Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
29 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
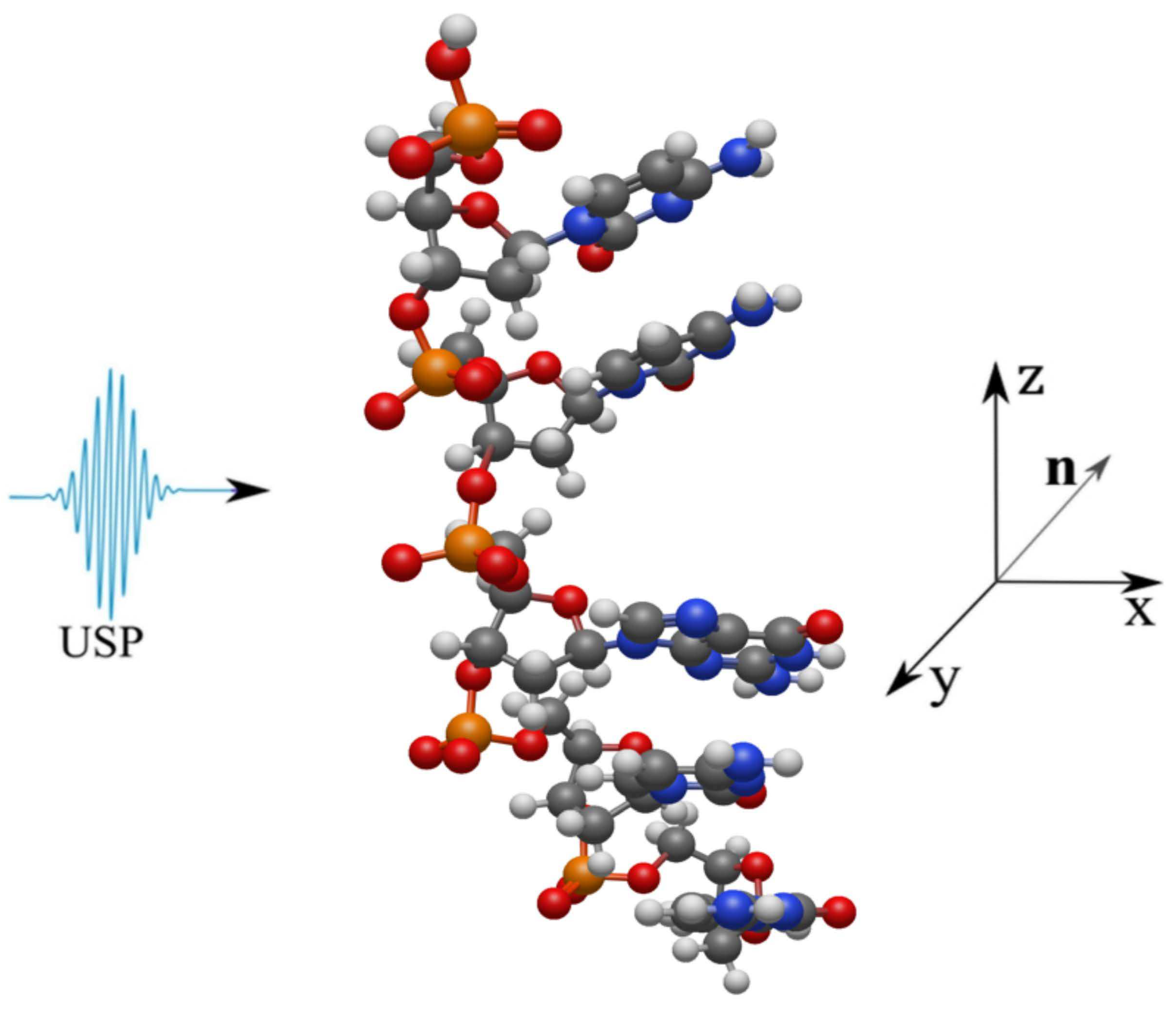
2. Scattering of attosecond laser pulses
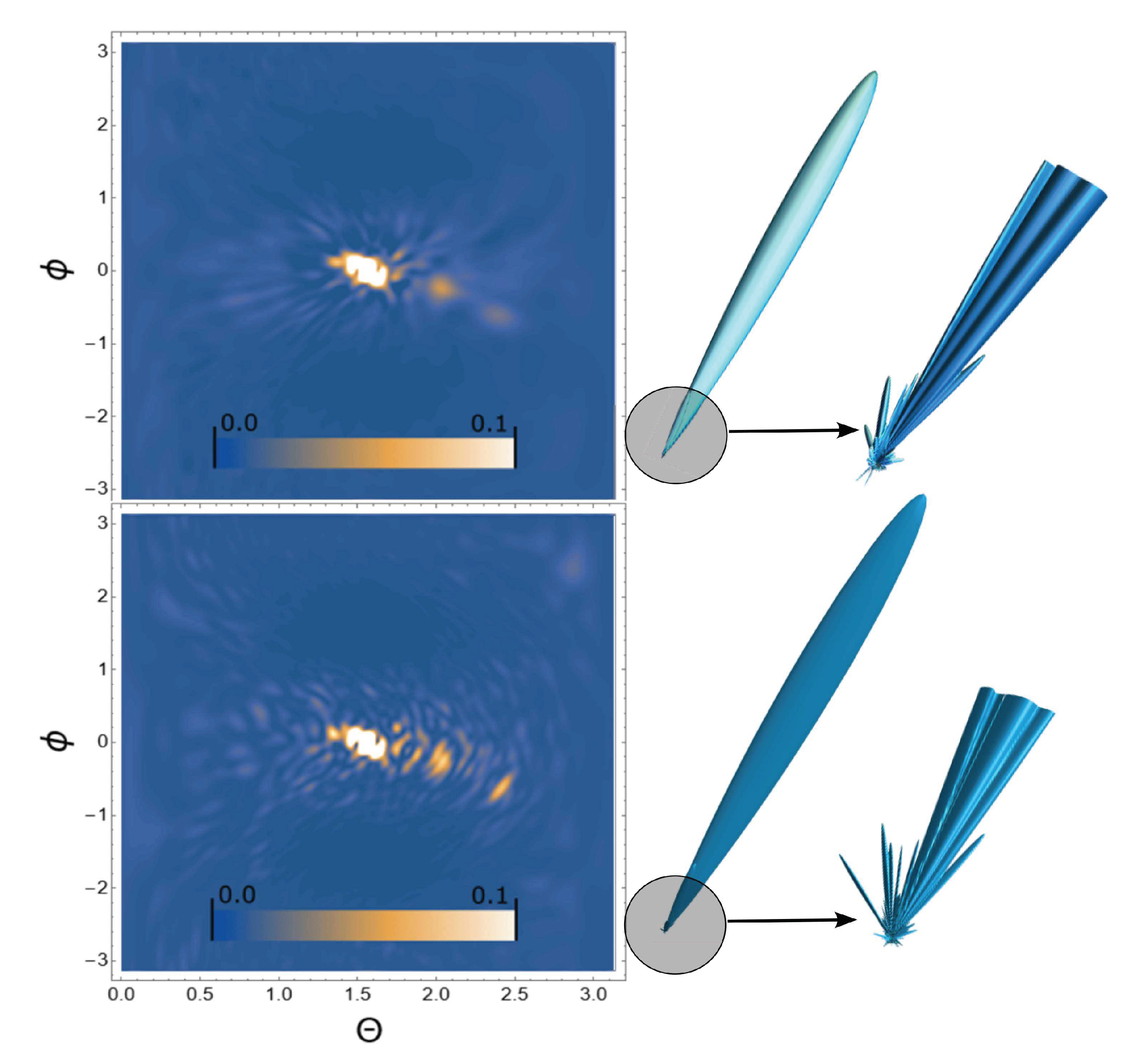
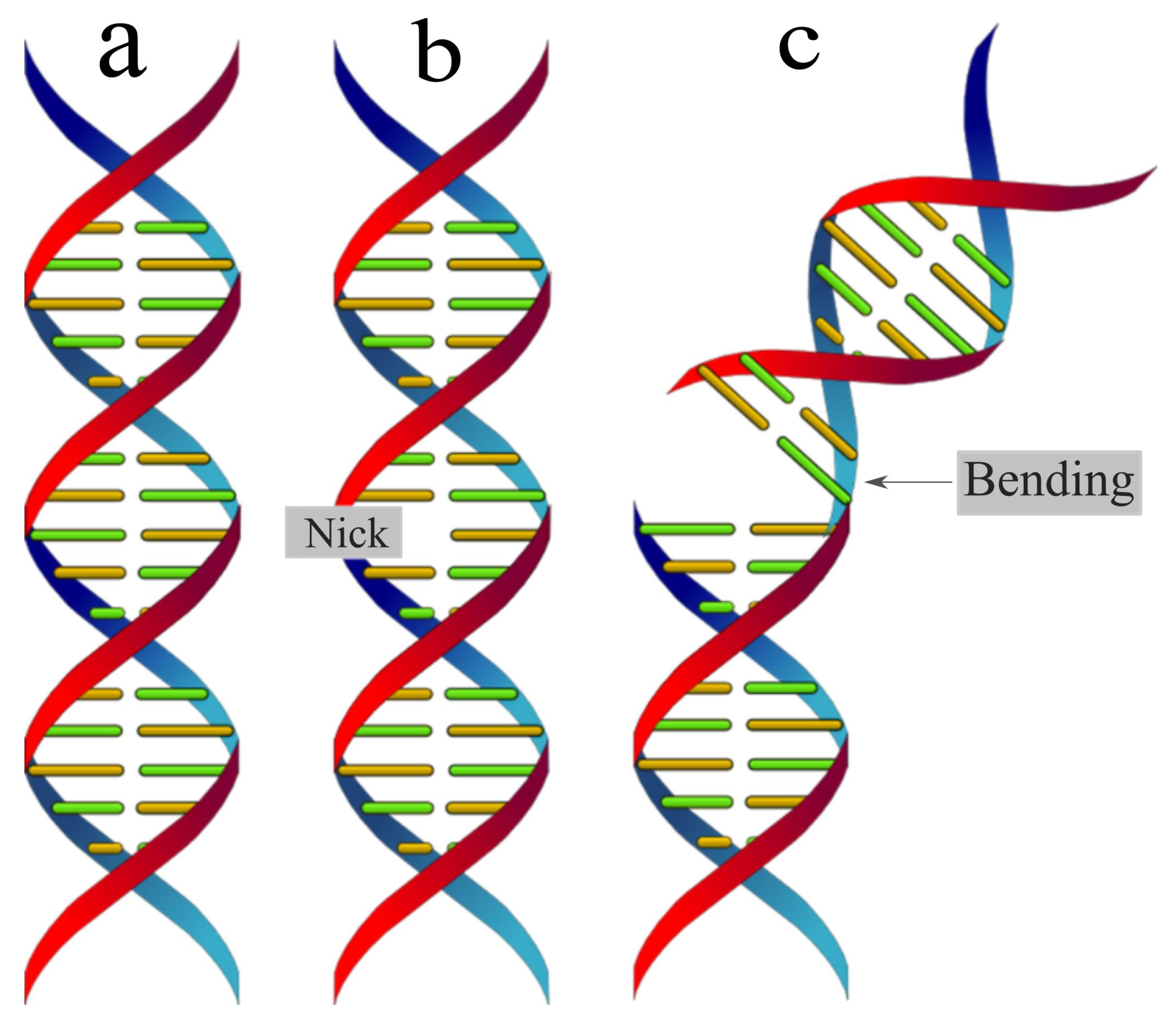
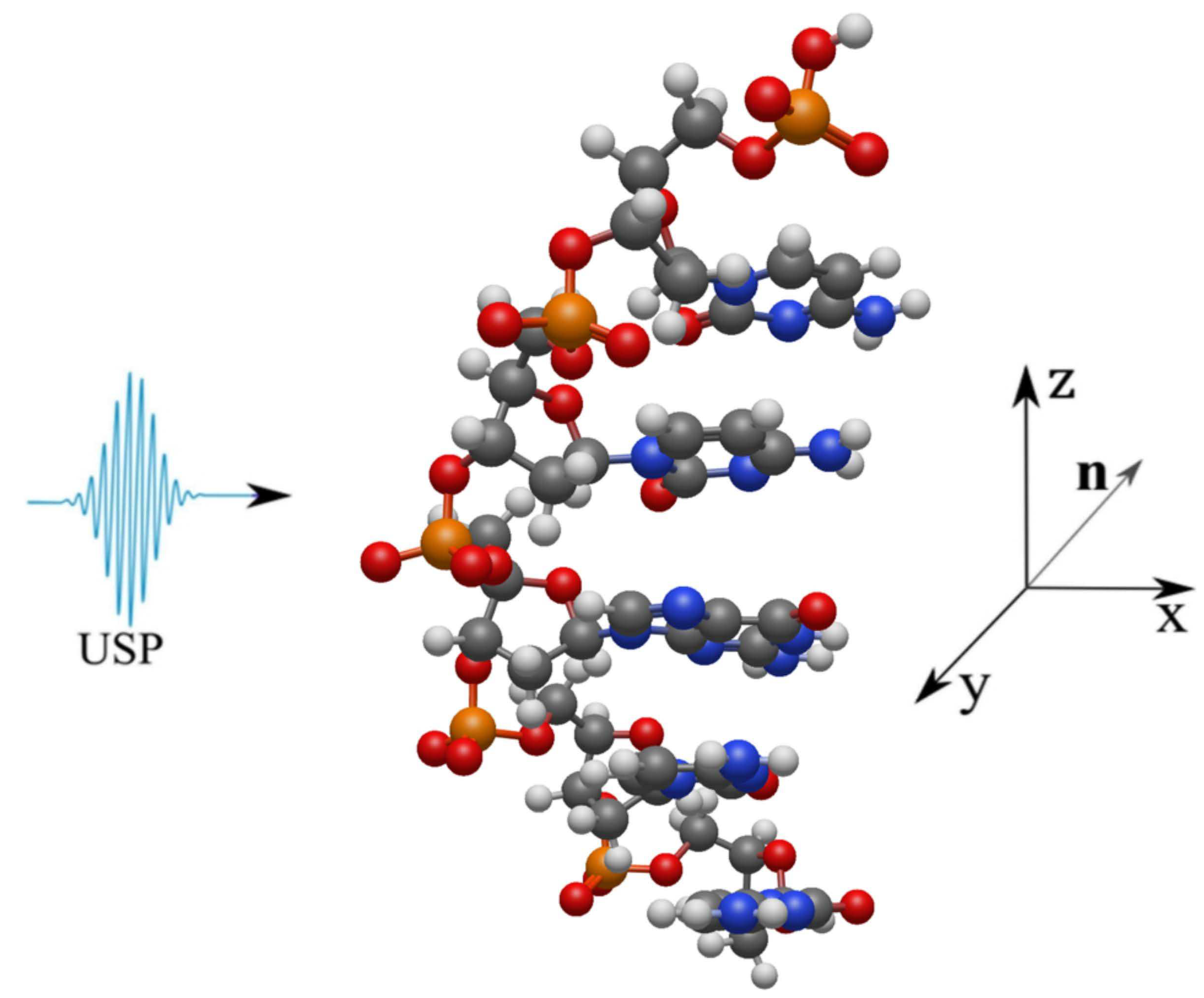
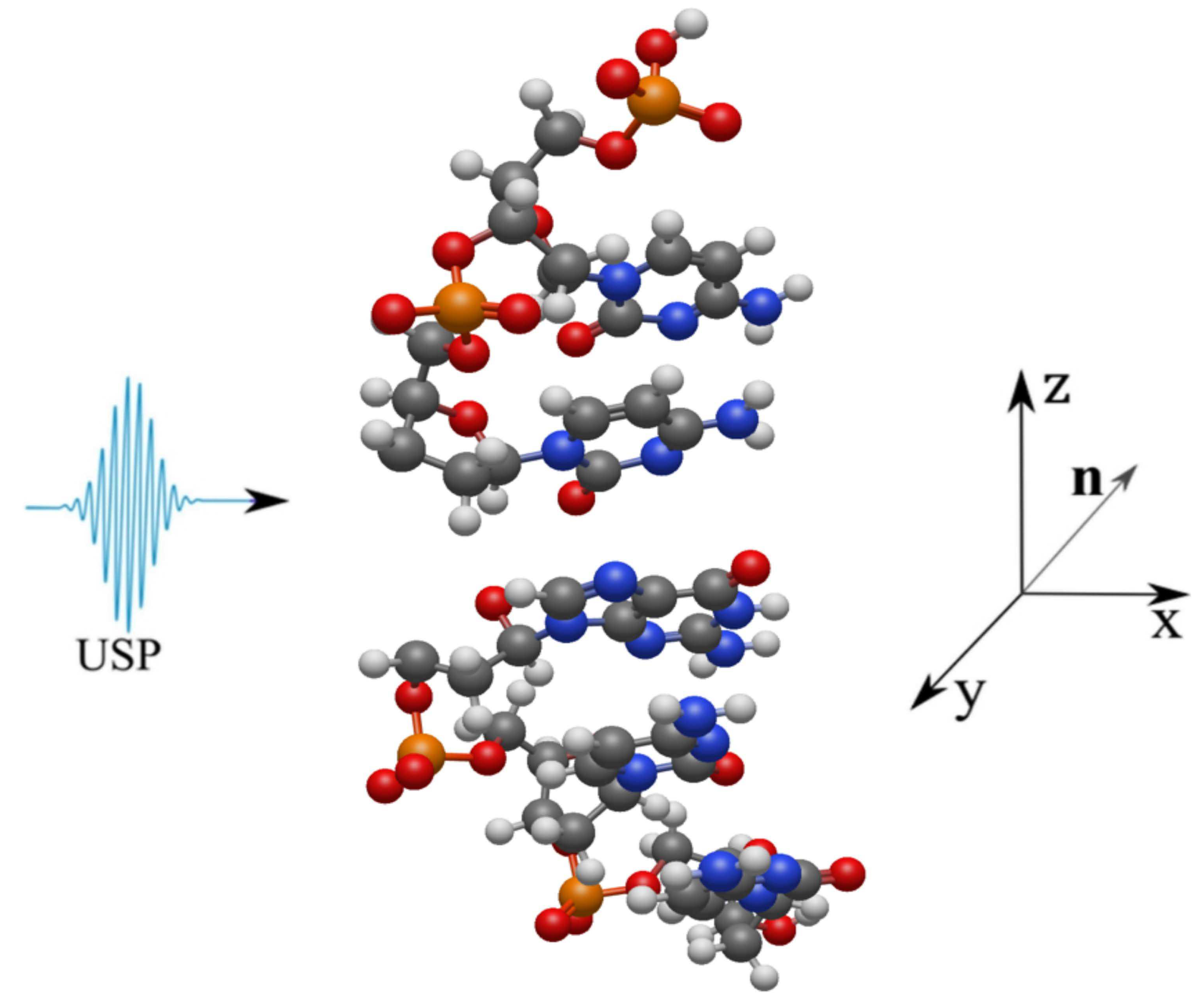
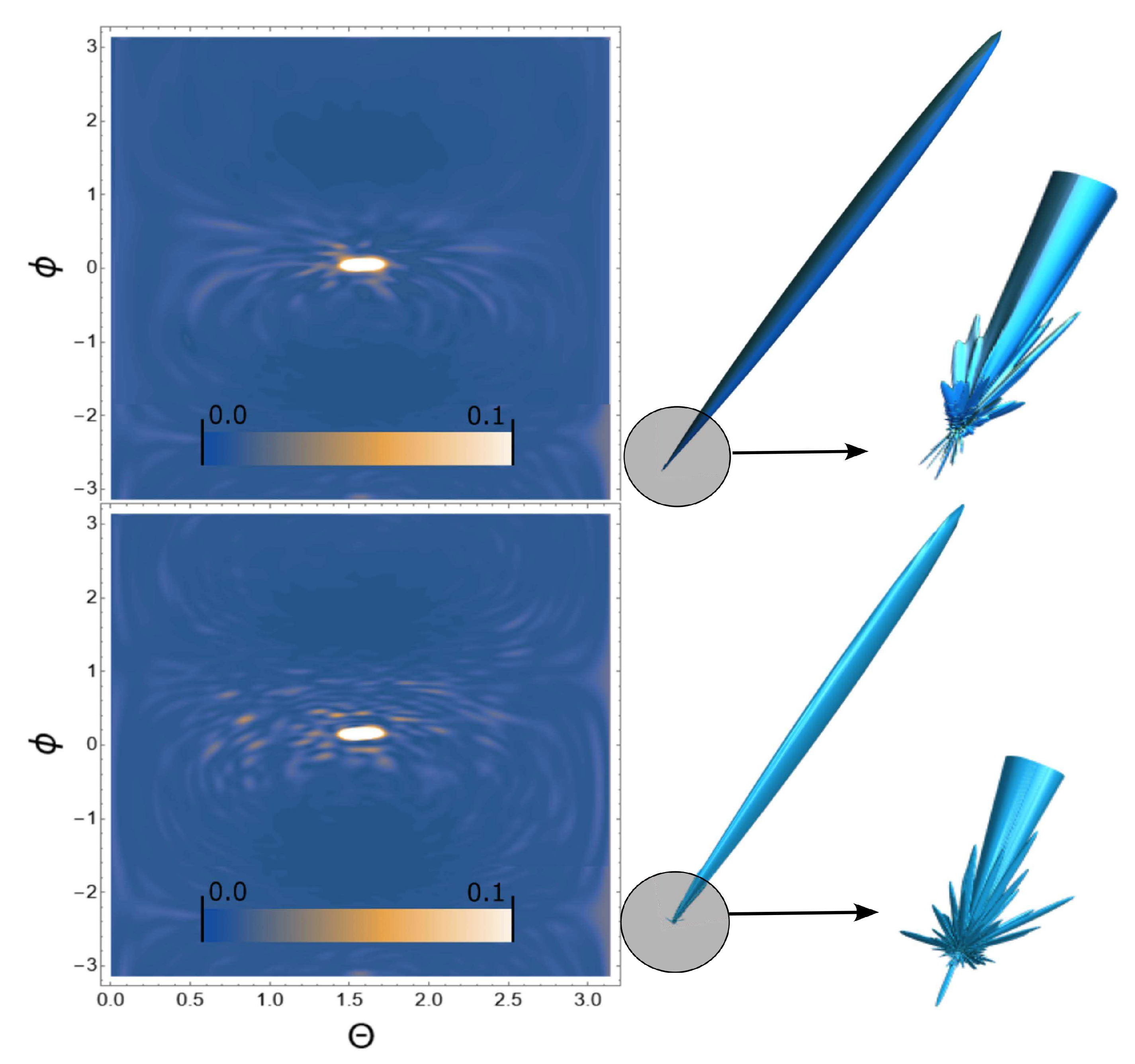
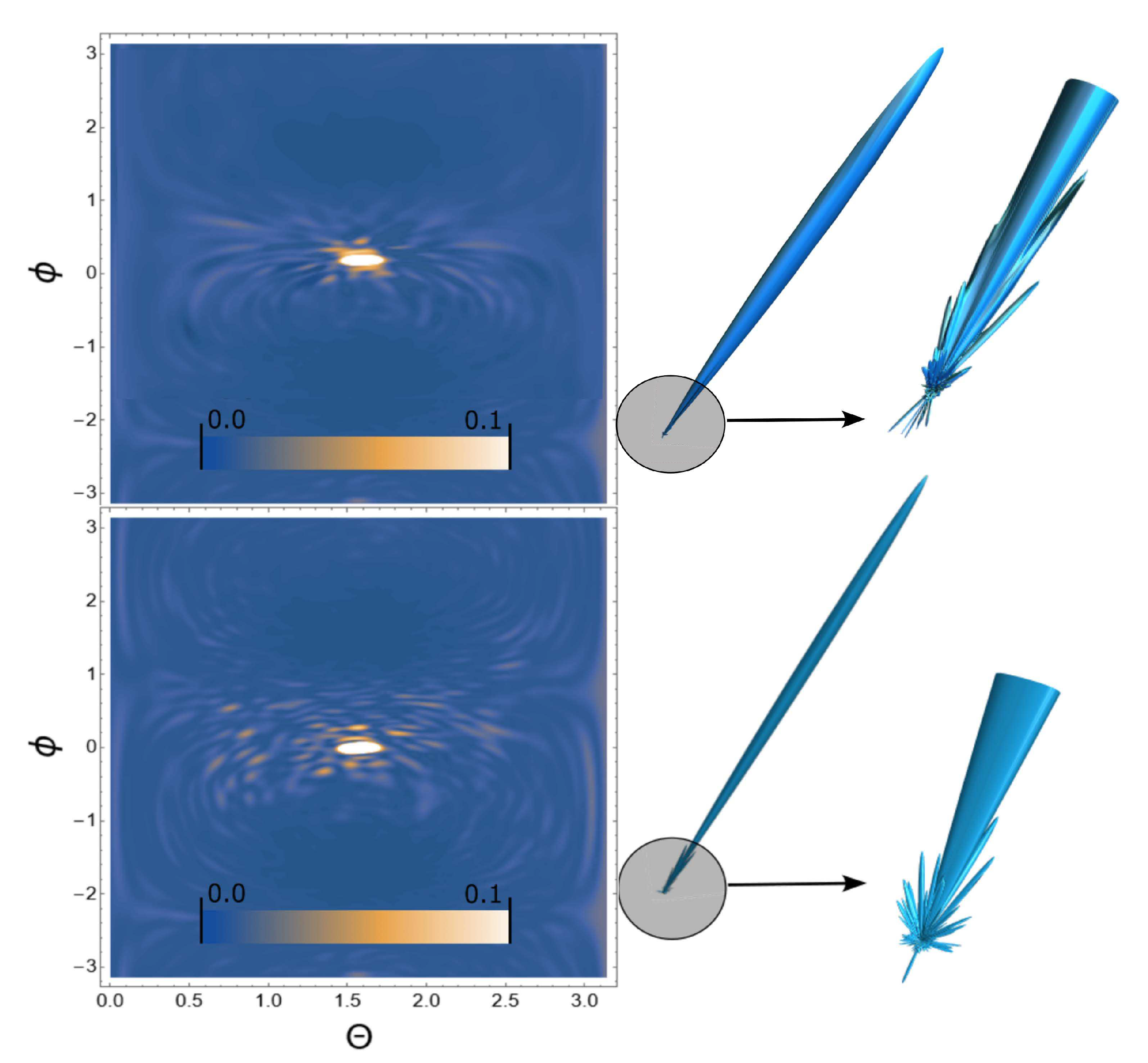
3. Results
4. Conclusion and discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suryanarayana, C.; Grant, N.M. X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach; Plenum Press, New York and London, 1998.
- Jones, N. Crystallography: Atomic secrets. Nature 2018, 505, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, U.; Holy, V.; Baumbach, T. High-Resolution X-Ray Scattering. Springer Science+Business Media: New York, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Benediktovich, A.; Feranchuk, I.; Ulyanenkov, A. Theoretical Concepts of X-Ray Nanoscale Analysis. Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- James, R. The Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-rays (Ox Bow); Woodbridge, Conn.: Ox Bow Press, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, G.; Vendrell, O.; Santra, R. Imaging electronic quantum motion with light. PNAS 2012, 109, 11636–11640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauptman, H.A. The phase problem of x-ray crystallography. Reports on Progress in Physics 1991, 54, 1427–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, F.; Ivanov, M. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, P.; Zürch, M.; Cushing, S.K.; Neumark, D.M.; Leone, S.R. The ultrafast X-ray spectroscopic revolution in chemical dynamics. Nature Reviews Chemistry 2018, 2, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Marceau, C.; Villeneuve, D.M. Attosecond imaging of molecules using high harmonic spectroscopy. Nature Reviews Physics 2019, 1, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenlein, R.; Elsaesser, T.; Holldack, K.; Huang, Z.; Kapteyn, H.; Murnane, M.; Woerner, M. Recent advances in ultrafast X-ray sources. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2019, 377, 20180384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, S.R.; McCurdy, C.W.; Burgdörfer, J.; et al. What will it take to observe processes in “real time”? Nature Photonics 2014, 8, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseev, M.K.; Matveev, V.I.; Makarov, D.N. Diagnostics of Nanosystems with the Use of Ultrashort X-Ray Pulses: Theory and Experiment (Brief Review). JETP Lett. 2021, 114, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astapenko, V.A.; Sakhno, E.V. Excitation of a quantum oscillator by short laser pulses. Applied Physics B 2020, 126, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmej, F.; Astapenko, V.; Lisitsa, V.; Li, X.; Khramov, E. Scattering of ultrashort laser pulses on “ion-sphere” in dense plasmas. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2019, 59, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.; Kharlamova, A. Scattering of X-ray Ultrashort Pulses by Complex Polyatomic Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.N.; Makarova, K.A.; Kharlamova, A.A. Specificity of scattering of ultrashort laser pulses by molecules with polyatomic structure. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eseev, M.; Makarova, K.; Makarov, D. Scattering of Ultrashort X-ray Pulses on Diamonds with NV Centers. Crystals 2022, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.; Kharlamova, A. Peculiarities of Scattering of Ultrashort Laser Pulses on DNA and RNA Trinucleotides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.D.; et al. DNA nicks induce mutational signatures associated with BRCA1 deficiency. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymami, J.; Coll, M.; van der Marel, G.A.; et al. Molecular structure of nicked DNA: a substrate for DNA repair enzymes. PNAS 1990, 87, 2526–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odell, M.; Sriskanda, V.; Shuman, S.; Nikolov, D.B. Crystal Structure of Eukaryotic DNA Ligase–Adenylate Illuminates the Mechanism of Nick Sensing and Strand Joining. Molecular Cell 2000, 6, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Nandakumar, J.; Smith, P. Structural basis for nick recognition by a minimal pluripotent DNA ligase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2007, 14, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athreya, N.; Milenkovic, O.; Leburton, J.P. Interaction dynamics and site-specific electronic recognition of DNA-nicks with 2D solid-state nanopores. npj 2D Mater Appl 2020, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D. Quantum theory of scattering of ultrashort electromagnetic field pulses by polyatomic structures. Optics Express 2019, 27, 31989–32008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eseev, M.; Goshev, A.; Makarova, K.; Makarov, D. X-ray diffraction analysis of matter taking into account the second harmonic in the scattering of powerful ultrashort pulses of an electromagnetic field. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, D.; Eseev, M.K.; Makarova, K.A. Analytical wave function of an atomic electron under the action of a powerful ultrashort electromagnetic field pulse. Optics Letters 2019, 44, 3042–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvat, F.; Martnez, J.; Mayol, R.; Parellada, J. Analytical Dirac-Hartree-Fock-Slater screening function for atoms (Z = 1-92). Phys. Rev. A 1987, 36, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroju, P.K.; Grazioli, C.; Fraia, M.D.; et al. Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser. Nature 2020, 578, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duris, J.; Li, S.; Driver, T.; Champenois, E.G.; et al. Tunable isolated attosecond X-ray pulses with gigawatt peak power from a free-electron laser. Nature Photonics 2020, 14, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).