1. Introduction
Gastric cancer was the sixth most frequent cancer with 1,089,103 new patients and the third leading cause of cancer death with 768,793 deaths worldwide in 2020 [
1]. In Japan, it is the second most common cancer with 129,475 new cases in 2017 and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths with 42,931 fatalities in 2019 [
2]. Efforts to combat gastric cancer have led to the exploration of immune checkpoint inhibitor(ICI)s in various clinical trials. Notably, the phase Ib study (KEYNOTE-012) demonstrated a response rate of 22.2% in PD-L1 positive patients treated with pembrolizumab [
3]. Similarly, the phase Ib study (JAVELIN) revealed a response rate of 9.0% for avelumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer [
4]. Furthermore, the phase III trial (ATTRACTION-2) demonstrated the efficacy of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, in improving overall survival (OS) by 1.2 months (5.3 months vs. 4.1 months, HR 0.63 [95%CI 0.50-0.78], p<0.001) compared to placebo in patients with unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric cancer refractory to standard therapy [
5]. Subsequently, based on these encouraging results, nivolumab gained approval in Japan on September 22, 2017, for treating unresectable advanced, or recurrent gastric cancer that has progressed after chemotherapy. Notably, nivolumab was designated as the standard of care for third-line treatment in the Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition) [
6].
A limited response rate characterizes the therapeutic efficacy of nivolumab in gastric cancer, but those patients who do respond often achieve long-term survival. Conversely, patients who are unlikely to respond are compelled to switch to alternative chemotherapy strategies, such as trifluridine/tipiracil, to achieve stable disease [
7]. Identifying biomarkers that can predict both initial and long-term treatment responses is essential to improve treatment outcomes. Additionally, understanding the mechanisms of treatment resistance is crucial for selecting appropriate combination therapies. Therefore, there is a clear need to establish reliable biomarkers and investigate treatment resistance mechanisms to develop more effective therapies.
In our recent studies [
8,
9], we developed an “Immunogram” using RNA sequencing data to assess the intratumoral immune response characteristics in individual patients. Building upon this, we applied the Immunogram to a cohort of 29 gastric cancer surgery cases, successfully classifying gastric cancer into four distinct groups [
10]. In addition to utilizing RNA sequencing data, we employed flow cytometry and liquid factor analysis to comprehensively analyze the intra-tumoral immune response. This multi-layered approach revealed that our classification did not align with conventional clinical classifications. However, it provided valuable insights into various aspects of the intra-tumor immune response, including cancer antigen counts, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, genetic mutations, tumor microenvironment, tumor-infiltrating T lymphocyte (TIL) dysfunction, and infiltration exclusion. As a result, our approach proved to be a valuable tool for evaluating the intratumor immune response.
In this prospective study, we used the aforementioned methods to compare the intra-tumoral immune response in gastric cancer patients before and early on-treatment nivolumab therapy. Our primary objectives were to uncover the immunological mechanisms contributing to treatment resistance and its underlying factors and identify biomarkers that can predict the efficacy of nivolumab treatment for gastric cancer. By investigating these aspects, we aimed to enhance our understanding of nivolumab’s effectiveness and shed light on potential strategies to overcome treatment resistance in gastric cancer.
2. Results
2.1. Study Design and Baseline Characteristic
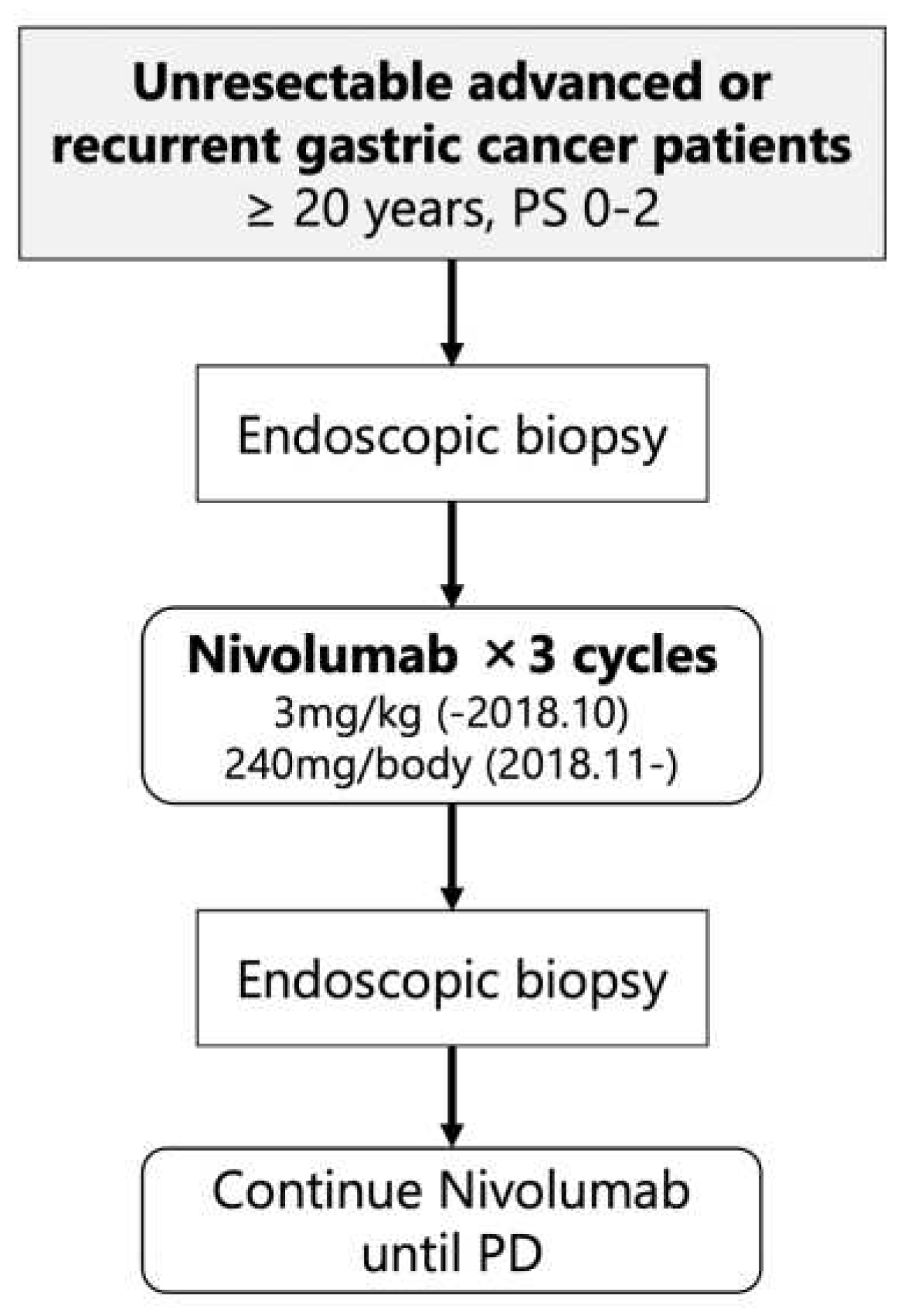
This study was a single-arm, prospective interventional study at the University of Tokyo Hospital (
Figure 1). The patients in the study received nivolumab monotherapy as their third or later line therapy at either 3mg/kg (until October 2018) or 240mg/body (from November 2018). Endoscopic biopsies were performed before initiating treatment (pre-treatment) and after completing three courses of nivolumab therapy (early-on-treatment). The purpose of these biopsies was to analyze the intratumoral immune response at an early stage of nivolumab treatment in patients with unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric cancer, with the aim of identifying predictive biomarkers for nivolumab efficacy. The primary endpoint of the clinical trial was the durable clinical benefit rate (DCBR), with durable clinical benefit (DCB) defined as disease control for more than 4 months. The secondary endpoints included the response rate (RR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and immunological response.
From October 1, 2017, a total of 19 patients (10 males, median age 67 years) were enrolled, all of whom had received nivolumab as the third or later line of therapy. The recruitment for the study was supposed to reach 50 patients, but it was halted before the planned completion on March 31, 2023. This was due to the challenges in recruiting participants for endoscopy studies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the standard therapy for eligible patients changed, making it even more difficult to recruit new patients. Clinical data were censored on March 31, 2023; the median follow-up time was 5.1 months (0.8-64.6). All patients underwent pre-biopsy, and in 18 cases, sufficient tumor tissue was obtained for analysis (hereafter referred to as immunological analysis cases). Fourteen patients could complete three courses of nivolumab therapy and post-biopsy could be performed, and sufficient tumor tissue for analysis was obtained in all cases (
Table 1 and
Table S1).
2.2. Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy
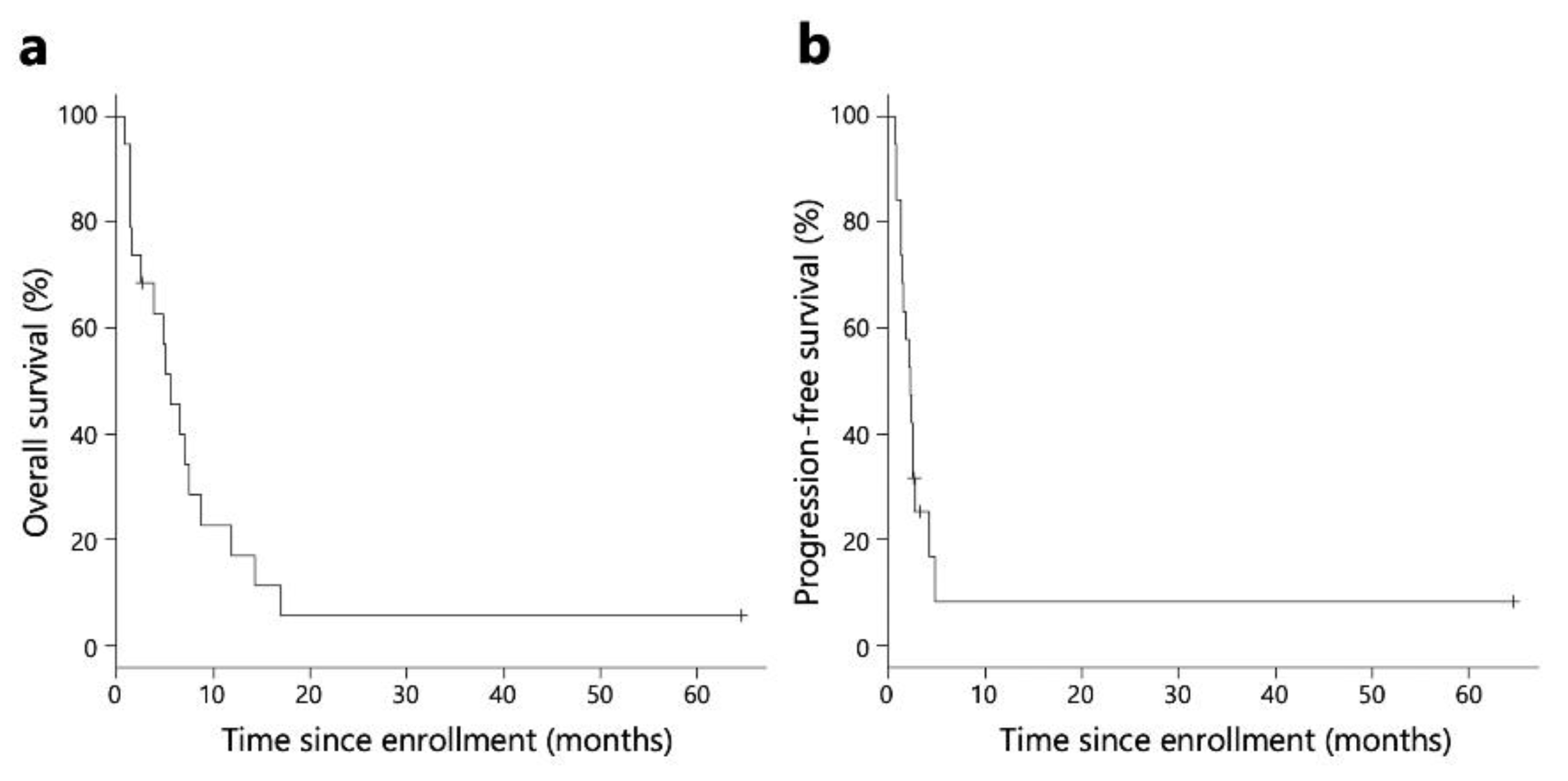
The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed that the median OS and PFS for all patients were 5.5 and 2.3 months, respectively (
Figure 2). The median OS and PFS for patients included in the immunological analysis were 5.5 and 2.4 months, respectively. (
Figure S1).
The DCBR of all patients was 15.8% [95% Confidence interval (CI), 3.4-39.6] (n=3). Among the 18 patients in the immunological analysis, the DCBR was 16.7% (n=3) (
Table 2). Response rate (RR), disease control rate (DCR), PFS, and OS are shown in
Table 2.
2.3. Immunogram Analysis
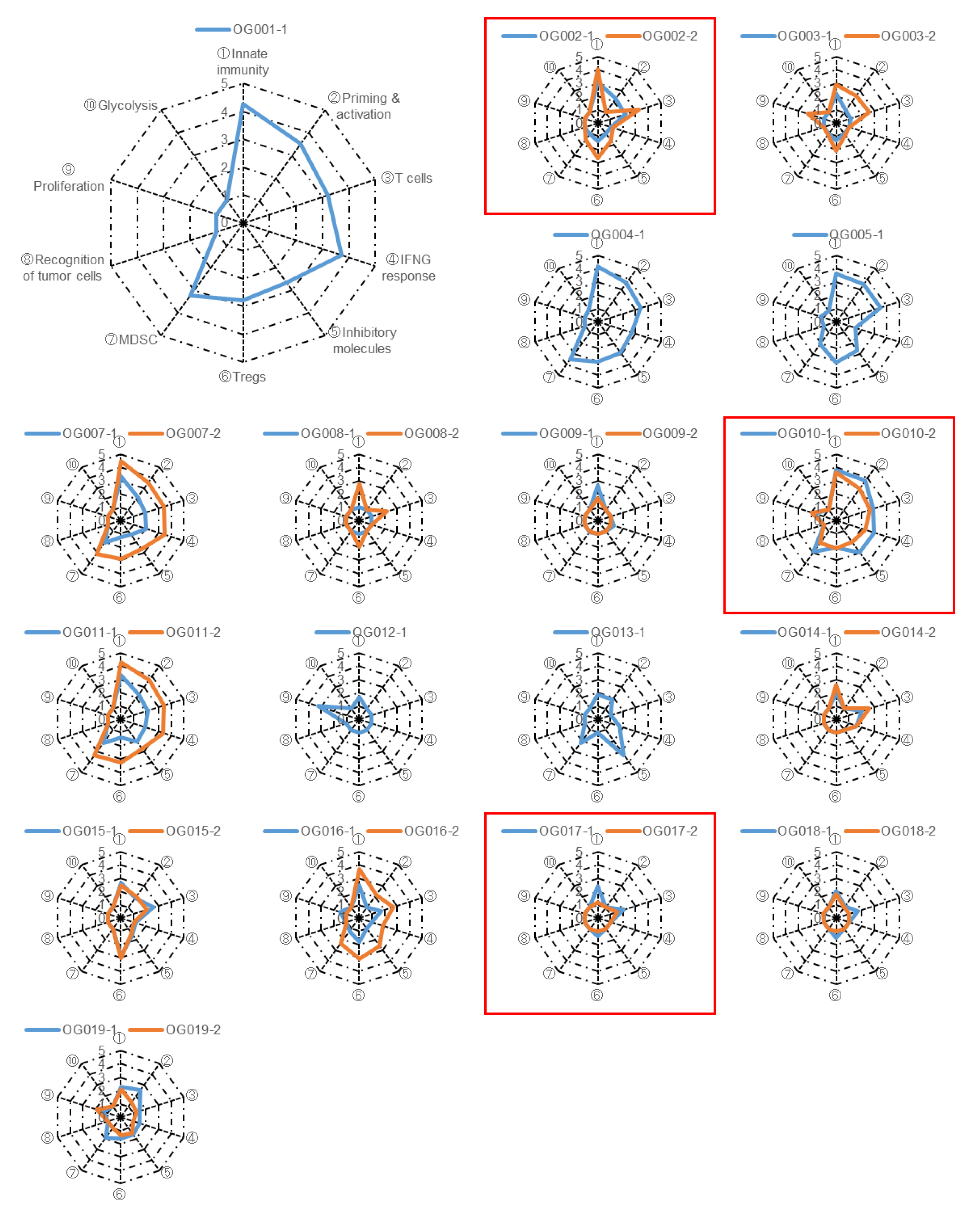
To assess the anti-tumor immune response elicited by anti-PD-1 monotherapy, we extracted RNA from biopsy specimens and conducted RNA sequencing(RNA-Seq) analysis. We focused on ten gene sets associated with anti-tumor immunity, proliferation, and metabolism (
Table S2). Subsequently, we performed single-sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA) on the tumor samples and converted the scores of the ten gene sets into immunogram scores following the methodology outlined in the Materials and Methods section. The resulting immunogram scores were plotted on a radar chart to generate individual immunograms (
Figure 3), which exhibited considerable variation among patients, indicating that the immune responses within the tumor and tumor microenvironment (TME) are distinct for each case. Notably, in certain patients, the orange line representing the on-treatment tumor expanded around the blue line representing the pre-treatment tumor, effectively enclosing it. This observation suggests that anti-tumor immune responses were activated by anti-PD-1 monotherapy in these particular patients (
Figure 3). However, immunogram scores were low and did not show improvement with the treatment in the majority of patients.
2.4. Biomarker for Anti-PD-1 Monotherapy
We investigated the molecular biomarkers for DCB in anti-PD-1 monotherapy using pre-treatment and early-on treatment samples. Immunogram scores for each axis were compared between patients with and without DCB (DCB and non-DCB). As shown in
Figures S2 and S3, there was no statistically significant difference between these two groups.
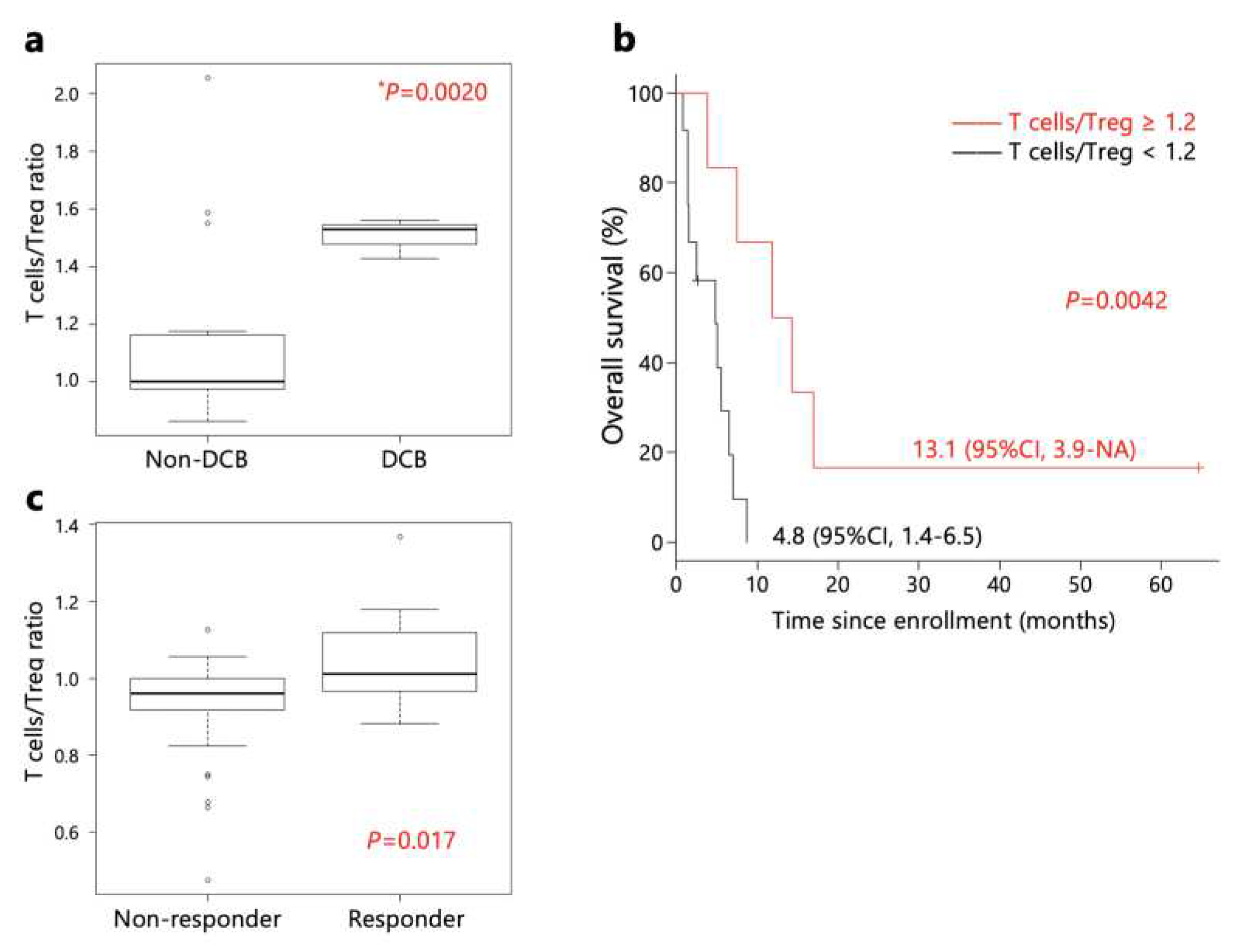
However, the ratio of T cells/Tregs immunogram scores in pre-treatment samples was higher in patients with DCB than non-DCB patients (
Figure 4a). Furthermore, patients with a T cells/Tregs immunogram score ratio ≥ 1.2 exhibited longer OS than patients with a ratio < 1.2 (
Figure 4b). Additionally, a comparison of T cells/Tregs immunogram scores of the PRJEB25780 study in Korea [
11] revealed higher scores in responders (
Figure 4c)
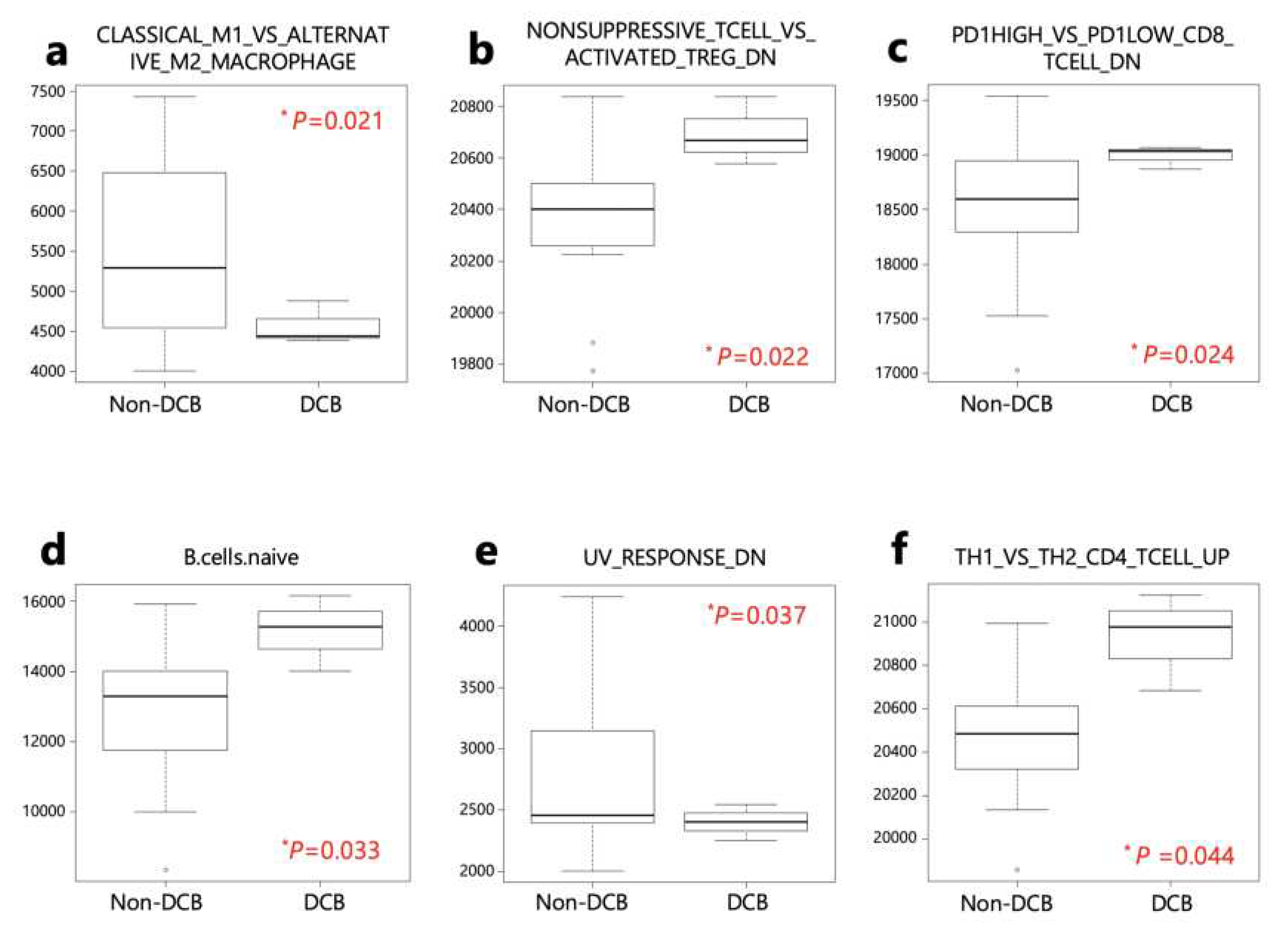
The ssGSEA analysis was performed on patients with DCB and non-DCB using 140 gene sets from the Human Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) (
Table S3). Four activated processes were enriched in patients with DCB, while 2 were enriched in non-DCB patients (
Table S4 and
Figure 5).
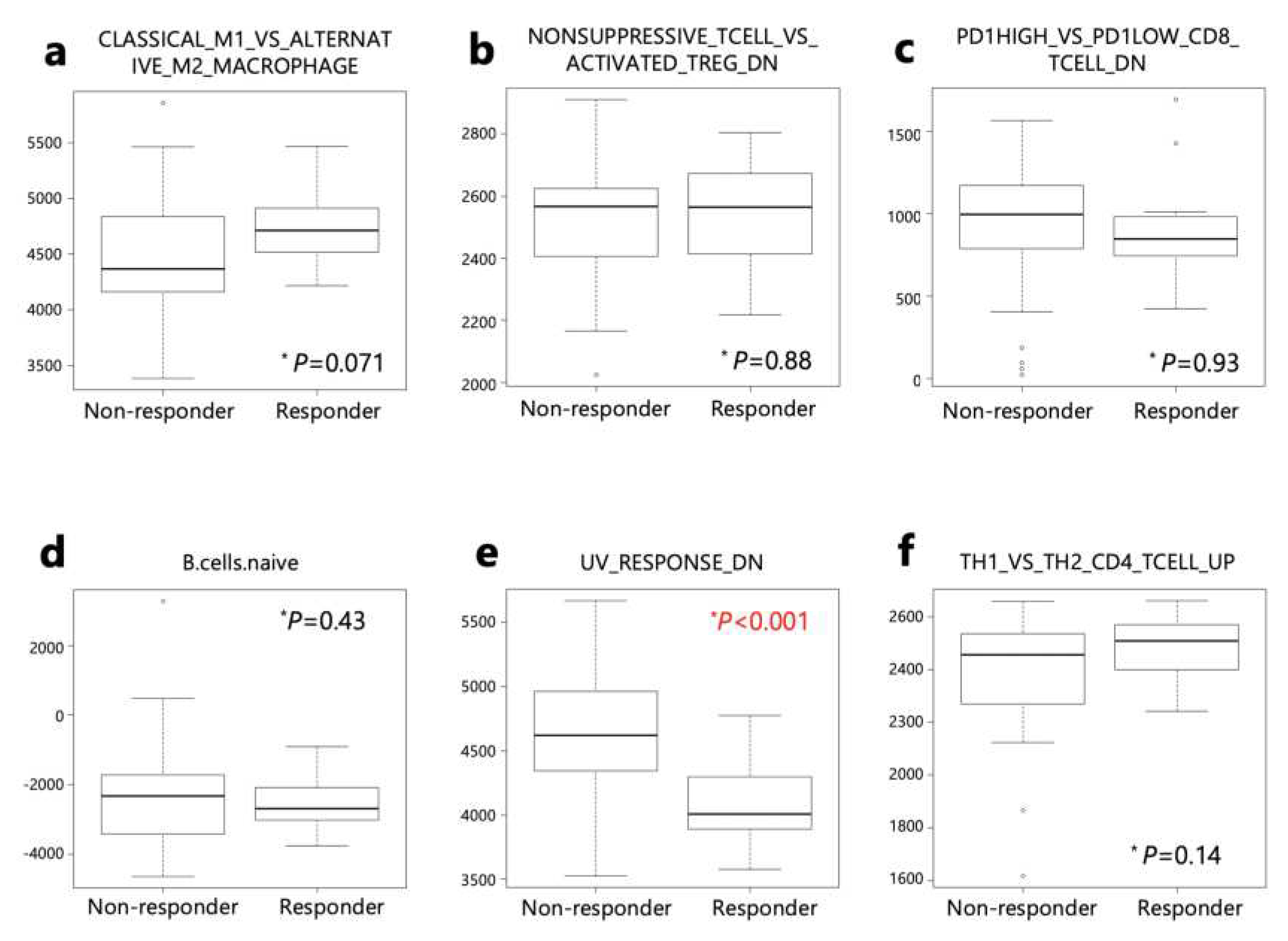
These 6 gene sets were then applied to responders and non-responders in the PRJEB25780 study (
Table S5). Genes down-regulated in response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation (HALLMRK_UV_RESPONSE_DN) was significantly lower in responders than non-responders (
Figure 6).
2.5. TCR Repertoire Analysis
In addition to transcriptome analysis, TCRβ genes were amplified from cDNA, and the TCR repertoire was evaluated based on the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) sequences. The Shannon-Weaver index (SWI), which represents the diversity of the TCR repertoire, was compared (
Table 3 and
Figure S4). SWIs of DCB patients were found to be larger than those of non-DCB patients in pre-treatment tumors, while SWIs of DCB patients were smaller than those of non-DCB patients in early-on-treatment tumors. In patients with DCB, the SWI of on-treatment tumors was smaller than that of pre-treatment tumors, whereas in patients without DCB, the SWI of on-treatment tumors was larger than that of pre-treatment samples (
Table 3 and
Figure S4). These results indicate that anti-PD-1 monotherapy increased T cell clonality in DCB patients, while T cell diversity was increased in non-DCB patients.
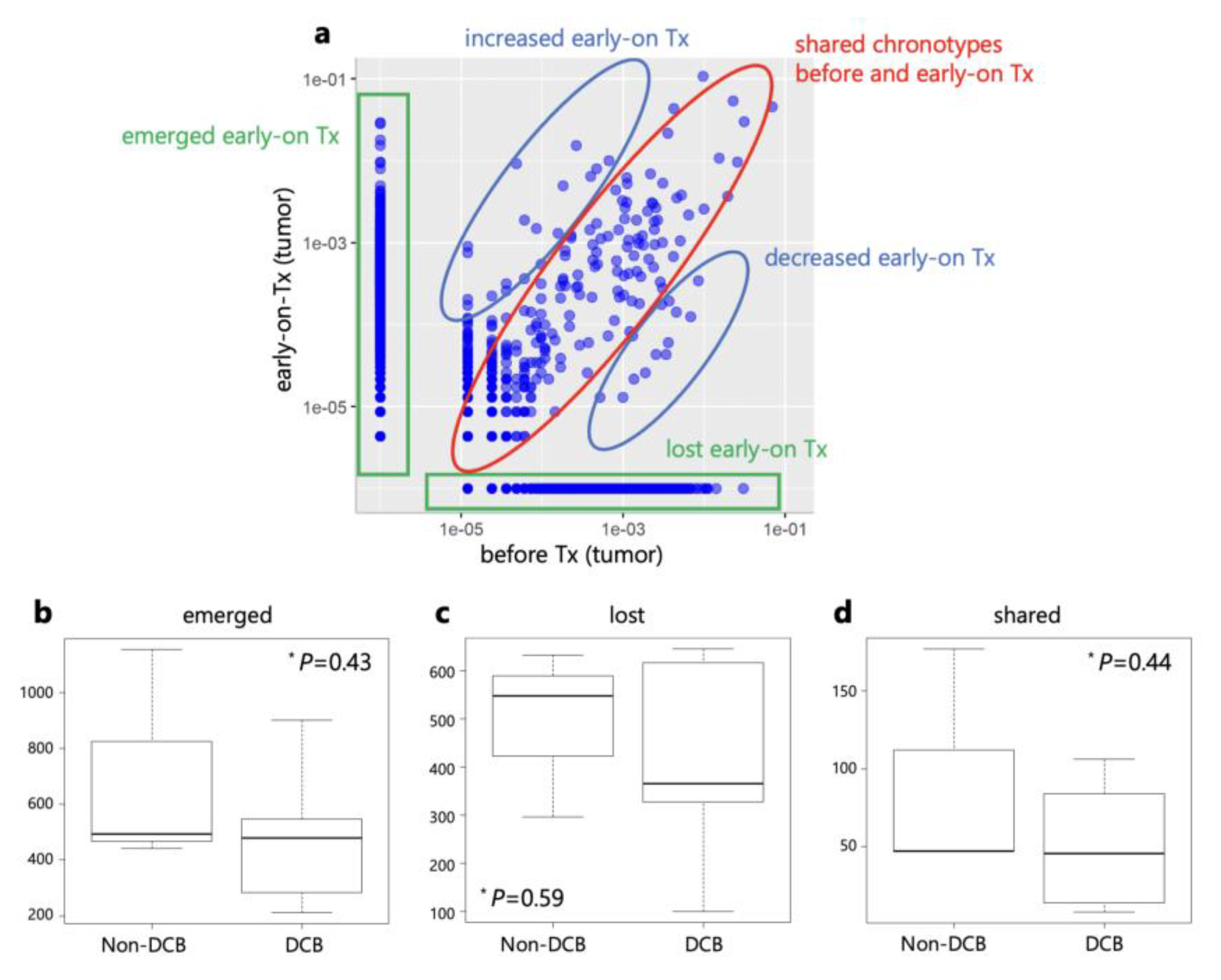
The clonal replacement of TILs by ICIs has been reported [
12,
13,
14,
15]. Therefore, we compared the frequencies of individual T cell clones in tumors before and during treatment using the CDR3 sequences. After anti-PD-1 monotherapy, TCR clones were categorized into three groups: lost, shared, and emerged clones (
Figure 7). Next, we compared the number of clonotypes between DCB and non-DCB patients. There were no significant differences in the numbers of lost, shared, and emerged clonotypes between DCB and non-DCB patients.
2.6. Immunological Classification of Gastric Cancer
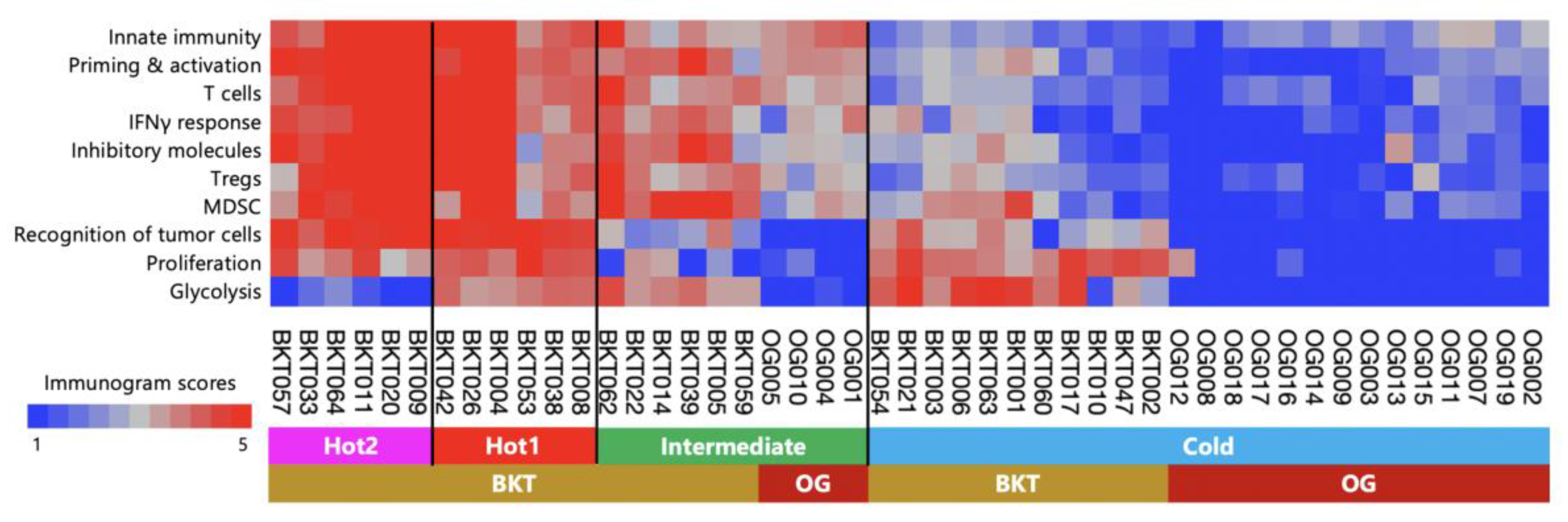
Previously, we conducted an examination of surgically resected gastric cancer in the BKT study and proposed an immunological classification of gastric cancer based on immunogram scores [
10]. Surgically resected gastric cancer demonstrated four immune signatures representing the main subtypes: Hot1, Hot2, Intermediate, and Cold. In this study, we observed that the tumors in patients who received nivolumab monotherapy as their third or later line therapy were more advanced and immunologically suppressed compared to the surgically resectable tumors. Therefore, we performed a hierarchical cluster analysis by combining a total of 18 patients from this study and 29 patients from the BKT study. Tumors in the BKT cohort were classified into all four subtypes (
Figure 8). In contrast, out of the 18 pre-treatment tumors in this study, 14 were classified as cold tumors, 4 were classified as intermediate subtype, and none were classified as Hot1 or Hot2 tumors.
3. Discussion
In this study, we analyzed the tumor immune response in a group that achieved DCB with nivolumab monotherapy as a third-line treatment for gastric cancer, compared to a group that did not achieve DCB. DCB was observed in 15.8% of the intent-to-treat population. The secondary endpoints, including an ORR of 15.8%, median OS of 5.5 months, and median PFS of 2.3 months, demonstrated comparable results to the ATTRACTION-2 trial [
5]. Despite a slightly unfavorable patient background with a performance status (PS) 2 of 37% in the real-world setting, the efficacy of nivolumab was confirmed.
No significant changes were observed in individual immunograms before and early-on treatment, and no consistent changes were identified among cases that achieved DCB. Furthermore, TCR repertoire analysis revealed that newly emerged clonotypes were detected in the on-treatment tumors. However, clonal replacement was not associated with the efficacy of the treatment. As mentioned earlier (
Figure 8), at the stage of third or later line therapy, the tumors had already transitioned into Cold tumors, and it was believed that it was no longer a stage where the immune response could be altered simply by inhibiting PD-1.
To investigate potential biomarkers predicting treatment efficacy, we conducted an analysis of gene expression profiles from pre-treatment tumor transcriptomes in two separate groups: the DCB group (cases from this study) and the responder group (cases from the PRJEB25780 study). In terms of the signature of tumor-infiltrating immune cells, we observed that a high T cells/Tregs ratio and a low signature of genes down-regulated in response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation were associated with successful DCB and treatment response. Despite the limited number of cases analyzed, we observed that clinical benefits were accompanied by an immune response.
Compared to surgical cases, the majority of cases in this study were characterized by Cold tumors (
Figure 8). All cases were in the third-line or later treatments, and it is possible that they developed into Cold tumors as a result of tumor progression or the influence of past chemotherapy. In gastric cancer, it may be effective to use immune checkpoint inhibitors at a more frontline setting before the tumor transitions from a Hot to Cold state. In fact, the results of two phase III (CheckMate 649 and ATTRACTION-4) trials that evaluated the combination of chemotherapy with nivolumab in first-line treatment have established it as the standard treatment [
16,
17].
As a limitation of this study, due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, we were only able to accumulate a significantly smaller number of cases than originally planned (50 cases). As a result, there is a possibility that the statistical power of the analysis is insufficient. Additionally, a considerable number of cases were unable to have early-on-treatment tissue samples collected primarily due to disease progression, potentially limiting the ability for adequate before-and-after comparisons. Now that the COVID-19 situation has improved, we have initiated a prospective study to evaluate the tumor immune response before and after nivolumab containing treatment in primary therapy for gastric cancer.
In conclusion, this study highlights the significance of the tumor immune response in determining the efficacy of nivolumab for gastric cancer. Considering the frustrating situation where the tumor-infiltrating immune response is weakened due to past treatments in third-line therapy, it is considered advisable to initiate treatment at an earlier stage to achieve improved immunotherapeutic effects. However, to fully optimize the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in gastric cancer treatment, it is imperative to conduct further validation studies with larger cohorts. Continued research in this direction will pave the way for more effective and personalized therapeutic strategies.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection
Patients with unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric or esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma were eligible for inclusion in the study if their tumor tissues could be accessed through endoscopy at the University of Tokyo Hospital. Other criteria for eligibility included being 20 years of age or older, having an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2, and having an evaluable lesion according to RECIST version 1.1 (measurable lesions were not required). Additionally, patients needed to be at least 42 days post-failure of standard chemotherapy and at least 14 days after their last chemotherapy infusion. Adequate organ and marrow functions were determined through laboratory tests, including assessments of neutrophil count, hemoglobin (Hb) levels, platelet count (PLT), total bilirubin (T-Bil), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and serum creatinine (Cre).
The study had certain exclusion criteria, which were as follows: patients with synchronous or metachronous double cancers, except for intramucosal tumors that had been curatively resected through local therapy within the past 5 years; patients with active infections requiring systemic therapy; patients with active autoimmune diseases or a history of chronic or recurring autoimmune diseases; patients with a history of interstitial pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, or irradiation pneumonitis; patients with active diverticulitis or inflammatory bowel disease; patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus or thyroid diseases; patients with unstable angina within the past 3 weeks or a history of acute myocardial infarction within the past 3 months; patients with severe psychological illness; pregnant or lactating women or women of childbearing potential; patients within 4 weeks after receiving a live vaccination or 2 weeks after receiving an inactivated vaccination; patients deemed unfit to participate in the study by the investigator.
4.2. Clinical Sample Processing and RNA Extraction
The tissues were collected immediately after endoscopic biopsy, stored in RNAlater Stabilization Solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific K.K.,Tokyo, Japan) and cryopreserved until use. Total RNA samples from tissues were extracted using the AllPrep DNA/RNA/miRNA Universal Kits (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted RNAs were then assessed for quality and quantity. For next-generation sequencing (NGS), RNA samples meeting the following criteria were selected: a concentration of ≥ 20.0 ng/μL, a total amount of ≥ 0.4 μg, and an RNA integrity number (RIN) of ≥ 7.0, as assessed using the Agilent 2200 TapeStation (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
4.3. RNA-Sequence (RNA-Seq)
For RNA-Seq library preparation, we used the NEBNext
® UltraTM RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina
® (Agilent Technologies), following the manufacturer’s protocols. The prepared libraries were sequenced as 150-bp paired-end reads on the NovaSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at VERITAS (Danvers, MA, USA). On average, each sample yielded approximately 35.1 million reads of 150 base pairs in length. The obtained reads were aligned to the reference genome (GRCh38/hg38) using STAR (v.2.5.2b). Expression values were calculated as fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped (FPKM) using HTSeq (v.0.6.1) and the R programming language (version 3.4.3;
https://www.r-project.org/).
4.4. Computational Methods to Analyze RNA-Seq Data
We calculated a ssGSEA score using R version 3.6.2 with the GSVA package version 1.38.2. To depict the immunological status of the tumor in each patient, we constructed an immunogram based on RNA-Seq data [
9]. Incorporated gene sets are listed in
Table S2. Similar ssGSEA was applied to the TCGA mRNA data of 375 gastric cancer patients. We obtained the mean (
M) and standard deviation (SD) of the ssGSEA score of these 375 gastric cancer patients for each gene set. The score for each axis of the immunogram in each patient was calculated as the [immunogram score] = 3 + 1.5 × (ssGSEA score −
M)/SD. This formula was applied for all axes of the immunogram of a patient.
4.5. TCR Repertoire Analysis
TCR genes were amplified using adaptor ligation-mediated PCR [
18]. High-throughput sequencing was performed using the Illumina Miseq paired-end platform (2 × 300 bp) (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Assignment of TRBV and TRBJ segments in TCR genes was performed based on the international ImMunoGeneTics information system
® (IMGT) database (
http://www.imgt.org). A unique sequence read was defined as a sequence read having no identity in TRBV, TRBJ and deduced amino acid sequence of CDR3 with the other sequence reads. The copy number of identical unique sequence reads was counted in each sample and then ranked in order of the copy number. Total read counts were adjusted by the amount of input mRNA (read count/μg). Percentage occurrence frequencies of sequence reads with TRBV and TRBJ genes in total sequence reads were calculated. Then SWI was calculated for them.
4.6. Hierarchical Clustering
We utilized an unsupervised hierarchical clustering algorithm for the transcriptome analysis data. This analysis used R version 3.6.2 with the pheatmap package version 1.0.12. To generate the hierarchical clustering, we calculated the squared Euclidean distance between the samples. This distance measure quantifies the dissimilarity between samples based on their transcriptome profiles. We then applied an agglomerative algorithm with Ward’s method, which iteratively merges clusters to minimize the within-cluster variance.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method and the log-rank test. Data were censored on March 31, 2023. Patients who were lost to follow-up were censored at the date of last contact or follow-up. PFS was calculated from the date of study enrollment to the date of disease progression or death from any cause. OS was calculated from the date of study enrollment to the date of death from any cause. Patients who were alive on March 31, 2023, were censored for OS analysis. Tumor response was evaluated according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, version 1.1 [
19], based on computed tomography (CT) findings. The best overall response was assessed as complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), non-CR/non-PD, or progressive disease (PD). Patients with clinically progressed disease status were defined as PD without undergoing a CT scan in this study. Disease control was defined as no PD.
The Kaplan–Meier method with a log-rank test and Cox regression analysis were performed to evaluate relapse-free survival and OS. All statistical analyses were performed with EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan), which is a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). More precisely, it is a modified version of R commander designed to add statistical functions frequently used in biostatistics [
20].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: The Kaplan–Meier survival analysis; Figure S2: The comparison of immunogram scores of pre-treatment tumors between DCB and non-DCB Patients; Figure S3: The comparison of immunogram scores of early-on-treatment tumors between DCB and non-DCB Patients; Figure S4: Comparison of TCRβ repertoire diversity between pre-treatment (Pre-Tx) and early-on-treatment (early-on-Tx) tumors; Table S1: Patients’ characteristics; Table S2: Gene-sets used for Immunogram; Table S3: Gene-sets used for ssGSEA analysis; Table S4: Enrichment scores for individual patients calculated using ssGSEA based on 140 gene sets; Table S5: Enrichment scores of ssGSEA using six gene sets showing statistical significance in our study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, YS, YSe and KK; methodology, HY; software, TH; investigation YK, KN, AK, NS, RI, YO, KY, SA and SN; formal analysis TK ; data curation, YS, YK; writing—original draft preparation, YS and KK; writing—review and editing, HY, YK, KN and YSe; visualization, YS and YK; supervision, YSe; project administration, KK; funding acquisition, YSe and KK. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by ONO Pharmaceutical co., ltd., and Bristol Myers Squibb (YSe). This research was also supported in part by AMED under Grant Number JP20ck0106639h0001 (KK).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research protocol received approval from the Ethical Committee of the University of Tokyo Hospital (P2017008). The study is registered with the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN-CTR) under the registration number UMIN000033110. This study was conducted in compliance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and the Good Clinical Practice guidelines established by the International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are deposited on the Japanese Genotype–Phenotype Archive (Accession no. JGAS000639). [
21]
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yaeko Furuhashi and Mikiko Shibuya for excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Sato reports personal fees from ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, MSD KK, TAIHO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work. Dr. Kakimi reports grants from TAKARA BIO Inc. outside the submitted work. The Department of Immunotherapeutics, The University of Tokyo Hospital, is an endowed department by TAKARA BIO Inc. The other authors have no competing interests to disclose. Author Mr. Tetsuro Hisayoshi was employed by the company cBioinformatics, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Information Service Cancer Statistics in Japan 2021; Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research, 2021.
- Muro, K.; Chung, H.C.; Shankaran, V.; Geva, R.; Catenacci, D.; Gupta, S.; Eder, J.P.; Golan, T.; Le, D.T.; Burtness, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-012): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.C.; Arkenau, H.T.; Lee, J.; Rha, S.Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Wyrwicz, L.; Kang, Y.K.; Lee, K.W.; Infante, J.R.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Avelumab (anti-PD-L1) as first-line switch-maintenance or second-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: Phase 1b results from the JAVELIN Solid Tumor trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.K.; Boku, N.; Satoh, T.; Ryu, M.H.; Chao, Y.; Kato, K.; Chung, H.C.; Chen, J.S.; Muro, K.; Kang, W.K.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer 2020, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Doi, T.; Dvorkin, M.; Mansoor, W.; Arkenau, H.T.; Prokharau, A.; Alsina, M.; Ghidini, M.; Faustino, C.; Gorbunova, V.; et al. Trifluridine/tipiracil versus placebo in patients with heavily pretreated metastatic gastric cancer (TAGS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasaki, T.; Nagayama, K.; Kuwano, H.; Nitadori, J. ichi; Sato, M.; Anraku, M.; Hosoi, A.; Matsushita, H.; Morishita, Y.; Kashiwabara, K.; et al. An Immunogram for the Cancer-Immunity Cycle: Towards Personalized Immunotherapy of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kushihara, Y.; Saito, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kakimi, K. A novel scoring method based on RNA-Seq immunograms describing individual cancer-immunity interactions. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4031–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Wada, I.; Odaira, K.; Hosoi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nagaoka, K.; Karasaki, T.; Matsushita, H.; Yagi, K.; Yamashita, H.; et al. Integrative immunogenomic analysis of gastric cancer dictates novel immunological classification and the functional status of tumor-infiltrating cells. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Cristescu, R.; Bass, A.J.; Kim, K.-M.K.K.-M.M.K.K.-M.M.K.; Odegaard, J.I.; Kim, K.-M.K.K.-M.M.K.K.-M.M.K.; Liu, X.Q.; Sher, X.; Jung, H.; Lee, M.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, K.E.; Satpathy, A.T.; Wells, D.K.; Qi, Y.; Wang, C.; Kageyama, R.; McNamara, K.L.; Granja, J.M.; Sarin, K.Y.; Brown, R.A.; et al. Clonal replacement of tumor-specific T cells following PD-1 blockade. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.D.; Madireddi, S.; de Almeida, P.E.; Banchereau, R.; Chen, Y.J.J.; Chitre, A.S.; Chiang, E.Y.; Iftikhar, H.; O’Gorman, W.E.; Au-Yeung, A.; et al. Peripheral T cell expansion predicts tumour infiltration and clinical response. Nature 2020, 579, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoma, A.M.; Suo, S.; Wang, Y.; Gunasti, L.; Porter, C.B.M.; Nabilsi, N.; Tadros, J.; Ferretti, A.P.; Liao, S.; Gurer, C.; et al. Tissue-resident memory and circulating T cells are early responders to pre-surgical cancer immunotherapy. Cell 2022, 185, 2918–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, J.; Inozume, T.; Sax, N.; Ariyasu, R.; Ishikawa, M.; Yamashita, K.; Kawazu, M.; Ueno, T.; Irie, T.; Tanji, E.; et al. PD-1 blockade therapy promotes infiltration of tumor-attacking exhausted T cell clonotypes. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.K.; Chen, L.T.; Ryu, M.H.; Oh, D.Y.; Oh, S.C.; Chung, H.C.; Lee, K.W.; Omori, T.; Shitara, K.; Sakuramoto, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in patients with HER2-negative, untreated, unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ATTRACTION-4): a randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-contr. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, K.; Shini, T.; Matsutani, T.; Suzuki, R. A new high-throughput sequencing method for determining diversity and similarity of T cell receptor (TCR) α and β repertoires and identifying potential new invariant TCR α chains. BMC Immunol. 2016, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, Y.; Mashima, J.; Kosuge, T.; Katayama, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Kaminuma, E.; Ogasawara, O.; Okubo, K.; Takagi, T.; Nakamura, Y. The DDBJ Japanese genotype-phenotype archive for genetic and phenotypic human data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D18–D22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).