Submitted:
28 September 2023
Posted:
30 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
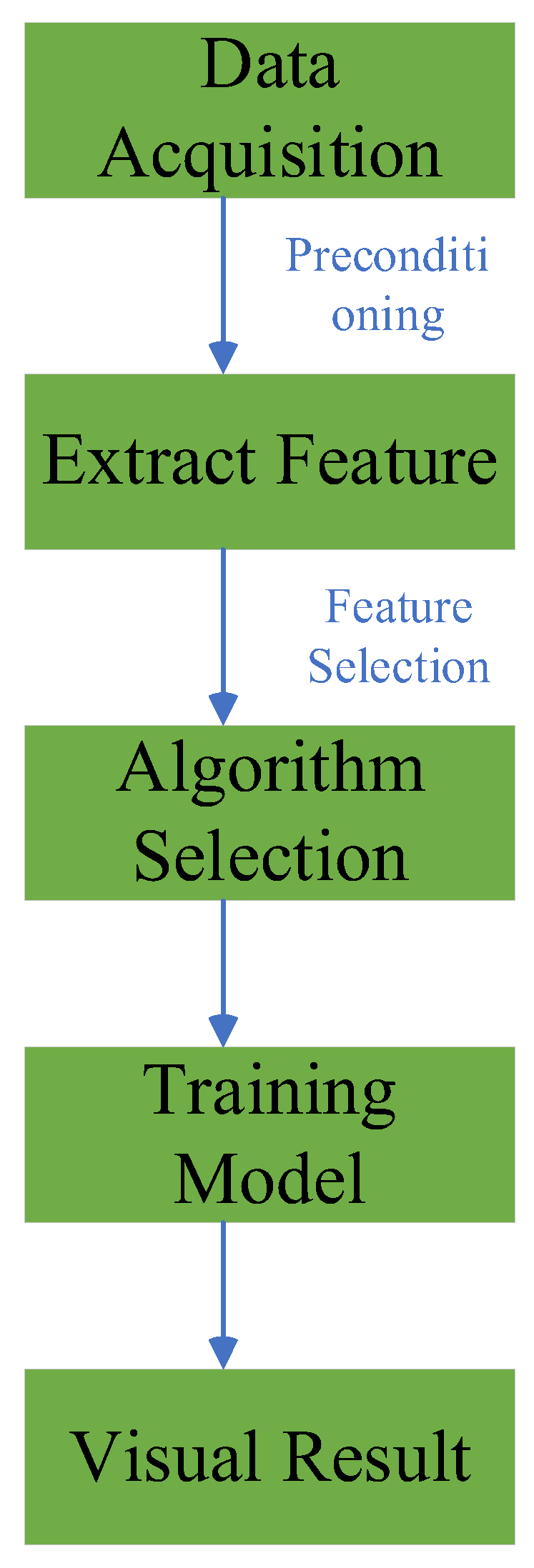
1. Introduction
2. Optimisation algorithms related to medical image analysis
- (1)
- Image Enhancement Algorithms
- (2)
- Image Segmentation Algorithms
- (3)
- Feature Extraction Algorithms
- (4)
- Classification and Recognition Algorithms
- (5)
- Image Registration Algorithm
- (6)
- Visualisation algorithms
- (7)
- Deep Learning Algorithms
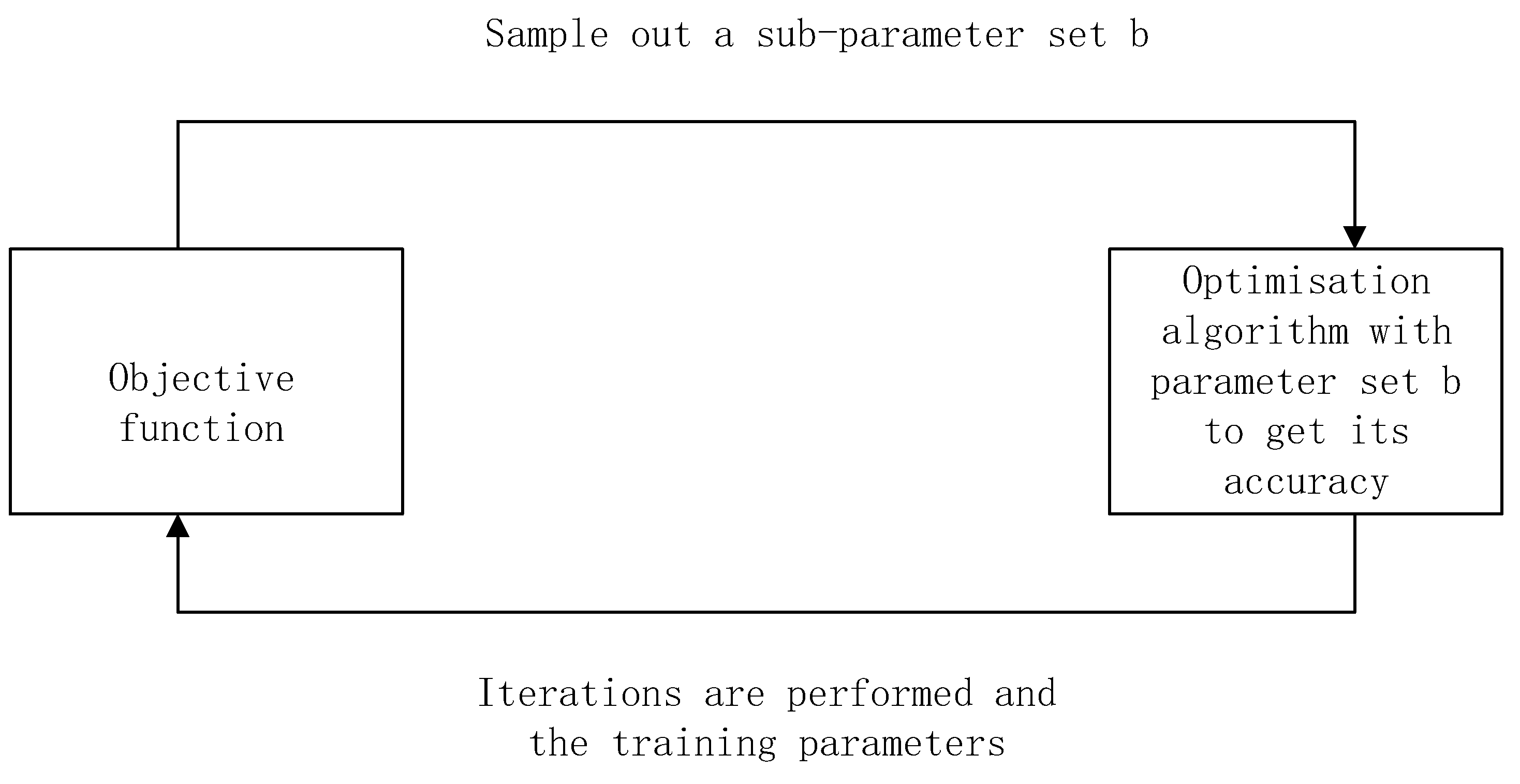
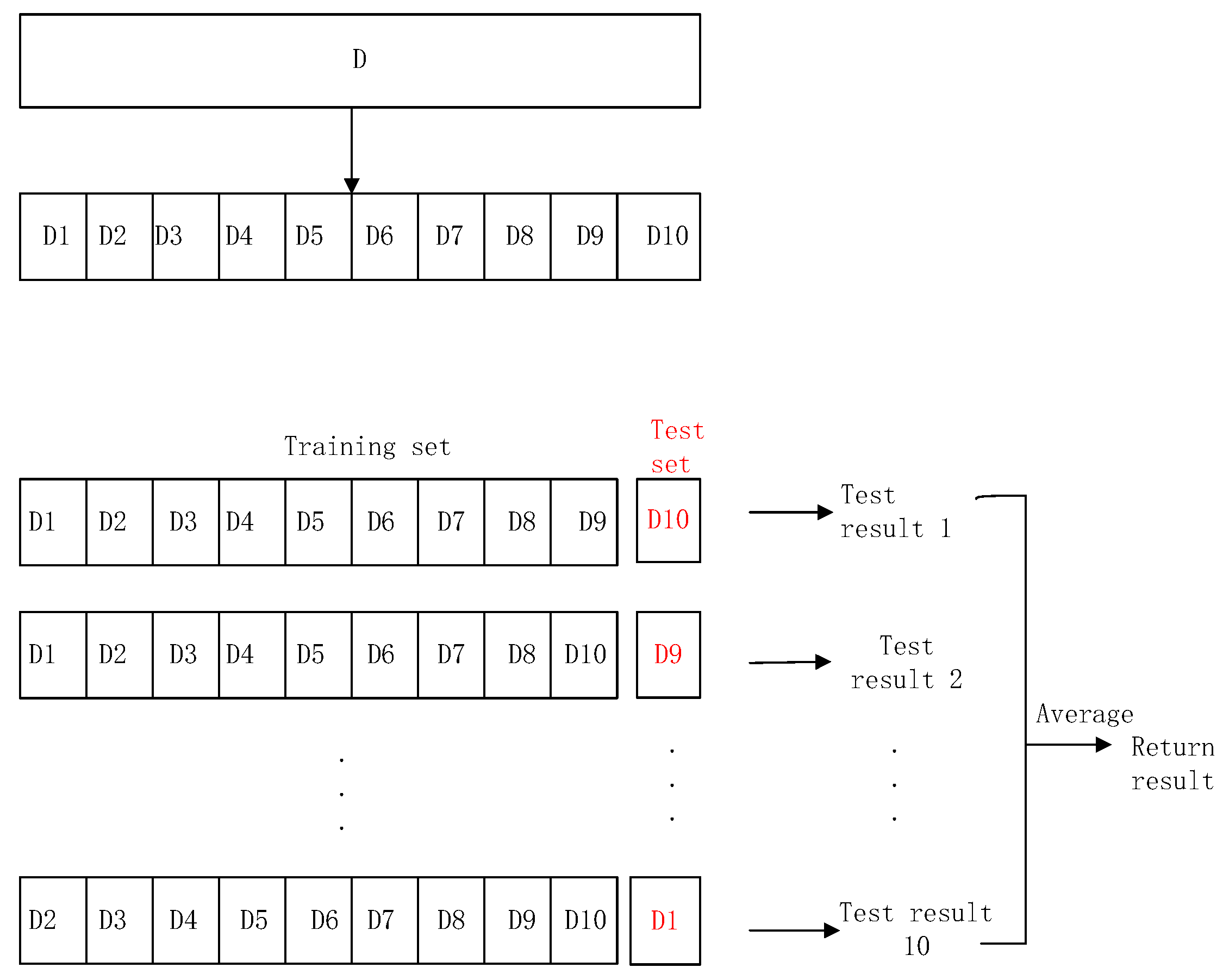
3. Optimization in Fine-tuning
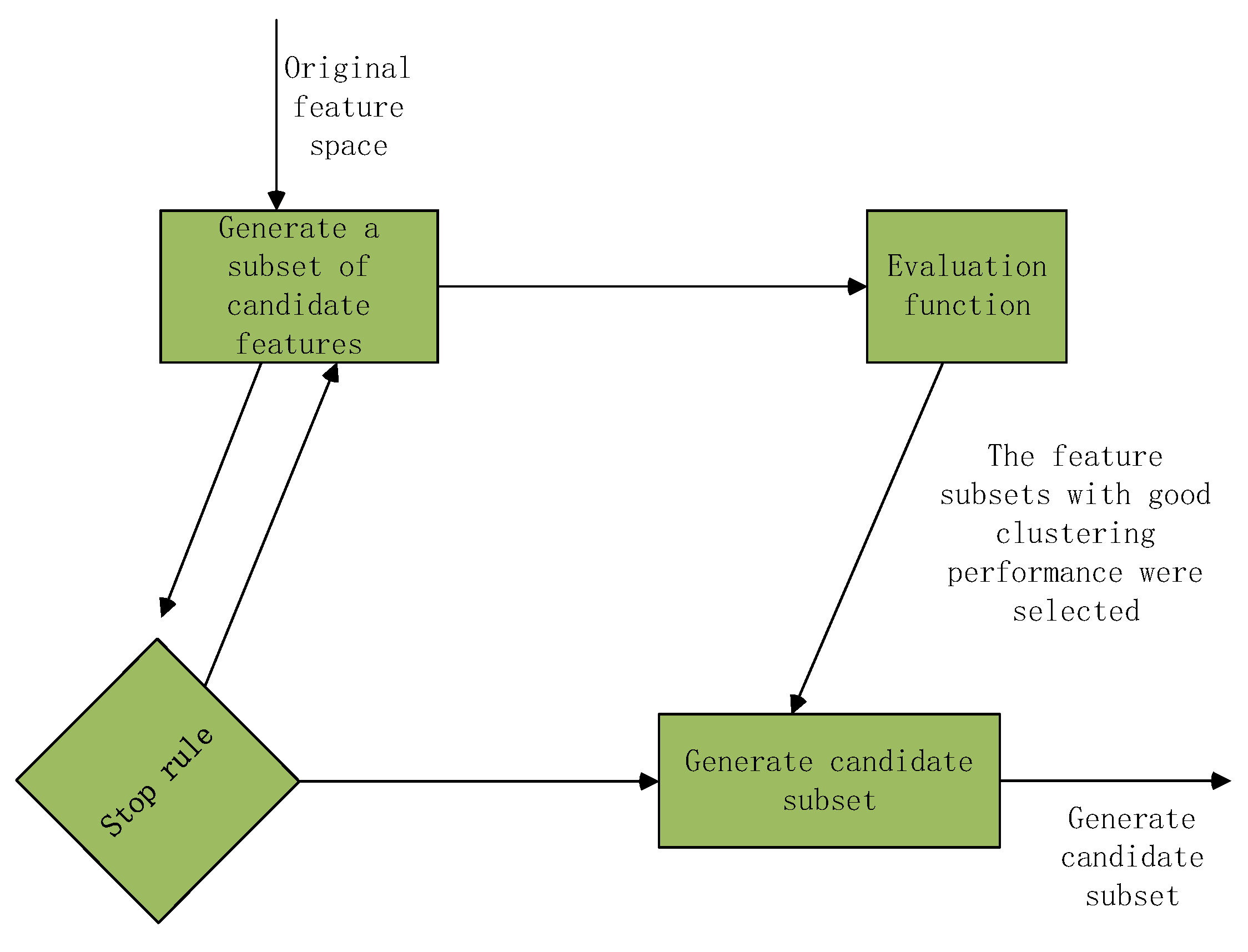
4. Optimization in Feature Selection
5. Optimization in Resource Allocation
- (1)
- Resource planning. Optimisation can assist healthcare organisations in long-term resource planning by analysing historical data, patient demographics and forecasting demand. It can help determine the optimal allocation of resources such as hospital beds, medical staff, equipment and medications to meet expected demand while minimising waste and reducing costs.
- (2)
- Employee Scheduling. For hospitals and clinics, optimisation can be used to create efficient staff schedules that take into account factors such as staff availability [56], skill levels and patient needs. This ensures that the right people are on duty at the right time to provide quality care while maintaining a reasonable workload [57].
- (3)
- Patient triage. During a surge in patient demand, such as during a pandemic or natural disaster, optimisation algorithms can help healthcare providers prioritise patients based on the severity of their condition and available resources. This ensures that critically ill patients receive immediate attention and appropriate care.
- (4)
- Supply Chain Management. Optimisation techniques can be used to manage the supply chain [58] of healthcare resources such as medicines, personal protective equipment (PPE) and medical devices. This helps maintain adequate stock levels, minimise waste and avoid shortages.
- (5)
- Operating theatre scheduling. In the surgical sector, optimisation can optimise surgery scheduling, OR utilisation and staff allocation. This reduces patient wait times, optimises the use of expensive operating theatres and improves overall surgical workflow.
- (6)
- Telemedicine and remote monitoring. Optimisation can be used to determine the most efficient allocation of resources for telemedicine services and remote patient monitoring, ensuring that patients can access care remotely while minimising pressure on on-site resources.
- (7)
- Emergency Response. During an emergency or disaster, optimisation models can help emergency responders allocate medical resources efficiently. This includes deploying medical teams, ambulances, and supplies to a disaster area based on real-time data and predicted needs.
- (8)
- Resource allocation for rare diseases. For diseases with low prevalence, optimisation can help to allocate specialised resources, such as rare disease specialists or specialised equipment, to areas of greatest need [59], ensuring equitable access to care.
- (9)
- Budget allocation. Healthcare organisations and government agencies can use optimisation to allocate budgets efficiently, ensuring that funds are allocated to the areas of healthcare that are most in need, while meeting the needs of the population.
6. Conclusion and Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgment
References
- Beutel, J.; Kundel, H.L.; Van Metter, R.L. Handbook of Medical Imaging - Volume I. Physics and Psychophysics; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin; Daniel, L. Informatics in radiology: Measuring and improving quality in radiology: meeting the challenge with informatics. Radiographics 2011, 31, 1511–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recht, M.P.; Dewey, M.; Dreyer, K.; Langlotz, C.; Niessen, W.; Prainsack, B.; Smith, J.J. Integrating artificial intelligence into the clinical practice of radiology: challenges and recommendations. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3576–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Yang, S.; Yu, B.; Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Sun, R.; Wang, B.; Nie, P.; Hou, F.; Huang, C.; et al. CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram for the prediction of pathological grade in bladder cancer: a multicenter study. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisci, S.; Piana, M.; Ruggiero, V.; Scussolini, M. A Regularized Affine-Scaling Trust-Region Method for Parametric Imaging of Dynamic PET Data. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2021, 14, 418–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtlein, C.R.; Maroun, M.K.; Krol, A.; Gifford, H.; Bodei, L.; O'Donoghue, J.; Häggström, I.; Xu, Y. A deblurring/denoising corrected scintigraphic planar image reconstruction model for targeted alpha therapy. In Proceedings of the Conference on Medical Imaging: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University Reports Findings in Artificial Intelligence (Application of Artificial Intelligence Nuclear Medicine Automated Images Based on Deep Learningin Tumor Diagnosis). Robotics & Machine Learning Daily News, 2022.
- Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Barbieri, M.; Mahmood, F. Data-efficient and weakly supervised computational pathology on whole-slide images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Hassanpour, S. MHAttnSurv: Multi-head attention for survival prediction using whole-slide pathology images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 106883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuo, Y.; Toshibumi, M. Ophthalmological Imager; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, B.; Xie, P.; Xing, E. On the Automatic Generation of Medical Imaging Reports; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, S.; Biswas, G.H.; Samanta, H.; Shahid, S. A Comprehensive Review on Medical Imaging Technologies to Detect Brain Stroke. ITM Web Conf. 2023, 53, 01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-C. Chest X-Rays Abnormalities Localization and Classification Using an Ensemble Framework of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Vietnam. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 10, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogier, V.D.S.; Bhaskhar, N.; Rubin, D.; Langlotz, C.; Chaudhari, A. Exploring Image Augmentations for Siamese Representation Learning with Chest X-Rays. 2023.
- Watkins, K.; Paus, T.; Lerch, J.; Zijdenbos, A.; Collins, D.; Neelin, P.; Taylor, J.; Worsley, K.; Evans, A. Structural Asymmetries in the Human Brain: a Voxel-based Statistical Analysis of 142 MRI Scans. Cereb. Cortex 2001, 11, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, K.; Ziegler, G.; Klöppel, S.; Gaser, C.; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Estimating the age of healthy subjects from T1-weighted MRI scans using kernel methods: Exploring the influence of various parameters. NeuroImage 2010, 50, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Ng, W.S.; Teo, M.Y.; Lim, H.C. Computerised prostate boundary estimation of ultrasound images using radial bas-relief method. . Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 1997, 35, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Nakamoto, M.; Tamaki, Y.; Sasama, T.; Sakita, I.; Nakajima, Y.; Monden, M.; Tamura, S. Image guidance of breast cancer surgery using 3-D ultrasound images and augmented reality visualization. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 1998, 17, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaala, A.; Terrissa, L.S.; Zerhouni, N.; Devalland, C. Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Spitzoid Lesions Classification Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics (IJHISI) 2021, 16, 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Meng, D. Stein variational gradient descent with learned direction. Inf. Sci. 2023, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadi, D.; Fredette, M.; Senecal, S. Read the Signs: Towards Invariance to Gradient Descent's Hyperparameter Initialization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10133. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Sala, L.; Curado, M.; Tortosa, L.; Vicent, J.F. Deep learning model of convolutional neural networks powered by a genetic algorithm for prevention of traffic accidents severity. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 2023, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidi, S.; Mazouzi, M. Optimization Approach for Yard Crane Scheduling Problem using genetic algorithm in Container Terminals. ITM Web Conf. 2023, 52, 02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, D. Research on Optimization of Profile Parameters in Screw Compressor Based on BP Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Energies 2023, 16, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Singh, M.; Williamson, D.P. Special Issue: Integer Programming and Combinatorial Optimization (IPCO) 2021 PREFACE. Mathematical Programming 2023. [CrossRef]
- Karuno, Y.; Tomozawa, A.; Tsuji, K. An Integer Programming Formulation of Collecting Weighted Items in Directed Bipartite Graphs with a Budget Constraint. In Proceedings of the 11th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; et al. Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, K.; Shevgoor, S.K. Improving Clinical Diagnosis Performance with Automated X-ray Scan Quality Enhancement Algorithms. 2022.
- Liu, X.; Pedersen, M.; Wang, R. Survey of natural image enhancement techniques: Classification, evaluation, challenges, and perspectives. Digital Signal Processing 2022, 127, 103547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlouche, S.; Achour, K. A new approach to image segmentation using genetic algorithm with mathematical morphology. 2022.
- Wei, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, S. Fuzzy subspace clustering noisy image segmentation algorithm with adaptive local variance & non-local information and mean membership linking. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 110, 104672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Sallehuddin, M. Multi-scene design analysis of integrated energy system based on feature extraction algorithm. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, N.; Qiu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Ma, T.; Li, F.; Yao, D.; Xu, P. Multimodal collaborative BCI system based on the improved CSP feature extraction algorithm. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2022, 4, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Sharanya, B. Recognition and prevention of cyberharassment in social media using classification algorithms. 2021.
- Chen, Y.-X.; Xie, R.; Yang, Y.; He, L.; Feng, D.; Shen, H.-B. Fast Cryo-EM Image Alignment Algorithm Using Power Spectrum Features. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 4795–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Miao, X.; He, C. Image stitching by disparity-guided multi-plane alignment. Signal Process. 2022, 197, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, V.; Scholtes, I. HOTVis: Higher-Order Time-Aware Visualisation of Dynamic Graphs: Graph Drawing and Network Visualization. In Proceedings of the 28th International Symposium, GD 2020, Revised Selected Papers. Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 September 2020; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.D.; Li, X.; Khan, M. Design and Development of a Data Structure Visualisation System Using the Ant Colony Algorithm. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Formerly Recent Patents Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, P.; Zhu, W. Deep Learning on Graphs: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xu, Z.; Xia, T.; Zhang, J.; Jin, D. DeepMM: Deep Learning Based Map Matching with Data Augmentation. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, PP, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Phillips, P.; Yuan, T.-F. Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease by Three-Dimensional Displacement Field Estimation in Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Alzheimer's Dis 2016, 50, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Phillips, P.; Wang, S. Smart detection on abnormal breasts in digital mammography based on contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization and chaotic adaptive real-coded biogeography-based optimization. Simulation 2016, 92, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ji, G.; Dong, Z. Exponential wavelet iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithm with random shift for compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2014, 10, 116–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Lu, L.; Zhou, X. Feature selection using a sinusoidal sequence combined with mutual information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, A. A tutorial-based survey on feature selection: Recent advancements on feature selection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huo, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, A. Feature extraction of brain mri by stationary wavelet transform and its applications. J. Biol. Syst. 2010, 18, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, K.; Mohanrasu, S.; Kashkynbayev, A.; Rakkiyappan, R. Minkowski distance measure in fuzzy PROMETHEE for ensemble feature selection. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Wei, G. Color image enhancement based on HVS and PCNN. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2010, 53, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touches, T.D.; Munda, M.; Cornet, T.; Gerkens, P.; Hellepute, T. Feature selection with prior knowledge improves interpretability of chemometrics models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zou, J.; Yang, S.; Yao, X. Evolutionary Dynamic Multi-objective Optimisation: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, M. KALLE KEPLER Optimisation of patient doses and image quality in diagnostic radiology. 2009.
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-based Learning Methods: Optimisation Theory. 2000; pp. 79–92. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Tang, C.; Zhang, X. Diagnosis of COVID-19 by Wavelet Renyi Entropy and Three-Segment Biogeography-Based Optimization. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2020, 13, 1332–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.A.; Ramkumar, M.; Schoenherr, T.; Singh, S. The role of operations and supply chain management during epidemics and pandemics: Potential and future research opportunities. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2023, 175, 103139. [Google Scholar]
- Kiwanuka, F.N.; Karadsheh, L.; Alqatawna, J.; Amin, A.H.M. Modeling Employee Flexible Work Scheduling As A Classification Problem. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 3281–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, D.; Bürgy, R.; Desaulniers, G.; Soumis, F. A decomposition-based heuristic for large employee scheduling problems with inter-department transfers. Euro J. Comput. Optim. 2019, 7, 325–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, L.A.; Ganga, G.M.D.; Filho, M.G.; de Santa-Eulalia, L.A.; Chikhi, T.; Mosconi, E. Present and future perspectives of blockchain in supply chain management: a review of reviews and research agenda. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad-Sajadi, R.; Heo, C.Y.; Clergue, V. Reprint of: Instilling the core tenets of hospitality in healthcare services: The role of service assurance and social presence. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Phillips, P.; Yang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic resonance brain classification by a novel binary particle swarm optimization with mutation and time-varying acceleration coefficients. Biomedical Engineering-Biomedizinische Technik 2016, 61, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KhanMohammadi, E.; Talaie, H.; Azizi, M. A healthcare service quality assessment model using a fuzzy best–worst method with application to hospitals with in-patient services. Heal. Anal. 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Hanandeh, E.S.; Abu Zitar, R.; Thanh, C.-L.; Khatir, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Revolutionizing sustainable supply chain management: A review of metaheuristics. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zou, L.; Lu, S.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Detection of Left-Sided and Right-Sided Hearing Loss via Fractional Fourier Transform. Entropy 2016, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dutta, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Chapter Thirteen - Surrogate model-driven bio-inspired optimization algorithms for large-scale and high-dimensional problems. In Biomimicry for Aerospace; Shyam, V., Eggermont, M., Hepp, A.F., Eds., Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 353–382. [Google Scholar]
- MiarNaeimi, F.; Azizyan, G.; Rashki, M. Horse herd optimization algorithm: A nature-inspired algorithm for high-dimensional optimization problems. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2020, 213, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-D.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.-D.; Hou, X.-X.; Liu, F.-Y.; Jia, W.-J.; Yang, M.-M.; Phillips, P.; Wang, S.-H. Alcoholism detection by medical robots based on Hu moment invariants and predator–prey adaptive-inertia chaotic particle swarm optimization. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 63, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Advances in data preprocessing for biomedical data fusion: an overview of the methods, challenges, and prospects. Information Fusion 2021, 76, 376–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicator | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Information Gain | Metrics for decision trees and feature selection that measure the extent to which features affect the target variable by calculating the reduction in uncertainty of the target variable if the features are known.| |
| Information Gain Ratio | The information gain is extended by considering the ratio of entropy and conditional entropy of features to reduce the preference for features with a large number of values. |
| Chi-Square Test | Used to assess the association between the features and the target variable, the chi-square statistic between the features and the target variable was calculated and used to determine if they were independent. |
| Mutual Information | A measure of how much information is shared between two random variables, which can be used to measure the correlation between the feature and the target variable. |
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient | Used to assess the linear relationship between two continuous variables and can be used to identify features that are highly correlated with the target variable. |
| Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient | Used to assess the monotonic relationship between two variables and can be used to identify the characteristics of the monotonic relationship with the target variable. |
| Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) | Used to compare differences in means between multiple groups and can be used to assess differences in means for different characteristics on a target variable. |
| Recursive Feature Elimination(RFE) | The importance of features is assessed by recursively removing the least important features, using model performance as an evaluation metric. |
| Relative Importance | For tree-based models (e.g., random forests), the metric used to measure the extent to which features contribute to model performance. |
| AUC-ROC | Metrics for biry classification problems that measure the classification performance of features and assess the degree of separation between positive and negative examples. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




