Submitted:
29 September 2023
Posted:
03 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background information on the hydrogen evolution reaction
1.2. Importance of studying the kinetics of HER
1.3. Definition and types of electrolytes used in HER studies
1.4. Significance of electrolytes in HER kinetics
2. Influence of Electrolyte Composition on HER Kinetics
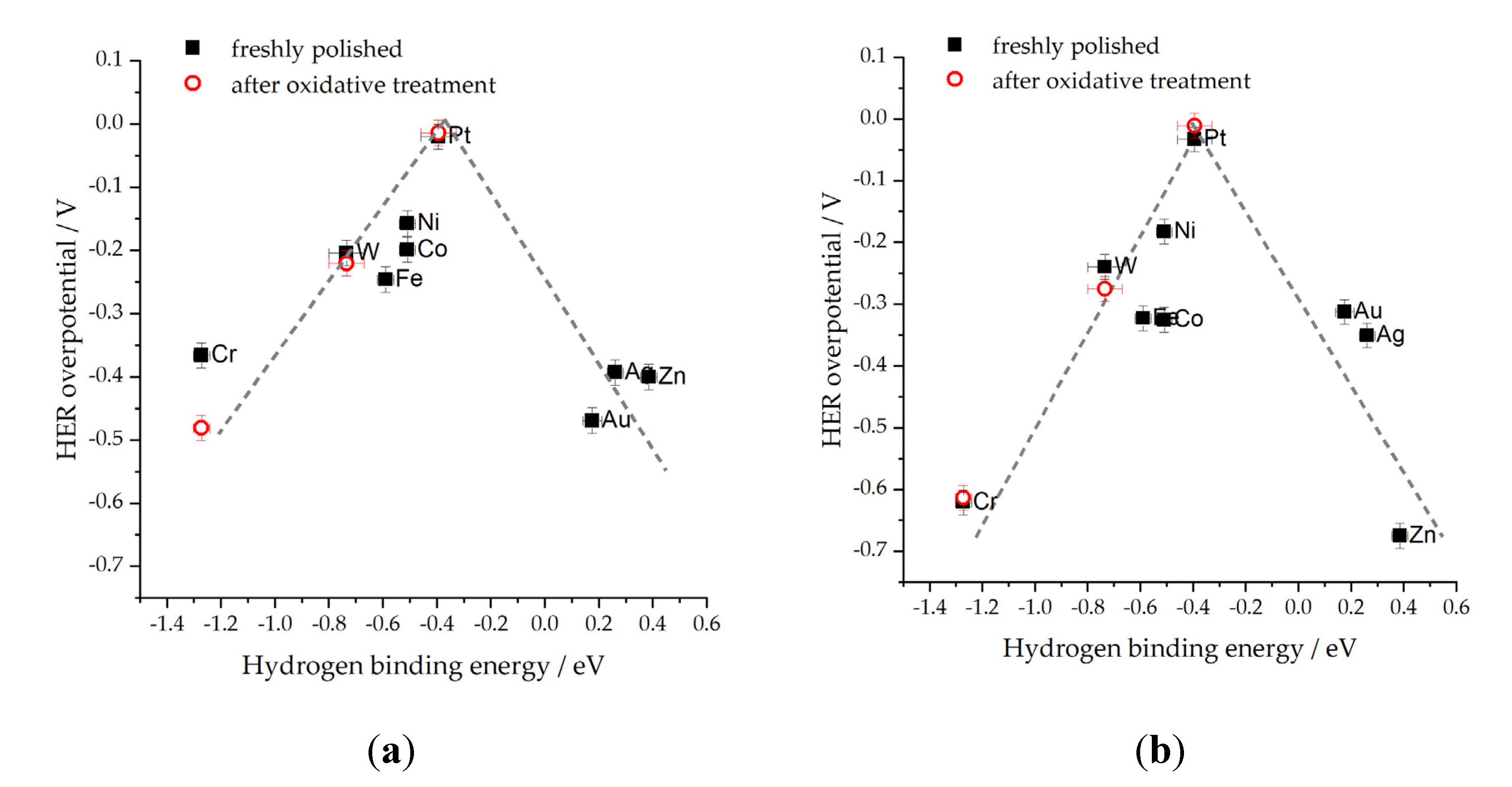
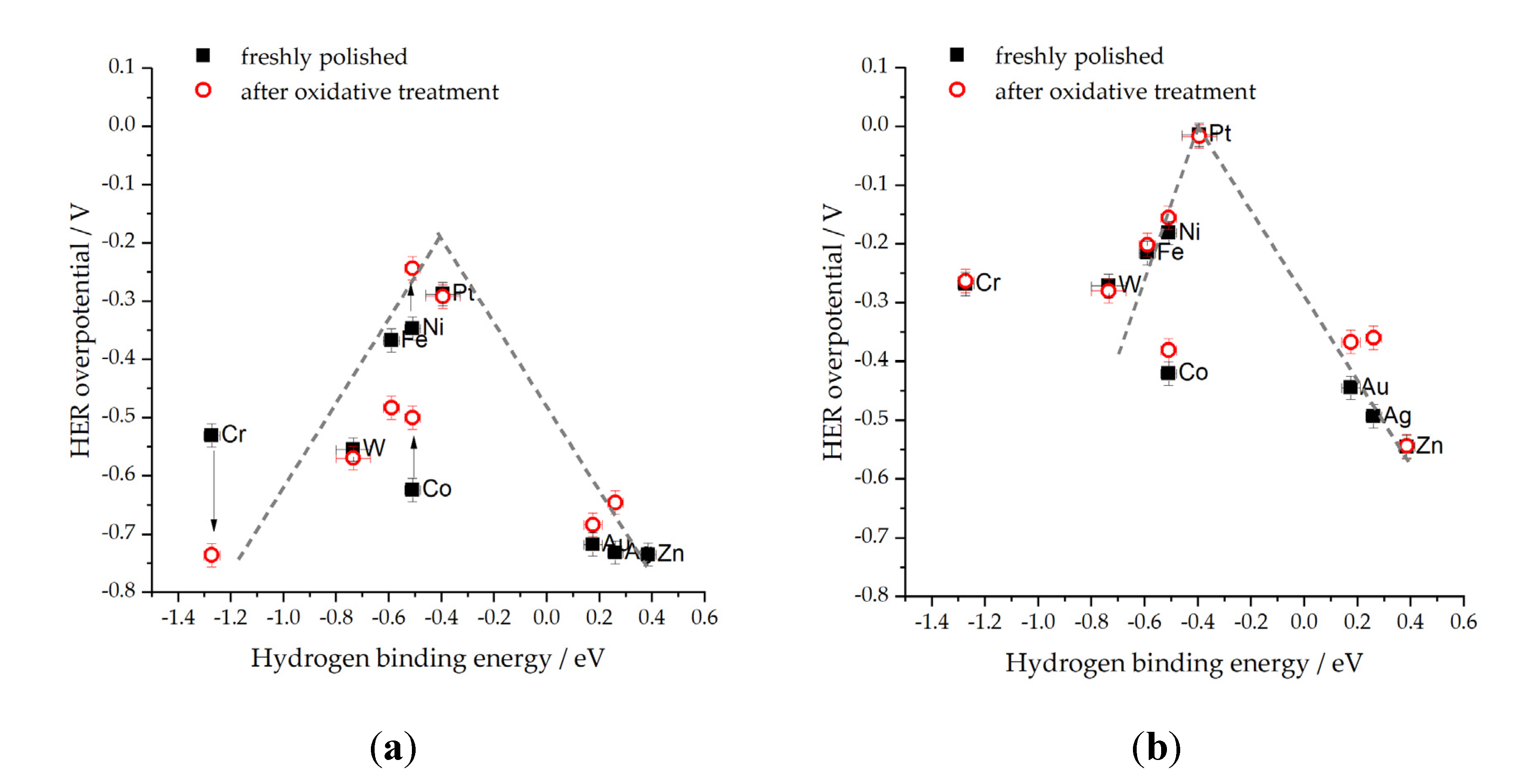
2.1. Effect of electrolyte pH on HER kinetics
- (i)
- The HBE is pH-dependent [14,72,76]. This concept has helped to explain numerous experimental findings, even though some inconsistencies still exist [72,76,77]. For illustration, if the HBE were to increase, it would account for the positive potential shift of HUPD on PGM-electrodes when they change from an acidic to an alkaline electrolyte. Nevertheless, despite demonstrating considerably lower HER activity in alkaline electrolytes than in acidic ones, the Pt(111) surface remains largely unaffected by this shift caused by the HUPD [71,78,79]. Furthermore, if there were a universal increase in the HBE with pH, it would enhance the HER electrocatalytic activity of metals that weakly bind hydrogen (such as Au). However, this contradicts the experimental observations [71].
- (ii)
- The proton donor (H3O+ or H2O) is pH dependent [41]. In other words, the proton donor can switch from H3O+ in an acidic environment to H2O in an alkaline environment.
- (iii)
- At the electrode|electrolyte interface, there is a pH-dependent water reorganization energy. According to Koper et al. [80], the water-reorganization energy related to proton-electron transfer would be higher because interfacial fields are stronger in an alkaline environment. Rossmeisl et al. [81] initiated an attempt to address pH in density functional theory (DFT) calculation and applying the scheme to Pt(111)|electrolyte(water) interface as an example, they have observed that the adsorbate coverage and water orientation were affected by pH [81]. Recent studies by Rossmeisl et al. have associated the reduction in HER activity at high pH with changes in the configurational entropy of the proton as it crosses the outer Helmholtz plane [82]. Cheng et al. [83] carried out full solvent Quantum Mechanics Molecular Dynamics (QMMD) simulations to explicitly simulate the water/Pt(100) interface at applied voltage (U) from +0.29 V to -0.46 V, which is equivalent to pH from 0.2 to 12.8 at U = 0.3 V (RHE). The study deduced that the pH-dependent HBE on the noble metal is mostly caused by changes in water adsorption. They discovered that the electrode exhibited a tendency to repel water as the applied voltage was made more negative, which in turn boosted the hydrogen binding.
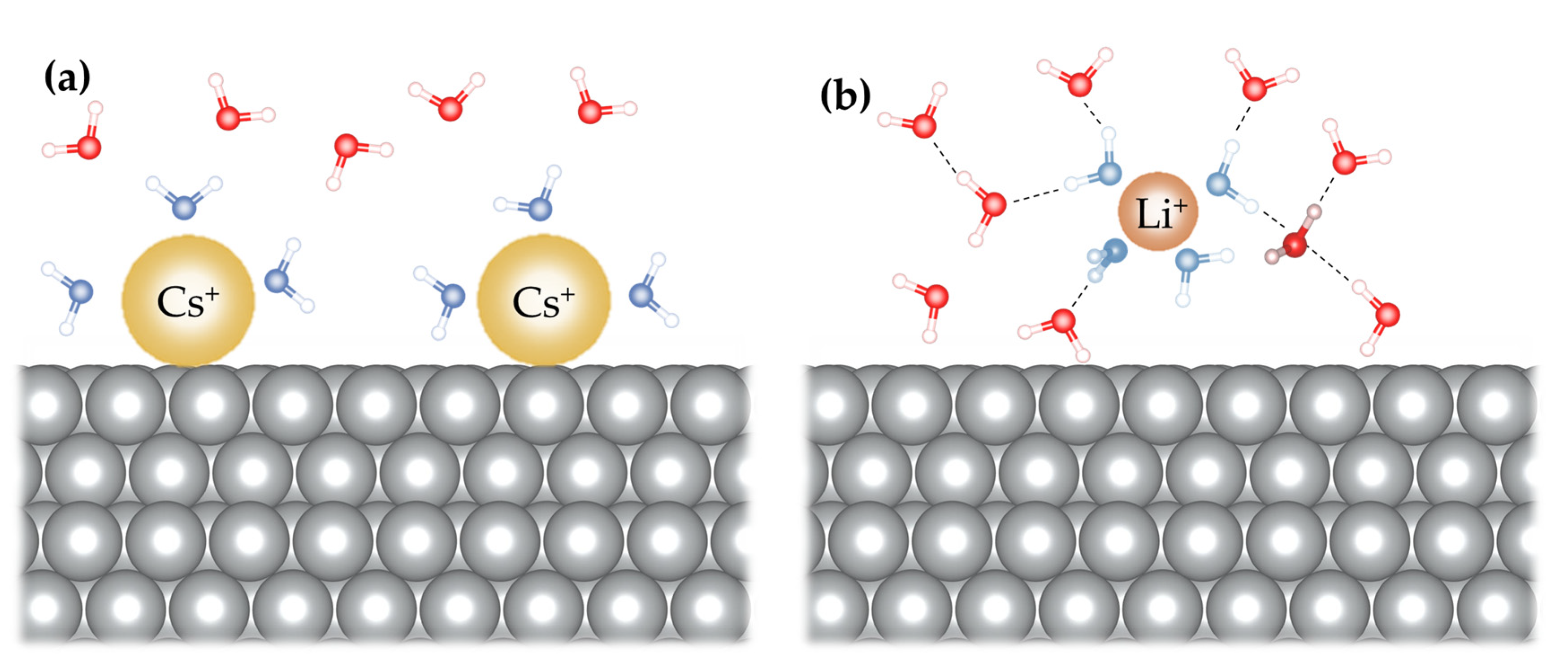
2.2. Impact of different cations and anions on HER kinetics
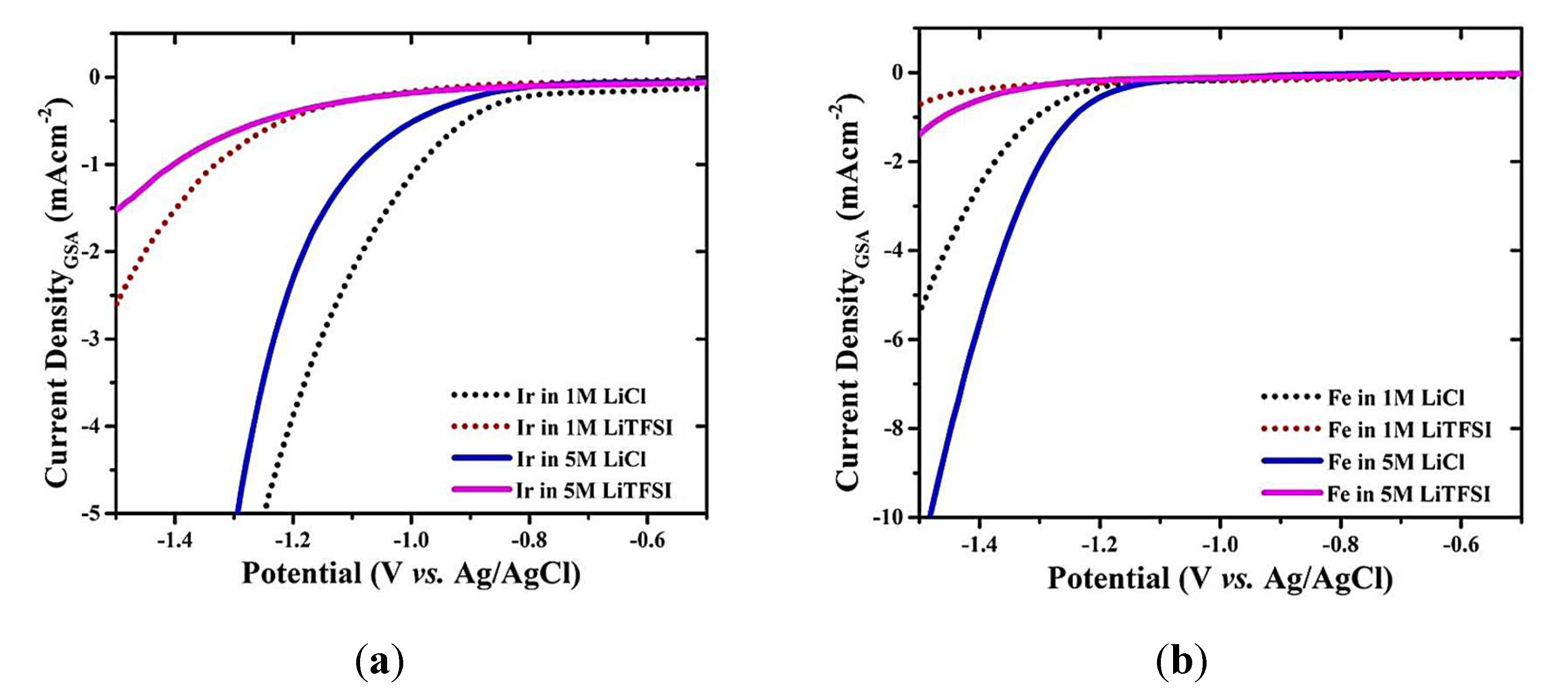
2.3. Electrolyte Concentration and HER Kinetics
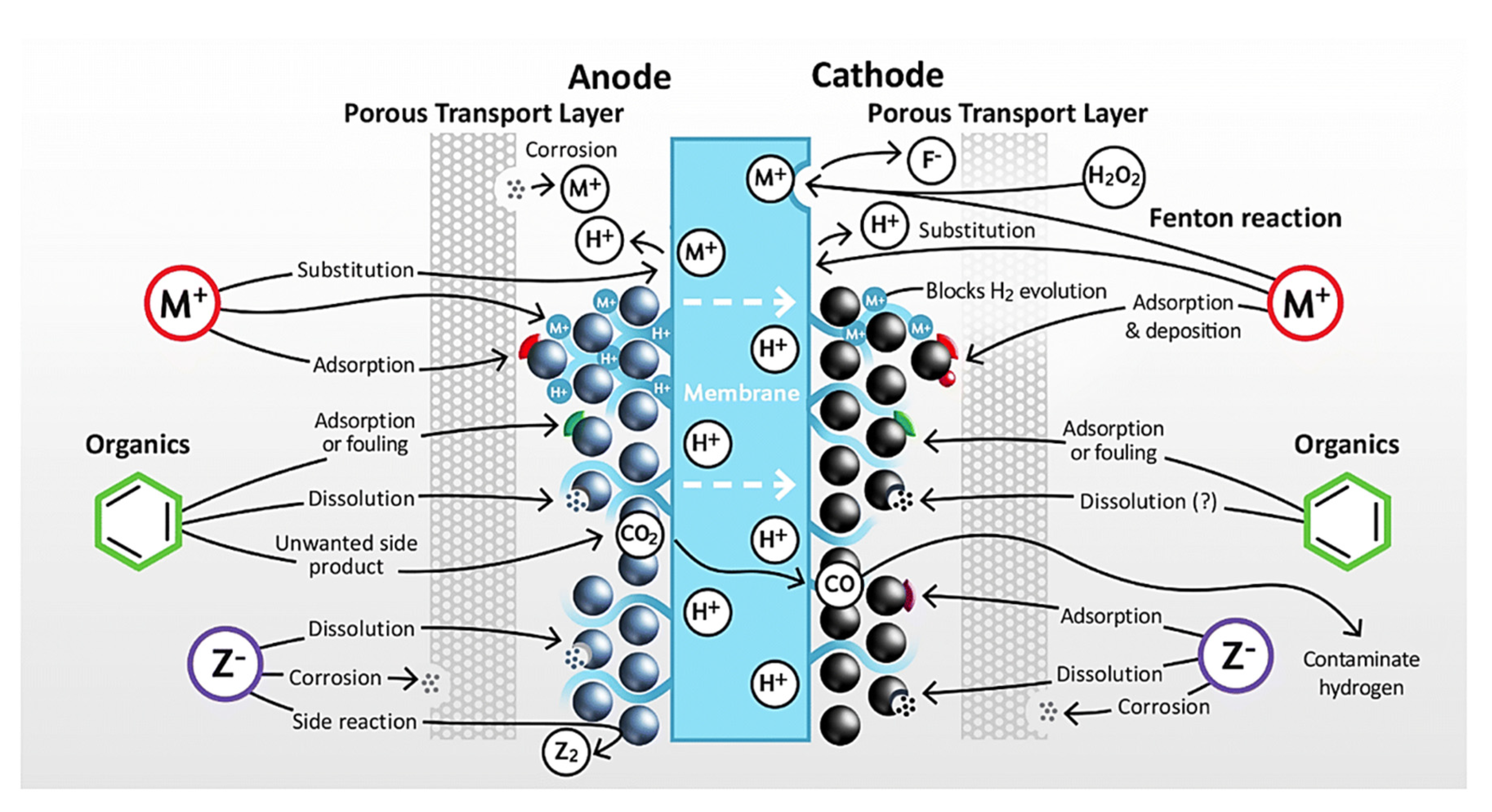
2.4. Effect of electrolyte impurities
3. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mikołajczyk, T. The impact of pollutants on catalyst performance during hydrogen evolution reaction: A brief review. Synth. Met. 2023, 296, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Olvera, Z.; Crespo-Yapur, A.; Rodríguez, O.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L.; Martínez, L.M.; Videa, M. Nickel-Based Electrocatalysts for Water Electrolysis. Energies 2022, 15, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Al-Attas, T.; Roy, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Ghaffour, N.; Thangadurai, V.; Larter, S.; Hu, J.; Ajayan, P.M.; Kibria, G. Seawater electrolysis for hydrogen production: a solution looking for a problem? Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W. Water Splitting: From Electrode to Green Energy System. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriak, J.M.; Toro, C.; Choi, K.-S. Chemistry of Materials for Water Splitting Reactions. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 7325–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Zhang, D. Recent progress in alkaline water electrolysis for hydrogen production and applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Hitt, J.L.; Turner, J.A.; Mallouk, T.E. Renewable electricity storage using electrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 117, 12558–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Yu, L.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Water splitting by electrolysis at high current densities under 1.6 volts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossar, E.; Murphy, F.; Baranova, E.A. Nickel-based anodes in anion exchange membrane water electrolysis: a review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, A.; Chandran, M.; Dhanusuraman, R. A comprehensive review on the electrochemical parameters and recent material development of electrochemical water splitting electrocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 3843–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xu, B.; Shen, L.; Shen, D.; Li, M.; Guo, L.-H. Functions and performance of ionic liquids in enhancing electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reactions: a comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19452–19469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasatti, S. Work function, electronegativity, and electrochemical behaviour of metals. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1972, 39, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov, J.K.; Bligaard, T.; Logadottir, A.; Kitchin, J.R.; Chen, J.G.; Pandelov, S.; Stimming, U. Trends in the Exchange Current for Hydrogen Evolution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, J23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Myint, M.; Chen, J.G.; Yan, Y. Correlating the hydrogen evolution reaction activity in alkaline electrolytes with the hydrogen binding energy on monometallic surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutić, S.J.; Dobrota, A.S.; Fako, E.; Skorodumova, N.V.; López, N.; Pašti, I.A. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction-From Single Crystal to Single Atom Catalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, “Investigation of the hydrogen electrode reactions on Ni electrocatalysts in alkaline medium,” 2017. [Online]. Available: https://tel.archives-ouvertes. 0200.
- Brauns, J.; Turek, T. Alkaline Water Electrolysis Powered by Renewable Energy: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Villarino, A.M.; Peltier, C.R.; Macbeth, A.J.; Yang, Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Shi, Z.; Krumov, M.R.; Lei, C.; Rodríguez-Calero, G.G.; et al. Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis: The Future of Green Hydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 7901–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, A.P.; Theerthagiri, J.; Madhavan, J. Insights on Tafel Constant in the Analysis of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 23943–23949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štrbac, S.; Smiljanić, M.; Wakelin, T.; Potočnik, J.; Rakočević, Z. Hydrogen evolution reaction on bimetallic Ir/Pt(poly) electrodes in alkaline solution. Electrochimica Acta 2019, 306, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Durst et al., “(Invited) Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction (HOR/HER) on Pt Electrodes in Acid vs. Alkaline Electrolytes: Mechanism, Activity and Particle Size Effects,” ECS Trans, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 1069–1080, Aug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Enhancing the Understanding of Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation Reactions on Pt(111) through Ab Initio Simulation of Electrode/Electrolyte Kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4985–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intikhab, S.; Snyder, J.D.; Tang, M.H. Adsorbed Hydroxide Does Not Participate in the Volmer Step of Alkaline Hydrogen Electrocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8314–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrum, I.T.; Koper, M.T.M. The role of adsorbed hydroxide in hydrogen evolution reaction kinetics on modified platinum. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinländer, P.J.; Herranz, J.; Durst, J.; Gasteiger, H.A. Kinetics of the Hydrogen Oxidation/Evolution Reaction on Polycrystalline Platinum in Alkaline Electrolyte Reaction Order with Respect to Hydrogen Pressure. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F1448–F1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, P.S.; Singh, A.R.; Chan, K. pH Effects on Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation over Pt(111): Insights from First-Principles. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6194–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Garcia-Esparza, A.T.; Takanabe, K. Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, A.P.; Madhavan, J.; Murugan, K. Recent advances in hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts on carbon/carbon-based supports in acid media. J. Power Sources 2018, 398, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzele, S.; Fichtner, J.; Garlyyev, B.; Schwämmlein, J.N.; Bandarenka, A.S. On the Dominating Mechanism of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction at Polycrystalline Pt Electrodes in Acidic Media. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9456–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, N.M.; Grgur, B.N.; Ross, P.N. Temperature-Dependent Hydrogen Electrochemistry on Platinum Low-Index Single-Crystal Surfaces in Acid Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 5405–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, J.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Bonde, J.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K. Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Durst, C. J. Durst, C. Simon, F. Hasché, and H. A. Gasteiger, “Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction Kinetics on Carbon Supported Pt, Ir, Rh, and Pd Electrocatalysts in Acidic Media,” J Electrochem Soc, vol. 162, no. 1, pp. F190–F203, Dec. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Shao-Horn, Y. Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction Kinetics on Platinum: Acid vs Alkaline Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, J.; Siebel, A.; Simon, C.; Hasché, F.; Herranz, J.; Gasteiger, H.A. New insights into the electrochemical hydrogen oxidation and evolution reaction mechanism. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovića, N.M.; Sarraf, S.T.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Ross, P.N. Hydrogen electrochemistry on platinum low-index single-crystal surfaces in alkaline solution. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 3719–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Ross, P.; Markovic, N. Temperature dependent surface electrochemistry on Pt single crystals in alkaline electrolytes: Part 2. The hydrogen evolution/oxidation reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 524-525, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Tripkovic, D.; Strmcnik, D.; Chang, K.-C.; Uchimura, M.; Paulikas, A.P.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Enhancing Hydrogen Evolution Activity in Water Splitting by Tailoring Li + -Ni(OH) 2 -Pt Interfaces. Science 2011, 334, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Tripkovic, D.; Chang, K.-C.; Strmcnik, D.; Paulikas, A.P.; Hirunsit, P.; Chan, M.; Greeley, J.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M(Ni,Co,Fe,Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsounaros, I.; Meier, J.C.; Klemm, S.O.; Topalov, A.A.; Biedermann, P.U.; Auinger, M.; Mayrhofer, K.J. The effective surface pH during reactions at the solid–liquid interface. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auinger, M.; Katsounaros, I.; Meier, J.C.; Klemm, S.O.; Biedermann, P.U.; Topalov, A.A.; Rohwerder, M.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Near-surface ion distribution and buffer effects during electrochemical reactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 16384–16394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strmcnik, D.; Uchimura, M.; Wang, C.; Subbaraman, R.; Danilovic, N.; van der Vliet, D.; Paulikas, A.P.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Markovic, N.M. Improving the hydrogen oxidation reaction rate by promotion of hydroxyl adsorption. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Garcia-Esparza, A.T.; Takanabe, K. Mechanistic Switching by Hydronium Ion Activity for Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation over Polycrystalline Platinum Disk and Platinum/Carbon Electrodes. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Takanabe, K. Identification of intrinsic catalytic activity for electrochemical reduction of water molecules to generate hydrogen. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 15111–15114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Aceituno, J.; Lapidus, G. A Kinetic-Mechanistic Study of The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Sulfuric Acid Solutions with Different Electrode Materials. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2012, 15, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, M.; Önal, A.M. High Durability and Electrocatalytic Activity Toward Hydrogen Evolution Reaction with Ultralow Rhodium Loading on Titania. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 156501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, G.K.; Jovanović, A.Z.; Dobrota, A.S.; Skorodumova, N.V.; Pašti, I.A. Hydrogen Evolution Volcano(es)—From Acidic to Neutral and Alkaline Solutions. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.M.; Beck, J.R.; Lvov, S.N. Electrochemical kinetics of the hydrogen reaction on platinum in concentrated HCl(aq). Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 57, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-Q.; Liao, L.-W.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.-X. Temperature Effect on Hydrogen Evolution Reaction at Au Electrode. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Vasileff, A.; Qiao, S.-Z. The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Solution: From Theory, Single Crystal Models, to Practical Electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7568–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.; Feky, H.; Helal, N.; Mohammed, H. Cathodic hydrogen evolution on molybdenum in NaOH solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 9625–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meethal, R.P.; Saibi, R.; Srinivasan, R. Hydrogen evolution reaction on polycrystalline Au inverted rotating disc electrode in HClO4 and NaOH solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 14304–14318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, D.; Hnát, J.; Dobrota, A.S.; Pašti, I.A.; Paidar, M.; Bouzek, K. The effect of surface modification by reduced graphene oxide on the electrocatalytic activity of nickel towards the hydrogen evolution reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 26864–26874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Kemppainen, E.; Dorbandt, I.; Bors, R.; Xi, F.; Schlatmann, R.; van de Krol, R.; Calnan, S. Understanding the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Kinetics of Electrodeposited Nickel-Molybdenum in Acidic, Near-Neutral, and Alkaline Conditions. ChemElectroChem 2020, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrii, O.A.; Tsirlina, G.A. Electrocatalytic activity prediction for hydrogen electrode reaction: intuition, art, science. Electrochimica Acta 1994, 39, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miousse, D.; Lasia, A.; Borck, V. Hydrogen evolution reaction on Ni-Al-Mo and Ni-Al electrodes prepared by low pressure plasma spraying. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, P. Calculations of the exchange current density for hydrogen electrode reactions: A short review and a new equation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 644, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, S.; Hamann, C. The pH-dependence of the hydrogen exchange current density at smooth platinum in alkaline solution (KOH). J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1975, 60, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Sequeira, C.; Macciò, D.; Saccone, A.; Figueiredo, J. Platinum–rare earth electrodes for hydrogen evolution in alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.; Cardoso, D.; Šljukić, B.; Santos, D.; Sequeira, C. Electrochemistry of hydrogen evolution in ionic liquids aqueous mixtures. 8th International Symposium on Materials (MATERIAIS) / 18th National Materials Conference of Sociedade-Portuguesa-de-Materiais. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 407–412.
- Zhou, Z.; Pei, Z.; Wei, L.; Zhao, S.; Jian, X.; Chen, Y. Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution under neutral pH conditions: current understandings, recent advances, and future prospects. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 3185–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Engelhard, M.H.; Luo, L.; Miller, A.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Pan, H.; Nie, Z.; et al. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution in Neutral pH Solutions: Dual-Phase Synergy. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 8712–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, M.D.; Logan, B.E. Electrolyte effects on hydrogen evolution and solution resistance in microbial electrolysis cells. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Janssen, M.; Oezaslan, M. Effect of Monovalent Cations on the HOR/HER Activity for Pt in Alkaline Environment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F66–F73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Kaley, N.M.; Mondal, J.; Narayanan, T.N. Engineering the hydrogen evolution reaction of transition metals: effect of Li ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15795–15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.; Tilak, B. Interfacial processes involving electrocatalytic evolution and oxidation of H2, and the role of chemisorbed H. Electrochimica Acta 2002, 47, 3571–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W. Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrum, I.T.; Janik, M.J. pH and Alkali Cation Effects on the Pt Cyclic Voltammogram Explained Using Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 120, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Park, K.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kang, K. Aqueous Rechargeable Li and Na Ion Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11788–11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Borodin, O.; Gao, T.; Olguin, M.; Ho, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, K. “Water-in-salt” electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries. Science 2015, 350, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, A.B.; Varela, A.S.; Dionigi, F.; Fanchiu, H.; Miller, C.; Trinhammer, O.L.; Rossmeisl, J.; Dahl, S. Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution: Sabatier’s Principle and the Volcano Plot. J. Chem. Educ. 2012, 89, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, J.; Durst, J.; Fabbri, E.; Pătru, A.; Cheng, X.; Permyakova, A.A.; Schmidt, T.J. Interfacial effects on the catalysis of the hydrogen evolution, oxygen evolution and CO2-reduction reactions for (co-)electrolyzer development. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W. Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strmcnik, D.; Lopes, P.P.; Genorio, B.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Markovic, N.M. Design principles for hydrogen evolution reaction catalyst materials. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, N.; Jr., P.R. Surface science studies of model fuel cell electrocatalysts. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 45, 117–229. [CrossRef]
- Danilovic, N.; Subbaraman, R.; Strmcnik, D.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N. Electrocatalysis of the HER in acid and alkaline media. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2013, 78, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Sheng, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Xu, B.; Yan, Y. Universal dependence of hydrogen oxidation and evolution reaction activity of platinum-group metals on pH and hydrogen binding energy. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501602–1501602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Huang, B.; Pan, J.; Liu, Q.; Han, J.; Xiao, L.; Lu, J.; Zhuang, L. Pt–Ru catalyzed hydrogen oxidation in alkaline media: oxophilic effect or electronic effect? Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 8, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Niet, M.J.; Garcia-Araez, N.; Hernández, J.; Feliu, J.M.; Koper, M.T. Water dissociation on well-defined platinum surfaces: The electrochemical perspective. Catal. Today 2013, 202, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, N.M.; Schmidt, T.J.; Grgur, B.N.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J.; Ross, P.N. Effect of Temperature on Surface Processes at the Pt(111)−Liquid Interface: Hydrogen Adsorption, Oxide Formation, and CO Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8568–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma-Yanez, I.; Wallace, W.D.Z.; Sebastián-Pascual, P.; Climent, V.; Feliu, J.M.; Koper, M.T.M. Interfacial water reorganization as a pH-dependent descriptor of the hydrogen evolution rate on platinum electrodes. Nat. Energy 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.; Chan, K.; Ahmed, R.; Tripković, V.; Björketun, M.E. pH in atomic scale simulations of electrochemical interfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10321–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.; Chan, K.; Skúlason, E.; Björketun, M.E.; Tripkovic, V. On the pH dependence of electrochemical proton transfer barriers. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, L.; Merinov, B.V.; Goddard, W.A. Explanation of Dramatic pH-Dependence of Hydrogen Binding on Noble Metal Electrode: Greatly Weakened Water Adsorption at High pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7787–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Shinagawa and K. Takanabe, “Electrolyte Engineering toward Efficient Hydrogen Production Elec-trocatalysis with Oxygen-Crossover Regulation under Densely Buffered Near-Neutral pH Conditions,” Journal of Physical Chemistry C, vol. 120, no. 3, pp. 1785–1794, Jan. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Murthy, A.P.; Govindarajan, D.; Theerthagiri, J.; Madhavan, J.; Parasuraman, K. Metal-doped molybdenum nitride films for enhanced hydrogen evolution in near-neutral strongly buffered aerobic media. Electrochimica Acta 2018, 283, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Takanabe, K. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution under Densely Buffered Neutral pH Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 20453–20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Takanabe, K. Towards Versatile and Sustainable Hydrogen Production through Electrocatalytic Water Splitting: Electrolyte Engineering. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1318–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanan, M.W.; Nocera, D.G. In Situ Formation of an Oxygen-Evolving Catalyst in Neutral Water Containing Phosphate and Co 2+. Science 2008, 321, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterman, D.A.; Surendranath, Y.; Nocera, D.G. A Self-Healing Oxygen-Evolving Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3838–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanan, M.W.; Yano, J.; Surendranath, Y.; Dincă, M.; Yachandra, V.K.; Nocera, D.G. Structure and Valency of a Cobalt−Phosphate Water Oxidation Catalyst Determined by in Situ X-ray Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13692–13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, L.D.S.; Bergel, A.; Féron, D.; Basséguy, R. Hydrogen production by electrolysis of a phosphate solution on a stainless steel cathode. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 8561–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Zhu, X. Qin, Y. Yao, and M. Shao, “PH-Dependent Hydrogen and Water Binding Energies on Platinum Surfaces as Directly Probed through Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy,” J Am Chem Soc, vol. 142, no. 19, pp. 8748–8754, May 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Sun et al., “Electrodeposited cobalt-sulfide catalyst for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical hy-drogen generation from water,” J Am Chem Soc, vol. 135, no. 47, pp. 17699–17702, Nov. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Danilovic, N.; Subbaraman, R.; Strmcnik, D.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N. Electrocatalysis of the HER in acid and alkaline media. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2013, 78, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Pearce, P.E.; Duan, Y.; Dubouis, N.; Marchandier, T.; Grimaud, A. Importance of Water Structure and Catalyst–Electrolyte Interface on the Design of Water Splitting Catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 8248–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strmcnik, D.; Kodama, K.; van der Vliet, D.; Greeley, J.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Marković, N.M. The role of non-covalent interactions in electrocatalytic fuel-cell reactions on platinum. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoczko, J.; Colic, V.; Ganassin, A.; Schuhmann, W.; Bandarenka, A.S. Influence of the alkali metal cations on the activity of Pt(111) towards model electrocatalytic reactions in acidic sulfuric media. Catal. Today 2015, 244, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Strmcnik et al., “Effects of Li+, K+, and Ba2+ cations on the ORR at model and high surface area Pt and Au surfaces in alkaline solutions,” Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, vol. 2, no. 21, pp. 2733–2736, Nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- García, N.; Climent, V.; Orts, J.M.; Feliu, J.M.; Aldaz, A. Effect of pH and Alkaline Metal Cations on the Voltammetry of Pt(111) Single Crystal Electrodes in Sulfuric Acid Solution. Chemphyschem 2004, 5, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Li, J.; Jiao, L.; Doan, H.T.T.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Abraham, K.M.; Mukerjee, S.; Jia, Q. Unifying the Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation Reactions Kinetics in Base by Identifying the Catalytic Roles of Hydroxyl-Water-Cation Adducts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3232–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Garlyyev, B.; Watzele, S.; Liang, Y.; Fichtner, J.; Pohl, M.D.; Bandarenka, A.S. Influence of Alkali Metal Cations on the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity of Pt, Ir, Au, and Ag Electrodes in Alkaline Electrolytes. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2326–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubouis, N.; Grimaud, A. The hydrogen evolution reaction: from material to interfacial descriptors. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9165–9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Rao, R.R.; You, S.; Myint, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Giordano, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Cation- and pH-Dependent Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation Reaction Kinetics. JACS Au 2021, 1, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Rao, R.R.; You, S.; Myint, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Giordano, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Cation- and pH-Dependent Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation Reaction Kinetics. JACS Au 2021, 1, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.C.O.; Goyal, A.; Moerland, P.; Koper, M.T.M. Understanding Cation Trends for Hydrogen Evolution on Platinum and Gold Electrodes in Alkaline Media. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14328–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Narayanan, T.N. Effect of ‘water-in-salt’ electrolytes in the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction of carbon nanotubes. J. Physics: Energy 2020, 2, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Narayanaru, S.; Narayanan, T.N. Tuning the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Metals by Lithium Salt. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 7116–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanovic, I.; Atanassov, P.; Garzon, F.; Henson, N.J. Density Functional Theory Study of the Alkali Metal Cation Adsorption on Pt(111), Pt(100), and Pt(110) Surfaces. ECS Trans. 2014, 61, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlyyev, B.; Xue, S.; Watzele, S.; Scieszka, D.; Bandarenka, A.S. Influence of the Nature of the Alkali Metal Cations on the Electrical Double-Layer Capacitance of Model Pt(111) and Au(111) Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.N.; McCrum, I.T.; Janik, M.J. Alkali cation specific adsorption onto fcc(111) transition metal electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13699–13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taji, Y.; Zagalskaya, A.; Evazzade, I.; Watzele, S.; Song, K.-T.; Xue, S.; Schott, C.; Garlyyev, B.; Alexandrov, V.; Gubanova, E.; et al. Alkali metal cations change the hydrogen evolution reaction mechanisms at Pt electrodes in alkaline media. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Koper, M.T.M. The Interrelated Effect of Cations and Electrolyte pH on the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Gold Electrodes in Alkaline Media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13452–13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, G.A.; Zeledón, J.A.Z.; Gunasooriya, G.T.K.K.; Dull, S.M.; Perryman, J.T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Stevens, M.B.; Jaramillo, T.F. Acid anion electrolyte effects on platinum for oxygen and hydrogen electrocatalysis. Commun. Chem. 2022, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E. Lamy-Pitara, S. El Mouahid, and J. Barbier, “Effect of anions on catalytic and electrocatalytic hydro-genations and on the electrocatalytic oxidation and evolution of hydrogen on platinum,” 2000. [Online]. Available: www.elsevier.nl/locate/electacta.
- Quaino, P.; Juarez, F.; Santos, E.; Schmickler, W. Volcano plots in hydrogen electrocatalysis – uses and abuses. 2014, 5, 846–854. [CrossRef]
- Arminio-Ravelo, J.A.; Jensen, A.W.; Jensen, K.D.; Quinson, J.; Escudero-Escribano, M. Electrolyte Effects on the Electrocatalytic Performance of Iridium-Based Nanoparticles for Oxygen Evolution in Rotating Disc Electrodes. Chemphyschem 2019, 20, 2956–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faid, A.Y.; Foroughi, F.; Sunde, S.; Pollet, B. Unveiling hydrogen evolution dependence on KOH concentration for polycrystalline and nanostructured nickel-based catalysts. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2022, 52, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Park, E.J.; Zhu, W.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, H.; Lin, Y.; Serov, A.; Zulevi, B.; Baca, E.D.; et al. Highly quaternized polystyrene ionomers for high performance anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.N.; Oshchepkov, A.G.; Cherstiouk, O.V.; Simonov, P.A.; Nazmutdinov, R.R.; Savinova, E.R.; Bonnefont, A. Influence of the NaOH Concentration on the Hydrogen Electrode Reaction Kinetics of Ni and NiCu Electrodes. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossar, E.; Houache, M.S.; Zhang, Z.; Baranova, E.A. Comparison of electrochemical active surface area methods for various nickel nanostructures. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 870, 114246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Takanabe, K. Impact of solute concentration on the electrocatalytic conversion of dissolved gases in buffered solutions. J. Power Sources 2015, 287, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwe, S.; Mei, B.; Masa, J.; Schuhmann, W.; Ventosa, E. Overcoming cathode poisoning from electrolyte impurities in alkaline electrolysis by means of self-healing electrocatalyst films. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Dosche, C.; Oezaslan, M. Fundamental Aspects of Contamination during the Hydrogen Evolution/Oxidation Reaction in Alkaline Media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 024506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gunathunge, C.M.; Agrawal, N.; Montalvo-Castro, H.; Jin, J.; Janik, M.J.; Waegele, M.M. Impact of Alkali Metal Cations and Iron Impurities on the Evolution of Hydrogen on Cu Electrodes in Alkaline Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, S.; Cai, Y.; Louie, M.W.; Trotochaud, L.; Bell, A.T. Effects of Fe Electrolyte Impurities on Ni(OH)2/NiOOH Structure and Oxygen Evolution Activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 7243–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanion, M.; Najafpour, M.M. Oxygen-evolution reaction by gold and cobalt in iron and nickel free electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 46, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, S.; Trotochaud, L.; Cheng, M.; Head-Gordon, M.; Bell, A.T. Experimental and Computational Evidence of Highly Active Fe Impurity Sites on the Surface of Oxidized Au for the Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Water in Basic Media. ChemElectroChem 2015, 3, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Koh, J.R.; Yeo, B.S. Mechanistic Study of the Synergy between Iron and Transition Metals for the Catalysis of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 3790–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O.; Conway, B.E. Studies in hydrogen overpotential. The effect of catalytic poisons at platinized platinum and nickel. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1949, 45, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Conway, B. Poisoning effects of arsenic species on H adsorption and kinetic behaviour of the H2 evolution reaction at Pt in KOH solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 395, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.J.; Qian, S.Y.; Conway, B.E. Arsenic poisoning effects on cathodic polarization and hydrogen adsorption at platinum and steel electrodes in KF · 2HF melts. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1996, 26, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Murawski, J.; Shinde, D.V.; Stephens, I.E.L.; Hinds, G.; Smith, G. Impact of impurities on water electrolysis: a review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 1565–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwe, S.; Mei, B.; Masa, J.; Schuhmann, W.; Ventosa, E. Overcoming cathode poisoning from electrolyte impurities in alkaline electrolysis by means of self-healing electrocatalyst films. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, C.; Maji, T.K. MOF derived carbon based nanocomposite materials as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26728–26754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumera, M. Materials Electrochemists’ Never-Ending Quest for Efficient Electrocatalysts: The Devil Is in the Impurities. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7087–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. Will Any Crap We Put into Graphene Increase Its Electrocatalytic Effect? ACS Nano 2020, 14, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Electrode | electrolyte | applied potential (V vs Ag/AgCl) |
duration (mins) | hydrogen concentrationn (ppm) |
rate of formation (×10−8 mol·s−1·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 0.1 M LiTFSI | −1.1 | 5 | 16550 | 4056 |
| Pt | 20 M LiTFSI | −1.1 | 5 | 15799 | 3872 |
| Au | 0.1 M LiClO4 | −1.5 | 5 | 5755 | 2635 |
| Au | 5 M LiClO4 | −1.5 | 5 | 7773 | 3559 |
| Au | 0.1 M LiTFSI | −1.5 | 5 | 7950 | 3640 |
| Au | 20 M LiTFSI | −1.5 | 5 | 15577 | 7132 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





