1. Introduction
Oral cancer comprises cancers of the lips, tongue, and other oral structures, and it is the most prevalent form of head and neck cancer. According to the most recent report on cancer statistics worldwide, published in 2020 by the WHO's International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [
1], oral cancer ranks 16th among malignant tumors worldwide, with a global incidence rate of 2%, approximately 378,000 people; the mortality rate is 1.8%, around 178,000 people. Both the incidence and mortality rates are highest in the Asian region. Cancer originates from genetic mutations and is mainly associated with interactions between environmental, genetic, and metabolic factors[
2,
3,
4,
5,
6].
The risk factors for oral cancer include heavy tobacco use [
7] and excessive alcohol consumption [
8,
9,
10]. Smoking and alcohol consumption have been proven to be the primary risk factors for oral squamous cell carcinoma, with a synergistic effect that increases the risk by 35 times [
11]. Chewing betel nut, which contains betel nut extracts like ripe areca nut extracts (rANE) and tender areca nut extracts (tANE), increases the risk of oral cancer because it promotes the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the upregulation of the expression of inflammatory factors including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and interleukin-1 (IL-1) [
12,
13].
Infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV) was linked to a rising rate of oral and oropharyngeal cancer in the past few decades, especially among young people [
14,
15,
16]. HPV expresses viral oncoproteins E6 and E7, which inactivate the host's tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) p53 and pRb, leading to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of cancer [
8,
17,
18]. Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) typically arises from premalignant lesions, resulting in significant histological alterations in the oral mucosa, and the vast majority of oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas [
19,
20]. Most oral precancerous lesions are leukoplakia, erythroplakia, submucosal fibrosis, and a small percentage of patients may develop actinic keratosis [
20,
21]. If any of these lesions occur, surgical excision or further histological examination is necessary to prevent progression to tumors [
15,
21]. Surgical removal is the preferred treatment method for OSCC, and other therapies include surgery combined with radiotherapy (RT)/chemotherapy (CT), immunotherapy, and photodynamic therapy (PDT) [
15,
22,
23].
The goal of the resection surgery is to completely remove local disease symptoms and neck lymph node metastasis, but the recurrence rate remains at 25% to 48% [
20,
24,
25]. Among 20% to 30% of patients, it has also been observed that the recurrence at the primary site is more common than local and distant site recurrence. Local recurrence accounts for 10%-15% of deaths [
20,
26], while distant site recurrence accounts for 1% to 3.8% [
26,
27,
28]. Surgical and radiation treatments can lead to tissue hypoxia and fibrosis, making it difficult to detect malignant cells in fibrotic tissue, which is the causes of local recurrence. Slootweg et al. examined 394 patients who underwent oral cancer tumor resection and found that the local recurrence rate was lower in patients with negative margins of adjacent tissues (3.9%) compared to patients with positive margins (21.9%) [
20,
29]. In addition to recurrent OSCC at the primary site, tongue cancer is most prone to neck lymph node metastasis and has the greatest tumor thickness. Neck lymph node metastasis and extracapsular spread (ECS) of lymph nodes are both major factors contributing to poor prognosis in oral cancer [
22,
30]. ECS can increase distant metastasis and mortality rates. Patients with neck metastases who are without ECS had a 52% chance of surviving for 5 years, while those who do have ECS have a 28% chance [
20,
31]. Lungs are the most frequent location of distant metastasis, and people who develop this condition typically only have a lifespan of 8–9 months [
20,
25]. Clinical research data indicates an 5-year survival rate of approximately 64% for all stages of OSCC patients [
32]. However, the presence of neck lymph node metastasis decreases the 5-year survival rate by about 50% [
20,
33]. It also indicates that metastasis, or the spread of cancer cells from their original site to other organs, is a major contributor to cancer-related mortality [
34]. ECS tumor EMT levels can predict the prognosis and survival of head and neck cancer, with shorter overall and disease-free survival, a greater recurrence rate, and wider spread shown in tumors with a higher EMT proportion [
35].
The initial phase in metastasis is epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which can reduce cell-cell adhesion and increase tumor cell adherence to the matrix. To further their invasion and intravasation, tumor cells release matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to destroy the extracellular matrix (ECM). At this point, tumor cells can either expand inside blood arteries, bursting them open, or induce endothelial cell death, allowing tumor cells to extravasate via the spaces created by the dead endothelial cells and spread to other organs and tissues [
36]. Finally, tumor cells form a favorable microenvironment for tumor colonization with immune cells and other stromal components, continuously proliferating to form a tumor[
37,
38]. TGF-, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), NOTCH, Wnt/-catenin, STAT3, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), Hedgehog, extracellular matrix-mediated (ECM-mediated), Hypoxia, Hippo, ET-1, CAV-1, and Oxidative stress are just some of the signaling pathways that can regulate EMT [
39,
40,
41]. These signaling pathways regulate the production of transcription factors like Zeb, Snail, and Twist, which then activate EMT by inducing stromal marker gene expression and inhibiting epithelial marker gene expression [
40,
42]. The TGF- signaling pathway, the zinc-finger E-box-binding homeobox ZEB1 and ZEB2, the zinc-finger binding transcription factors Snail and Slug, and the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors Twist all play critical roles in upregulating EMT and can synergize with one another to promote EMT expression. Essential steps in the initiation of EMT include the binding of these proteins to the promoter regions of cell adhesion-related genes and the subsequent regulation of the expression of EMT-related proteins [
40,
42,
43]. Twist1 can activate EMT by upregulating Vimentin [
40,
44]. Twist is mainly activated by TGF-β, Wnt/β-catenin, STAT3, and hypoxia signaling pathways, initiating EMT [
45]. Studies have shown that Twist can downregulate E-cadherin and promote the expression of N-cadherin, fibronectin, and Vimentin [
46]. In human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells (HPAE), activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway can induce Twist1 expression [
40]. Twist is also associated with promoting cancer cell metastasis, angiogenesis, invasion, extravasation, and chromosomal instability. Moreover, high expression of Twist can protect cancer cells from apoptosis [
47]. Research has shown that increased expression of Twist1/2 in cancer cells can inhibit the expression of p53 and Rb, leading to anti-cellular senescence and death [
45,
47]. In BALB/c mice implanted with mouse breast cancer cells such as 67NR, 168FARN, 4TO7, and 4T1, Twist1 was found to bind to the promoter of Snail2, upregulating Snail2 protein expression to induce EMT and promote breast tumor metastasis [
43,
48]. Relevant studies have shown that the transcription factors SNAIL and ZEB2, associated with EMT, can upregulate MMP expression, further promoting cancer cell invasion [
42]. It has been demonstrated through studies [
49] that tumors with high MMP expression have a poor prognosis and a higher chance of recurrence. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) also has a role for MMP-9 in tumor invasion and metastasis [
49,
50]. Several studies have shown that MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9 are expressed in OSCC cells and tissues [
51]. In addition, SAS human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells and GNM human gingival cancer with neck lymph node metastases have been demonstrated to exhibit MMP-2 and MMP-9, which is linked to migration and invasion [
52,
53].
Cell apoptosis is an irreversible process and is considered a unique and important programmed cell death mode that maintains cellular homeostasis within tissues. The pathways involved can be broadly classified as either extrinsic (involving death receptors) or intrinsic (involving mitochondria). Cell apoptosis is crucial in various developmental processes and requires strict regulation. Developmental defects, autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, and cancer are all possible outcomes of apoptotic dysregulation [
54]. Transmembrane death receptors, mostly derived from the tumor necrosis factor receptor gene superfamily, mediate the extrinsic pathway. The death receptors of the TNF receptor family contain a death domain rich in cysteine residues in their extracellular structure, which binds to procaspase-8 and self-catalyzes into cleaved caspase-8. This further cleaves and activates caspase-3 and promotes the cleavage of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerases (PARP), leading to cell apoptosis. Multiple non-receptor stimuli, such as growth factors, hormones, radiation, toxins, hypoxia, viral infection, and free radicals, are involved in the intrinsic pathway. These conditions trigger the release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm by increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane, leading to a loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Apoptosomes are formed when cytochrome c binds to Apaf-1 and procaspase-9. [
55,
56]. After being cleaved, procaspase-9 then activates caspase-3, which in turn induces cell death. Cytoplasmic adapter proteins with death domains are recruited by ligands and death receptors such as FasL/FasR, TNF-/TNFR1, Apo3L/DR3, Apo2L/DR4, and Apo2L/DR5. Through death domain dimerization, Fasligand (FasL) binds to procaspase-8 and establishes a connection with the Fas-associated death domain (FADD). As a result, procaspase-8 is cleaved and activated by the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC), which in turn activates caspase-3 and promotes cell apoptosis [
54]. NF-kB, Sp1, IFN, c-Myc, FKHRL1, and c-jun are only some of the transcription factors that can influence FasL production [
57,
58]. These transcription factors can increase the expression of FasL and potentially further activate downstream caspases to promote cell apoptosis. Recent study has revealed an important regulatory role for the JNK signaling pathway in Fas-mediated cell death. Researchers Suhara et al. reported that knocking down FasL expression in VSMCs using adenoviral transfection of a dominant negative c-jun mutant (Adeno-TAM67) was successful. Since c-jun is primarily regulated by JNK, when JNK is inhibited, c-jun is unable to enter the nucleus for transcriptional activity, leading to decreased FasL expression. Based on these results, it has been demonstrated that JNK can upregulate the transcription of the FasL gene [
57]. Current research also indicates that the JNK pathway can induce cell apoptosis in OSCC [
59]. Therefore, this pathway deserves further investigation.
Substances found in nature have been shown to have anti-tumor properties against several distinct cancers. They also improve immunological function, increase survival, and increase chemotherapy's effectiveness [
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. For example, Juniperus communis extract can promote apoptosis in OSCC cells through the exogenous Fas/FasL pathway [
65]. The important fatty acid ALA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). Because the human body cannot produce it on its own, ALA must be taken in through food or other means [
66]. Walnuts, flaxseeds, hemp seeds, and their oils all contain ALA, an important polyunsaturated fatty acid obtained from plants. Green leafy vegetables, canola oil, soybean oil, and it all contain trace amounts [
67]. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are two of the most essential long-chain fatty acids produced from ALA through a sequence of desaturation and elongation processes [
68]. Membrane fluidity, protein and cellular function, eicosanoid metabolism, gene expression, and cell signaling are all crucially regulated by EPA and DHA, which are derived from fish oil or ALA-rich plant lipids. EPA and DHA integrate into a cascade that operates in parallel with the inflammation cascade governed by the metabolism of arachidonic acid (AA) [
69,
70]. Previous studies into the EPA cascade's anti-inflammatory effects found that it mitigated the AA cascade's inflammatory effects, suggesting that the EPA cascade had this property [
71]. Numerous studies have indicated the anticancer effects of ALA, which can inhibit the growth of human breast cancer cells and suppress the proliferation of human renal cancer cells [
72,
73,
74,
75,
76]. ALA upregulates the expression of caspase-3 to induce apoptosis in human colon cancer cells (HT-29) [
77]. ALA also induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by increasing Bax expression and decreasing Bcl-2 expression, which results in the release of cytochrome c, which in turn activates caspase-3 and promotes PARP cleavage [
78]. Studies have also shown that ALA inhibits EMT in MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T human breast cancer cells by upregulating E-cadherin expression and downregulating Twist1, Snail2, N-cadherin, Vimentin, and fibronectin expression [
79]. The capacity of SiHa and HeLa human cervical cancer cells to migrate is inhibited by ALA because it reduces the production of MMP-2 and MMP-9 [
80]. The growth, adhesion, and invasion of HT29, HCT116, and MCA38 human and mouse colon cancer cells, respectively, are all suppressed by this compound [
81]. Animal studies have also shown that a diet high in ALA from fish oil (1 g/day, containing 54.5% ALA) slows the progression of breast cancer in rats [
82], and that a diet high in ALA from mice (content ranging from 17.2% to 43.12%) slows the progression of prostate cancer in mice. [
83]. Although ALA has been demonstrated to combat various types of cancer, there is limited research on its relevance to oral cancer, and further investigation is warranted.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
SAS and GNM human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines were provided by Professor Chen-Chia Yu of Chung Shan Medical University for this study. The cells were grown in DMEM with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin added. Cells were incubated in a humidified incubator at 37°C. Additionally, the medium was changed every one to two days.
2.2. Cell Viability Analysis
Cell metabolic activity was measured using the MTT assay. SAS (2.5 × 105) and GNM (4 × 105) cell lines were treated with serial concentrations of ALA (0–800 μM) for 24 hours. Then, the cells were assessed for viability using the MTT reagent. To ascertain the results, the absorbance was detected at 570 nm using a microplate reader.
2.3. Total Protein Extraction
SAS (6 × 105 in 6 cm dish) and GNM (1 × 106 in 6 cm dish) cell lines were treated with different concentrations of ALA (0–200 μM) for different time durations. After treatment, the cells were scraped and lysed using an ultrasonic cell disruptor (Vibra-Cell™, Sonics & Materials, Inc., CT, USA). After cell lysis, the samples were centrifuged at 4°C and 15,000 rpm (20,600g) for 30 minutes using a refrigerated microcentrifuge (3,500 Centrifuge, KUBOTA, OSA, Japan). The resulting supernatant can be used for protein quantification, sample preparation, or stored at -20°C.
2.4. Nuclear and Cytosolic Protein Extraction
SAS and GNM cell lines were seeded at density of 3 × 106 and 3.6 × 106 cells in 10 cm culture dishes, treated with 200 and 400 μM ALA for 0, 15, 30, and 60 minutes, and then centrifuged at 4°C and 8,500 rpm (6,600g) for 5 minutes using a refrigerated microcentrifuge. Then the sample was subjected to 30 minutes of shaking at 4°C using an orbital shaker (Intelli-Mixer RM-2, Daigger Scientific, NJ, USA). Cytosolic protein was extracted from the supernatant, and nuclear protein was extracted from the pellet. Both protein extracts could be used for protein quantification, sample preparation or stored at -20°C.
2.5. Mitochondrial Protein Extraction
SAS and GNM cells were seeded at a density of 1.8 × 106 and 2.1 × 106, respectively, in 10 cm culture dishes and treated with various concentrations of ALA (0, 50, 100, and 200 μM) for 16 hours. The cells were then harvested and cytosol was extracted using a buffer mix. The supernatant was collected and saved. The supernatant was further centrifuged at 4°C and 10,400 rpm (10,000g) for 30 minutes, and the resulting supernatant was collected as the cytoplasmic fraction. Next, 80 μL of mitochondria extraction buffer mix was added to the Eppendorf tube containing the pellet. The tube was vortexed (Vortex-Genie 2, Scientific Industries, Inc., NYC, USA) for 10 seconds to separate the mitochondria, which could be directly used for sample preparation or stored at -20°C in a freezer.
2.6. Western Blotting
Semidry transfer to a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane was used to transfer the proteins that had been separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The transferred PVDF membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in PBS. Primary antibodies were selected based on the research objectives and incubated with the membranes overnight at 4°C. The membranes were then washed three times with PBST at room temperature. Secondary antibodies were selected based on the research objectives and incubated with the membranes for 1 hour at room temperature. After three washes with PBST, the antibodies bound to the protein blots were detected using ImageQuant (LAS-4000, FUJIFILM, TYO, Japan). The following primary antibodies and reagents were used in this study: caspase-8 antibody (9746) (1:500), Anti-phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185, Thr221/Tyr223) antibody (07-175) (1:1000), β-actin antibody (MAB1501) (1:4000), Fas antibody (GTX13550) (1:1000), Fas Ligand antibody (GTX66619) (1:1000), Bid antibody (GTX110568) (1:1000), E-cadherin antibody (GTX100443) (1:1000), Vimentin antibody (GTX100619) (1:5000), Twist 1/2 antibody (GTX127310) (1:1000), MMP-2 antibody (GTX104577) (1:1000), c-jun antibody (SC-1694) (1:1000), GAPDH antibody (SC-32233) (1:500), Anti-JNK 1/2 antibody (A1HO1362) (1:500), Anti-caspase 9 antibody (ab32539) (1:500), Anti-cleaved-caspase 3 antibody (ab2302) (1:500), Anti-cytochrome c antibody (ab13575) (1:1000), Anti-Poly-(ADP-Ribose)-Polymerase antibody (11835238001) (1:1000), COXIV Polyclonal antibody (11242-1-AP) (1:1000), MMP-9 antibody (NBP2-13173) (1:1000). The following secondary antibodies were used: Mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) (1:6000), Rabbit IgG H&L antibody (ab97051) (1:6000).
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
Culture-Inserts were attached to 3 cm culture dishes, and 70 μL of SAS (1.5 × 104) and GNM (3 × 104) cells were seeded into the grids on both sides of the Culture-Insert. After incubation for 24 hours, 2 mL of DMEM medium was added to each plate, and the Culture-Insert was removed vertically. The images were taken at a 100X magnification level using a microscope. Subsequently, serial concentrations of 0–100 μM or 0–200 μM ALA were added to the dishes, and they were incubated in a cell culture incubator for 24 or 48 hours. The cells were observed and photographed under a microscope at 100x magnification, and the images were quantified using Image J.
2.8. Cell Invasion Assay
An 8.0 μm pore invasion chamber coated with Matrigel was set up then SAS (1.5 × 104) and GNM (3 × 104) cells were seeded into it. The cells were incubated for 24 hours and then treated with serial concentrations of ALA (0–100 μM or 0–200 μM). After a further day of incubation, the cells were fixed and stained for microscopic examination. Image J was then used to perform the analysis on the images.
2.9. Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
SAS and GNM cell lines were separately seeded in 6 cm culture dishes at a density of 6 × 105 and 1 × 106 cells, respectively. Serial concentrations of ALA (0–200 μM or 0–400 μM) were added to the dishes and the cells were treated for 24 hours or 0, 12, or 24 hours with 200, 400 μM ALA. The morphology of cells was examined and photographed at 100x magnification. After treatment, the cells were detached, collected, and detected by flow cytometry. Flow cytometry was used for the detection and quantification of cell apoptosis. The scatter plot displayed annexin V fluorescence-labeled cells on the x-axis and propidium iodide fluorescence-labeled cells on the y-axis. By combining annexin V and propidium iodide staining the results could be distinguished using flow cytometry. Finally, the data were quantified using Flow JO analysis software.
2.10. Cell Colony Formation Assay
SAS and GNM cell lines were separately seeded in a 6-well plate at a density of 2 × 102 and 2 × 103 cells, respectively. Serial concentrations of ALA (0–100 μM, or 0–200 μM) were added to the wells and cells were cultured for 9 days. And the absorbance was measured at 645 nm using a microplate reader. It is reasonable to calculate the colony-forming fraction by comparing the absorbance readings of the control and treatment groups. After treatment, colonies were quantified using Image J software. The percentage of colonies was determined by comparing the absorbance values of the control group and the treatment group.
2.11. Gelatinase Zymography Analysis
SAS and GNM cell lines were separately seeded in a 6-cm culture dish at a density of 6 × 105 and 1×106 cells, respectively. Then treated with serial concentrations of ALA (0–200 μM, or 0–400 μM), and incubated for 24 hours. Electrophoresis was performed on the collected conditioned medium after it had been combined with a loading buffer. The gel was washed twice, incubated in reaction buffer (containing 1% NaN3, 2 M Tris base pH 8.0, and 1 M CaCl2), stained (containing Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250, naphthol blue black methanol, and acetic acid), and destained (containing methanol and acetic acid). The enzyme activity was quantified using Alphaeasefc Software.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data for each group were presented as mean ± SD. SPSS was used for statistical analysis on the experimental data. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test was used for analysis. Significant differences between groups were denoted by different letters when the p-value was <0.05. The statistical data in all
Figures were analyzed using the t-test (Student's two-tailed t-test), and significance was indicated by asterisks (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001) compared to control. Graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism software, and the pathway diagram for the conclusion was created using BioRender (
http://biorender.com).
4. Discussion
The basic structure of the cell membrane is lipids, with PUFAs, especially n-6 PUFA arachidonic acid (AA), being one of the most essential components [
89]. AA can be converted into eicosanoids by phospholipase A2 (PLA2), which are linked to tumor growth, progression, and metastasis [
90,
91]. Recent studies on the anticancer properties of n-3 PUFAs has focused mostly on EPA and DHA present in fish oil, and these fatty acids have been demonstrated to have an effect against many different types of cancer [
92,
93,
94]. It has also been demonstrated that they improve the efficacy and tolerability of chemotherapy[
95]. Researchers have found that n-3 PUFAs influence immunological responses, inflammation, cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis in cancer cells via blocking the production of prostaglandins [
96]. n-3 PUFAs have been shown to modulate membrane fluidity or modify the structure and composition of lipid rafts, thereby inhibiting the growth of breast cancer cells [
97,
98]. The maximum concentration of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is found in flaxseed oil, which is an excellent source of ALA supplementation [
72,
99]. According to research, ALA is advantageous to the human body and has anticancer properties. A case-control study suggested that ALA consumption may protect against the development of bladder cancer [
100]. ALA can inhibit liver cancer cell COX-2 expression and promote apoptosis [
101]. In ACI-T mice implanted with subcutaneous hepatoma 3924A cells, a diet high in 10% ALA for 28 days significantly suppressed the expression of fatty acid synthase and promoted death in tumor tissues [
101]. In BALB/c mice with MCF-7 human breast cancer xenografts and thymectomy, feeding them ALA-rich flaxseed oil (40 g/kg) for 8 weeks inhibited tumor growth and induced apoptosis [
102]. A recent study found that ALA inhibits the growth of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231), as well as cervical cancer cells (SiHa and HeLa), by lowering the generation of nitric oxide (NO) and triggering lipid peroxidation [
103]. ALA can also stabilize HIF-1 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and downregulate fatty acid synthase to initiate mitochondrial apoptosis [
68]. Although numerous studies have verified ALA's anticancer properties, its effects on oral cancer are still unknown.
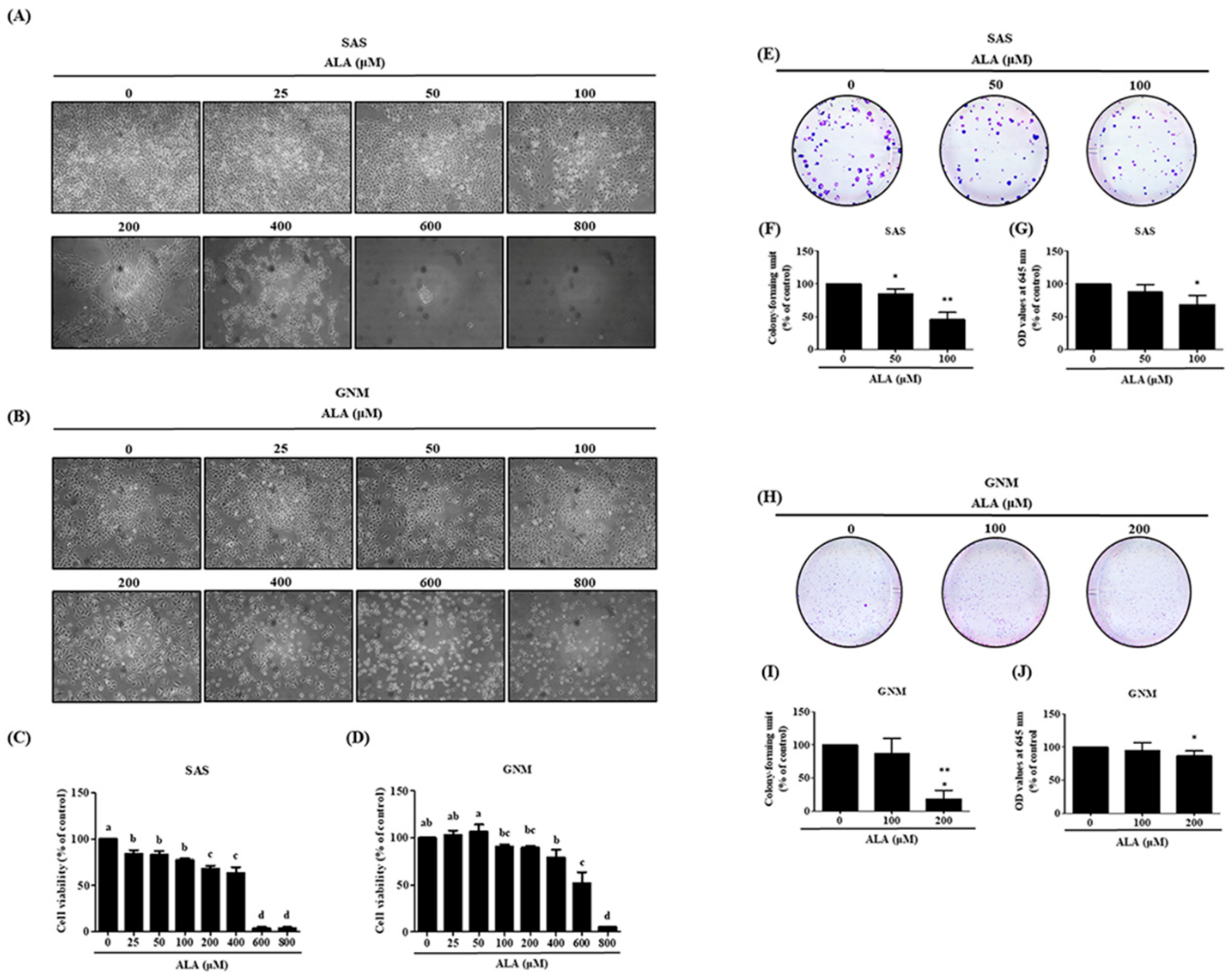
In this study, SAS and GNM cells were used as experimental models to investigate the anticancer effects and mechanisms of ALA. 24 hours were spent treating cells with variable concentrations of ALA (0, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, and 800 μM). It was discovered that 100 and 200 μM ALA did not induce cytotoxicity in SAS and GNM cells, whereas 200 and 400 μM ALA significantly reduced cell viability. In the 800 μM ALA treatment group, only about 5% of the cells were viable (
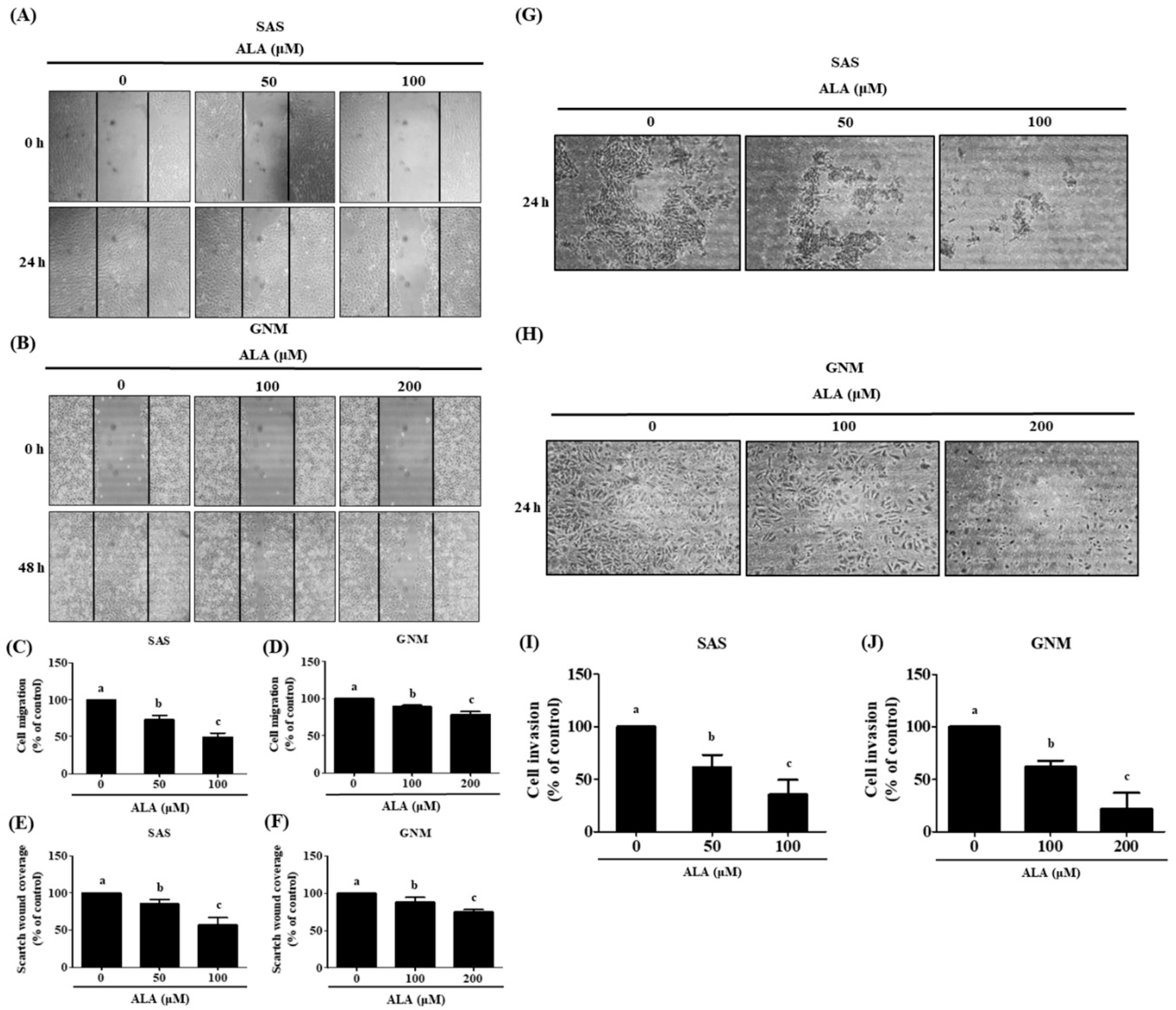
Figure 1). Consequently, non-lethal concentrations of ALA (50, 100, and 100, 200 μM) were chosen for further study of their effects on cell migration. As shown in
Figure 2, treatment of SAS and GNM cells with 100 and 200 μM ALA for 24 hours inhibited migration and invasion. These results suggest that GNM cells are more malignant than SAS cells because they require larger amounts of ALA to prevent migration and invasion. Human osteosarcoma (MG63, 143B, and U2OS) cells' proliferation and invasion have been demonstrated to be suppressed by 80 μM ALA in previous research [
104]. Proliferation of breast cancer cells (MCF-7, BT-474, MDA-MB 231, and MDA-MB 468) can be suppressed by ALA at concentrations ranging from 20 to 200 μM by downregulating the expression of proteins such cyclin-D1, progesterone receptor, and caveolin-1 and upregulating the expression of estrogen receptor [
73,
74]. SiHa and HeLa human cervical cancer cell migration can be blocked by ALA (10–80 μM) by downregulation of VEGF, MMP-2, and MMP-9 expression. [
80]. Human esophageal cancer cell lines OE19 and OE33 had their proliferation, colony size, adhesion, and migration suppressed by 0.5–5 mM ALA because to its ability to activate the AMPK signaling pathway and increase expression of tumor suppressor genes p53, p21, and p27 [
105]. Different cell lines have varying ALA tolerances, and ALA inhibits cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating diverse signaling pathways. Downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of N-cadherin, fibronectin, and vimentin expression has been linked to Twist1, which is one of the primary transcription factors that induce EMT. It plays an important part in cancer development and spread [
46,
47]. Studies show that E-cadherin is downregulated and Twist is overexpressed in OSCC tumor tissues relative to normal tissues[
106]. Nuclear expression of Twist is significantly correlated with clinical stage and lymph node metastasis in OSCC cells compared to normal oral mucosal cells [
85], suggesting that Twist plays a crucial role in the development and lymph node metastasis of OSCC. Nuclear expression of Twist is significantly correlated with clinical stage and lymph node metastasis in OSCC cells compared to normal oral mucosal cells[
85], indicating that Twist plays a crucial role in the development and lymph node metastasis of OSCC. Recent work in our group found that ALA suppresses EMT, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells [
79]. However, it is unclear if ALA controls EMT in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Figure 3 shows that a dose-dependent inhibition of Twist expression was seen when ALA (100 μM and 200 μM) was applied to SAS and GNM human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. The expression of Vimentin was downregulated while that of E-cadherin was upregulated as a result of ALA therapy. Oral cancer cell migration and invasion can be encouraged by elevated MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and activity [
53]. The expression and enzymatic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in SAS and GNM cells are suppressed by ALA, as shown in
Figure 5. These results suggest that ALA can reduce the expression and activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9, promote the expression of E-cadherin, and so prevent the migration and invasion of SAS and GNM cells. DHA has been proven in studies to reduce MMP-9 production and activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells via blocking DNA-binding activity of NF-B and AP. More research is needed to confirm whether or not ALA can suppress MMP expression in SAS and GNM cells by modulating NF-B and AP-1 [
107].
Auto-activation of procaspase-8, caspase-3, and PARP activation are all known to follow FasL interaction to the Fas receptor and begin extrinsic apoptosis [
54]. However, the release of cytochrome c and the activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway are both triggered by the cleavage of Bid, which occurs upon caspase-8 activation, to generate tBid, which then inserts into the mitochondrial membrane. As a result, Bid has been singled out as an integral connector between extrinsic and intrinsic pathways [
108]. Previous studies have shown that the caspase-8/Bid pathway can trigger apoptosis in oral cancer cells [
86]. Increased cell proliferation and invasion capabilities, as well as a poor prognosis, have all been linked to a low FasL/Fas ratio in patients with OSCC [
109]. ALA was administered at various concentrations to SAS and GNM human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. High concentrations of ALA substantially decreased Fas expression and increased FasL protein expression, resulting in the activation of caspase-8 and extrinsic apoptosis (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). Additionally, ALA treatment further activates Bid via caspase-8, resulting in intrinsic apoptosis. These results are consistent with Lee et al.'s findings [
65]. FasL is known to be expressed by T cells during immune responses; it can bond to Fas on the membranes of tumor cells and induce apoptosis. There are two forms of FasL: membrane-bound FasL (mFasL) and soluble FasL (sFasL). mFasL is cleaved by MMP to produce the latter [
58]. Increased sFasL can compete with mFasL on T cells to bind to Fas receptors on the membranes of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting the signaling that induces cell apoptosis and suppressing the immune system's attack on malignancies [
109]. The findings of this study demonstrated that ALA effectively inhibited the expression of MMPs, suggesting that ALA may also inhibit the production of sFasL to reduce competitive binding with membrane-bound mFasL. Through the interaction between mFasL and Fas receptors on cancer cells, ALA may induce apoptosis. Future experiments can investigate this hypothesis. Previous research has demonstrated that JNK can upregulate the expression of FasL and induce apoptosis in OSCC cells [
57,
59] Pretreatment with SP600125 substantially inhibited JNK phosphorylation and decreased the expression of FasL induced by ALA, according to the findings of this study. ALA induces JNK phosphorylation, upregulates FasL expression, and promotes cell apoptosis. In a 4-week human investigation, participants consumed 6 g of flaxseed oil cake (containing approximately 5.74 g of ALA) daily; at the conclusion of the study, their plasma ALA concentration increased significantly from 85.13 μM to 249.97 μM [
110]. On the basis of these findings, it can be estimated that to increase the plasma ALA concentration by 100, 200, or 400 μM, an additional daily intake of 3.75, 7.5, or 15 g of flaxseed oil (each containing 3.6, 7.2, or 14.4 g of ALA) for 4 weeks would be necessary to achieve the target values, which could improve the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. In previous human trials, 30 mL of flaxseed oil was administered for 4 weeks, and in another study, flaxseed pastries with a high flaxseed content (containing 59% ALA, approximately 23.6 g) were consumed for 30 days [
99,
111]. It has been reported that 50 grams of flaxseed consumed daily has no negative effects on the human organism [
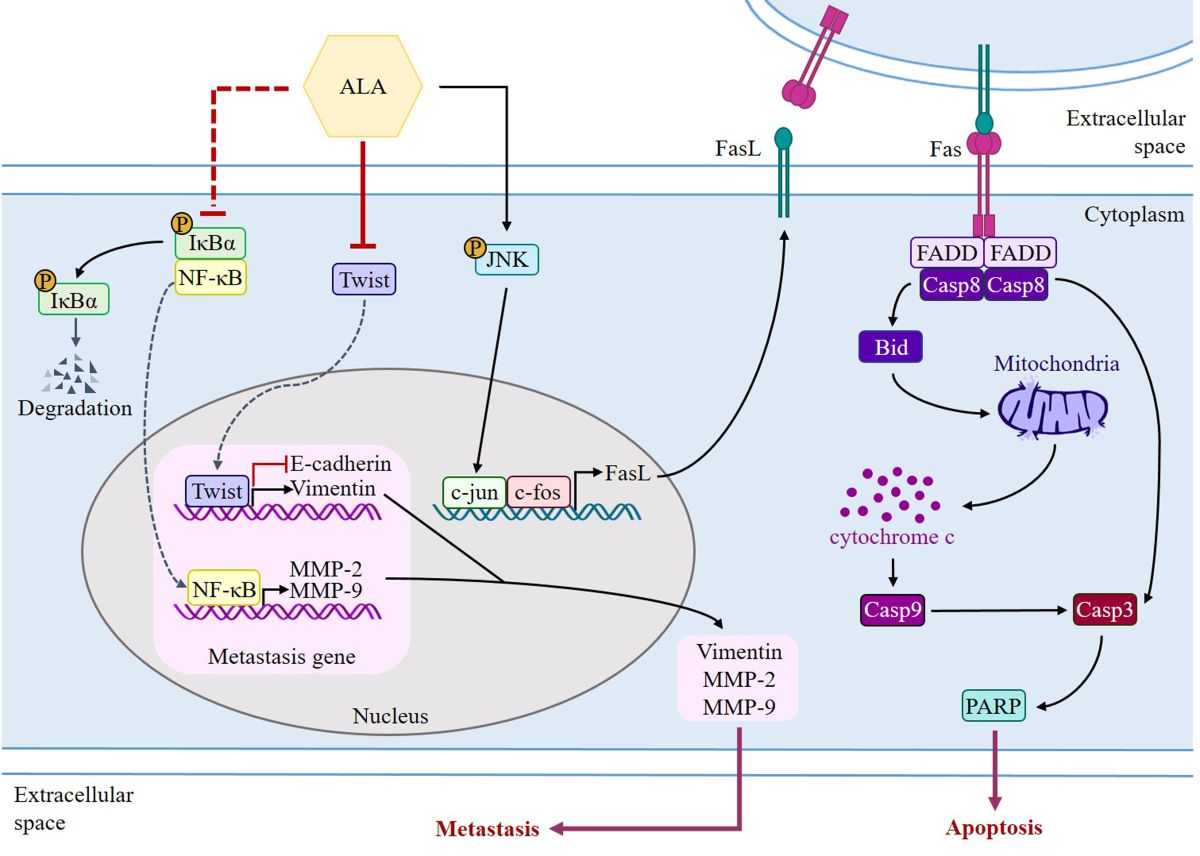
112]. Multiple studies have found that ALA can prevent the migration and invasion of SAS and GNM oral squamous cell carcinoma cells, as well as downregulate the expression of Twist and EMT-related proteins. Apoptosis in SAS and GNM oral squamous cell carcinoma cells can be induced by ALA through elevation of FasL expression and activation of the FasL/caspase signaling pathway. The use of ALA as a targeted therapeutic in clinical settings is feasible. Additional study can be conducted to discover whether ALA can influence the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma via other signaling pathways, and more in-depth animal tests can be performed, all with the hope that ALA can serve as an auxiliary therapy for OSCC patients.
Figure 1.
Effect of ALA on morphology and cell viability in SAS cells and GNM cells. (A) The morphology of SAS cells (B) The morphology of GNM cells. (C) The cell viability was determined using the MTT assay of SAS. (D) The cell viability was determined using the MTT assay of GMN. (E-G) The SAS cells growth and proliferation were determined using the colony formation assay. (H-J) The GNM cells growth and proliferation was determined using the colony formation assay. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Significance of difference in weeks of different tests was evaluated by Tukey’s multiple range test statistical analysis. Different superscript letters a, b, c, d indicate that the statistically different from each other (P<0.05).
Figure 1.
Effect of ALA on morphology and cell viability in SAS cells and GNM cells. (A) The morphology of SAS cells (B) The morphology of GNM cells. (C) The cell viability was determined using the MTT assay of SAS. (D) The cell viability was determined using the MTT assay of GMN. (E-G) The SAS cells growth and proliferation were determined using the colony formation assay. (H-J) The GNM cells growth and proliferation was determined using the colony formation assay. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Significance of difference in weeks of different tests was evaluated by Tukey’s multiple range test statistical analysis. Different superscript letters a, b, c, d indicate that the statistically different from each other (P<0.05).
Figure 2.
Depicts the effect of ALA on cell migration and invasion in SAS and GNM cells. SAS cells (A) and GNM cells (B) were treated for 24 or 48 hours with 0, 50, 100, or 0, 100, 200 μM ALA. (C-F) The wound healing assay was used to measure cell migration. (G) SAS cells and (H) GNM cells were treated for 24 hours with 0, 50, 100, or 0, 100, 200 μM ALA. The cell invasion was measured using the Boyden chamber assay (I, J). The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 2.
Depicts the effect of ALA on cell migration and invasion in SAS and GNM cells. SAS cells (A) and GNM cells (B) were treated for 24 or 48 hours with 0, 50, 100, or 0, 100, 200 μM ALA. (C-F) The wound healing assay was used to measure cell migration. (G) SAS cells and (H) GNM cells were treated for 24 hours with 0, 50, 100, or 0, 100, 200 μM ALA. The cell invasion was measured using the Boyden chamber assay (I, J). The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 3.
The effect of ALA on the expression of EMT-related proteins in SAS and GNM cells. For 24 hours, cells were treated with 0, 50, 100, 200 μM or 0, 100, 200, 400 μM ALA. (A) Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin in SAS cells. (B) SAS cell E-Cadherin expression quantification. (C) SAS vimentin expression quantification. (D) Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin in GNM cells. (E) Quantification of E-Cadherin expression in GNM cells. (F) Quantification of vimentin expression in GNM cells. (G) Twist expression in SAS cells. (H) SAS cell twist expression quantification. (I) Twist expression in GNM cells. (J) Quantification of twist expression in GNM cells. (K) SAS cell MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. (L) SAS cell pro-MMP9 expression quantification. (M) SAS cell MMP-2 expression measurement. (N) Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in GNM cells. (O) Quantification of pro-MMP9 expression in GNM cells. (P) Quantification of MMP-2 expression in GNM cells. (Q) Protein expression and enzyme activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in SAS cells. (R) MMP-2 enzyme activity in SAS cells. (S) MMP-9 enzyme activity in SAS cells. (T) Protein expression and enzyme activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in GNM cells. (U) MMP-2 enzyme activity in GNM cells. (V) MMP-9 enzyme activity in GNM cells. Western blotting was used to evaluate the protein expression of various proteins. Gelatin zymography was used to assess enzyme activity. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey‘s multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 3.
The effect of ALA on the expression of EMT-related proteins in SAS and GNM cells. For 24 hours, cells were treated with 0, 50, 100, 200 μM or 0, 100, 200, 400 μM ALA. (A) Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin in SAS cells. (B) SAS cell E-Cadherin expression quantification. (C) SAS vimentin expression quantification. (D) Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin in GNM cells. (E) Quantification of E-Cadherin expression in GNM cells. (F) Quantification of vimentin expression in GNM cells. (G) Twist expression in SAS cells. (H) SAS cell twist expression quantification. (I) Twist expression in GNM cells. (J) Quantification of twist expression in GNM cells. (K) SAS cell MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. (L) SAS cell pro-MMP9 expression quantification. (M) SAS cell MMP-2 expression measurement. (N) Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in GNM cells. (O) Quantification of pro-MMP9 expression in GNM cells. (P) Quantification of MMP-2 expression in GNM cells. (Q) Protein expression and enzyme activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in SAS cells. (R) MMP-2 enzyme activity in SAS cells. (S) MMP-9 enzyme activity in SAS cells. (T) Protein expression and enzyme activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in GNM cells. (U) MMP-2 enzyme activity in GNM cells. (V) MMP-9 enzyme activity in GNM cells. Western blotting was used to evaluate the protein expression of various proteins. Gelatin zymography was used to assess enzyme activity. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey‘s multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
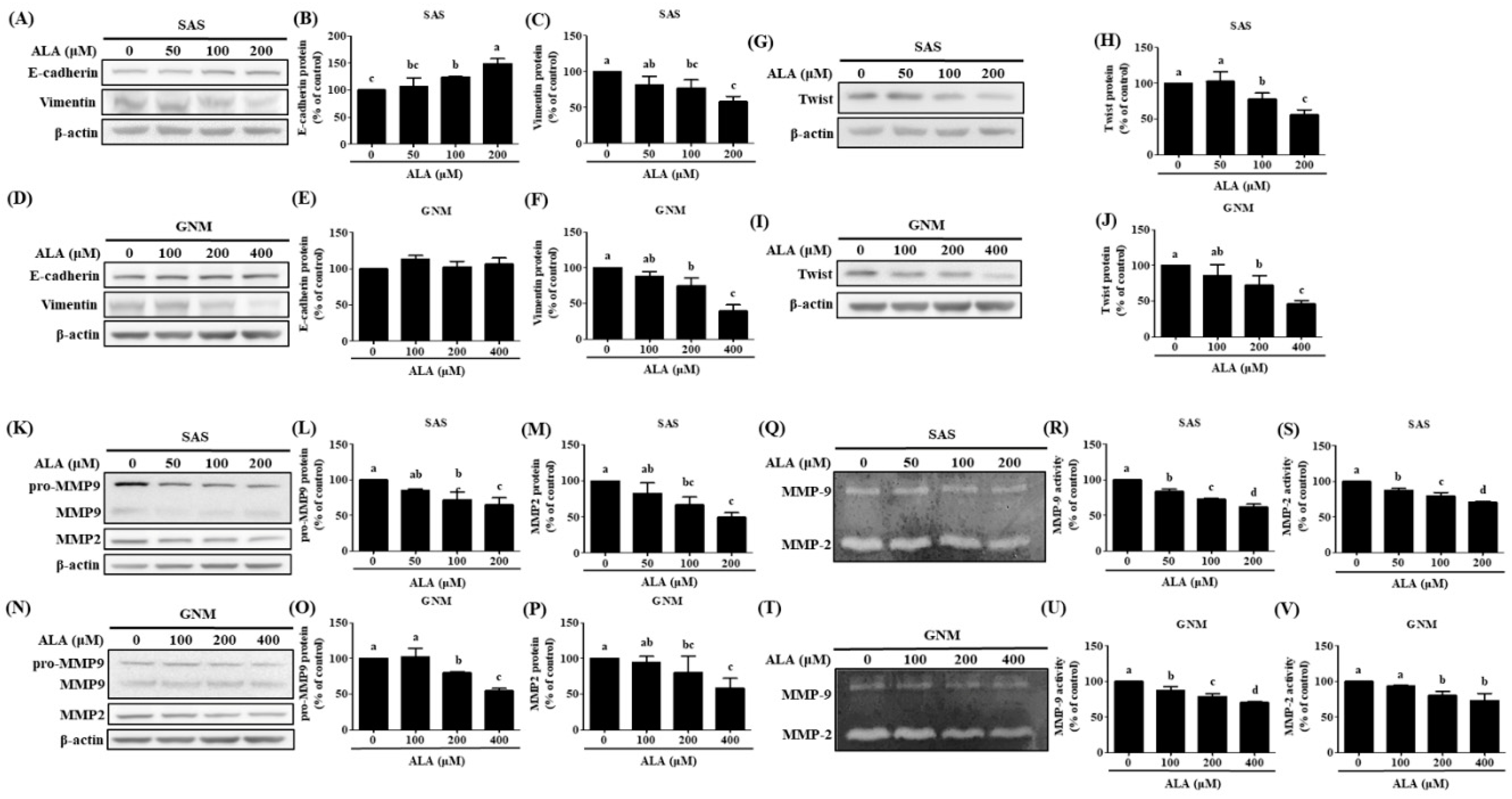
Figure 4.
Effect of ALA on the degree of apoptosis in SAS cells and GNM cells. SAS and GNM cells were treated for 24 hours with 0, 50, 100, 200, 400, or 600 μM ALA. (A) The level of apoptosis in SAS cells. (B) Apoptosis levels in GNM cells. (C) SAS cell apoptosis %. (D) GNM cell apoptosis %. (E) Apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells. (F) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 8 expression quantification. (G) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 9 expression was quantified. (H) Apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells. (I) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 8 expression in GNM cells. (J) Quantification of cleaved caspase 9 expression in GNM cells. (K) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 3 expression quantification. (L) SAS cell cleaved-caspase PARP expression was quantified. (M) GNM cell cleaved-caspase 3 expression was quantified. (N) GNM cell cleaved-caspase PARP expression was quantified. (O) Cytochrome c protein expression in mitochondria in SAS cells. (P) Cytochrome c cytosol protein expression in SAS cells. (Q) SAS cell mitochondria and cytoplasm protein expression of cytochrome c quantitation. (R) Cytochrome c protein expression in mitochondria in GNM cells. (S) Cytochrome c cytosol protein expression in GNM cells. (T) Quantification of mitochondrial and cytosol protein expression of cytochrome c in GNM cells. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 4.
Effect of ALA on the degree of apoptosis in SAS cells and GNM cells. SAS and GNM cells were treated for 24 hours with 0, 50, 100, 200, 400, or 600 μM ALA. (A) The level of apoptosis in SAS cells. (B) Apoptosis levels in GNM cells. (C) SAS cell apoptosis %. (D) GNM cell apoptosis %. (E) Apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells. (F) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 8 expression quantification. (G) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 9 expression was quantified. (H) Apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells. (I) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 8 expression in GNM cells. (J) Quantification of cleaved caspase 9 expression in GNM cells. (K) SAS cell cleaved-caspase 3 expression quantification. (L) SAS cell cleaved-caspase PARP expression was quantified. (M) GNM cell cleaved-caspase 3 expression was quantified. (N) GNM cell cleaved-caspase PARP expression was quantified. (O) Cytochrome c protein expression in mitochondria in SAS cells. (P) Cytochrome c cytosol protein expression in SAS cells. (Q) SAS cell mitochondria and cytoplasm protein expression of cytochrome c quantitation. (R) Cytochrome c protein expression in mitochondria in GNM cells. (S) Cytochrome c cytosol protein expression in GNM cells. (T) Quantification of mitochondrial and cytosol protein expression of cytochrome c in GNM cells. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
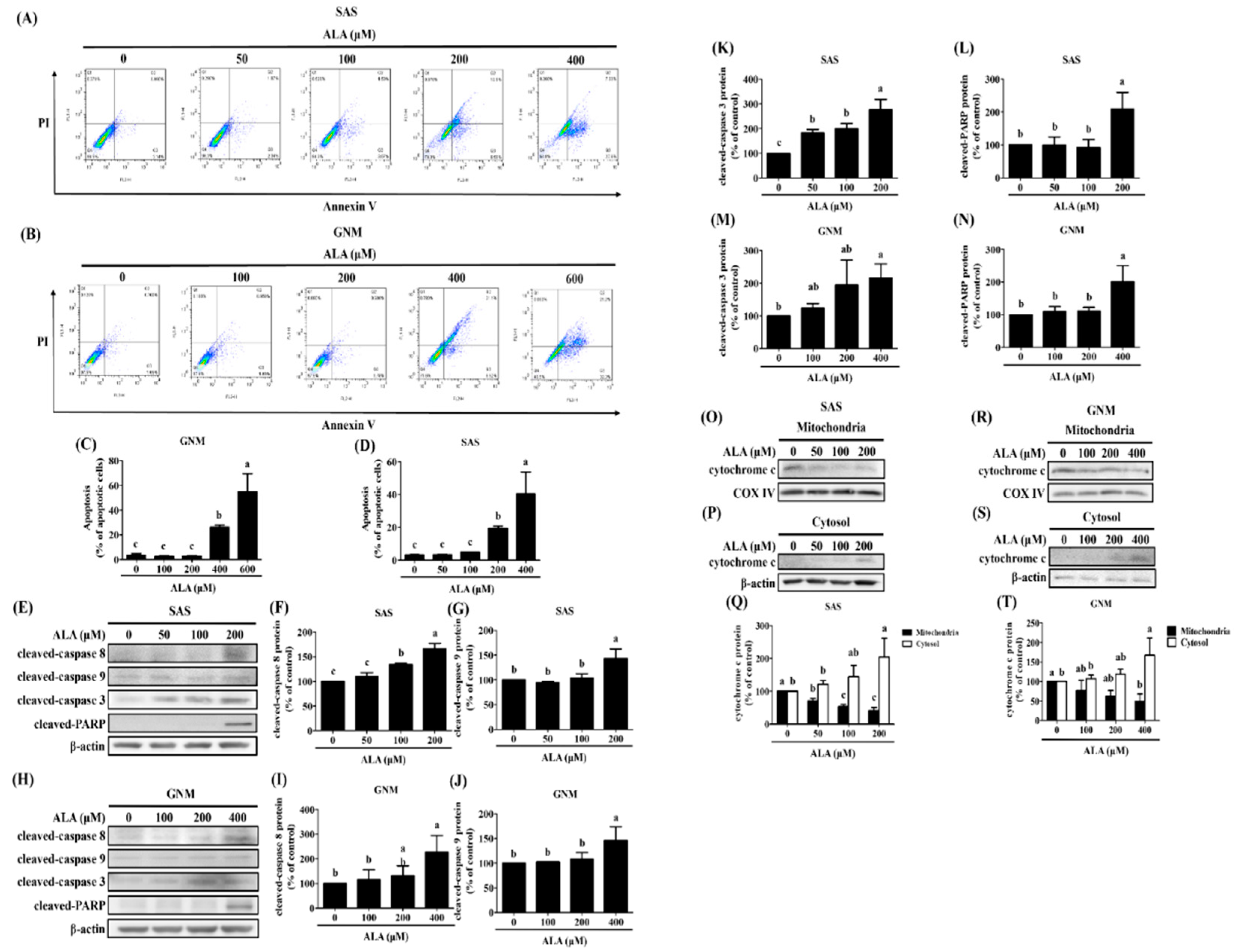
Figure 5.
The effect of ALA on Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells at various time points and ALA concentrations. (A) Fas, FasL, and Bid expression in SAS cells at various ALA concentrations. (B) Quantification of Fas expression in SAS cells at various ALA doses. (C) SAS cell FasL expression measurement under various ALA concentrations. (D) Bid expression measurement of SAS cells at various ALA concentrations. (E) Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of Fas expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. SAS cell (G) FasL expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (H) cleaved-caspase 8 expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (I) Bid expression measurement of SAS cells at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (J) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 9 expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (K) SAS cells cleaved-caspase 3 expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (L) Quantification of cleaved-PARP expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 5.
The effect of ALA on Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells at various time points and ALA concentrations. (A) Fas, FasL, and Bid expression in SAS cells at various ALA concentrations. (B) Quantification of Fas expression in SAS cells at various ALA doses. (C) SAS cell FasL expression measurement under various ALA concentrations. (D) Bid expression measurement of SAS cells at various ALA concentrations. (E) Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of Fas expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. SAS cell (G) FasL expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (H) cleaved-caspase 8 expression in SAS cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (I) Bid expression measurement of SAS cells at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (J) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 9 expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (K) SAS cells cleaved-caspase 3 expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (L) Quantification of cleaved-PARP expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
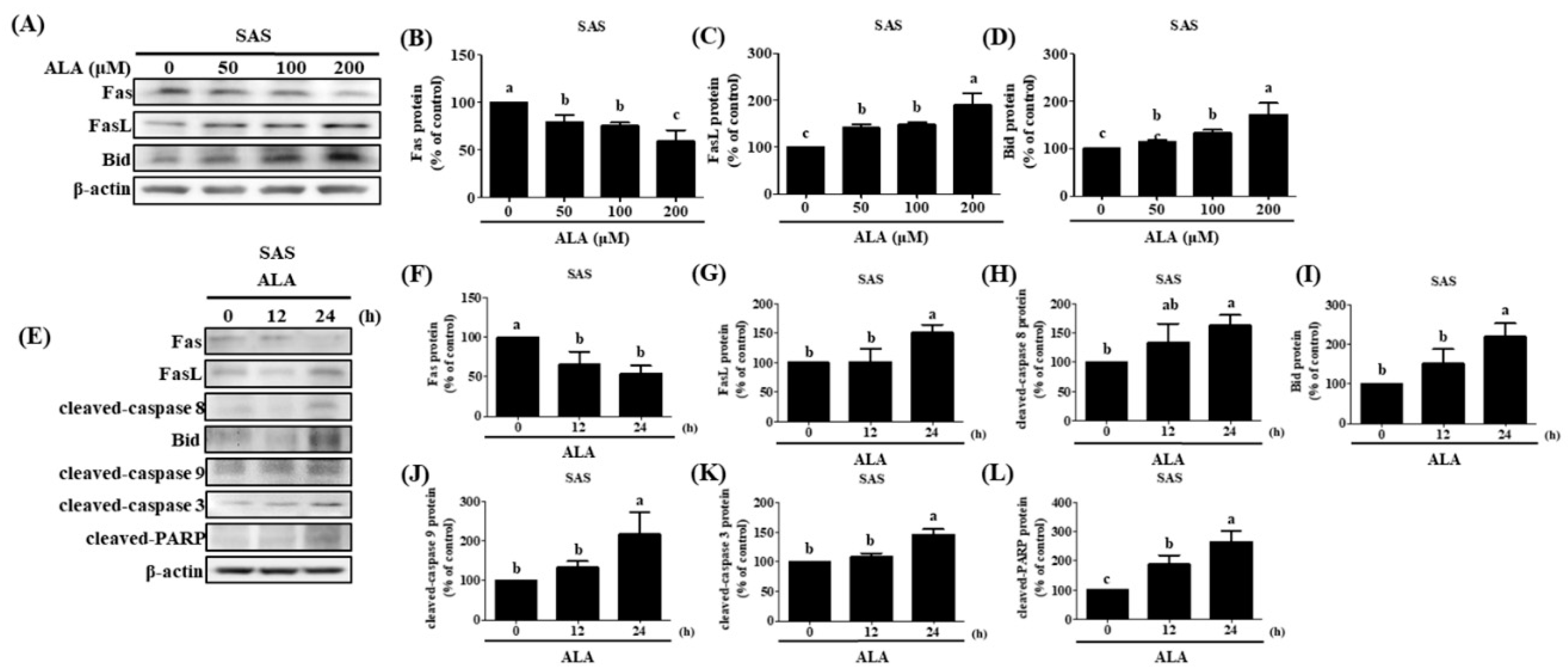
Figure 6.
The effect of ALA on Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells at various time points and ALA concentrations. (A) Fas, FasL, and Bid expression in GNM cells at various ALA concentrations. (B) Quantification of Fas expression in GNM cells at various ALA doses. (C) GNM cell FasL expression measurement under various ALA concentrations. (D) Bid expression measurement of GNM cells at various ALA concentrations. (E) Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of Fas expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. GNM cell (G) FasL expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (H) cleaved-caspase 8 expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (I) Bid expression measurement of GNM cells at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (J) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 9 expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (K) GNM cells cleaved-caspase 3 expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (L) Quantification of cleaved-PARP expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 6.
The effect of ALA on Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells at various time points and ALA concentrations. (A) Fas, FasL, and Bid expression in GNM cells at various ALA concentrations. (B) Quantification of Fas expression in GNM cells at various ALA doses. (C) GNM cell FasL expression measurement under various ALA concentrations. (D) Bid expression measurement of GNM cells at various ALA concentrations. (E) Fas, FasL, Bid, and apoptosis-related protein expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of Fas expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. GNM cell (G) FasL expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (H) cleaved-caspase 8 expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (I) Bid expression measurement of GNM cells at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (J) Quantification of cleaved-caspase 9 expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (K) GNM cells cleaved-caspase 3 expression measurement at various timepoints after ALA treatment. (L) Quantification of cleaved-PARP expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b, and c show that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
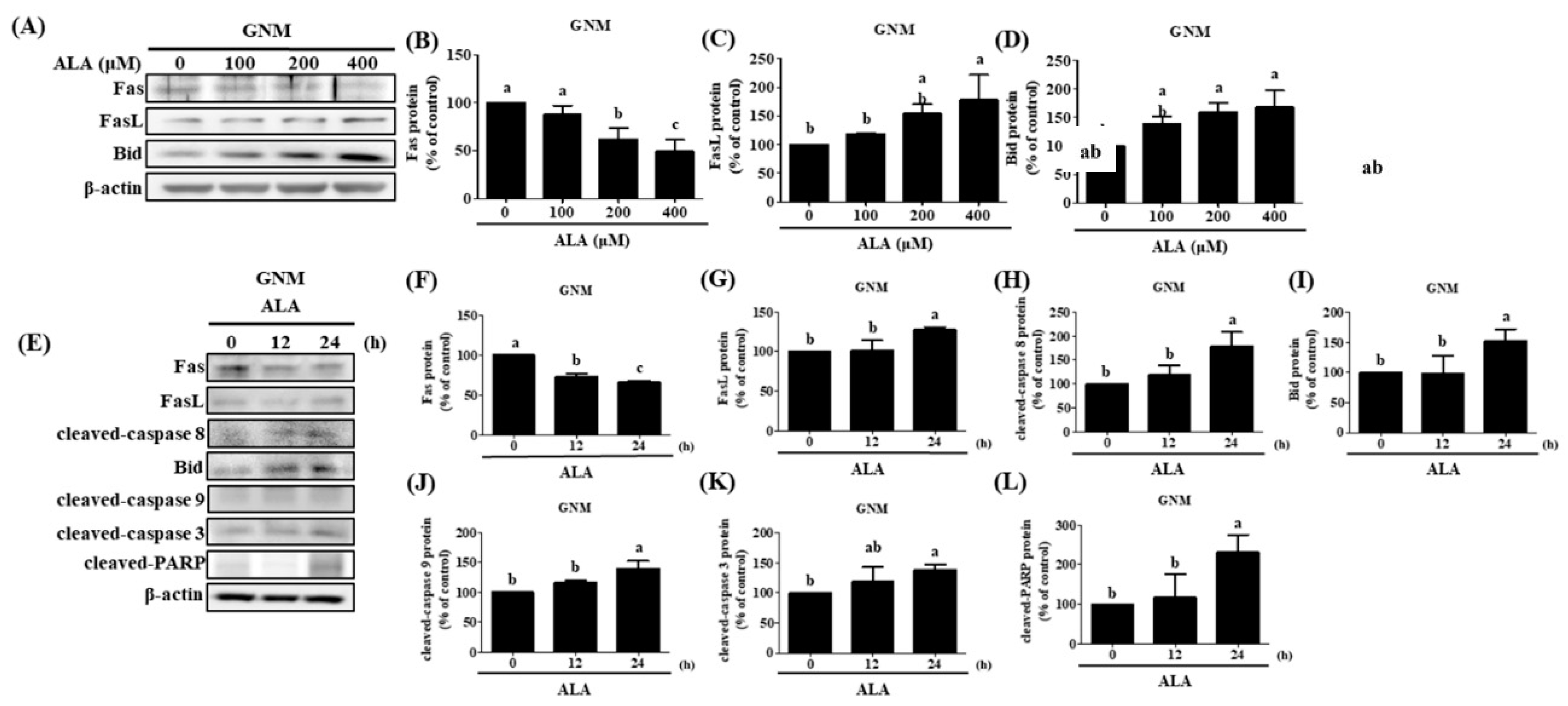
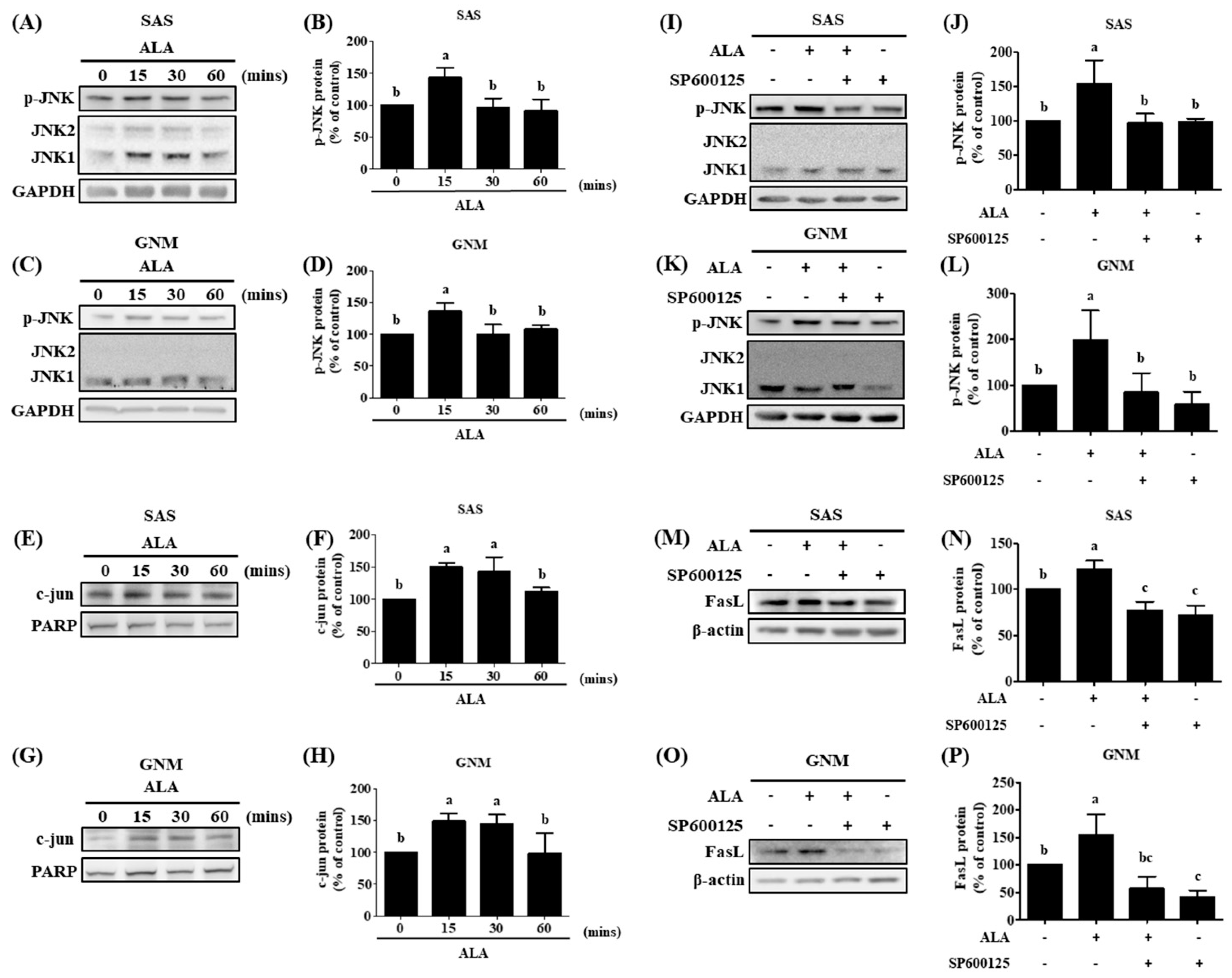
Figure 7.
Effect of ALA on p-JNK protein expression and c-jun protein accumulation of nucleus and JNK inhibitor on p-JNK and FasL protein expression in SAS and GNM cells at different time points. SAS and GNM cells were exposed to 200 or 400 μM ALA for 0, 15, 30, and 60 minutes. (A) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (B) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (C) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (D) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (E) c-jun and PARP protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of c-jun protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (G) c-jun and PARP expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (H) Quantification of c-jun and protein expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (I) Protein expression of p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 in SAS cells after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (J) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in SAS after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (K) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. (L) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in GNM cells after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (M) FasL protein expression in SAS cells after JNK inhibitor treatment (N) FasL protein expression quantification in SAS cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. (O) FasL protein expression in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment (P) FasL protein expression quantification in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. Western blotting was used to determine protein expression. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b imply that the are statistically different (P<0.05).
Figure 7.
Effect of ALA on p-JNK protein expression and c-jun protein accumulation of nucleus and JNK inhibitor on p-JNK and FasL protein expression in SAS and GNM cells at different time points. SAS and GNM cells were exposed to 200 or 400 μM ALA for 0, 15, 30, and 60 minutes. (A) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (B) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (C) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (D) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in GNM cells at various time points after ALA treatment. (E) c-jun and PARP protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (F) Quantification of c-jun protein expression in SAS cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (G) c-jun and PARP expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (H) Quantification of c-jun and protein expression in GNM cells at various time periods after ALA treatment. (I) Protein expression of p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 in SAS cells after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (J) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in SAS after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (K) p-JNK, JNK1, and JNK2 protein expression in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. (L) Quantification of p-JNK protein expression in GNM cells after treatment with a JNK inhibitor. (M) FasL protein expression in SAS cells after JNK inhibitor treatment (N) FasL protein expression quantification in SAS cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. (O) FasL protein expression in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment (P) FasL protein expression quantification in GNM cells after JNK inhibitor treatment. Western blotting was used to determine protein expression. The mean and standard deviation are used to express the values. Tukey's multiple range test statistical analysis was used to assess the significance of differences in weeks across different tests. Different superscript letters a, b imply that the are statistically different (P<0.05).