Submitted:
13 October 2023
Posted:
17 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Quality
2.1.1. Product and Equipment Edge System
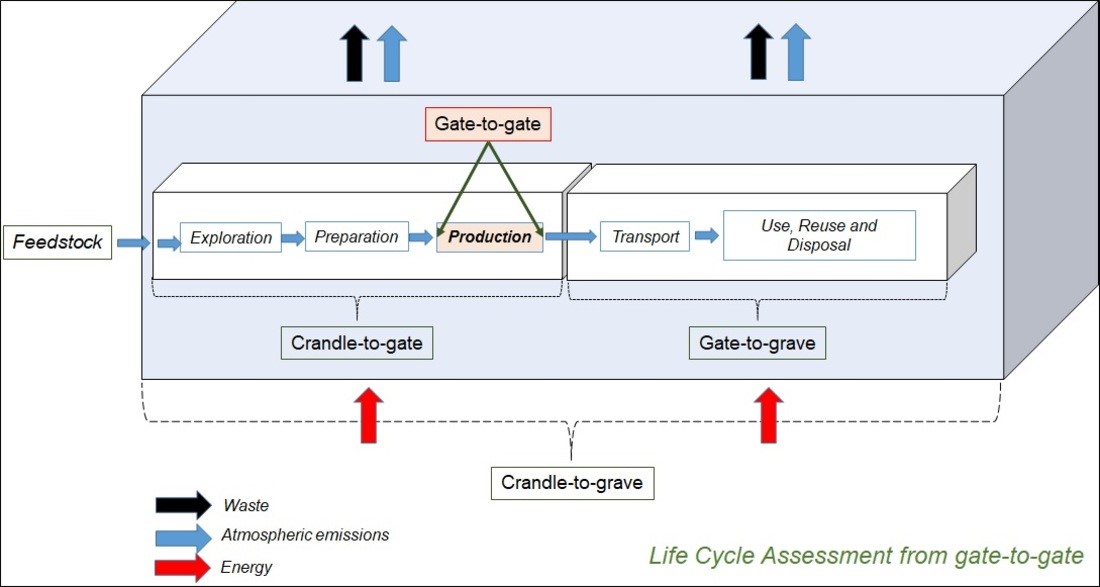
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory Analysis (LCI)
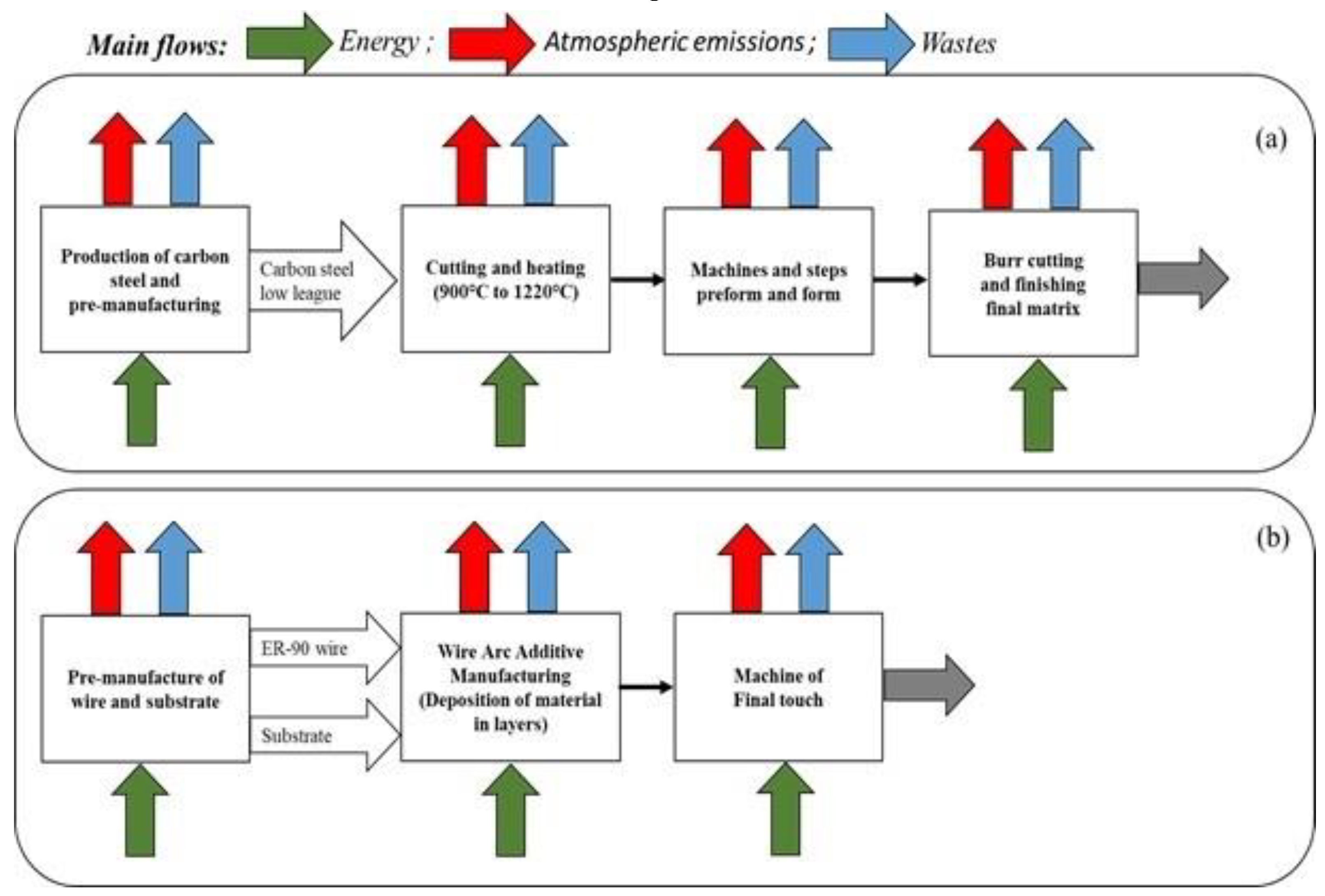
2.2.1. Conventional Manufacturing Data (Forging)
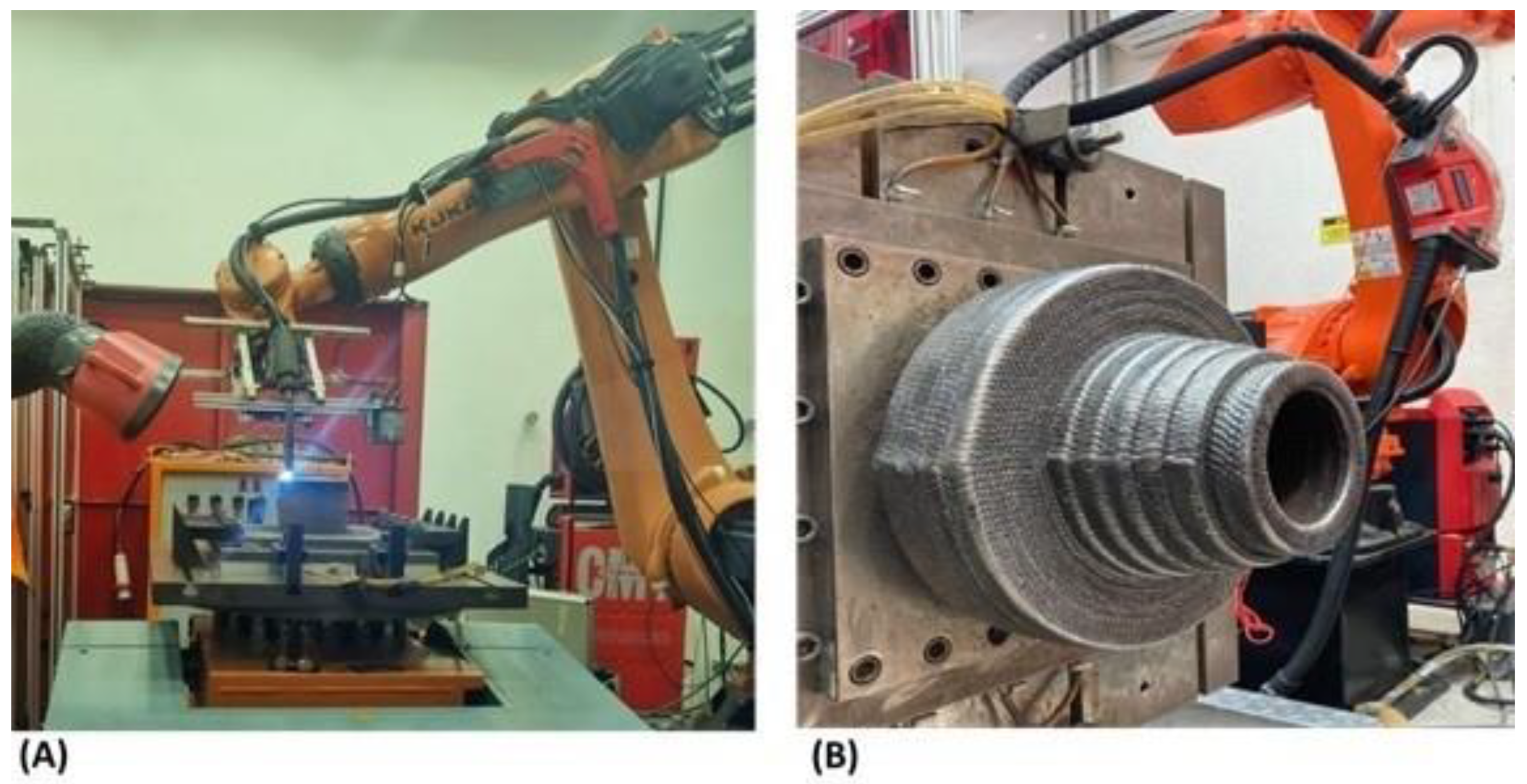
2.2.2. Impacts on WAAM Material Production and Pre-Manufacturing
2.3. Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA)
2.3.1. Calculation of Energy Demand in WAAM Process
2.3.2. Calculation of CO2e Emissions in WAAM Process
2.3.3. Calculation of Waste Generation from Conventional and Additive Manufacturing
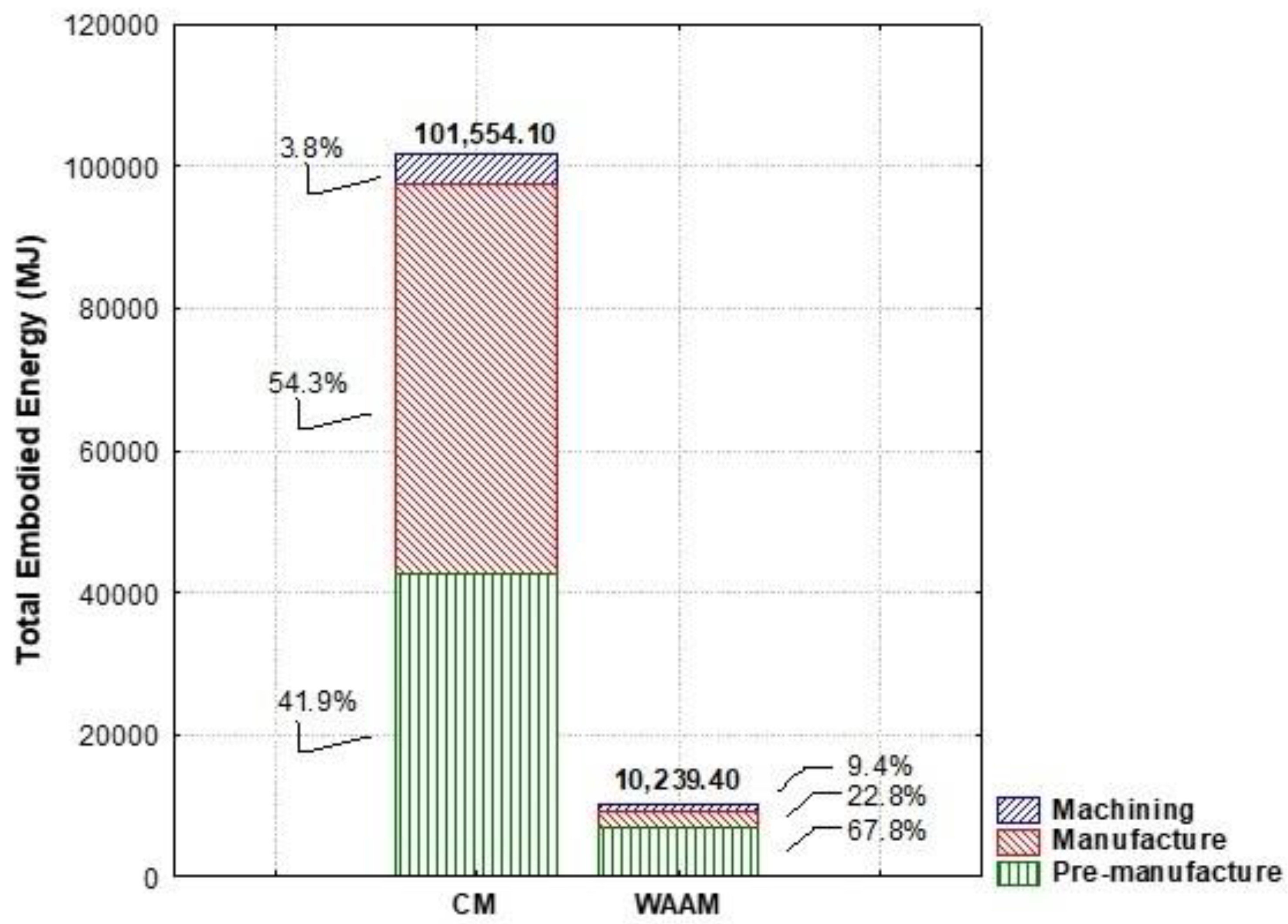
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Impact
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nuttah, M.M.; Roma, P.; Nigro, G.L.; Perrone, G. Understanding blockchain applications in Industry 4.0: From information technology to manufacturing and operations management. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, K.; Akman, G. Investigating changes of total quality management principles in the context of Industry 4.0: Viewpoint from an emerging economy. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao-Ubillos, J.; Camino-Beldarrain, V.; Intxaurburu-Clemente, G.; Velasco-Balmaseda, E. Industry 4.0 and potential for reshoring: A typology of technology profiles of manufacturing firms. Comput. Ind. 2023, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavacciuolo, L.; Ferraro, G.; Ponsiglione, C.; Primario, S.; Quinto, I. Technological innovation-enabling industry 4.0 paradigm: A systematic literature review. Technovation 2023, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wang, K.; Lee, P.K.; Yeung, A.C. The impact of industry 4.0 on supply chain capability and supply chain resilience: A dynamic resource-based view. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, C.L.; Al Aziz, R.; Ahmed, T.; Misbauddin, S.; Moktadir, A. Impact of industry 4.0 technologies on sustainable supply chain performance: The mediating role of green supply chain management practices and circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. Sazzadur Rahman, Tapotosh Ghoshb, Nahid Ferdous Aurna, M. Shamim Kaiser, Mehrin Anannya, A.S.M. Sanwar Hosend. Machine learning and internet of things in industry 4.0: A review. Meas.: Sens. 2023, 28, 100822 [CrossRef].
- Mohd Javaid, AbidHaleem,Ravi Pratap Singh,Rajiv Suman. An integrated outlook of Cyber–Physical Systems for Industry 4.0: topical practices, architecture, and applications. Green Technologies and Sustainability. 2023, 1, 1000001 [CrossRef].
- Hajoary, P.K. Industry 4.0 Maturity and Readiness- A case of a Steel Manufacturing Organization. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 217, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiemwonyi, O.; Alam, M.N.; Hago, I.E.; Azizan, N.A.; Hashim, F.; Hossain, S. Green innovation behaviour: Impact of industry 4.0 and open innovation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, C.K.; Leong, K.F. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Principles and Applications: The 5th Edition of Rapid Prototyping: Principles and Applications; WSPC: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebler, M.; Schoot Uiterkamp, A.J.M. , Visser, C. A global sustainability perspective on 3D printing technologies. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, G.; Psarommatis, F. Maximizing Energy Efficiency in Additive Manufacturing: A Review and Framework for Future Research. Energies 2023, 16, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ding, D.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Norrish, J. A review of the wire arc additive manufacturing of metals: properties, defects and quality improvement. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samruddha Kokare, J.P. Oliveira, Radu Godina. Life cycle assessment of additive manufacturing processes: A review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 60, 536–559 [CrossRef]. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM F42/ISO TC 261 Develops Additive Manufacturing Standards. ASTM International, 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/COMMIT/F42_AMStandardsStructureAndPrimer.pdf (accessed on 10 Oct. 2022).
- ASTM. F2792-12a Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies, ASTM International. West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, 2012. Available online: https://www.astm.org/f2792-12a.html (accessed on 10 Oct 2022).
- ASTM International.: Committee F42 on additive manufacturing Technologies, 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/COMMITTEE/F42.htm (accessed on 10 Oct. 2022).
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. Wire-feed additive manufacturing of metal components: technologies, developments and future interests. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priarone, P.C.; Campatelli, G.; Montevecchi, F.; Venturini, G.; Settineri, L. A modelling framework for comparing the environmental and economic performance of WAAM-based integrated manufacturing and machining. CIRP Ann. 2019, 68, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, K.; Srinivas, M.N.; Rajak, S. Wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminium alloys: A review. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 41, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samruddha Kokare, J.P. Oliveira, Radu Godina. A LCA and LCC analysis of pure subtractive manufacturing, wire arc additive manufacturing, and selective laser melting approaches. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 67–85 [CrossRef]. [Google Scholar]
- Priarone, P.C.; Campatelli, G.; Catalano, A.R.; Baffa, F. Life-cycle energy and carbon saving potential of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing for the repair of mold inserts. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar Hussain Shah, Nicolas Hadjipantelis, Lulu Walter, Rupert J. Myers, Leroy Gardner. Environmental life cycle assessment of wire arc additively manufactured steel structural componentes. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 389, 136071 [CrossRef].
- Caldeira-Pires, A; Souza-Paula, M.C. De & Villas Bôas, R.C. A Avaliação do ciclo de vida: a ISO 14040 na América Latina. Brasília: Abipti, 2005, pp.337.
- Ferreira, H.; Leite, M.G.P. A Life Cycle Assessment study of iron ore mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Bacenetti, J.; Adamczyk, J.; Ferrante, V.; Messineo, A.; Huisingh, D. Investigating energy and environmental issues of agro-biogas derived energy systems: A comprehensive review of Life Cycle Assessments. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, S.; Das, B.B. Life Cycle Assessment of construction materials: Methodologies, applications and future directions for sustainable decision-making. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Iain Sword, Alexander Gallowa, Athanasios Toumpi. An environmental impact comparison between wire +arc additive manufacture and forging for the production of a titanium componente. SM&T. 2023, 36, e00600 2005 [CrossRef].
- Da Silva GA, Kulay LA. Environmental performance comparison of wet and termal routes for phosphate fertilizer production using LCA—a Brazilian experience. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 1321–5 [CrossRef].
- Benedikt Nilges, C’elia Burghardt, Kosan Rohb, Christiane Reinert, Niklas von der Aßen. Comparative life cycle assessment of industrial demand-side management via operational optimization. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 177, 108323 [CrossRef].
- Farjana, S.H.; Tokede, O.; Tao, Z.; Ashraf, M. Life cycle assessment of end-of-life engineered wood. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 887, 164018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L. Life cycle assessment and multi-objective optimization for industrial utility systems. Energy 2023, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhausen, R.; Rostek, L.; Miao, Z.C.; Zeller, V. Combinations of material flow analysis and life cycle assessment and their applicability to assess circular economy requirements in EU product regulations. A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, A.; Arosio, V.; Peressut, A.B.; Latorrata, S.; Dotelli, G. Greenhouse Gas Implications of Extending the Service Life of PEM Fuel Cells for Automotive Applications: A Life Cycle Assessment. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ige, O.E.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Different Portland Cement Types in South Africa. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, G.; De Gisi, S.; Todaro, F.; Notarnicola, M. Environmental Comparison of Different Mechanical–Biological Treatment Plants by Combining Life Cycle Assessment and Material Flow Analysis. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.A. Life Cycle Assessment: a review of the methodology and its application to sustainability. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Ekvall, T.; Guinée, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Hellweg, S.; Koehler, A.; Pennington, D.; Suh, S. Recent developments in Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, A.C.; Rohwer, M.B.; Friedrich, E.; von Blottnitz, H. Status of life cycle assessment and engineering research in South Africa. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2002, 7, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hischier R, Ugaya C, Anderi da Silva G, lamb CMR, Rodriguez D. Capacity building for a national life cycle inventory database—lessons learned in real world. Case study of Swiss-Brazilian capacity building Project. 2nd International Conference on Life Cycle Assessment (CILCA), São Paulo, Brazil; 2007.
- de Eicker, M.O.; Hischier, R.; Kulay, L.A.; Lehmann, M.; Zah, R.; Hurni, H. The applicability of non-local LCI data for LCA. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margarita Ossés de Eiker, Roland Hischier, Hans Hurni, Rainer Zah. Using non-local databases for the environmental assessment of industrial activies: The case of Latin America. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 145–157 [CrossRef].
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P.; Gao, W.; Qin, F.; Wu, X.; Xiong, J. Efficiency and sustainability analysis of biogas and electricity production from a large-scale biogas project in China: an emergy evaluation based on LCA. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Association of Technical Standards. ABNT NBR ISO 14040: Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and structure. Brazil, 2009a.
- Brazilian Association of Technical Standards. ABNT NBR ISO 14044: Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. Brazil, 2009b.
- Priarone, P.C.; Ingarao, G.; Lunetto, V.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Settineri, L. The Role of re-design for Additive Manufacturing on the Process Environmental Performance. Procedia CIRP 2018, 69, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Aço Brasil. Relatório 2020 de Sustentabilidade. 2021. Available online: https://acobrasil.org.br/relatoriodesustentabilidade/index.html (accessed on 17 Feb. 2023).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Informação em Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovações e Comunicações (IBICT). O que é Avaliação do Ciclo de Vida. Available online: http://acv.ibict.br/ (accessed on 19 Apr. 2023).
- ELCD Europian Reference Life Cycle Database. 2009. Available online: https://data.jrc.ec.europa.eu/collection/EPLCA (accessed on 05 Aug. 2023).
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Forest Lands. In Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Hayama, Japan, 2006; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- IEA—Energy Technology Perspectives 2020, Energy Technology Perspectives; 2020.

| Sustainability Indicator | Reference | Process and Material | Average (2018–2020) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GHG emissions (kg CO2e kg-1 crude steel) |
Brazil Steel Institute: World Steel Association | Crude steel production | 1.8 |
| Brazil Steel Institute: IPCC methodology (2021) | Crude steel production | 1.7 | |
| OpenLca: IMPACT 2002+ | Hot rolling of steel | 1.846 | |
| Steel drawing | 0.455 | ||
| OpenLca: ReCiPe 2016Midpoint (H) | Hot rolling of steel | 1.959 | |
| Steel drawing | 0.495 | ||
| OpenLca: IPCC 2013 GWP 100a | Hot rolling of steel | 1.926 | |
| Steel drawing | 0.486 | ||
| Solid waste (kg kg-1 crude steel) |
Brazil Steel Institute | Specific generation of Co-products and wastes |
0.620 |
| Embodied energy (MJ kg-1 crude steel) |
World Steel Association | Crude steel production | 20.4 |
| Layer gap in flange thickening | Cords per layer | Waiting time per cord (min) | Total waiting time between cords (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | 9 | 2 | 80 |
| 6-7 | 8 | 28 | |
| 8-9 | 7 | 24 | |
| 10-11 | 6 | 20 | |
| 12-13 | 5 | 16 | |
| 14-41 | 4 | 168 | |
| Total time spent waiting between cords (min): | 336 | ||
| Waiting time between layers (min): | 4.5 | ||
| Number of layers: | 41 | ||
| Total time spent waiting between layers (min): | 180 | ||
| Number of layers in the central cylinder deposition (each layer has 1 cord): |
120 | ||
| Waiting time between layers (min): | 2 | ||
| Total time spent waiting between layers in the central cylinder (min): | 238 | ||
| Total time spent during WAAM initialization and adjustment (min) | 30 | ||
| Total time spent with WAAM in stand-by (Tmasb) | 784 | ||
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Electrical power demand: Machining machine 1 (inside diameter machining) |
23.18 kW |
| Total time on Machine 1 | 4 hours |
| Electrical power demand: Machining machine 2 (parts drilling machining) |
17.31 kW |
| Total time on Machine 2 | 10 hours |
| Gases present in the shielding gas |
Total volume ( L) used in the process |
Total mass (kg) used in the process |
GHG emissions (kg CO2e) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ar | 255.0 | 79,18 | 70,0 |
| CO2 (8%) | 24.3 | 8,31 | 23,4 |
| Total present in shielding gas (Cfgas) | 93,4 | ||
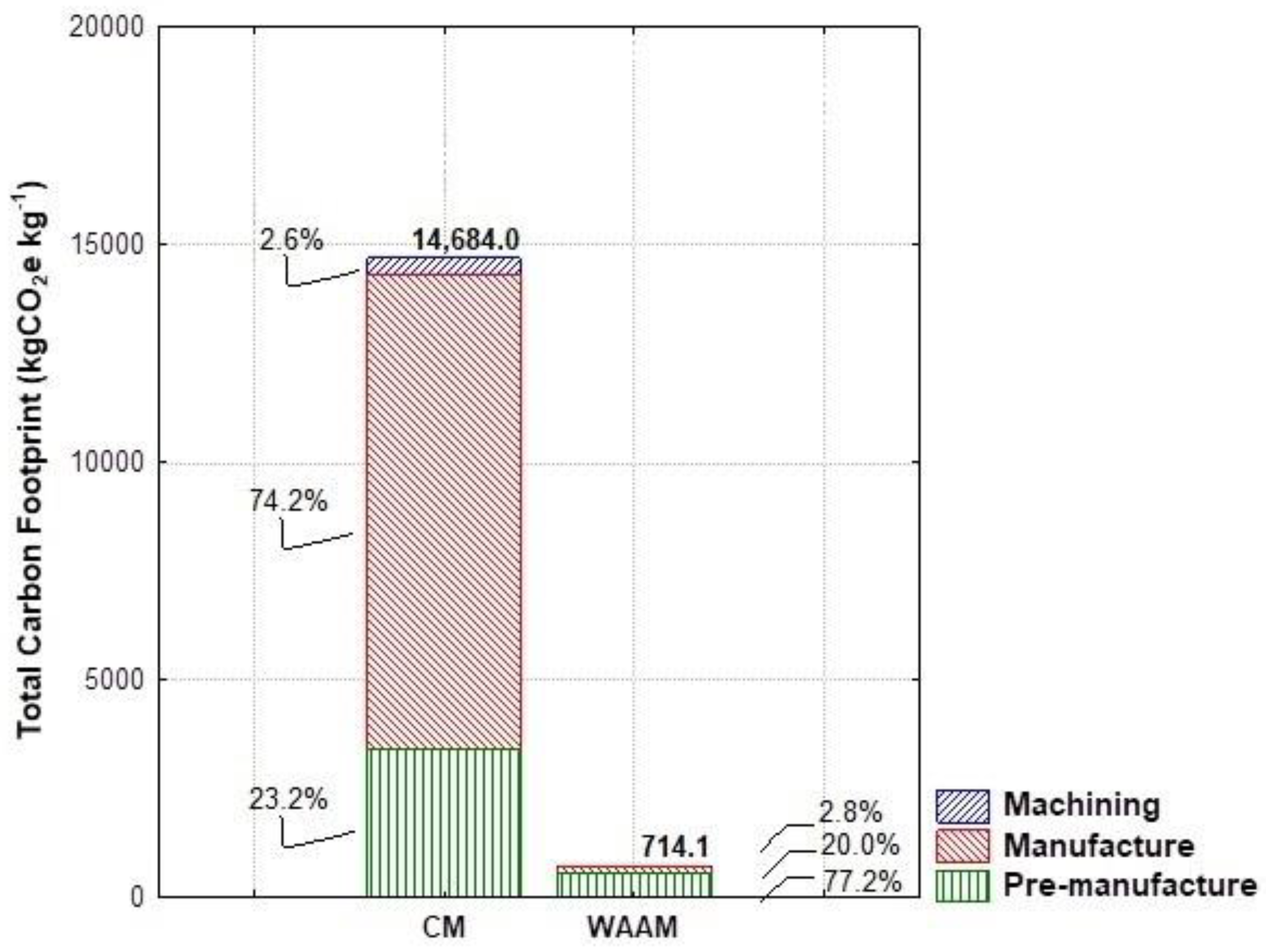
| Conventional Manufacturing Results | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-manufacture (step 1) | ||
| Embodied specific energy | 125 | MJ kg-1 |
| Specific carbon footprint ratio | 10 | kg CO2e Kg-1 |
| Mass of material used | 340.50 | kg |
| Total Embodied energy | 42,561.90 | MJ |
| Total Carbon Footprint | 3,404.95 | kg CO2e |
| Subtractive Manufacturing (step 2 and 3) | ||
| Specific energy consumption | 45 | kWh kg-1 |
| Specific carbono footprint ratio | 32 | kgCO2e Kg-1 |
| Total Embodied Energy | 55,160.20 | MJ |
| Total Carbon Footprint | 10,895.85 | kg CO2e |
| Machining (step 4) | ||
| Embodied specific energy | 40 | MJ kg-1 |
| Specific carbono footprint ratio | 4 | kgCO2e Kg-1 |
| Total Embodied Energy | 3,832.0 | MJ |
| Total Carbon Footprint | 383.2 | kg CO2e |
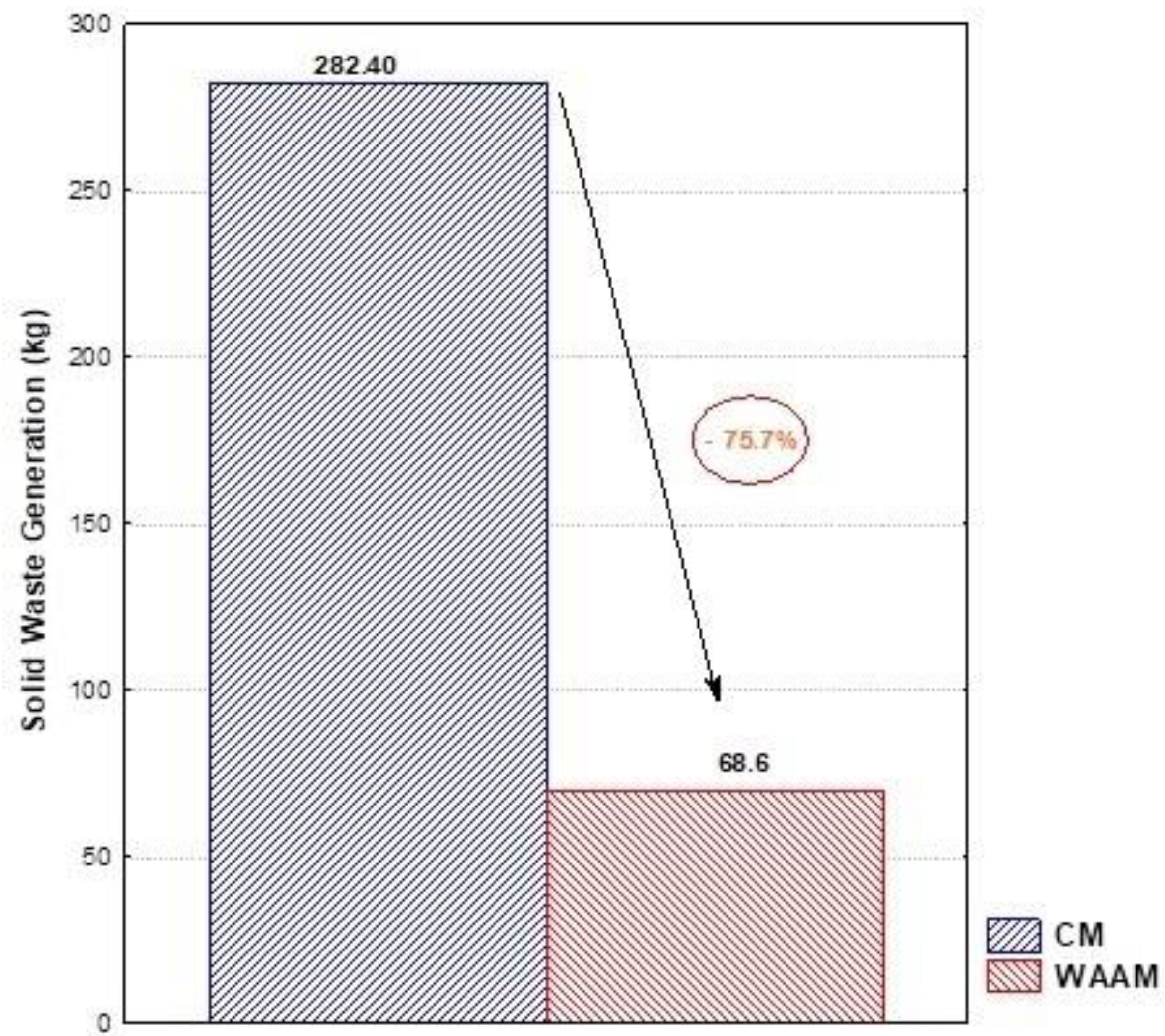
| Solid Waste Generation | ||
| Block volume | 0.04332 | m³ |
| Steel density | 7.860 | Kg m-³ |
| Mass of material used | 340.5 | kg |
| Final part mass (post machining) | 58.1 | kg |
| Solid Waste generated | 282.40 | kg |
| WAAM results | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-manufacture (step 1) | ||
| Embodied specific energy | 54.8 | MJ kg-1 |
| Specific carbon footprint ratio | 4.35 | kgCO2e Kg-1 |
| Total mass of the flange once deposited | 126.7 | kg |
| Total Embodied Energy | 6943.2 | MJ |
| Total Carbon Footprint | 551.1 | kgCO2e |
| Additive Manufacturing—deposition (step 2 and 3) | ||
| WAAM system power demand in stand-by mode (Pmasb) | 0.0426 | kW |
| Total stand-by time (Tmasb) | 13.07 | hours |
| Waam system power demand in operation (Pmad) | 3.5 | kW |
| Time spent in deposition (Tmad) | 61.1 | hours |
| Embodied energy of shielding gas (Egas) | 0.0285 | MJ L-1 |
| Shielding gas consumption flow (Cg) | 15.0 | L min-1 |
| WAAM unit process electrical energy demand (EWAAM2) | 2339.1 | MJ |
| Carbon Emission Factor of the local electricity network | 0.0759 | kgCO2e kWh-1 |
| Carbon Footprint in WAAM2 | 142.82 | kgCO2e |
| Machining | ||
| Electrical power demand in machining 1 (Pmq1) | 23.18 | kW |
| Total time 1 (Tmq1) | 4 | hours |
| Electrical power demand in machining 2 (Pmq2) | 17.314 | kW |
| Total time 2 (Tmq2) | 10 | hours |
| WAAM unit process electrical energy demand (EWAAM3) | 957.10 | MJ |
| Carbon Footprint in WAAM3 | 20.19 | kgCO2e |
| Solid Waste Generation | ||
| Mass deposited at WAAM (initial mass) | 95.8 | kg |
| Substrate mass | 30.9 | kg |
| Total mass deposited initially | 126.7 | kg |
| Mass of the final part (after machining) | 58.1 | kg |
| Waste generated | 68.6 | kg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





