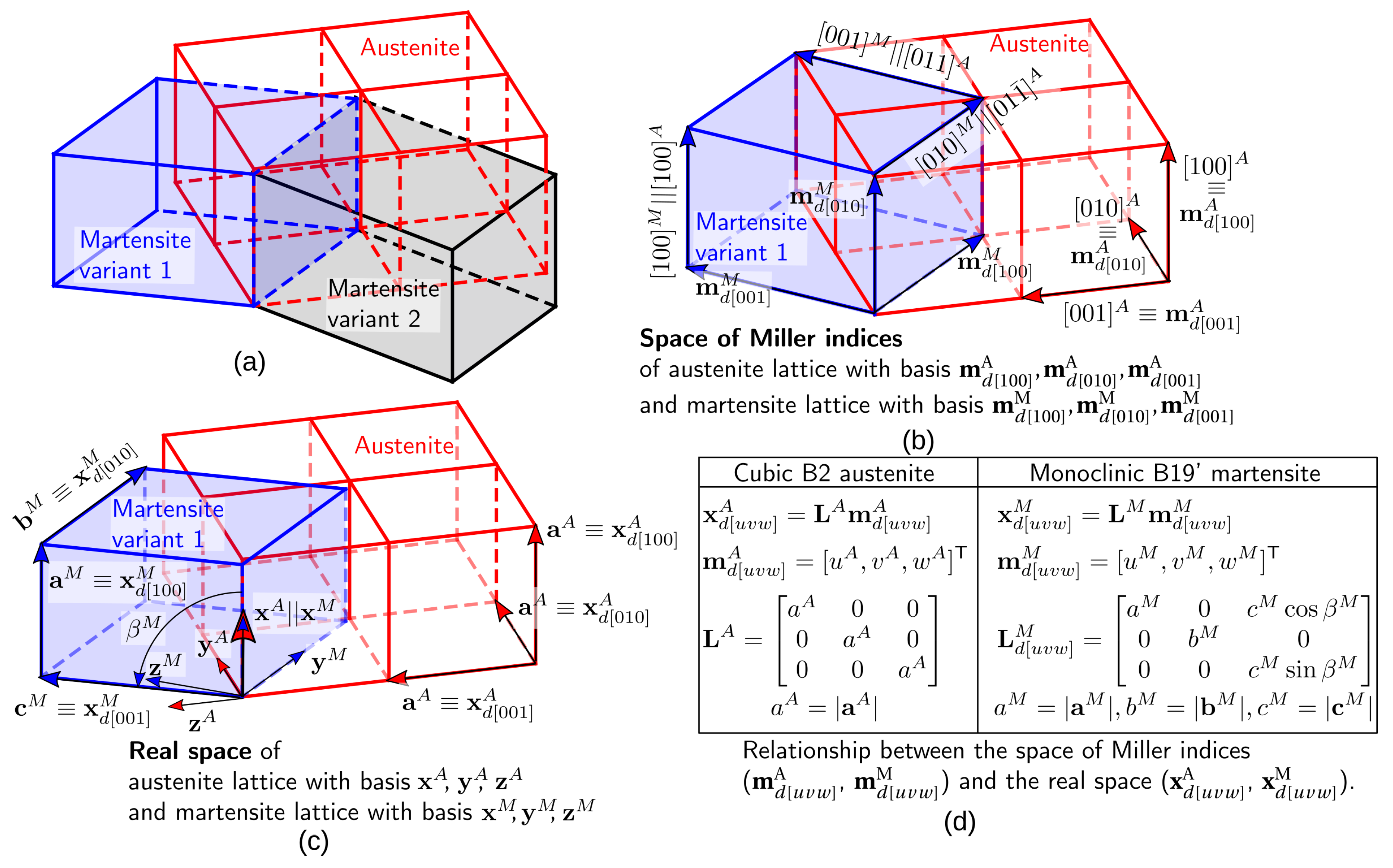
Appendix A.2. Lattice correspondence
| Basal lattice directions of martensite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correspondence | [100]M | [010]M | [001]M | |
| variant notation | Corresponding lattice directions of austenite | |||
| 1 | [100]A | [01]A | [011]A | |
| 2 | [100]A | [01]A | [0]A | |
| 3 | [100]A | [011]A | [01]A | |
| 4 | [100]A | [0]A | [01]A | |
| 5 | [00]A | [01]A | [0]A | |
| 6 | [00]A | [10]A | [101]A | |
| 7 | [010]A | [101]A | [10]A | |
| 8 | [010]A | [0]A | [01]A | |
| 9 | [00]A | [10]A | [0]A | |
| 10 | [00]A | [10]A | [110]A | |
| 11 | [001]A | [0]A | [10]A | |
| 12 | [001]A | [110]A | [10]A | |
| Lattice directions of austenite | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correspondence | ||||||
| variant notation | Corresponding lattice directions of martensite | |||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| 3 | ||||||
| 4 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 7 | ||||||
| 8 | ||||||
| 9 | ||||||
| 10 | ||||||
| 11 | ||||||
| 12 | ||||||
| Variant 1 | Variant 2 | Variant 3 | Variant 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variant 5 | Variant 6 | Variant 7 | Variant 8 |
| Variant 9 | Variant 10 | Variant 11 | Variant 12 |
Appendix A.3. Real space orientation relationships
Appendix A.4. Transformation deformation gradients
Appendix A.5. Lattice matrices of elastically distorted austenite and martensite
Appendix A.6. Deformation gradients for elastically distorted lattices
Appendix A.7. Directional Transformation Strains
Appendix B. Supplementary Figures
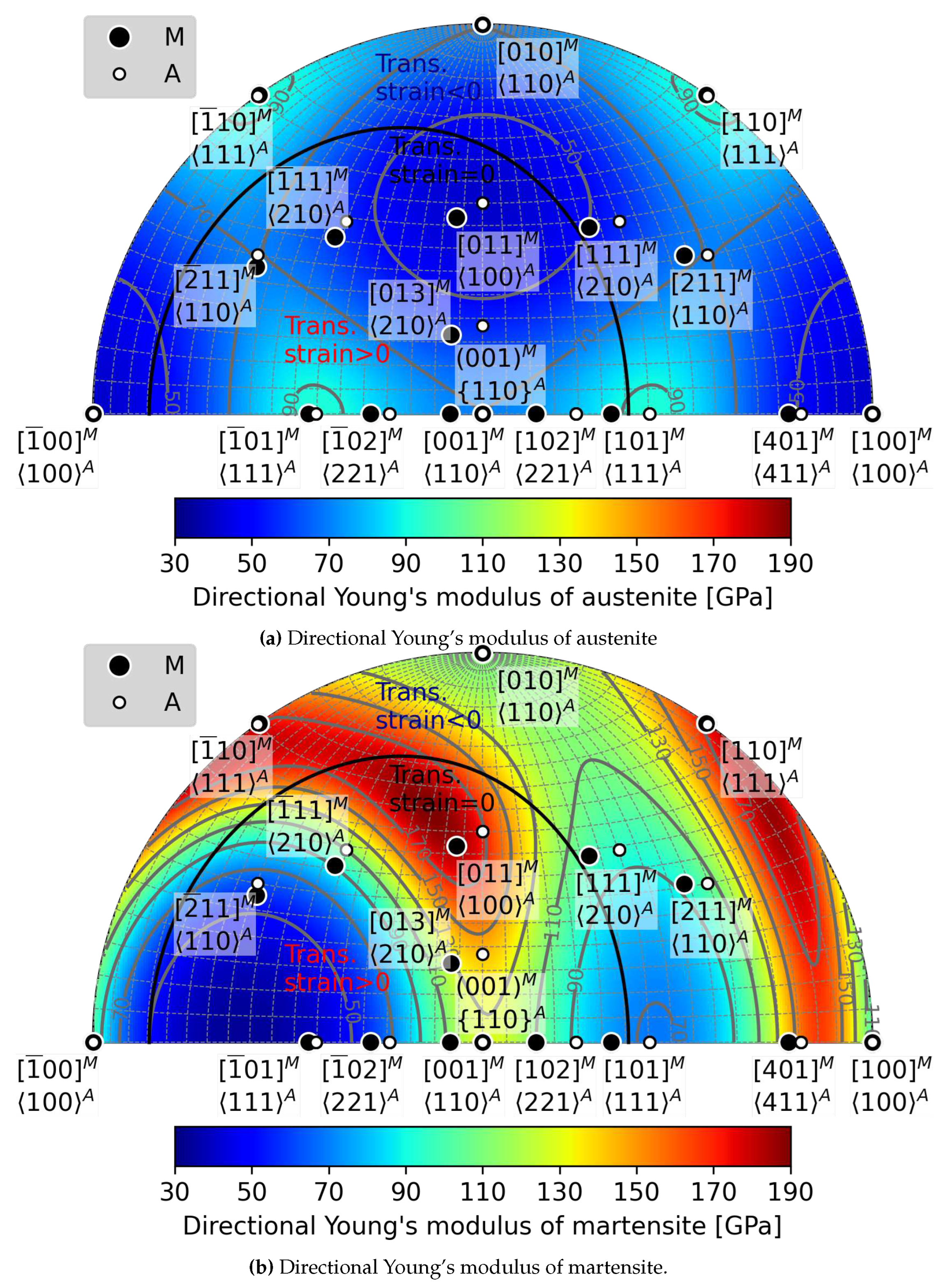
Appendix B.1. Directional Young’s modulus of austenite
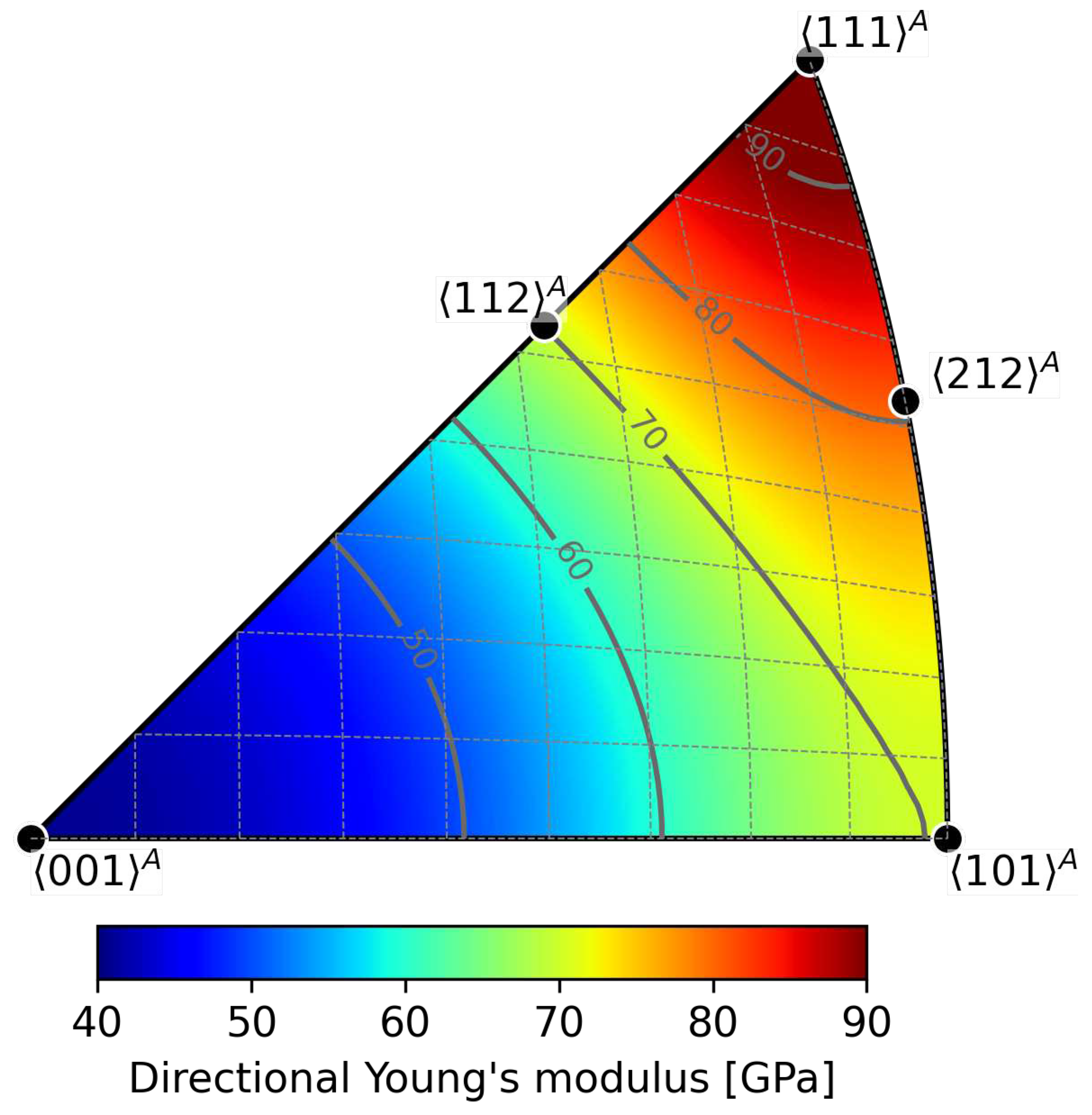
Appendix B.2. Deviations of ε2 direction from [010] M
Appendix B.3. Magnitudes of ε2 for Calculated Habit Planes
References
- James, R.D.; Zhang, Z.; James, R.D.; Zhang, Z. A Way to Search for Multiferroic Materials with “Unlikely” Combinations of Physical Properties. In Magnetism and Structure in Functional Materials; Planes, A., Manosa, L., Saxena, A., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; pp. 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Bumke, L.; Chluba, C.; Quandt, E.; James, R.D. Phase engineering and supercompatibility of shape memory alloys. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K. Microstructure of martensite : Why it forms and how it gives rise to the shape-memory effect; Oxford University Press, 2003; p. 288.
- Porta, F.D.; Heima, A.; Shinohara, Y.; Akamine, H.; Nishida, M.; Inamura, T. Triplet condition: A new condition of supercompatibility between martensitic phases. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 169, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.; James, R. Fine phase mixtures as minimizers of energy. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1987, 100, 13–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hane, K.; Shield, T. Microstructure in the cubic to monoclinic transition in titanium–nickel shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kimura, S.; Otsuka, K.; Suzuki, Y. The habit plane and transformation strains associated with the martensitic transformation in Ti-Ni single crystals. Scr. Metall. 1984, 18, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, O.; Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K.; Tamura, H. Crystallography of martensitic transformation in Ti-Ni single crystals. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, T.; Bando, Y.; Ohba, T.; Otsuka, K. Electron Microscopy Study of Twins in Martensite in a Ti-50.0 at%Ni Alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM 1992, 33, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayron, C. What EBSD and TKD Tell Us about the Crystallography of the Martensitic B2-B19’ Transformation in NiTi Shape Memory Alloys. Crystals 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, T.; Nishiura, T.; Kawano, H.; Hosoda, H.; Nishida, M. Self-accommodation of B19’ martensite in Ti–Ni shape memory alloys. Part III. Analysis of habit plane variant clusters by the geometrically nonlinear theory. Philos. Mag. 2012, 92, 2247–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waitz, T. The self-accommodated morphology of martensite in nanocrystalline NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, L.; Šittner, P.; Sedlák, P.; Seiner, H.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Sedmák, P.; Vronka, M. Beyond the strain recoverability of martensitic transformation in NiTi. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 116, 232–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Molnárová, O.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P. Recoverability of large strains and deformation twinning in martensite during tensile deformation of NiTi shape memory alloy polycrystals. Acta Mater. 2019, 180, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šittner, P.; Sedlák, P.; Seiner, H.; Sedmák, P.; Pilch, J.; Delville, R.; Heller, L.; Kadeřávek, L. On the coupling between martensitic transformation and plasticity in NiTi: Experiments and continuum based modelling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 98, 249–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šittner, P.; Molnárová, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Tyc, O.; Heller, L. Deformation twinning in martensite affecting functional behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys. Materialia 2020, 9, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, E.; Heller, L.; de Prado, E.; Kopeček, J. Temperature and microstructure dependent tensile behavior of coarse grained superelastic NiTi. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delville, R.; Malard, B.; Pilch, J.; Sittner, P.; Schryvers, D. Transmission electron microscopy investigation of dislocation slip during superelastic cycling of Ni–Ti wires. Int. J. Plast. 2011, 27, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, L.; Seiner, H.; Šittner, P.; Sedlák, P.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L. On the plastic deformation accompanying cyclic martensitic transformation in thermomechanically loaded NiTi. Int. J. Plast. 2018, 111, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tyc, O.; Molnárová, O.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P. Tensile Deformation of Superelastic NiTi Wires in Wide Temperature and Microstructure Ranges. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2019, 5, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Molnárová, O.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P. Temperature and microstructure dependence of localized tensile deformation of superelastic NiTi wires. Mater. Des. 2019, 174, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyc, O.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P. Tensile Deformation of Superelastic NiTi Wires in Wide Temperature and Microstructure Ranges. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2021, 7, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Detwinning in shape memory alloy. Prog. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 3, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Molnárová, O.; Tyc, O.; Heller, L.; Seiner, H.; Šittner, P. Evolution of martensitic microstructures in nanocrystalline NiTi wires deformed in tension. Acta Mater. 2021, 218, 117166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Heller, L.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Šittner, P. In-situ synchrotron x-ray diffraction texture analysis of tensile deformation of nanocrystalline superelastic NiTi wire at various temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Cayron, C.; Logé, R. An investigation on reorientation and textural evolution in a martensitic NiTi rolled sheet using EBSD. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 159, 103468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucsek, A.N.; Dale, D.; Ko, J.Y.P.; Chumlyakov, Y.; Stebner, A.P. Measuring stress-induced martensite microstructures using far-field high-energy diffraction microscopy. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2018, 74, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourbabak, S.; Orekhov, A.; Samaee, V.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Schryvers, D. In-Situ TEM Stress Induced Martensitic Transformation in Ni50.8Ti49.2 Microwires. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2019, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirry, W.; Schryvers, D. In situ transmission electron microscopy of stress-induced martensite with focus on martensite twinning. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2008, 481-482, 420–425, Proceedings of the 7th European Symposium on Martensitic Transformations, ESOMAT 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The effect of microstructure on stress-induced martensitic transformation under cyclic loading in the SMA Nickel-Titanium. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 89, 16–30. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Cayron, C.; Logé, R. Revealing the microstructure evolution of the deformed superelastic NiTi wire by EBSD. Acta Mater. 2023, 255, 119069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalena, L.; Bucsek, A.N.; Pagan, D.C.; Hommer, G.M.; Bigelow, G.S.; Obstalecki, M.; Noebe, R.D.; Mills, M.J.; Stebner, A.P. Structure-Property Relationships of a High Strength Superelastic NiTi–1Hf Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Miura, N.; Zhang, J.; Otsuka, K.; Tanaka, K.; Koiwa, M.; Suzuki, T.; Chumlyakov, Y.; Asai, M. A comparative study of elastic constants of Ti–Ni-based alloys prior to martensitic transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 312, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sun, J.; Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Experimental study of elastic constant softening prior to stress-induced martensitic transformation. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 174103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. MIYAZAKI and K. OTSUKA. THE SHAPE MEMORY MECHANISM ASSOCIATED WITH THE MARTENSITIC TRANSFORMATION IN Ti-Ni. Acta Metall. 1989, 7, 1873–1884.
- Šittner, P.; Heller, L.; Pilch, J.; Curfs, C.; Alonso, T.; Favier, D. Young’s modulus of austenite and martensite phases in superelastic NiTi wires. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaparova, E.; Heller, L.; Tyc, O.; Sittner, P. Thermally induced reorientation and plastic deformation of B19’ monoclinic martensite in nanocrystalline NiTi wires. Acta Mater. 2023, 242, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.F.; Windl, W. Lattice stability, elastic constants and macroscopic moduli of NiTi martensites from first principles. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 6232–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geometry of crystals, polycrystals, and phase transformations. Geometry of Crystals, Polycrystals, and Phase Transformations, 2017; 1–252. [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; Kern, R.; Picus, M.; Hoyer, S.; van Kerkwijk, M.H.; Brett, M.; Haldane, A.; del Río, J.F.; Wiebe, M.; Peterson, P.; Gérard-Marchant, P.; Sheppard, K.; Reddy, T.; Weckesser, W.; Abbasi, H.; Gohlke, C.; Oliphant, T.E. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, L. Jupyter notebook containing computations the result of which are presented in this work. The notebook is available for download here. github.com, Accessed 04/10/2023.
- Otsuka, K.; Sawamura, T.; Shimizu, K. Crystal structure and internal defects of equiatomic TiNi martensite. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 1971, 5, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, K.; Smith, D. The crystallography of the martensitic transformation in equiatomic nickel-titanium. Acta Metall. 1981, 29, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayron, C. The Correspondence Theory and Its Application to NiTi Shape Memory Alloys. Crystals 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [-] |
| 169 | 141 | 33 | 14 | 2.4 |
| [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] | [GPa] |
| 223 | 129 | 99 | 27 | 241 | 125 | -9 | 200 | 4 | 76 | -4 | 21 | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





