1. Introduction
Graph processing is an invaluable tool for data analytics, as illustrated by the plethora of relatively recent work aiming at achieving high performance for graph algorithms [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6], such as PageRank [
7], or graph querying/mining [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14], e.g., using PGQL [
15]. At the heart of each graph system lies the graph data structure, which stores the vertices and their edges, and whose performance largely contributes to the general performance of the system. The ideal graph structure should offer excellent read-only performance, fast mutations (i.e., vertex or edge insertions and deletions), and low memory consumption with or without mutations.
Classic graph data structures typically trade some characteristics for others (see
Section 2.1). Adjacency lists enable quick graph updates and consume relatively little memory, but sacrifice performance, as they lead to expensive pointer chasing. Adjacency matrices enable quick edge updates, but sacrifice vertex insertions and consume a lot of memory. Finally, the Compressed Sparse Row (CSR) representation offers a good memory footprint with excellent read-only performance by completely sacrificing mutability: even a single vertex or edge insertion requires complete reallocation of the underlying structures. There have been efforts to improve the update-friendliness of CSR (see
Section 2.2). These include in-place update techniques [
16,
17], batching techniques [
18,
19], and changeset-based updates with delta maps [
20] and multi-versioning [
3]. A multi-versioning solution is used in LLAMA [
3], a state-of-the-art update-friendly graph structure that enables mutability on top of CSR by appending delta snapshots. Furthermore, GraphOne [
21] uses dual versioning: it combines edge lists and adjacency lists to store graph snapshots of the graph. Both LLAMA and GraphOne first store incoming updates in buffers to allow for faster updates, and then move the newly-inserted edges or vertices to the main structure and create snapshots. However, having a frequent flow of graph updates—which is the common case in real-life scenarios, such as financial transactions—results in a large number of delta logs, and thus high memory utilization and decreased performance. Compaction operations on these data structures are often expensive, hindering the benefits of fast mutability. Very often, users simply need to operate on the most up-to-date version of the graph data, which calls for supporting fast in-place graph updates. In-place updates do not require rebuilding the entire vertex/edge structures; instead, an update is directly stored using either extra space that already exists within the structure or by reallocating only part of the edge/vertex tables. Existing graph structures with in-place mutations include STINGER [
22] and Teseo [
23]. STINGER relies on adjacency lists that store edges in linked lists of blocks, while Teseo extends CSR by using Packed Memory Arrays (PMAs) [
24] to store the edge table. PMAs are arrays with gaps augmented with an implicit B+ tree that makes it possible to track empty elements in the array. Although these techniques allow for a higher update throughput as compared to LLAMA or GraphOne, STINGER and Teseo exhibit slow scan performance due to non cache-friendly designs (see
Section 4 for a performance analysis).
In this paper, we introduce CSR++
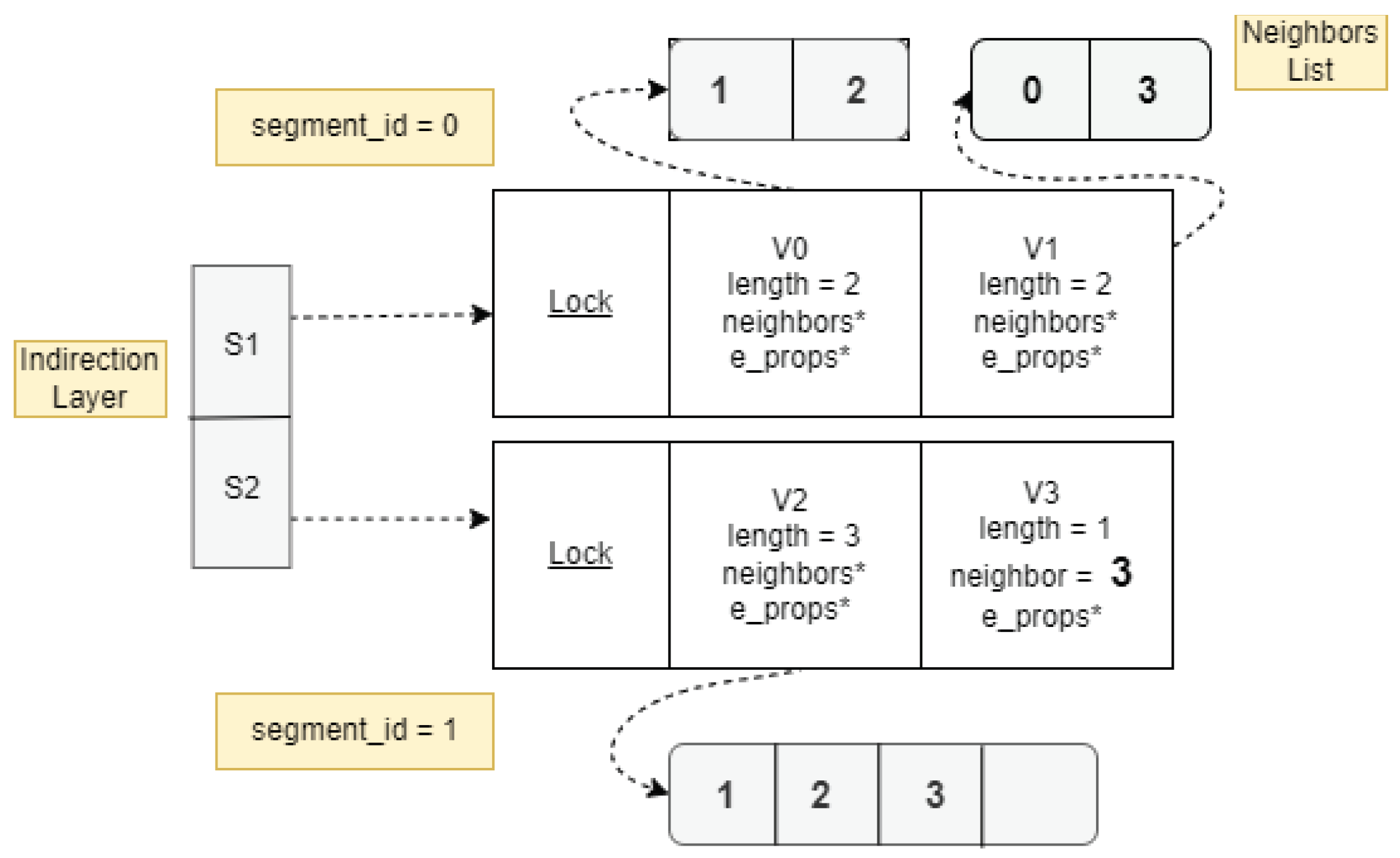
1, a concurrent graph data structure with performance comparable to CSR, efficient in-place updates, and memory consumption proportional to the number of mutations. CSR++ maintains the array-continuity that makes CSR very fast. In particular, vertices are stored in arrays that are segmented for better update-friendliness. As in CSR, vertex IDs in CSR++ are implicitly determined by the location of the vertex, but include both the segment ID and where in the segment the vertex lies. Accordingly, the 64 bits of vertex IDs are split into {int segment_id; int in_segment_id}, which makes vertices directly addressable. Due to segmentation, inserting a new vertex is as simple as (i) if needed, appending a new segment to the array of segments, and (ii) appending the vertex to that segment.
In contrast to CSR, and like adjacency lists, CSR++ can independently manage the edges of each vertex. If a vertex has two or more edges, CSR++ holds a pointer to an array storing the edges. To reduce memory usage, for single-edge vertices, the target vertex of the edge is inlined in lieu of the array pointer. All in all, CSR++ maintains the array-oriented structures of CSR for performance, while enabling per-vertex edge list modifications to enable fast updates as with adjacency lists.
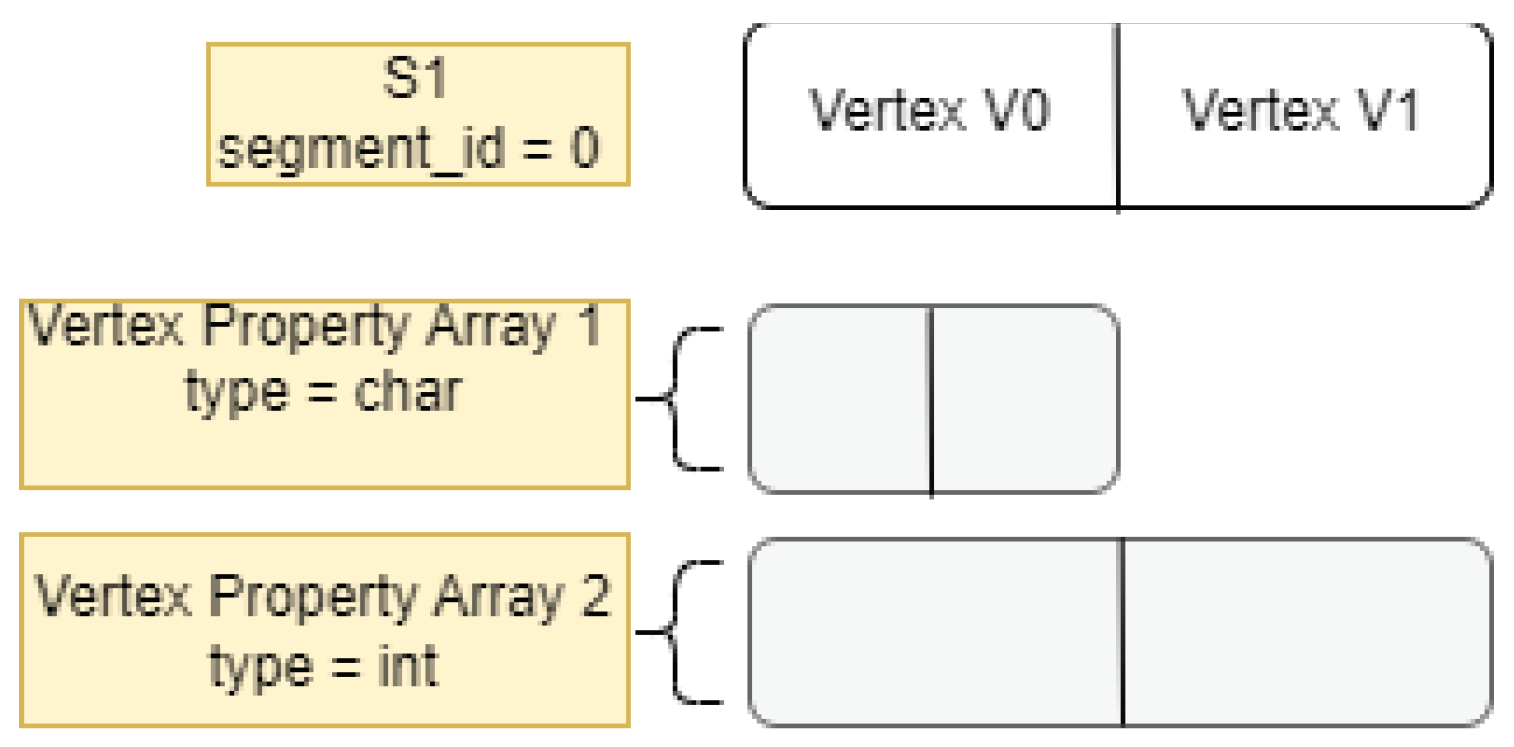
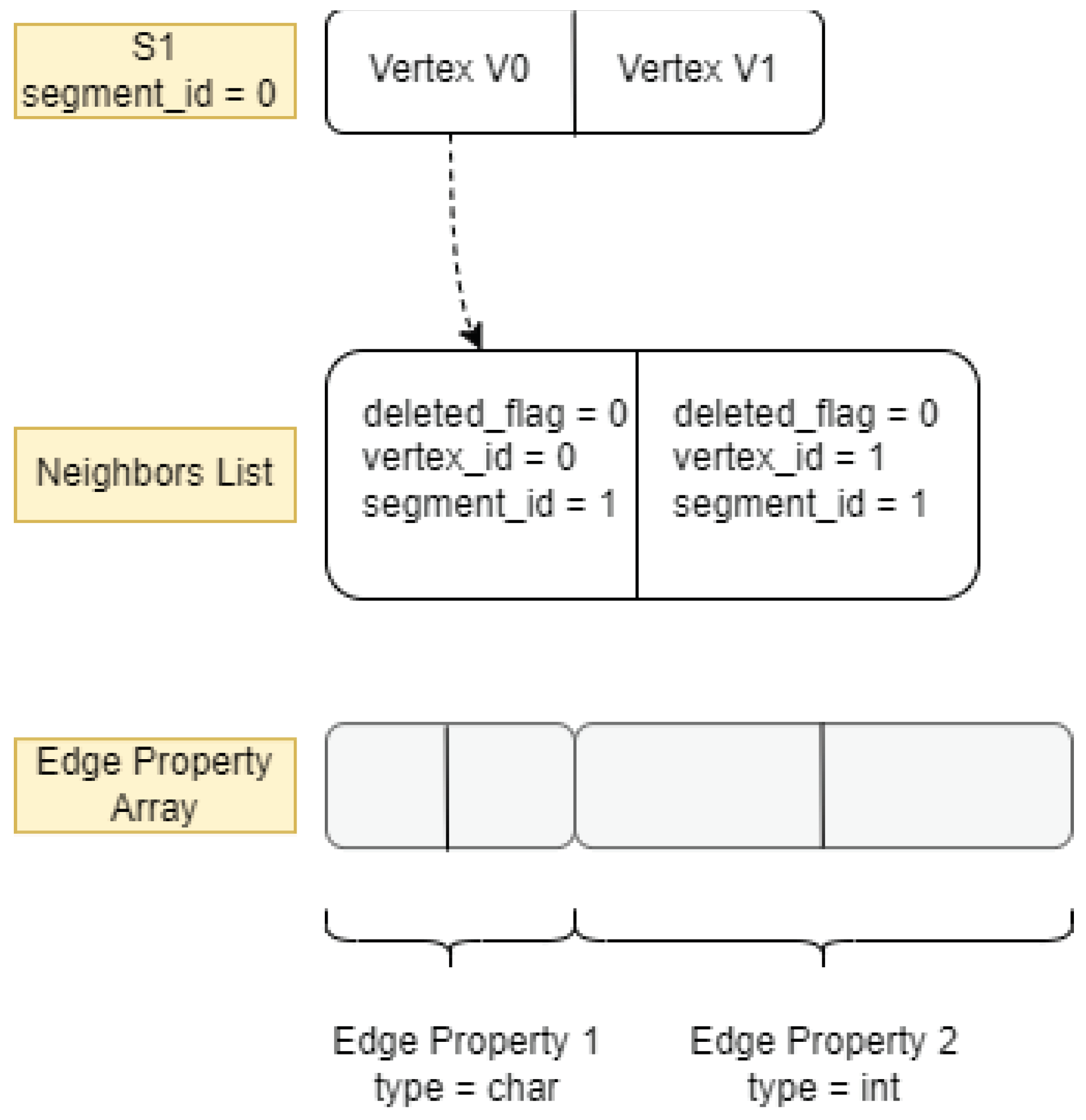
Apart from vertices and edges, graph structures also need to store vertex and edge properties, which are a prominent feature of property graphs. CSR++ includes segmentation techniques to enable fast property updates when new vertices or edges are inserted. Vertex properties are stored in segmented arrays, and each vertex holds a pointer to an array of edge property values, which allows for fast per-segment or per-vertex reallocation of property arrays.
We evaluate CSR++ on both read and update workloads, with various graphs and graph algorithms, and compare it against CSR, adjacency lists, LLAMA [
3], STINGER [
22], Teseo [
23], and GraphOne [
21]. Our results indicate that CSR++ is much faster than the other update-friendly data structures, while being almost as fast as CSR on read-only workloads. Moreover, in the two scenarios where mutations are performed in batch mode and in single vertex/edge mode, respectively, CSR++’s update throughput exceeds all the evaluated graph data structures while consuming much less memory. In particular, CSR++ performs on average within 10% of the read-only performance of CSR with 36 threads and is an order of magnitude faster for updates. Furthermore, CSR++ is faster than LLAMA for most read-only workloads, it is almost 2× faster in applying batched updates, and it consumes 4× less memory when 100 update batches are applied on a base graph. Finally, CSR++ outperforms adjacency-list-based graph structures, namely GraphOne and STINGER, as well as the tree-based Teseo, being up to 3× faster for workloads with updates and up to 4× faster for read-only workloads with 36 threads. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
CSR++, a new graph data structure that supports fast in-place updates without sacrificing read-only performance or memory consumption.
Our thorough evaluation that shows that CSR++ achieves the best of both read-only and update-friendly worlds.
An in-depth analysis of the design space, regarding memory allocation, segment size, and synchronization mechanisms, to further improve the read and update performance of CSR++.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents related work, as well as the necessary background on graphs and graph updates.
Section 3 and
Section 4 describe and evaluate CSR++ , respectively. Finally,
Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Background & Related Work
Graphs are a prominent data model in the current era of big data and data deluge [
27]. The advantage of graphs over the traditional relational model is that they can inherently model entities and their relationships. While the relational model needs to join tabular data in order to process foreign key relationships, graph processing engines have built-in ways to efficiently iterate over graphs [
28], e.g., over the neighbors of vertices, and they support a plethora of imperative languages for writing graph algorithms (such as Green-Marl [
4,
29]), as well as declarative languages for pattern-matching queries (such as PGQL [
15], SPARQL [
30], and Gremlin [
31]).
Graphs can be represented with different models and data representations. A popular model is the RDF (Resource Description Framework) graph data model [
30] [
32], which became popular with the rise of the semantic web [
33]. RDF regularizes the graph representation as a set of triples. RDF adds links for all data, including constant literals, and does not explicitly store vertices, edges, or properties separately. Not storing graphs in their native format adds significant overhead [
34], as RDF engines are forced to process and join a large number of intermediate results.
This paper focuses on a more recent model, the Property Graph (PG) model [
14,
35], which is widely adopted by various graph databases and processing systems (such as Neo4J [
11] and PGX [
12,
36]). PG represents the topology of a graph natively as vertices and edges, and stores properties separately in the form of key-value pairs. This separation allows for quick traversals over the graph structure. Classical graph algorithms, such as PageRank [
7] and Connected Components, are very naturally expressed on top of property graphs [
4].
In order for graph processing engines to provide efficient solutions for large-scale graphs, they rely on efficient data structures, which potentially reside in main memory [
3,
6,
37,
38], to store and process vertices and their relationships. One of the key challenges for in-memory graph processing engines is to design data structures with reasonable memory footprint [
3] that can support fast graph algorithm execution [
29] [
39] and query pattern matching [
40], while supporting topological modifications, i.e., additions or removals of vertices and edges, either in batches or in a streaming fashion [
18,
41]. In the rest of this section, we discuss the most prominent data structures in related work [
38], and motivate the necessity of the novel CSR++. In
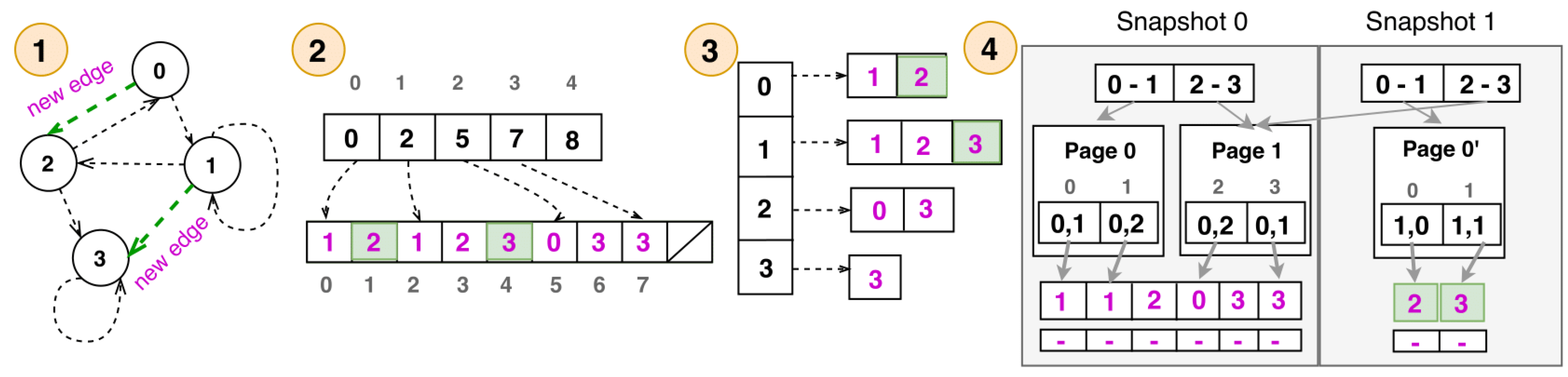
Figure 1, we show an example of a graph and how it is represented in different formats.
2.1. Graph Representations
2.1.1. Adjacency Matrices and Lists
An adjacency matrix represents a graph with a matrix M, where V is the number of vertices in the graph. A non-zero entry represents the directed edge from a source vertex to a destination vertex . An adjacency matrix is not preferred for sparse graphs, i.e., graphs where the number of edges , due to increased memory footprint and decreased performance in analytics.
Adjacency lists represent the graph with a set of vertices, where each vertex is associated with a list of neighbors, as shown in
Figure 1 (3). An adjacency list typically consumes less memory than an adjacency matrix, since for a given vertex, only the existing edges need to be stored. Typical adjacency lists use linked lists, but more cache-friendly variants exist, such as Blocked Adjacency Lists which represent adjacencies with simple arrays [
6] or with linked lists of buckets of fixed size that store the edges [
2,
42]. As an example, in the popular Boost C++ Library [
43]’s implementation of adjacency lists, the edge structures can be configured to be either vectors, lists, or sets. Although adjacency lists can handle mutations efficiently, they underperform in read-only workloads, as we show in
Section 4.
2.1.2. Compressed Sparse Row (CSR)
CSR [
29] is a data structure that is commonly used for sparse graphs, because it compresses adjacencies. CSR uses two arrays: a vertex array and an edge array. In the vertex array, each vertex is identified by its array index. The element at this index is the index in the edge array where the first destination neighbor of the vertex is stored, as shown in
Figure 1 (2). The index of the last destination neigbor in the edge array does not need to be stored, as it is equal to the index of the first destination neighbor of the next vertex minus one. In terms of graph mutations, CSR is very inefficient. For example, to add an edge, the whole edge array needs to be reallocated and filled again; the destination neighbors that follow the newly-inserted destination neighbor are shifted by one element.
2.2. Graph Mutations
Graph mutations, or updates, mostly refer to vertex or edge insertions and deletions. Although CSR is one of the most popular data structures for representing a graph, it is, as mentioned above, very limiting for graph mutations. This has prompted a lot of related work on mutable data structures to represent graphs that can efficiently digest sets of updates. Streaming graph systems differ in their way of ingesting and storing updates, depending on the application domain. The ingestion of updates can be done in bulk, with alternating phases: pending updates wait for currently-executing queries to finish before they start executing, and pending queries wait for currently-executing updates to finish before they start executing. Update ingestion can also be concurrent with query execution, but in that case, the system needs to guarantee consistency on the data and at user level [
44].
2.2.1. In-Place Updates
Techniques that use in-place updates employ the aforementioned static data structures in a way that allows for in-place digestion of sets with insertions and deletions of vertices and edges, without requiring the expensive rebuild of the data structure. For instance, Dense [
45] is a concurrent graph adjacency matrix that supports mutations and partial traversals through a coordination protocol, but does not handle graph properties. NetworKit [
16], in order to perform edge insertions, stores adjacency vectors that double the size of the initial array to reserve enough space for new incoming edges. Madduri et al. [
19] use the same underlying technique but define a configurable size of the new edge array instead of using a factor of 2.
STINGER [
22] and Hornet [
46] are two state-of-the-art in-place update graph frameworks that are based on Blocked Adjacency Lists. They aim to improve the spatial locality of adjacency lists by storing edges in blocks of sizes that are multiples of cache lines. Subsequent research [
47,
48] further improves the performance of STINGER to allow for in-place updates that are executed concurrently with queries and aims at achieving high rates of updates, on different platforms. DISTINGER is a distributed framework that is based on STINGER’s data structure, while CUSTINGER leverages GPUs. To allow for better performance, both STINGER and Hornet implement their own internal memory managers that optimize the memory allocations that are required when applying mutations. For both insertions and deletions, Hornet’s internal memory manager implements a B+ tree to efficiently keep track of empty space. STINGER is optimized for batch updates, however, as we show in
Section 4.8, it struggles in the case of individual updates.
Wheatman et al. [
17] propose PCSR, which is another data structure that implements the bulk update scheme, using Packed Memory Arrays (PMAs) [
24]. They implement a variant of CSR that leaves space at the end of each adjacency list to allow efficient single-threaded mutations. PCSR uses PMAs to store CSR data structures and allows for an order of magnitude faster updates with a constant factor slowdown for search as compared to CSR. PPCSR [
49] is a more recent work that implements a concurrent version of PCSR. Even though PPCSR is faster than CSR, by design, it consumes 2× the space of CSR due to the empty PMA slots. PPCSR defines intra-operations, i.e., internal data structure operations such as the rebalancing of its implicit tree, which happens during resizing. It also defines inter-operations, i.e., concurrent reads or writes to the graph structure which are protected by locks. Maciej Besta et al. [
50] study the performance of HTM [
51] in graph analytics as an alternative to atomic instructions, by designing the Atomic Active Messages (AAM) mechanism which allows for faster analytics performance on the Intel Haswell and IBM Blue Gene/Q architectures. Their evaluation model compares HTM to atomic instructions in analytical workloads. They only discuss static graph analysis and do not address dynamic graph problems such as vertex or edge insertions. We employ similar techniques in CSR++ to ingest mutations, but in a concurrent fashion, while also supporting graph property mutations.
2.2.2. Batching
The sources of changes can be continuous streams of updates [
18,
42] or single changes applied as “local” mutations. Generally, when applying a batch of updates, frameworks perform pre-processing to re-arrange the batches in ways that can speed up the mutations. For instance, Madduri et al. [
19] apply techniques on the list of new edges, such as sorting, re-ordering, and partitioning, in order to exploit parallelism when the changes are applied. Similarly, CSR++ groups updates by their source vertices, and uses multiple threads to perform fast edge insertions, as we explain in
Section 3.2.
2.2.3. Multi-Versioning and Deltas
One way to extend CSR to support fast updates is by allocating a separate structure to store only the new changes [
20] in delta maps. Furthermore, by using deltas, the following systems can run analytical workloads on different static versions (snapshots) of the changing graph over time. LLAMA [
3] is a state-of-the-art snapshot-based graph system that implements multi-versioning by storing deltas as separate snapshots and supports concurrent access to those snapshots (see
Figure 1 (4)). Graphite [
52] is an in-memory relational column-store that also implements multi-versioning snapshots using deltas. ASGraph [
2] limits its read access to one snapshot at a time but still ensures high performance by extending its underlying data structure [
42] with temporal attributes.
GraphOne [
21] is another recent multi-versioning solution that outperforms LLAMA and STINGER in update ingestion and analytics. It builds on a dual versioning approach that is based on a hybrid store. It relies on adjacency lists that offer a coarse-grained snapshot mechanism, in combination with a separate circular edge log to store the new edges as they arrive. As in most systems that use a separate store for the update operations and aim for high analytics performance, the edges need to be “moved” to the base structure. With LLAMA, a new level (i.e., snapshot) is created once the write-optimized store is “flushed” into the Read-Optimized Store (ROS). With Teseo, although the data is initially updated in-place, i.e., the edges are stored in ROS segments, when no more space is available in the segments, a separate Write-Optimized Store (WOS) buffer is created. The WOS is indexed by a sequential ART trie, and it is incorporated into the main structure of sparse arrays during rebalancing operations.
The downside of the above approaches is two-fold. First, maintaining separate snapshots increases the memory requirements of the system, as a frequent flow of graph updates results in a large number of deltas. Second, the performance of analytics is degraded because these approaches need to read from both the original structure and the deltas and reconcile them. A solution to the potential performance degradation is to periodically merge the delta maps into the CSR data structure. This operation, which is called compaction, can become very expensive, often zeroing the mutability performance benefits of these structures. For users who wish to operate on the most up-to-date version of the graph data, we show that CSR++, which is designed for in-place graph mutations, achieves better analytics and update performance than LLAMA [
3], with up to an order of magnitude lower memory requirements (see
Section 4).
4. Evaluation
In this section, we give answers to the several key questions regarding the performance and memory consumption of CSR++:
Before dive into the answers of those questions, we perform, in
Section 4.1–
Section 4.3, a sensitivity analysis of important CSR++ configuration parameters, namely segment sizes, memory allocators, and synchronization mechanisms.
Overall, we use four datasets in
Table 1 to compare the graph structure configurations in
Table 2, in various workload configurations and the algorithms in
Table 3. In order to evaluate with several workloads and state-of-the-art graph data structures, we use two benchmark drivers: (i) the driver and the algorithms in Green-Marl [
26] (includes BGL, CSR, and LLAMA) and (ii) the ones in the Graph Framework Evaluation (GFE driver) [
26] (includes LLAMA, STINGER, GraphOne, and Teseo). We evaluate the Green-Marl benchmarks with the two real-world graphs, namely LiveJournal (4.8 million vertices and 68 million edges) and Twitter (41 million vertices and 1.4 billion edges), while the GFE driver with two supported synthetic graphs with different scale factors, namely the graph500-22 from the LDBC Graphalytics Benchmark [
56], and a generated graph Uniform-24 with a uniform edge distribution.
Experimental Methodology
For every result point, we perform five iterations and plot the median. We report the execution time as a function of the number of threads. For most analytics workloads we use CSR as the baseline. We run our benchmarks on a two-socket, 36-core machine with 384 GB of RAM. Its two 2.30 Ghz Intel Xeon E5-2699 v3 CPUs have 18 cores (36 hardware threads) and 32 KB, 256 KB and 46 MB L1, L2, and LLC caches, respectively. We disable Intel TurboBoost and do not use Intel Hyper-Threading in any of the experiments. For results with HTM, we perform our experiments on a smaller machine with 14 cores (28 hardware threads) and similar hardware as it is the only machine we have access to with support for HTM. Both CSR++ and the other evaluated systems are implemented in C++ with optimization level -O3 and -fopenmp on Linux 7.3.
We use the evaluated graphs as follows. For the read-only and deletion workloads, we initially load the whole graph structures. For workloads with insertions, we initially load 80% of the graph and then insert batches of different sizes, generated using the graph split techniques used for loading and testing in the original LLAMA paper [
3]. The first split contains the 80% of the graph (≈1.1 billion edges for Twitter) that is loaded as a base graph. Then, the remaining 20% is split using a random uniform distribution over
N files; we refer to
N as the number of batches. Depending on the workload, we refer in figures to either the batch size (e.g., 1% corresponds to splitting the 20% in 20 batches, hence 1% of the overall graph), or the number of batches.
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis: Segment Size
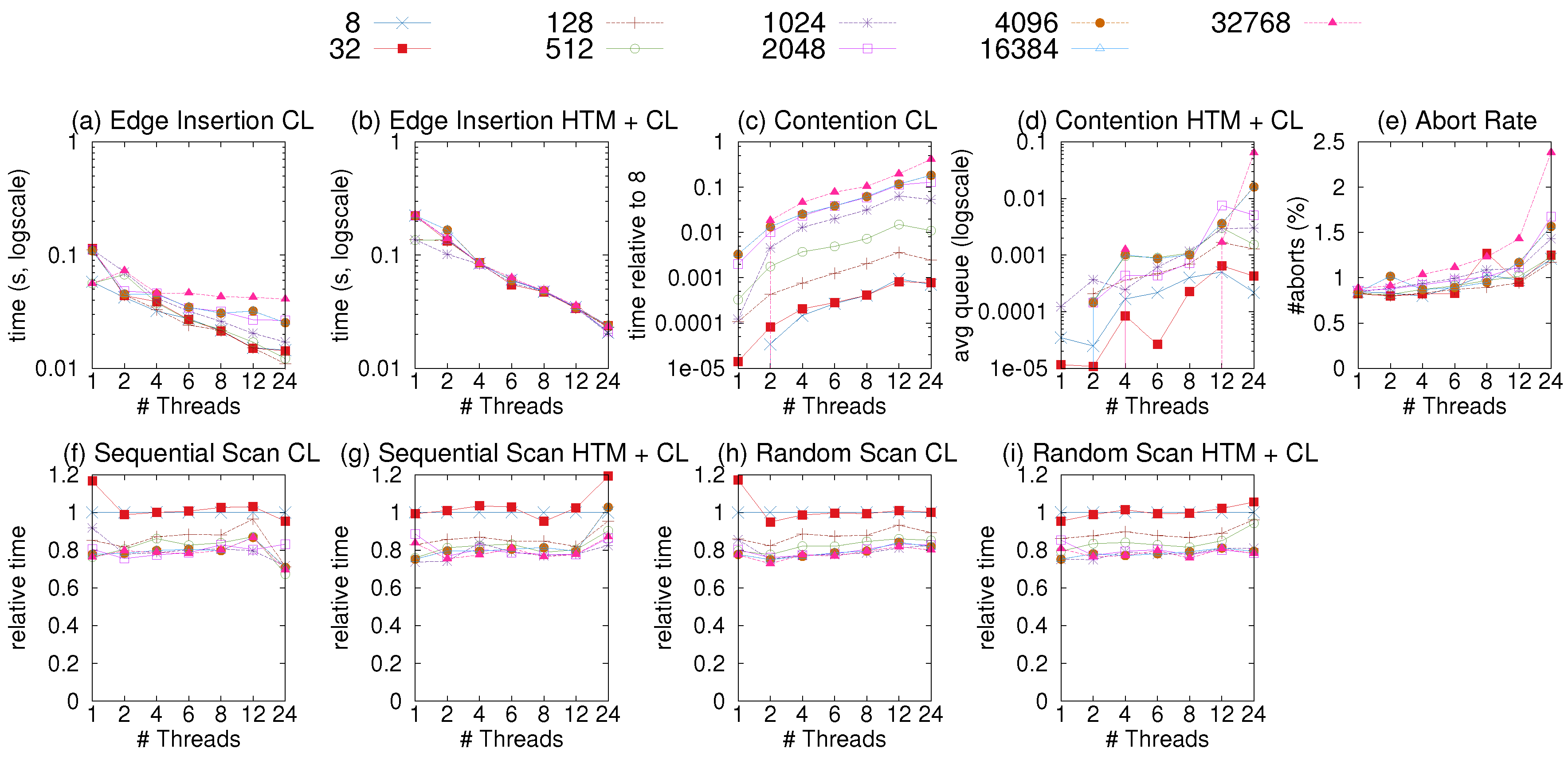
We evaluate the impact of the segment size (i.e., the number of vertices per segment) on the update performance of CSR++. To check the update scalability of CSR++, we set the size of the segment to different number of vertices, and measure the time it takes to insert a batch of new edges. We generate an artificial workload with ~100 thousand vertices and 2 million edges, where the edges have a random uniform distribution. We initially load the vertices in an empty graph, and then insert the edges as one batch. The source vertices of the edges are randomly shuffled. The shuffling allows us to evaluate the non-sequential access to the vertices in segments to observe a more real-world scenario where source vertices in each batch might not be adjacent in the initial graph.
Figure 5a shows the time it takes to insert the edges. We observe that the bigger the size of the segments, the slower the insertion. This is mainly due to conflicts when multiple threads are updating vertices that belong to the same segment. We use a profiler ticket lock (taken from [
58]) to quantify the contention caused at the vertex level by measuring the average queue on each lock.
Figure 5c shows the contention data we gathered while executing the experiment of
Figure 5a. We observe a high level of contention for the larger segments which explains the slower insertions, and can be improved by using finer-grained locking.
Moreover, we analyze the read-only performance of CSR++ with different segment sizes with a sequential scan over all edges. As
Figure 5f, the very small segment sizes lead to performance degradation due to heavier indirection (i.e., having to follow more pointers) and the worse cache behavior, as the complementary segment structures consume some extra memory, as described below.
Finally,
Table 4 shows the memory overhead when using different sizes of segments for a graph of ~100 thousand vertices. In addition to the vertices in a graph, we store a pointer (8 bytes) and a ticket lock (64 bytes) per segment, therefore the memory overhead of segments is calculated like the following:
memory = number_of_segments * [sizeof(segment_pointer) + sizeof(ticket_lock)]. As shown in
Table 4, even for the smallest size of segments, the memory overhead does not exceed 9KB which is negligible compared to the memory consumption of the entire graph. In the remaining experiments of this paper, we fix the segment size to 128, which gives the best balance between scans and updates.
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis: Improving Update Performance with HTM
HTM allows us to implement a fine-grained synchronization mechanism (i.e., at the cache level instead of the segment level) with no memory penalties that we would encounter when using locks.
Figure 5b and
Figure 5d respectively show the time and contention when inserting the same workload described in
Section 4.1 using HTM and a coarse lock (i.e., one lock per segment) as a fallback for HTM transaction aborts. We observe that HTM reduces the contention as shown in
Figure 5d which eventually improves the update performance of CSR++, especially for segments with larger sizes as shown in
Figure 5b. For scenarios with lower contention, (e.g., for segments with a small number of vertices such as 8 or 32 we do not observe a significant benefit from using HTM, and the cost of starting and committing transactions only lowers the overall performance. We set the default number of vertices per segment to 128 as it gives the best scan/update tradeoff, but users can configure it to a different size. We do not use HTM in the rest of our experiments as it helps only very highly contested workloads, which seems unrealistic.
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis: Memory Allocators
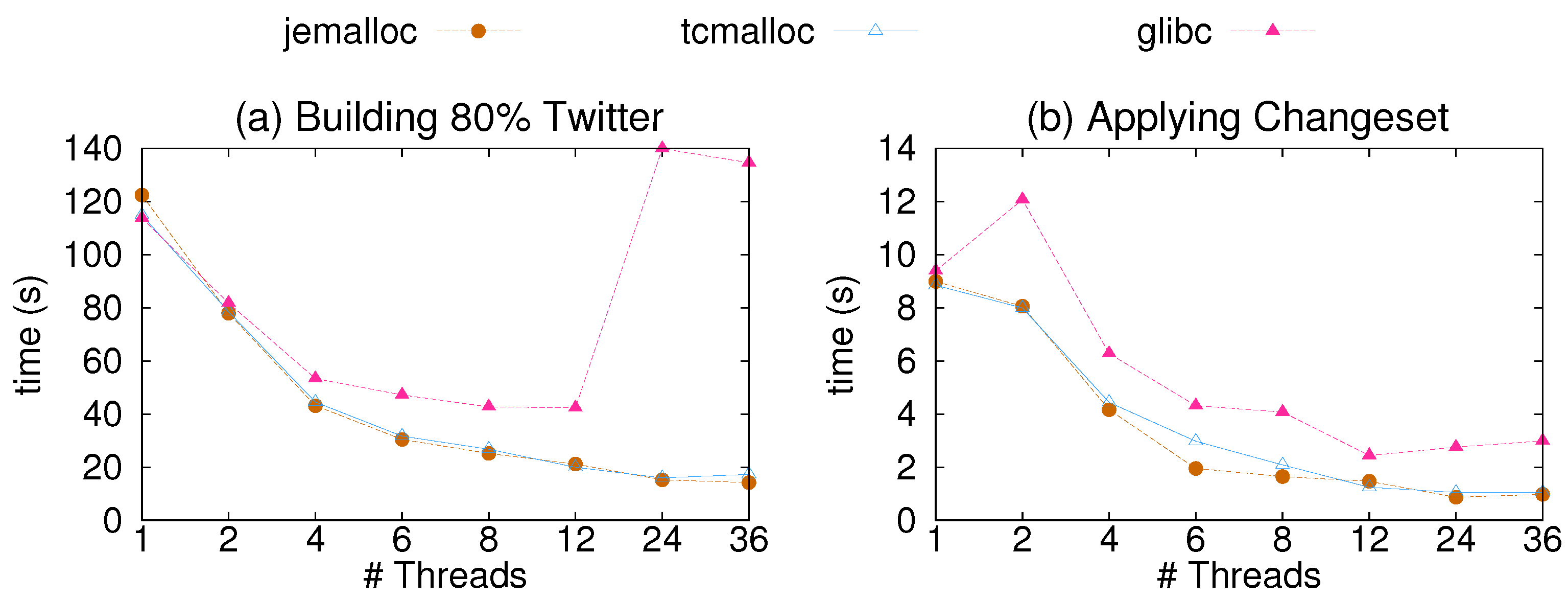
Another configuration parameter that affects the performance of CSR++ is the memory allocator. In
Figure 6, we show the results of a sensitivity analysis of CSR++ using three different libraries for memory allocation. We show the performance gain from Jemalloc [
59] and TCMalloc [
60], compared to glibc for edge insertions. As shown in the figure, CSR++ performs better using Jemalloc, which is an implementation of malloc that scales with the number of threads. Jemalloc allocates multiple arenas and assigns them to multiple threads in round robin. Memory requests are then done on the arena level with minimum conflicts. Using Jemalloc also results in lower memory consumption since it reduces memory fragmentation even after running for a long period of time.
4.4. Read-Only: Algorithms
We load the graph in memory and execute the evaluated Green-Marl algorithms. We report the execution time taken to complete each algorithm and examine how it scales with multiple threads.
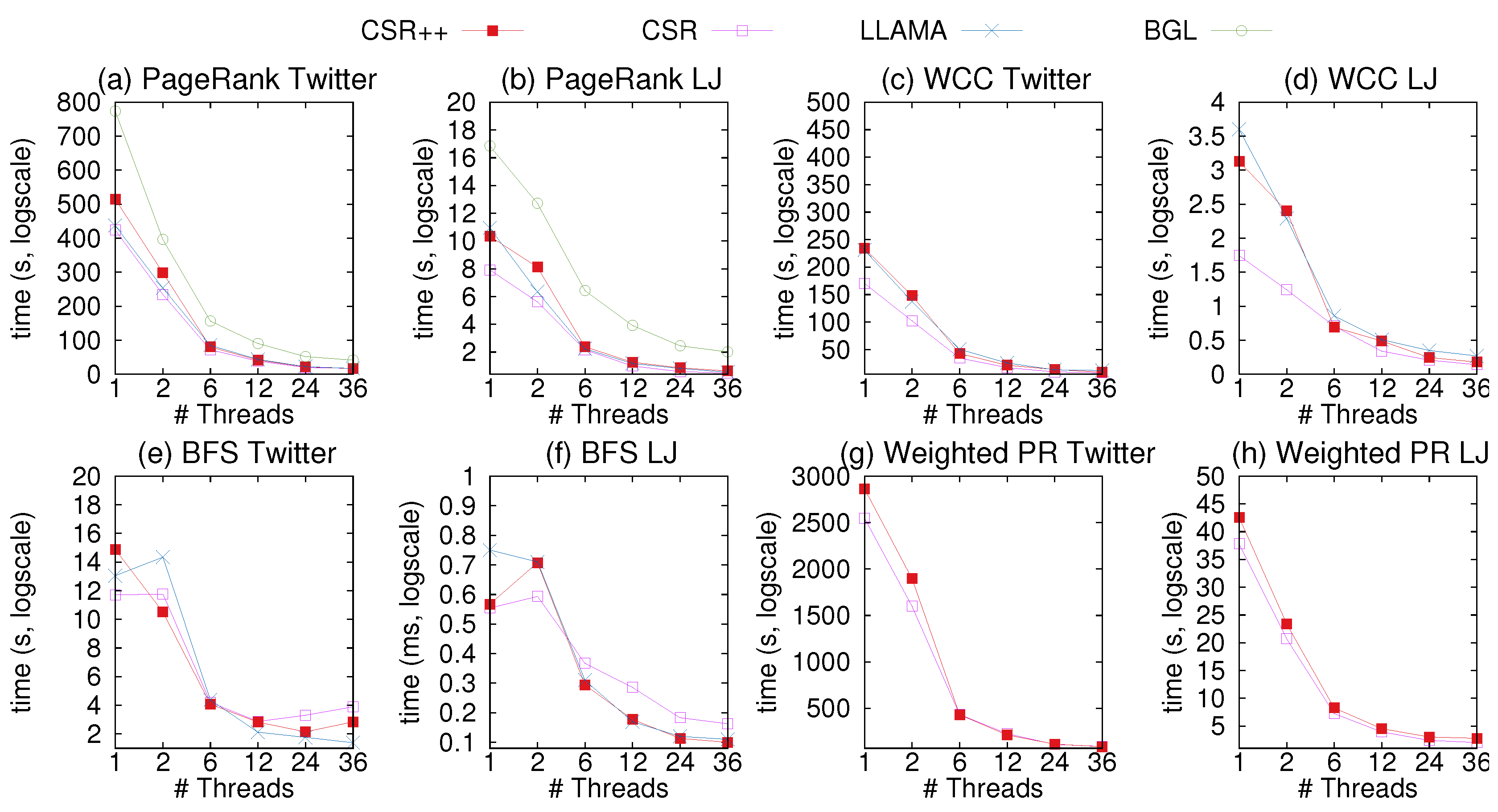
Figure 7 includes the results for CSR++, CSR, BGL adjacency lists, and LLAMA. As expected, the read-only CSR provides the best performance in this workload, since with CSR, any graph access, for vertices, edges, and properties is as simple and efficient as an indexed array access. Still, CSR++ delivers performance comparable to CSR, especially in the presence of multi-threading. This is due to the fact that initially, all segment are stored in a contiguous manner when loading the graph from files. Similarly, we use a memory manager to allocate a contiguous memory chunk to store all edge arrays in a cache-aligned manner, which makes CSR++ physical layout resemble that of CSR. Still, over all datapoints, CSR++ is on average 15% slower than CSR, while with 36 threads, CSR++ is on average less than 10% slower than CSR. This is due to the extra cost of the indirection layer to access segments, which we can configure to bypass in case of initially loaded graphs.
As shown in
Figure 7, we evaluate BGL adjacency lists only with PageRank. The reason for this is that the other algorithms require reverse-to-forward edge mapping, which is not supported out of the box in BGL. Still, the results of PageRank are conclusive: Plain adjacency lists cannot deliver performance comparable to read-friendly structures such as CSR and CSR++. Based on these results, and for simplicity of presentation, we omit adjacency lists from the experiments in the rest of the paper.
CSR++ is faster for four out of the six configurations by 16% on average with 36 threads. When loading a graph directly in LLAMA, all edges are sorted and reside contigously in the same delta. Therefore, the read-only design of LLAMA is practically a compact CSR, making LLAMA fast in read-only workloads. However, as we discuss in Section X, after applying updates on LLAMA, edges are stored in different deltas as edge fragments. Access to a neighbor list requires access to a linked list of edge fragments, making LLAMA slow compared to CSR++ and other state-of-the art data structures. Overall, the two systems perform within 1% of each other on average. LLAMA is faster than CSR++ for Pagerank with Livejournal and for BFS on Twitter.
For Weighted PageRank, we only evaluate CSR and CSR++ and omit LLAMA because it does not support edge properties out of the box. CSR++ still performs close to CSR as shown in
Figure 7h,i. With 36 threads, CSR++ is 1% faster than CSR on Twitter and 42% slower for Livejournal. The slowdown in Livejournal is due to the small size of the graph: With CSR’s representation, all data is served from the last level cache, while CSR++ needs to slightly spill to main memory. These results show that the representation of edge properties in CSR++ performs comparably to CSR, especially on large graphs.
Overall, CSR++ is very fast on read-only workloads, especially in the presence of concurrency, which is the intended use case of graph analytics.
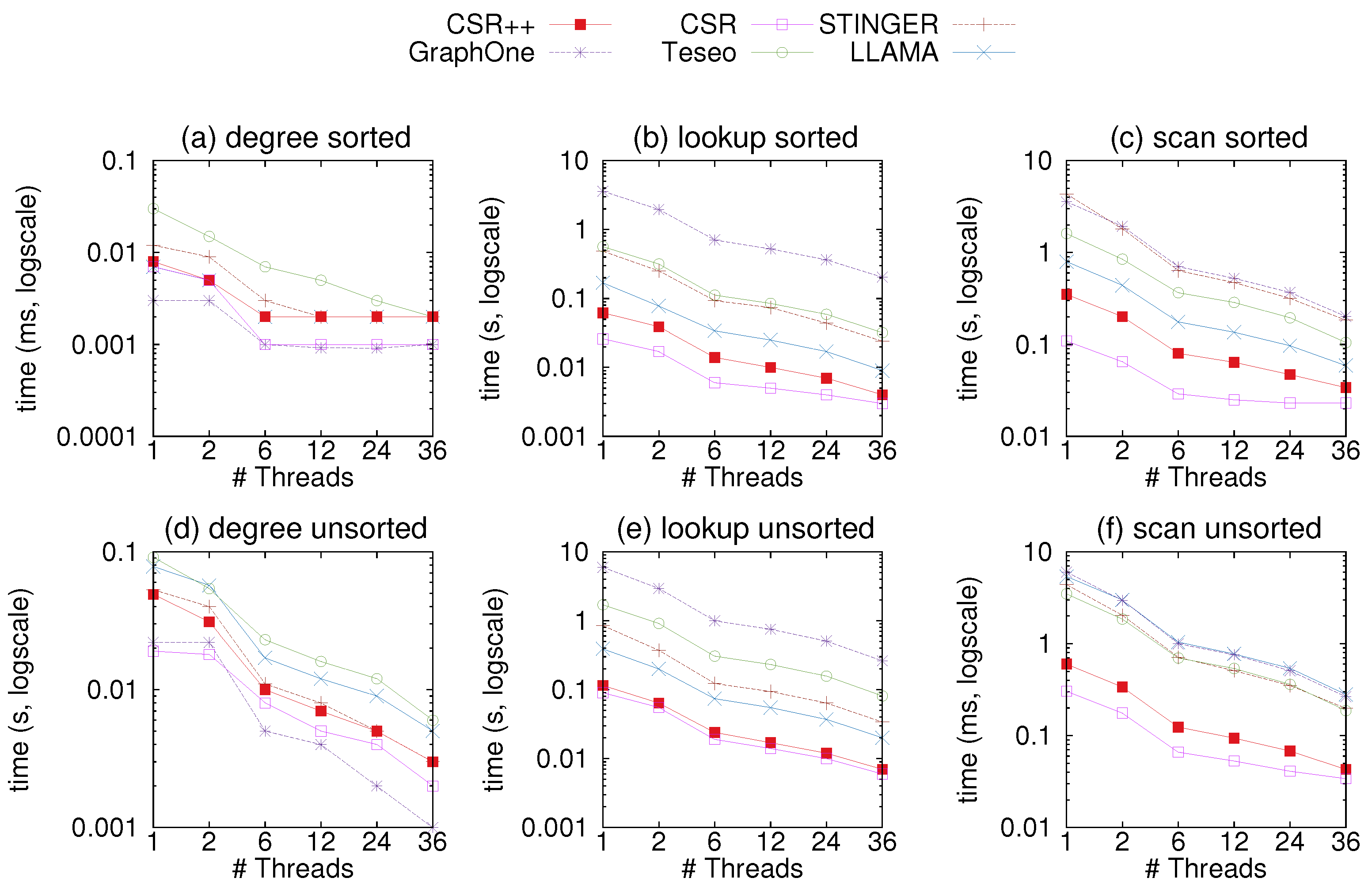
4.5. Read-Only: Sequential and Random Scans
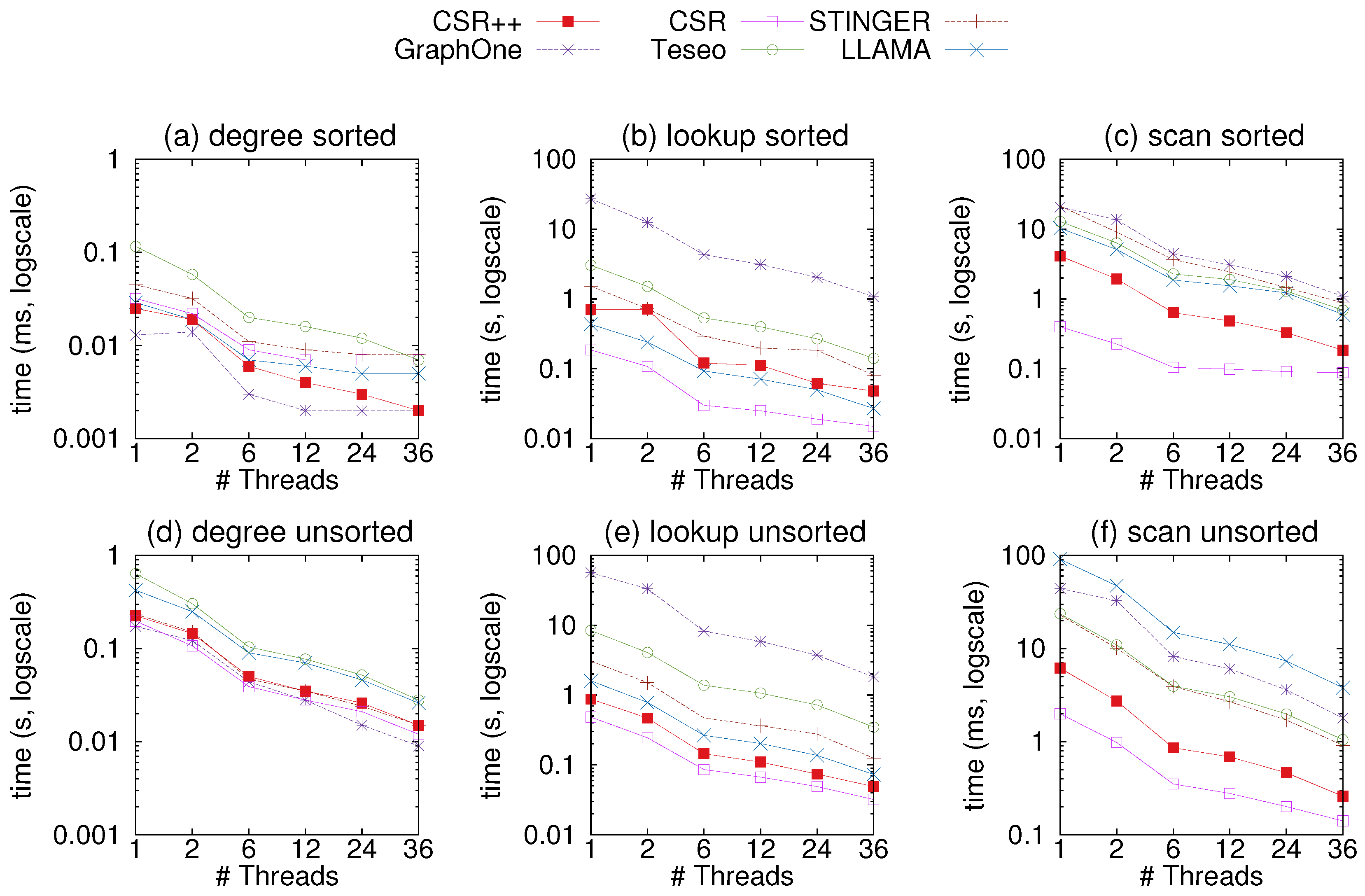
In this GFE experiment, we measure the performance of CSR++ and other systems using read-only workloads to scan the whole graph or parts of it. For this matter, we opted for three workloads:
Retrieving all neighbors of all vertices in the graph,
Figure 8c,f and
Figure 9c,f
As memory accesses can affect the performance of the systems, we choose to iterate over the vertices in sorted and unsorted order, to simulate sequential and random scans.
Figure 8 shows the results of the experiment on the uniform-24 graph, while
Figure 9 shows results on graph500-22. In most plots, CSR performs best with the exception of
Figure 8a where GraphOne retrieves degrees faster as it stores them in a separate structure called a multi-versioned degree array. This array allows for direct access whereas in CSR, degrees must be calculated using two indices in the vertex table. However, GraphOne seems to be the slowest at neighbor retrieval since it copies edges into an extra buffer when reading. CSR++ is at least an order of magnitude faster than GraphOne, Teseo, and STINGER due to its compact design which gives performance close to that of CSR. This is a due to CSR++ applying updates in-place and not storing them in extra layers as the other data structures. Moreover, CSR++ stores edges for the same vertex contiguously, and does not scatter them across multiple deltas, making CSR++ ideal for both single and batch updates. . We attribute Teseo’s slower performance to the fact that it stores sparse vertices in a dense domain using a hashmap. When scanning vertices, Teseo translates the logical identifiers of the vertices, which incurs an additional cost. LLAMA performs well in almost all read-only workloads, however, it exhibits a slowdown when vertices are accessed out of order, as can be seen in
Figure 8f, where LLAMA is the slowest to scan the whole graph. The results with graph500-22 in
Figure 9 follow similar trends as the ones on graph uniform-24.
4.6. Updates: Vertex Insertions
Vertex insertions in CSR++ are very lightweight, mainly due to segmentation (see
Section 3.2).
Table 5 shows the time to insert different number of vertices on a fully loaded Twitter graph (the choice of the graph has little impact on the performance of vertex insertions in CSR++), when the graph contains either no vertex properties or 50 vertex properties. Vertex insertions are fast: with 10 M insertions, inserting a vertex takes an average of 118 and 126 nanoseconds per vertex with no and 50 properties, respectively. Vertex properties are lightweight in CSR++, as they require just one memory allocation per property per segment.
4.7. Updates: Batch Edge Insertions
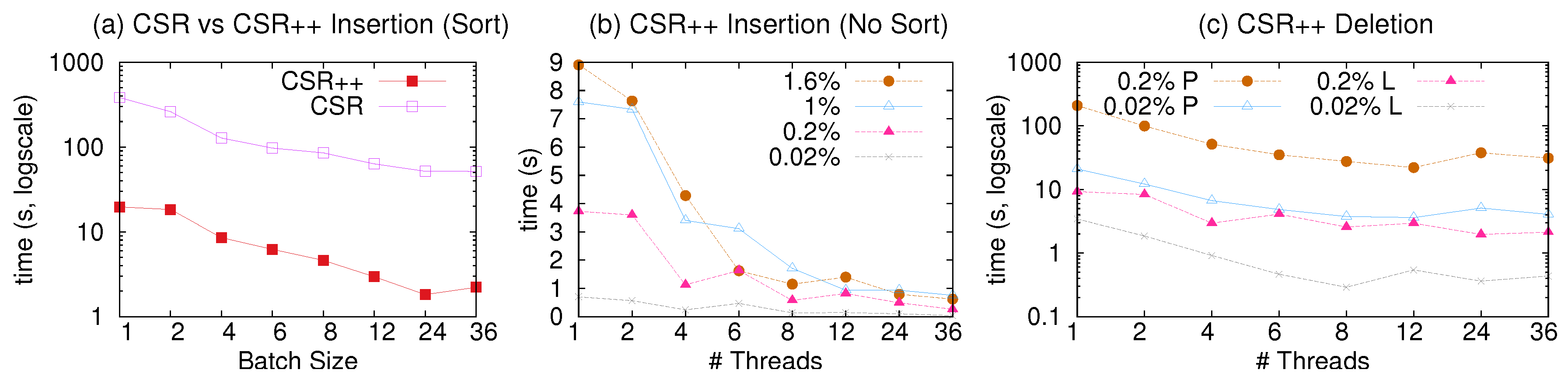
We evaluate the time it takes to insert all edges of one batch in both forward and reverse structures (plus edge semi-sorting).
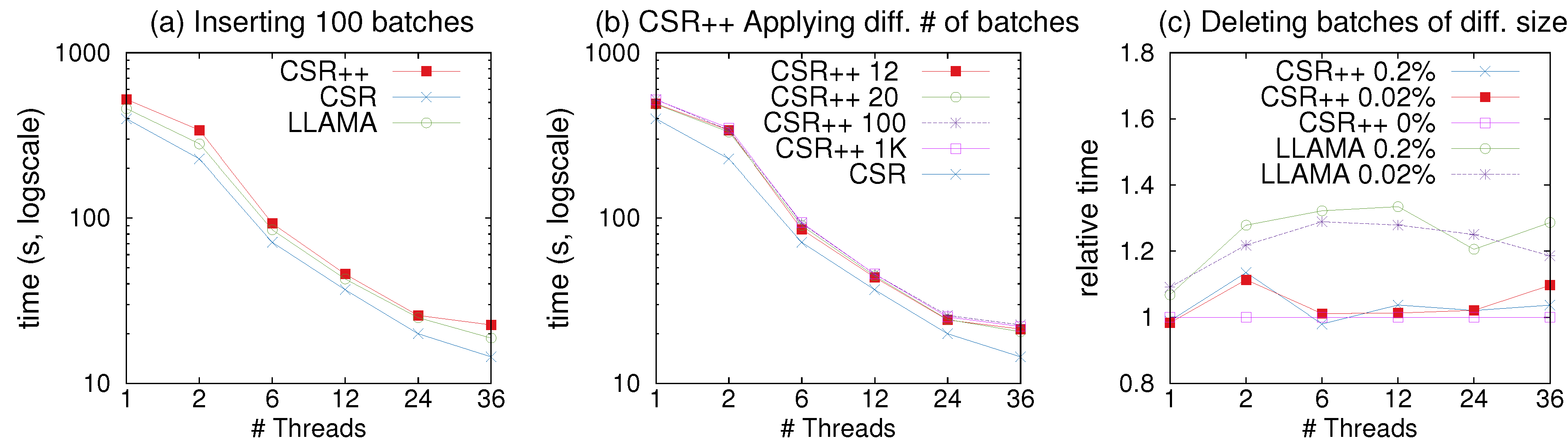
Figure 10a shows the results. CSR++ completes this full batch insertion one order of magnitude faster than CSR. CSR completes all batch insertions in the same amount of time, regardless of the batch size, since it takes the same amount of time to rebuild the whole graph at every update. In contrast, CSR++ performs localized graph updates and thus delivers fast performance that is proportional to the batch size.
Next, we examine the scalability of edge insertions with CSR++ using the same workloads and exploiting multi-threading. The results are shown in
Figure 10b. We isolate insertions by removing the edge semi-sorting that takes a significant amount of overall insertion time, since CSR++ does not rely on semi-sort for read performance. CSR++ achieves good scalability for up to 12 threads. For more threads, performance does not improve, in part because of the effects of memory contention and NUMA, but mainly because of actual vertex contention: Twitter is a very skewed graph, hence many of the edge insertions land in the same high degree vertices, hindering parallelism. Note that for these workloads, due to limited space, we only show the results with Twitter; we reach very similar conclusions with the smaller LiveJournal graph.
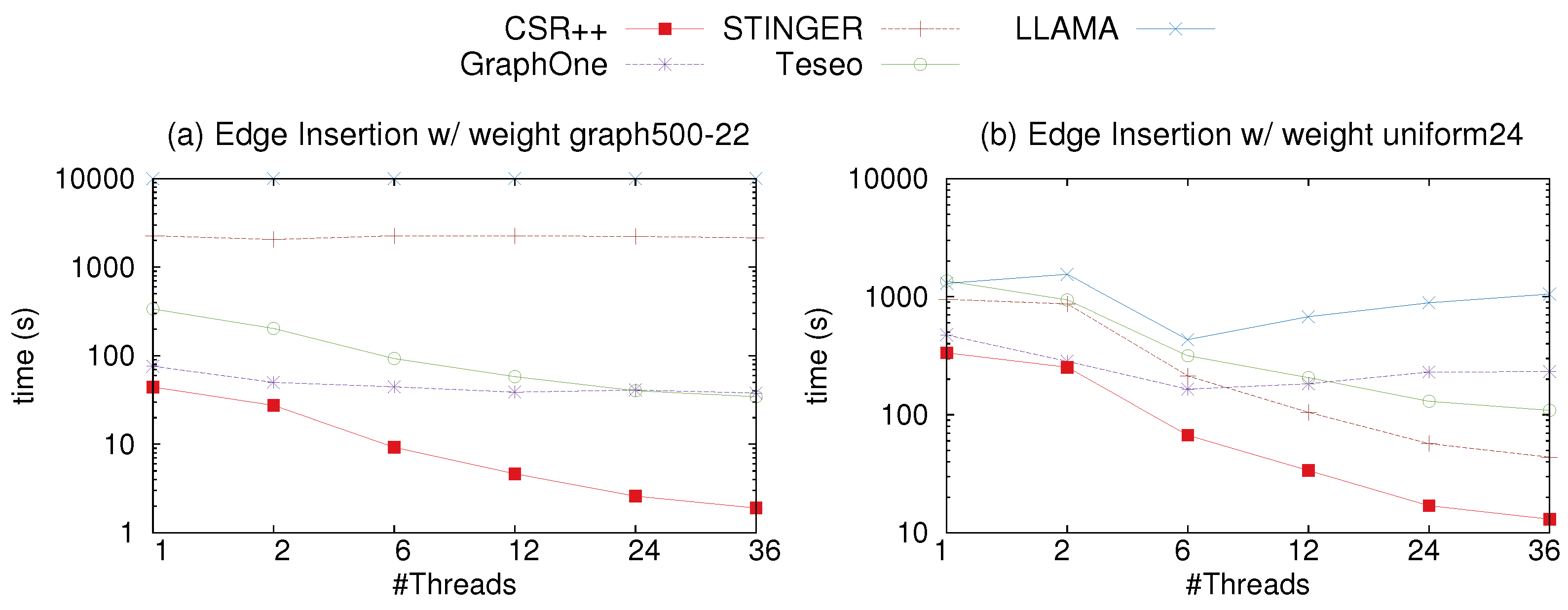
4.8. Updates: Edge Insertions with Properties
To evaluate the insertion performance of CSR++ with an edge property, we simulate a stream of edges of two scale factors using the graph500-22 and the uniform-24, then compare the results to LLAMA and two state-of-the-art in-place update libraries for dynamic graphs, namely STINGER and GraphOne. Edges have a single property (called weight) and all vertices are initially loaded into the graph. For GraphOne, LLAMA and Teseo, we report the time to insert the edges and we do not include the build time, which takes long. Similar to LLAMA, in GraphOne, the changes are first appended to a write store, implemented as a circular buffer. The archiving phase, i.e., the build phase, moves the changes to the base graph stored in a multi-versioned adjacency list and creates a new level/version. We attribute the slow performance of GraphOne shown in the figures to the fact that GraphOne uses a circular buffer when applying the updates. If the archiving phase is delayed the circular buffer gets filled and the threads are blocked until the buffer is emptied into the main store. Moreover, although Teseo implements in-place updates, it requires a rebalancing of the implicit trees to manage the gaps for the incoming edges in the segments, causing its slowdown compared to CSR++. We observe from
Figure 11a,b, that CSR++ outperforms the four libraries. CSR++ is up to 2.6× faster than STINGER, due to the fact that STINGER performs a search over the neighbors of a vertex upon every edge insertion. If the edge is found, it updates the timestamp and the weight, otherwise depending on the availability of memory, it allocates a block to store the new edge. Moreover, CSR++ is 2.8× than GraphOne, and 9.5× than LLAMA on the uniform-22 graph. On the uniform-24, CSR++ is up to 2.6× faster than STINGER, up to 2.2× than GraphOne, and 12× faster than LLAMA. For example, Twitter nowadays averages 5700 tweets per second, and peaked at 140,000 tweets per second [
49]. As shown in
Table 5, CSR++ would easily be capable to support such workload. In reality, CSR++ is much faster than the others that what we reported above, because building is an integral part for using those data structures.
4.9. Updates: Memory Consumption
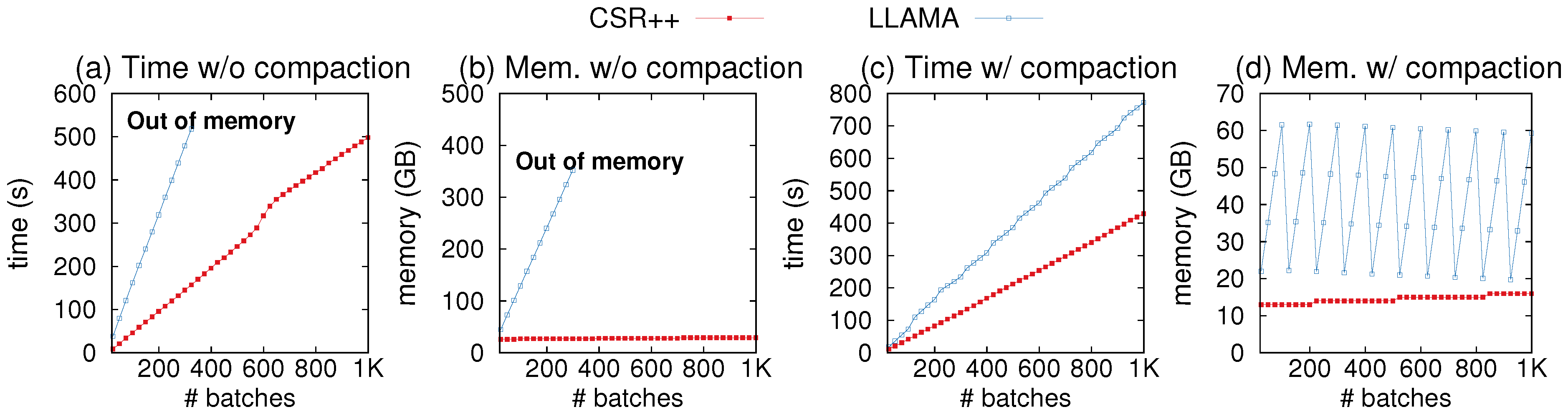
We compare CSR++ to the other data structure in terms of memory consumption in the presence of updates. First, we compare CSR++ to LLAMA for graph insertions. In
Figure 12, we show the edge insertion latency and memory consumption as we apply 1000 batches of insertions (equivalent to the 0.02% workload in
Figure 10), and print the memory usage and timestamp after inserting each batch. As shown in
Figure 12a,b, the memory usage of LLAMA explodes after applying 370 batches, causing the system to run out of memory. In contrast, CSR++ consumes memory proportional to the actual graph size. Additionally, CSR++ is up to 2.7× faster in performing the insertions.
LLAMA provides a function to compact all snapshots into a single one.
Figure 12c,d show the performance of CSR++ and LLAMA with compaction. After every 100 batches, we compact all 100 snapshots. LLAMA’s memory usage increases until compaction is invoked, but it is still higher than CSR++ even immediately after compaction. Note that the compaction method in LLAMA does not provide instructions for building the reverse edges, hence these figures show the performance of inserting only forward edges. In principle, building the reverse edges is significantly more expensive than building forward edges, i.e., if the reverse operation was included, the cost of compacting would be significantly higher. Compacting 100 snapshots with only direct edges in LLAMA takes up to 40 s with a single thread and 5–7 s with 36 threads. As shown in
Figure 12c, CSR++ is still consistently faster than LLAMA by a factor of approximately 1.8×.
Second, we compare CSR++ to other data structures, by measuring the memory consumption and update throughput. We load the uniform-24 graph, then apply a stream of edge updates with 36 threads, using a log of updates as provided by the GFE framework. The updates consist of a mix of edge insertions and deletions. For CSR++, we use physical deletion without a binary search (i.e., every deletion needs to pay the price of a linear scan in the neighbor list of a vertex), as we do not sort edges after each operation. As we show later, this does not affect how high performing CSR++ is compared to other systems.
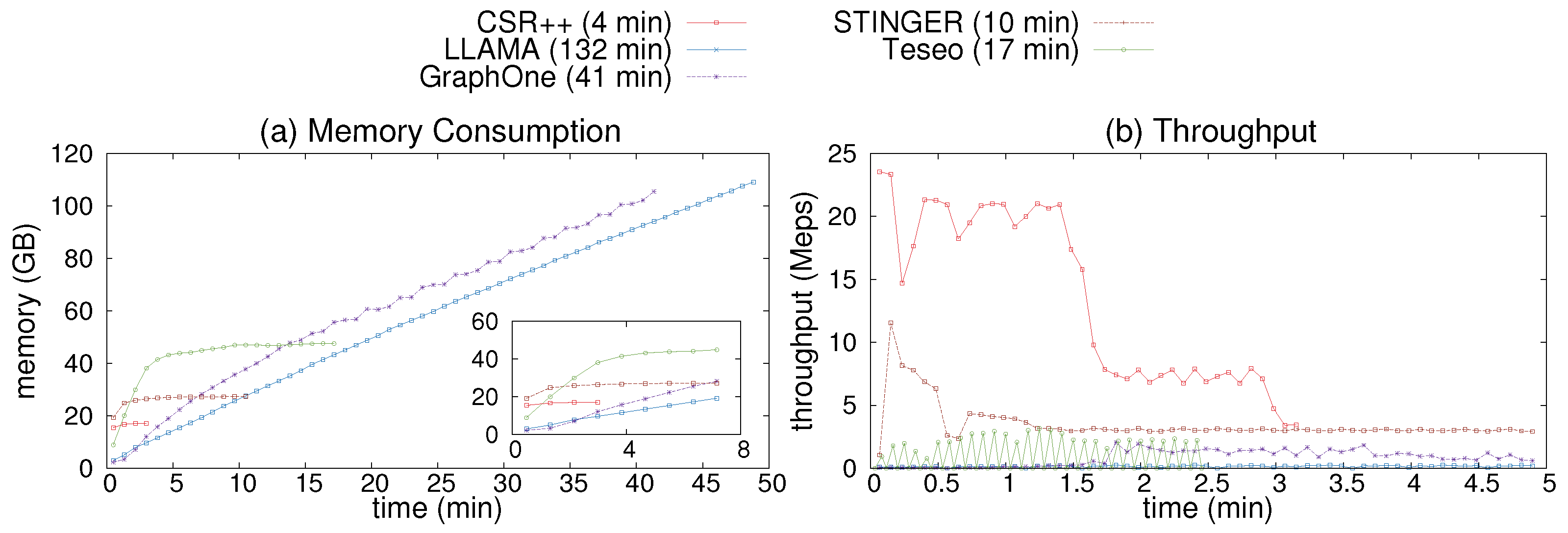
Figure 13a shows memory consumption during the first 70 min of the execution of the experiment. LLAMA creates multiple snapshots which causes an out-of-memory error as it exceeds the memory size after multiple updates (similarly to the experiment of
Figure 12d). GraphOne is second to consume more memory as it lacks an implementation of garbage/memory collection. STINGER, Teseo, and CSR++ incur less memory overhead since they perform in-place updates. After the first 10 batches of the updates, they all have stable memory consumption until the end of the execution.
Figure 13b shows the update throughput during the first 7 min. CSR++ and STINGER exhibit a high update throughput, reaching up to 24 and 10 Meps (million edges per second) respectively. This is due to the fact that both systems perform updates in place. On the other hand, Teseo and GraphOne are slower but still achieve higher throughput than LLAMA, with up to 2.5 Meps and 2 Meps respectively. Teseo performs transactional updates which incurs more overhead, while GraphOne does not guarantee the consistency of updates internally.
4.10. Updates: Edge Deletions
To support edge deletions, we modify our vertex and edge iterators in CSR++ to check whether a vertex or an edge is deleted, using the embedded flag in their respective structures. For LLAMA, we enable the deletion vector which similarly adds the cost of checking whether edges are deleted.
Figure 10c shows the time CSR++ takes to perform edge deletions. Each data point represents the time to delete a whole batch of edges. The scalability is almost linear relative to the number of threads, and, as we increase the batch size, the effect of multi-threading is more noticeable.
With a single thread, deletions are more computationally heavy, and therefore slower than insertions, as can be seen in
Figure 10b,c. As we mention earlier, CSR++ does not store edge indices (it would be very memory consuming), which means that for every edge that is deleted, the thread needs to perform a (binary) search to find the target edge to delete logically. Note that the cost for supporting physical deletion of edges in CSR++ can “easily” be proportional to the cost of having to reshuffle edge properties to match the new edge array. As can be seen in
Figure 10c, physical deletions are an order of magnitude slower than logical deletions, however, memory consumption is lower. Both approaches scale well using multiple threads.
4.11. Analytics after Graph Updates
To evaluate CSR++ in a more realistic mutation context, we first load the initial 80% of the graph and simulate the insertion of a stream of updates (batches of new edges and new vertices), and then we evaluate PageRank. For insertions, this workload shows the impact of updates on the performance of the graph structures, e.g., for CSR++, reallocations of edge arrays and the added pointers to newly-allocated segments. For deletions, we examine the overhead of the extra conditional branch to check the deleted flags and the cost of virtual deletions.
Figure 14 shows the performance of PageRank with CSR++ and LLAMA after applying mutations to the graph using the benchmarks in Green-Marl. In
Figure 14a, we observe that, after inserting 100 batches of new edges, the performance of CSR++ only decreases by a factor of less than 1.25× as compared to CSR, which shows the moderate overhead that is caused by the continuous reallocations of edge arrays and the copy-on-write of the indirection layer. Additionally, LLAMA is faster than CSR++ by a factor of 1.12× but consumes ≈5× more memory than CSR++ (see also
Table 6). This is due to the 100 snapshots LLAMA stores as multi-versioning support. If we need to perform analytics on the latest version of the graph (which is the case of most real-world scenarios), the significant memory overhead of these snapshots may not be worth the minimal performance improvement.
Figure 14b shows a breakdown of the performance of CSR++ when inserting different numbers of new batches: Increasing the number of batches results in more reallocations and copy-on-write operations. CSR++ scales well in all cases and keeps the moderate overhead of ≈1.25× over CSR even after inserting 1000 batches.
Finally,
Figure 14c shows the performance of CSR++ and LLAMA after deleting one batch of edges of different sizes, relative to CSR++’s performance without deletions. As we mention earlier, we modified the iterators in CSR++ to check for deletion flags in vertices and edges. We delete up to 23 million edges from the 1.47 billion total edges of Twitter, and as expected, the performance is similar to that of the baseline (i.e., without deletions). The extra conditional branches in CSR++ do not introduce considerable overhead. In case there are only few deletions, branch prediction makes sure that these deletion checks have minimal overhead, resulting in performance close to the original implementation (i.e., without deletion checks). In contrast, LLAMA’s performance significantly suffers when enabling support for deletions and makes LLAMA ≈ 30% slower than CSR++.
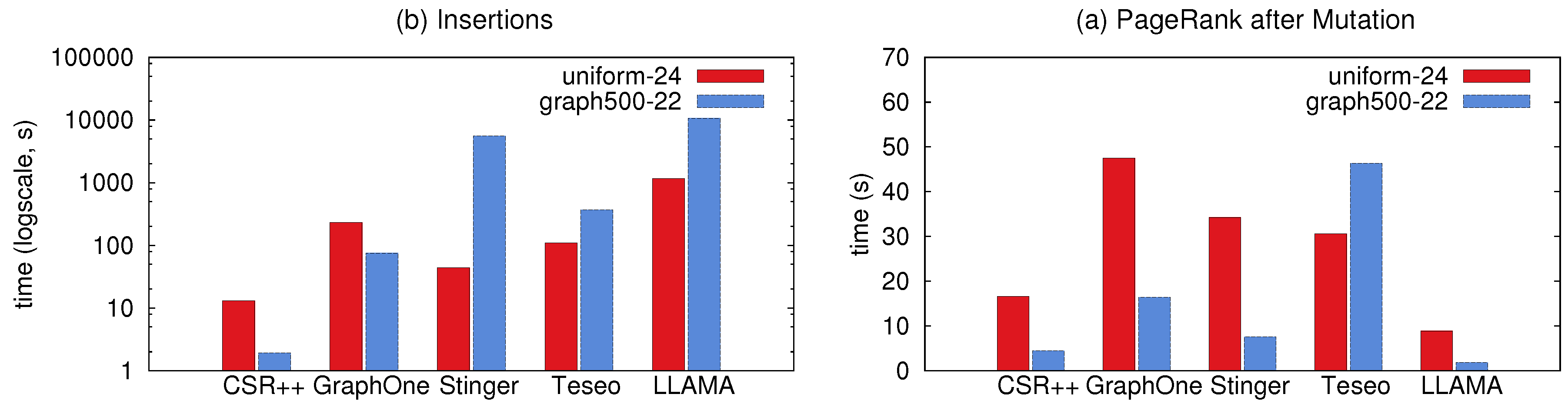
Figure 15 shows the performance of different systems when executing PageRank after applying a stream of updates using the benchmarks in GFE driver. In this experiment, we start with an empty graph then insert all vertices and edges as a stream to build uniform-24 graph and graph500-22. In
Figure 15b we report the update latency for both graphs (i.e., the time to insert all edges), before running PageRank as measured in
Figure 15a. For LLAMA, the insertion time includes the time to merge the snapshots and build the base level considering the multiple snapshots created during the insertions. The compacted levels cause LLAMA to have the best performance in PageRank as it resembles CSR.
4.12. Memory Footprint
We calculate the memory footprint of Twitter and LiveJournal graphs stored in CSR, CSR++, and LLAMA (read-optimized), both just after loading them in memory and after applying different numbers of batch insertions on Twitter (
Table 6).
As shown in
Table 6, CSR is the most compact representation and consumes the least memory—at the cost of mutability. The memory overhead of LLAMA is small when storing one snapshot (i.e., before applying mutations), but as can be seen in the same
Table 6, this overhead increases steeply when applying batches. It is primarily due to storing different delta snapshots of the graph for versioning. As mentioned earlier, for realistic workloads such as applying updates at a high frequency and then running analytics on recent versions of the graph, this memory overhead may lead to out-of-memory errors. As a reference, we include a second variant of LLAMA with implicit linking across snapshot versions, which trades performance for memory. The memory savings of this variant are low, however, and its performance is significantly worse (hence why our performance figures do not include it).
The default version of CSR++ has a moderate memory overhead of 33% compared to CSR, due to the pre-allocation of extra space for edge arrays. When this optimization is disabled, memory is allocated in a tight manner and CSR++ consumes closely to CSR.
Figure 1.
(1) An example graph with newly-inserted edges in green, represented in different graph structures: (2) CSR, (3) adjacency lists, and (4) LLAMA with implicit linking and deletion vectors.
Figure 1.
(1) An example graph with newly-inserted edges in green, represented in different graph structures: (2) CSR, (3) adjacency lists, and (4) LLAMA with implicit linking and deletion vectors.
Figure 2.
The building blocks of CSR++ for graph topology representation: segments, vertices and edges.
Figure 2.
The building blocks of CSR++ for graph topology representation: segments, vertices and edges.
Figure 3.
Diagram for Vertex Properties representation in CSR++.
Figure 3.
Diagram for Vertex Properties representation in CSR++.
Figure 4.
Diagram for Edge Properties representation in CSR++.
Figure 4.
Diagram for Edge Properties representation in CSR++.
Figure 5.
Sensitivity analysis of segment size. (a,c) Execution time and lock contention when inserting a batches of 2 million edges of different sizes in CSR++ using one lock per segment 1 to 24 threads; (b,d) Execution time and lock contention when inserting a batches of 2 million edges of different sizes in CSR++ using HTM and one lock per segment 1 to 24 threads; (f,h) Execution time of Sequential and Random scans using one lock per segment compared to the performance with size 8; (g,i) Execution time of Sequential and Random scans using HTM and lock elision compared to the performance with size 8; (e) Abort rate of HTM transactions when executing insertions form plot (b).
Figure 5.
Sensitivity analysis of segment size. (a,c) Execution time and lock contention when inserting a batches of 2 million edges of different sizes in CSR++ using one lock per segment 1 to 24 threads; (b,d) Execution time and lock contention when inserting a batches of 2 million edges of different sizes in CSR++ using HTM and one lock per segment 1 to 24 threads; (f,h) Execution time of Sequential and Random scans using one lock per segment compared to the performance with size 8; (g,i) Execution time of Sequential and Random scans using HTM and lock elision compared to the performance with size 8; (e) Abort rate of HTM transactions when executing insertions form plot (b).
Figure 6.
Impact of allocators on the update performance of CSR++. (a) Time to load 80% of Twitter (∼1.12 billion edges) in CSR++ using 3 different allocators using 1 to 36 threads; (b) Time to insert a batch of 1.6% (∼22 million edges) on the previously loaded 80% of Twitter in CSR++ without sorting using 1 to 36 threads and 3 different allocators.
Figure 6.
Impact of allocators on the update performance of CSR++. (a) Time to load 80% of Twitter (∼1.12 billion edges) in CSR++ using 3 different allocators using 1 to 36 threads; (b) Time to insert a batch of 1.6% (∼22 million edges) on the previously loaded 80% of Twitter in CSR++ without sorting using 1 to 36 threads and 3 different allocators.
Figure 7.
Read-only performance of CSR, CSR++, LLAMA, and adjacency lists (BGL).
Figure 7.
Read-only performance of CSR, CSR++, LLAMA, and adjacency lists (BGL).
Figure 8.
Scan performance on uniform-24 using multiple threads. (a,d) Time to retrieve out-degrees of all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and the other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (b,e) Time to retrieve the first neighbor in the list of neighbors for all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (c,f) Time to retrieve all neighbors of all vertices respectfully, in the graph in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads.
Figure 8.
Scan performance on uniform-24 using multiple threads. (a,d) Time to retrieve out-degrees of all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and the other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (b,e) Time to retrieve the first neighbor in the list of neighbors for all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (c,f) Time to retrieve all neighbors of all vertices respectfully, in the graph in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads.
Figure 9.
Scan performance on graph500-22 using multiple threads. (a,d) Time to retrieve out-degrees of all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and the other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (b,e) Time to retrieve the first neighbor in the list of neighbors for all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (c,f) Time to retrieve all neighbors of all vertices respectfully, in the graph in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads.
Figure 9.
Scan performance on graph500-22 using multiple threads. (a,d) Time to retrieve out-degrees of all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and the other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (b,e) Time to retrieve the first neighbor in the list of neighbors for all sorted and unsorted vertices respectfully, in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads; (c,f) Time to retrieve all neighbors of all vertices respectfully, in the graph in CSR++ and other systems using 1 to 36 threads.
Figure 10.
Graph mutations on Twitter. (a) Time to insert batches of edges of different sizes in CSR and CSR++ and sorting the edge arrays using 36 threads; (b) Time to insert different batch sizes in CSR++ without sorting using 1 to 36 threads; (c) Time to delete batch sizes of 0.2% and 0.02% from Twitter in CSR++ using physical (P) and logical (L) deletions.
Figure 10.
Graph mutations on Twitter. (a) Time to insert batches of edges of different sizes in CSR and CSR++ and sorting the edge arrays using 36 threads; (b) Time to insert different batch sizes in CSR++ without sorting using 1 to 36 threads; (c) Time to delete batch sizes of 0.2% and 0.02% from Twitter in CSR++ using physical (P) and logical (L) deletions.
Figure 11.
Edge insertions on graph500-22 and uniform-24. (a) Time to insert the edges of uniform-22 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne, Teseo and LLAMA using 1 to 24 threads; (b) time to insert the edges of uniform-24 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne, Teseo and LLAMA using 1 to 24 threads.
Figure 11.
Edge insertions on graph500-22 and uniform-24. (a) Time to insert the edges of uniform-22 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne, Teseo and LLAMA using 1 to 24 threads; (b) time to insert the edges of uniform-24 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne, Teseo and LLAMA using 1 to 24 threads.
Figure 12.
Memory consumption and batch insertion latency of update workloads with 36 threads. (a,b) Comparing CSR++ and LLAMA without compaction; (c,d) Comparing CSR++ and LLAMA with compaction after every 100th batch insertion.
Figure 12.
Memory consumption and batch insertion latency of update workloads with 36 threads. (a,b) Comparing CSR++ and LLAMA without compaction; (c,d) Comparing CSR++ and LLAMA with compaction after every 100th batch insertion.
Figure 13.
(a) Memory consumption of updates on graph uniform-24 during the first hour of execution; (b) Update throughput on uniform-24 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne and LLAMA using 36 threads during the first 7 min of the execution.
Figure 13.
(a) Memory consumption of updates on graph uniform-24 during the first hour of execution; (b) Update throughput on uniform-24 as a stream of single updates in CSR++, STINGER, GraphOne and LLAMA using 36 threads during the first 7 min of the execution.
Figure 14.
PageRank performance after graph updates. (a) Comparing performance of CSR, CSR++, and LLAMA after applying 100 (of size 0.2%) batches of new edges; (b) Performance of CSR++ after applying 12 (1.6%), 20 (2%), 100 (0.2%) and 1000 (0.02%) batches of new edges, CSR is used as a baseline; (c) Performance of CSR++ and LLAMA after deleting one batch of edges of different sizes.
Figure 14.
PageRank performance after graph updates. (a) Comparing performance of CSR, CSR++, and LLAMA after applying 100 (of size 0.2%) batches of new edges; (b) Performance of CSR++ after applying 12 (1.6%), 20 (2%), 100 (0.2%) and 1000 (0.02%) batches of new edges, CSR is used as a baseline; (c) Performance of CSR++ and LLAMA after deleting one batch of edges of different sizes.
Figure 15.
Performance of data structures in LDBC Graphalytics Pagerank after inserting edges to an empty graph from the Uniform-24 and Graph500-22 graphs. (a) Performance of CSR++ after running PageRank on a populated graph; (b) the latency of edge insertions into an empty graph prior to the execution of PageRank in (a).
Figure 15.
Performance of data structures in LDBC Graphalytics Pagerank after inserting edges to an empty graph from the Uniform-24 and Graph500-22 graphs. (a) Performance of CSR++ after running PageRank on a populated graph; (b) the latency of edge insertions into an empty graph prior to the execution of PageRank in (a).
Table 1.
Data sets used in our evaluation.
Table 1.
Data sets used in our evaluation.
|
Data Set
|
#Vertices
|
#Edges
|
Source
|
| Twitter |
41 million |
1.4 billion |
real-world graph |
| LiveJournal |
4.8 million |
68 milion |
real-world graph |
| Graph500-22 |
2.3 million |
64 million |
synthetic |
| Uniform-24 |
8 million |
260 million |
synthetic |
Table 2.
Graph structures and the configurations that we use in our evaluation.
Table 2.
Graph structures and the configurations that we use in our evaluation.
|
Name
|
Type
|
Configuration
|
| CSR++ |
Segmentation based |
Pre-allocated extra space for new edges. Deletion support enabled only on deletion workloads, in order to have fair comparison to LLAMA that does not support deletions by the default. |
| BGL [43] |
Adjacency list |
Bidirectional with default parameters. |
| CSR [53] |
CSR |
Implementation in the Green-Marl library [53]. |
| LLAMA [57] |
CSR with delta logs |
Read- and space-optimized with explicit linking. The fastest overall variant of LLAMA. Deletion support enabled only on deletion workloads. |
| STINGER [22] |
Blocked Adjacency List |
Linked list of blocks storing up to 14 edges. |
| GraphOne [21] |
Multi-level Adjacency List and Circular Edge Log |
Ignored archiving phase. |
| Teseo [23] |
Transactional Fat Tree based on Packed Memory Arrays |
Asynchronous rebalances delayed to 200ms and 1MB maximum leaf capacity. |
Table 3.
Algorithms used in our evaluation.
Table 3.
Algorithms used in our evaluation.
|
Algorithm
|
Description
|
| PageRank |
Computes ranking scores for vertices based on their incoming edges. |
| Weakly Connected Components (WCC) |
Computes affinity of vertices within a network. |
| Breadth-First Search (BFS) |
Traverses the graph starting from a root vertex, visits neighbors, and stores the distance of vertices from the root vertex, as well as parents. |
| Weighted PageRank |
Computes ranking scores like the original PageRank, but with weights and allows a weight associated with every edge. It requires accesses to edge properties. |
Table 4.
Memory overhead for different segment sizes of CSR++.
Table 4.
Memory overhead for different segment sizes of CSR++.
| Segment Size |
8 |
32 |
128 |
512 |
1024 |
2048 |
4096 |
16,384 |
32,768 |
| Memory overhead in bytes |
869,616 |
217,368 |
54,288 |
13,536 |
6768 |
3384 |
1656 |
360 |
144 |
Table 5.
Time to add new vertices to the Twitter graph in milliseconds.
Table 5.
Time to add new vertices to the Twitter graph in milliseconds.
|
#Vertices
|
10 K
|
100 K
|
1 M
|
10 M
|
| Time (ms)—0 vertex properties
|
1.6 |
11 |
120 |
1188 |
| × (ms)—50 vertex properties |
10 |
32 |
181 |
1259 |
Table 6.
Memory footprint of different graph structures in GB in read-only workloads and after inserting a different number of batches (Twitter-x, where x is the number of batches).
Table 6.
Memory footprint of different graph structures in GB in read-only workloads and after inserting a different number of batches (Twitter-x, where x is the number of batches).
|
Graph Structure
|
LiveJournal
|
Twitter
|
Twitter-12
|
Twitter-20
|
Twitter-100
|
| CSR |
0.53 |
11.09 |
11.09 |
11.09 |
11.09 |
| CSR++ read-only |
0.57 |
11.54 |
- |
- |
- |
| CSR++ |
0.82 |
16.55 |
16.55 |
16.55 |
16.55 |
| LLAMA |
0.58 |
11.56 |
21.66 |
27.03 |
78.00 |
| LLAMA implicit linking |
0.58 |
11.56 |
19.02 |
23.99 |
73.64 |