1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance is now a critically alarming threat to the global community due to emergence of bacteria that can survive treatment with all sorts of antibiotics partly due to uncontrollable antibiotic usage [
1]. WHO has declared it as one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity with an estimation of 700,000 deaths annually worldwide and every country is potentially affected [
2]. In 2019, an estimated 1.27 million people died from antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, more death than HIV/AIDS or Malaria [
3]. If not properly addressed, the number is projected to grow to 10 million per year by 2050 [
4]. Along with this, infections with AMR leads to serious illnesses and prolonged hospital admissions, increases in healthcare costs, higher costs in second line drugs and treatment failures [
5]. According to different studies, it is projected that AMR could cost from
$300 billion to more than
$ 1 trillion annually by 2050 worldwide [
6] .
On 27 February 2017, the WHO published the list of global priority pathogens (GPP) – a catalog of several species of bacteria grouped under three priority tiers according to their antimicrobial resistance; critical, high and medium with
K. pneumoniae amongst the first priority/critical pathogens [
7]. Recently, the rapid rise of extended-spectrum β- lactamase (ESBL) producing
K. pneumoniae has significantly been detected in different parts of the world [
8] making treatment of the
K. pneumoniae infections with beta lactam antibiotics challenging. Moreover, carbapenems which are preferred agents for treatment of serious infections caused by ESBL-producing
K. pneumoniae are no longer effective to some strains [
9]. This has led to reintroduction of colistin for the treatment of carbapenems-resistant gram-negative bacteria like
K. pneumoniae. This antibiotic regarded as “last-line” drug for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria was introduced in clinical practice in 1950s [
10]. However, It was abandoned in most parts of the world in the early 1980s because of the reported high incidence of nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity [
11].
The exact mechanism to explain the antibacterial action of Colistin is still elusive. However the most plausible mechanism is that, colistin targets lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the gram-negative bacteria membrane [
12]. Colistin has a strong positive charge and a hydrophobic acyl chain that give them a high binding affinity to LPS molecules [
13]. The cationic polypeptide of Colistin interact electrostatically with anionic LPS molecules and competitively displace divalent cations (magnesium and calcium ions) from them causing disruption of the membrane [
14]. Magnesium and calcium ions act as stabilizers of the LPS molecules [
15]. Therefore, their disruption results in increased permeability of the cell envelope, leakage of the cell contents and subsequently, cell death [
16].
Regrettably, with its increased use or misuse of colistin in human and animal medicine, colistin resistance in gram negative bacteria in particular
K. pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and
Acinetobacter baumanii has been detected in many countries [
17], making infections caused by these bacteria untreatable by our current arsenal of antibiotics. Mechanism of colistin resistance in
K. pneumoniae largely relies on modification of Lipid A moiety of LPS through addition of phosphoethanolamine (PEtN) and 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose (L-Ara4N) [
18] that results in decrease in the negative charge on the bacterial surface. This reduces the electrostatic interaction between polycationic colistin and lipopolysaccharide resulting into subsequent reduction of lipopolysaccharide binding to colistin leading to resistance [
19]. Lipid A modification with L-Ara4N is mediated by genes located exclusively on the chromosome [
20]. However, lipid A modification with PEtN is mediated by either chromosomally mediated genes or plasmid-encoded genes [
21].
Despite of the menace of colistin resistance, there is paucity of molecular details with regard to colistin resistance especially in East Africa and Uganda is no exception. This scenario necessitated more comprehensive research particularly application of genomics that could shed light into the molecular details on K. pneumoniae. Therefore, this study aimed at establishing the genetic features determining the colistin resistance in multi-drug resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolates obtained from patients admitted at Mulago National Referral Hospital in Kampala, Uganda.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial strains
The study used 31 archived K. pneumoniae isolates from “colistin resistance among gram-negative rods study”. That parent study was a hospital based cross-sectional study conducted between 25/10/2021 to 25/10/2022 among the patients admitted in the ICU of Mulago National Referral Hospital. The isolates were obtained from rectal swabs of these patients hospitalized in the ICU for advanced respiratory support with diagnoses including meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, hypertension, diabetic ketoacidosis, acute kidney injury and nephrotic syndrome. The other indications for ICU admission included brain diseases such as brain tumor, post-tumor resection, post-craniotomy and hematoma evacuation and severe subarachnoid hemorrhage. Of this only 7/31 (22.58%) isolates were resistant to colistin and were chosen for whole genome sequencing. Before this, these isolates that had been phenotypically identified as colistin resistant K. pneumoniae were consecutively retrieved from the – 800C freezer, thawed and sub-cultured on MacConkey. Isolates were then re-identified as K. pneumoniae based on gram negative rod morphology, negative oxidase test, negative indole test, negative motility test, positive urease test, positive simmon’s citrate Agar test and triple sugar iron test. All 7 isolates grew upon subculturing and they were all re-confirmed as K. pneumoniae on all the seven criteria set for this study.
2.2. Genomic DNA isolation
A total of 7 colistin resistant
K. pneumoniae isolates were inoculated on Mueller Hinton Agar plates and incubated for 24 h at 37
oC. The bacterial DNA was extracted using a CTAB protocol as previously described by Willner et al, 2012 [
22]. For analysis of extracted DNA, gel electrophoresis was carried out. DNA purity was determined on the Nanodrop 2000 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in which the purity ratio (A260:A280) was determined by determining the absorbance value at 280 nm. DNA was quantified on the Qubit dsDNA fluorometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Whole genome Sequencing (WGS)
WGS of the isolates was carried out at Humanizing Genomics, Macrogen Inc, in Seoul, Republic of Korea. A quality control experiment was conducted to evaluate the quantity and condition of DNA before library preparation and sequencing. Quantity of DNA was done by QuantiFluor®dsDNA system (promega, cat.#E2671) and verification of the genomic DNA integrity was done using an agilent technologies 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Part # G2939BA). For preparation of ready-to-sequence libraries of bacterial genomes, Nextera DNA XT library preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) was used following manufacturers recommended protocol followed by sequencing using Illumina Novaseq 6000 platform at Humanizing Genomics, Macrogen Inc, in Seoul in South Korea. Illumina sequencing generated paired-end short reads with approx. 50-fold coverage and an average length of 150bp.
2.4. Raw data quality assessment, genome assembly and Annotation
FastQC v0.12.1 was used for quality check for Sequenced raw data and Trimmomatic v0.39 was used for trimming raw reads to remove adaptors and low-quality sequences. The raw reads were de novo assembled using SPAdes v.3.15.5 and assembly quality was assessed using BUSCO v5.4.7. Chromosomes were generated by mapping the de novo assembly-derived contigs to relevant reference genomes using the MeDuSa pipeline. Plasmids were separately de novo-assembled using plasmid SPAdes v3.15.5 and then scaffolded with MeDuSa against closest references recovered from NCBI BLASTn and/or plasmid database (PLSDB). The assembled genomes were annotated using the Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (PGAP)
2.5. Gene detection, Multi-locus Sequence typing (MLST) and phylogenetic analysis
Resistance genes determination was done using online databases including Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD), ResFinder and PlasmidFinder. To study the molecular chromosomal mechanisms of colistin resistance, chromosomal loci alterations or disruptions implicated in colistin resistance were analyzed
in silico by running the BLAST program (BLASTn) by aligning the assembled contigs against wild type gene sequence of
Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae HS11286 [
23] A change in protein level was explored with the NCBI BLASTx tool. To establish individual gene polymorphism for Colistin resistance, the phenotypic effect of amino acid substitutions on protein function were predicted using polymorphism phenotyping v2 web tool (PolyPhen-2) as described G. Yadav et al and Azam et al [
24,
25]. To determine the phylogenetic relatedness a concatenated marker gene maximum-likelihood tree was constructed using a number of
K. pneumoniae reference genomes chosen based on BLAST similarity results, clonal complexes and sequence types. Pairwise alignment and visualization of selected genomes with the respective reference strains was achieved through the MAFFT [
26] using default parameters. The sequences were first processed with PhyloSift, the phylogenetic tree was then constructed using RAXML [
27], visualized and edited with Dendroscope [
28]. Genome-based phylogeny were first deduced from the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center (PATRIC) database [
29]. Strain identification and possible closest relatives were further done using the Type Strain Genome Server (TYGS), which integrates several algorithms including genome to genome distance [
30]. Pathogenwatch platform integrating Kleborate v2.0 and Kaptive 2.0 was employed for Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST). Briefly to confirm the taxonomic placement and predict the possible closest strains, each assembly was uploaded and analyzed with the Microbial Genomes Atlas (MiGA) using TypeMat algorithm.
2.6. Data availability
Whole genome sequence data were submitted to the National center for Biotechnology information (NCBI). They are archived under accession project number PRJNA985059
3. Results
3.1. General description of sequenced Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
Only 5/7 DNA samples from colistin resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates passed quality control and were sequenced. The isolates were multidrug resistant (MDR) showing resistance to second, third and fourth generation cephalosporins (Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime, Cefepime), augmentin, piperacillin/tazobactam, imipenem, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, amikacin, gentamicin, tigecycline, chloramphenicol, fosfomycin, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim and colistin.
3.2. Genomic features of K. pneumoniae strains, Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and Phylogenetic analysis
Whole genomes were generated from all isolates via illumina short-read sequencing (Illumina Novaseq 6000). The genome size and the number of genes in each strain varied. Mean number of genes across all strains was 5962.4 genes and the genome sizes ranged from 5.2 Mb to 5.4 Mb with GC content averaging 57.48%, typical of
K. pneumoniae genomes [
23]. The average N50 was 303,298 base pairs. The isolates had 1-4 plasmid replicons, averaging 3 per isolate.
In silico multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) results from Klebolate analysis revealed a number of sequence types (STs) of
K. pneumoniae including ST1119, ST231, ST17, ST540-1LV and ST39. These results indicated that
K. pneumoniae were largely oligoclonal. General features of each genome were investigated and are summarized in
Table 1.
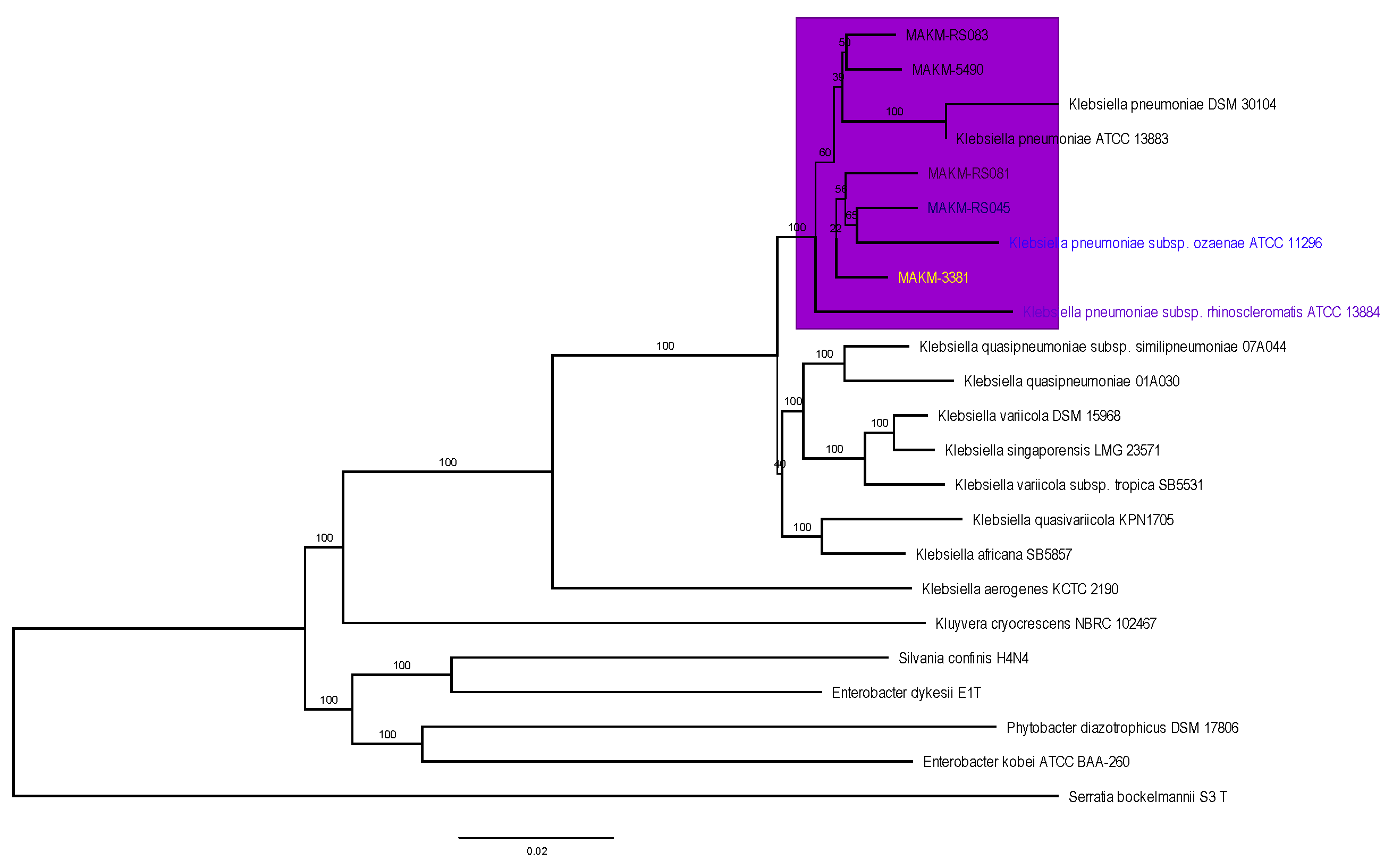
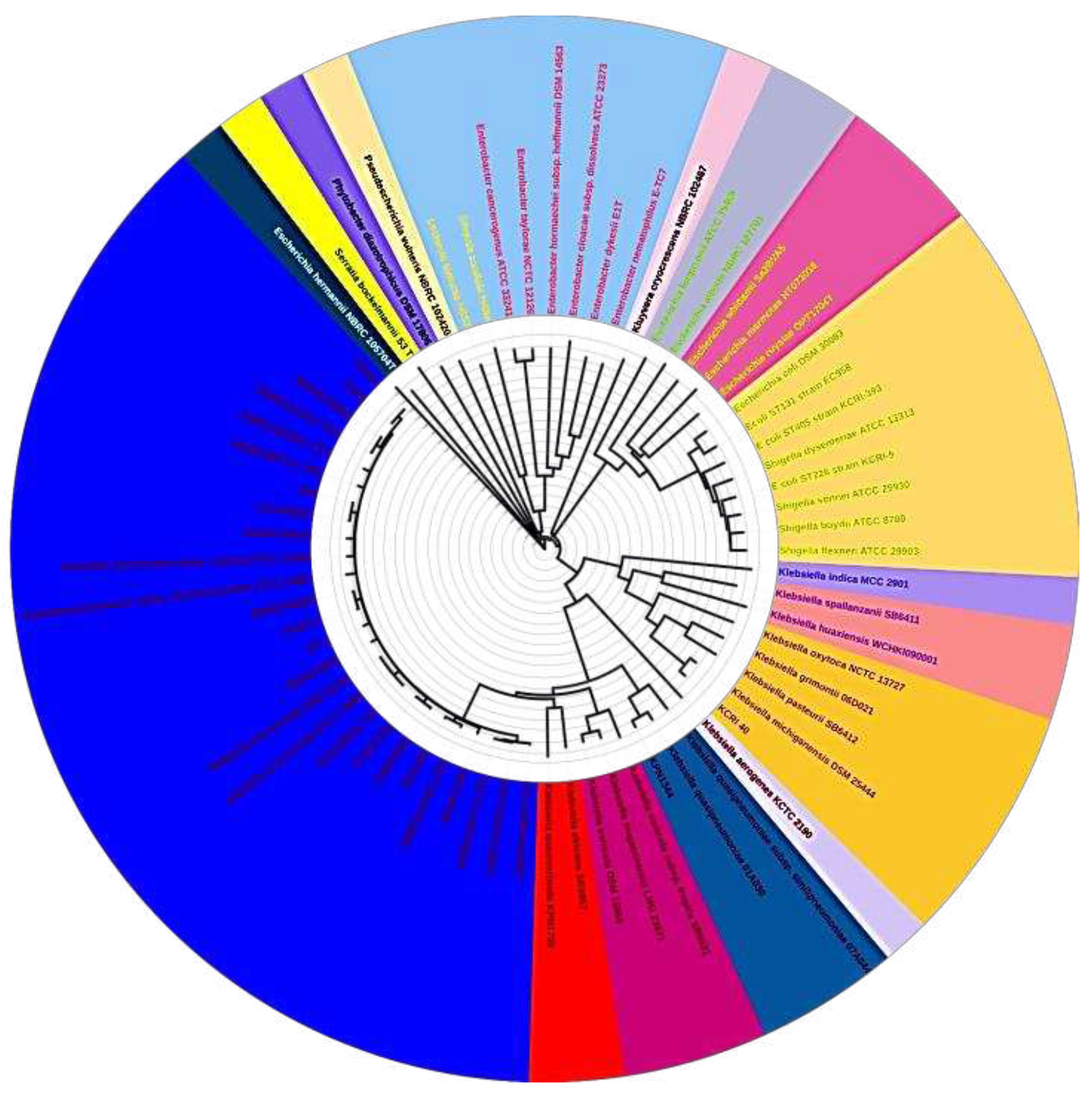
The evolutionary relationship of the five sequenced
K.pneumoniae strains was inferred using the maximum likelihood proteome and core genome phylogenomic analysis and put in context with other completely sequenced strains of
K. pneumoniae as shown in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2
3.3. Antimicrobial resistance determinants
Whole genome sequence (WGS) analysis of antimicrobial resistance genes via the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) revealed the presence of multiple resistance genes encoding for resistance within and between antibiotic classes. (
Table 2) The isolates carried β-lactamase genes, including extended-spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) and carbapenemase genes (
blaSHV-1,
blaSHV-11,
blaTEM-1,
blaCTX-M-15,
blaOXA-1, CRP and H-NS), Glycopeptide resistance genes (VanG), aminoglycoside resistance genes (baeR, aadA5, aadA2), Peptide resistance genes that include colistin resistance genes (ArnT, OmpA, eptB), Macrolide (Mrx, mphA), Fluoroquinolone resistance genes (adeF, emrR, rsmA, QnrS1). The isolates also had resistance genes for other antibiotic classes including msbA, tet (A) and tet (D), oqxA, sul2 for nitroimidazole, tetracycline, nitrofurantoin and sulfamexothazole respectively. Resistance to other antibiotic classes was conferred by: trimethoprim -dfrA17, dfrA12, fosfomycins-fosA6, Ecol_UhpT_FOF and even disinfectants and antiseptics – leuO, qacEdelta1. Several genes for multi-drug efflux were detected; they included Ecol_MarR_MULT, Hinf_PBP3_BLA, Kpne_KpnE, Kpne_KpnG, Kpne_KpnH, Kpne_KpnF, Kpne_ramR, Kpne_OmpK37, marA Kpne_KpnE, LptD and marA.
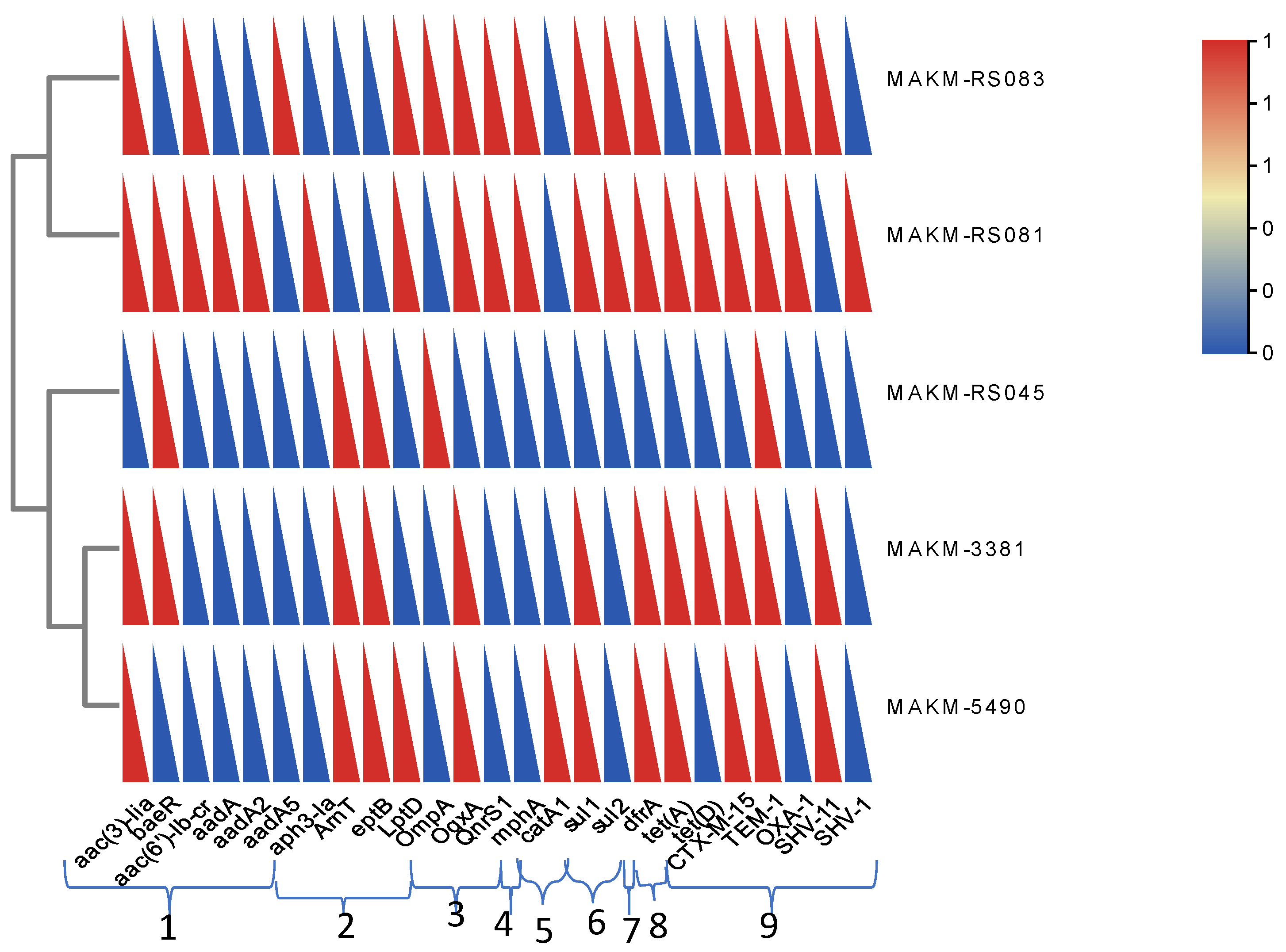
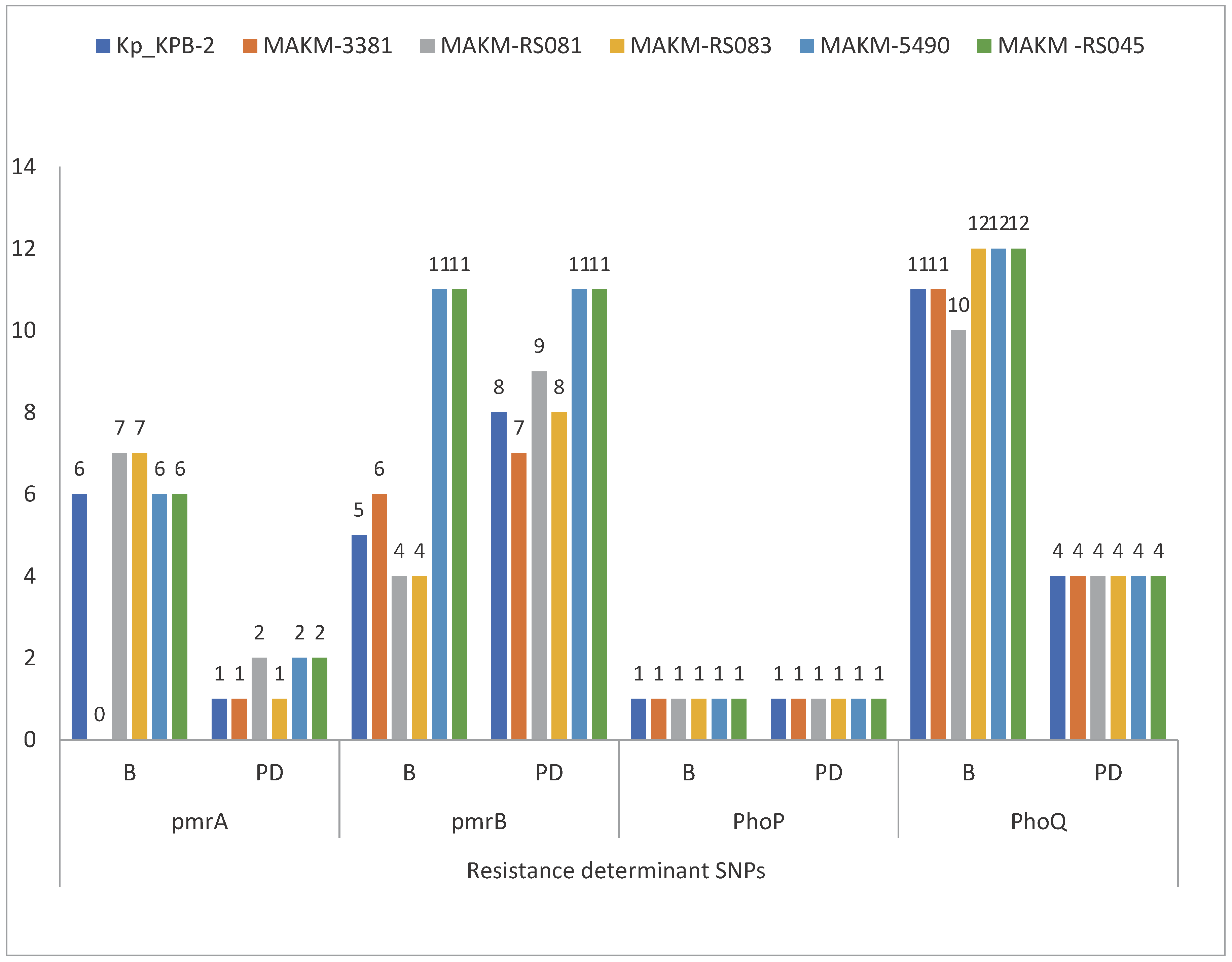
Some common resistant genes detected in each isolate are shown in
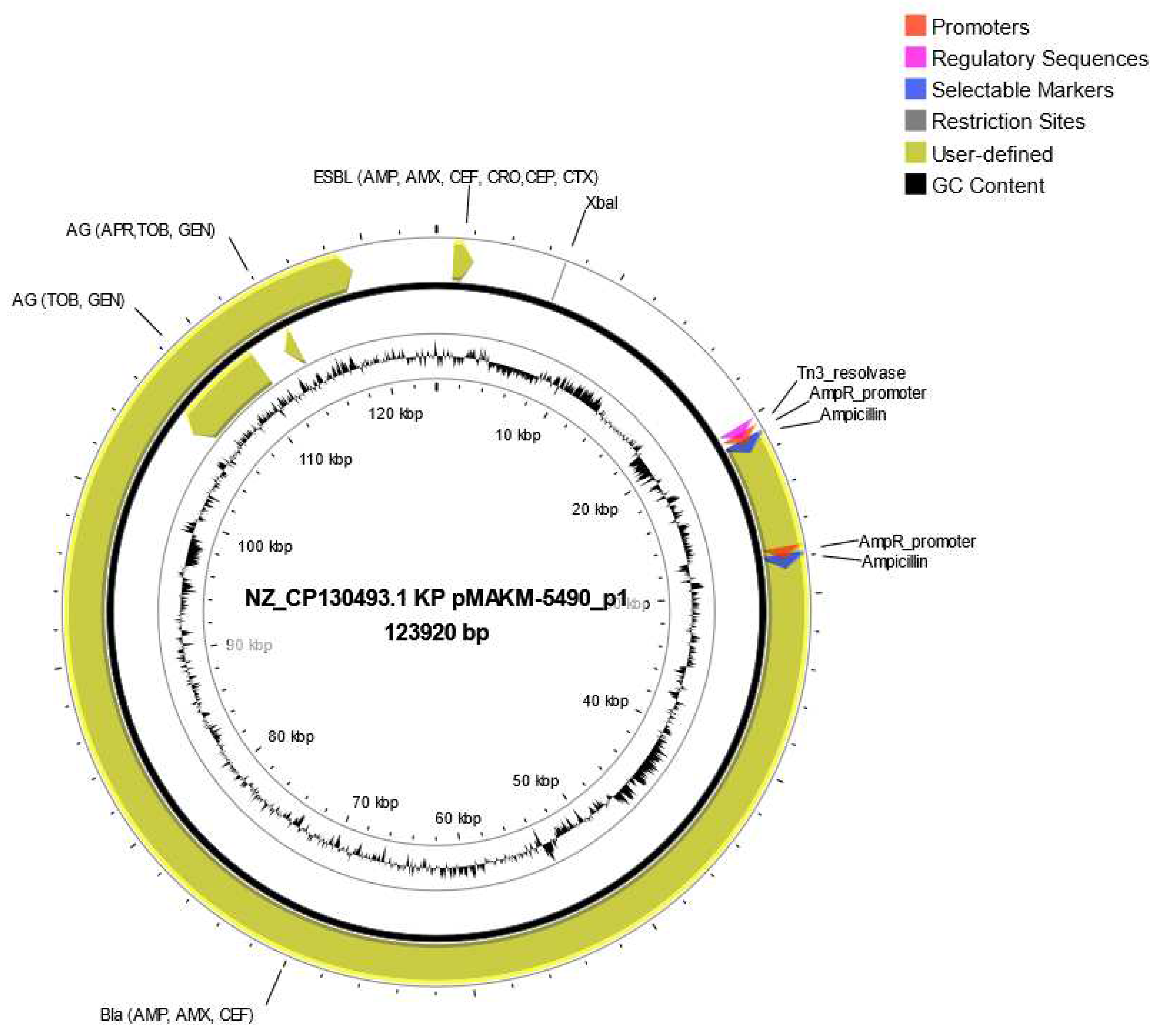
Figure 3. Besides, ResFinder results showed all strains harbored plasmid carrying several resistant genes, for instance the strain MAKM 5490 harbored a plasmid carrying several ESBL genes and aminoglycoside resistance genes, all of which were encoded by the plasmid NZ CP130493.1Kp pMAKM-5490_p1shown in
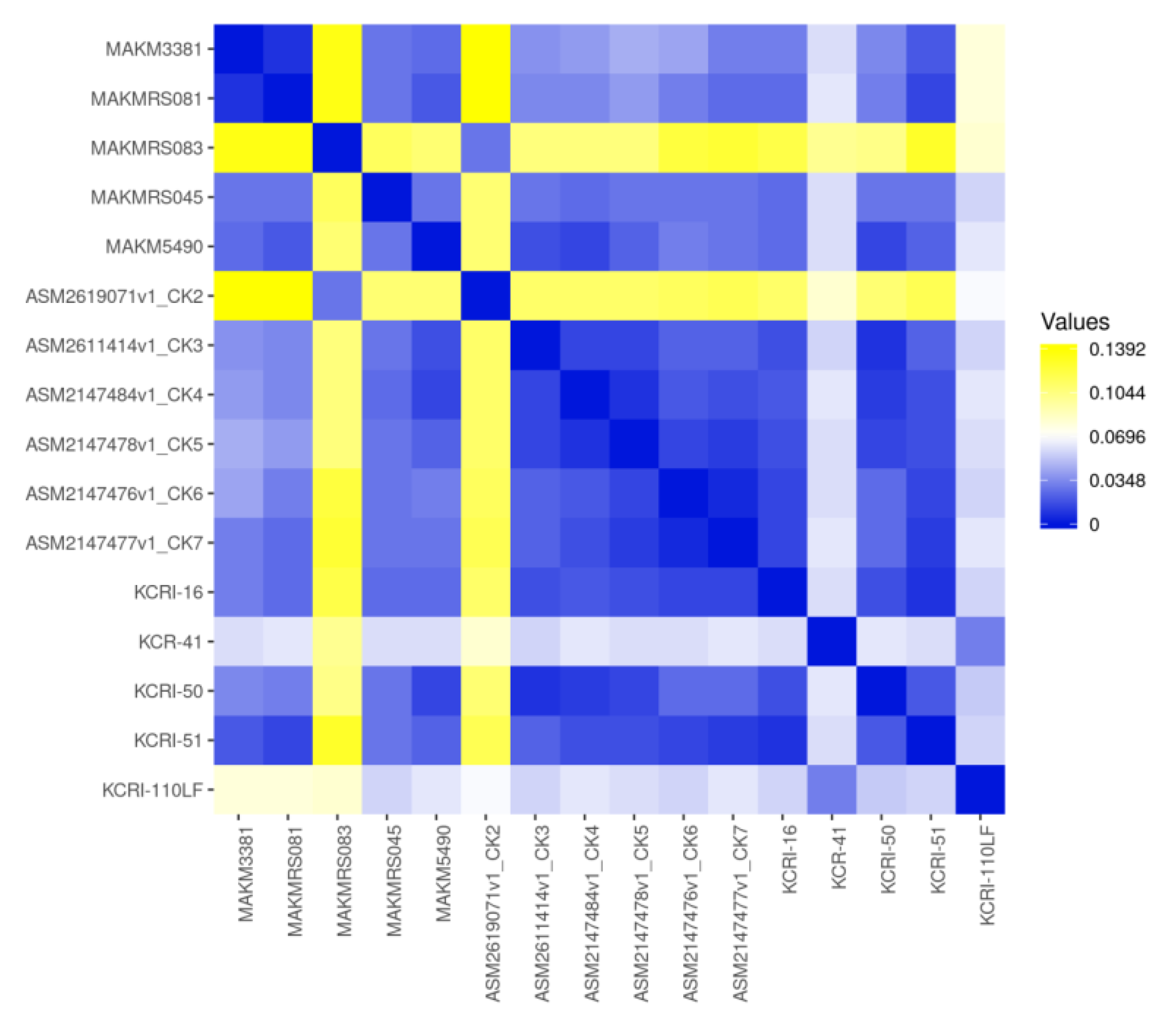
Figure 4. Overall the isolates showed many resistance genes when compared with other strains as indicated in the heatmap (
Figure 5)
3.4. Colistin resistance determinants
Concerning genetic determinants related to colistin resistance, the BLAST results, CARD and ResFinder analysis revealed several genetic modifications in chromosomal loci. The sequence analysis of the commonly known genes involved in colistin resistance revealed several polymorphisms in nucleotide sequences of
pmrA/pmrB and
phoP/phoQ operon likely affecting the function of these proteins. There were non-synonymous deleterious mutations in
pmrA (H219N, G53S),
pmrB (N8T, G250C, A252G, D150V, L332M, L237R, H267P, R315P, Q331H, R256G, T157P),
phoP (T151A) and
phoQ (F163L, L30Q
, H234Y, A351D) (
Figure 6)
Additionally there were non-synonymous deleterious mutations in
mgrB (C28G). The insertion sequences IS1 and IS5 are highly implicated in colistin resistance, which occurs via modification or the inactivation of
mgrB gene. The later plays role in the regulation the
phoP/Q gene [
31]. Therefore, insertion-mediated inactivation of the mgrB gene upregulates the arnBCADTEF operon, a glycosyl transferase, which adds 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose to lipids A, and PhoP/Q two component signaling pathway, resulting in resistance to colistin. In this work, insertion transposase genes for both of the insertion sequences were identified in all the five isolates and are located in the chromosomal DNA at different genomic positions (
Table 3).
4. Discussion
Multidrug resistance has become a major health threat of our time imperiling the improvement in medical health care in consideration of the increased morbidity, length of hospitalization and poor clinical outcome. With the emergence of colistin resistant K. pneumoniae strains, the untreatable infections are obvious. It is therefore crucial to curtail this problem through rapid detection and genetic characterization of clinical relevant bacteria like K. pneumoniae to curb their spread. Whole genome sequencing has emerged as a transformative tool in the field of clinical microbiology and is now increasingly employed in clinical settings and research to investigate antimicrobial resistance and virulence of bacteria for active surveillance.
Our study revealed several genetic determinants of colistin resistance which included pmrA, pmrB, phoP, phoQ and mgrB gene mutations. There were significant non-synonymous deleterious mutations in these genes in all isolates. Chromosomal mutation in the regulatory genes PhoP/PhoQ, pmrA/pmrB and mgr B are important mechanisms leading to resistance (chromosomal mediated resistance). The mutation results in modification in the lipid A of the LPS on the bacterial surface, reducing the binding of Colistin. Other studies’ findings are in agreement with these results and implicate the high prevalence of mutation in these genes with colistin resistance. [
32]. Notably, numerous amino acid substitutions were observed in pmrB, the finding are supported by previous studies which also observed this trend. [
33]. Our study did not identify plasmid-borne mcr genes. In this study, we also identified mutations in arnT and eptB genes. Mutations in arnT and eptB mediate colistin resistance via antibiotic target alteration [
34]. It is therefore likely that these mutations could also explain colistin resistance in the isolates.
One particularly crucial observation is that Colistin resistant
K. pneumoniae harbored high multidrug resistance genes. The high MDR genotypes in this study is possibly attributed to chromosomal mutations and plasmid carrying genes conferring resistance to β-lactams, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, aminoglycosides, among others. One of the most prevalent resistant genes was the β-lactamase genes in particular ESBL genes,
blaTEM,
blaCTX-M, and
blaSHV gene families. These findings depict a closely similar pattern from a study conducted by Liu et al, [
35]. The high prevalence of
blaCTX-M-15 and
blaTEM-1 coincide with the observation from clinical
K. pneumoniae sample isolates in a county clinical emergence hospital Romania [
36] which revealed worrying increase of these ESBL genes as well as recent worldwide reports on the distribution of these ESBL genes [
37]
With regard to fluoroquinolone resistance, a specific fluoroquinolone resistant gene QnrS1 which protect antibiotic target was detected in two isolates. The detection of several efflux pump genes such as adeF, CRP, emrR,_ramR, marA, and rsmA in the isolates offers the significant reason for their fluoroquinolone resistance. On the same note, the detected mutation in Kpne_ramR which is a repressor that regulate Ram A expression may cause upregulation of AcrAB consequently leading to alteration of antibiotic target hence resistance.
Similar to other studies macrolide resistant genes mphA, Mrx and other multi drug-efflux genes were identified. Inspite of macrolide not being used in treatment of gram–negative infections, their presence in these K. pneumoniae isolates or any other gram-negative bacteria may serve as the reservoir of resistance genes that can be transferred to gram-positive bacteria thus enhancing resistance.
Consistent with the previous studies, fosfomycin resistance gene such as plasmid–encoded enzyme FosA6 was identified [
38]. Another resistance gene Ecol_UhpT_FOF though rarely reported in many studies has been detected in one isolate.
Regarding sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim; sul2 and sul1 genes were detected and confer resistance to sulfamethoxazole through antibiotic target protection/alteration [
39] whereas in trimethophoprim dfrA17 and dfrA12 genes were detected, each in one isolate.
Like in other previous studies, tet (A) and tet(D) were identified as the tetracycline resistance genes [
40]. Other multi-efflux pump genes like AdeF, H-NS, Kpne_ramR, marA, and OqxA were also detected. Among chloramphenicol resistance, an antibiotic efflux gene rsmA was prevalent. Most importantly, the commonly detected gene catI that mediate resistance through antibiotic inactivation was identified in only one isolate..
Aminoglycoside are vital in treatment of K.pneumoniae infections. In our study aac(3)-IIa was detected in four isolates and different multidrug efflux genes including BaeR, Kpne_KpnE, Kpne_KpnG, Kpne_KpnH, Kpne_KpnF and genes were found in high frequency. Also aadA5 and aadA2 genes that mediate resistance to aminoglycoside through antibiotic inactivation were each detected in one isolate.
5. Conclusion
The study indicates many Chromosomal mutation in the regulatory genes involved in Colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae isolates. This hints a grim situation which warrants attention. Besides, the findings revealed a relatively high proportion of antimicrobial resistant genes. Therefore vigilance surveillance with the use of high throughput technology is necessary to limit further spread of colistin among K. pneumoniae strains to minimize the potential risk of pan-drug resistance. Finally our study had some limitations; colistin resistance databases are still less exhaustive. Due to resource limitations, we sequenced only five isolates, which although few, still give significant snapshot of genomic determinants of colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, MAKM; Formal analysis, MAKM, RSM Investigation, MAKM, RSM, SS, EK Methodology, MAKM, RSM, SS Visualization, MAKM; Writing – original draft, MAKM, EK; Writing – review & editing, MAKM, RSM, SM, BA; Supervision, SM, BA, EK.; Project Administration, EK. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Ethical Approval
Ethics approval was obtained from the institutional ethics Committee, the Makerere University School of Biomedical Sciences-Research and Ethics Committee (SBS-REC).
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prestinaci F, Pezzotti P, Pantosti A. Antimicrobial resistance: a global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathogens and Global Health 2015. [CrossRef]
- Jansen KU, Knirsch C, Anderson AS. The role of vaccines in preventing bacterial antimicrobial resistance. Nat Med 2018;24:10–9. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Fan H, Zi H, Hu H, Li B, Huang J, et al. Global and Regional Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections in 2019. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022;11:2817. [CrossRef]
- Thompson T. The staggering death toll of drug-resistant bacteria. Nature 2022. [CrossRef]
- Majumder MAA, Rahman S, Cohall D, Bharatha A, Singh K, Haque M, et al. Antimicrobial Stewardship: Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance and Protecting Global Public Health. Infection and Drug Resistance 2020;13:4713–38. [CrossRef]
- Dadgostar P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infection and Drug Resistance 2019;12:3903. [CrossRef]
- Savoldi A, Carrara E, Gladstone BP, Azzini AM, Göpel S, Tacconelli E. Gross national income and antibiotic resistance in invasive isolates: analysis of the top-ranked antibiotic-resistant bacteria on the 2017 WHO priority list. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2019;74:3619–25. [CrossRef]
- H E, I U-H, S M, A Z, M MJ. Detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae: comparison of phenotypic characterization methods. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 2013;29. [CrossRef]
- Patel G, Huprikar S, Factor SH, Jenkins SG, Calfee DP. Outcomes of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection and the Impact of Antimicrobial and Adjunctive Therapies. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2008;29:1099–106. [CrossRef]
- Falagas ME, Kasiakou SK, Saravolatz LD. Colistin: The Revival of Polymyxins for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;40:1333–41. [CrossRef]
- Tamma PD, Lee CK. Use of Colistin in Children. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2009;28:534. [CrossRef]
- Velkov T, Roberts KD, Nation RL, Thompson PE, Li J. Pharmacology of polymyxins: new insights into an ‘old’ class of antibiotics. Future Microbiology 2013;8:711–24. [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi EA, Ferguson EL, Thomas DW. Colistin past and future: A bibliographic analysis. Journal of Critical Care 2013;28:219.e13-219.e19. [CrossRef]
- Otilonium bromide boosts antimicrobial activities of colistin against Gram-negative pathogens and their persisters | Communications Biology n.d. https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-022-03561-z (accessed September 8, 2023).
- Conly JM, Johnston BL. Colistin: The phoenix Arises. Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology NaN/NaN/NaN;17:267–9. [CrossRef]
- Hamel M, Rolain J-M, Baron SA. The History of Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Progress and Challenges. Microorganisms 2021;9:442. [CrossRef]
- Granata G, Petrosillo N. Resistance to Colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae: A 4.0 Strain? Infectious Disease Reports 2017;9:7104. [CrossRef]
- Haeili M, Javani A, Moradi J, Jafari Z, Feizabadi MM, Babaei E. MgrB Alterations Mediate Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Iran. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017;8. [CrossRef]
- Wright MS, Suzuki Y, Jones MB, Marshall SH, Rudin SD, van Duin D, et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Colistin-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae Reveal Multiple Pathways of Resistance. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2014;59:536–43. [CrossRef]
- Berglund B. Acquired Resistance to Colistin via Chromosomal And Plasmid-Mediated Mechanisms in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infectious Microbes & Diseases 2019;1:10. [CrossRef]
- Nang SC, Han M-L, Yu HH, Wang J, Torres VVL, Dai C, et al. Polymyxin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae: multifaceted mechanisms utilized in the presence and absence of the plasmid-encoded phosphoethanolamine transferase gene mcr-1. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2019;74:3190–8. [CrossRef]
- Willner D, Daly J, Whiley D, Grimwood K, Wainwright CE, Hugenholtz P. Comparison of DNA Extraction Methods for Microbial Community Profiling with an Application to Pediatric Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples. PLOS ONE 2012;7:e34605. [CrossRef]
- Liu P, Li P, Jiang X, Bi D, Xie Y, Tai C, et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae HS11286, a Multidrug-Resistant Strain Isolated from Human Sputum. Journal of Bacteriology 2012;194:1841–2. [CrossRef]
- Yadav G, Azam M, Upmanyu K, Jain M, Gaind R, Singh R. Multiple variants of phoP/Q and pmrAB TCRS conferring colistin resistance in XDR/MDR clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae in India. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020;101:15. [CrossRef]
- Azam M, Gaind R, Yadav G, Sharma A, Upmanyu K, Jain M, et al. Colistin Resistance Among Multiple Sequence Types of Klebsiella pneumoniae Is Associated With Diverse Resistance Mechanisms: A Report From India. Front Microbiol 2021;12:609840. [CrossRef]
- Katoh K, Rozewicki J, Yamada KD. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2019;20:1160–6. [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A Rapid Bootstrap Algorithm for the RAxML Web Servers. Systematic Biology 2008;57:758–71. [CrossRef]
- Huson DH, Richter DC, Rausch C, Dezulian T, Franz M, Rupp R. Dendroscope: An interactive viewer for large phylogenetic trees. BMC Bioinformatics 2007;8:460. [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos DA, Assaf R, Aziz RK, Brettin T, Bun C, Conrad N, et al. PATRIC as a unique resource for studying antimicrobial resistance. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2019;20:1094–102. [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nature Communications 2019;10:2182. [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli Antonio, D’Andrea Marco Maria, Giani Tommaso, Di Pilato Vincenzo, Arena Fabio, Ambretti Simone, et al. In Vivo Emergence of Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Producing KPC-Type Carbapenemases Mediated by Insertional Inactivation of the PhoQ/PhoP mgrB Regulator. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2013;57:5521–6. [CrossRef]
- Yusof NY, Norazzman NII, Hakim SNWA, Azlan MM, Anthony AA, Mustafa FH, et al. Prevalence of Mutated Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 2022;7:414. [CrossRef]
- Jayol A, Poirel L, Brink A, Villegas M-V, Yilmaz M, Nordmann P. Resistance to Colistin Associated with a Single Amino Acid Change in Protein PmrB among Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates of Worldwide Origin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2014;58:4762–6. [CrossRef]
- Mathur P, Veeraraghavan B, Devanga Ragupathi NK, Inbanathan FY, Khurana S, Bhardwaj N, et al. Multiple mutations in lipid-A modification pathway & novel fosA variants in colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Science OA 2018;4:FSO319. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Lin Y, Wang Z, Hu N, Liu Q, Zhou W, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:673503. [CrossRef]
- Ghenea AE, Zlatian OM, Cristea OM, Ungureanu A, Mititelu RR, Balasoiu AT, et al. TEM,CTX-M,SHV Genes in ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Samples in a County Clinical Emergency Hospital Romania-Predominance of CTX-M-15. Antibiotics 2022;11:503. [CrossRef]
- Zhou K, Lokate M, Deurenberg RH, Arends J, Lo-Ten Foe J, Grundmann H, et al. Characterization of a CTX-M-15 Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Outbreak Strain Assigned to a Novel Sequence Type (1427). Frontiers in Microbiology 2015;6. [CrossRef]
- Guo Q, Tomich AD, McElheny CL, Cooper VS, Stoesser N, Wang M, et al. Glutathione-S-transferase FosA6 of Klebsiella pneumoniae origin conferring fosfomycin resistance in ESBL-producing Escherichia coli. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2016;71:2460–5. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Bi W, Dong G, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Dong T, et al. The new perspective of old antibiotic: In vitro antibacterial activity of TMP-SMZ against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection 2020;53:757–65. [CrossRef]
- Sheykhsaran E, Bannazadeh Baghi H, Soroush Barhaghi MH, Alizadeh N, Memar MY, Etemadi S, et al. The rate of resistance to tetracyclines and distribution of tetA, tetB, tetC, tetD, tetE, tetG, tetJ and tetY genes in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from Azerbaijan, Iran during 2017. Physiology and Pharmacology 2018;22:205–12.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).