3. Discussion
To date, the following materials are used in the endovascular treatment of hypervascularized formations of the head and neck: micro-spirals, polyvinyl alcohol-based particles, cyanoacrylate-based adhesives and NAGLEMs.
Intravascular embolization of hypervascularized formations of the head and neck in the vast majority of cases is used as a preparatory stage before microsurgical removal, thereby reducing the risks of intraoperative hemorrhagic com-plications, as well as increasing the radicality of the formations removal [
9]. The method of preoperative embolization consists in filling of the vascular network of the formation with an embolizing agent in order to stop the blood flow through the main afferents of the formation to facilitate its surgical removal. Due to the presence of a highly developed network of vessels in such formations, the main aim of embolization is to fill the entire volume of the vascular network as much as possible. Most vividly in our series this was demonstrated by the Face AVMs group and case #1. It was the adequate total filling of the entire AVM that allowed the complete removal of the hypervascularized formation and only NAGLEMs were able to cope with this task, previous attempts were unsuccessful. An unfilled part of the vascular network leads to the development of collateral blood flow, thereby increasing the risks of surgical complications, and may probably become a predictor of relapse [
3,
10]. (An unfilled part of the vascular network of the formation, with insufficient penetration of embolizate into the small vessels of the formation, increases the risks of intraoperative complications, and also leads to the development of collateral blood flow, thereby being a predictor of relapse). Due to the insufficient amount of scientific justification, embolization has not yet been considered as the final method of treatment, however, there are investigations showing the effectiveness of such interventions in high-risk patients [
11] Case #2 demonstrated the possibility of total shutdown of the AVM without subsequent removal, i.e. embolization in this case was an independent adequate method of treatment. Previous attempts at embolization with coils also did not lead to filling of the entire vascular network, which NAGLEMs subsequently coped with.
The process of successful embolization of hypervascularized formations depends on many factors, such as the experi-ence of the surgeon, the somatic status of the patient, competent anesthesia manual, equipment of the operating room, but, above all, on the properties of embolizing agents. Currently, there are no randomized studies comparing various embolizing agents in the treatment of hypervascularized formations of the head and neck, however, re-views and articles appear that allow assessing the effect of the properties of agents on the clinical outcome [
10].
The method of embolization of hypervascularized formations using microcoils solely is not used, since they can oc-clude only the proximal part of the afferents, while maintaining the filling of the main internal network of the hy-pervascularized formationby the collateral blood flow. There are few reports on the use of microcoils in preoperative embolization of paragangliomas and AVMs of soft tissues of the head. The main described advantage of preopera-tive embolization with microcoils is the ability of palpatory detection of them during surgery and the absence of risks of distal embolism [
12], among disadvantages there is a high cost of microcoils [
13]. To our opinion, microcoils alone (without NAGLEMs) cannot be used for embolization due to the preservation of blood flow through smaller afferents and microcirculatory network, which was well demonstrated by the AVMof the face group and in case#2.
The method of embolization by particles based on polyvinyl alcohol is based on the gradual introduction of a pre-pared solution of particles of different sizes from 100 to 1000 microns into the vascular network of the neoplasm, from smaller to larger [
14].When using this technique, it is almost never possible to embolize the vascular network completely, even with an-giographically complete shutdown of blood flow in the formation, it is necessary to remember about smaller vessels where particles cannot get due to their size [
15]. That is the reason why collaterals begin to form, through which the blood supply of the formation continues [
16]. According to Pauw BK et al. recanalization of paragangliomas of the jugular foramen area reaches 30% already 9 days after embolization with PVA particles [
17].
During embolization, it is necessary to take into account the presence of potentially dangerous anastomoses between ICA and ECA, as well as ECA and VA to prevent undesirable phenomena due to accidental migration of particles. Since PVA particles are X-ray negative, delivery is carried out with an iodine-containing contrast agent [
18]. Therefore, after contrast elimination, it is impossible to estimate the pools of probable random migrations [
15].
The lack of control of distal embolism, the high frequency of recanalization after embolization, reduced penetration into the tissue (compared with liquid embolizing agents) suggest that the spectrum of application of PVA particles in surgery of hypervascularized formations should be significantly narrowed.
Cyanoacrylate-based adhesives were the first from liquid embolic agents to appear [
19]. Rapid polymerization of cyanacrylates (from a few seconds) is the main problem of this group of embolizing agents when filling the vascular network of hypervascularized formations. Often the embolizate does not have time to fill the vascular network of the formation completely before its polymerization [
1]. The amount of lipiodol mixed with cyanoacrylate directly affects the polymerization rate, therefore, the degree of dilution is determined by the blood flow rate and the depth to which the penetration of glue is desirable [
20]. As a final result, embolization of hypervascularized formations by cyanoacrylates leads to their continued growth due to collaterals located distal to the afferents turned off by glue, and, thus, a dissonance is formed between the absence of afferent vessels available for further embolization and the extensive vascular network of hypervascular-ized formation formed. This was demonstrated in our both groups (both with facial AVM and with paragangliomas) where previous embolizations with cyanoacrylates did not lead to any result. In such situation, there are no emboli-zation possibilities and the treatment of such formations passes to microsurgeons, while the risks of intraoperative bleeding remain. For many years before the advent of non-adhesive compositions, cyanoacrylates remained the only available liquid embolic agents in the treatment of hypervascularized formations of the head and neck.
NAGLEMs (ONYX, SQUID, PHIL) are widely used for intravascular embolization of hypervascularized formations. All of the above NAGLEMs have certain potential advantages and disadvantages. Despite the structural differences, ONYX, Squid and PHIL have similar properties. All three non-adhesive compositions clog blood vessels as a result of “precipitation”, this mechanism is often compared to the solidification of a lava flow [
1]. ONYX and Squid consist of three components: EVOH copolymer (ethylene and vinyl alcohol copolymer), micronized tantalum powder and DMSO. Tantalum powder provides the compositions with radiopacity. PHIL consists of two copolymers, polylactide-co-glycolide and polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate, as active components, DMSO and triiodphenol (iodine compounds), the latter covalently bound to two copolymers, which ensures the radiopacity of the agent. DMSO is used as a solvent in all three agents. While cyanoacrylates polymerize over a period of several seconds to several minutes, in non-adhesive compositions, the polymerization mechanism can take up to 30-40 minutes, depending on the size of the embolized blood vessels and the speed of blood flow in them. This aspect provides more controlled embolization, longer injection time and, consequently, better penetration and filling of the target formation, but also contributes to undesirable diffusion into normal arteries. A significant difference between SQUID and ONYX is the smaller size of tantalum powder granules [
2,
4]. The smaller size of tantalum granules is aimed at increasing the uniformity of radiopacity and improving visibility with longer injections [
21].
Compared to ONYX and SQUID, PHIL flows forward more like a column rather than like the above behavior with precipitation from outside to inside. PHIL has a fairly high embolic capacity. Compared to SQUID 18 and Onyx 18, smaller volumes of PHIL are required for the same degree of embolization [
19]. All three agents have several versions of different viscosities in their lines (ONYX18, ONYX20 and ONYX34, SQUID12 and SQUID18, PHIL25 PHIL30 PHIL35), which significantly expands the boundaries of their use. De-pending on the speed of the shunting process, the volume of formation, it is possible to select the necessary version of the embolizing agent, which will provide faster and more effective penetration into the target vascular network [
19]. In our series detailing the treatment of patients with hypervascularised masses, we were able to develop the concept of curative embolisation through the use of NAGLEM distal penetration into the smallest vessels, along with the distribution of non-adhesive embolytes throughout the tumour stroma. This approach is further exemplified in Case #3 where
(Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14) demonstrate its success. This endovascular embolization served as a standalone treatment since the vasculature was entirely disconnected, and the paraganglioma did not necessitate any additional removal.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design
This is a case–control, non-randomized study. The case series was designed to evaluate the effectiveness and results of the use of these NAGLEMs in treatment of patients in our clinic and compare with other emboliс agents. The study was conducted at the North-Western district scientific and clinical center named after L. G. Sokolov Federal Medical and Biological Agency & Almazov National Research Medical Center in St. Petersburg, Russia. Patients were enrolled in the study from November 2015 to May 2023.
We analyzed the technical features, effectiveness and safety of endovascular treatment of two groups of hypervascularized pathological formations localized in the soft tissues of the head and neck in 23 patients operated from 2015 to 2023. The age of the patients ranged from 29 to 76 years and averaged 55 ± 13 (M ± SD) years. In technical features, the type of Squid embolizing agent was evaluated in 12 cases (52.2%), Onyx – in 8 (34.8%), Phil – in 1 (4.3%) or a combination of Onyx+Squid – in 2 (8.7%), the type of delivery microcatheter , of which 91.3% prevailed (n=21) DMSO-compatible balloon catheters Scepter C, XC (Microvention) and microcatheters Headway (Microvention) 8,7% (n=2), respectively. The effec-tiveness was assessed based on the degree of shutdown of the vascular network of formations (total shutdown was achieved in 73.9% (n=17) cases, and subtotal 26.1% (n=6)) and the outcome on the mRs scale, the average of which was 1. Safety was assessed by the presence of complications that developed in 1 case (4.3%), changes in postopera-tive MRI that was performed in all patients at the time of discharge from the clinic.
5.2. NAGLEMs embolization technique
Embolization was carried out according to the following method. After performing angiography in standard projec-tions, afferents to the formation were determined, blood flow was assessed along the anterior and posterior commu-nicant arteries. A DMSO-compatible microcatheter or balloon catheter was inserted into the identified afferents and microangiography was performed, with an assessment of the so-called dangerous anastamoses. Then, through the same catheters and balloons for the delivery of NAGLEMs, embolization of hypervascularized formations was car-ried out with NAGLEMs injection to achieve maximum distal penetration. In cases where only DMSO-compatible microcatheters were used, surgical intervention was lengthened due to the time required for formation due to reflux and the formation of a proximal "plug". In one case coils were used according to the “Pressure Cooker Technique” de-scribed earlier for AVM of the brain [
22] . In some cases, a DMSO compatible balloon catheter was installed to protect against cerebral vascular embolism in the internal carotid artery. After the introduction of NAGLEMs, a control angiography was performed, in which the degree of embolization was assessed.
5.3. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using the StatTech v. 3.1.10 program (developed by Stattech LLC Russia).
Quantitative indicators were evaluated for compliance with the normal distribution using the Shapiro-Wilk criterion (with the number of subjects less than 50) or the Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion (with the number of subjects more than 50).
Quantitative indicators having a normal distribution were described using arithmetic averages (M) and standard deviations (SD), the boundaries of the 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
In the absence of a normal distribution, quantitative data were described using the median (Me) and the lower and upper quartiles (Q1 – Q3).
Categorical data were described with absolute values and percentages. Comparison of the two groups by a quantita-tive indicator having a normal distribution, provided that the variances are equal, was performed using the Student's t-test.
Comparison of three or more groups by a quantitative indicator having a normal distribution was performed using one-factor analysis of variance, a posteriori comparisons were carried out using the Tukey criterion (provided that the variances are equal).
The comparison of the two groups by a quantitative indicator, the distribution of which differed from the normal one, was performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test.
Comparison of three or more groups by a quantitative indicator, the distribution of which differed from the normal one, was performed using the Kraskel-Wallis criterion, a posteriori comparisons were performed using the Dunn criterion with the Hill correction.
The comparison of percentages in the analysis of four-field conjugacy tables was performed using the exact Fisher criterion (with values of the expected phenomenon less than 10).
The comparison of percentages in the analysis of multipole conjugacy tables was performed using Pearson's chi-square criterion. The direction and closeness of the correlation between the two quantitative indicators were assessed using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (with a distribution of indicators other than normal). A predictive mod-el characterizing the dependence of a quantitative variable on factors was developed using the linear regression method.
The construction of a predictive model of the probability of a certain outcome was carried out using the logistic re-gression method. A measure of certainty indicating the part of the variance that can be explained by logistic regres-sion was the Nigelkirk coefficient R2.
A full statistical analysis can be seen in the Supplementary Materials.
To assess the diagnostic significance of quantitative signs in predicting a certain outcome, the method of analysis of ROC curves was used. The separating value of the quantitative attribute at the cut-off point was determined by the highest value of the Yuden index. An analysis of the available literature was also performed. The Pubmed library was searched for articles using following key-words: "AVM of the head and neck, embolization of extracranial AVMs, embolization of paragangliomas, embolic agent". Criteria for articles inclusion: a series of patients with hypervas-cularized formations of the head and neck and the use of embolizing agents in their treatment. The exclusion criteria were: percutaneous embolization. A total of 7 articles were selected [
14,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P. (Andrey Petrov), A.I. and U.S.; data curation, US, A.P.(Andrey Petrov), A.I. and A.P. (Anna Petrova); formal analysis, E.K., N.T. and A.P. (Anna Petrova); investigation, A.P. (Andrey Petrov), A.P. (Anna Petrova) and A.I.; methodology, L.R.; project administration, A.I., U.S.. and A.P. (Andrey Petrov); supervision, L.R. and A.P. (Andrey Petrov); writing—original draft, A.P. (Andrey Petrov), E.K, N.T. and A.I.; writing—review and editing, L.R., A.P. (Andrey Petrov), A.I. and U.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
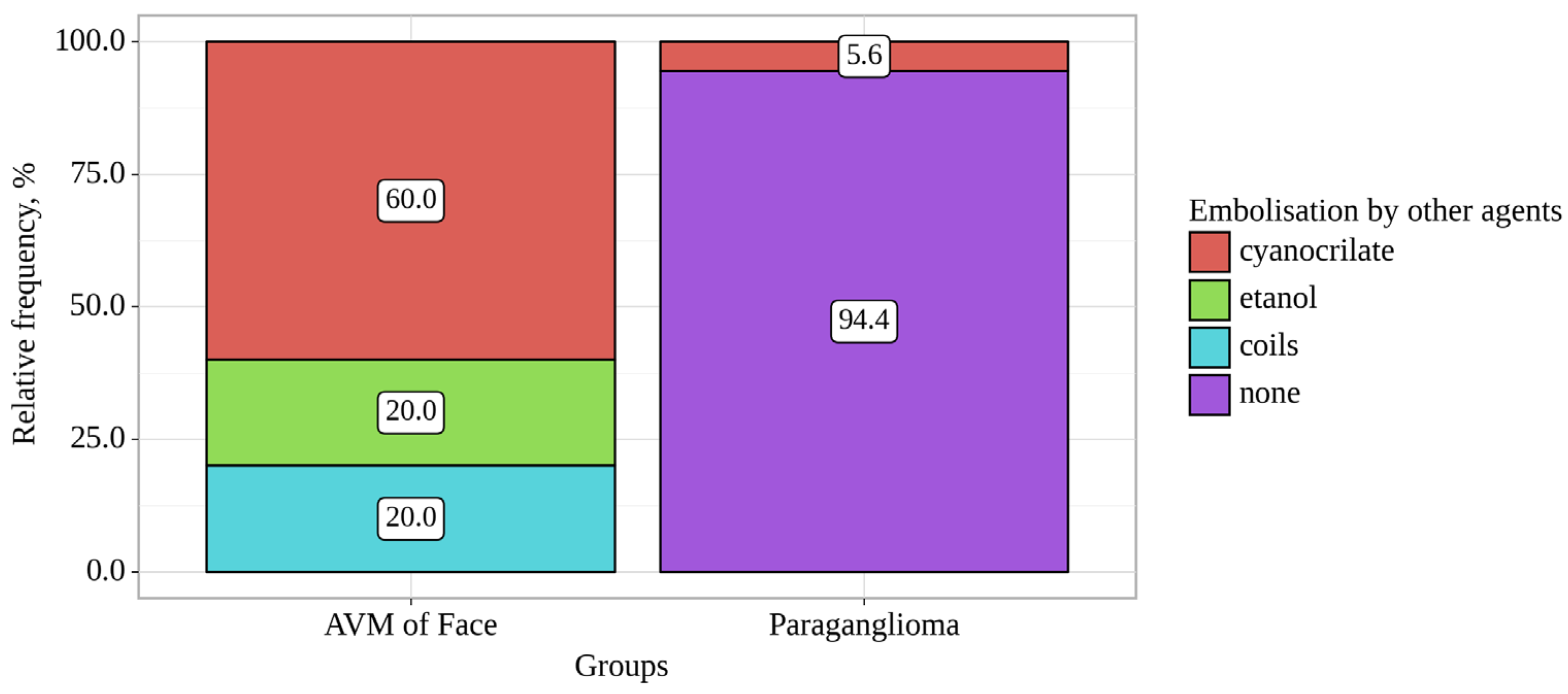
Figure 1.
Analysis of Embolisation by other agents conditioning on Groups.
Figure 1.
Analysis of Embolisation by other agents conditioning on Groups.
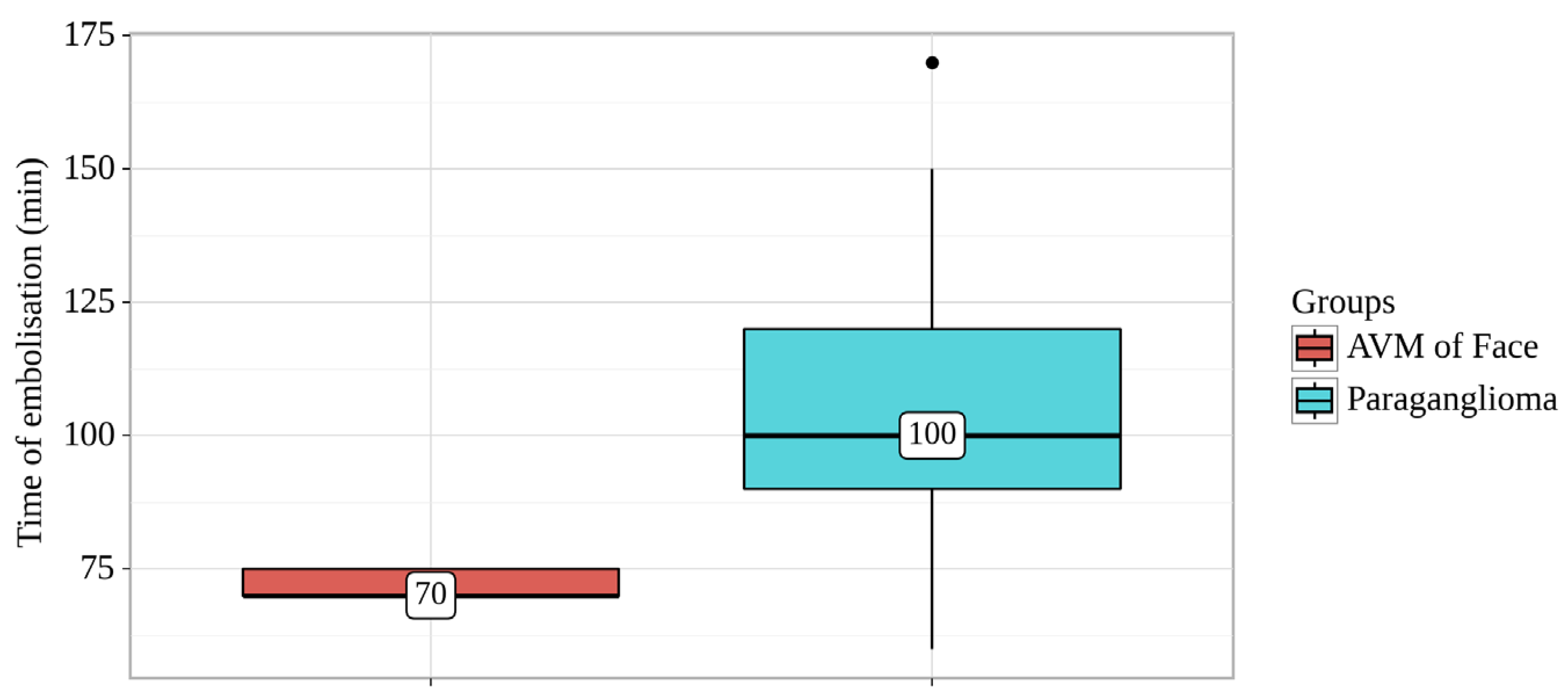
Figure 2.
Analysis of Time of embolisation conditioning on Groups.
Figure 2.
Analysis of Time of embolisation conditioning on Groups.
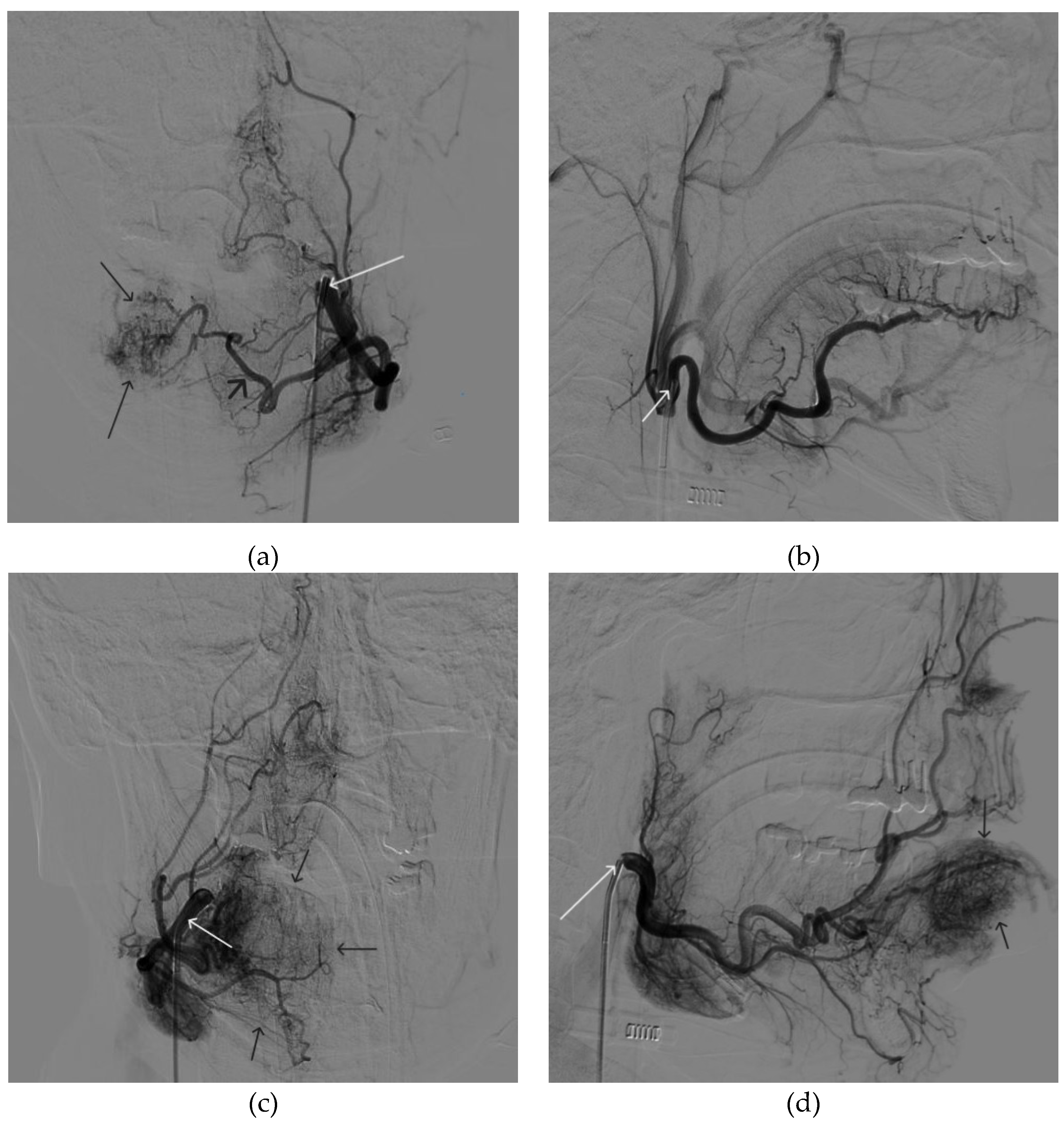
Figure 3.
Digital subtraction angiography from the facial arteries: a, b – straight and lateral projections on the left; c, d – straight and lateral projections on the right (white arrows indicate catheters at the ostium of the facial arteries, black long arrows indicate filling of the lower lip AVM, black short arrow indicates the afferent AVM from the left facial artery). There is filling of the AVM from the afferent from the left facial artery.
Figure 3.
Digital subtraction angiography from the facial arteries: a, b – straight and lateral projections on the left; c, d – straight and lateral projections on the right (white arrows indicate catheters at the ostium of the facial arteries, black long arrows indicate filling of the lower lip AVM, black short arrow indicates the afferent AVM from the left facial artery). There is filling of the AVM from the afferent from the left facial artery.
Figure 4.
The process of introducing Onyx-18 into the AVM of the lower lip (the white arrow indicates the microcatheter, the black arrow indicates the spread of embolizate along the vascular network of the formation).
Figure 4.
The process of introducing Onyx-18 into the AVM of the lower lip (the white arrow indicates the microcatheter, the black arrow indicates the spread of embolizate along the vascular network of the formation).
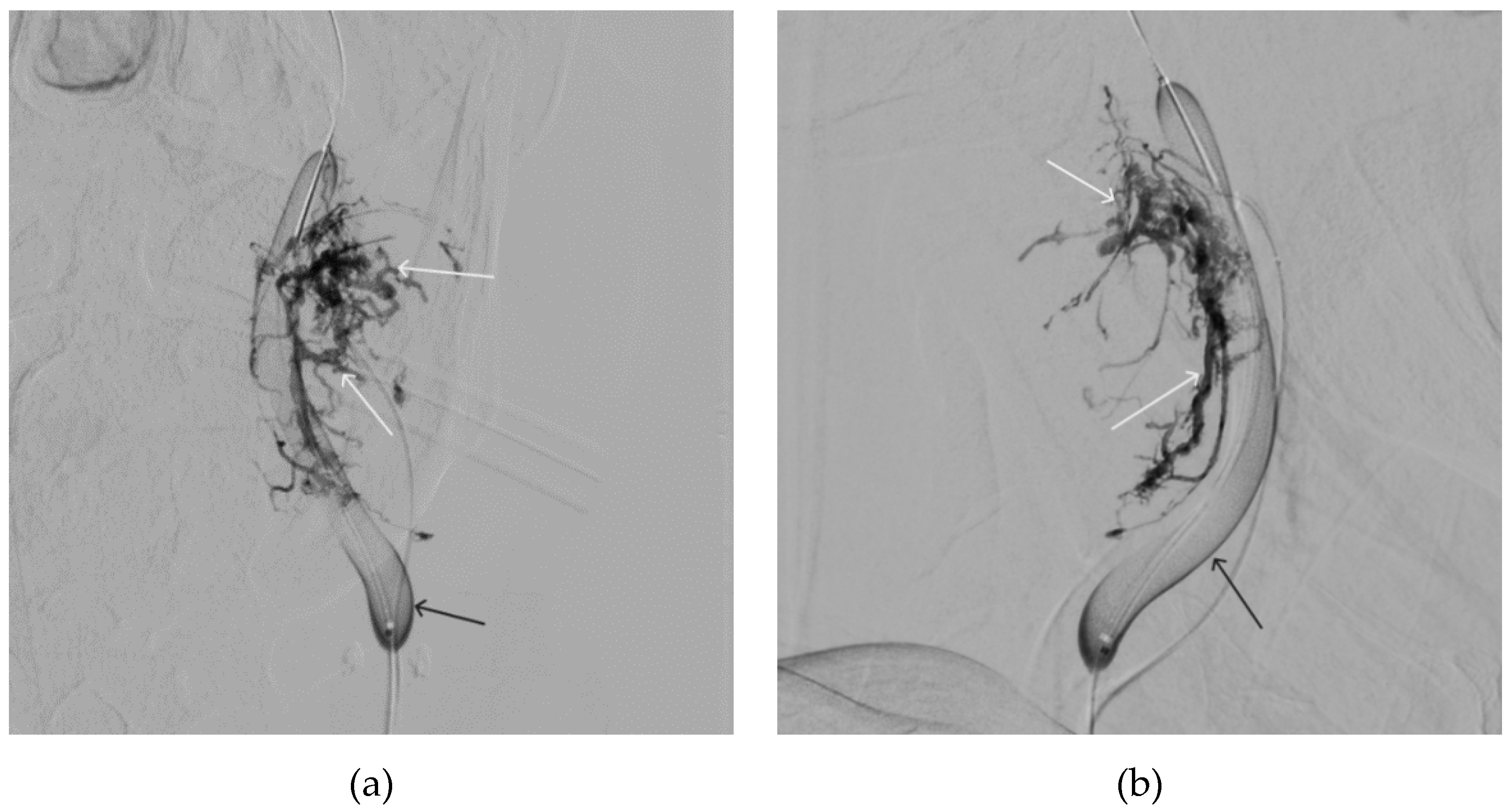
Figure 5.
X-ray in single shot mode. The NAGLEMs cast is visualized, filling the vascular network (the white arrow indicates the guiding catheter at the ostium of the left facial artery, the black arrow indicates the karst).
Figure 5.
X-ray in single shot mode. The NAGLEMs cast is visualized, filling the vascular network (the white arrow indicates the guiding catheter at the ostium of the left facial artery, the black arrow indicates the karst).
Figure 6.
Digital subtraction angiography from the right and left facial arteries: a - direct projection; b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate catheters at the ostium of the facial arteries, black arrows indicate embolizate karst). The absence of AVM contrast is noted.
Figure 6.
Digital subtraction angiography from the right and left facial arteries: a - direct projection; b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate catheters at the ostium of the facial arteries, black arrows indicate embolizate karst). The absence of AVM contrast is noted.
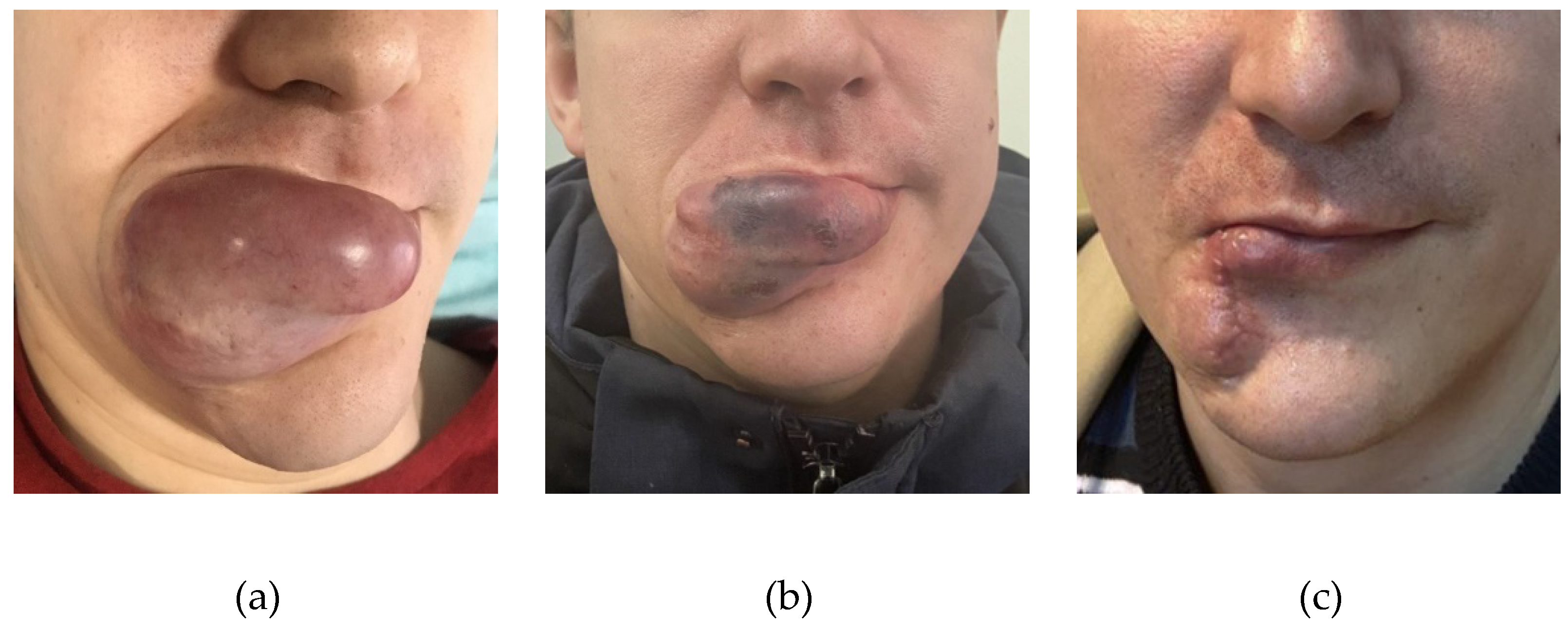
Figure 7.
a - The appearance of the AVM before embolization, b - the appearance of the AVM after embolization, c - the patient after surgical removal of the AVM.
Figure 7.
a - The appearance of the AVM before embolization, b - the appearance of the AVM after embolization, c - the patient after surgical removal of the AVM.
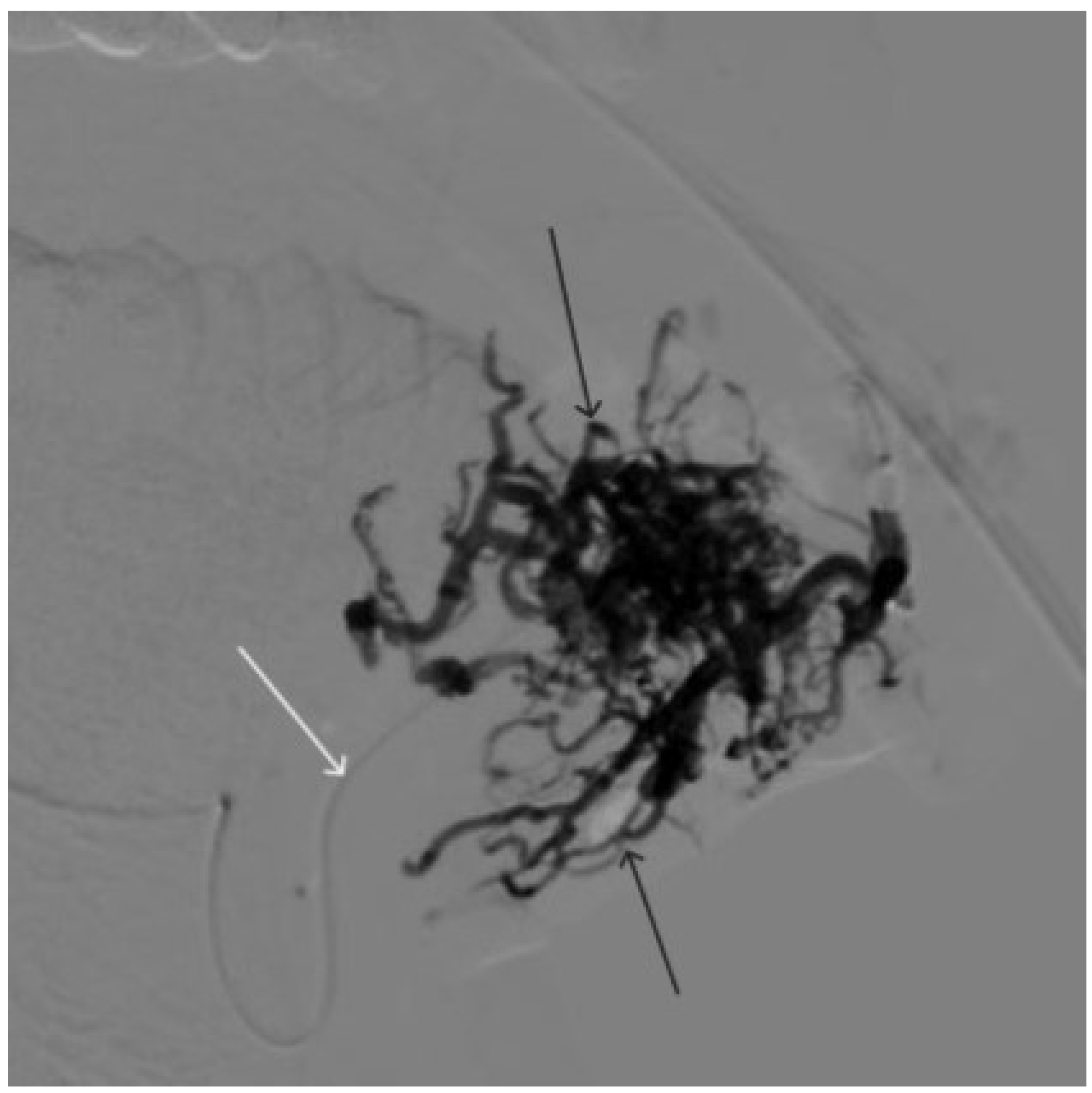
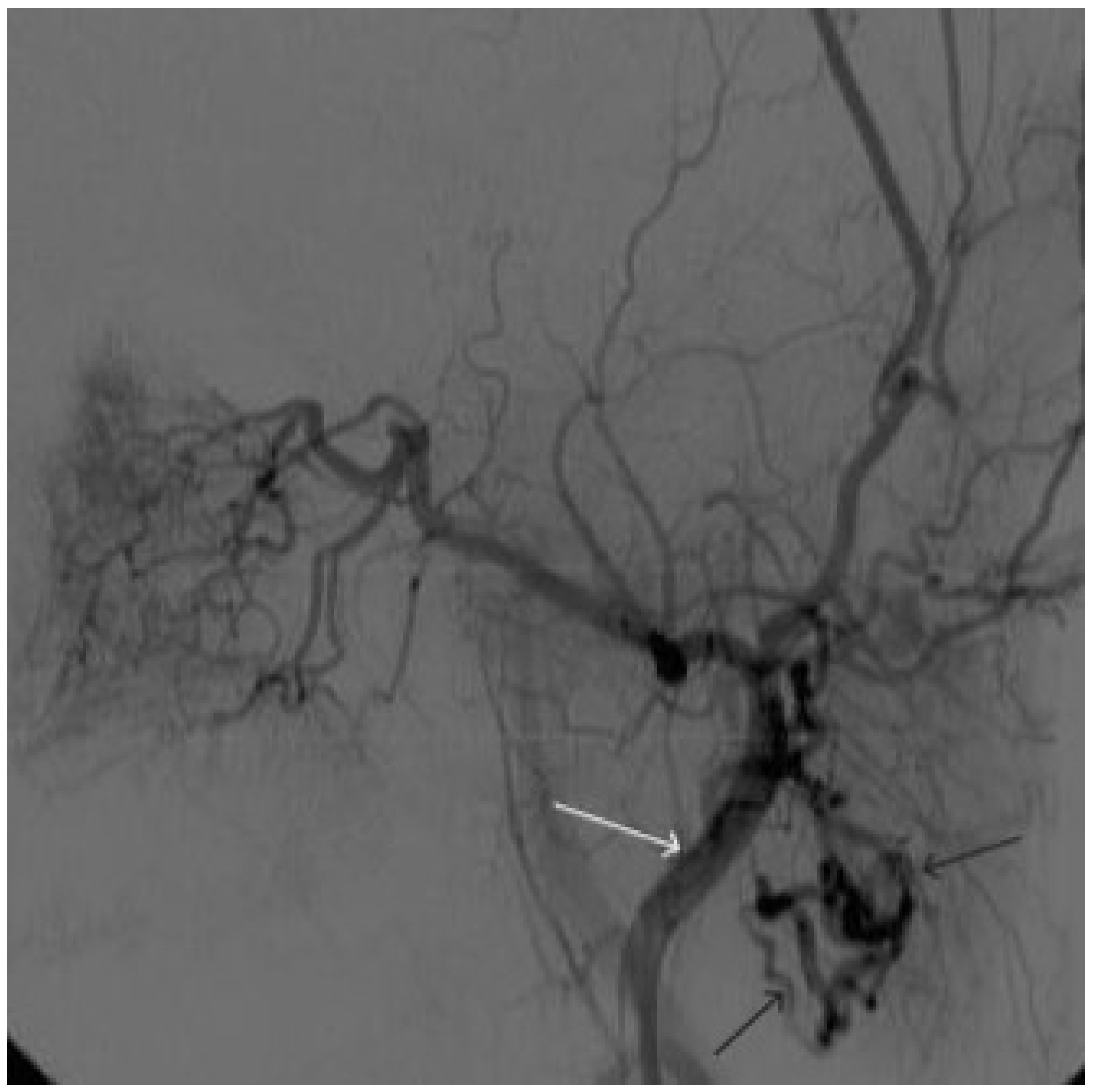
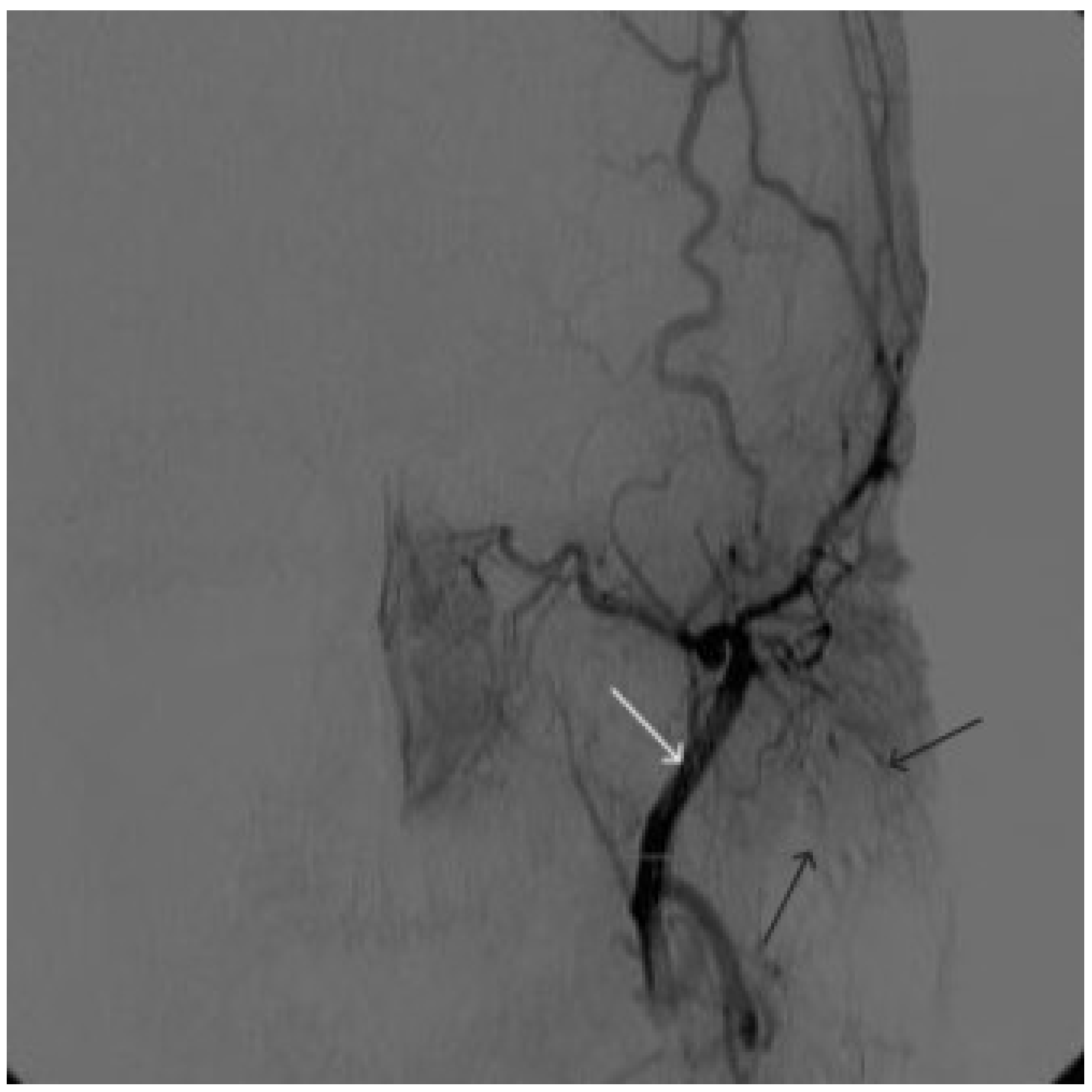
Figure 8.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left external carotid artery, direct projection (white arrow indicates catheter in the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate contrast AVM.
Figure 8.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left external carotid artery, direct projection (white arrow indicates catheter in the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate contrast AVM.
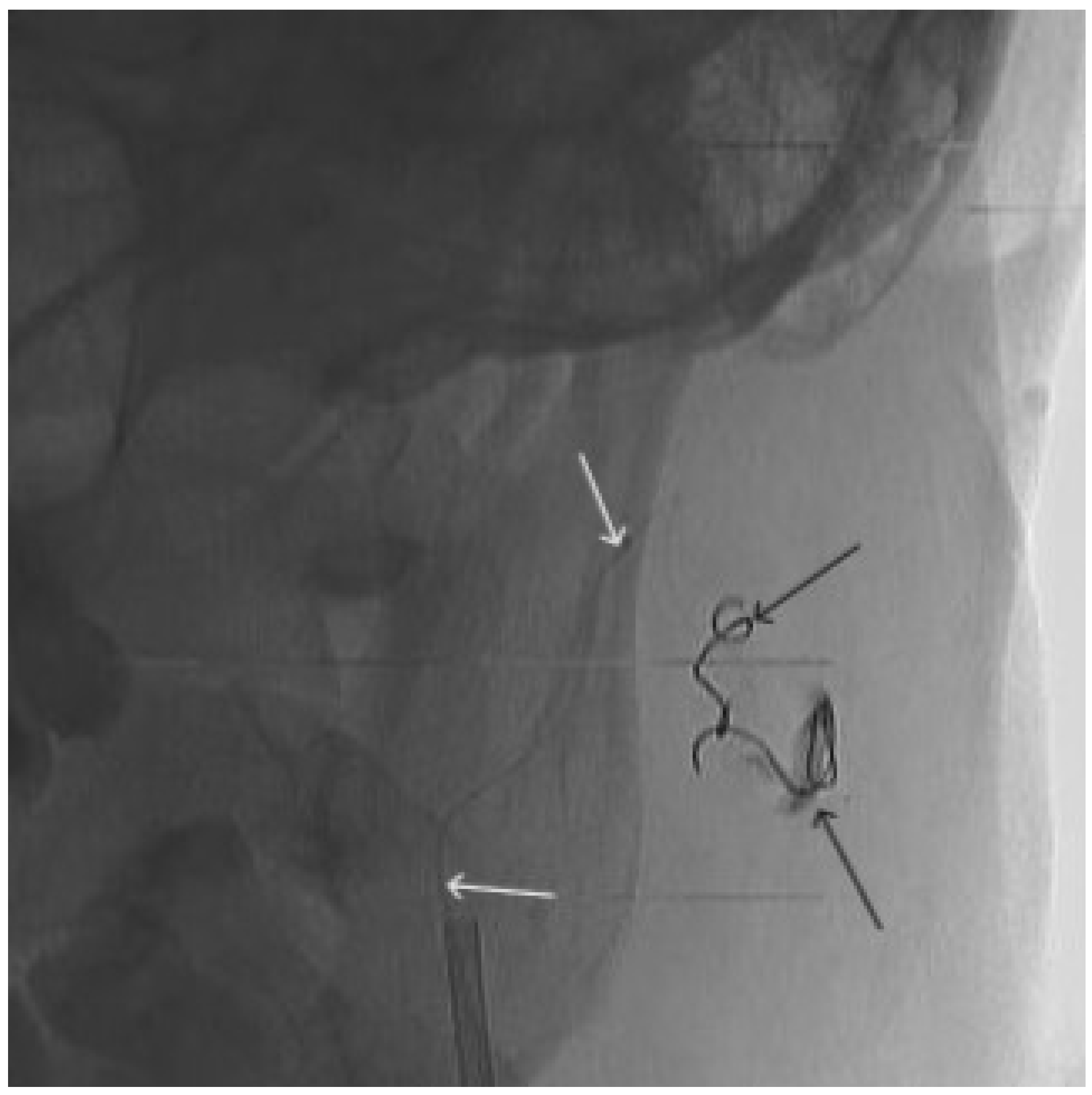
Figure 9.
X-ray, direct projection (the white arrow indicates a microcatheter in the left external carotid artery, the black arrows indicate a complex of microcoils from the previous stage of embolization.
Figure 9.
X-ray, direct projection (the white arrow indicates a microcatheter in the left external carotid artery, the black arrows indicate a complex of microcoils from the previous stage of embolization.
Figure 10.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left external carotid artery, direct projection (white arrow indicates the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate the boundaries of the filled AVM).
Figure 10.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left external carotid artery, direct projection (white arrow indicates the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate the boundaries of the filled AVM).
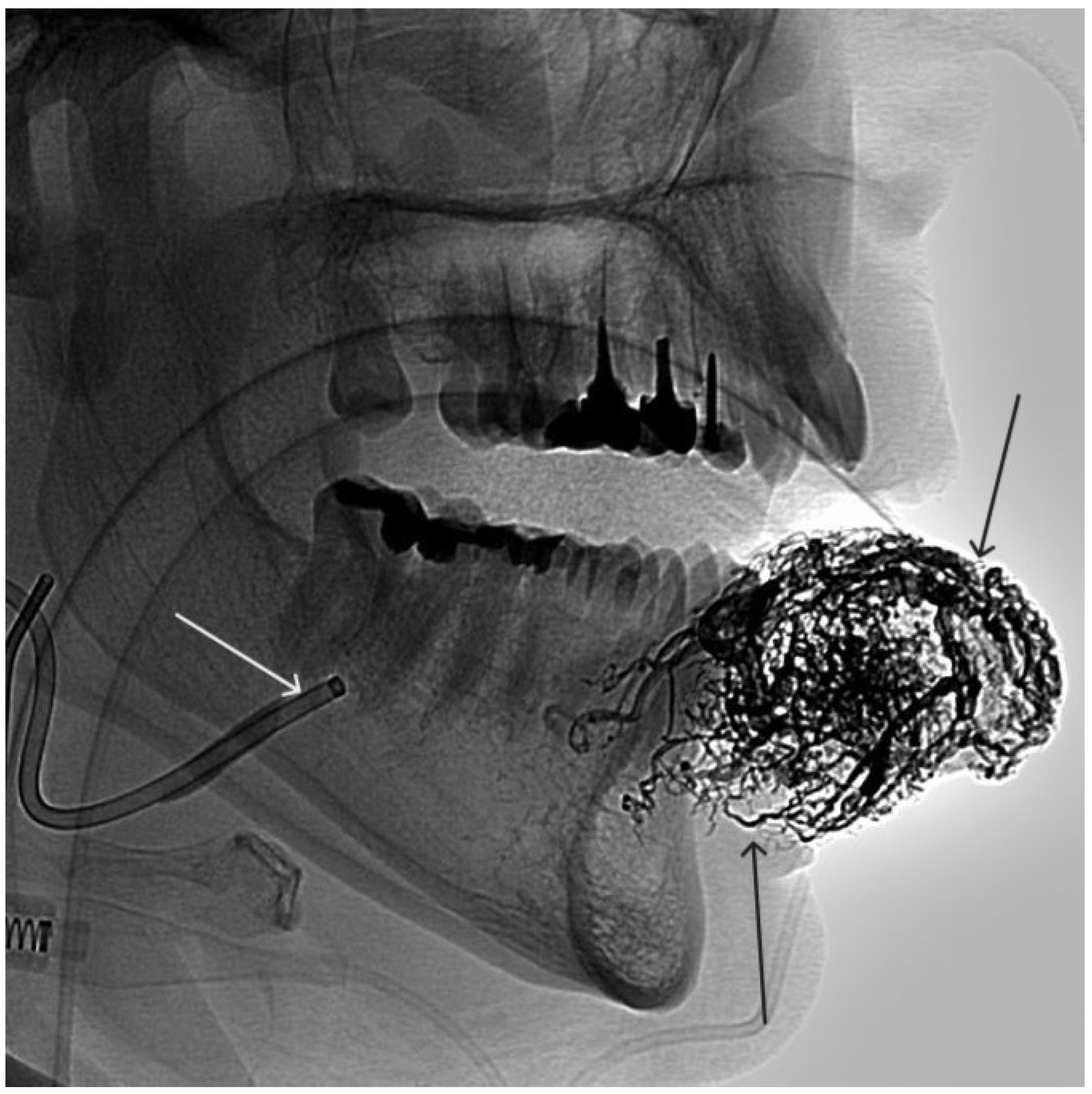
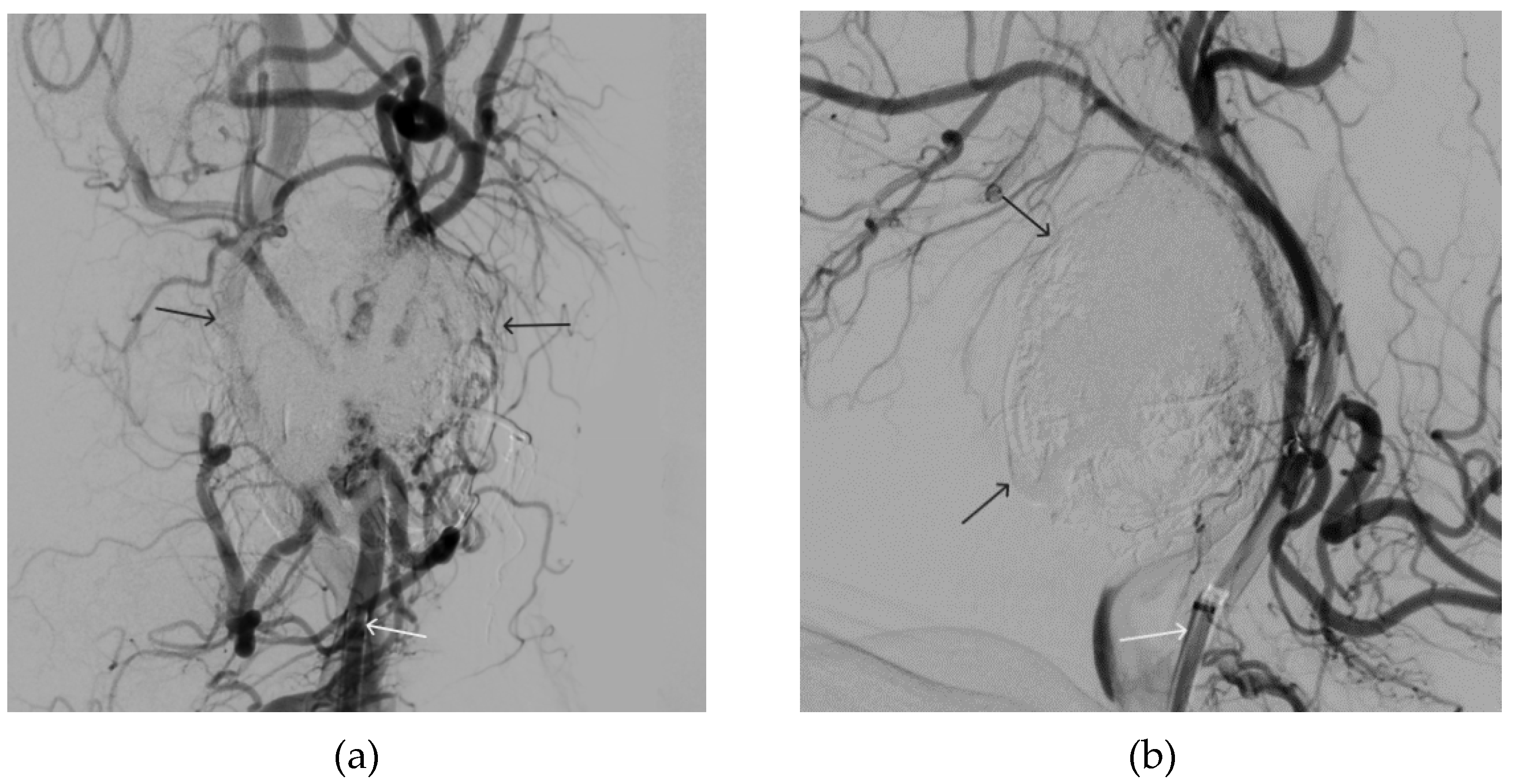
Figure 11.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left common carotid artery: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate the left internal carotid artery, long black arrows indicate the external carotid artery, short black arrows indicate the boundaries of the paraganglioma).
Figure 11.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left common carotid artery: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate the left internal carotid artery, long black arrows indicate the external carotid artery, short black arrows indicate the boundaries of the paraganglioma).
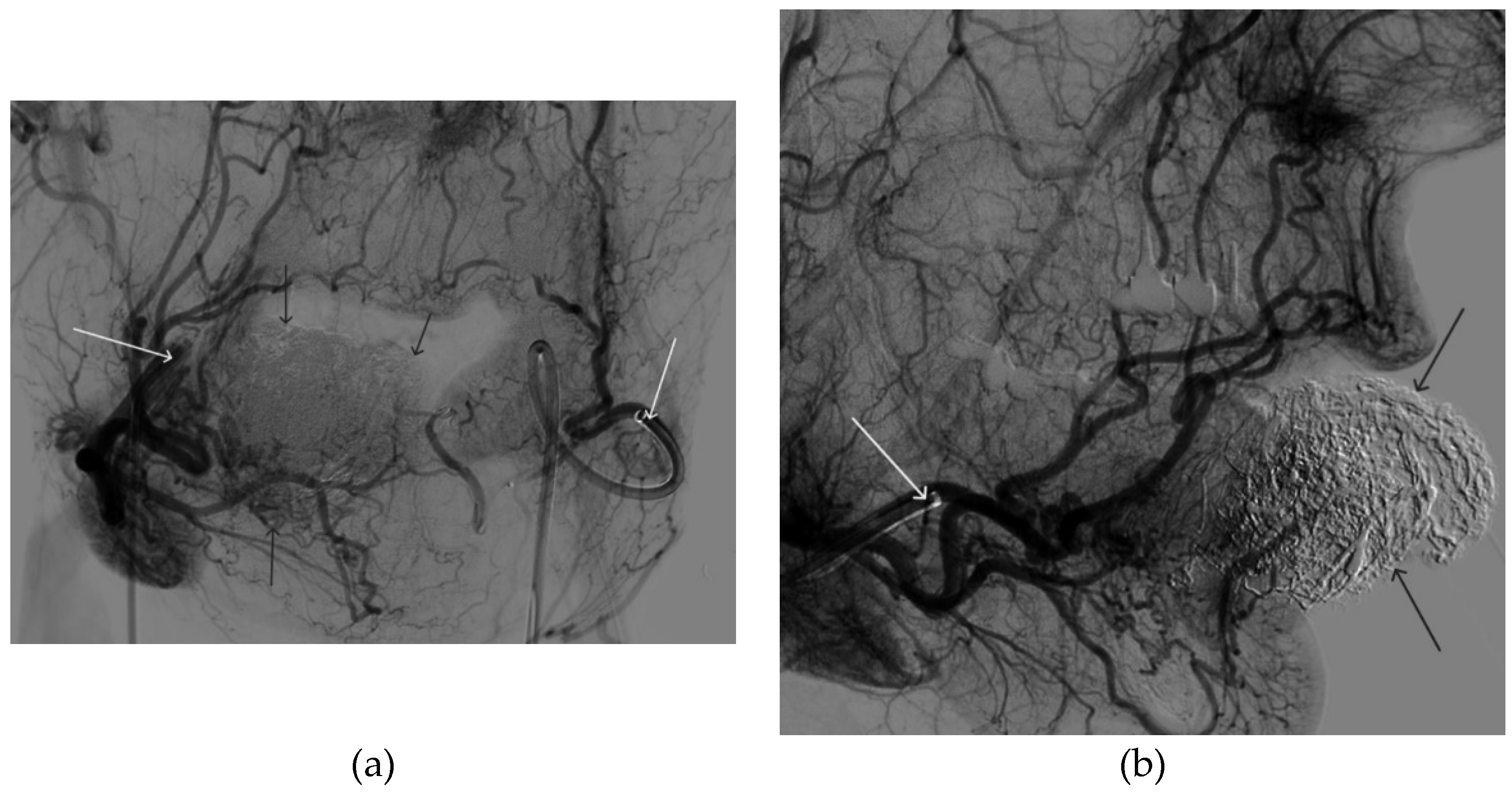
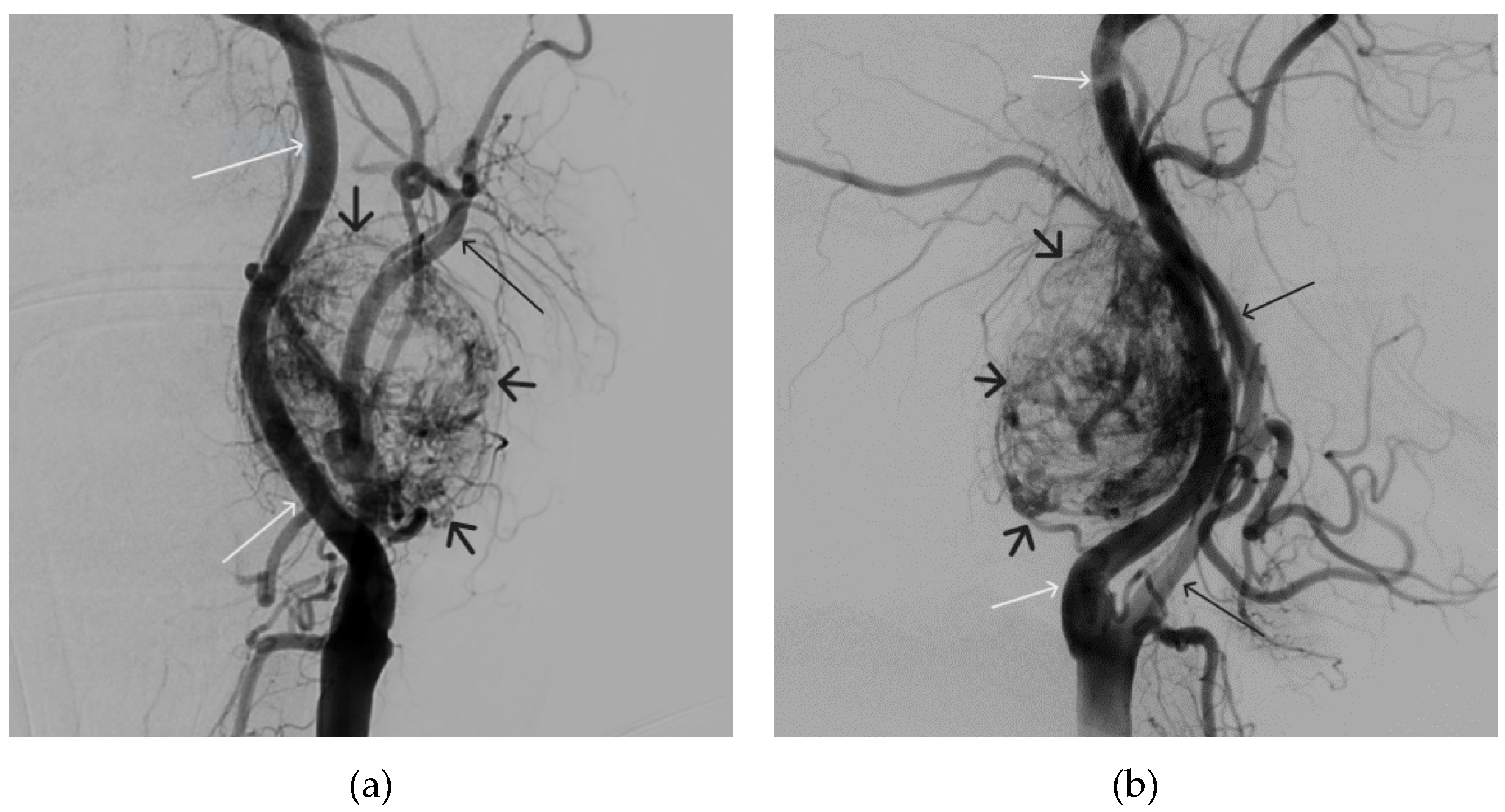
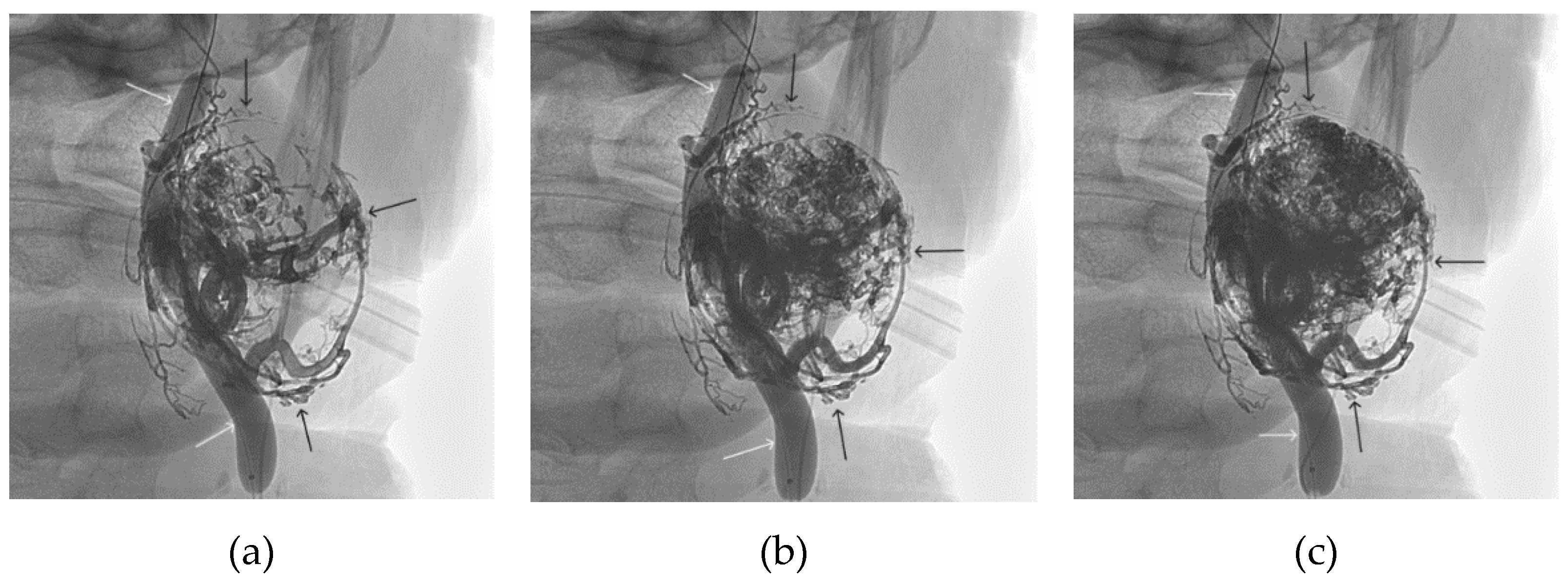
Figure 12.
Distribution of Onyx-18 along the vascular network of the paraganglioma: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate filling of the vascular network of the paraganglioma, black arrows indicate an inflated balloon in the left internal carotid artery).
Figure 12.
Distribution of Onyx-18 along the vascular network of the paraganglioma: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate filling of the vascular network of the paraganglioma, black arrows indicate an inflated balloon in the left internal carotid artery).
Figure 13.
X-ray in single shot mode. a, b and c – demonstrate gradual spreading of Onyx-18 (NAGLEMs cast) through the vascular network of the paraganglioma direct projections (black arrows indicate filling of the vascular network of the paraganglioma, white arrows indicate an inflated balloon in the left internal carotid artery).
Figure 13.
X-ray in single shot mode. a, b and c – demonstrate gradual spreading of Onyx-18 (NAGLEMs cast) through the vascular network of the paraganglioma direct projections (black arrows indicate filling of the vascular network of the paraganglioma, white arrows indicate an inflated balloon in the left internal carotid artery).
Figure 14.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left common carotid artery: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate the guiding catheter in the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate the boundaries of the embolized paraganglioma).
Figure 14.
Digital subtraction angiography from the left common carotid artery: a – direct projection, b - lateral projection (white arrows indicate the guiding catheter in the left external carotid artery, black arrows indicate the boundaries of the embolized paraganglioma).
Table 1.
Summary of the demographic and treatment data of two patient groups treated by NAGLEMs embolisation.
Table 1.
Summary of the demographic and treatment data of two patient groups treated by NAGLEMs embolisation.
| Variables |
Face AVMs
(n=5) |
Paragangliomas
(n=18) |
| Age (years), M ± SD |
42 ± 6 |
58 ± 12 |
| Sex (female/male) |
3/2 |
13/5 |
Number of treatment stages
(Me, Q₁ – Q₃) |
2, 2 - 2 |
1, 1 - 2 |
Number of NAEM embolisation steps
(Me, Q₁ – Q₃) |
1, 1 - 1 |
1, 1 - 2 |
| Open Surgical Interventions after embolization (%) |
3 (60,0 %) |
1 (5,6 %) |
| Coils while NAEM embolisation (%) |
none |
2 (11,1 %) |
| Total embolisation (%) |
5 (100 %) |
12 (66,7 %) |
| Type of catheter (%) |
Scepter C, XC (100 %)
(Microvention) |
Scepter C, XC (88,9 %)
Headway (11,1 %)
(Microvention) |
mRS before embolization
Me, Q₁ – Q₃ |
0, 0 - 0 |
1, 0 - 1 |
mRS at discharge
Me, Q₁ – Q₃ |
0, 0 - 1 |
1, 0 - 1 |