Submitted:
29 September 2023
Posted:
30 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
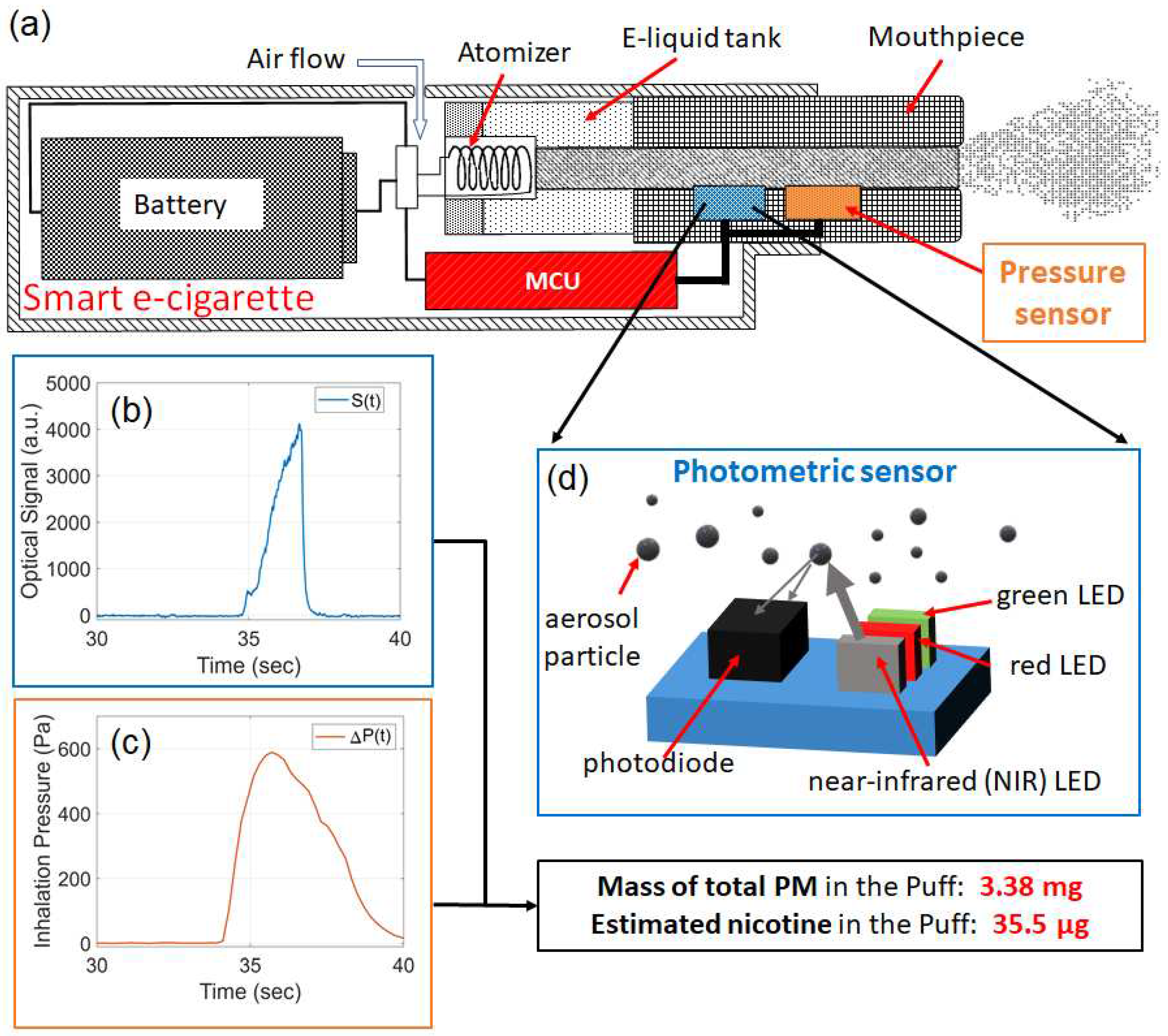
2. E-cig Topography Sensor Working Principle
3. Materials and Methods
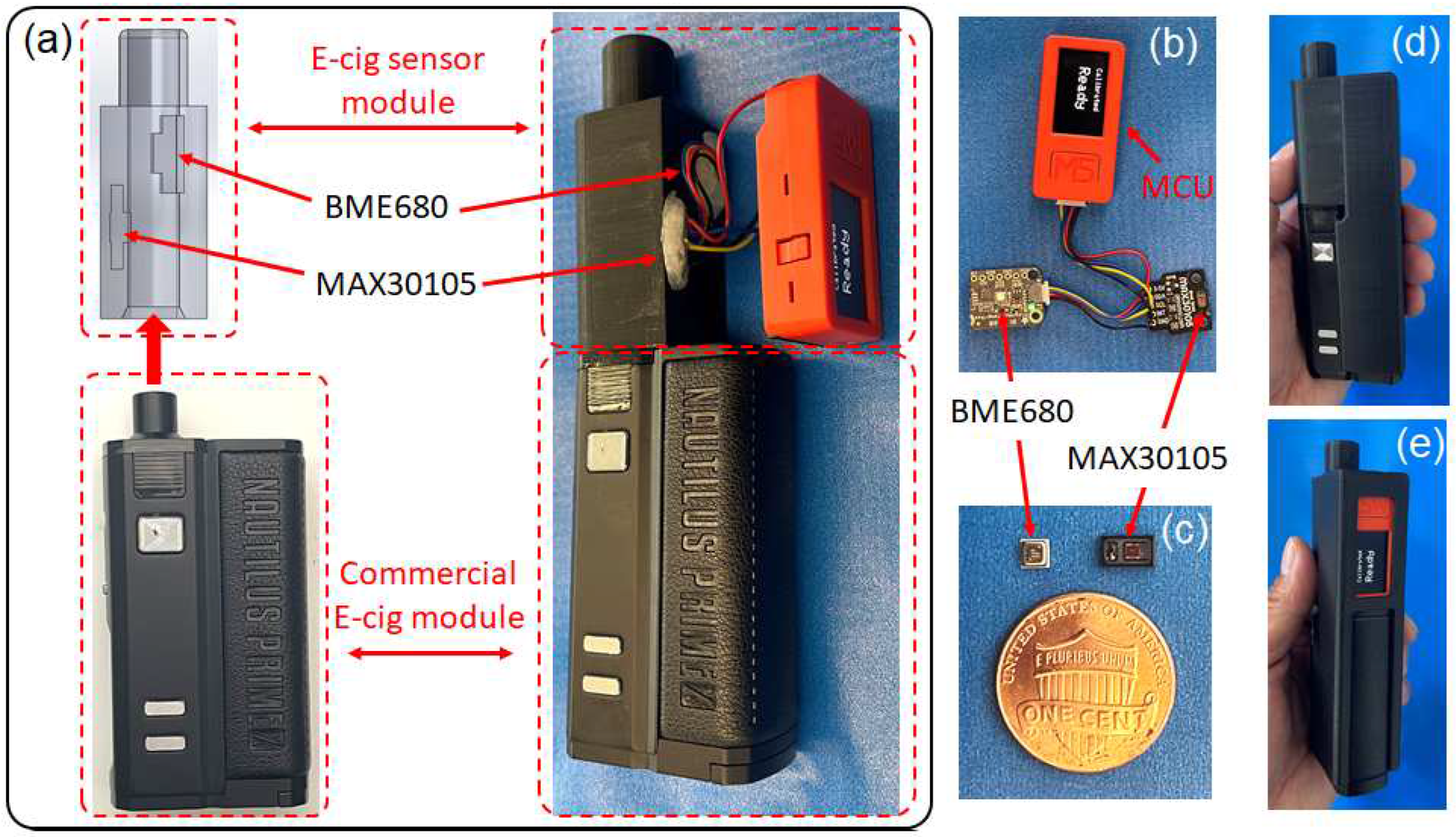
3.1. Prototype of E-cig Topography Sensor and Smart E-cigarette
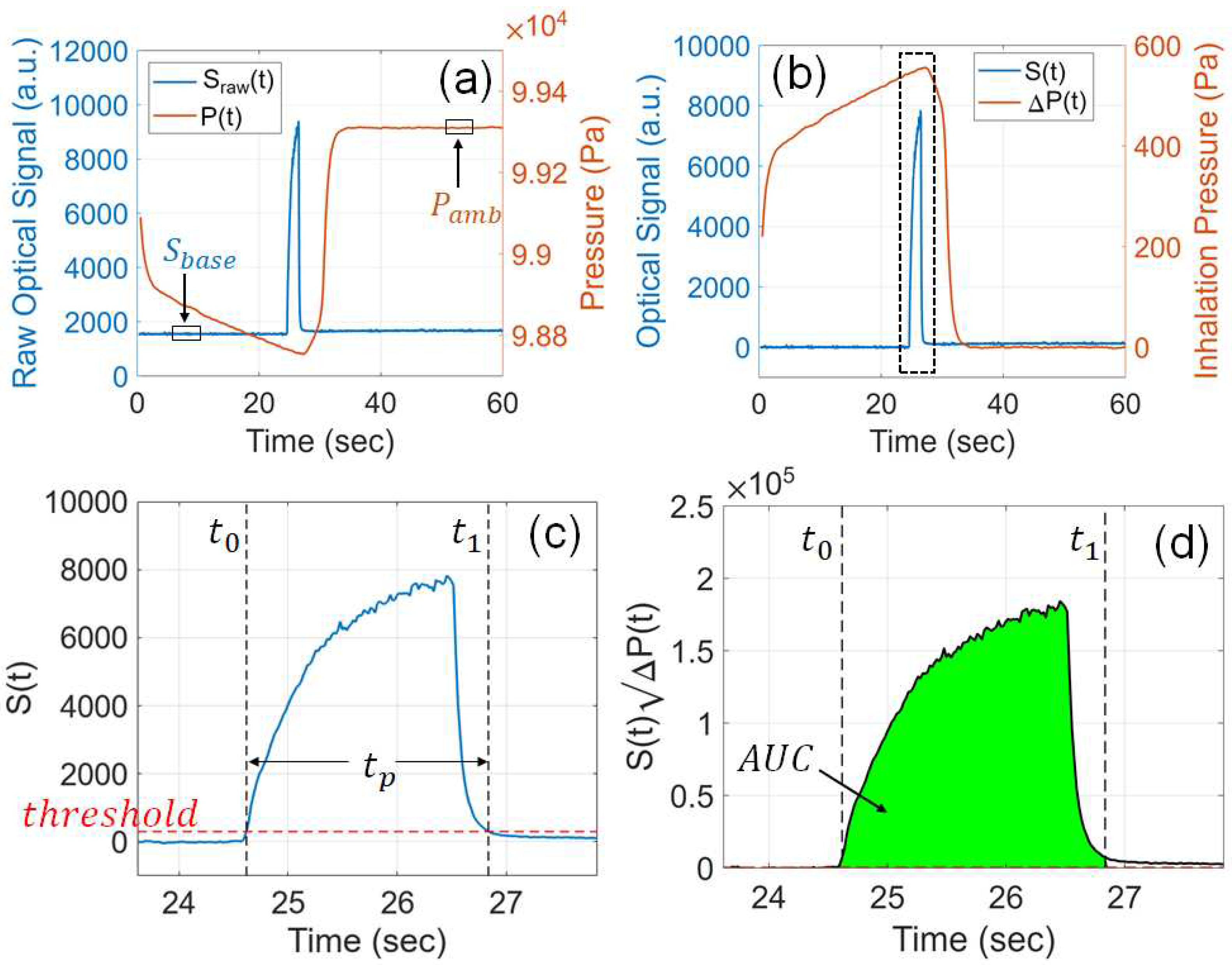
3.2. Sensor Signal Processing
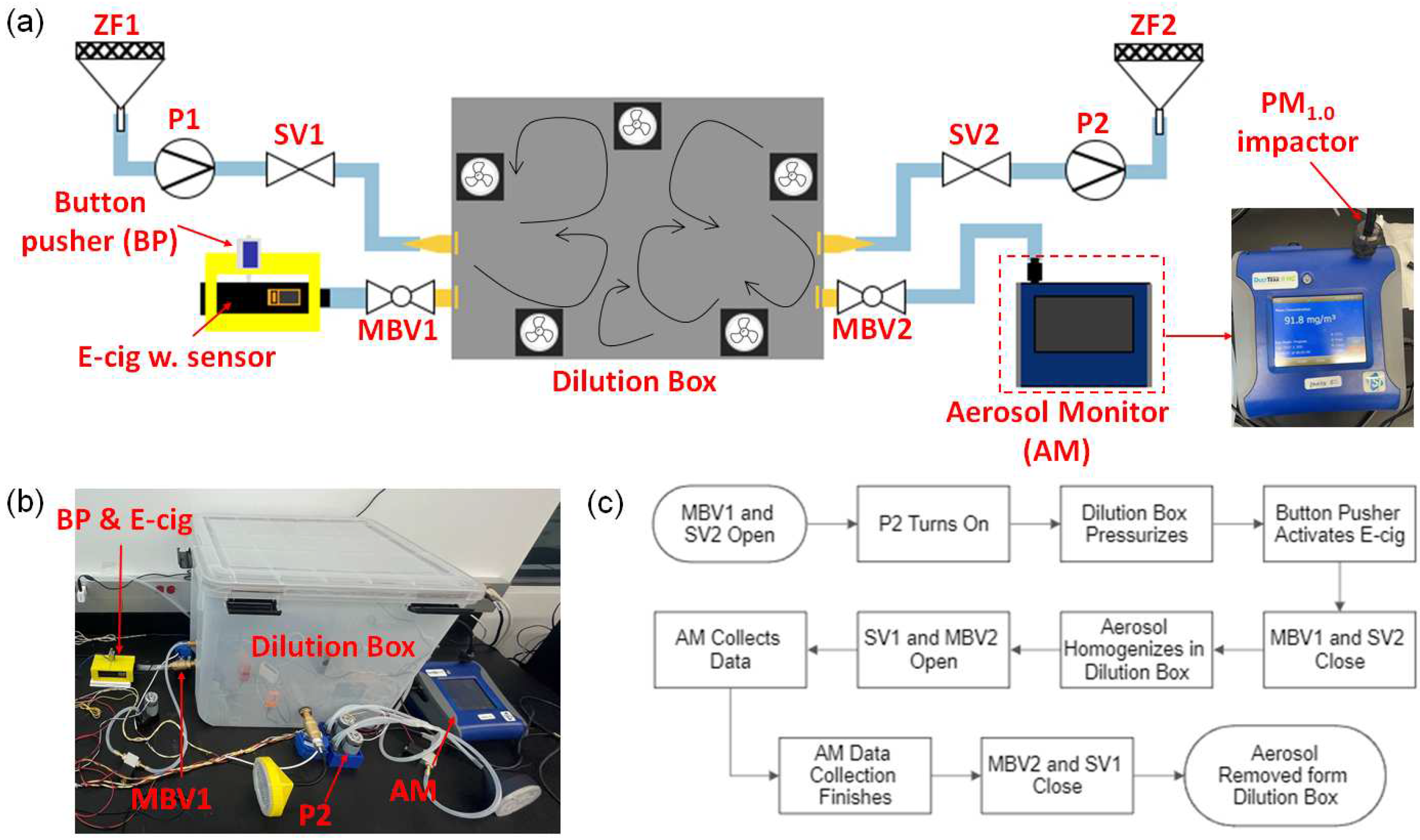
3.3. Vaping Machine and Reference Measurement
3.4. Sensor Calibration
3.5. Sensor Validation
3.6. Effects of Atomizer Power
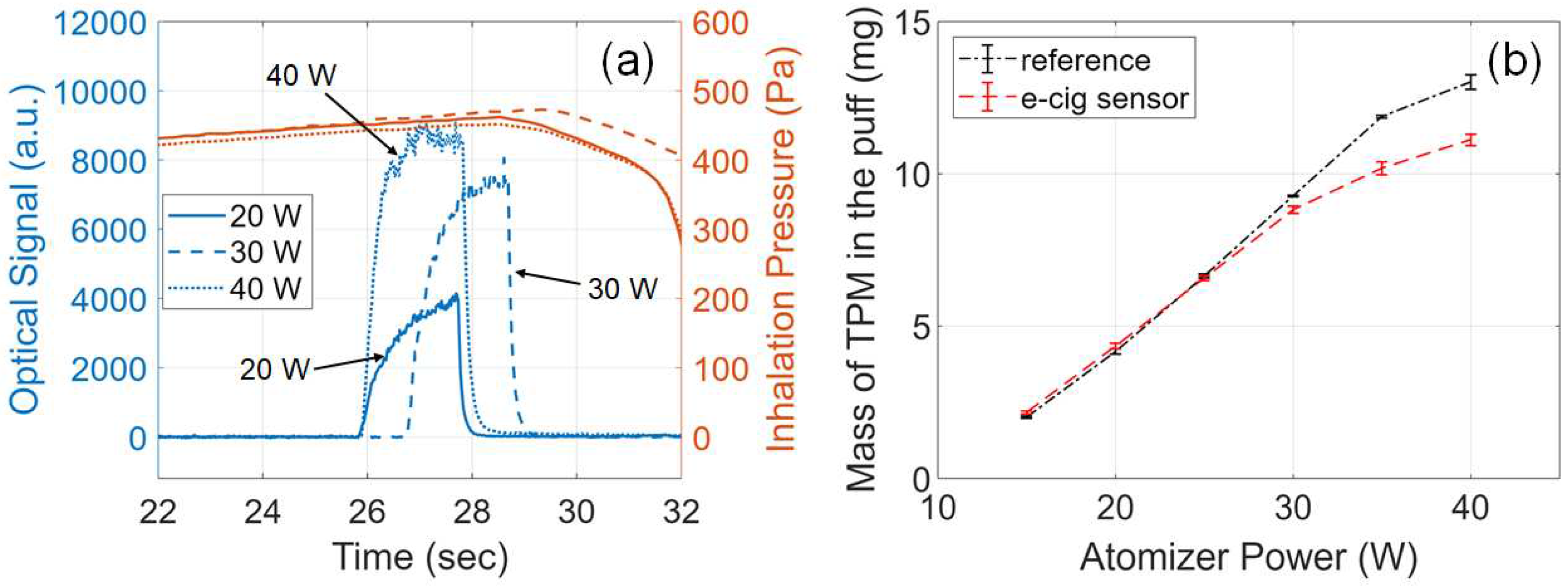
3.7. Effects of Puff Duration
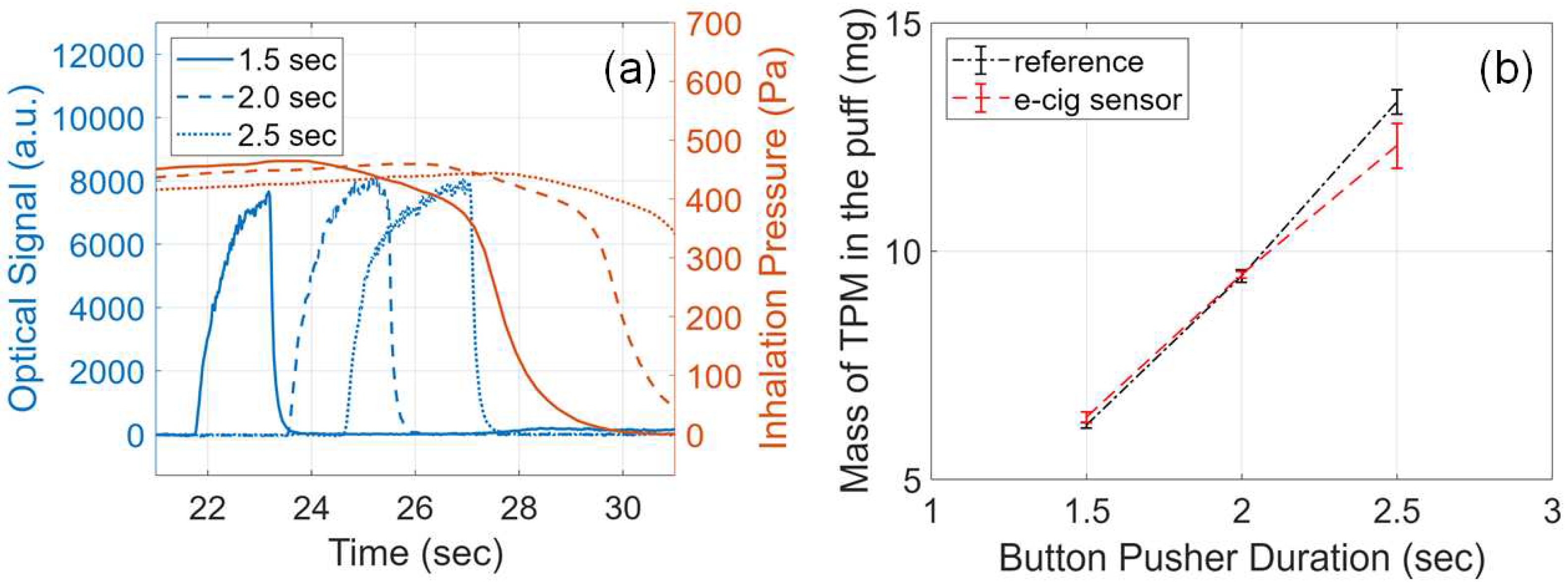
3.8. Effects of Inhalation Pressure
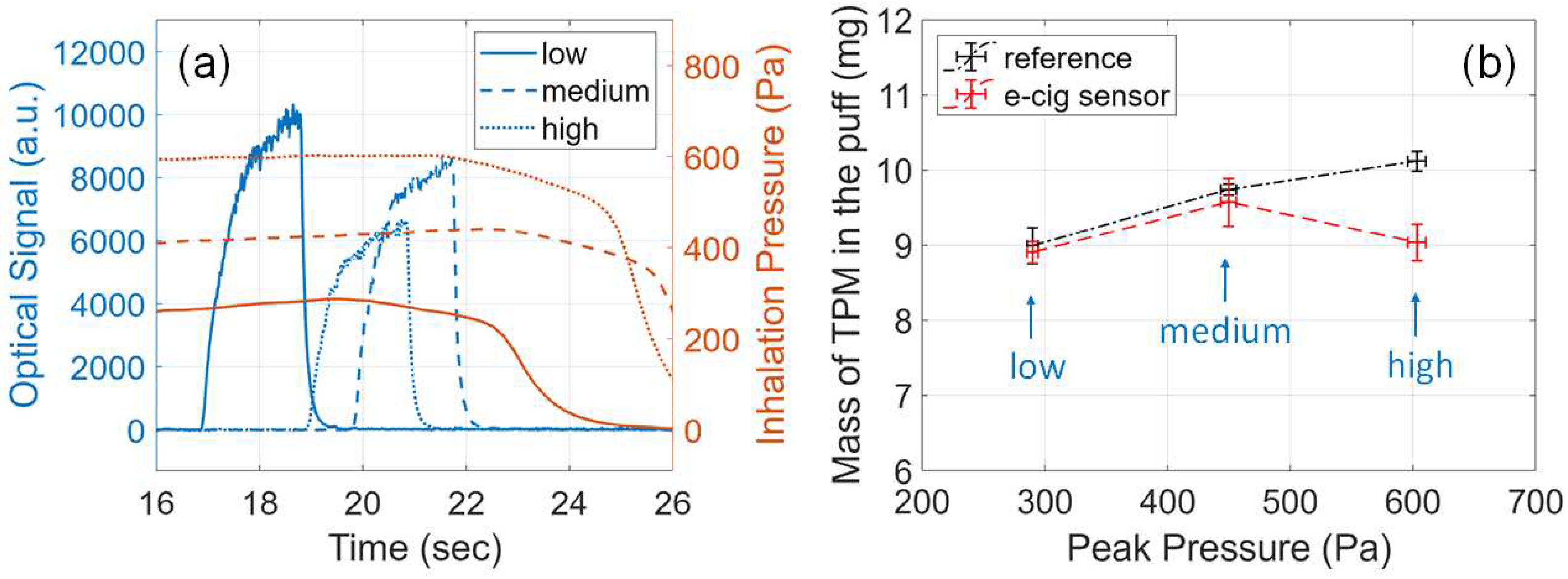
3.9. Effects of Cold Atomizer Coil
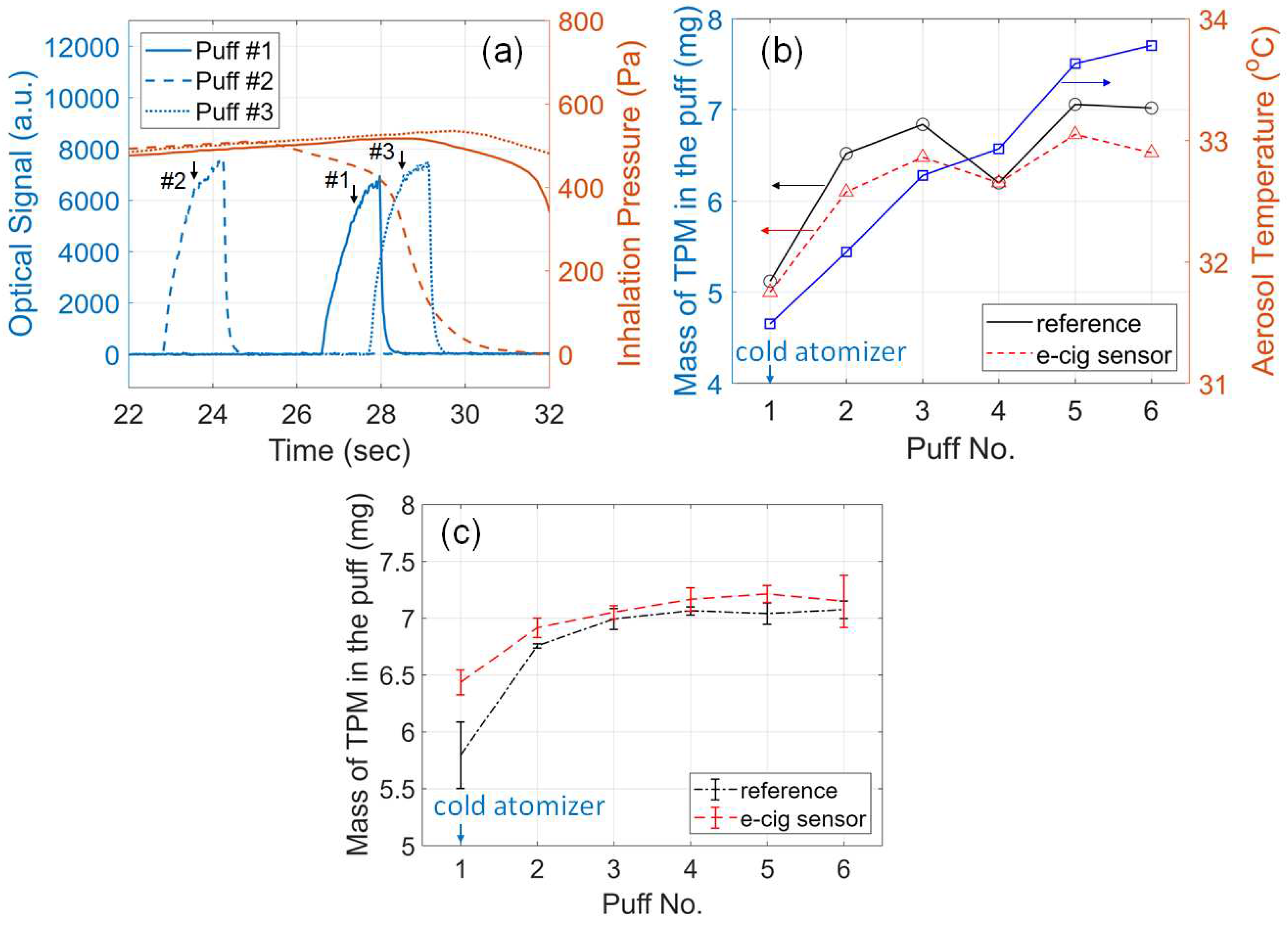
3.10. Tracking a User’s Puff Topography
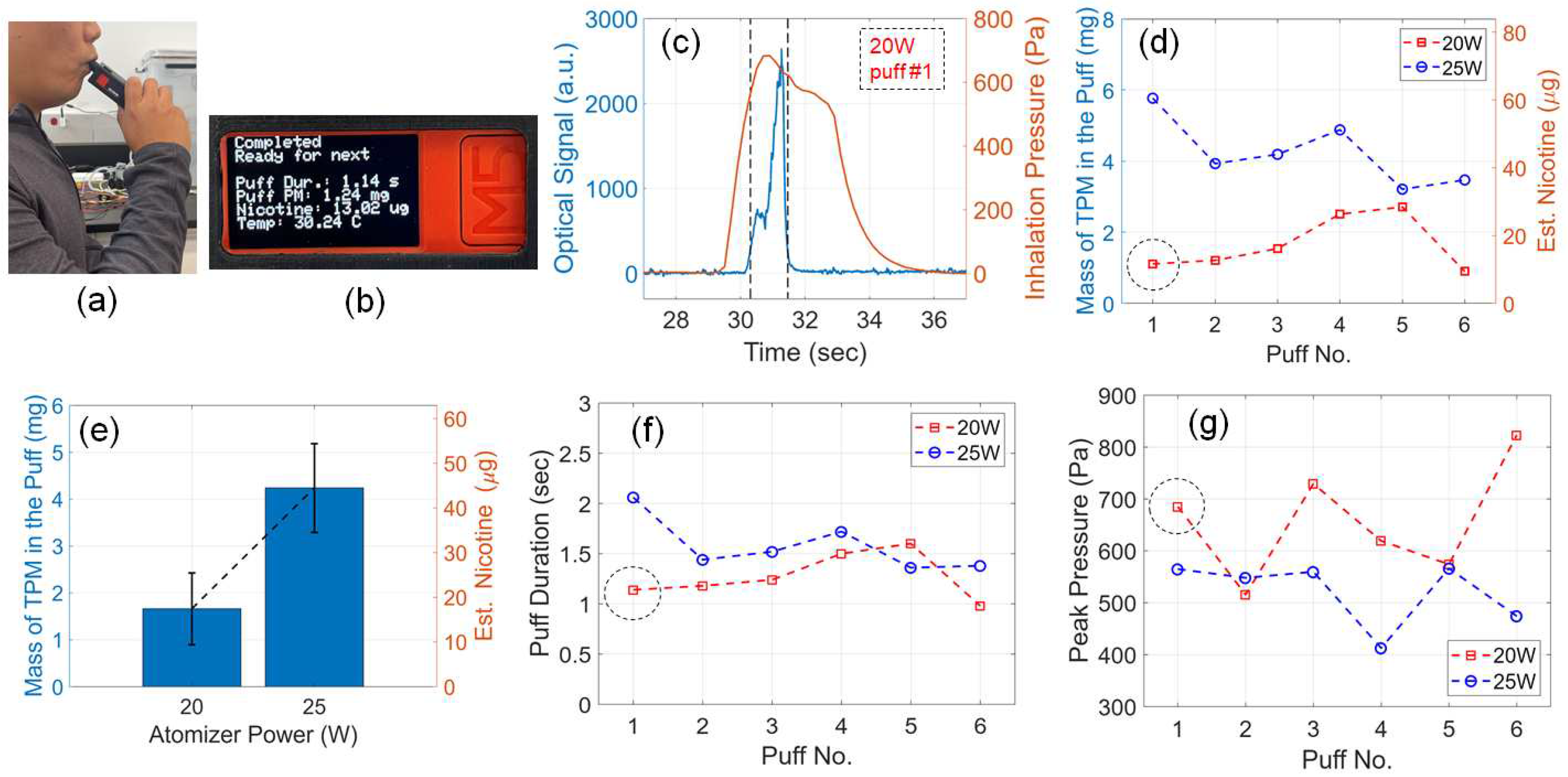
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E-CIG | Electronic Cigarette |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| TPM | Total Particulate Matter |
| MCU | Micro-Controller Unit |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compound |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
Appendix A. List of Symbols and Tables of Experimental Data
| Symbol | Description |
| Baseline-subtracted optical signal measured by the photometric sensor | |
| Inhalation pressure measured by the pressure sensor | |
| Calibration coefficient | |
| Peak optical signal | |
| Peak inhalation pressure | |
| Puff duration measured from the optical signal | |
| Mass concentration of the generated e-cigarette aerosol | |
| Volumetric flow rate of the generated e-cigarette aerosol | |
| Area under the curve of | |
| Mass of total particulate matter (TPM) in the puff, measured by the e-cig topography sensor | |
| Reference mass of TPM in the puff, measured by the vaping machine and the aerosol monitor | |
| concentration of the diluted aerosol in the box, measured by the aerosol monitor | |
| Volume of the dilution box | |
| Button pusher duration | |
| Pressurization duration to pump air out of the dilution box to control the inhalation pressure |
| No. | (Pa) | (a.u.) | (mg/m) | (mg) | Cal. Coeff. |
| 1 | 485.5 | 7533.2 | 90.1 | 8.52 | 3.4743×10 |
| 2 | 462.9 | 7471.6 | 89.4 | 8.46 | 3.5497×10 |
| 3 | 444.9 | 7636.2 | 85.7 | 8.11 | 3.5146×10 |
| First calibration coefficient = 3.5129×10 | |||||
| 4 | 514.9 | 8211.4 | 101.0 | 9.55 | 3.4034×10 |
| 5 | 509.7 | 8286.1 | 101.0 | 9.55 | 3.3361×10 |
| 6 | 508.7 | 8715.0 | 100.0 | 9.46 | 3.2571×10 |
| Second calibration coefficient = 3.3322×10 | |||||
| No. | Power (W) | (Pa) | (a.u.) | (mg/m) | (mg) | (mg) | Relative error |
| 1 | 15 | 454.0 | 2284.9 | 21.0 | 1.99 | 2.16 | 8.73% |
| 2 | 15 | 473.4 | 2149.6 | 21.9 | 2.07 | 2.12 | 2.33% |
| 3 | 15 | 484.9 | 2286.7 | 21.1 | 2.00 | 2.25 | 12.72% |
| 4 | 20 | 462.1 | 4149.2 | 42.8 | 4.05 | 4.22 | 4.23% |
| 5 | 20 | 456.4 | 4261.2 | 44.8 | 4.24 | 4.39 | 3.58% |
| 6 | 20 | 448.8 | 4444.5 | 44.6 | 4.22 | 4.44 | 5.23% |
| 7 | 25 | 457.3 | 6184.5 | 69.4 | 6.57 | 6.59 | 0.38% |
| 8 | 25 | 456.8 | 6233.4 | 71.2 | 6.74 | 6.48 | 3.79% |
| 9 | 25 | 471.0 | 6149.3 | 70.4 | 6.66 | 6.68 | 0.30% |
| 10 | 30 | 467.4 | 7556.7 | 97.8 | 9.25 | 8.69 | 6.07% |
| 11 | 30 | 458.5 | 7874.7 | 98.0 | 9.27 | 8.80 | 5.08% |
| 12 | 30 | 472.8 | 8058.3 | 98.6 | 9.33 | 8.99 | 3.62% |
| 13 | 35 | 487.8 | 8192.4 | 126.0 | 11.92 | 9.95 | 16.52% |
| 14 | 35 | 483.6 | 8004.3 | 126.0 | 11.92 | 10.16 | 14.76% |
| 15 | 35 | 466.4 | 8853.4 | 125.0 | 11.83 | 10.46 | 11.54% |
| 16 | 40 | 451.5 | 9215.5 | 141.0 | 13.34 | 11.17 | 16.26% |
| 17 | 40 | 451.5 | 9112.7 | 137.0 | 12.96 | 11.33 | 12.58% |
| 18 | 40 | 445.2 | 8737.3 | 135.0 | 12.77 | 10.88 | 14.81% |
| No. | (sec) | (Pa) | (a.u.) | (mg/m) | (mg) | (mg) | Relative error |
| 1 | 1.5 | 464.6 | 7664.5 | 65.3 | 6.18 | 6.20 | 0.37% |
| 2 | 1.5 | 452.0 | 7913.4 | 66.3 | 6.27 | 6.43 | 2.52% |
| 3 | 1.5 | 458.3 | 8247.9 | 64.8 | 6.13 | 6.47 | 5.55% |
| 4 | 2.0 | 461.1 | 8327.1 | 99.1 | 9.37 | 9.50 | 1.33% |
| 5 | 2.0 | 459.5 | 8107.2 | 98.9 | 9.36 | 9.40 | 0.47% |
| 6 | 2.0 | 459.1 | 8508.0 | 102.0 | 9.65 | 9.58 | 0.72% |
| 7 | 2.5 | 456.7 | 8627.5 | 144.0 | 13.62 | 12.96 | 4.86% |
| 8 | 2.5 | 444.2 | 8090.0 | 140.0 | 13.24 | 11.77 | 11.13% |
| 9 | 2.5 | 441.2 | 8430.8 | 137.0 | 12.96 | 12.22 | 5.71% |
| No. | (sec) | (Pa) | (a.u.) | (mg/m) | (mg) | (mg) | Relative error |
| 1 | 28 | 287.4 | 10314.8 | 91.6 | 8.67 | 8.82 | 1.78% |
| 2 | 28 | 296.6 | 9544.0 | 97.5 | 9.22 | 8.80 | 4.59% |
| 3 | 28 | 286.4 | 10254.4 | 96.2 | 9.10 | 9.11 | 0.10% |
| 4 | 54 | 441.2 | 8605.3 | 102.0 | 9.65 | 9.77 | 1.25% |
| 5 | 54 | 456.3 | 8512.9 | 104.0 | 9.84 | 9.83 | 0.09% |
| 6 | 54 | 451.9 | 7900.1 | 103.0 | 9.74 | 9.13 | 6.30% |
| 7 | 112 | 602.8 | 6652.7 | 105.0 | 9.93 | 8.70 | 12.41% |
| 8 | 112 | 612.5 | 7143.7 | 108.0 | 10.22 | 9.25 | 9.46% |
| 9 | 112 | 594.8 | 7144.5 | 108.0 | 10.22 | 9.17 | 10.25% |
References
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.; Glantz, S.A. E-cigarettes: a scientific review. Circulation 2014, 129, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Cheng, J.M. Electronic cigarettes: product characterisation and design considerations. Tobacco Control 2014, 23, ii4–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, S.L.C.; Wu, L.T. E-cigarette prevalence and correlates of use among adolescents versus adults: a review and comparison. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2014, 54, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.M.; Howell, D.N.; White, J.R.; Andrenyak, D.M.; Layton, M.E.; Roll, J.M. Variable and potentially fatal amounts of nicotine in e-cigarette nicotine solutions. Tobacco Control 2014, 23, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breland, A.; Soule, E.; Lopez, A.; Ramôa, C.; El-Hellani, A.; Eissenberg, T. Electronic cigarettes: what are they and what do they do? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2016, 1394, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, M.; Logue, J.M.; Montesinos, V.N.; Russell, M.L.; Litter, M.I.; Gundel, L.A.; Destaillats, H. Emissions from electronic cigarettes: key parameters affecting the release of harmful chemicals. Environmental Science & Technology 2016, 50, 9644–9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.A.; Olmedo, P.; Navas-Acien, A.; Goessler, W.; Cohen, J.E.; Rule, A.M. E-cigarettes as a source of toxic and potentially carcinogenic metals. Environmental Research 2017, 152, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, Z.R.; Das, A.; O’Connor, R.J.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Wei, B.; Travers, M.J. Brief report: lead levels in selected electronic cigarettes from Canada and the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Agnihotri, R. Health effects of trace metals in electronic cigarette aerosols—a systematic review. Biological Trace Element Research 2019, 188, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, R.; Chaffee, B.; Jakubovics, N.; Kist, R.; Preshaw, P. Electronic Cigarettes and Oral Health. Journal of Dental Research 2021, 100, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, R.; Bhatnagar, A. Cardiorespiratory and Immunologic Effects of Electronic Cigarettes. Current Addiction Reports 2021, 8, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, D.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, T. Toxicity of electronic cigarettes: A general review of the origins, health hazards, and toxicity mechanisms. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 772, 145475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ween, M.P.; Moshensky, A.; Thredgold, L.; Bastian, N.A.; Hamon, R.; Badiei, A.; Nguyen, P.T.; Herewane, K.; Jersmann, H.; Bojanowski, C.M.; Shin, J.; Reynolds, P.N.; Crotty Alexander, L.E.; Hodge, S.J. E-cigarettes and health risks: more to the flavor than just the name. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2021, 320, L600–L614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Villarreal, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Lin, S.; Talbot, P. Metal and Silicate Particles Including Nanoparticles Are Present in Electronic Cigarette Cartomizer Fluid and Aerosol. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Knysak, J.; Gawron, M.; Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Kurek, J.; Prokopowicz, A.; Jablonska-Czapla, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Havel, C.; others. Levels of selected carcinogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigarettes. Tobacco Control 2014, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, C.A.; Sundar, I.K.; Watson, R.M.; Elder, A.; Jones, R.; Done, D.; Kurtzman, R.; Ossip, D.J.; Robinson, R.; McIntosh, S.; Rahman, I. Environmental health hazards of e-cigarettes and their components: Oxidants and copper in e-cigarette aerosols. Environmental Pollution 2015, 198, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; To, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Talbot, P. Strategies to reduce tin and other metals in electronic cigarette aerosol. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0138933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheev, V.B.; Brinkman, M.C.; Granville, C.A.; Gordon, S.M.; Clark, P.I. Real-time measurement of electronic cigarette aerosol size distribution and metals content analysis. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016, 18, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, D.L.; Crow, A.P.; Nelson, J.M.; Johnson, R.A. Trace metals derived from electronic cigarette (ECIG) generated aerosol: potential problem of ECIG devices that contain nickel. Frontiers in Physiology 2017, 7, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, P.; Goessler, W.; Tanda, S.; Grau-Perez, M.; Jarmul, S.; Aherrera, A.; Chen, R.; Hilpert, M.; Cohen, J.E.; Navas-Acien, A.; Rule, A.M. Metal Concentrations in e-Cigarette Liquid and Aerosol Samples: The Contribution of Metallic Coils. Environmental Health Perspectives 2018, 126, 027010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Li, J.; Talbot, P. Effects of model, method of collection, and topography on chemical elements and metals in the aerosol of tank-style electronic cigarettes. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler-Ramadas, Radhika andSandner, I.; Haider, S.; Grabovac, I.; Dorner, T.E. Real-time measurement of electronic cigarette aerosol size distribution and metals content analysis. Wiener klinische Wochenschrift 2021, 133, 1020–1027. [CrossRef]
- Schober, W.; Szendrei, K.; Matzen, W.; Osiander-Fuchs, H.; Heitmann, D.; Schettgen, T.; Jörres, R.A.; Fromme, H. Use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) impairs indoor air quality and increases FeNO levels of e-cigarette consumers. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health 2014, 217, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Paik, S.Y. Association between electronic cigarette use and asthma among high school students in South Korea. PloS One 2016, 11, e0151022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talih, S.; Balhas, Z.; Eissenberg, T.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; El Hellani, A.; Baalbaki, R.; Saliba, N.; Shihadeh, A. Effects of User Puff Topography, Device Voltage, and Liquid Nicotine Concentration on Electronic Cigarette Nicotine Yield: Measurements and Model Predictions. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2014, 17, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, F.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Vigo, P. Influential parameters on particle concentration and size distribution in the mainstream of e-cigarettes. Environmental Pollution 2014, 184, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Burns, A.E.; Tran, L.N.; Abellar, K.A.; Poindexter, M.; Li, X.; Madl, A.K.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Nguyen, T.B. Impact of e-Liquid Composition, Coil Temperature, and Puff Topography on the Aerosol Chemistry of Electronic Cigarettes. Chemical Research in Toxicology 2021, 34, 1640–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ilievski, V.; Slavkovich, V.; Olmedo, P.; Domingo-Relloso, A.; Rule, A.M.; Kleiman, N.J.; Navas-Acien, A.; Hilpert, M. Effects of e-liquid flavor, nicotine content, and puff duration on metal emissions from electronic cigarettes. Environmental Research 2022, 204, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpless, N. How FDA is Regulating E-Cigarettes. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-voices-perspectives-fda-leadership-and-experts/how-fda-regulating-e-cigarettes.
- Behar, R.Z.; Hua, M.; Talbot, P. Puffing Topography and Nicotine Intake of Electronic Cigarette Users. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.; Slayford, S.; Vas, C.; Gee, J.; Costigan, S.; Prasad, K. Development, validation and application of a device to measure e-cigarette users’ puffing topography. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 35071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shu, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, Y. Effects of design parameters and puff topography on heating coil temperature and mainstream aerosols in electronic cigarettes. Atmospheric Environment 2016, 134, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Bozhilov, K.; Ghai, S.; Talbot, P. Elements including metals in the atomizer and aerosol of disposable electronic cigarettes and electronic hookahs. PloS One 2017, 12, e0175430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsalinos, K.; Poulas, K.; Voudris, V. Changes in Puffing Topography and Nicotine Consumption Depending on the Power Setting of Electronic Cigarettes. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2017, 20, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, E.; Greenlee, S.; Oni, T.; Sadhasivam, B.; Queimado, L. The Effect of Flow Rate on a Third-Generation Sub-Ohm Tank Electronic Nicotine Delivery System—Comparison of CORESTA Flow Rates to More Realistic Flow Rates. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, E.; Oni, T.; Cai, C.; Rehman, B.; Hwang, J.; Watson, T. Validation of a High Flow Rate Puff Topography System Designed for Measurement of Sub-Ohm, Third Generation Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzun, T.; Lazurko, M.; Munhenzva, I.; Barsanti, K.C.; Huang, Y.; Jensen, R.P.; Escobedo, J.O.; Luo, W.; Peyton, D.H.; Strongin, R.M. E-cigarette airflow rate modulates toxicant profiles and can lead to concerning levels of solvent consumption. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, E.L.; Queimado, L.; Wang, J.; Regens, J.L.; Johnson, D.L. Electronic cigarette power affects count concentration and particle size distribution of vaping aerosol. PloS One 2018, 13, e0210147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, H.A.; Patterson, J.L.; Halquist, M.S.; Kosmider, L.; Turner, J.B.M.; Poklis, J.L.; Poklis, A.; Peace, M.R. The effect of electronic cigarette user modifications and e-liquid adulteration on the particle size profile of an aerosolized product. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechasseur, A.; Altmejd, S.; Turgeon, N.; Buonanno, G.; Morawska, L.; Brunet, D.; Duchaine, C.; Morissette, M.C. Variations in coil temperature/power and e-liquid constituents change size and lung deposition of particles emitted by an electronic cigarette. Physiological Reports 2019, 7, e14093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourchez, J.; Parisse, S.; Sarry, G.; Perinel-Ragey, S.; Vergnon, J.M.; Clotagatide, A.; Prévôt, N. Impact of power level and refill liquid composition on the aerosol output and particle size distribution generated by a new-generation e-cigarette device. Aerosol Science and Technology 2018, 52, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, S.L.; Song, C.; Moldoveanu, S.C.; Cole, S.K. Particle Size Distribution of E-Cigarette Aerosols and the Relationship to Cambridge Filter Pad Collection Efficiency. Contributions to Tobacco & Nicotine Research 2015, 26, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CORESTA. Cooperation Centre for Scientific Research Relative to Tobacco (CORESTA). [https://www.coresta.org].
- Dunkhorst, W.; Lipowicz, P.; Li, W.; Hux, C.; Wang, Q.; Koch, W. In-situ characterization of e-cigarette aerosols by 90°-light scattering of polarized light. Aerosol Science and Technology 2018, 52, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Smart Electronic Cigarettes with Built-in Aerosol Sensors. 2022 IEEE Sensors, 2022, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Soulet, S.; Duquesne, M.; Toutain, J.; Pairaud, C.; Lalo, H. Experimental Method of Emission Generation Calibration Based on Reference Liquids Characterization. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillman, I.; Kistler, K.; Stewart, E.; Paolantonio, A. Effect of variable power levels on the yield of total aerosol mass and formation of aldehydes in e-cigarette aerosols. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2016, 75, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Gao, N. Vaporization characteristics and aerosol optical properties of electronic cigarettes. Environmental Pollution 2021, 275, 116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampos, S.; Kostenidou, E.; Farsalinos, K.; Zagoriti, Z.; Ntoukas, A.; Dalamarinis, K.; Savranakis, P.; Lagoumintzis, G.; Poulas, K. Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations. Toxics 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasisto, H.S.; Zhang, Q.; Merzsch, S.; Waag, A.; Peiner, E. A phase-locked loop frequency tracking system for portable microelectromechanical piezoresistive cantilever mass sensors. Microsystem Technologies 2014, 20, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkhorst, W.; Lipowicz, P.; Koch, W. Characterization of highly concentrated organic aerosols by optical extinction in the mid infrared regime: Application to e-cigarettes. Journal of Aerosol Science 2016, 94, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Black, D.; McQuay, M.Q.; Bonin, M.P. Laser-based techniques for particle-size measurement: A review of sizing methods and their industrial applications. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 1996, 22, 267–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R. Particle characterization: light scattering methods; Vol. 13, Springer Science & Business Media, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Huynh, B.K.; Chen, Y.; Fletcher, D.F.; Young, P.; Zhu, B.; Traini, D. An Investigation into the Powder Release Behavior from Capsule-Based Dry Powder Inhalers. Aerosol Science and Technology 2015, 49, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Lee, B. Development of a Portable Monitoring System for Indoor E-Cigarettes Emission. 2020 IEEE SENSORS, 2020, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Sousan, S.; Pender, J.; Streuber, D.; Haley, M.; Shingleton, W.; Soule, E. Laboratory determination of gravimetric correction factors for real-time area measurements of electronic cigarette aerosols. Aerosol Science and Technology 2022, 56, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Luo, X.; Tai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Xie, G.; Su, Y. Ni-Co-P hollow nanobricks enabled humidity sensor for respiratory analysis and human-machine interfacing. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 370, 132441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z. Advances in health rehabilitation devices based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





