Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sodium alginate oxidation
2.2. Nano-hydroxyapatite synthesis
2.3. Analyses methods and techniques
3. Results and Discussion
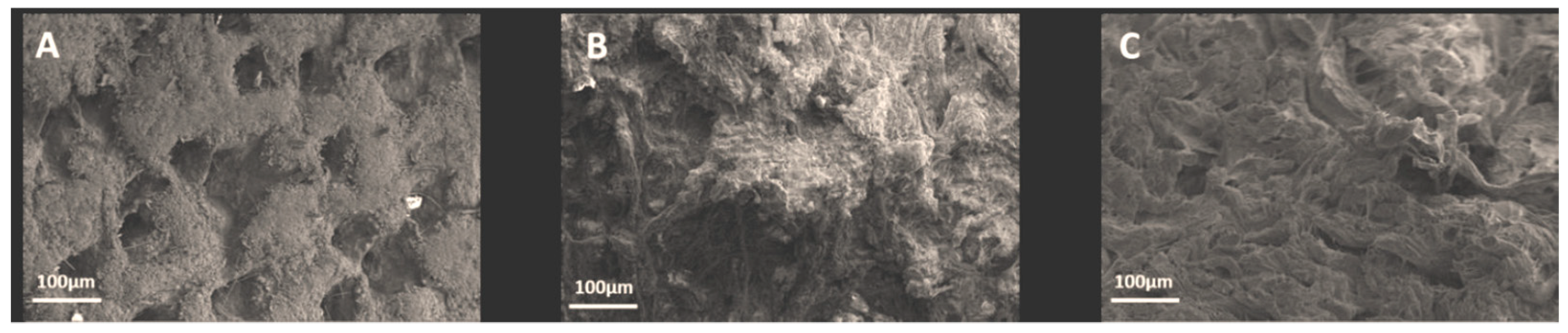
3.1. Laboratory scale tanning test using OSA and nano-HAp: study of their interaction with collagen using micro-DSC, NMR-MOUSE, ATR-FTIR and SEM-EDS
3.1.1. Hydrothermal stability of collagen-OSA chemical matrix by micro-DSC
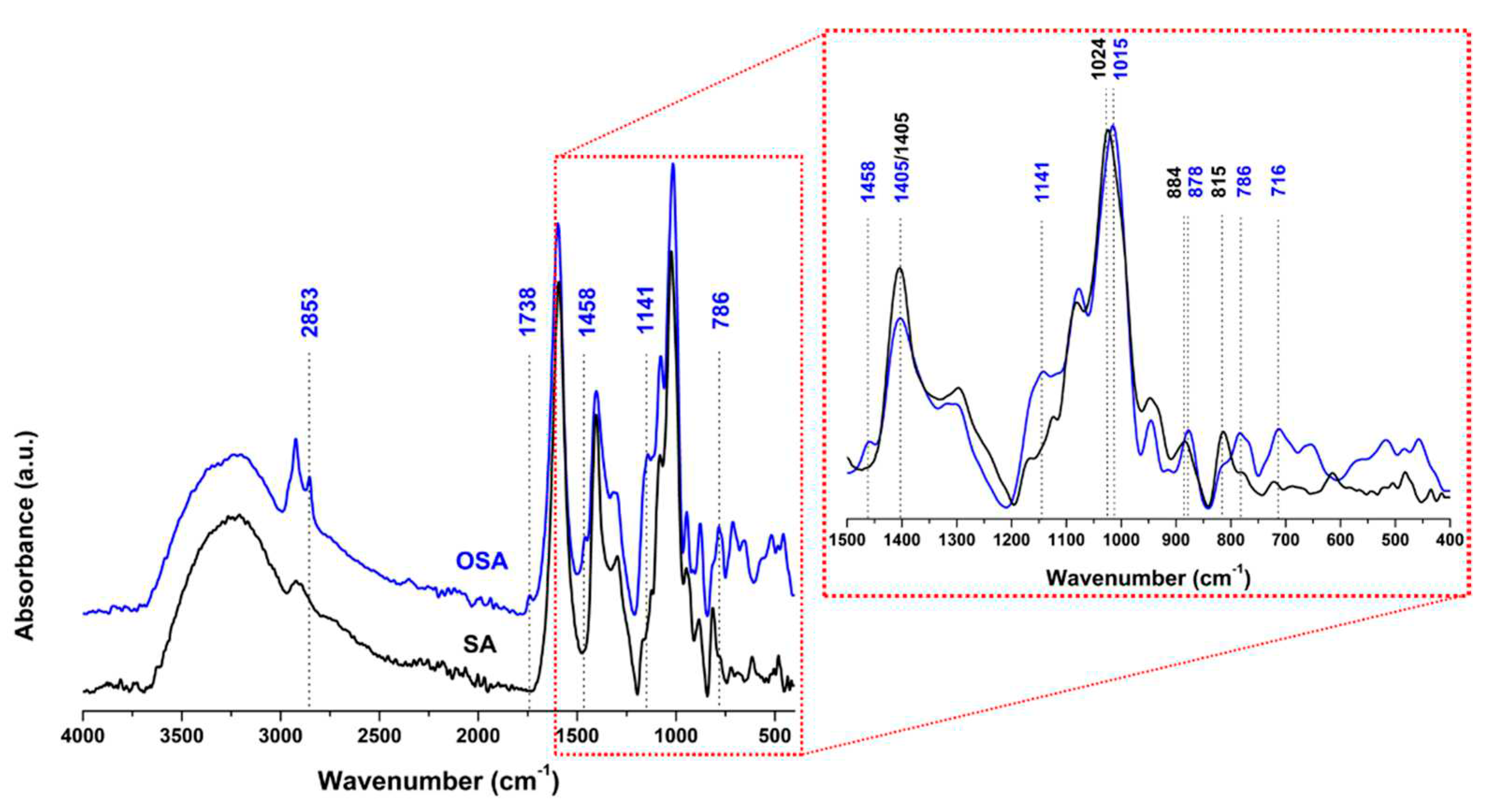
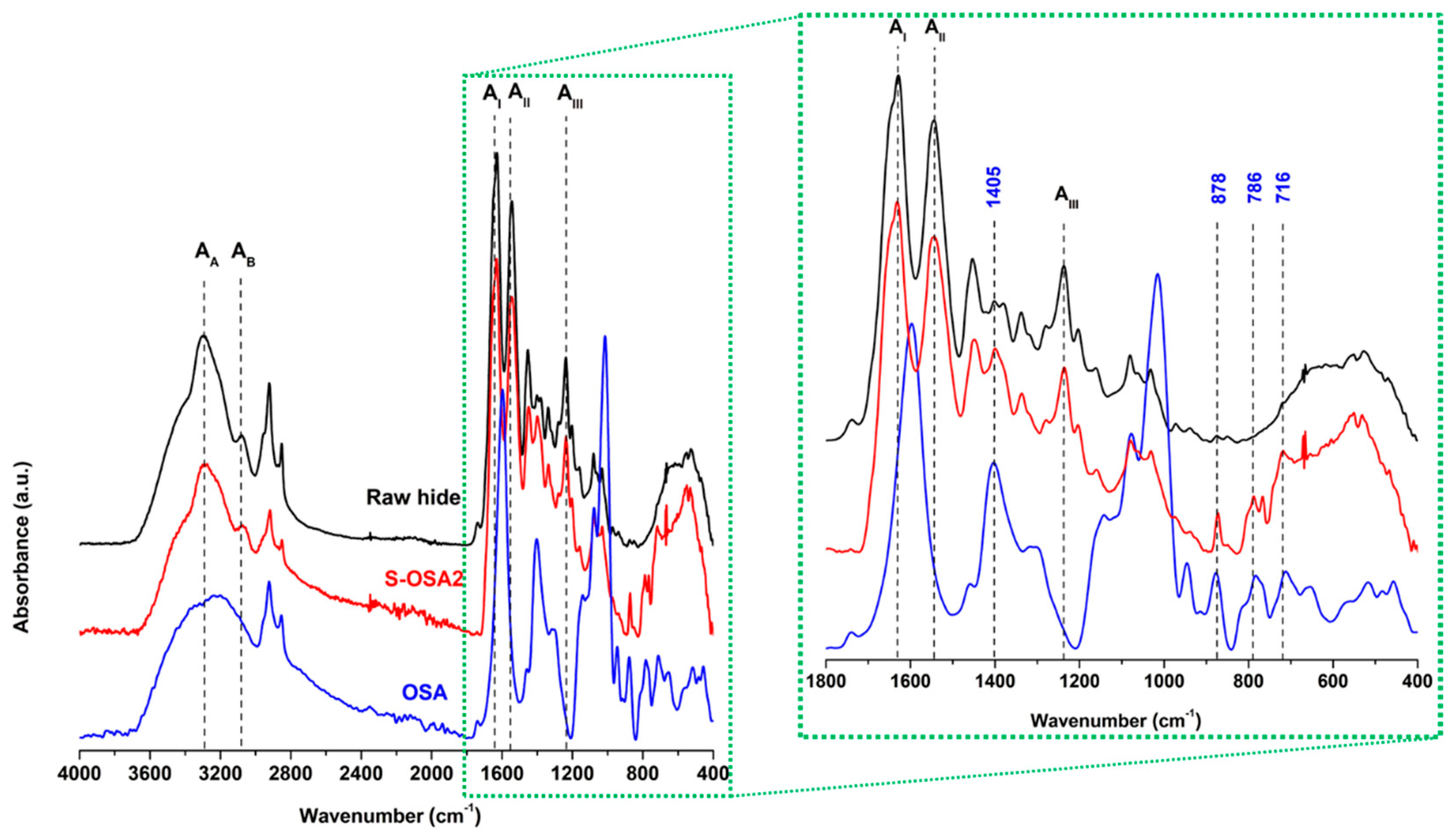
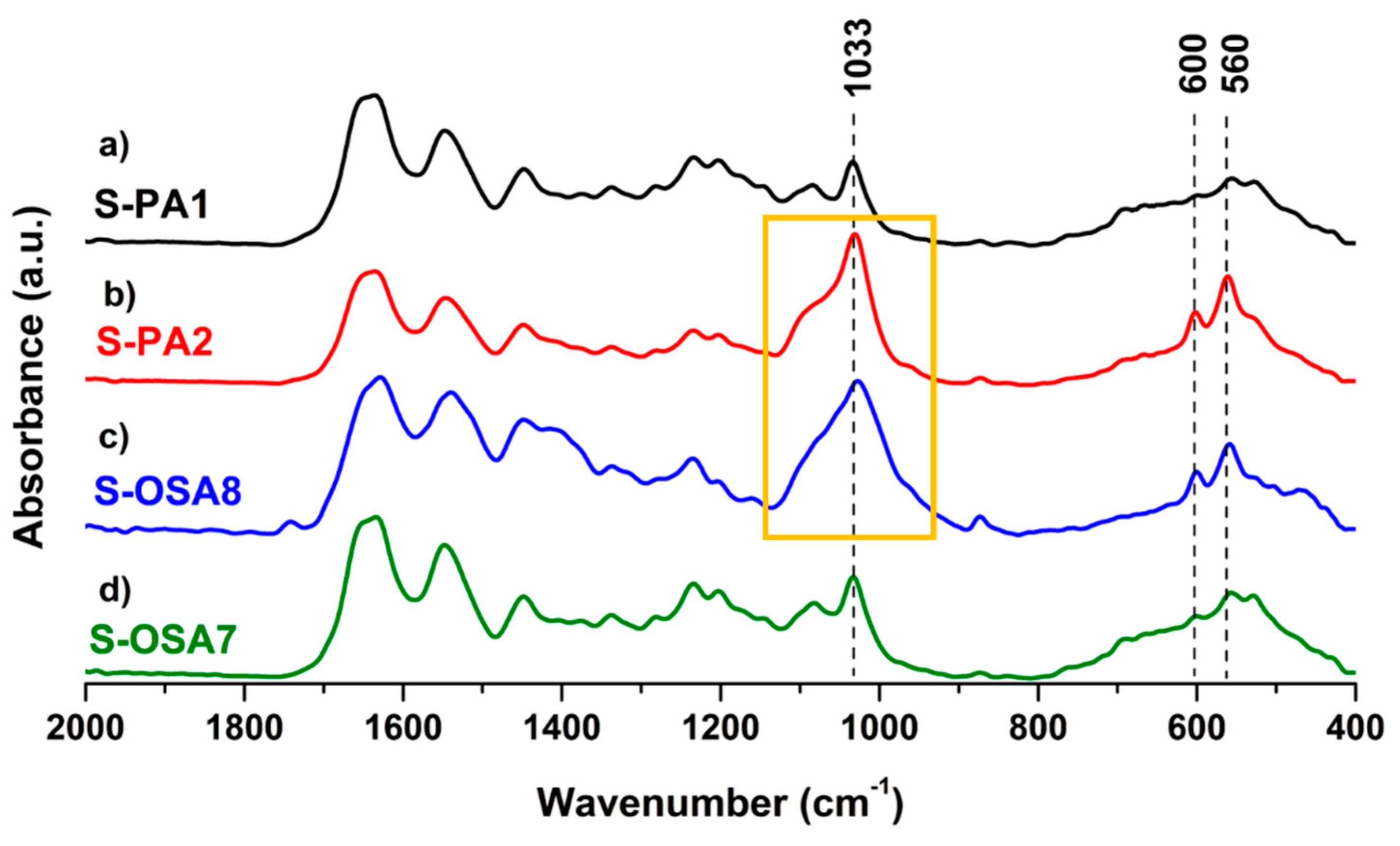
3.1.2.1. H NMR and FTIR-ATR analysis of collagen-OSA chemical matrix in leather
3.2. Laboratory scale tanning test with OSA as tanning agent and nano-HAp wet treatment
3.3. From laboratory to industrial scale: a scale-up framework for a tanning process using OSA and nano-HAp
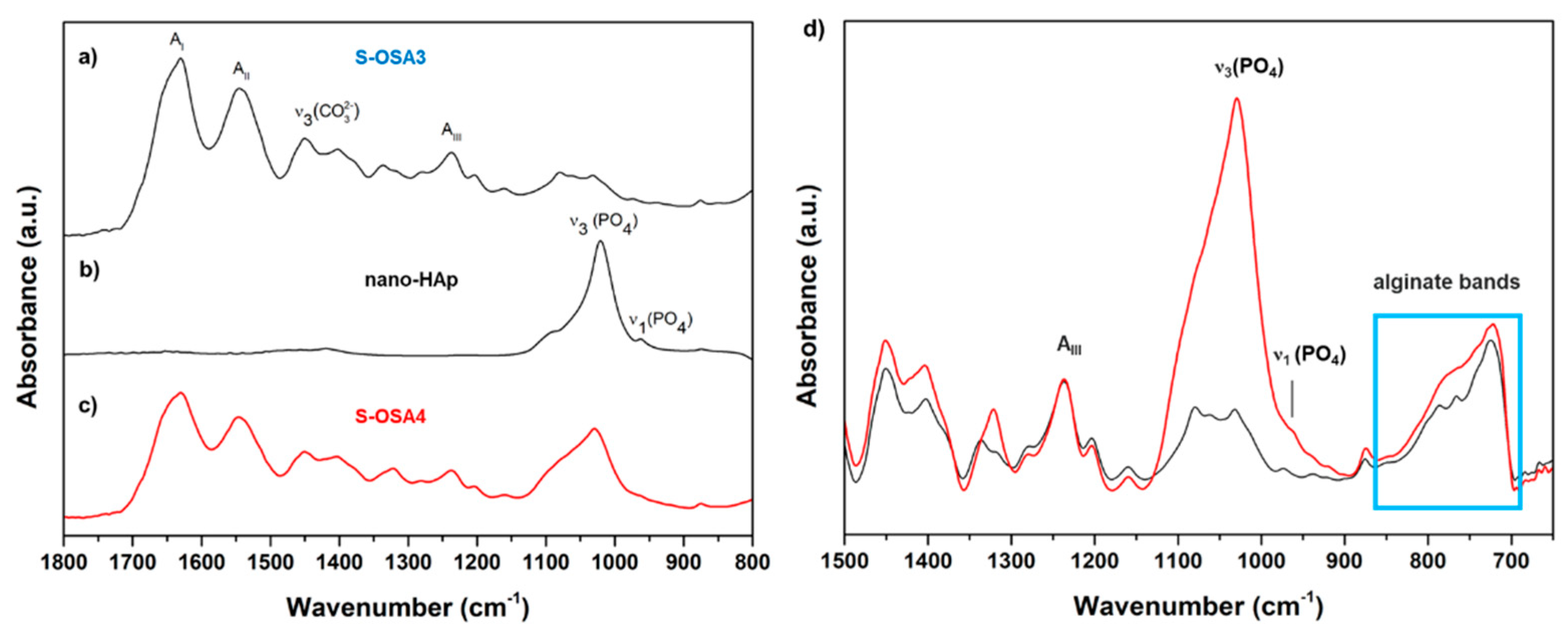
3.3.1. Thermal stability and chemical characterization
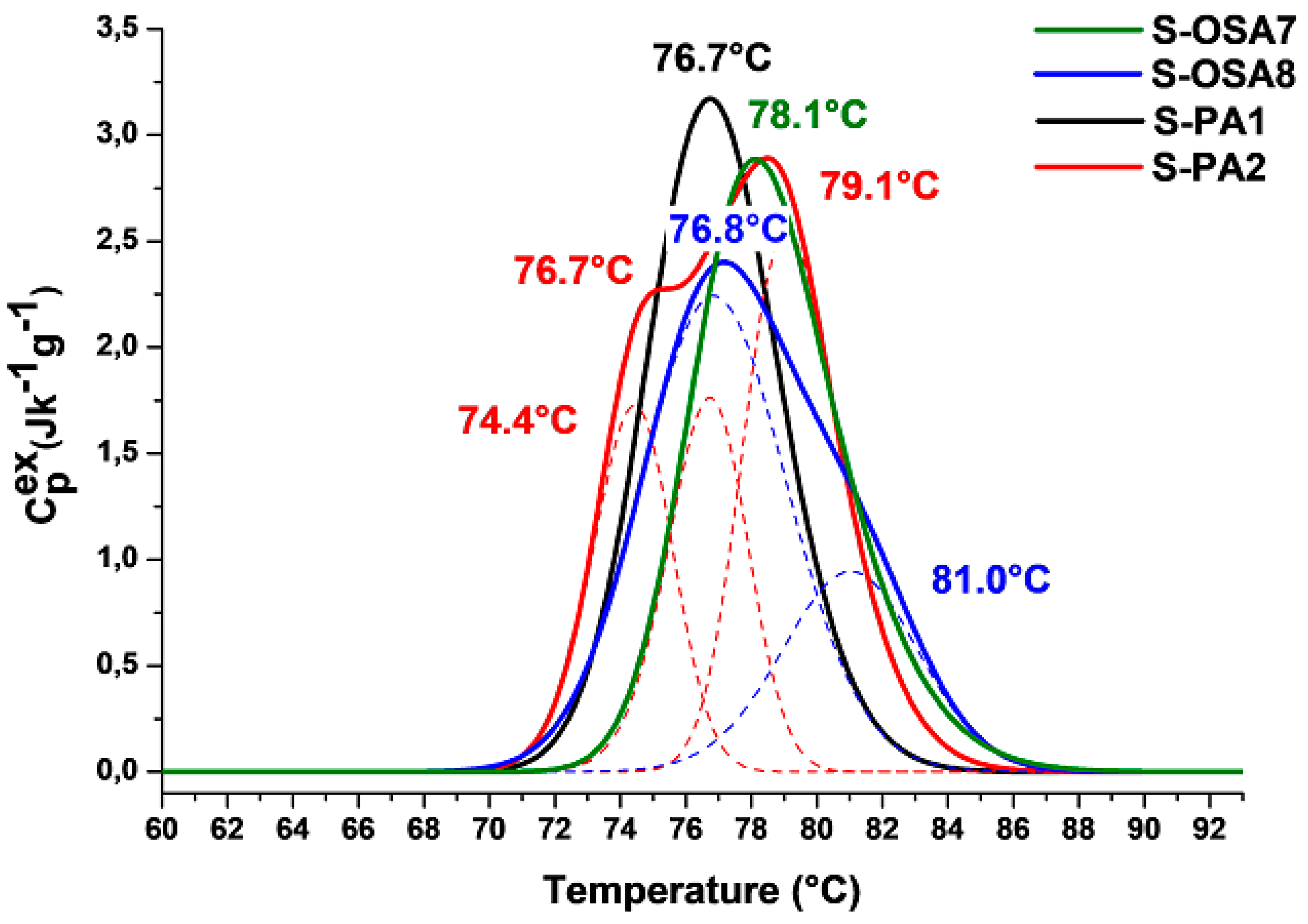
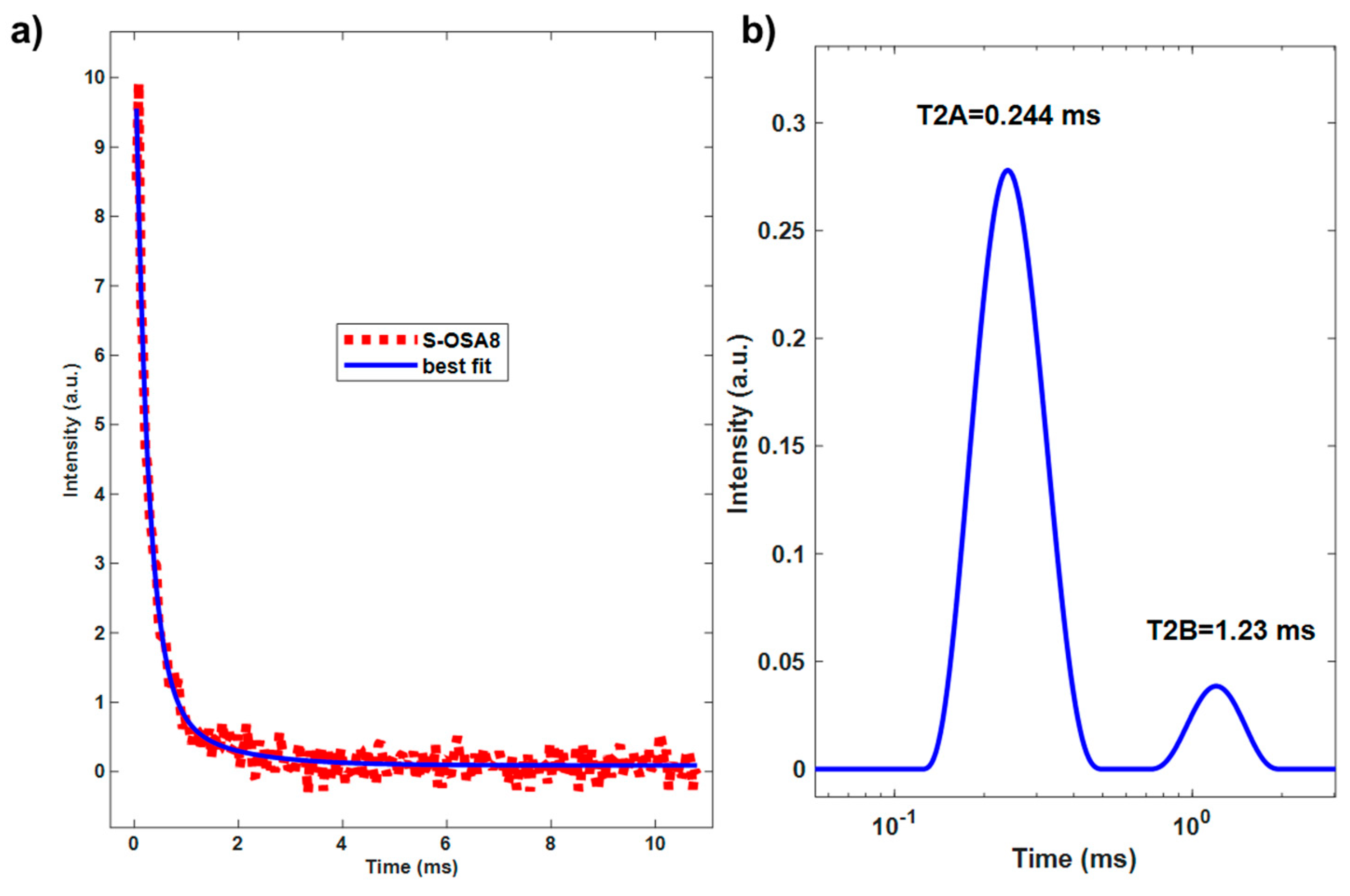
| Sample | Tanning agent/nano-HAp | T1 (ms) | WA | T2A (ms) | WB | T2B (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-OSA7 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.2) | 34 | 86 | 0.302 | 14 | 1.11 |
| S-OSA8 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.2) + 1% nHAp | 25.4 | 92 | 0.244 | 8 | 1.23 |
| S-PA1 | commercial poly-aldehyde (PA) | 29 | 83 | 0.205 | 17 | 0.756 |
| S-PA2 | commercial poly-aldehyde (PA) + 1% nHAp | 26 | 89 | 0.236 | 9 | 0.854 |
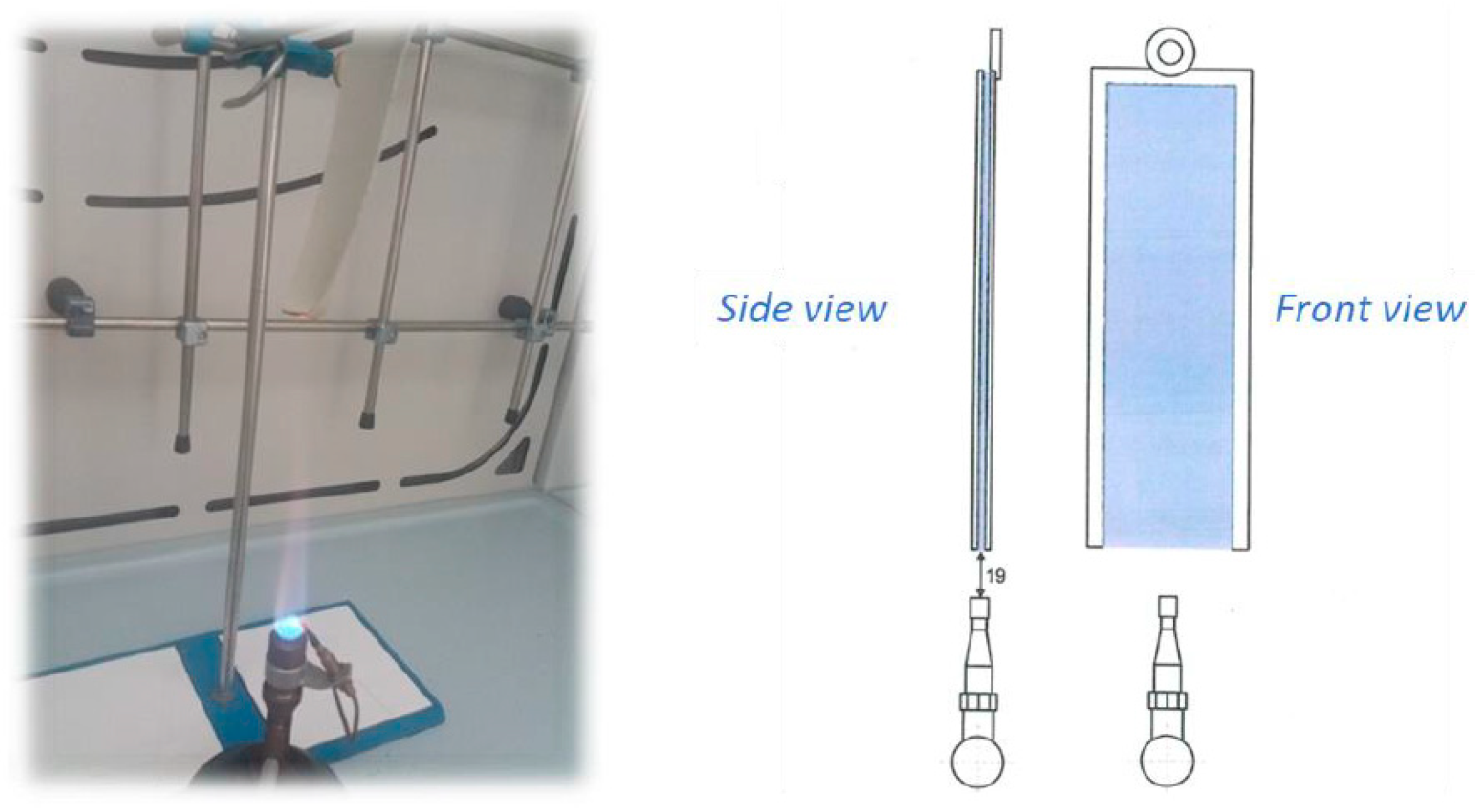
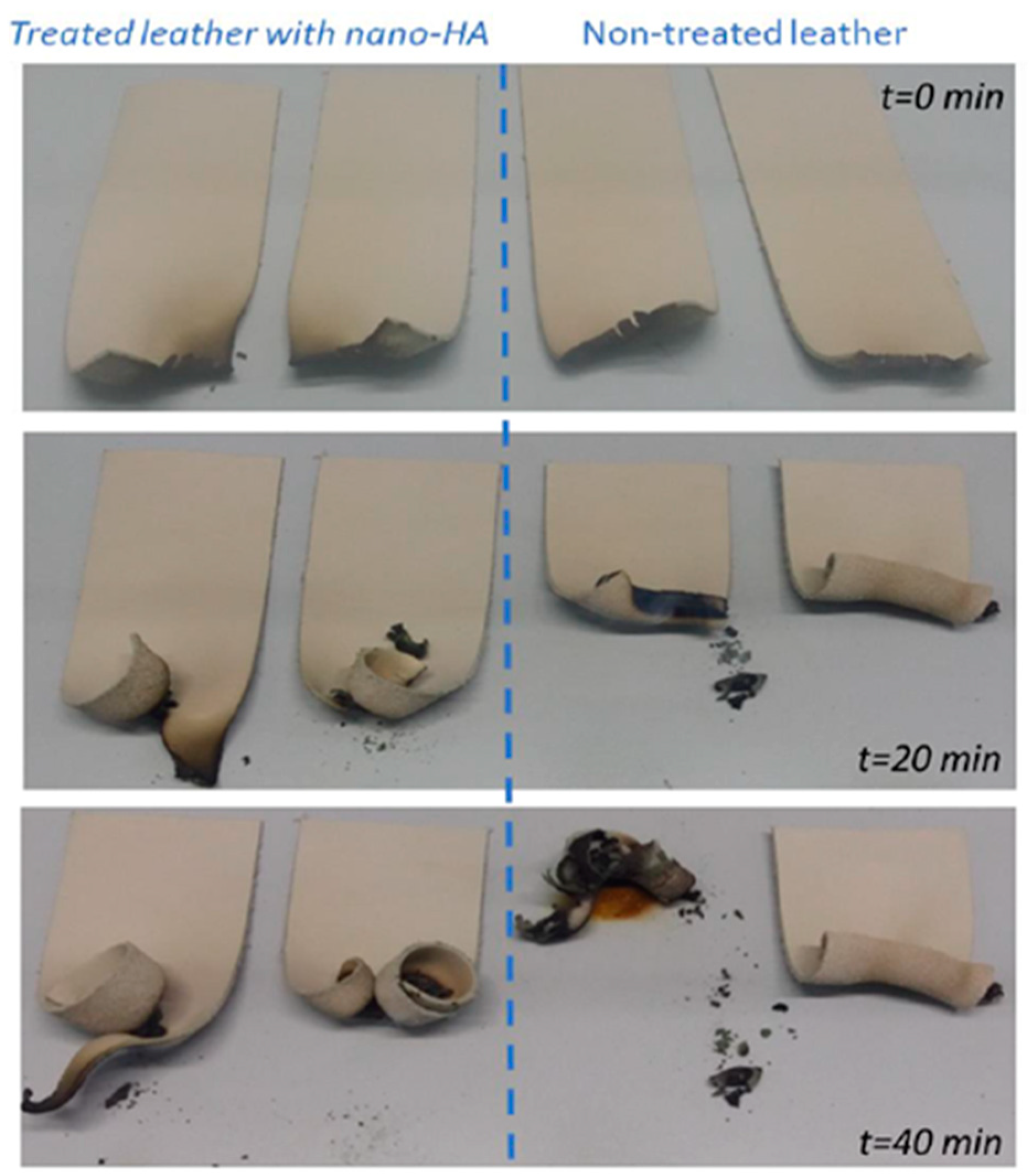
3.3.2. Fire resistance characterization
3.3.2. Physical mechanical characterization
| Test name | Technical characteristic | UM | S-OSA7 | S-OSA8 | S-PA1 | S-PA2 | Standard method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thickness | mm | 1.7 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 1.9 | SR EN ISO 2589:2016 |
| Tensile strength and percent elongation | Elongation at cracking | % | 54.5 | 56.5 | 47.5 | 55.4 | SR EN ISO 3376:2020 |
| Elongation at break | % | 63.6 | 54.5 | 71.3 | 55.1 | ||
| Tensile strength | N/mm2 | 18.7 | 12.3 | 20.3 | 12.0 | ||
| Tear strength | N/mm2 | 12.9 | 13.7 | 13.3 | 13.8 | ||
| Tear strength in extension | Tear resistance | N | 53.2 | 45.0 | 57.5 | 42.7 | SR EN ISO 3377-1:2012 |
| Tear resistance on two edges | Tear resistance | N | 123.2 | 77.7 | 147.3 | 77.7 | SR EN ISO 3377-2:2016 |
| Softness | Ring opening Ø 20mm |
mm | 2.6 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 1.9 | SR EN ISO 17235:2016 |
| Ø 25mm | mm | 4.3 | 3.1 | 3.9 | 2.3 | ||
| Ø 35mm | mm | 5.9 | 4.4 | 5.4 | 3.5 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma’arfi, F.; Khan, M.Y.; Husain, A.; Khanam, A.; Hasan, Z. Contamination of Water Resources with Potentially Toxic Elements and Human Health Risk Assessment: Part 1. In Contamination of Water; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 123–141 ISBN 978-0-12-824058-8.
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N. Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Environment and Its Bi-oremediation Strategies. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2016, 34, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, T.; Lin, S.; Xu, P.; Zhou, L.; Dai, C.; Hao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, Z.; et al. The Effect of Hex-avalent Chromium on the Incidence and Mortality of Human Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on Published Epidemiological Cohort Studies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiner, M.; Rezić, I.; Steffan, I. Determination of Total Chromium in Tanned Leather Samples Used in Car In-dustry. Coll. Antropol. 2011, 30, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pouliot, B.P.; Mass, J.; Kaplan, L. Using XRF for the Identification of Chrome Tanning in Leather.; Miami, Flor-ida, 16/05 2015; p. 120.
- Velusamy, M.; Chakali, B.; Ganesan, S.; Tinwala, F.; Shanmugham Venkatachalam, S. Investigation on Pyroly-sis and Incineration of Chrome-Tanned Solid Waste from Tanneries for Effective Treatment and Disposal: An Experimental Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29778–29790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammenn, J.; Huebsch, C.; Schilling, E.; Dannheim, B. Chemistry of Syntans and Their Influence on Leather Quality. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2015, 110, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, S.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B. Formaldehyde Formation during the Preparation of Dial-dehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose Tanning Agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Sheng, N.; Gu, Z.; Feng, W.; Yin, H.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. A Soft Tissue Adhesive Based on Alde-hyde-Sodium Alginate and Amino-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Preparation through the Schiff Reaction. Front. Mater. Sci. 2017, 11, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Yu, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, F.; Ye, J. Disrupted Metabolic Pathways and Potential Human Diseases Induced by Bisphenol S. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, N. Nishad; Kumar, T.P.; Kumar, D.R.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U. Wet White Leather Processing: A New Combination Tanning System. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2006, 101, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Yi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, B. Preparation of a Highly Effective Organic Tanning Agent with Wide Molecular Weight Distribution from Bio-Renewable Sodium Alginate. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12330–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Lesieur, S.; Labarre, D.; Jayakrishnan, A. Periodate Oxidation of Sodium Alginate in Water and in Ethanol–Water Mixture: A Comparative Study. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurikar, A.; Seow, X.T.; Lawrie, G.; Martin, D.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Grøndahl, L. Degradable Alginate Hydrogels Crosslinked by the Macromolecular Crosslinker Alginate Dialdehyde. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroguz, A.Z.; Baysal, K.; Adiguzel, Z.; Baysal, B.M. Alginate/Polyoxyethylene and Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Application in Tissue Engineering. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayatpisheh, S.; Poon, Y.F.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J.; Chan, V.; Chan-Park, M.B. Aligned 3D Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Tissue via Layer by Layer Technique inside Microchannels with Novel Combination of Collagen and Oxidized Alginate Hydrogel. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2011, 98A, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, V.; Jayakrishnan, A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Anti-Fungal Activities of Sodium Algi-nate-Amphotericin B Conjugates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, B.; Papageorgiou, D.G.; Silva, R.; Zehnder, T.; Gul-E-Noor, F.; Bertmer, M.; Kaschta, J.; Chrissafis, K.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Fabrication of Alginate–Gelatin Crosslinked Hydrogel Microcapsules and Evalua-tion of the Microstructure and Physico-Chemical Properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reakasame, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Oxidized Alginate-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fu, W.; Zhang, D.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Wan, C. Evaluation of Novel Alginate Dialdehyde Cross-Linked Chi-tosan/Calcium Polyphosphate Composite Scaffolds for Meniscus Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, K.Y. Cartilage Regeneration Using Biodegradable Oxidized Alginate/Hyaluronate Hydrogels: Cartilage Regeneration Using Biodegradable Hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Singha, K.; Ray, S.; Dey, P.; Sa, B. Adipic Acid Dihydrazide Treated Partially Oxidized Alginate Beads for Sustained Oral Delivery of Flurbiprofen. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Xiao, L.; Shi, X. A Dynamic and Self-Crosslinked Polysaccharide Hydrogel with Autonomous Self-Healing Ability. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3971–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadir, K.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Alsberg, E.; Damm, K.L.; Anderson, K.W.; Mooney, D.J. Degradation of Partially Oxi-dized Alginate and Its Potential Application for Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Differential Physical, Rheological, and Biological Properties of Rapid in Situ Gelable Hydrogels Composed of Oxidized Alginate and Gelatin Derived from Marine or Porcine Sources. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Lu, C.; Liu, P. Disintegration-Controllable Stimuli-Responsive Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Microcap-sules via Covalent Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; De Bank, P.A.; Luetchford, K.A.; Acosta, F.R.; Connon, C.J. Oxidized Alginate Hydrogels as Niche Environments for Corneal Epithelial Cells: Oxidised Alginate Hydrogels As Niche Environments. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 3393–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Registration Dossier - ECHA Available online:. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/it/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/15527 (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Potassium Periodate | 7790-21-8 Supplier and Manufacturer - BuyersGuideChem Available online:. Available online: https://www.buyersguidechem.com/chemical_supplier/Potassium_periodate (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Lucia, A.; Herwijnen, H.W.G.; Oberlerchner, J.T.; Rosenau, T.; Beaumont, M. Resource-Saving Production of Dialdehyde Cellulose: Optimization of the Process at High Pulp Consistency. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 4679–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisukuri, C.M.; Bednarz, R.J.; Kampf, C.; Arndt, S.; Waldvogel, S.R. Robust and Self-Cleaning Electrochemical Production of Periodate. ChemSusChem 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, S.; Ramalingam, S.; Rao, J.R. Preparation and Application of Biodegradable Nanocomposite for Cleaner Leather Processing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 158, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.B.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dhamodharan, D.; Divakaran, N.; Mubarak, S.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y. Waterborne Poly-urethane/Graphene Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites with Improved Mechanical and Thermal Properties for Leather Coatings Using Screen Printing. Polymer 2019, 170, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, X.; Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Lv, B.; Zhang, J. Nanocomposite-Based Green Tanning Process of Suede Leather to Enhance Chromium Uptake. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 72, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Ma, J.; Lv, B.; Zhang, J. Special Review: Collagen Modification Using Nanotechnologies: A Review. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2013, 108, 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Wegst, U.G.K.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired Structural Materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, P.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.-L.; Cui, D.-X. The Photoluminescence, Drug Delivery and Im-aging Properties of Multifunctional Eu3+/Gd3+ Dual-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanorods. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9031–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.-J. Multifunctional Calcium Phosphate Nanostructured Materials and Biomedical Applica-tions. Curr. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Promotion of Bone Regeneration by Nanofibrous Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Scaffolds by Effects on Integrin-BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway in BMSCs. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4404–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Hu, Z.W.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X.Y.; Ma, W. J. Effect of Hydroxyapatite on Fire Resistance and Smoke Sup-pression of Polyurethane Fire-Retardant Coating. Xiandai HuagongModern Chem. Ind. 2015, 35, 88–91.
- Elbasuney, S.; Maraden, A. Novel Thermoset Nanocomposite Intumescent Coating Based on Hydroxyapatite Nanoplates for Fireproofing of Steel Structures. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.-X.; Chen, Q.-J.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.-L.; Yang, M.-B. Thermal Properties and Flame Retardancy of Polycarbonate/Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Shabanian, M.; Aryanasab, F.; Mangin, R.; Laoutid, F.; Saeb, M.R. Inclusion of Modified Lignocel-lulose and Nano-Hydroxyapatite in Development of New Bio-Based Adjuvant Flame Retardant for Poly(Lactic Acid). Thermochim. Acta 2018, 666, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dholakiya, B.Z. mar Use of Non-Traditional Fillers to Reduce Flammability of Polyester Resin Composites. Po-limeri 2009, 30, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrao, C.; Vesce, E.; Evola, R.S.; Rebba, E.; Arcidiacono, C.; Martra, G.; Beltramo, R. Chemistry behind Leather: Life Cycle Assessment of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Preparation on the Lab-Scale for Fireproofing Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhno, Y.; Ivanchenko, P.; Iafisco, M.; Tampieri, A.; Martra, G. A Step toward Control of the Surface Struc-ture of Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Effect of Carboxylates on the {010} P-Rich/Ca-Rich Facets Ratio. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5928–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B. Preparation of Oxidized Sodium Alginate with Different Molec-ular Weights and Its Application for Crosslinking Collagen Fiber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aina, V.; Lusvardi, G.; Annaz, B.; Gibson, I.R.; Imrie, F.E.; Malavasi, G.; Menabue, L.; Cerrato, G.; Martra, G. Magnesium- and Strontium-Co-Substituted Hydroxyapatite: The Effects of Doped-Ions on the Structure and Chemico-Physical Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2867–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collagen and Skin Structure. In Tanning Chemistry: The Science of Leather; Covington, A.D., Wise, W.R., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2019; p. 0 ISBN 978-1-78801-204-1.
- Carsote, C.; Şendrea, C.; Micu, M.-C.; Adams, A.; Badea, E. Micro-DSC, FTIR-ATR and NMR MOUSE Study of the Dose-Dependent Effects of Gamma Irradiation on Vegetable-Tanned Leather: The Influence of Leather Thermal Stability. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 189, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsote, C.; Badea, E. Micro Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Micro Hot Table Method for Quantifying Deterioration of Historical Leather. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendrea, C.; Carsote, C.; Radu, M.; Badea, E.; Miu, L. The Effect of Gamma Irradiation on Shrinkage Activity of Collagen in Vegetable Tanned Leather. Rev Chim 2017, 68, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, N.; Di Tullio, V.; Carsote, C.; Badea, E. 13 C Solid-State NMR Complemented by ATR-FTIR and Mi-cro-DSC to Study Modern Collagen-Based Material and Historical Leather. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Covington, A.D.; Wise, W.R. Tanning Chemistry the Science of Leather; The Royal Society of Chemistry: homas Graham House, Science Park, Milton Road, Cambridge, CB4 0WF, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, J.; Shi, B. Effect of Sodium Chloride on Structure of Collagen Fiber Network in Pickling and Tanning. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2016, 111, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Li, G. Effects of NaCl on the Rheological Behavior of Collagen Solution. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2013, 25, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Niu, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K. Preparation and Properties of Self-Cross-Linking Hy-drogels Based on Chitosan Derivatives and Oxidized Sodium Alginate. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 19752–19766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theory of Tanning: The Concept of Link–Lock. In Tanning Chemistry: The Science of Leather; Covington, A.D., Wise, W.R., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2019; p. 0 ISBN 978-1-78801-204-1.
- Masic, A.; Badea, E.; Ceccarelli, R.; Della Gatta, G.; Coluccia, S. Studio comparativo DSC e SEM/ESEM di pergamene antiche e invecchiate artificialmente. In Proceedings of the Lo stato dell’arte2- Conservazione, confronto e restauro di esperienze; Il prato: Genova, 29/9, 2004; pp. 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Carşote, C.; Badea, E.; Miu, L.; Gatta, G.D. Study of the Effect of Tannins and Animal Species on the Thermal Stability of Vegetable Leather by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucos, A.; Gaidau, C.; Badea, E.; Miu, L. Influence of Glycerin on Denaturation Temperature of Chrome- and Vegetable-Tanned Leather. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2015, 60, 1093. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Long, Z.; Shan, Z. Development of Aldehyde and Similar-to-Aldehyde Tanning Agents. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümich, B.; Perlo, J.; Casanova, F. Mobile Single-Sided NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2008, 52, 197–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendrea, C.; Badea, E.; Miu, L.; Ignat, M.; Iovu, H. Unilateral NMR for Damage Assessment of Vegetable - Tanned Leather. Correlation with Hydrotermal Properties. 2014. [CrossRef]
- van Stiphout, T.A.P.; Pel, L.; Galvosas, P.; Prabakar, S.; Holmes, G. NMR Transverse Relaxation Analysis of Leather Looseness.; Eindhoven University of thecnology: Eindhoven, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sendrea, C.; Micu, M.-C.; Hadimbu, E.; Paunescu, S.M.; Caniola, I.M.; Ignat, M.; Miu, L.; Badea, E. Micro DSC and NMR MOUSE Studies of Collagen–Vegetable Tannin Interaction Mechanism during Leather Making. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems.
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. A Study on the Correlation between the Oxidation Degree of Oxidized Sodium Alginate on Its Degradability and Gelation. Polymers 2022, 14, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Mohandes, F. Thermosensitive Alginate–Gelatin–Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Scaffolds as Potential Injectable Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18423–18431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; He, Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Acid- and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from the Scales of Miiuy Croaker (Miichthys Miiuy). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Younes, I.; Ayed, H.B.; Maalej, H.; Montero, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Dahia, M.; Mechichi, T.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Structural, Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Sodium Alginate Isolated from a Tunisian Brown Seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekh, M.I.; Zhu, G.; Xiong, W.; Wu, W.; Stadler, F.J.; Patel, D.; Zhu, C. Dynamically Bonded, Tough, and Con-ductive MXene@oxidized Sodium Alginate: Chitosan Based Multi-Networked Elastomeric Hydrogels for Physical Motion Detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, S0141813022023923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirrah, I.N.; Lokanathan, Y.; Zulkiflee, I.; Wee, M.F.M.R.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. A Comprehensive Review on Collagen Type I Development of Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering: From Biosynthesis to Bioscaffold. Bio-medicines 2022, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutini, M.; Corno, M.; Costa, D.; Ugliengo, P. How Does Collagen Adsorb on Hydroxyapatite? Insights From Ab Initio Simulations on a Polyproline Type II Model. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 7540–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.A.; Avery, N.C. Thermal Stabilization of Collagen in Skin and Decalcified Bone. Phys. Biol. 2011, 8, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şendrea, C.; Carsote, C.; Badea, E.; Adams, A.; Niculescu, M.; Iovu, H. Non-Invasive Characterization of Col-lagen Based Materials by NMR-Mouse and ATR-FTIR. Sci. Bull.-Univ. Politeh. Buchar. 2016, 78, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, A.; Avci, Ç.B.; Kerdar, S.N.; Amini, H.; Amini, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Sakai, S.; Bagca, B.G.; Ozates, N.P.; Rahbarghazi, R.; et al. Interaction of Alginate with Nano-Hydroxyapatite-Collagen Using Strontium Provides Suitable Osteogenic Platform. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Ghitulica, C.; Voicu, G.; TRANDAFIR, V.; MÂNZU, D.; FICAI, M.; PALL, S. Colagen / Hydroxyapatite Interactions in Composite Biomaterials. Mater. Plast. 2009, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Chandía, N.P.; Matsuhiro, B.; Mejías, E.; Moenne, A. Alginic Acids in Lessonia Vadosa: Partial Hydrolysis and Elicitor Properties of the Polymannuronic Acid Fraction. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathlouthi, M.; Koenig, J.L. Vibrational Spectra of Carbohydrates. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Elsevier, 1987; Vol. 44, pp. 7–89 ISBN 978-0-12-007244-6.
- Kourkoumelis, N.; Lani, A.; Tzaphlidou, M. Infrared Spectroscopic Assessment of the Inflammation-Mediated Osteoporosis (IMO) Model Applied to Rabbit Bone. J. Biol. Phys. 2012, 38, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambri, M.L.; Giordano, E.D.; Bozzano, P.B.; Bonifacich, F.G.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Zelada, G.I.; Gargicevich, D.; Recarte, V.; Lambri, O.A. Thermal Degradation of Type I Collagen from Bones. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.A.; Ghelashvili, M. Polymer-in-a-Box Mechanism for the Thermal Stabilization of Collagen Molecules in Fibers. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cai, W.; Chu, F.; Zhou, F.; Liang, S.; Ma, C.; Hu, Y. Hydroxyapatite/Polyurea Nanocomposite: Prep-aration and Multiple Performance Enhancements. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
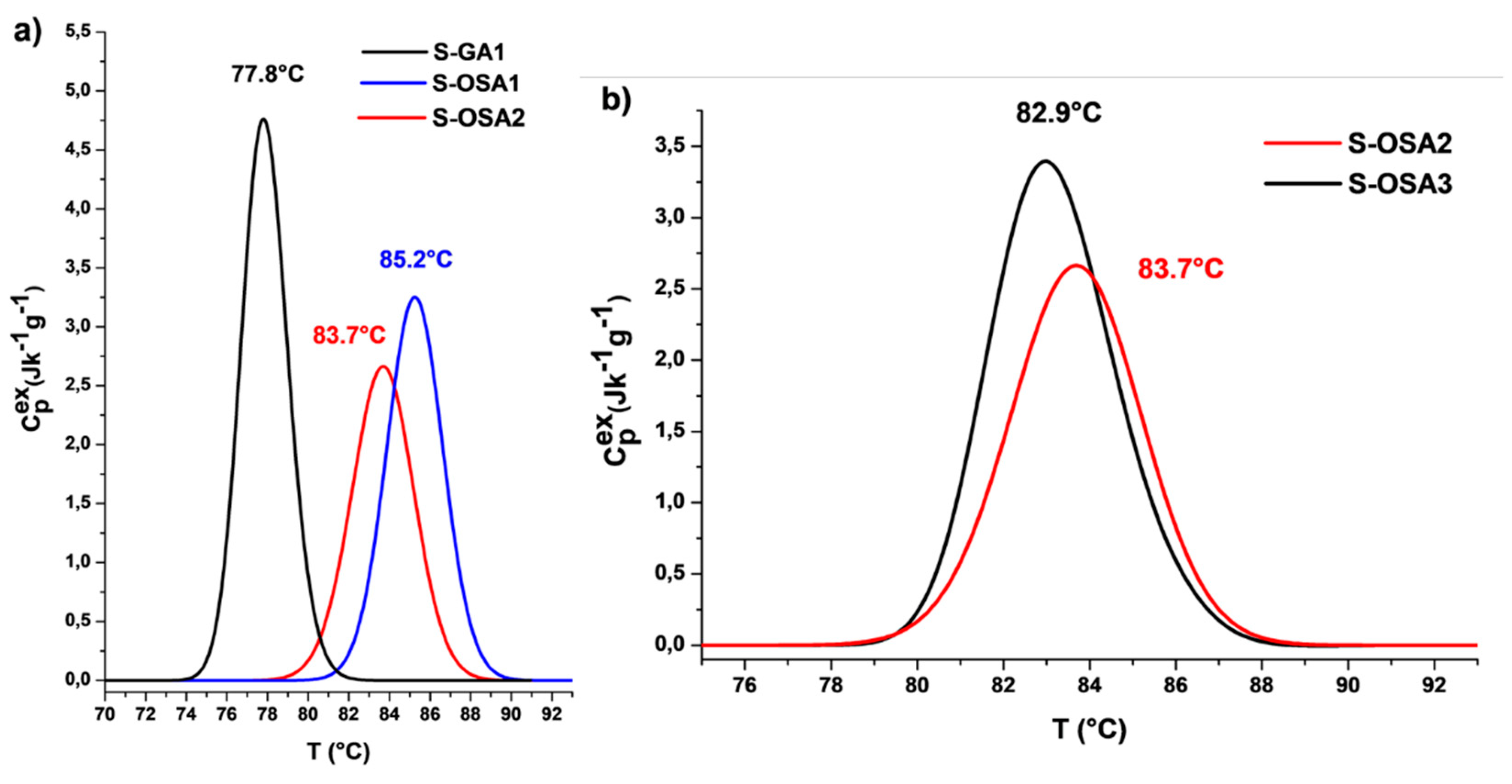

| Sample symbol | Tanning agent | NaCl (%) |
Ts (°C) |
Tmax (°C) | Tonset (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | ΔT1/2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-GA1 | commercial glutaraldehyde (GA) | 12 | 79 | 77.8 | 75.4 | 13.6 | 2.6 |
| S-OSA1 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.8) | 12 | 88 | 85.2 | 82.3 | 12.8 | 3.2 |
| S-OSA2 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.8) | 6 | 86 | 83.7 | 80.3 | 11.3 | 3.4 |
| S-OSA3 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.2) | 6 | 84 | 82.9 | 80.1 | 10.2 | 3.5 |
| Sample name | Tanning agent | T1 (ms) | WA (%) | T2A (ms) | WB (%) | T2B (ms) | WC (%) |
T2C (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
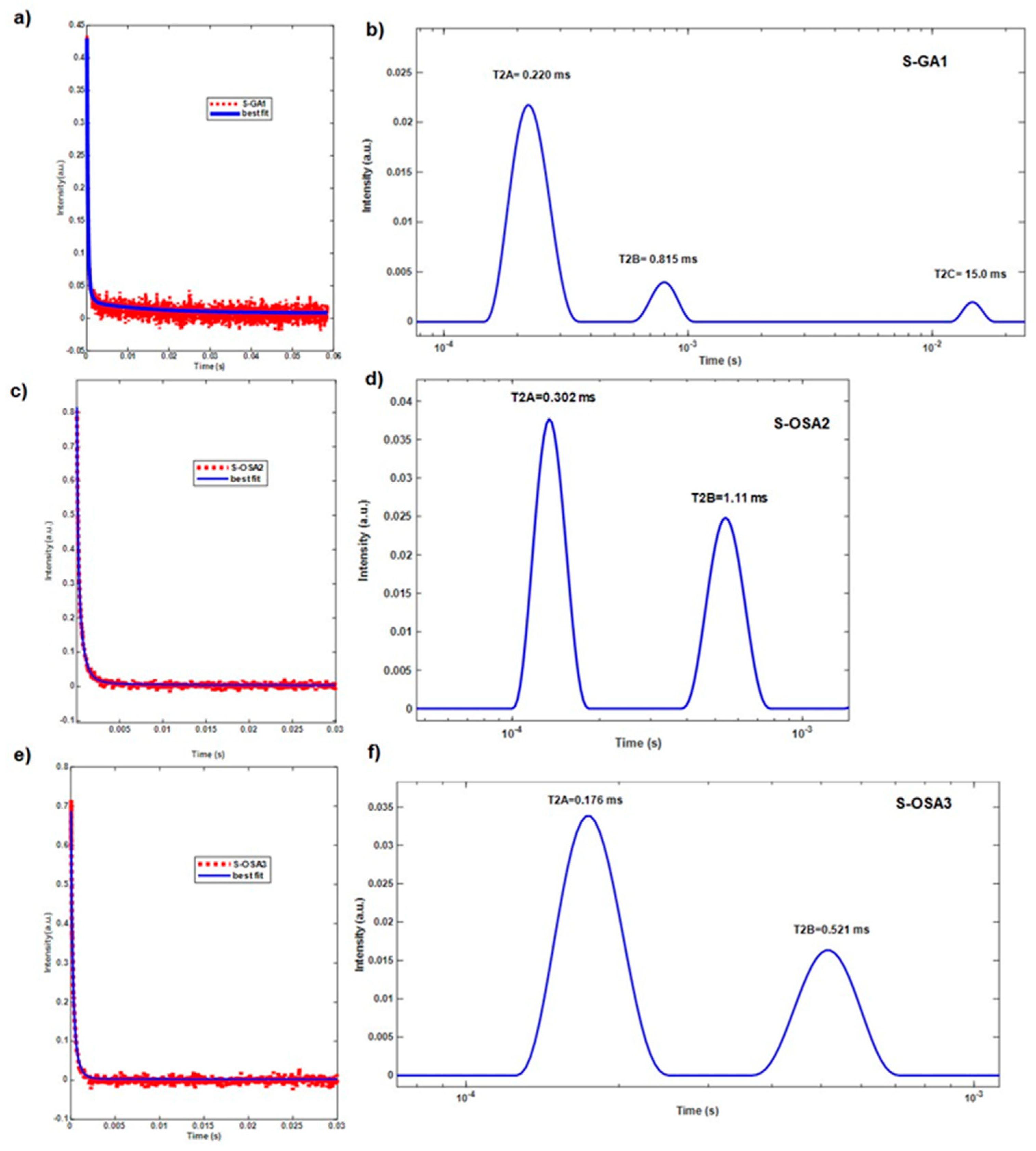
| S-GA1 | commercial glutaraldehyde (GA) | 30 | 85 | 0.220 | 12 | 0.815 | 3 | 15.0 |
| S-OSA2 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.8) | 34 | 86 | 0.302 | 14 | 1.11 | - | - |
| S-OSA3 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio 1:0.2) | 31 | 64 | 0.176 | 32 | 0.521 | - | - |
| Sample name | nHAp (%) | Tonset (°C) | Tmax (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | ΔT1/2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
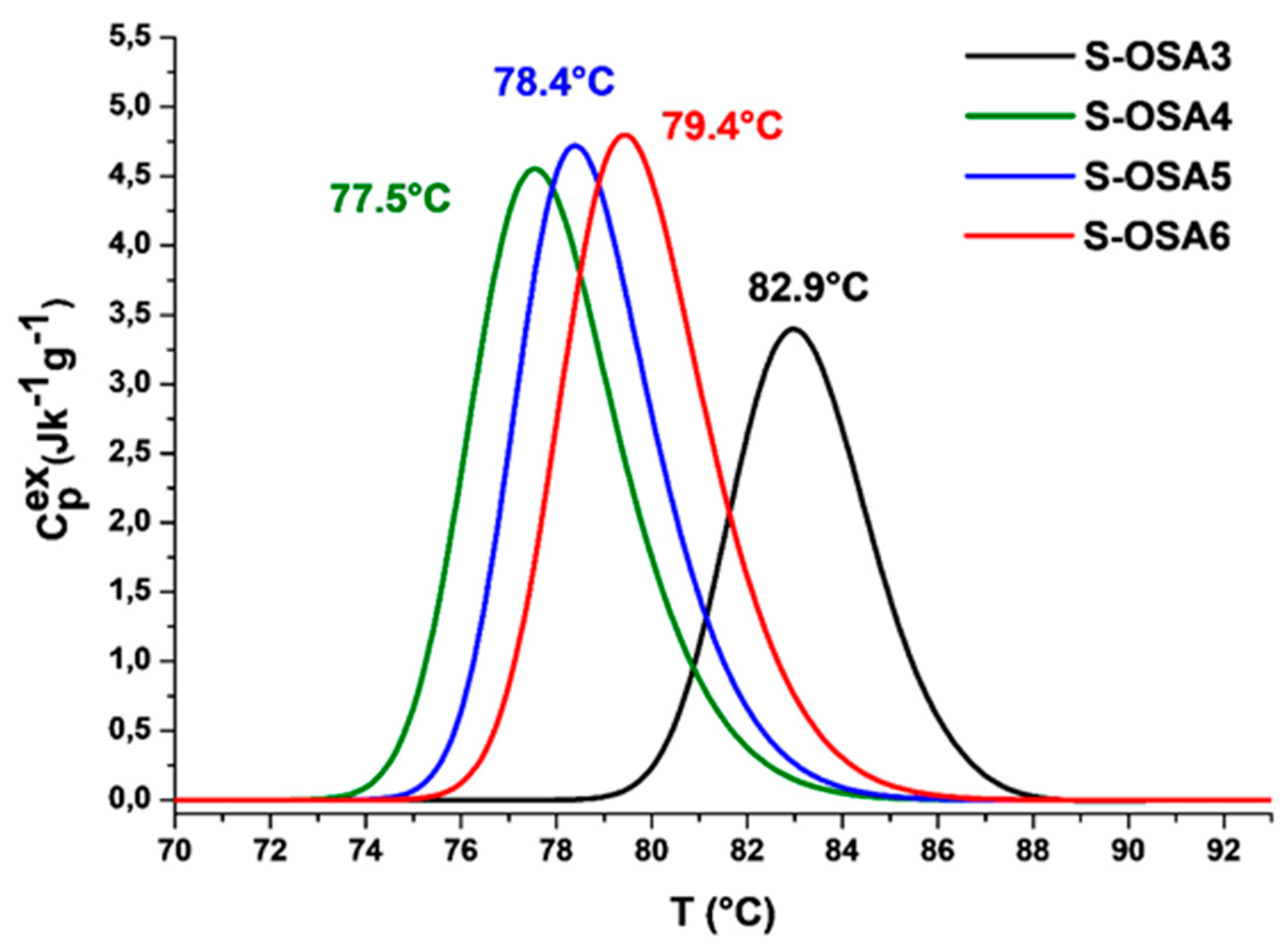
| S-OSA3 | 0 | 80.1 | 82.9 | 12.8 | 3.5 |
| S-OSA4 | 1.0 | 74.6 | 77.5 | 18.0 | 3.6 |
| S-OSA5 | 1.5 | 75.6 | 78.4 | 17.4 | 3.3 |
| S-OSA6 | 3.0 | 76.2 | 79.4 | 18.5 | 3.5 |
| Sample symbol | Tanning agent/ nano-HAp |
Timax (°C) |
Tonset (°C) |
ΣΔHi (J·g−1) | % ΔHi | ΔT1/2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-OSA7 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio of 1:0.2) | T1=78.1 | 73.7 | 16.1 | ΔH1 = 100 | 5.1 |
| S-OSA8 | OSA (SA:KIO4 molar ratio of 1:0.2) + nano-HAp (1%) |
T1=81.0 T2=76.8 |
72.1 | 17.5 | ΔH1 = 28 ΔH2 = 72 |
7.1 |
| S-PA1 | commercial poly-aldehyde (PA) | T1=76.7 | 72.7 | 18.1 | ΔH2 = 100 | 4.7 |
| S-PA2 | commercial poly-aldehyde (PA) + nano-HAp (1%) |
T1=79.1 T2=76.7 |
71.5 | 20.6 | ΔH1 = 26.0 ΔH2 = 74.0 |
7.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





