1. Introduction
Bacterial infection is one of the primary health problems in underdeveloped nations. The situation gets worse when germs acquire ongoing resistance to the existing antibiotics. As the currently known antibiotics become less effective against new bacterial strains, researchers are forced to create new antibacterial medicines with exciting potential. The metal nanoparticles are the most promising antibacterial agents among these new medicines. As nanoparticles target multiple biomolecules at once and prevent the development of bacterial resistance, it is hypothesised that nanoparticles with antibacterial potentials have the ability to lessen the formation of resistant bacteria [
1].
The majority of organic dyes utilized in industries including those used in textile, paper, paints, and medicine are non-biodegradable. Because of their numerous adverse effects, these dyes are considered a significant environmental problem. These colouring agents are extremely hazardous as they cause a number of health-related problems including excessive perspiration, cognitive confusion, and methemoglobonemia [
2]. In the dying process, about 10% of the total dyes are estimated to be consumed while the remainder are discharged to the water reservoir which reduces the supply of oxygen to aquatic life and reduces the algal photosynthetic ability in water thus adversely and permanently affecting the ecosystem [
3,
4,
5].
In today's science, technology, and engineering fields’ nanotechnology research is one of the most active areas because it tries to understand the significance of this technology for advancing society. Recent studies have shown that green nanotechnology is more significant than other chemical and physical technologies in many respects. An environmentally friendly, consistent method for making precious metal nanoparticles has been revealed by research in bionanotechnology.
A number of researchers have investigated the biosynthesis of nanomaterials by using different types of biological sources i.e., bacteria, fungi, and plant extracts [
6]. The biological synthesis of nanoparticles using plants, fungi, and bacteria are economic and environmentally friendly [
2]. The biological molecules obtained from these biological sources are used in situ reducing as well as capping agents[
7]. Typically nanoparticles are clusters ranging in size from 1-100 nm. A number of properties such as size, nature, composition crystallinity, and composition are used to understand the nature of metal NPs. Nanoparticles have many uses in different areas such as catalysis, electronics, diagnosis as well and infection control [
8]. It is recognized that both unicellular and multicellular organisms may have the ability to build metal composites either extracellularly or intracellularly. Additionally, the ability of microbes like fungi and bacteria to control the manufacturing of metal nanomaterials is employed to discover novel materials.
Rhododendron arboreum a member of the family Ericaceae is one of the most important medicinal plants. This plant is distributed throughout the world mostly concentrated in China, India, Malaysia, and Nepal [
9,
10]. In Pakistan, this plant occurs in the Hazara Division and Kashmir.
R. arboreum has a number of medicinal uses in folk. The dried flowers of this plant have efficacy in the treatment of diarrhea and blood dysentery[
11]. The young leaves of
R. arboreum are used for alleviating the headache when applied on the forehead [
12]. Chemical analysis of
R. arboreum revealed the presence of a number of bioactive constituents. The leaves of
R. arboreum contained a number of bioactive compounds such as epicatechin, synergic acid, quercitine-3-O- galactoside, and quercitirine [
13], while from the flowers three bioactive compounds such as quercetin, rutin, and coumaric acid were reported[
14].
In the present study, ZnNPs were prepared from the bark extract of Rhododendron arboreum using the green method and were characterized through different instrumental techniques. The biosynthesized ZnNPs were evaluated for their antibacterial activity against different pathogenic bacteria and their MIC and MBC values were determined. Furthermore, the biosynthesized nanoparticles were exploited for their anti-biofilm potential and finally, the underlying bactericidal mechanisms were determined.
2. Results and discussion
2.1. UV-visible Spectrophotometry and Band Gap Energy
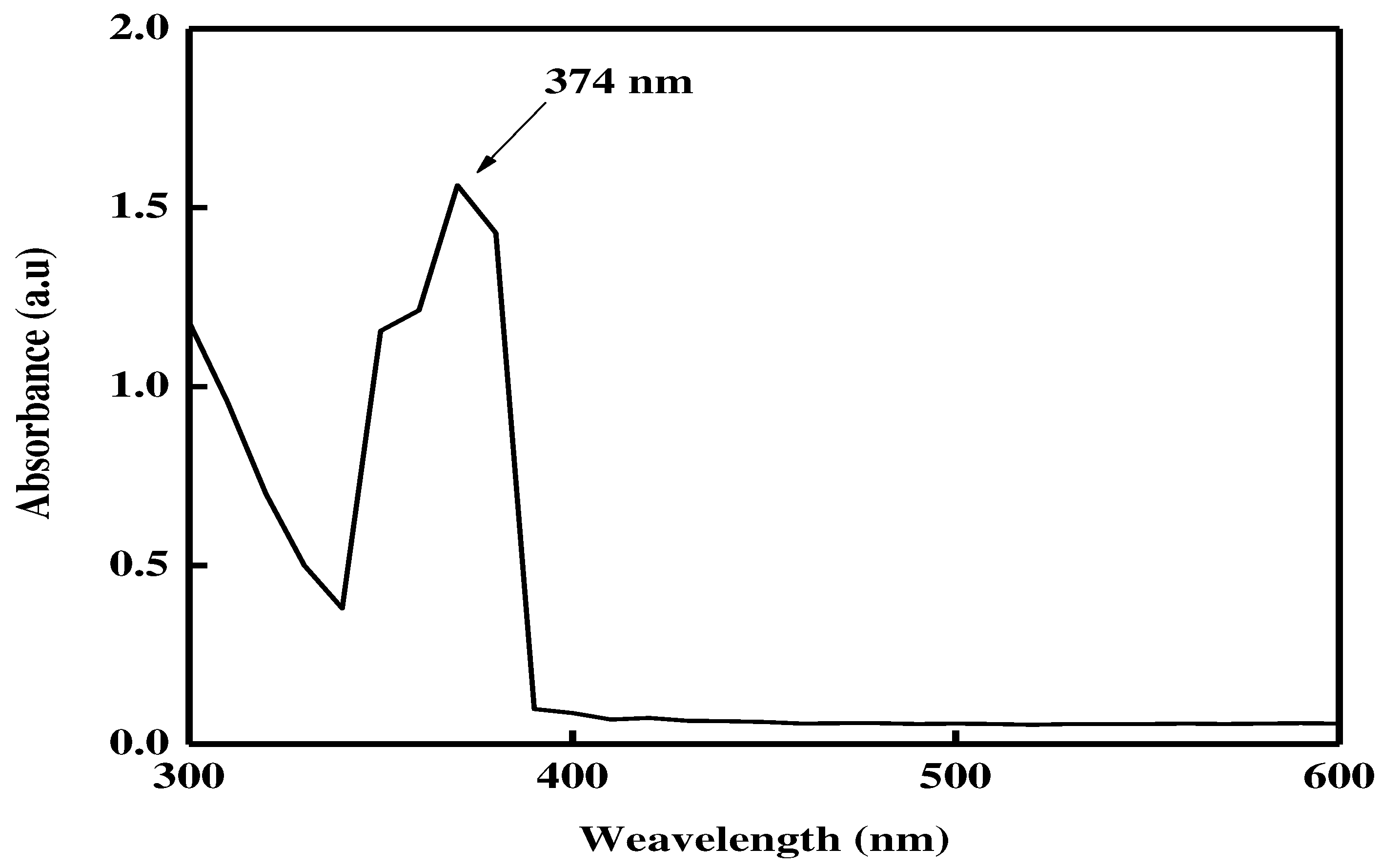
The spectrum of the reaction of 2 mM ZnCl
2 with
R. arboreum aqueous extract with surface plasmon resonance at 374 nm suggested the production of zinc NPs, as seen in the UV-visible spectrum[
15]. The biosynthesized ZnNPs showed distinctive spectrum characteristics that zinc exhibited neither in bulk metals nor in molecular form [
16]. The biogenesis of zinc nanoparticles was therefore validated by UV-visible spectrometric measurement. For the first conformation of the biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles, UV-visible spectrometry is a crucial approach since each metal nanoparticle displayed a different surface plasmon resonance value [
17] as shown in
Figure 1.
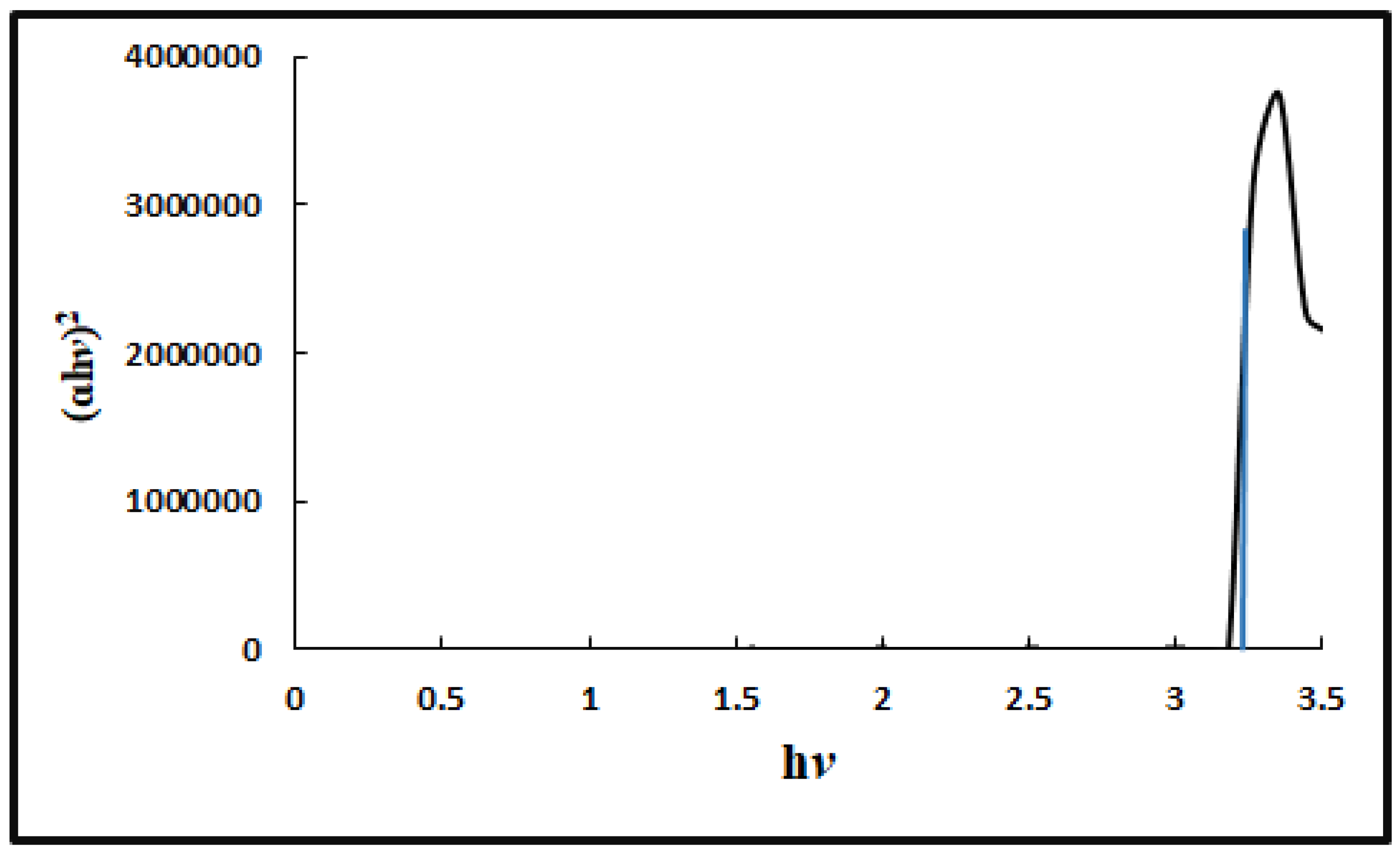
The Eg (band gap energy) of ZnNps was determined from UV/Vis absorption spectrophotometry. The Eg was calculated by plotting (
ɑh
v)
2 against the photon energy (h
v) as shown in
Figure 2. The Eg was calculated from the extrapolation of the linear part of the plot and was found to be 3.2 eV, which is less than the reported value of 3.4 eV [
18].
2.2. FTIR, EDX, and XRD analysis
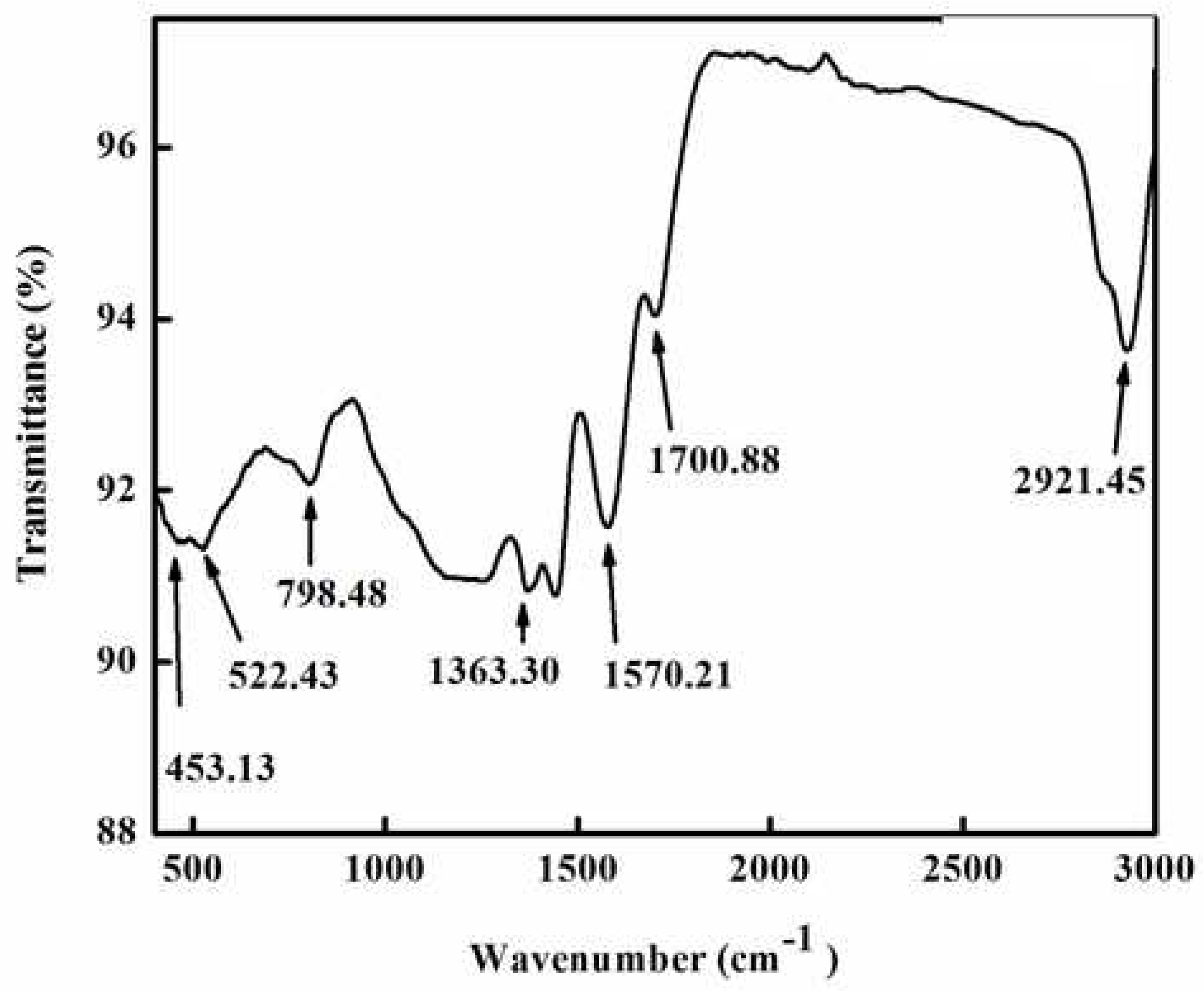
Different types of functional groups that were crucial to the reduction and stabilisation of zinc metal were identified using FTIR spectroscopy. The Fourier transform spectrum of green synthesized ZnNPs by extract of
R. arboreum is shown in
Figure 3. The FTIR spectrum displayed various peaks at 2921, 1700, 1570, 1363, 798, 522, and 453 cm
−1. The peaks observed at 2921 and 1700 cm
−1 correspond to O-H and C-H bond stretching. Similarly, the peaks at 1570, 1363 , and 798cm
−1 indicated the presence of a C=O bond and symmetric bending of CH
3, respectively. The intense peaks at 522 cm
−1 were attributed to C-C and N-H vibration. The formation of ZnNPs was confirmed by the major peak at 453 cm
−1 [
19,
20].
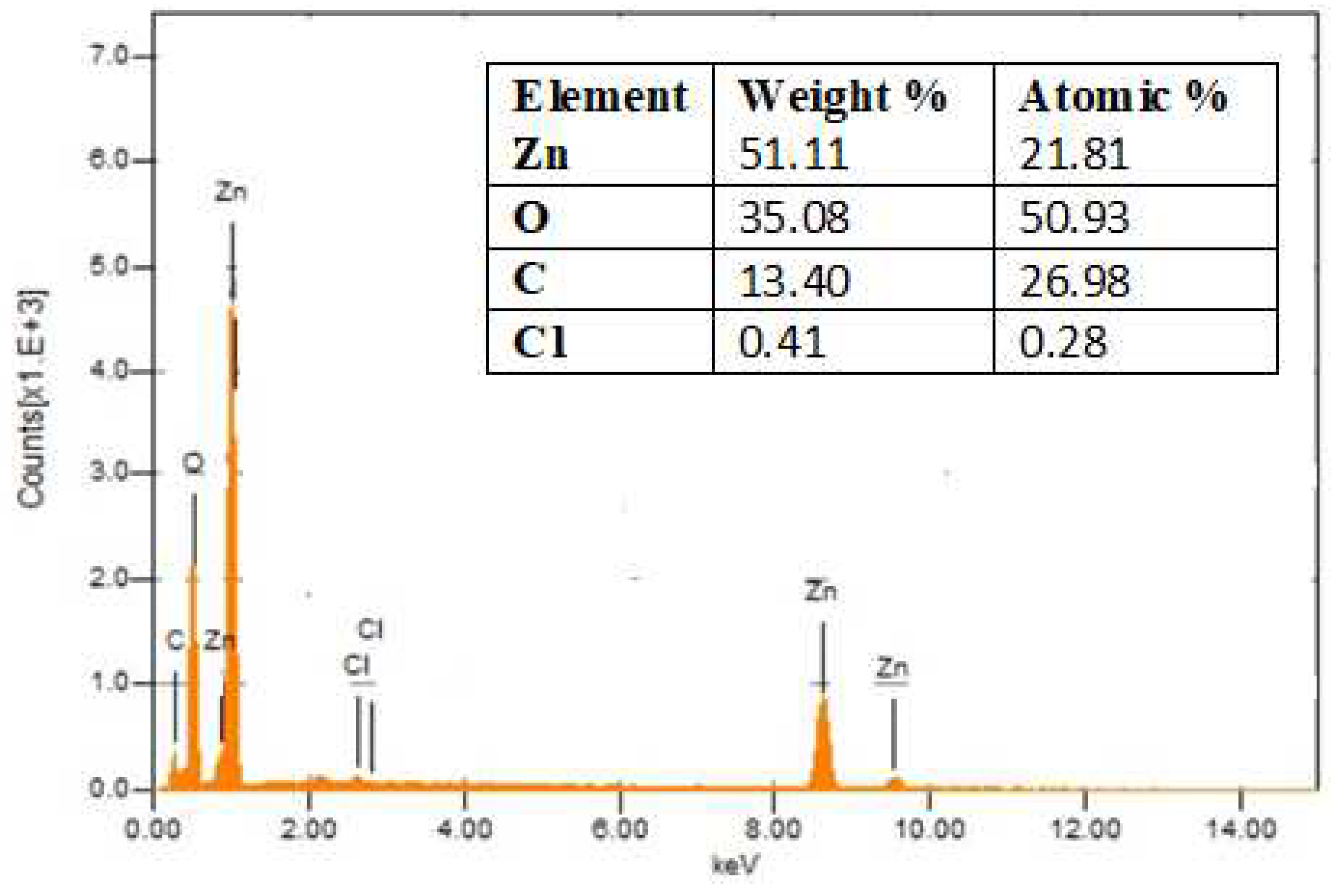
EDX spectrometry was also used to investigate ZnNP formation. We received quantitative and qualitative data from EDX regarding the sample's elemental makeup. The EDX spectrum of biosynthesized ZnNPs showed that Zn was present in substantial amounts (51.11%), but other elements including carbon were also found in minor amounts and may have derived from the plant extract. The EDX spectra confirmed the synthesis of ZnNPs as the peak for Zn was present. The minor peaks for Cl might be due to the precursor salt used in the synthesis of nanoparticles as shown in
Figure 4.
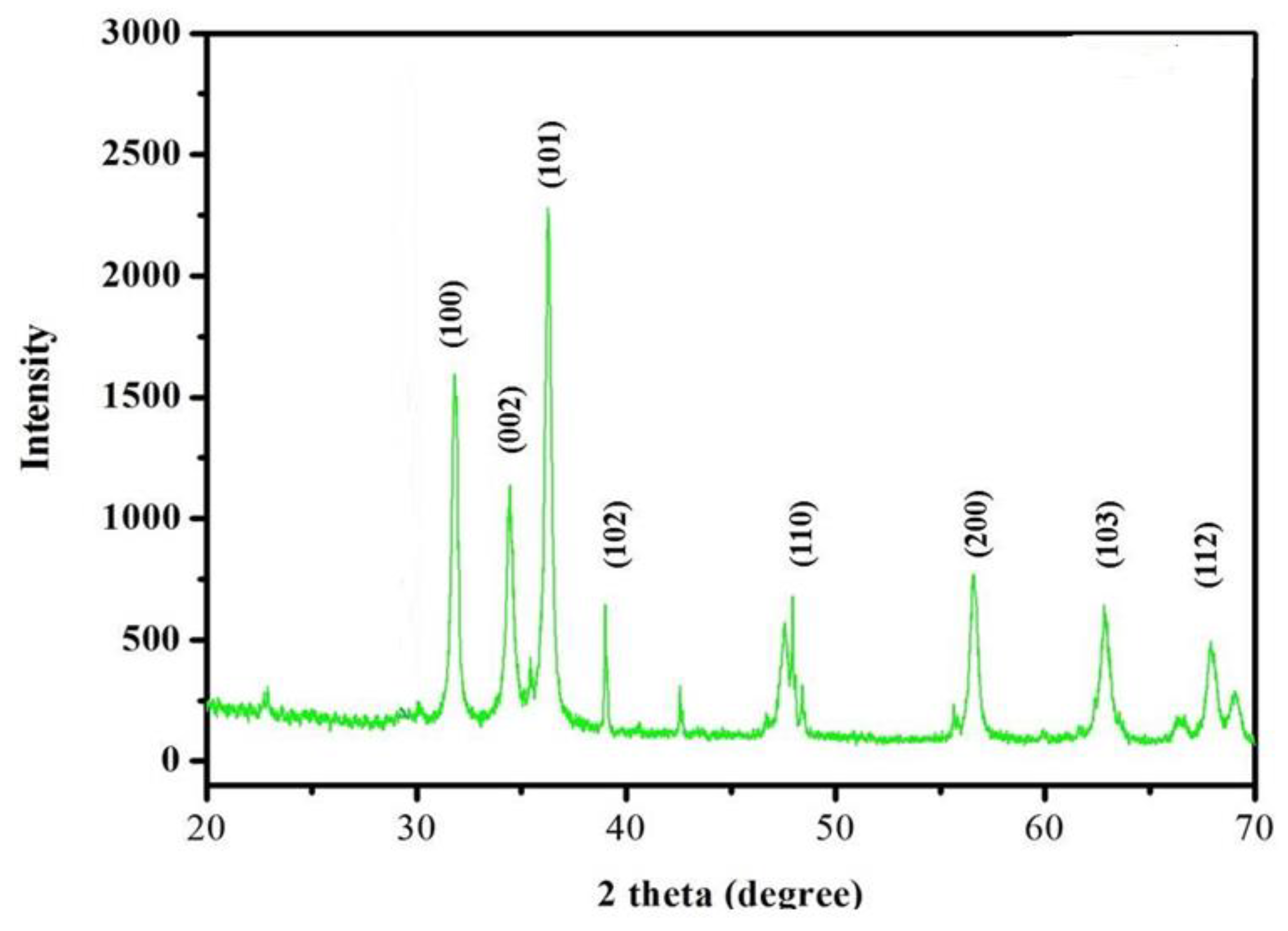
The diffraction peaks could be used to easily index the hexagonal wurzite structure of ZnNPs. The peaks (100), (002), (101), (102), (110), (103), (200), and (112), corresponded to 2Ө of 31.821, 34.4651, 36.2886, 47.5941, 56.6508, 62.9114, 66.4064, 67.9868, 69.1113, 72.6063 and 76.9826, respectively. The sample exhibited identical patterns and lacked crystalline impurities thus indicating the phase purity of ZnNPs. The findings are in agreement with the reported work[
18]. The crystallite size of the ZnNPs was calculated from the most intense peak using Scherer’s formulae. The Crystallite size calculated for ZnNPs was found to be 66.20 nm (
Figure 5).
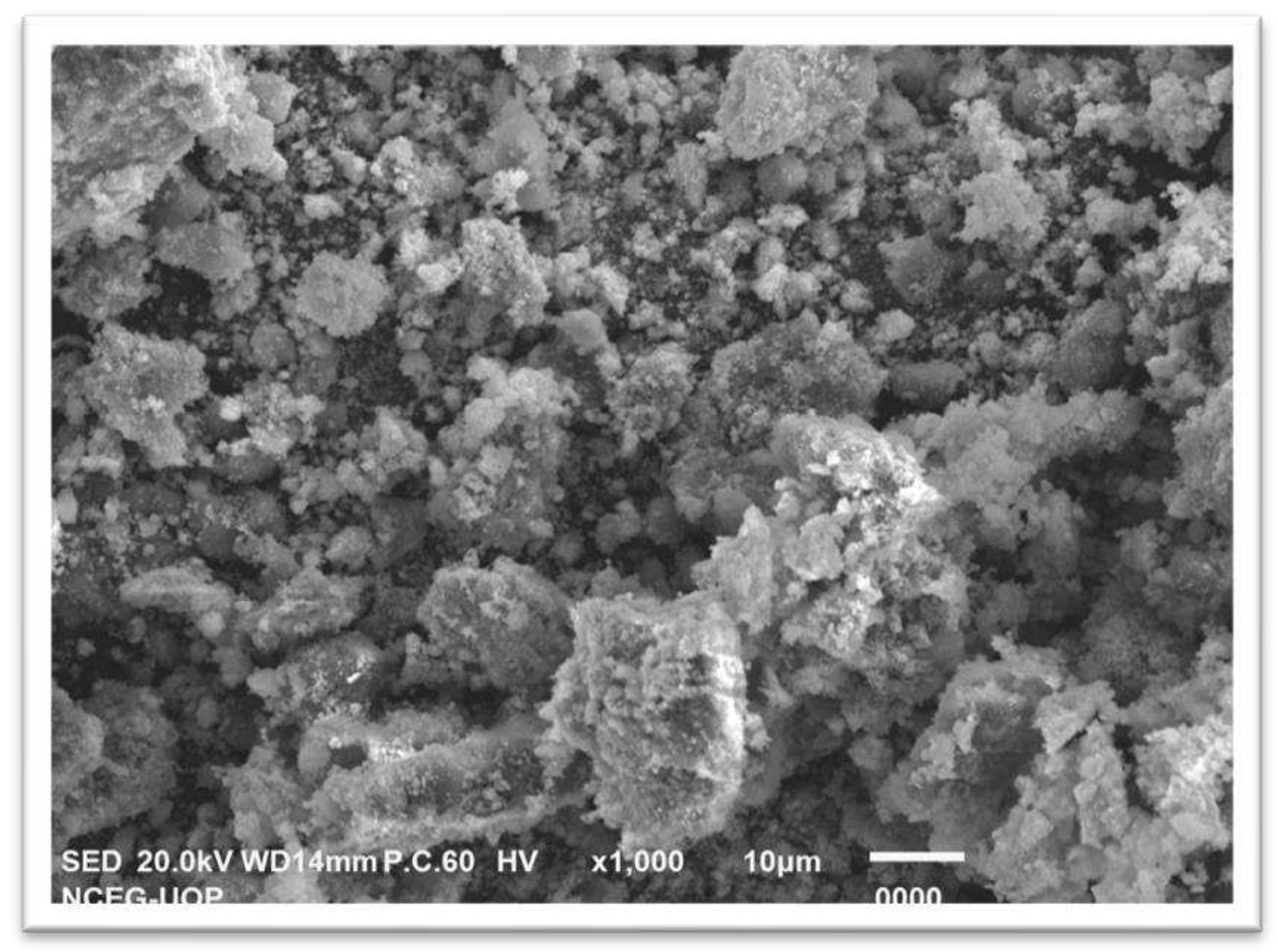
2.3. Scanning electron microscopic analysis
SEM analysis was used to investigate the shape and microstructure of the synthesised ZnNPs as shown in figure 6. The SEM micrograph of the biosynthesized ZnNPs demonstrated the presence of spherical-shaped nanoparticles. From the SEM micrograph, the individual particle size could not be deduced but the material is composed of porous and uniformly dispersed agglomerated NPs [
21].
2.4. Antibacterial activity
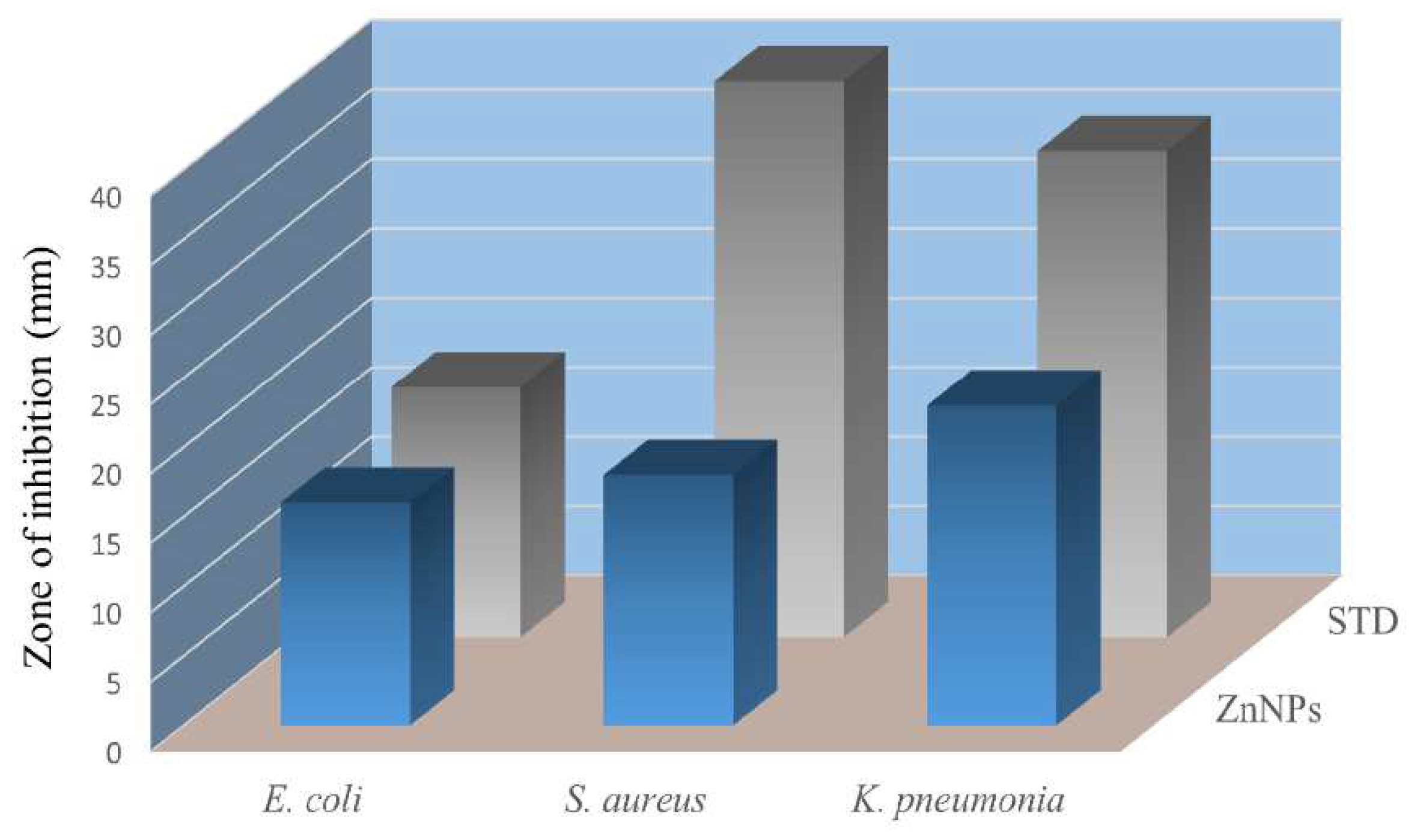
The antibacterial potential of the green synthesised zinc nanoparticles was assessed against clinically isolated pathogenic bacteria such as
E. coli,
S. aureus, and
K. pneumonia. ZnNPs inhibited the growth of
K. pneumonia and
S. aureus with zones of inhibition of 23 and 18 mm, respectively, while in the case of
E. coli the activity was good with a zone of inhibition of 16 mm. These results are comparable with the standard antibiotic levofloxacin as shown in
Figure 7.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values of the test sample were also investigated. The MIC and MBC values of the biosynthesized ZnNPs against
K. pneumonia,
S. aureus, and
E.coli were 34±0.21 and 11.71±0.47, 47±0.11 and 23.86±0.84 and 94±0.18 and 40.43±0.16 µg/ml, respectively (
Table 1).
2.5. Membrane damage assay
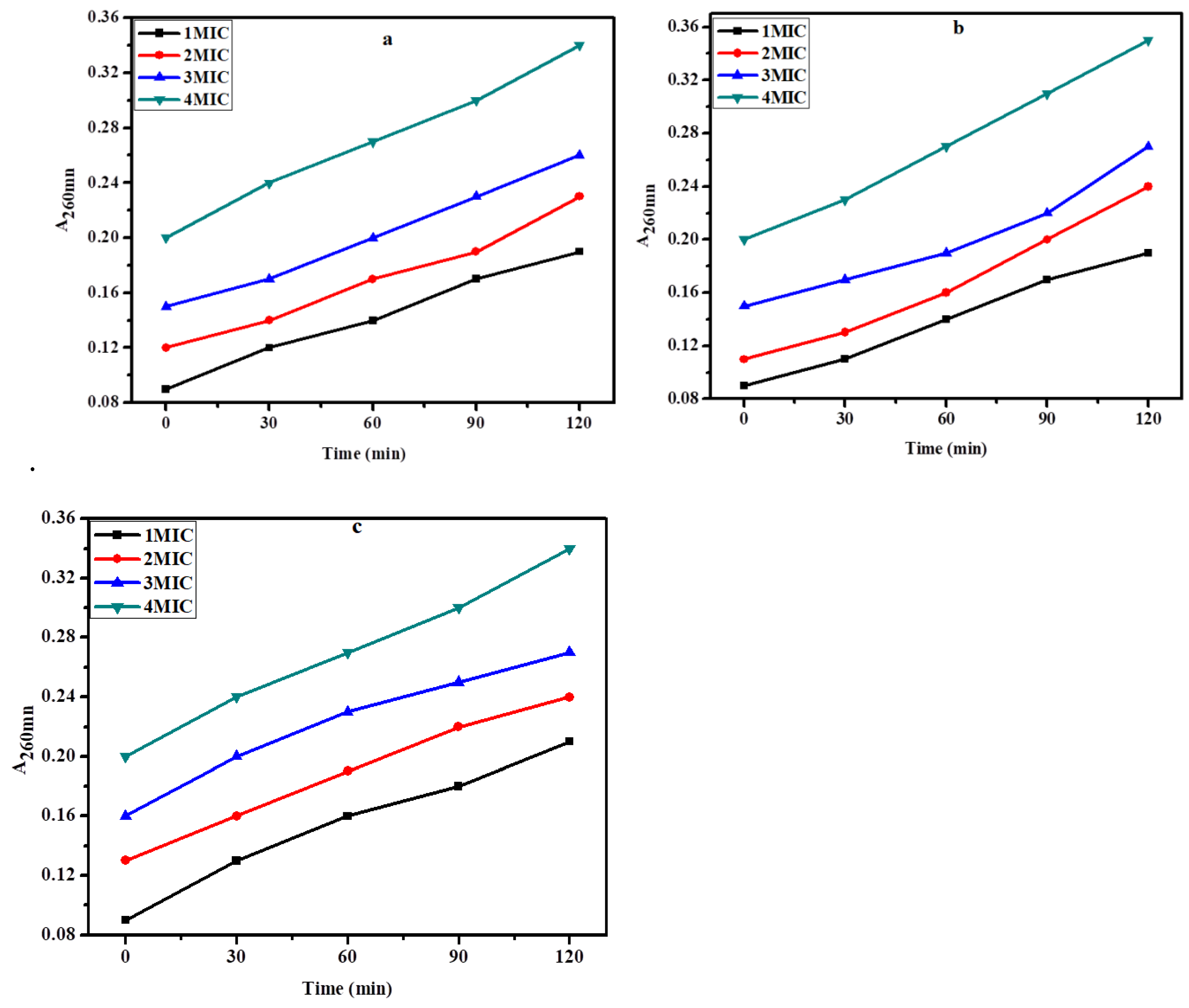
The structural strength of the bacterial cell was determined by looking at the injury that the biosynthesized zinc NPs to the cell membrane of bacteria. Upon exposure to the biosynthesized ZnNPs the cell contents that got released were determined by measuring their A
260 value. Treatment of
E. coli,
S. aureus, and
K. pneumonia with zinc nanoparticles demonstrated a considerable increase in the concentration of intracellular contents with the increase in concentration and time of exposure as depicted by the elevated A
260. The data clearly show that the biosynthesized zinc NPs considerably damage the test bacteria's membrane. The membrane-damaging effect of ZnNPs was increased with an increase in the concentration and time of exposure. In the case of
K. pneumonia the membrane was seriously damaged with A
260 value of 0.34 at 4MIC and at 120 min of exposure. However, in the case of
S. aureus and
E. coli the A
260 values for extracellular substances released were 0.31 and 0.28 at 120 min of exposure at 4MIC, respectively. It is thought that the basic mechanism behind damaging the bacterial cell might be the establishment of hydrogen bonds between the free NH group present in the biosynthesized ZnNPs and the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell. This is most likely one of the most important explanations for the bactericidal potential of biosynthesized ZnNPs (
Figure 8a, b, and c).
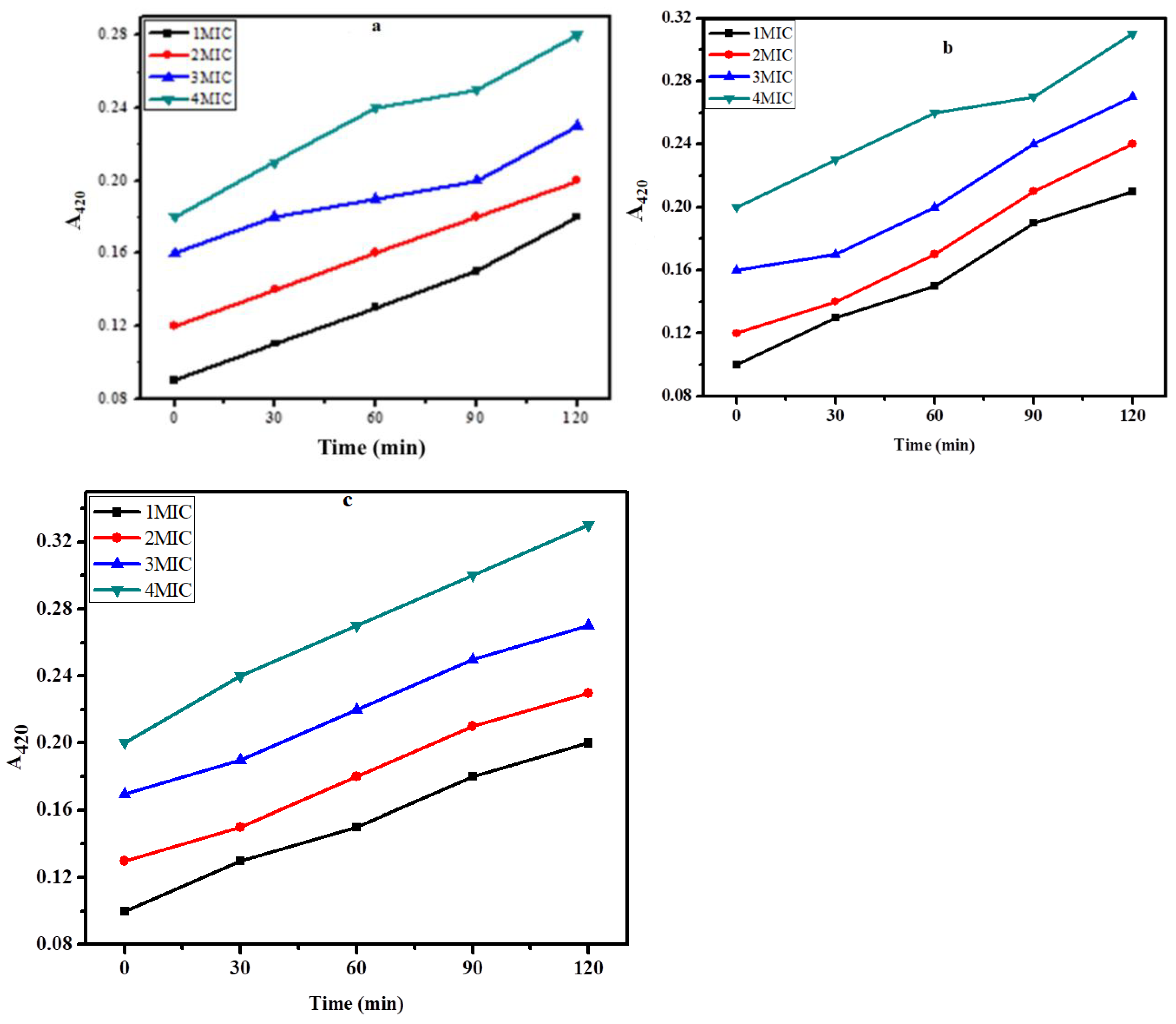
2.6. Inner membrane permeability assay
The assay for destroying bacterial inner membranes is based on the enzyme β-galactosidase, which is secreted when bacterial inner membranes are damaged. Lactose serves as β-galactosidase's real substrate. β-galactosidase converts ONPG into o-nitrophenol, a colour product with a wavelength of 420 nm [
22]. Cells suspension was treated with different concentrations i.e., 1xMIC, 2xMIC, 3xMIC, and 4xMIC of zinc NPs, and the cleavage of ONPG was measured for 2h as shown in figures 8a, b, and c for
E. coli,
S. aureus and
K. pneumonia, respectively. The hydrolysis rate of ONPG was increased as the time of interaction ZnNPs and test bacteria was increased. The maximal hydrolysis was obtained at 120 min for all test bacteria. Results showed that the green synthesized ZnNPs exhibited an effective inner membrane damaging action upon increasing the dose as well as time of interaction as showed by a greater A
420 value, suggesting higher permeability of the bacterial membrane to its entry. The potential mechanisms for the bactericidal activity of these biosynthesized ZnNPs might be the membrane binding or its passive diffusion via the cell membrane, resulting in the membrane's permeability as shown in
Figure 9a, b and c.
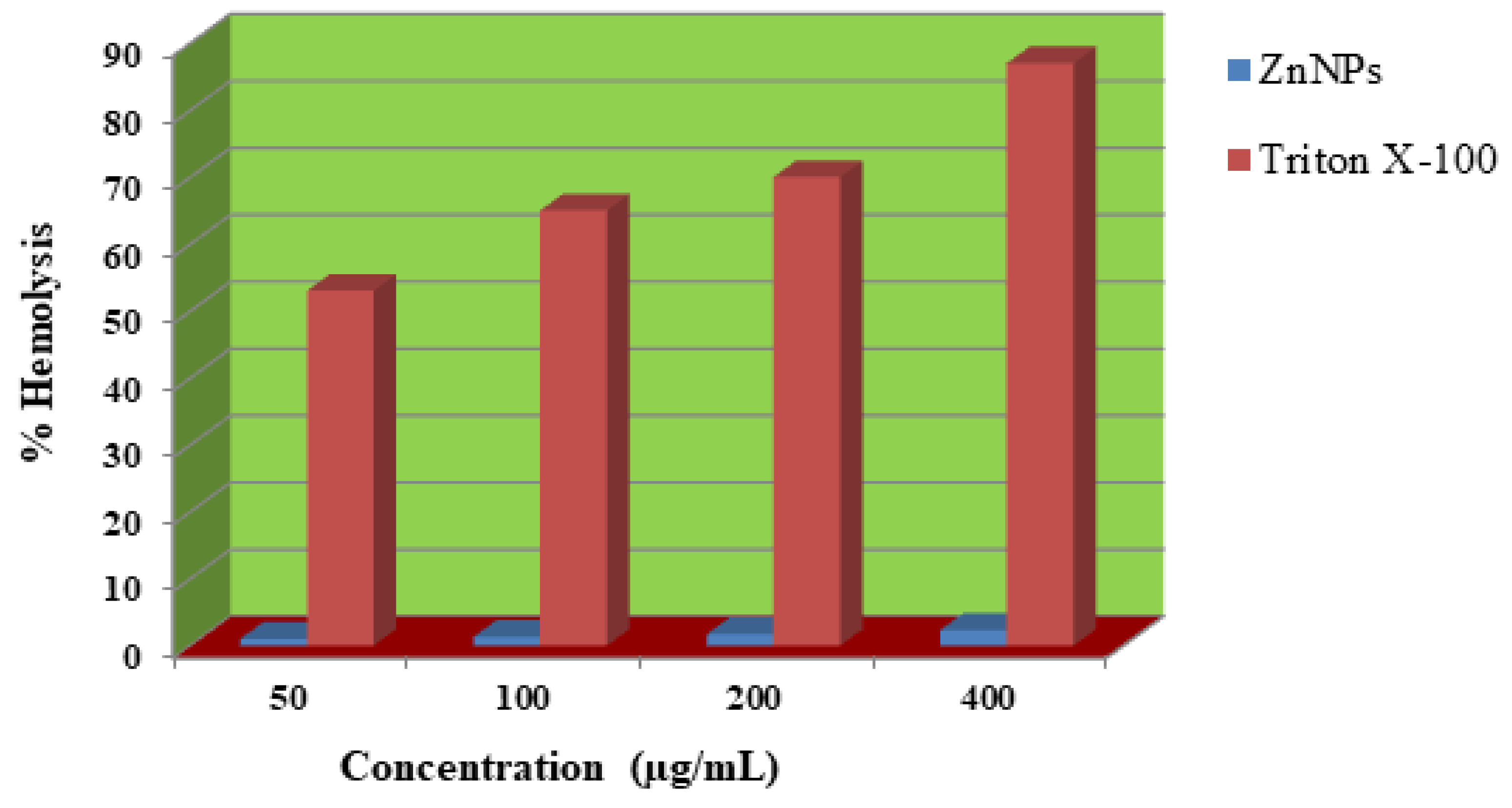
2.7. Hemolytic activity
Human red blood cells were used to test the hemolytic effect of biosynthesized ZnNPs. The effect was studied at concentrations of 50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL of the test sample. The test sample caused 1, 1.3, 1.7, and 2.3% lysis of red blood cells at 50, 100, 200, and 400µg/mL, respectively. Triton X-100 a standard haemolytic agent caused 87% of hemolysis at 400 µg/mL. Our finding demonstrated that the biosynthesized ZnNPs showed no hemolysis at 400 µg/mL (
Figure 10).
2.8. Photocatalytic degradation of dye
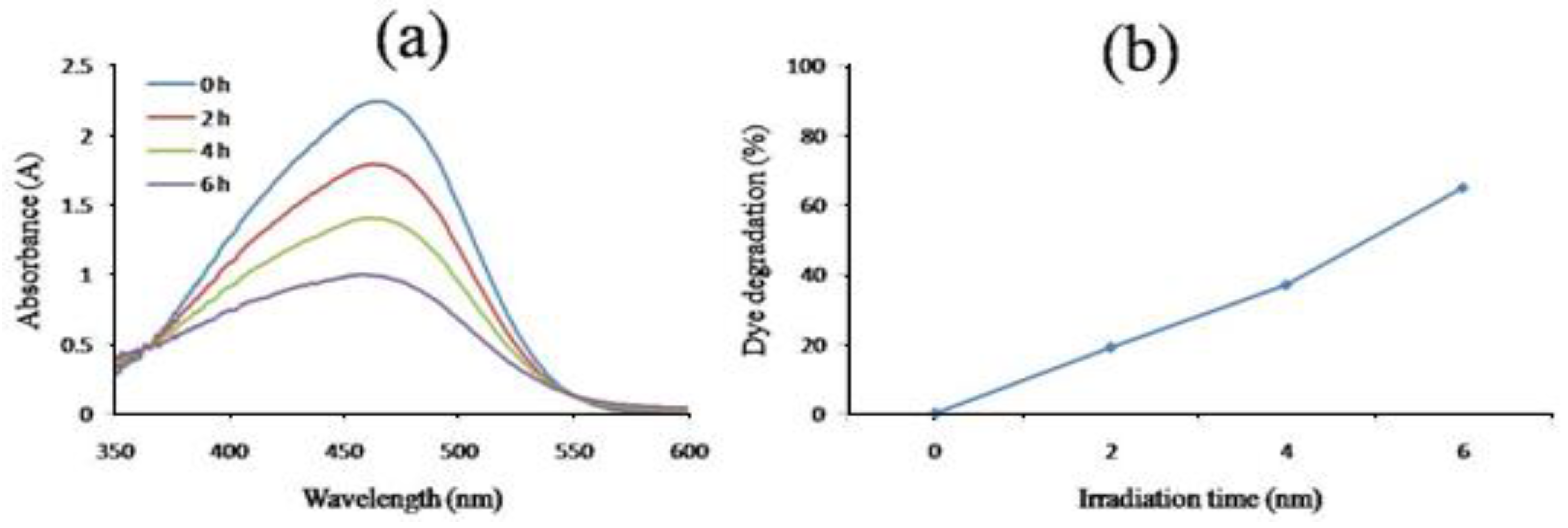
Under solar light illumination, the biosynthesized ZnNPs were tested for their capacity to catalytically destroy the methyl orange dye. Initially, the dye was kept in the sunlight without nanoparticles but no degradation of dye was noticed showing that solar irradiation had no effect on dye degradation. Methyl orange gives a broad absorption peak at 485 nm using UV-Visible spectrophotometer. The test sample had a greater ability to degrade the test dye as there occurred a continuous decrease in the absorption intensity.
Then the degradation of methyl orange was checked in the presence of sunlight using UV-Vis spectrometer. The UV- spectrum revealed that methyl orange gave an absorption peak at 485nm. it is clear that the photodegradation of MO dye accelerated with increasing the irradiation time. The percent degradation showed that ZnNPs destroyed around 19% dye in just 2 hours which increased to 37% and 65% by increasing the irradiation period to 4h and 6h, respectively as showed in
Figure 11a and b.
Bacterial pathogenesis is a serious health issue in developing countries. The situation becomes worse as bacteria develop resistance to a number of antibiotics. The development of MDR bacteria is an issue of serious concern both in hospitals and in the community. Thus there is a dire need to search out newer antimicrobial agents that are either bactericidal or bacteriostatic for multi-drug resistant bacteria without being affected by their resistance mechanisms. In this regard, nanoparticles are being extensively investigated to discover their antibacterial activity, with the goal of eventually developing a suitable antibacterial agent for the treatment of bacterial infections. Many types of inorganic and organic nanomaterials and nanoparticles have been prepared in order to demonstrate their effectiveness as an antibacterial agent against MDR bacteria[
23,
24].
Plants, a rich source of natural products, are now attracting the attention of the scientific community for the green synthesis of metal nanoparticles, as they are the promising source of antimicrobial agents having high antibacterial activity, low toxicity, low cost, and high availability [
25]. In the present study, we biologically synthesized zinc nanoparticles from the bark extract of
Rhododendron arboreum and were investigated as an antibacterial agent against clinically isolated pathogenic bacteria as well as a photocatalyst for the degradation of toxic dye.
In the current study,
R. arboreum stem bark extract was used for the green synthesis of ZnNPs.
R. arboreum is a rich source of phytochemicals such as alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids, steroids, saponins, glycosides, tannins, anthraquinones, phlobatanins and reducing sugars[
26]. These phytochemicals served as both reducing and capping agents for the formation of zinc nanoparticles. The formation of green synthesized zinc nanoparticles were confirmed through UV absorption at 374 nm which confirmed the synthesis of zinc nanoparticles. FTIR was used to identify different types of functional groups in the
R. arboreum bark extract that contributed to the biosynthesis of zinc nanoparticles. Other techniques employed in the characterization of ZnNPs included; SEM of biosynthesized ZnNPs revealed the presence of spherical, porous, and agglomerated nanoparticles particles. Moreover, the crystallite size of the biosynthesized nanoparticles was found to be 66.20 nm using XRD analysis. Thus, zinc nanoparticles were formed successfully by the active constituents present in the
R. arboreum bark extract which played their role in inhibiting the degradation and deformation of formed ZnNPs.
The MIC and MBC values of biosynthesized zinc nanoparticles were found significant against
E. coli, S. aureus, and
K. pneumonia. To study the possible mechanism behind the bactericidal action of ZnNPs, the impact of biosynthesized ZnNPs on the membrane properties was assessed. Bacterial membrane is one of the most important targets for many antimicrobial agents. Bacterial membrane is a powerful selective permeable barrier. If this barrier is compromised by certain agents it will produce negative effects on the bacterial cell which may ultimately lead to the death of the bacterium[
27]. In order to investigate the integrity of bacterial cell membranes, we monitored the gradual leakage of compounds with absorbance at 260 nm after treatment with ZnNPs. Interestingly the integrity of the bacteria cell membrane was significantly reduced (
p<0.05).
Different types of methods could be utilized for determining the permeability of outer and inner membranes. Determination of the A
260 value of intracellular compounds is one of the most important ones for assessing the integrity of the bacterial outer membrane. The green synthesized ZnNPs had a greater ability to seriously damage the bacterial outer membrane as evidenced from the enhanced A
260 value. It can be assumed that the green synthesized ZnNPs had disrupted the lipid-protein interactions in the bacterial membrane which in turn caused changes in the membrane permeability allowing the biosynthesized ZnNPs to enter into the cell [
28]. For assessing the effect of ZnNPs on the permeability of the inner membrane ONPG method was used. This method is based on the fact that the bacteria lose control of the inner membrane permeability as the green synthesized zinc nanoparticles penetrate into the bacterial cell [
29]. The biosynthesized zinc nanoparticles had increased the permeability of the bacterial inner membrane as evident from the increased production of o-nitrophenol a coloured product yielded after the hydrolysis of ONPG by β-galactosidase.
The increase in the permeability of the inner and outer membranes of selected bacteria following treatment with ZnNPs suggests that these two processes may work in concert and that the end outcome of these two mechanisms is the death of the bacterial cells. According to the literature metal nanoparticles have a number of targets in the bacterial cell but primarily they exert their antibacterial effect by interacting with and damaging bacterial cell membranes [
30].
One of the most significant classes of contaminants released into wastewater from textile and other industrial operations is organic dyes. The removal and degradation of the dyes have drawn a lot of interest globally due to their potential toxicity and visibility in surface waters. Dyes and their by-products have severe adverse effects on an individual’s organs such as the brain, liver, kidneys, and CNS and they can also cause cancer or mutagenic effects in some cases[
31]. The degradation of methylene blue dye by biosynthesized ZnNPs under solar light illumination at different time intervals was studied. The biosynthesized ZnNPs were found to be a promising source for the purification of wastewater polluted by organic dye.
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Collection of plant material and preparation of plant extract
Rhododendron arboreum bark was collected from Seran Valley Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, and was authenticated by an expert botanist, at Bacha Khan University, Charsadda. The air-dried bark (2.5 Kg) was repeatedly extracted with methanol (3 x 5L) at room temperature. The methanolic extract was filtered and concentrated through the rotary evaporator to afford a brownish crude methanolic extract. The crude extract (325 g) was then re-suspended in deionized distilled water. The aqueous crude extract was then used for the synthesis of ZnNPs.
3.2. Biosynthesis of Zinc NPs
About 0.1 M zinc chloride (ZnCl2) was mixed with 25 mL of R. arboreum extract and was stirred for two hours. The progression of the reaction was monitored through a UV spectrophotometer. The biosynthesized ZnNPs were separated from the reaction solution through centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 15 min. The precipitated ZnNPs were washed thrice with deionized water to remove the impurities and were dried subsequently. Finally, the purified ZnNPs were characterized through different techniques.
3.3. Antibacterial screening
The antibacterial effects of biosynthesized ZnNPs were tested using a well diffusion method. The bacterial inoculum was prepared in accordance with the NCCLS instructions. Each bacterium was cultured in broth medium and was incubated in a shaker incubator at 37°C for 3–4 hours until a turbidity of 0.5 McFarland units was attained. With the use of a sterilized cotton swab, the culture of the test bacterium was distributed on the surface of agar plates and left to dry for three to five minutes. A sterile cork borer was used to gently bore the wells in the agar plate.
The test sample and reference antibiotic were then added to the appropriate well and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. Results of the test and standard antibiotics were measured in mm, while levofloxacin was used as standard[
32].
Additionally, using a slightly modified broth dilution method, the MIC of zinc nanoparticles was found [
33]. The bacterial culture was injected into tubes with having sterilised broth medium. The test sample was added to the first tube so that the final concentration became 400 µg/mL and was serially diluted in a series of tubes having sterilized broth media to 12.5 µg/mL as the final concentration. The tubes were incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C. MIC was calculated as the lowest concentration of the test sample that inhibited the growth of bacteria. MBC of the test sample was obtained by streaking from the tubes used for MIC on agar plates with subsequent incubation for a period of 24 hrs at 37°C. The MBC was determined to be the lowest concentration of the test sample at which the bacterium did not show growth on an agar plate.
3.4. Membrane damage assay
The effect of the complex on cell membrane integrity was analyzed by measuring the A
260 value of the intracellular substances that get released upon interactions of ZnNPs with the bacterial cells [
34]. The culture was refreshed for 24 hours by transferring inoculum to broth medium from the agar plate followed by incubation at 37°C. Centrifugation of the refreshed culture was performed at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes. The bacterial pellet collected was thoroughly washed with PBS and suspended again in 0.01 mol L
-1PBS solution and optical density was set to 0.7 at 420 nm. Finally, 1.5 mL of different concentrations of test complexes was treated with 1.5 mL of test bacteria and the quantity of released intracellular substances was measured spectrophotometrically at 260 nm.
3.5. Inner Membrane Permeabilization Assay
In this assay, the released β-galactosidase enzyme was determined using the reported procedure [
35]. Test inoculum was prepared in broth medium having 2% of lactose. Then the bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation and re-suspended in 0.01 mol L
-1 PBS solution and the absorbance of the cell suspension was adjusted to 1.2 at 420 nm. Test samples (1.6 mL) at different concentrations were added to the culture (1.6 mL) followed by the addition of 150µl of 30 Mm ONPG and thorough mixing.
o-nitrophenol produced at different time intervals was measured at 420 nm.
3.6. Hemolytic Assay
To avoid blood coagulation, blood samples were taken from human donors in K
2-EDTA-coated tubes. Centrifugation was done at 14000 rpm for five minutes and the plasma was gently aspirated and the cell pellet was washed three times with PBS (pH 7.4). Diluted RBCs were mixed with varying concentrations of the test sample (1:1 ratio). Triton X-100 (20%) and PBS were used as positive and negative controls, respectively [
36]. All the tubes were shaken for 1 hour at 37°C before being centrifuged for 5 minutes at 14000 rpm to pellet the cells. The upper portion was collected in a clean test tube and the absorbance was checked at 540 nm. The following formula was used for the determination of percent hemolysis.
Where
At is the absorbance of test sample.
An is the absorbance of the negative control (PBS)
Ap is the absorbance of the positive control (Triton-X-100)
3.7. Photocatalytic methodology
Zinc NPs produced through green synthesis were used to accelerate the methyl orange dye's breakdown using sunlight. A beaker containing 10 mL methyl orange (25 ppm) and 0.1 mg of nanoparticles were exposed to solar light while being stirred continuously. The photodegradation reactions were conducted at Bacha Khan University, Pakistan, in direct sunshine at coordinates of 39°9°N and 71°44°E. The reaction was first run in complete darkness for 30 min to confirm adsorption and desorption equilibrium. Then in direct sunlight, the reactions were performed for thirty minutes, and aliquots of the reaction mixture were taken at predetermined intervals while being exposed to solar light irradiations, followed by centrifugation (14,000 rpm) and UV-vis spectrophotometric analysis. For the determination of percent degradation following formula was used.\
where Co is the initial dye concentration, C is the dye concentration after UV irradiation, Ao shows initial absorbance, and A is the dye absorbance after UV irradiation.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
All the bacterial eradication experiments were performed in triplicate and data were expressed as mean ±SD. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test was performed to find significant differences (p<0.05).
4. Conclusions
Nanotechnology can be used for the production of small-sized particles which can be used in different applications. According to studies, nanotechnology can be used to solve a variety of issues related to the environment, food, agriculture, textiles, and medicine. In recent times, the use of nanotechnology in controlling bacterial infections and purification of wastewater has produced good results. The present study involves the biosynthesis of ZnNPs using the bark extract of Rhododendron arboreum. The biosynthesized ZnNPs were characterized through different characterization techniques including UV-Vis, FTIR, EDX, XRD, and SEM. The biosynthesized ZnNPs were proved to be a good antibacterial agent inhibiting the growth of E. coli, S. aureus, and K. pneumonia. Biosynthesized ZnNPs seriously damaged the outer and inner membrane in the first phase of exposure causing the death of bacterial cells. The biosynthesized zinc NPs exhibited good catalytic activity which significantly degraded methyl orange. The rate of degradation of methyl orange was increased as the time of exposure was increased. Therefore, it can be concluded from the results that biosynthesized zinc NPs are capable of effectively controlling pathogenic bacteria and can be applied for the purification of contaminated water.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors of this article have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to the Pathology Department, Medical and Teaching Institute, Hayat Abad Medical Complex, Peshawar, Pakistan for providing the bacterial culture.
References
- Mirkhani, V.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Moghadam, M.; Habibi, M.H.; Rostami-Vartooni, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dyes Catalyzed by Ag Doped TiO2 Photocatalyst. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2009, 6, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of Dyes in Textile Effluent: A Critical Review on Current Treatment Technologies with a Proposed Alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esplugas, S.; Giménez, J.; Contreras, S.; Pascual, E.; Rodríguez, M. Comparison of Different Advanced Oxidation Processes for Phenol Degradation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houas, A.; Lachheb, H.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic Degradation Pathway of Methylene Blue in Water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birjandi, N.; Younesi, H.; Bahramifar, N.; Ghafari, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Sethupathi, S. Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation Treatment on Paper-Recycling Wastewater: Application of Response Surface Methodology. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 2013, 48, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal, A.A.A. juraifani; Azzah, A.G. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Aspergillus Niger, Fusarium Oxysporum and Alternaria Solani. African J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S. V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Chemical, Physical and Biological Methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Biomolecule-Nanoparticle Organizations Targeting Antimicrobial Activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, D.; Qian, Y.; Guan, B.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Fungus-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aspergillus Terreus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, D.; Nilsen, E.T.; Yildiz, O. Ecology, Competitive Advantges, and Integrated Control of Rhododendron: An Old Oramental yet Emerging Invasive Weed around the Globe. Floric. Ornam. Plant Biotechnol. 2006, 3, 408–421. [Google Scholar]
- Laloo, R.C.; Kharlukhi, L.; Jeeva, S.; Mishra, B.P. Status of Medicinal Plants in the Disturbed and the Undisturbed Sacred Forests of Meghalaya, Northeast India: Population Structure and Regeneration Efficacy of Some Important Species. Curr. Sci. 2006, 90, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, G. A Dictionary of the Economic Products of India; 2014. Available online: https://indianculture.gov.in/rarebooks/dictionary-economic-products-india-vol-iv.
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, U.K.; Gupta, A.P.; Sinha, A.K. Simultaneous Determination of Epicatechin, Syringic Acid, Quercetin-3-O-Galactoside and Quercitrin in the Leaves of Rhododendron Species by Using a Validated HPTLC Method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, A.; Prakash Gupta, A.; Kumar Sinha, A. Simultaneous Determination of Quercetin, Rutin and Coumaric Acid in Flowers of Rhododendron Arboreum by HPTLC. Chromatographia 2005, 62, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, P. Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy of Nanosized Metal Particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Inui, M.; Tada, M.; Goshima, K.; Okamoto, T.; Hidaka, H. KN-62, a Specific Ca++/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitor, Reversibly Depresses the Rate of Beating of Cultured Fetal Mouse Cardiac Myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 270, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Henglein, A. Physicochemical Properties of Small Metal Particles in Solution: “Microelectrode” Reactions, Chemisorption, Composite Metal Particles, and the Atom-to-Metal Transition. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 5457–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, F.; Saeed, K. Investigation of Photocatalytic Behavior of Undoped ZnO and Cr-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for the Degradation of Dye. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2021, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah; Akhtar, N. ; et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Fruit Extracts of Myristica Fragrans: Their Characterizations and Biological and Environmental Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Al-Radadi, N.S.; Jan, H.; Abdullah; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Rizwan, M.; Afsheen, Z.; Hussain, Z.; Uddin, M.N.; et al. Curcuma Longa Mediated Synthesis of Copper Oxide, Nickel Oxide and Cu-Ni Bimetallic Hybrid Nanoparticles: Characterization and Evaluation for Antimicrobial, Anti-Parasitic and Cytotoxic Potentials. Coatings 2021, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Thorat, P. V; Thakre, R. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Ocimum Tenuiflorum Leaves. Int. J. Sci. Res. ISSN (Online Index Copernicus Value Impact Factor 2013, 14, 2319–7064. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, Z.; Picciano, A.L.; Gosavi, P.M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Angevine, C.E.; Chavis, A.E.; Reiner, J.E.; Korendovych, I. V.; Caputo, G.A. Functional Characterization of a Melittin Analog Containing a Non-Natural Tryptophan Analog. Biopolymers 2015, 104, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otis, G.; Bhattacharya, S.; Malka, O.; Kolusheva, S.; Bolel, P.; Porgador, A.; Jelinek, R. Selective Labeling and Growth Inhibition of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa by Aminoguanidine Carbon Dots. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Nandi, S.; Jelinek, R. Carbon-Dot-Hydrogel for Enzyme-Mediated Bacterial Detection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Ahmed, B.; Khan, M.S.; Al-Shaeri, M.; Musarrat, J. Inhibition of Growth and Biofilm Formation of Clinical Bacterial Isolates by NiO Nanoparticles Synthesized from Eucalyptus Globulus Plants. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, M.; Ali, S.; Qaisar, M. Preliminary Phytochemical Screening of Flowers, Leaves, Bark, Stem and Roots of Rhododendron Arboreum. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 10, 472–476. Available online: https://www.idosi.org/mejsr/mejsr10(4)11/9.pdf.
- Baptista, P. V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-Strategies to Fight Multidrug Resistant Bacteria-"A Battle of the Titans". Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Char, C.D.; Guerrero, S.N.; Alzamora, S.M. Mild Thermal Process Combined with Vanillin plus Citral to Help Shorten the Inactivation Time for Listeria Innocua in Orange Juice. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Abrini, J.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y. Essential Oils of Origanum Compactum Increase Membrane Permeability, Disturb Cell Membrane Integrity, and Suppress Quorum-Sensing Phenotype in Bacteria. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Hashmi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. ROS Mediated Destruction of Cell Membrane, Growth and Biofilms of Human Bacterial Pathogens by Stable Metallic AgNPs Functionalized from Bell Pepper Extract and Quercetin. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khade, G. V.; Suwarnkar, M.B.; Gavade, N.L.; Garadkar, K.M. Green Synthesis of TiO2 and Its Photocatalytic Activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Pauli, M.; Bazerque, P. An Antibiotic Assay by the Agar Well Diffusion Method. Acta Biol Med Exp 1990, 15, 113–115. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303960600_An_antibiotic_assay_by_the_agar_well_diffusion_metho.
- Pithayanukul, P.; Tubprasert, J.; Wuthi-Udomlert, M. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Zingiber Cassumunar (Plai) Oil and a 5% Plai Oil Gel. Phyther. Res. 2007, 21, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Interactions between Dendrimer Biocides and Bacterial Membranes. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L. Chitosan Kills Bacteria through Cell Membrane Damage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, S.C.; Hahm, K.S.; Park, Y. A Helix-PXXP-Helix Peptide with Antibacterial Activity without Cytotoxicity against MDRPA-Infected Mice. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).