Submitted:
22 October 2023
Posted:
23 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
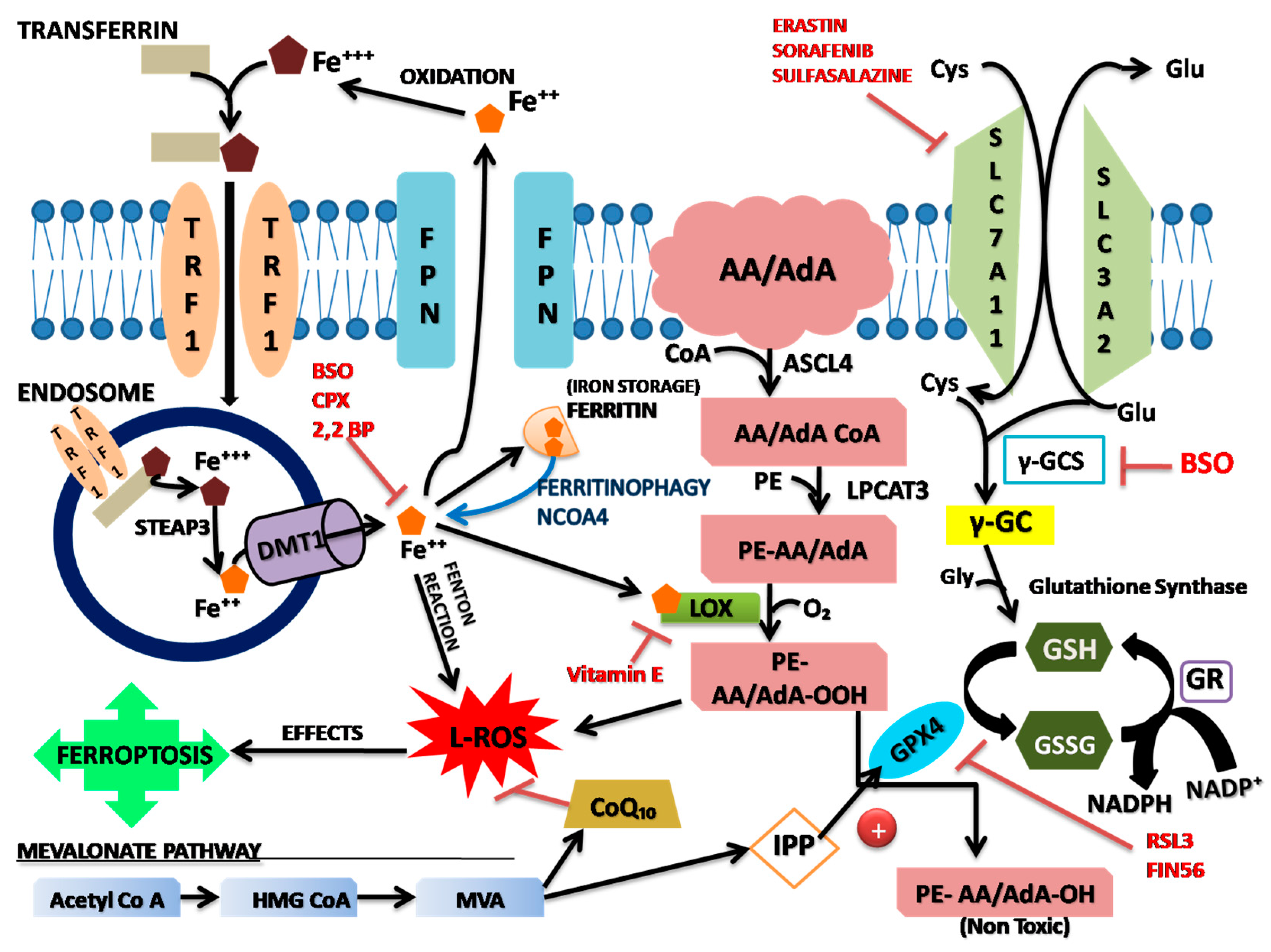
Stress mechanism of ferroptosis
Role of system Xc-
Iron metabolism pathway
Lipid metabolism pathway and accumulation of lipid peroxides
Non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation pathway
Lipid peroxidation pathway
GPX4 pathway
Mevalonate (MVA) pathway
Other pathways
References
- Abeysinghe, R.D.; Roberts, P.J.; Cooper, C.E.; MacLean, K.H.; Hider, R.C.; Porter, J.B. The environment of the lipoxygenase iron binding site explored with novel hydroxypyridinone iron chelators. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 7965–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.C.; Schmidt, P.J. Iron homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, J.P.F.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; Basavarajappa, D. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nature cell biology 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barradas, M.A.; Jeremy, J.Y.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Hoflbrand, A.V.; Dandona, P. Iron chelators inhibit human platelet aggregation, thromboxane A2 synthesis and lipoxygenase activity. FEBS letters 1989, 245, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.A.; Cookson, B.T. Salmonella induces macrophage death by caspase-1-dependent necrosis. Molecular microbiology 2000, 38, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.Y.; Dixon, S.J. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2016, 73, 2195–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sarkar, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Toxic metals and autophagy. Chemical research in toxicology 2014, 27, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Quan, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Liu, B. The latest view on the mechanism of ferroptosis and its research progress in spinal cord injury. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, Y. What is responsible for the initiating chemistry of iron-mediated lipid peroxidation: an update. Chemical Reviews 2007, 107, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.C.; Ang, E.T.; Tai, Y.K.; Tsang, F.; Lo, S.Q.; Ong, E.; Ong, W.Y.; Shen, H.M.; Lim, K.L.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Enhanced autophagy from chronic toxicity of iron and mutant A53T α-synuclein: implications for neuronal cell death in Parkinson disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2011, 286, 33380–33389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo-López, M.E.; Macêdo, G.L.; Pereira, S.I.; Arrifano, G.P.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L.; do Nascimento, J.L.M.; Herculano, A.M. Mercury and human genotoxicity: critical considerations and possible molecular mechanisms. Pharmacological research 2009, 60, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brabander, M.; Van Belle, H.; Aerts, F.; Van De Veire, R.; Geuens, G. Protective effect of levamisole and its sulfhydryl metabolite OMPI against cell death induced by glutathione depletion. International journal of immunopharmacology 1979, 1, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nature chemical biology 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; Morrison III, B. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Prokisch, H. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nature chemical biology 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagle, H.; Piez, K.A.; Oyama, V.I. The biosynthesis of cystine in human cell cultures. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1961, 236, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagle, H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science 1955, 122, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science 1959, 130, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.W.; Qian, M. Molecular bases of cellular iron toxicity. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2002, 32, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, Y.; Steller, H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 2011, 147, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Monian, P.; Quadri, N.; Ramasamy, R.; Jiang, X. Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Molecular cell 2015, 59, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.W. Biologic and pharmacologic regulation of mammalian glutathione synthesis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1999, 27, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, J.M. The role of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals in phospholipid peroxidation catalysed by iron salts. FEBS letters 1982, 150, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Liang, B.; Huang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wu, Z.; He, W.; Shi, M. Metabolic networks in ferroptosis. Oncology letters 2018, 15, 5405–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Berghe, T.V. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, B.; Wiernicki, B.; Ingold, I.; Qu, F.; Van Herck, S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayır, H.; Abhari, B.A.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Choi, S.M.; Meul, E. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. The Journal of clinical investigation 2018, 128, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.; Nakagawa, Y. Biological significance of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx, GPx4) in mammalian cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2003, 34, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Doll, S.; St Croix, C.; Dar, H.H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; Kapralov, A.A. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nature chemical biology 2017, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.U.; Park, S.U. Molecular cloning and characterization of mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway genes and triterpene accumulation in Panax ginseng. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry 2014, 57, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Banthiya, S.; Van Leyen, K. Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2015, 1851, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Zeng, G. Investigation, pollution mapping and simulative leakage health risk assessment for heavy metals and metalloids in groundwater from a typical brownfield, middle China. International journal of environmental research and public health 2017, 14, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, P.T.; Heiskala, M.; Peterson, P.A.; Yang, Y. The roles of iron in health and disease. Molecular aspects of medicine 2001, 22, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkermann, A.; Skouta, R.; Himmerkus, N.; Mulay, S.R.; Dewitz, C.; De Zen, F.; Prokai, A.; Zuchtriegel, G.; Krombach, F.; Welz, P.S.; Weinlich, R. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, 16836–16841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shoji-Kawata, S.; Sumpter, R.M.; Wei, Y.; Ginet, V.; Zhang, L.; Posner, B.; Tran, K.A.; Green, D.R.; Xavier, R.J.; Shaw, S.Y. Autosis is a Na+, K+-ATPase–regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy-inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia–ischemia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110, 20364–20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockshin, R.A.; Zakeri, Z. Apoptosis, autophagy, and more. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2004, 36, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Munshi, C.; Bhattacharya, S. The “Irony” of Ferroptosis: A Review on Neurological Challenges. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy 2022, T.H.; Schnaar, R.L.; Coyle, J.T. Immature cortical neurons are uniquely sensitive to glutamate toxicity by inhibition of cystine uptake. The FASEB Journal 1990, 4, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.H.; Miyamoto, M.; Sastre, A.; Schnaar, R.L.; Coyle, J.T. Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron 1989, 2, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, A.; Schneider, M.; Förster, H.; Roth, S.; Wirth, E.K.; Culmsee, C.; Plesnila, N.; Kremmer, E.; Rådmark, O.; Wurst, W.; Bornkamm, G.W. Glutathione peroxidase 4 senses and translates oxidative stress into 12/15-lipoxygenase dependent-and AIF-mediated cell death. Cell metabolism 2008, 8, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouta, R.; Dixon, S.J.; Wang, J.; Dunn, D.E.; Orman, M.; Shimada, K.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Lo, D.C.; Weinberg, J.M.; Linkermann, A.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136, 4551–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, F.J. Glutathione and HIV infection: reduced reduced, or increased oxidized? European journal of clinical investigation 1998, 28, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.M.H.C.M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T.D. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current medicinal chemistry 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.J.; Berry, M.J.; Moustafa, M.E.; Carlson, B.A.; Hatfield, D.L.; Faust, J.R. Inhibition of selenoprotein synthesis by selenocysteine tRNA [Ser] Sec lacking isopentenyladenosine. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 28110–28119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Green, M.; Choi, J.E.; Gijón, M.; Kennedy, P.D.; Johnson, J.K.; Liao, P.; Lang, X.; Kryczek, I.; Sell, A.; Xia, H. CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 569, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Shimoni, Y.; Yang, W.S.; Subramaniam, P.; Iyer, A.; Nicoletti, P.; Martínez, M.R.; López, G.; Mattioli, M.; Realubit, R.; Karan, C. Elucidating compound mechanism of action by network perturbation analysis. Cell 2015, 162, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death & Differentiation 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar]
- Yagoda, N.; von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; Smith, R. RAS–RAF–MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends in cell biology 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; Brown, L.M. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chemistry & biology 2008, 15, 234–245. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



