Submitted:
28 September 2023
Posted:
29 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Specimen preparation and irradiation
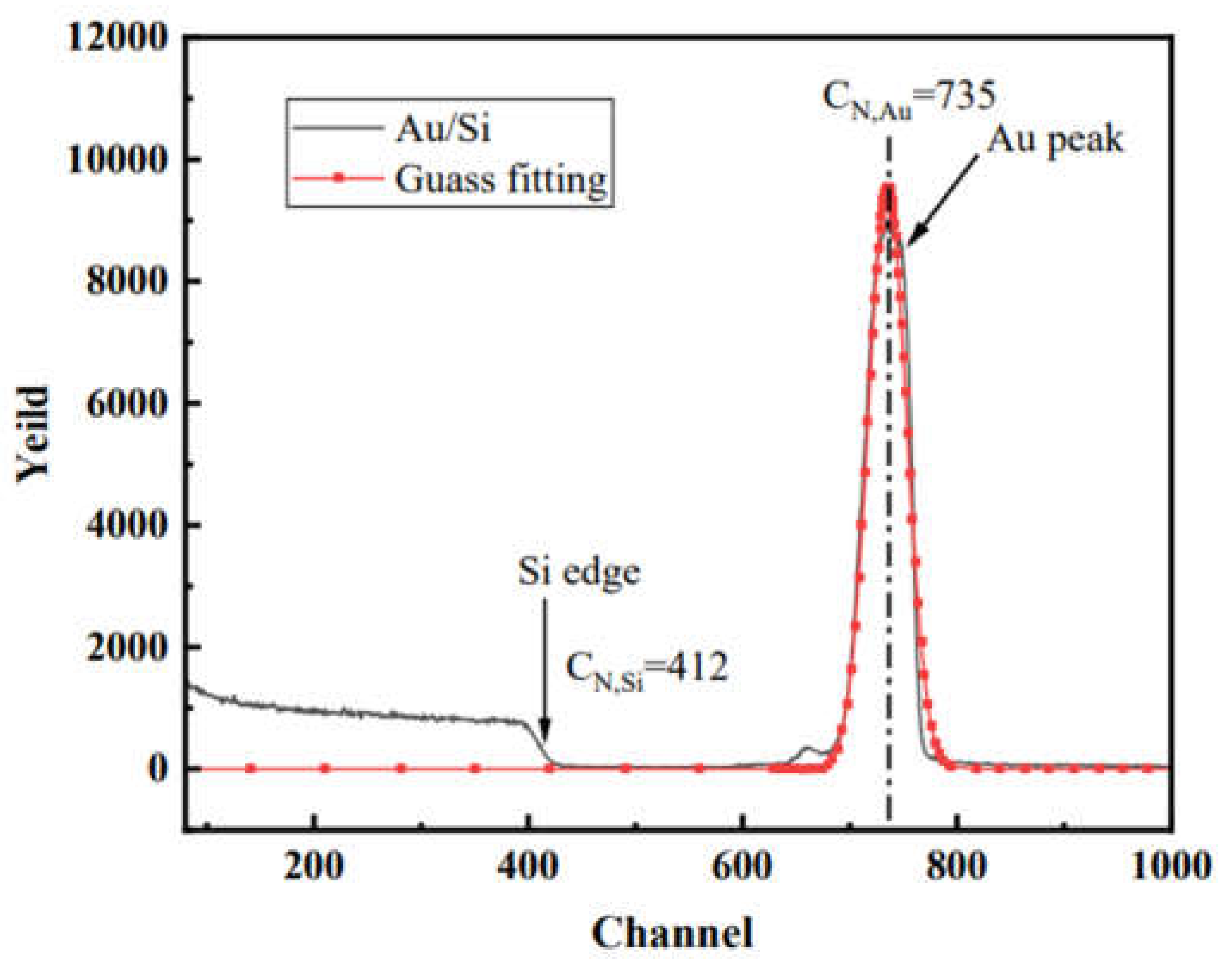
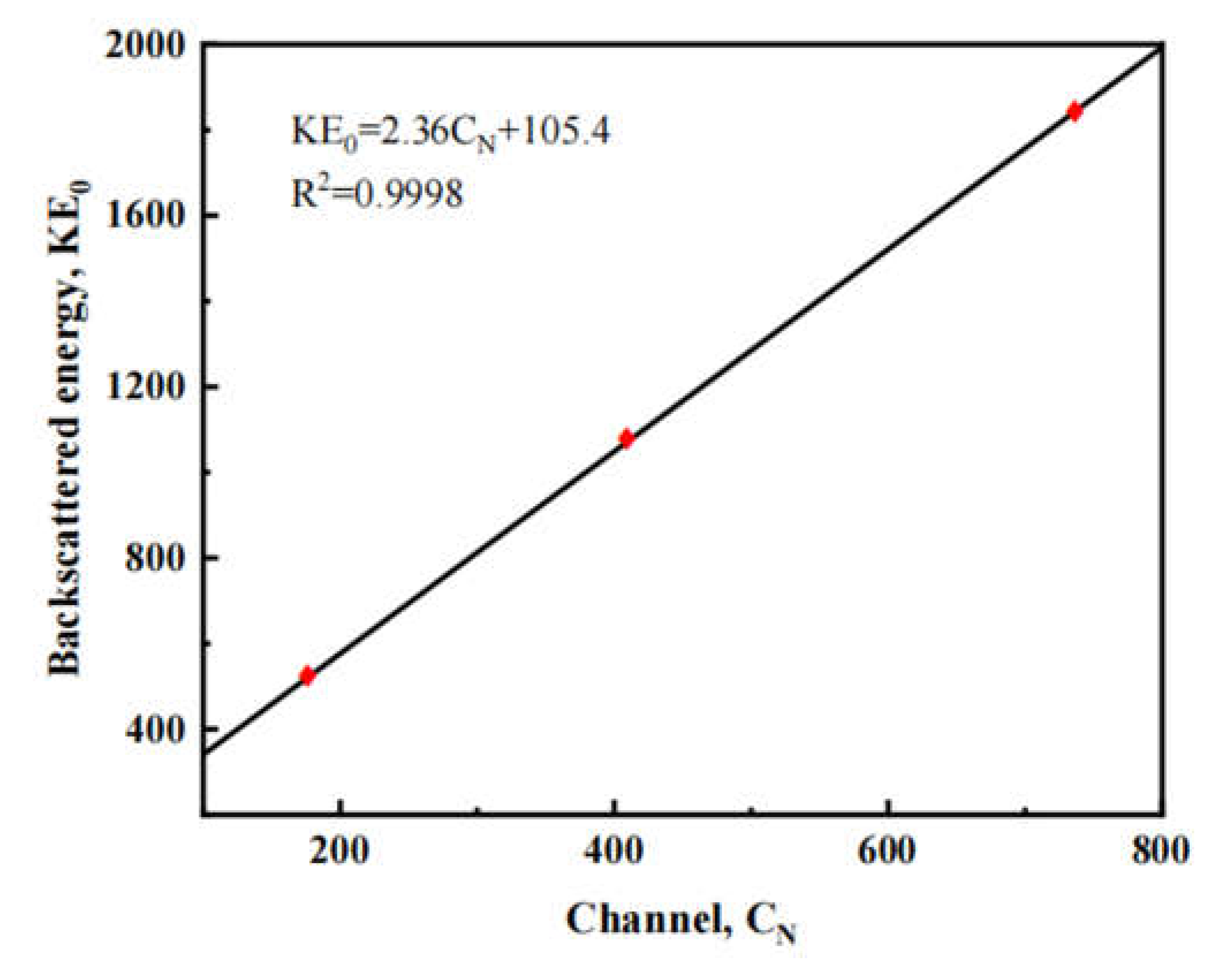
2.2. Characterizations
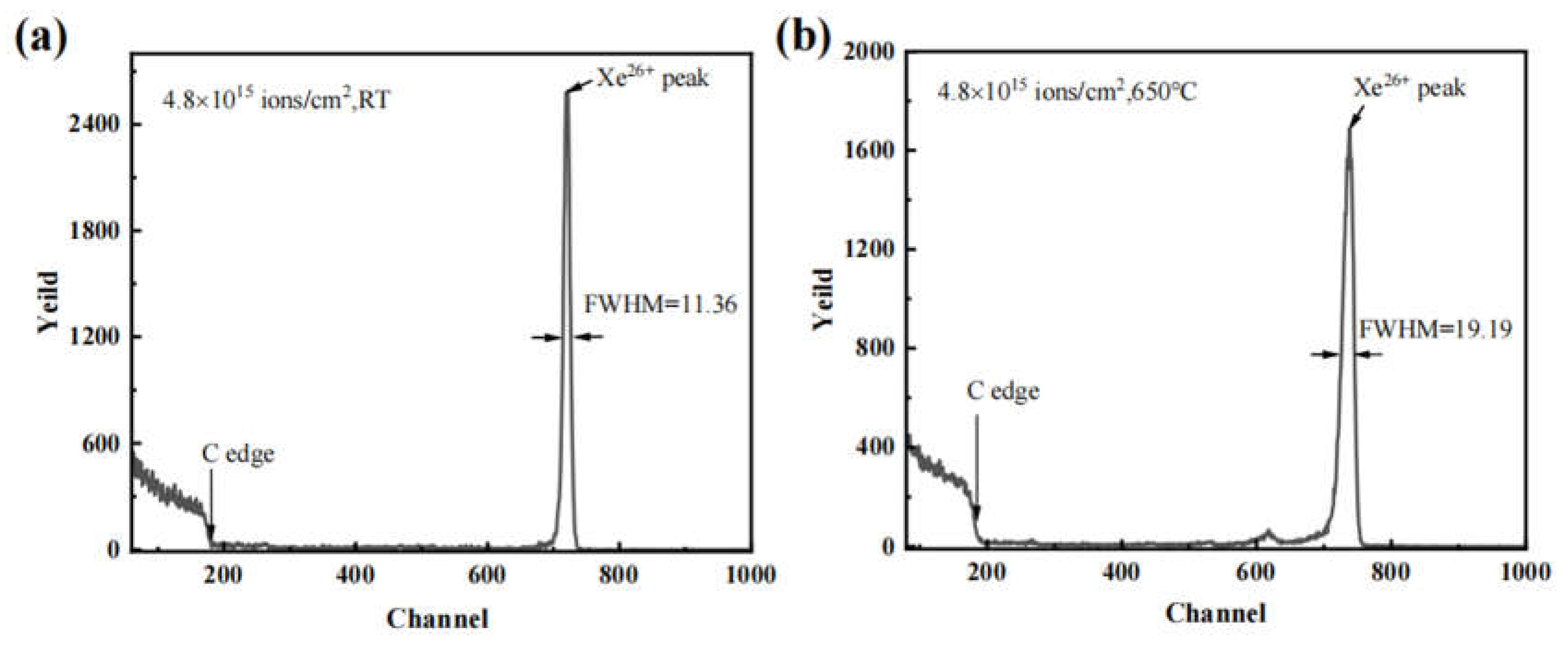
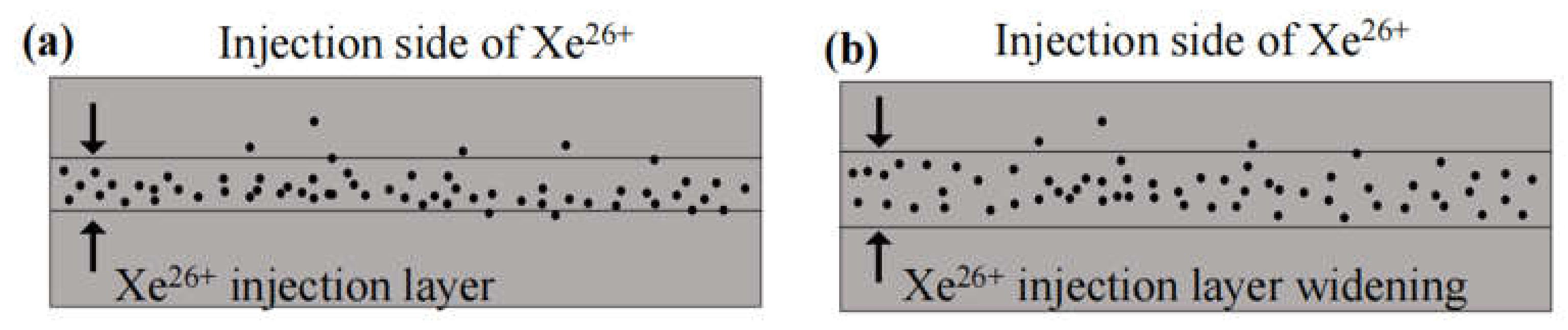
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Haubenreich, P.N.; Engel, J.R. Experience with the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment. Nuclear Applications and Technology 1970, 8, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.; Chvala, O.; Bereznai, G. A dynamic model of xenon behavior in the Molten Salt Reactor Experiment. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 144, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Eatherly, W.P. Graphite and Xenon Behavior and their Influence on Molten-Salt Reactor Design. Nuclear Applications and Technology 1970, 8, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkle, N.; Chvala, O. Effect of xenon removal rate on load following in high power thermal spectrum Molten-Salt Reactors (MSRs). Nucl. Eng. Des. 2023, 409, 112329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.C.; He, Z.; Liu, Z.J.; Song, J.L.; Tsang, D.K.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Self-sintered nanopore-isotropic graphite derived from green pitch coke for application in molten salt nuclear reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2019, 131, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Song, J.L.; Tang, Z.F.; He, Z.; Liu, X.D. The surface topography and microstructure of self-sintered nanopore graphite by Xe ions irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 146022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čajko, K.O.; Lukic-Petrovic, S.; Ćelić, N.; Noga, P.; Vaňa, D.J.A.S.S. Influence of different metal concentrations on the morphology of Ag–As2Ch3 thin films analyzed by Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, N.; Delabie, A.; Vantomme, A.; Vandervorst, W.; Meersschaut, J. Probing the spatial dimensions of nanoscale patterns with Rutherford backscattering spectrometry. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2023, 540, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodunrin, J.O.; Oeba, D.A.; Moloi, S.J. Exploring the Impact of Fe-Implantation on the Electrical Characteristics of Al/p-Si Schottky Barrier Diodes. Electronic Materials 2023, 4, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, D.A.; Danial, M.O.; Hanif, M.B.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Ramadan, M.; Khaliq, A.; Khan, A.F.; Subhani, T.; Motola, M. Intrinsic Properties and Future Perspective of HfO2/V2O5/HfO2 Multi-Layer Thin Films via E-Beam Evaporation as a Transparent Heat Mirror. Coatings 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, M.; Melon, B.; Salvestrini, L.; Fonseca, M.; Alves, E.; Jesus, A.P. Measurement of proton induced γ-ray emission cross sections on Al from 2.5 to 4.1MeV. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2014, 332, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laricchiuta, G.; Vandervorst, W.; Meersschaut, J. High-sensitivity Rutherford backscattering spectrometry employing an analyzing magnet and silicon strip detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2019, 439, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.B.; Lian, P.F.; Li, P.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Cheng, J.X.; Wang, Q.B.; Tang, Z.F.; Pan, T.J.; Song, J.L.; Liu, Z.J. Diffusion Behavior of Iodine in the Micro/Nano-Porous Graphite for Nuclear Reactor at High Temperature. C 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Huang, H.F.; Liu, J.Z.; Lei, Q.T.; Wang, C.J.; Han, Z.B.; Yang, G.; Li, Y. Helium release and lattice swelling in nickel foil irradiated by multiply-energy helium ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2019, 450, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhawana, M.B.; Theron, C.C.; Malherbe, J.B.; Van der Berg, N.G.; Botha, A.J.; Grote, W.; Wendler, E.; Wesch, W.; Chakraborty, P. Behavior of iodine implanted in highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) after heat treatment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2012, 273, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, M.; Chiari, M.; Pasquali, E.; Nannini, A.; Hadyńska-Klęk, K.; Sona, P.; Bazzacco, D.; Benzoni, G.; Camera, F.; Czelusniak, C.; et al. Applications of Rutherford backscattering analysis methods to nuclear physics experiments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2021, 486, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




