1. Introduction
The widespread use of plastic products worldwide has naturally led to the emergence of environmental pollution issues related to plastic waste [
1,
2,
3]. Typically, after the use of plastic products, they are disposed of through landfilling or incineration, resulting in associated soil and air pollution, along with high disposal costs [
4,
5]. To mitigate these challenges, active research is being conducted on plastic waste recycling. However, currently, only about 9% of plastic waste produced globally is recycled, while the remaining 91% goes unrecycled [
6]. Polyolefin, a thermoplastic resin, is a commonly used materials as a raw material for plastics and is extensively employed in various facets of daily life [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Polyolefin-based polymer refers to chain or ring-like hydrocarbon polymers characterized by one or more unsaturated groups. Notable examples of polyolefins include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyisobutene, and polybutene. These versatile resins are widely employed in packaging materials, tableware, films, and numerous other applications [
11,
12,
13,
14]. Numerous studies have been conducted to facilitate the recycling of polyolefin-based thermoplastic materials. Among these, notable approaches include the introduction of inorganic nanoparticles [
15,
16,
17,
18], radical-induced cross-linking reactions [
19,
20], and the utilization of silane monomers for cross-linking [
21,
22]. Regarding the incorporation of inorganic nanoparticles, extensive research has been devoted to enhancing the mechanical properties of polyolefins by integrating nano-silica particles, with a particular emphasis on mesoporous silica [
23,
24,
25]. It is generally observed that silica with a higher surface area leads to improved performance when introduced into waste plastics. However, commercially available silica often lacks a significantly high surface area, and the synthesis of mesoporous silica with a surface area exceeding 1000 m
2/g can be challenging due to complex production methods and the associated high costs. Furthermore, there are limitations in achieving performance improvements solely through the physical dispersion of silica nanoparticles, necessitating further research in this domain introduction of peroxides into recycled plastics. Upon exposure to a specific temperature threshold, peroxides generate oxygen radicals that react with unreacted unsaturated groups, thereby increasing cross-link density. While this can enhance physical properties, the presence of residual unreacted peroxides may lead to adverse effects [
26], making it a less desirable option. The use of silane monomers in cross-linking reactions involving unsaturated groups introduces silane monomers processing unsaturation groups into recycled plastics. These unsaturated groups of silanes react with the unsaturated group of the plastics, increasing the cross-linking density and receiving the inorganic properties of the silane. However, silane monomers are typically in liquid form, which can impose limitations during the mixing process. Moreover, relying solely on the introduction of silane monomers may have inherent constraints, necessitating further research efforts. In other words, there is a need for research aimed at increasing the concentration of inorganic components to enhance tensile strength while simultaneously addressing the compromise in flexibility performance resulting from the hindered crosslinking density due to the incorporation of inorganic additives.
In this research, we aim to enhance the physical properties of recycled plastics by simultaneously introducing vinyl functional groups during the synthesis of silica nanoparticles using our room-temperature synthesis method [
27], thereby increasing the crosslinking density. This is because the process of introducing vinyl functional groups after synthesizing silica nanoparticles can reduce the specific surface area and complicate the procedure. To synthesize silica nanoparticles with exceptionally high surface area, we propose the synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles using sodium silicate as a precursor while simultaneously introducing vinyl functional groups. This approach not only reduces material costs but also enhances process convenience compared to post-introducing vinyl functional groups into the nanoparticles. Ultimately, it allows for the cost-effective synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles that exhibit excellent performance when incorporated into recycled plastics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vinyl Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (V-MS)
In the first beaker, a silica precursor solution was prepared by mixing 600 mL of distilled water with sodium silicate solution. In the second beaker, a solution consisting of equal volumes of distilled water and ethanol (100 mL total) was prepared, and its pH was adjusted to 3 using hydrochloric acid (HCl). Subsequently, Vinyltrimethoxysilane (VTMS) was added dropwise to the second beaker, and the hydrolysis reaction was induced over a period of 3 hours. Upon completion of the hydrolysis reaction, the hydrolyzed VTMS solution in the second beaker, which had a pH above 12 due to the presence of sodium silicate, was added dropwise to the first beaker where the sodium silicate solution had been diluted. The pH was adjusted to 10 using additional hydrochloric acid, and then 20 mL of Cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTACl) was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours. After the stirring was completed, the solution was centrifuged to obtain a residue as a white slurry. To remove CTACl, this slurry was dispersed in a 1.0 M solution of HCl/Ethanol (EtOH) (1 L) and stirred for 24 hours. After 24 hours, another centrifugation was performed to collect a white slurry. This slurry was washed twice by dispersing it in a solution consisting of H2O/EtOH in a 1:1 volume ratio. Finally, the obtained slurry was dried in a convection oven at 80° for 10 hours to yield white powder.
2.2. Characterization of Vinyl Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
The morphology and particle shape of the synthesized mesoporous silica were examined using a Field Emission Transmission Electron Microscope (FE-TEM; HF-3300) under 300 kV conditions. Additionally, the specific surface area and porosity characteristics of the porous silica were analyzed using Nitrogen Adsorption-Desorption Isotherm (N2-sorption; QUANTACHROME, Qudrasorb SI). The measurements were conducted at a temperature of 77 K, maintained using liquid nitrogen. The adsorbed nitrogen was normalized to standard temperature and pressure. Prior to analysis, a heat treatment was performed at 200 °C for 6 hours to remove moisture and impurities adsorbed on the sample's surface. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) specific surface area was calculated from the linear portion (P/P0 = 0.05–0.30) of the BET equation. The volume and size of pores were calculated using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) equation. For properties confirmation of the mesopores, X-ray diffractometer (XRD; PANalytical X’pert PRO MRD) was employed. Measurements were conducted in 2θ scan mode with Cu-Kα rays (λ = 0.0154 nm). Finally, to confirm the introduction of vinyl functional groups, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FT-IR; Thermo, Nicolet iS50) was used for analysis.
2.3. Manufacturing Method of Polyethylene Compound
Polyethylene compounds were manufactured using a Twin Extruder (TEK20-L/D48(9B)-2SF-1V-AC2.2, SM Platek Co., LTD., Korea). Recycled polyethylene (Kwangduk Industry Co., KD-rePE_030A) was fed into the main feeder, along with silica with incorporated vinyl functional groups and carbon black N330 (OCI, Korea). TINUVIN 770 (BASF, USA) was utilized as an amine light stabilizer, UV-326 (Rianlon Corporation, China) as a UV stabilizer, LOXIOL 8314 (Emery Oleochemicals, USA) as both a lubricant and antistatic agent, and Zn-st (Duksan General Science, Korea) as a lubricant. All of these were introduced through the side feeder as additives. During this process, the internal temperature of the extruder was maintained at 150-160°C. Subsequently, the material was cooled and formed into pellet shapes. Afterward, the cross-linking reaction was carried out at 90°C for 30 minutes using dicumyl peroxide ([C6H5C(CH3)2]2O2, KWANGDUK Industry Co.), resulting in the final product of recycled PE with incorporated silica.
2.4. Characterization of Polyethylene Compounds
To evaluate the physical performance of recycled PE, analyses were conducted using the Melting Index test (QM280, Qmesys, Korea) and Universal Testing Machine (UTM, QM100s, Qmesys, Korea). The Melting Index was carried out in accordance with ASTM D123 standards. Using the UTM, various tests were conducted, including tensile strength, elongation, elastic modulus, flexural strength, and flexural modulus. Tensile strength, elongation, and elastic modulus were assessed by preparing specimens according to ASTM D638 standards. The tests were performed with a testing speed of 50 mm/min, a grip-to-grip distance of 115 mm, a gauge length of 50 mm, and a load cell capacity of 30,000 N. Flexural strength and flexural modulus were evaluated based on ASTM D790 standards. Specimens were prepared, and the tests were conducted with a testing speed of 2.8 mm/min, a grip-to-grip distance of 104 mm, and an elastic range of 0.05% to 0.25%.
3. Results and Discussion
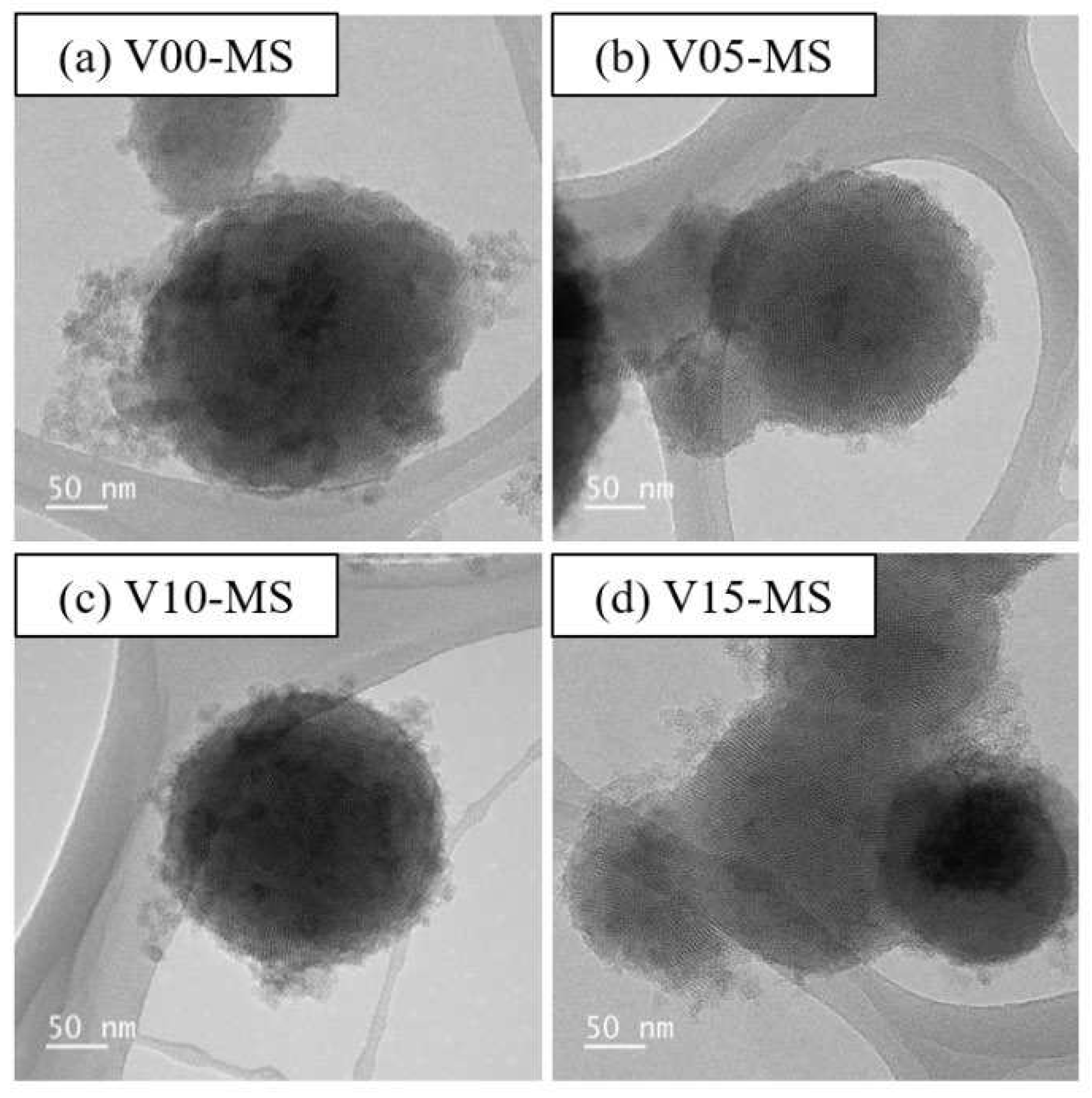
Vinyl functional groups were introduced into porous silica by adjusting the volume ratio of sodium silicate to VTMS from 40:0 to 25:15, as shown in
Table 1, and TEM images of the synthesized mesoporous silica are presented in
Figure 1. When the vinyl group content exceeded to 20 mL, gelation occurred and the reaction did not proceed. The TEM images confirm the successful formation of well-defined meso-sized pores in the vinyl functionalized MS nanoparticles (V-MS). Based on the TEM images, it can be observed that the meso-sized pores within the particles are partially arranged in a hexagonal configuration. However, it becomes increasingly difficult to identify a regular pore arrangement as the vinyl silane content increases.
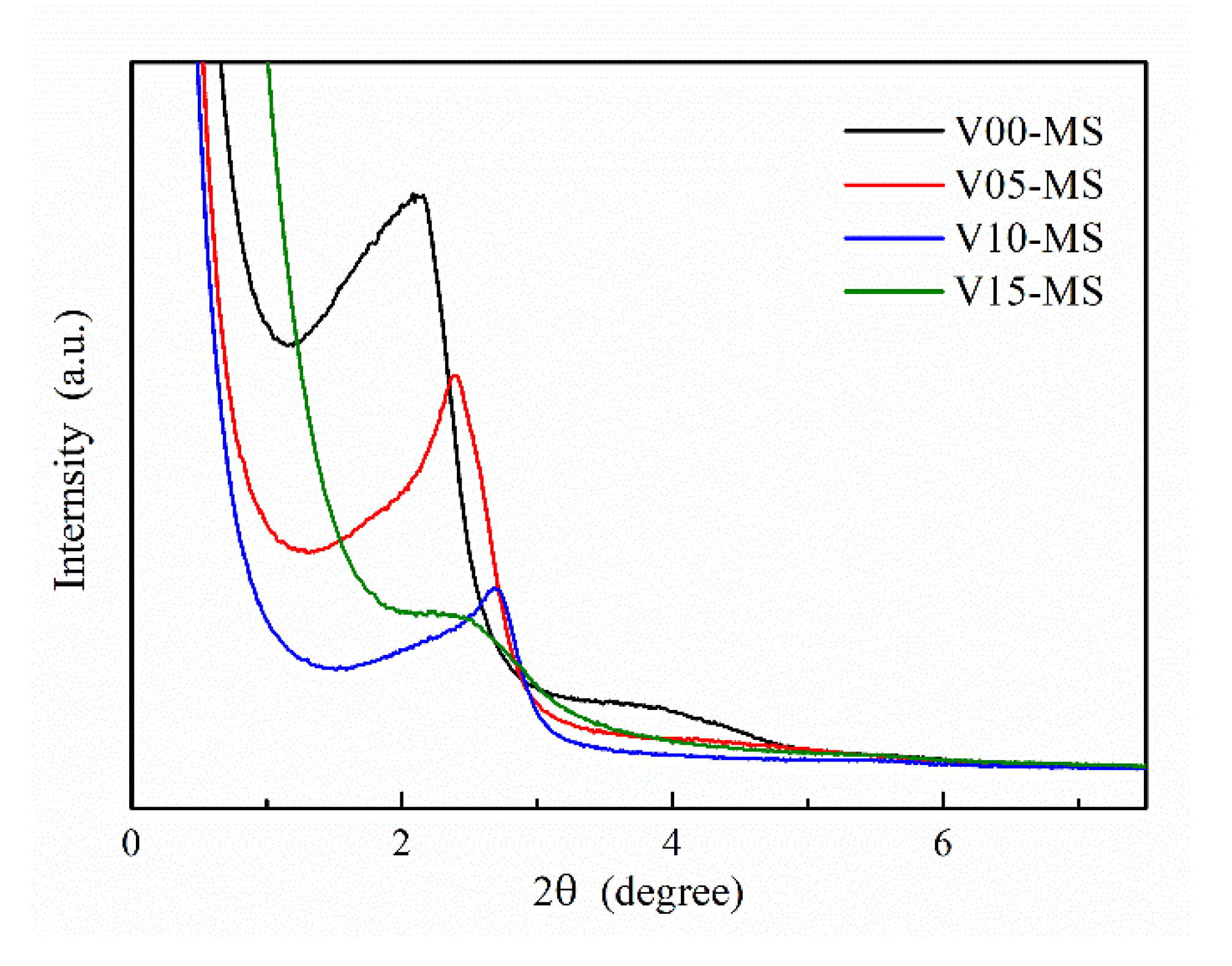
The low angle XRD analysis data of the V- MS nanoparticles are shown in
Figure 2. In the XRD result of V00-MS, which does not contain a vinyl functional group, a main peak corresponding to (100) is observed at around 2.06 in 2-theta. The small and broad peak approximately 3.91 in 2-theta, corresponding to (110), is also observed, confirming the hexagonal arrangement of the pore [
28]. However, the incorporation of vinyl silane during sample preparation renders the (110) peak undetectable in the XRD data, clearly indicating a significant reduction in the hexagonal pore arrangement of the MS nanoparticles. Additionally, it was observed that the main peak associated with (100) undergoes a noticeable rightward shift as the content of vinyl silane increases. It can be inferred a reduction in the pore size of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. The V15-MS sample, with the highest vinyl group content, shows broader peaks of XRD analysis compared to other samples, indicating an inconsistency in pore size. This can be attributed to the fact that the vinyl silane only possesses three alkoxysilane groups, leading to uneven silane polymerization when compared to other samples.
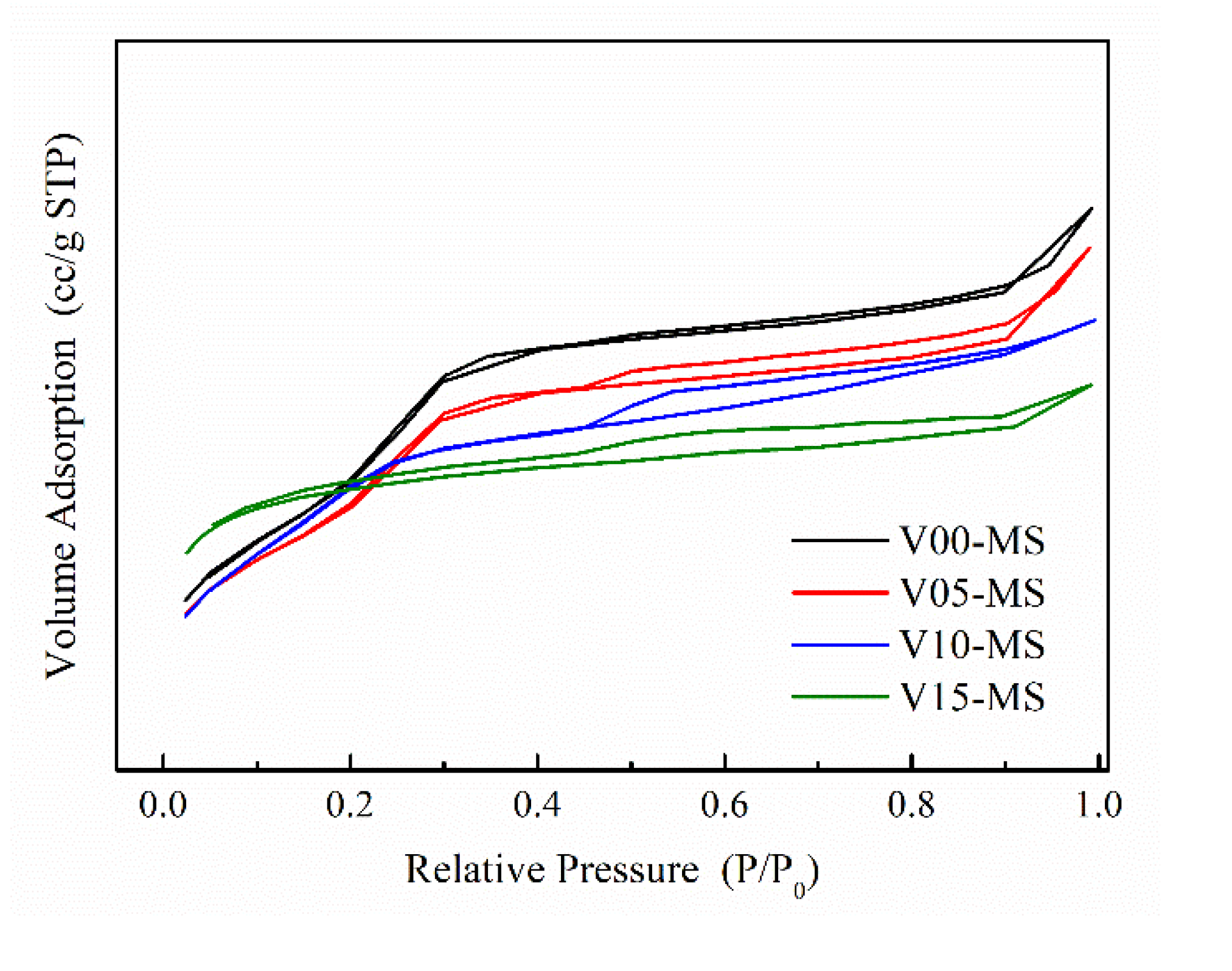
The N
2 adsorption-desorption isotherm graphs for silica samples with incorporated vinyl functional groups are presented in
Figure 3. It is evident that all four types of mesoporous silica nanoparticles exhibit a Type IV hysteresis loop pattern [
29]. Furthermore, the presence of separated adsorption and desorption curves suggests the existence of pores within the silica. The detailed pore properties of the MS are summarized in
Table 2.
As the amount of VTMS in the composite increases, it can be observed that the specific surface area decreases while the pore volume increases. Since VTMS possesses a three-functional alkoxy group in contrast to the sodium silicate, the cross-linking density between the silanes is lower than that of sodium silicate. it leads to the distribution of relatively large pores within the mesoporous silica nanoparticle. As a result, the increase in pore volume can be attributed to the decrease in specific surface area. While there doesn't seem to be a substantial difference in pore size, it can also be inferred that the presence of significant internal pores is suggested by the separation phenomenon between the adsorption and desorption curves, even at higher relative pressures (P/P0).
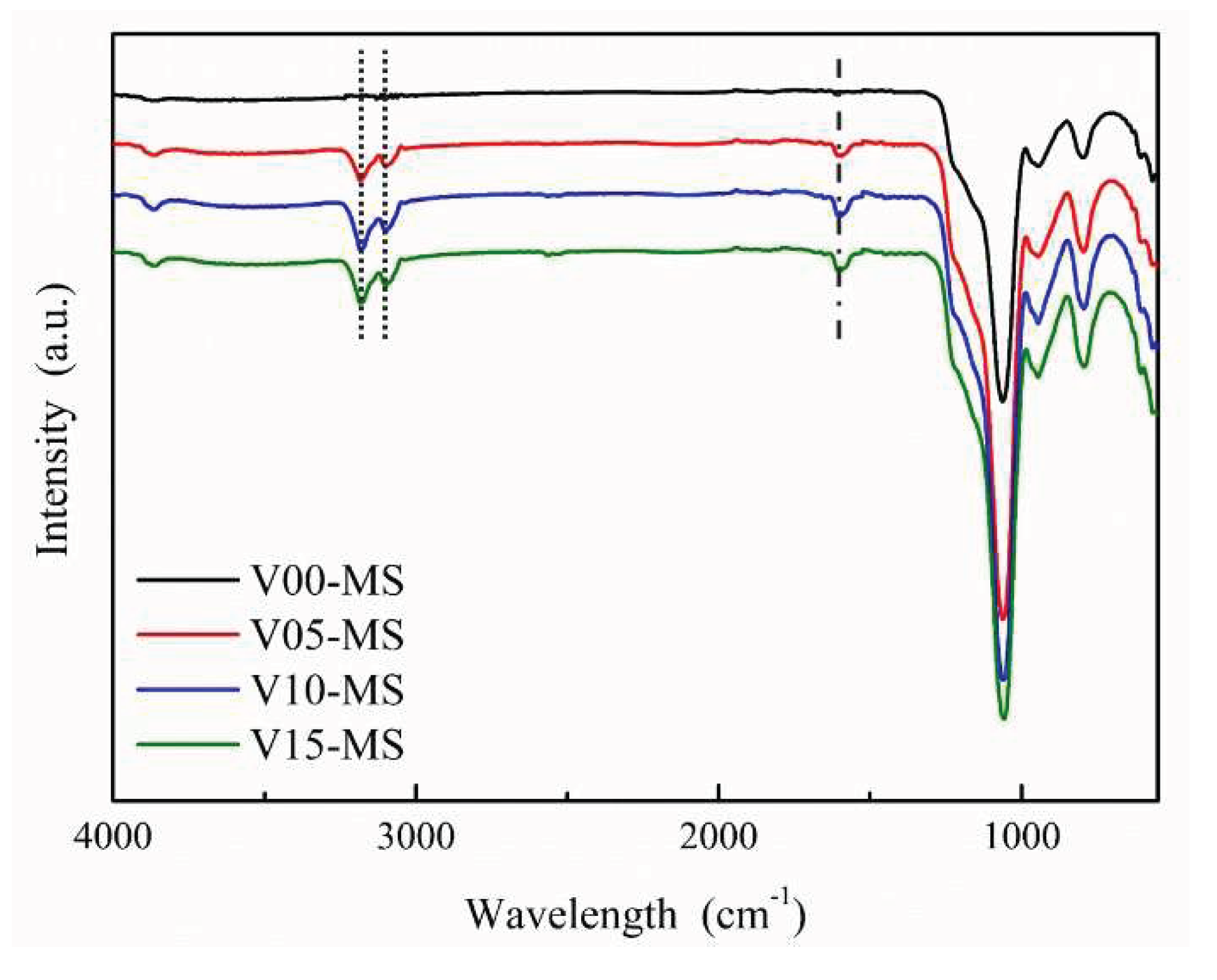
The FT-IR analysis results of mesoporous silica nanoparticles incorporating vinyl groups (V-MS) are shown in
Figure 4. Symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibrations of Si-O-Si were observed at 1057 cm
−1 and 1215 cm
−1, respectively [
27]. For the signal of vinyl group, a peak corresponding to the C=C double bond was detected at 1596 cm
−1 (dash line in
Figure 4), and C-H peaks associated with the C=C double bond were observed at 3097 cm
−1 and 3181 cm
−1 (dotted line in
Figure 4) [
30]. In V00-MS, there is no observable peak associated with vinyl groups. It can be noted that as the VTMS content increases, the peaks related to vinyl groups also increase. Nevertheless, when comparing V10-MS and V15-MS, the peaks associated with vinyl groups are nearly identical, suggesting that there may be a limit to the extent of vinyl group incorporation. These results indicate that vinyl groups have been successfully introduced into mesoporous silica.
Based on the analysis results of the MS samples with vinyl groups, we proceeded to manufacture pellets by incorporating them into recycled PE, followed by characterizing their properties. To determine the optimal MS nanoparticles with vinyl group content, we conducted a series of tests using V05-MS samples at various concentrations, and the results are presented in
Table 3.
The results show that with increasing V05-MS NPs content, both tensile and flexural strengths improve compared to virgin recycled polyethylene (rePE). However, a decrease in elongation, elastic modulus, and flexural modulus was observed. The most suitable composition was found to be 1 part of V05-MS NPs per 100 parts of recycled PE, demonstrating the most superior characteristics. This can be explained by the fact that as the content of mesoporous silica with introduced vinyl functional groups increases, there are challenges with dispersion during the production of recycled PE, leading to a decrease in performance. This is because that as the specific surface area of mesoporous silica increases, particularly due to its high surface energy, it induces aggregation. [
31] Therefore, while keeping the content of V-MS fixed at 1 part, the experiments were conducted with the varying content of the vinyl functional group, and the results are presented in
Table 4.
When various amounts of vinyl functional groups were introduced into mesoporous silica and mixed into recycled PE, V10-MS showed the best properties. As the vinyl content increases, there is a presumed enhancement in the physical properties of recycled PE, attributed to the escalating cross-linking density among vinyl functional groups. However, in the case of V15-MS, which introduced a similar amount of vinyl functional groups based on FT-IR measurements, the physical properties improved compared to the pure recycled PE sample. In contrast, when compared to V10-MS, the physical properties actually decreased. This is attributed to the fact that, even with a similar amount content of the vinyl functional groups, the specific surface area of silica mesoporous particles, due to their inherent porosity, is reduced, resulting in a slight reduction in the physical properties of recycled PE. The introduction of inorganic silica nanoparticles typically results in an increase in tensile strength due to the inherent performance of these inorganic particles, even in the absence of direct bonding with recycled PE. This often leads to a reduction in the flexibility or properties requiring flexibility, as is commonly observed. [
32] This can be observed in the performance indicators of recycled PE produced with VT00-MS, as evidenced in
Table 4. However, in the case of introducing silica with incorporated vinyl functional groups into recycled PE, it can be observed that performance indicators requiring flexibility also increase. This phenomenon is attributed to the silica nanoparticles becoming homogeneously cross-linked through chemical bonding rather than physical dispersion, resulting in an increase in cross-linking density and a more homogeneous composite structure. [
33] In conclusion, it can be stated that the introduction of mesoporous silica nanoparticles into recycled PE results in superior performance, with higher specific surface areas and higher vinyl group contents proving to be advantageous.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we synthesized mesoporous silica nanoparticles with incorporated vinyl functional groups using a hydrolysis process with sodium silicate solution and VTMS, without the need for additional polymerization or sintering processes. Previous research typically involved introducing vinyl functional groups after the synthesis of porous silica nanoparticles, but this approach often resulted in a significant decrease in specific surface area after vinyl group incorporation. However, with our synthesis method, we were able to produce mesoporous silica with high specific surface areas and incorporated vinyl functional groups through a straightforward process. This suggests the potential for practical application beyond the scope of this study.
We incorporated the synthesized mesoporous silica nanoparticles with vinyl functional groups into the production of recycled PE and compared its physical properties. The results showed that as the specific surface area and vinyl group content increased, all physical properties improved. Conventional introduction of silica nanoparticles into recycled PE generally led to an increase in tensile strength while reducing other performance indicators that require flexibility. However, with the incorporation of vinyl functional groups, it became possible to induce chemical bonding in the inorganic silica nanoparticles, leading to an increase in cross-linking density. As a result, not only tensile strength but also other flexibility-related performance indicators improved.
Through this study, our research team has confirmed the potential performance benefits of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with incorporated vinyl functional groups. We aim to further investigate its application in various recycled plastics and rubber materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-t.L., M.K. and J.Y.B.; methodology, J.-t.L. and M.K.; validation, J.-t.L., M.K. and J.Y.B.; formal analysis, J.-t.L. and M.K.; investigation, J.-t.L. and M.K.; resources, J.-t.L., M.K. and J.Y.B.; data curation, J.-t.L. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-t.L. and M.K.; writing—review and editing, J.-t.L., M.K. and J.Y.B.; visualization, J.-t.L. and M.K.; supervision, J.Y.B.; project administration, J.Y.B.; funding acquisition, J.Y.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (Synthesis of modified fluorosilicone-based liquid and solid type fluorosilicone elastomers and development of semiconductor application materials, 1415185209, 20011100, the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea)) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Ding, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, C. Current technologies for plastic waste treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiounn, T.; Smith, R.C. Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiao, X.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y. Progress and perspective for conversion of plastic wastes into valuable chemicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitlo, G.; Ali, I.; Maitlo, H.A.; Ali, S.; Unar, I.N.; Ahmad, M.B.; Bhutto, D.K.; Karmani, R.K.; Naich, S.R.; Sajjad, R.U.; Ali, S.; Afridi, M.N. Plastic Waste Recycling, Applications, and Future Prospects for a Sustainable Environment. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Anh, Y.; Kim, J. Optimal sorting and recycling of plastic waste as a renewable energy resource considering economic feasibility and environmental pollution. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Crespo, J.; Soto, M.; Amaya-Rivas, J.L.; Santos-Mendez, M. Carbon and water footprint for the recycling process of expanded polystyrene (EPS) post-consumer waste. Procedia CIRP. 2022, 105, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdy, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Artamendi, I.; Allen, B. Pyrolysis of polyolefin plastic waste and potential applications in asphalt road construction: A technical review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, C.; Shan, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. Recent developments on the zeolites catalyzed polyolefin plastics pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 238, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyananda, P.; Nguyen, D.; Huynh, V.; Hawkett, B.S. Decohesion of a polyolefin overlay from a substrate high density polyethylene layer by impact induced stress waves. Waste Manag. 2023, 171, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, B.; Yan, X.; Bai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, Y. Copyrolysis of Waste Cartons and Polyolefin Plastics under Microwave Heating and Characterization of the Products. ACS Omega. 2023, 8, 7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziadowiec, D.; Matykiewicz, D.; Szostak, M.; Andrzejewski, J. Overview of the Cast Polyolefin Film Extrusion Technology for Multi-Layer Packaging Applications. Mater. 2023, 16, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyuftin, A.A.; Pecorini, F.; Zanardi, E.; Kerry, J.P. Parameters Affecting the Water Vapour Permeability of Gelatin Films as Evaluated by the Infrared Detecting Method ASTM F1249. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.S. Development of antimicrobial polyolefin films containing lauroyl arginate and their use in the packaging of strawberries. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; John, A.; Cresnar, K.P.; Zemljic, L.F.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Active Agents Incorporated in Polymeric Substrates to Enhance Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties in Food Packaging Applications. Macromol. 2023, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, E.; Dicastillo, C.L.; Vidal, C.P.; Copello, G.; Reyes, C.; Gurada, A.; Galotto, M.J. Feasibility of Valorization of Post-Consumer Recycled Flexible Polypropylene by Adding Fumed Nanosilica for Its Potential Use in Food Packaging toward Sustainability. Polymers. 2023, 15, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.S.; Filippone, G. Effects of nanoparticles on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends – Challenges and opportunities. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, E.; Di Maio, L.; Scarfato, P.; Di Gregorio, F.; Incarnato, L. Reactive compatibilization and melt compounding with nanosilicates of post-consumer flexible plastic packagings. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 152, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stu¨rzel, M.; Kurek, A.; Anselm, M.; Halbach, T.; Mu¨lhaupt, R. Polyolefin Nanocomposites and Hybrid Catalysts. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2013, 258, 279. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.; Hanifpour, A.; Ghiassinejad, S.; van Ruymbeke, E. Polyolefins Vitrimers: Design Principles and Applications. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. Performance modifying techniques for recycled thermoplastics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, E.P.; García-Martínez, J.M. On Chemical Modified Polyolefins by Grafting of Polar Monomers: A Survey Based on Recent Patents Literature. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2010, 3, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaraj, D. Role of Compatibilization in Recycling Rubber Waste by Blending with Plastics. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2005, 78, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hees, T.; Zhong, F.; Stürzel, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Tailoring Hydrocarbon Polymers and All-Hydrocarbon Composites for Circular Economy. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 1800608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürzel, M.; Mihan, S.; Mülhaupt, R. From Multisite Polymerization Catalysis to Sustainable Materials and All-Polyolefin Composites. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandes, J.M.; Eren˜a, J.; Azkoiti, M.J.; Olazar, M.; Bilbao, J. Thermal recycling of polystyrene and polystyrene-butadiene dissolved in a light cycle oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2003, 70, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Adhikari, B. Dynamic vulcanization of recycled milk pouches (LDPE–LLDPE) and EPDM blends using dicumyl peroxide. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Lee, J.-t.; Bae, J.Y. Facile Mesoporous Hollow Silica Synthesis for Formaldehyde Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Jang, S.G. Characteristics of CO2 Capture by Tetraethylenepentamine Modified Mesoporous Silica Morphology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Jang, S.G. Preparation and Characterization of Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Hollow Silica for CO2 Capture. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, K.; Tian, X.; Hu, K.; Wnag, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Cui, P. Double Glass Transitions and Interfacial Immobilized Layer in in-Situ-Synthesized Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silica Nanocomposites. Macromolecules. 2010, 43, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna-Gutierrez, E.; Saiz-Arroyo, C.; Velasco, J.I.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A. Low Density Polyethylene/Silica Nanocomposite Foams. Relationship between Chemical Composition, Particle Dispersion, Cellular Structure and Physical Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Rupp, J.E.P.; Suter, U.W. Tensile properties of polyethylene-layered silicate nanocomposites. Polymer 2005, 46, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahankari, S.S.; Kar, K.K. Processing of styrene butadiene rubber–carbon black nanocomposites with gradation of crosslink density: Static and dynamic mechanical characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2008, 491, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).