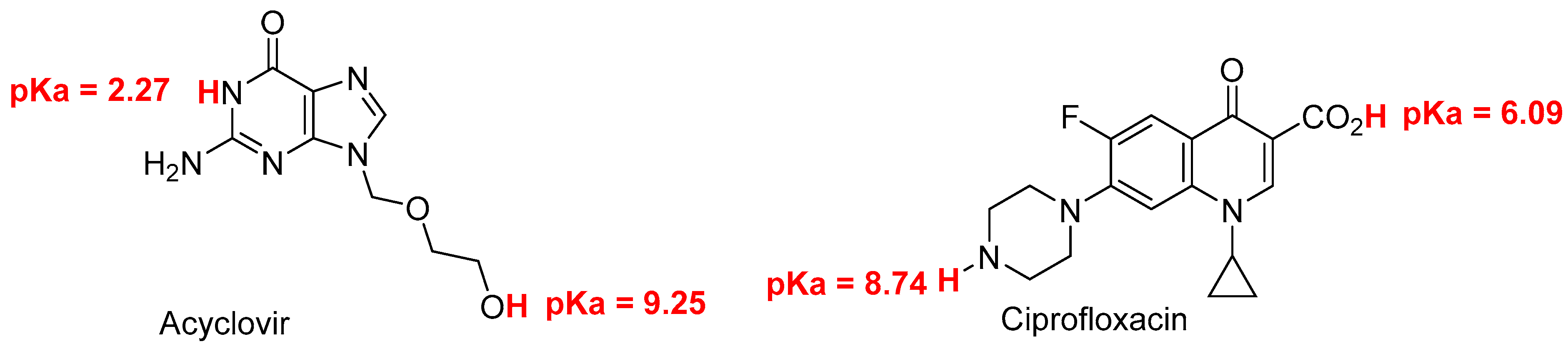1. Introduction
Intravenous (IV) drug administration plays a pivotal role in the treatment of severe infections and heavy pathologies. To ensure effective patient care, healthcare professionals frequently encounter the need for simultaneous or sequential administration of multiple medications. However, the co-administration of drugs via IV injection, best known as Y-site administration raises concerns about incompatibility and the potential for physicochemical interactions (PIC) that may compromise therapeutic efficacy, patient safety or both [
1,
2]. It is essential to differentiate a physicochemical incompatibility from a pharmacological drug interaction. In the case of physicochemical incompatibility, drugs interact and cancel each other out before reaching their target. On the other hand, in a pharmacological drug interaction, the drugs reach their biological target and produce their effects, which are themselves antagonistic or responsible for an increase in toxicity.
In this context, incompatibility studies are essential to assess the physical and chemical stability of drug combinations and to determine the potential for precipitation, pH changes, drug degradation, or the formation of byproducts with potential side effects [
3,
4,
5]. Such investigations provide valuable insights into the feasibility and safety of co-administration, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding IV drug therapy and ensuring optimal patient outcomes [
6,
7].
The incompatibility issue concerns the major classes of drugs and especially those bearing acidic and/or basic characters [
8].
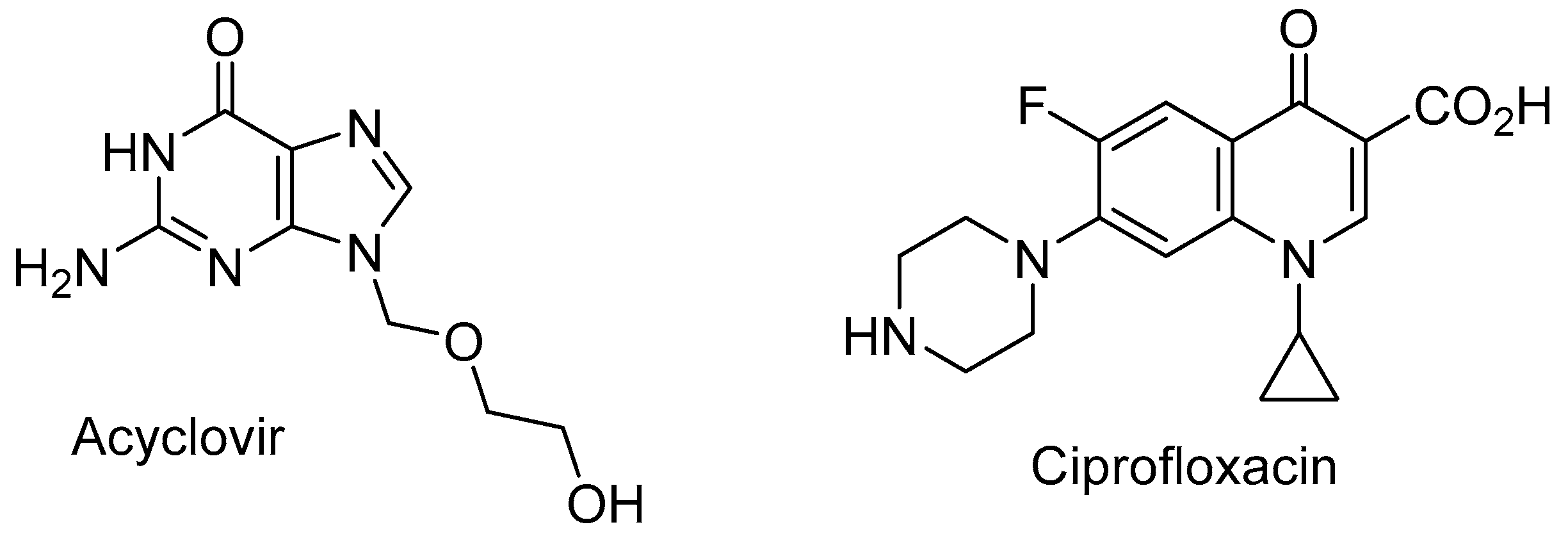
In this study, we focused our efforts on two major drugs: acyclovir and ciprofloxacin (
Figure 1). Acyclovir, (9-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]guanine), a nucleoside analogue of the guanosine family, is a widely used antiviral drug as tablets, topical creams and intravenous injections [
9]. Neutral acyclovir suffers from poor solubility in water (1.2−1.6 mg/mL at 25°C limiting its absorption into the gastrointestinal tract when taken orally [
10,
11]. Ciprofloxacin, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic agent in the fluoroquinolone class used to treat bacterial infections [
12]. The simultaneous administration of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin may be necessary in certain clinical scenarios, such as the treatment of patients with co-existing viral and bacterial infections or the prevention of secondary infections during viral outbreaks [
13]. Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate the incompatibility of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin solutions when co-administered via IV infusion.
Although individual compatibility/incompatibility studies were conducted for acyclovir and ciprofloxacin with other medications [
14,
15], limited or even non-existent scientific data regarding their compatibility when combined in a co-administration therapy (Y-cite administration). Considering the widespread use of these drugs, the absence of comprehensive compatibility information recalls significant challenges in clinical practice. Consequently, healthcare professionals must resort to empirical approaches or rely on anecdotal evidence to guide the co-administration of these two drugs.
The aim of this study is to investigate the incompatibility of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin solutions during Y-cite administration. By employing rigorous analytical techniques and monitoring key physicochemical parameters, we aim to provide evidence-based recommendations regarding the feasibility and safety of their simultaneous administration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Products, Solvents and Consumables
The following products, solvents and consumables have been used : acyclovir (Mylan) powder for injectable solution, ciprofloxacin (Fresenius Kabi) 400 mg/200 mL, sodium chloride (Fresenius Kabi) 0.9% (9g/1000 mL), methanol HPLC Grade (Carl Roth), distilled water, phosphoric acid (Sigma-Aldrich) 85%, di-sodium hydrogenophosphate (Prolabo), sodium hydroxide tablets (ChemLab), hydrochloric acid (ChemLab), vials (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Eppendorf and Falcon tubes.
2.2. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
Chromatographic analyses were performed using the Agilent 1100 series HPLC system (Agilent Technologies) equipped with degasser G1322A, binary pump G1312A, autosampler G1329A, thermostatted column compartment G1316A and MWD UV detector (G1365B). The compounds were separated on a Select® Peptide CSHTM C18, 150 x 4.6 mm, 2.5 μm, 130 Å column at 40 °C. The injection volume was fixed at 10 µL. Mobile phase, composed of distilled water (containing Na2HPO4, 20 mM and phosphoric acid, pH=3) and methanol (60/40, v/v), was used for isocratic elution at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The detector monitored the elution at 205, 260 and 273 nm for simultaneous detection of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin over a period of 10 minutes. The obtained chromatograms were analyzed using ChemStation B.04.03 software.
2.3. Stock Solutions Preparation
The sampling of adequate volume were realized with 200 µL and 1000 µL micropipettes (Eppendorf France). Ciprofloxacin stock solution was prepared directly by sampling the commercial solution 2 mg/mL, concentration currently used in clinical practices [
16]. Acyclovir stock solutions were prepared by weighting powder with a precision balance (Denver Instrument) and then, by reconstituting with sodium chloride 0.9% at 2 mg/mL, in a Falcon tube. The solutions were manually stirred and sonicated for a minute with a Sonicator (Elma). For the screening experiment, stock solutions were prepared as follows: Ciprofloxacin (2 mg/mL). Acyclovir (500 mg) was dissolved in NaCl 0.9 % (100 mL) at 5 mg/mL.
2.4. Screening of Solutions Preparation by Visual Inspection
To start our investigation on acyclovir and ciprofloxacin, we performed a series of tests analyzed by visual inspection to have a glimpse of the behavior of those two drugs when administrated concomitantly. Acyclovir (concentration, reconstitution solvent) and Ciprofloxacine (concentration, reconstitution solvent) were prepared at five volume ratios (1/1, 1/2, 2/1, 1/9, 9/1). Samples were prepared in 0.5 mL Eppendorf tubes (non-sterile), appropriate volume of each drug (to reach desired ratio) was added with precision pipette. Each sample was made in triplicate. The visual inspections were performed with the same background and the same light source and physical stability was assessed by two observers. A second and a third visual inspection was performed at t = 2h (+/- 20 min) and at t = 13h (+/-1h). Each result was described according to the following nomenclature: Q0: clear solution; Q1: small amount; Q2: important amount; Q3: huge amount. The aspect of the solution is described as follows: P: particles/precipitate; C: crystals.
2.5. Assays of Stability of Acyclovir and Ciprofloxaxin at Different pH Values
In order to study the behavior of single drug solutions, seven samples containing 1 mL of stock solution of acyclovir at 2 mg/mL (see stock solutions preparation,
Table 1S in supporting information) were prepared by adjusting the pH with successive additions of 10 µL of hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide solutions at different concentrations (100 µM, 1 mM, 10 mM, 100 mM, 1M, 6M). Tubes were shaken manually. The same method and conditions were implemented to study the behavior of ciprofloxacin. Two replicates for each drugs were realized. pH measurements were taken using a pH-meter (FP20 Mettler Toledo). Once the pH was adjusted, samples were diluted 50 times with mobile phase (methanol and distilled water, phosphate buffer, pH=3, 50/50, v/v) in Eppendorf tubes in order to reach a drug concentration in linearity range. To avoid sampling of crystals or precipitates, volume samplings with micropipettes were made delicately at the top of the Eppendorf tube. After dilution and agitation of tubes, samples were transferred in vials and visually inspected to check the absence or presence of precipitate and/or crystals. Then, RP-HPLC analysis was performed at 0, 2, 4 and 24h.
2.6. Compatibility Studies
2.6.1. Drug Mixtures Preparation
From acyclovir and ciprofloxacin stock solutions at 2 mg/mL, drug mixtures were prepared at different volume ratios (1:1, 2:1, 1:2, 9:1, 1:9) (for details, See
Table 1S in supporting information). Tubes were shaken manually. The ratio 1:2 were prepared in ten replicates, the ratios 1:1 and 2:1 in five replicates and the ratios 9:1 and 1:9 in triplicate. Before analyses, ratios 1:1, 2:1 and 1:2 were diluted 50 times and ratios 9:1 and 1:9, 20 times, with mobile phase (methanol and distilled water, phosphate buffer, pH = 3, 50/50, v/v) in order to obtain drug concentrations in the linearity ranges. To avoid sampling of crystals, volume sampling were made delicately at the top of the Eppendorf tube. After dilution and agitation of tubes, samples were transferred in vials and visually inspected to observe the presence/absence of impurities or crystals.
2.6.2. Preparation of Controls for the Two Drugs
From acyclovir stock solutions, controls were prepared in four replicates for ratios 1:1 and 2:1, in five replicates for ratio 1:2 and in triplicate for ratios 9:1 and 1:9. From ciprofloxacin stock solution, controls were prepared in four replicates for ratios 1:1, 2:1 and 1:2 and in triplicate for ratios 9:1 and 1:9. Mimicking theoretical concentrations, controls were prepared by adding corresponding volume of mobile phase (methanol and distilled water, phosphate buffer, pH = 3, 50/50, v/v). Then, each control was diluted 50 times for ratios 1:1, 2:1 and 1:2 and 20 times for ratios 9:1 and 1:9 with the same scheme as for drug mixtures.
2.6.3. Physical Compatibility Studies
Measurement of pH with indicating pH paper and visual inspection with unaided eye, facing daylight, as compared control solutions, immediately after mixing and after 2, 4 and 24h of contact, in order to observe physical changes of solutions (precipitation, color change…) were performed on each volume ratios.
2.6.4. Chemical Compatibility Studies
RP-HPLC analyses were performed on diluting samples immediately after preparation and after 2, 4 and 24h of contact. For controls, RP-HPLC analyses were realized only after preparation. The obtained data concerned peak area and permitted to calculate the mass of each drug in mixtures. A recovery percentage was defined as the ratio between the measured mass and theoretical mass of the drug in mixture. Therefore, a chemical incompatibility was characterized by a recovery percentage less than 90%, i.e. a decrease of 10% (5% in the case of drugs with a narrow therapeutic margin) of measured concentration compared with the theoretical concentration. The data were processed using Excel software.
2.7. HPLC Method Validation
Validation of parameters of the HPLC method was assessed in accordance with International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines concerning linearity as well as the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) [
17,
18].
2.7.1. Standard Solutions Preparation
An external calibration method, useful to quantify the amount of drug remaining in test samples. For Acyclovir, seven samples were prepared from stock solution (2 mg/mL) in duplicate via successive dilution (0.2; 0.15; 0.1; 0.05; 0.025; 0.01 and 0.005 mg/mL) with methanol and distilled water, phosphate buffer, pH=3, 50/50. For ciprofloxacin, five samples were prepared from stock solution (2 mg/mL) in triplicate via successive dilution (0.2; 0.1; 0.05; 0.005 ad 0.0025 mg/mL) with methanol and distilled water, phosphate buffer, pH=3, 50/50. After dilution, manual agitation, transfer in a vial and visual inspection in order to verify the absence of impurities or precipitates were performed. Then, samples were immediately analyzed by RP-HPLC (isocratic method, 40% methanol over 10 min).
2.7.2. System suitability
A system suitability testing was carried out by determining the peak retention time and the area, and by calculating the resolution, the selectivity factor, the number of theoretical plates and the symmetry factor [
17]. This test was performed on five replicates of the ratio 1:1 (v:v), analyzed immediately after mixing (for more details, see Table 2S in supporting information).
2.7.3. Specificity, Linearity, Range/Limit of Detection and Quantification
Specificity of the method was considered as validated if no peaks other than acyclovir and ciprofloxacin appeared on the chromatograms. Linearity was established through the construction of calibration curves using two standard ranges containing seven standard solutions for acyclovir and three standard ranges containing five standard solutions for ciprofloxacin (See Standard solutions preparation) [
17]. To assert linearity, the coefficient of determination (R2) had to be higher than 0.999 [
19]. The detection limit and the quantification limit were determined using the method based on the signal-to-noise ratio: LOD = (3*h*m)/(2*H) and LOQ = (10*h*m)/(2*H) (with h = higher fluctuation of the background noise in the blank, determined over a distance equal to 5 times the width at mid-height of the peak corresponding to the product concerned and located on either side of the place where the peak would be observed ; H = height of the peak concerned; m = theoretical drug mass).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening of Drug Mixtures at Different Ratios
Acyclovir and ciprofloxacin were mixed at five different ratios (volume/volume). The quantity of each drug is the same in each volume. Visual observation were made at three different time intervals. A shown in
Table 1, as expected at time zero, the solution was limpid and clear indicating the drugs are more likely to be intact and they are in their expected forms. After two hours, small amounts of crystals were observed except when the amount of acyclovir is in large excess (ratio 9/1). Important amount of crystals were observed after 24 hours for ratios 1/1, 1/2 and 1/9. However, no crystals were observed when acyclovir is prominent (ratios 2/1 and 9/1). These observations were confirmed by recovery studies using HPLC analyses (see section 4.3).
Table 1.
Visual observation of acyclovir/ciprofloxacin combinations.
Table 1.
Visual observation of acyclovir/ciprofloxacin combinations.
| Ratio |
1/1 |
1/2 |
2/1 |
1/9 |
9/1 |
| Time (h) |
0 |
2 |
24 |
0 |
2 |
24 |
0 |
2 |
24 |
0 |
2 |
24 |
0 |
2 |
24 |
| Observation |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3.2. Influence of pH on Recovery of Acyclovir and Ciprofloxacin
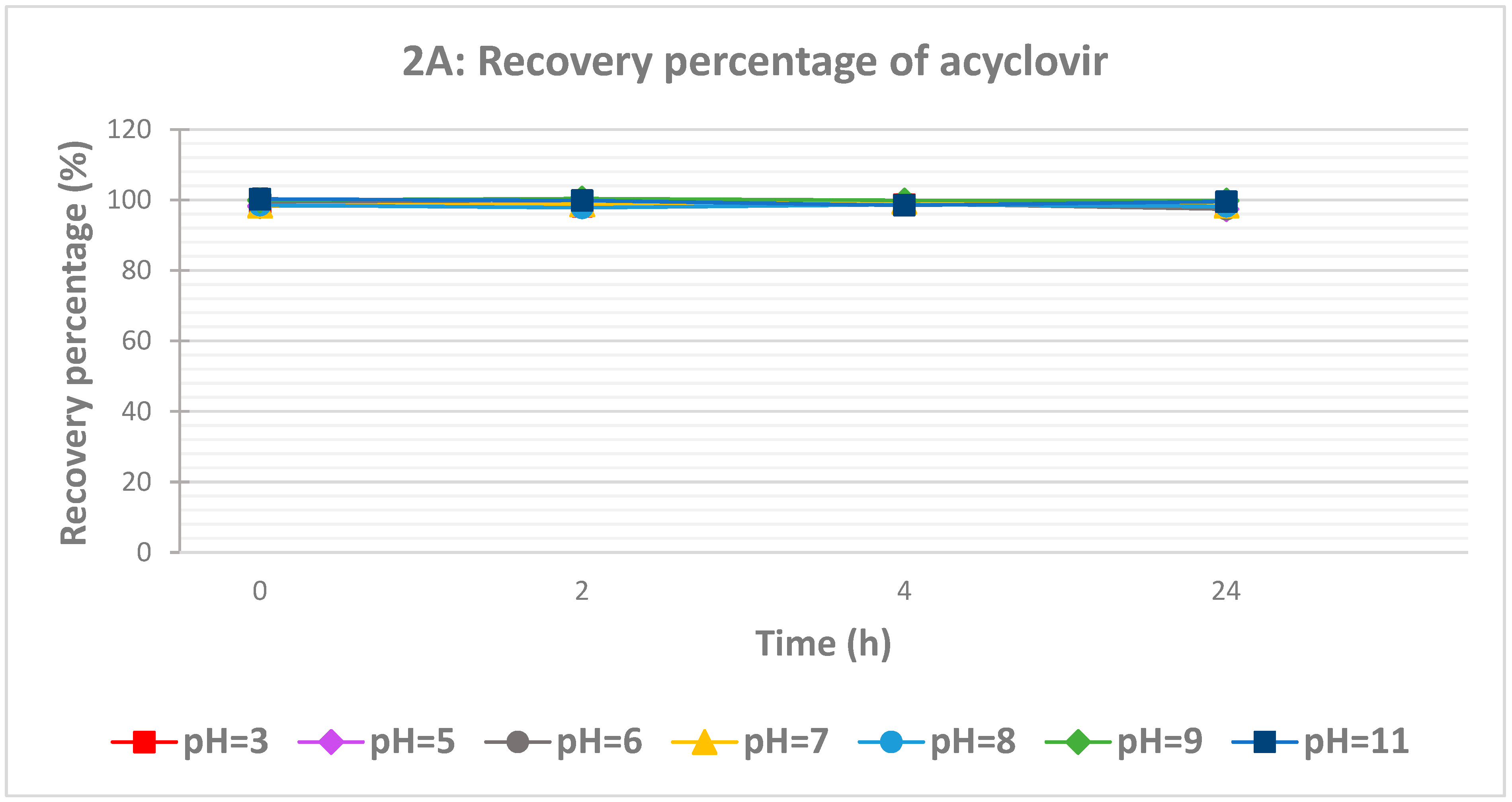
The influence of pH on the recovery of both drugs was studied at eight different pH ranging from 3 to 11 (
Figure 2). For acyclovir, the influence of pH was insignificant as the recovery was quantitative at different time intervals (
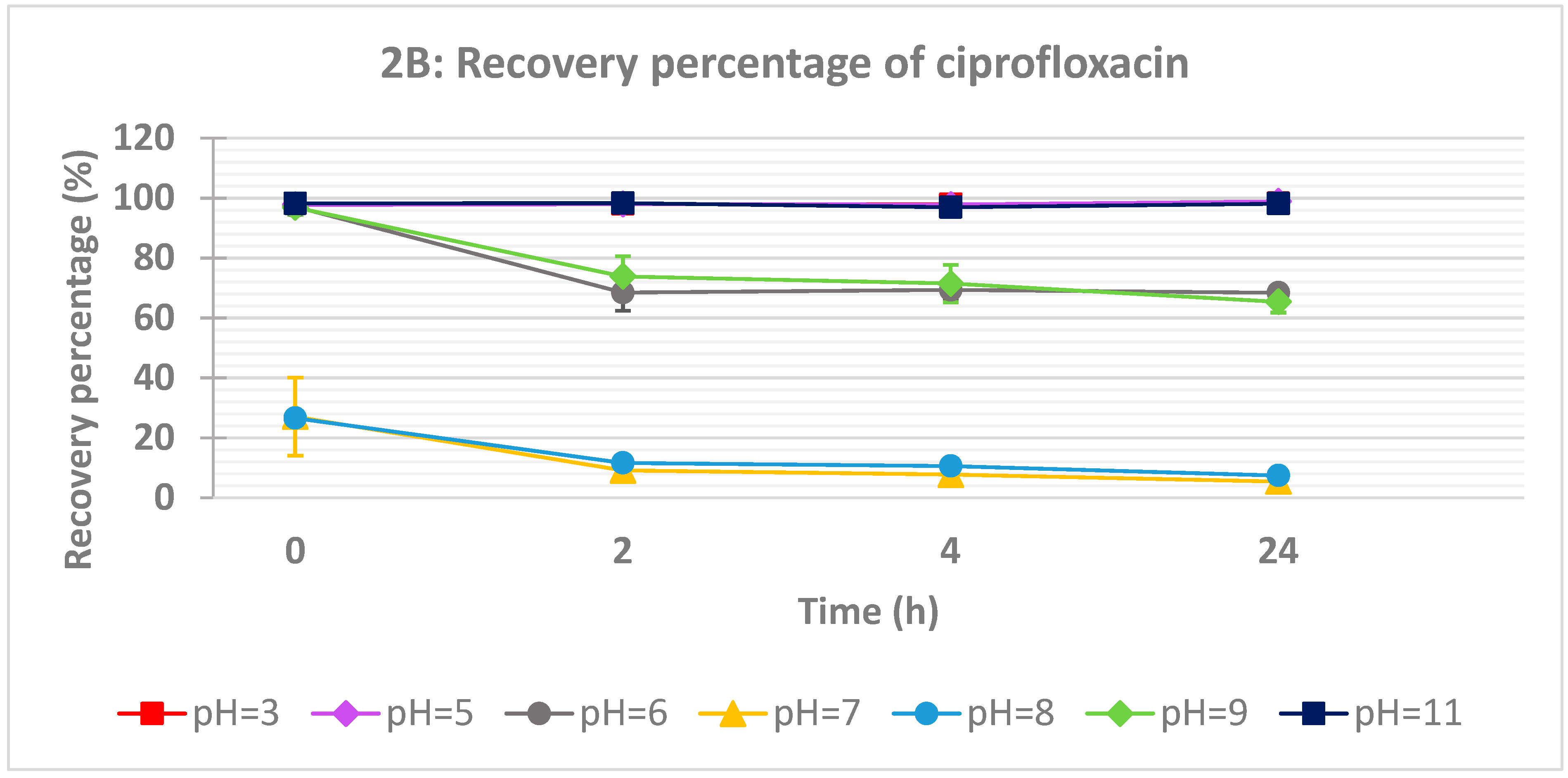
Figure 2A). However, the pH and time effects on ciprofloxacin recovery are more marked compared to acyclovir (
Figure 2B).
At near neutral pH values (7.22 and 7.97), the recovery of ciprofloxacin drops strongly even at time zero. The recovery was dropped below 10% after 24 hours. From the pKa values of ciprofloxacin (
Figure 3) [
20,
21], at neutral pH and near isoelectric point the carboxyl and the secondary amino groups are mainly charged but the sum of the charges is close to zero and the molecules as a whole is neutral resulting in the solubility dropping (
Figure 3). At slightly acidic conditions (pH = 5), around 75% of the drug was recovered after 2, 4 and 24 h. The same behavior is observed at slightly basic conditions (pH = 8.72 and 9.24). At strong acidic or basic conditions, the recovery is almost total. So as can be expected, ciprofloxacin is an amphoteric drug allowing that at acidic and basic conditions, the drug is in its ionized form which is compatible with higher solubility.
3.3. Compatibility/Incompatibility Studies by HPLC
3.3.1. Validation of the RP-HPLC Method
In order to asses that the system is working perfectly, we conducted the system suitability testing regarding the retention time, the resolution and selectivity factor [
17] (For more details, see Table 2S in the supporting information section).
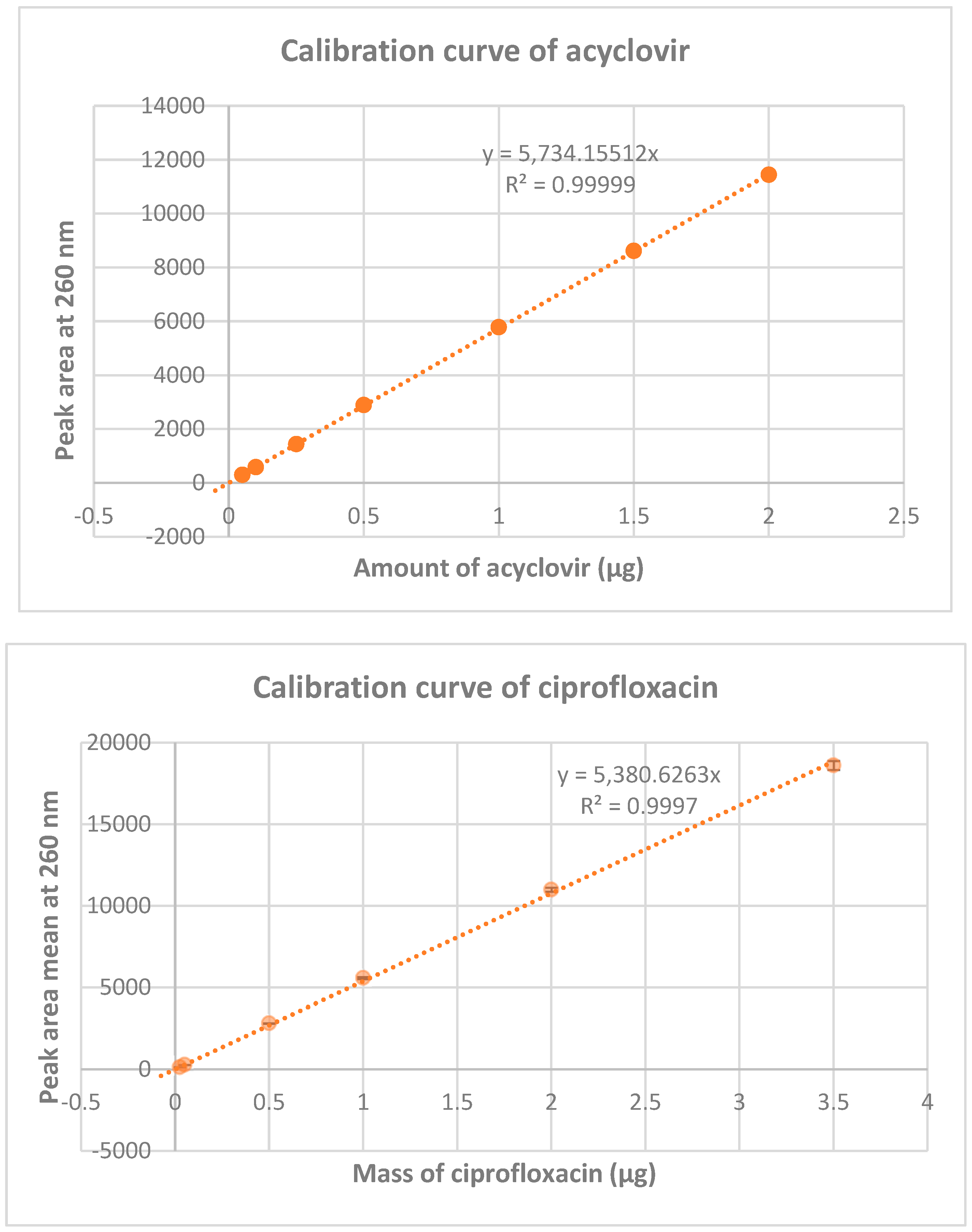
The calibration curves of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin were realized by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography and are shown in
Figure 3. The calibration curve of acyclovir indicate a linearity of the peak area from 0.05 to 2 µg (mass concentration of 0.005 to 0.2 mg/mL), whereas for ciprofloxacin it indicate a linearity of the peak area from 0.025 to 2 µg of ciprofloxacin (mass concentration of 0.0025 to 0.2 mg/mL). (for more details, see Table 3S in the see supporting information section). These curves were used to monitor the percentage of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin in mixtures at different ratios and different times intervals.
Figure 3.
Calibration curve of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin. Calibration were realized at 260 nm on two standard ranges (n=2) for acyclovir and n=3 for ciprofloxacin.
Figure 3.
Calibration curve of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin. Calibration were realized at 260 nm on two standard ranges (n=2) for acyclovir and n=3 for ciprofloxacin.
3.3.2. Compatibility/Incompatibility of Acyclovir and Ciprofloxacin Mixture
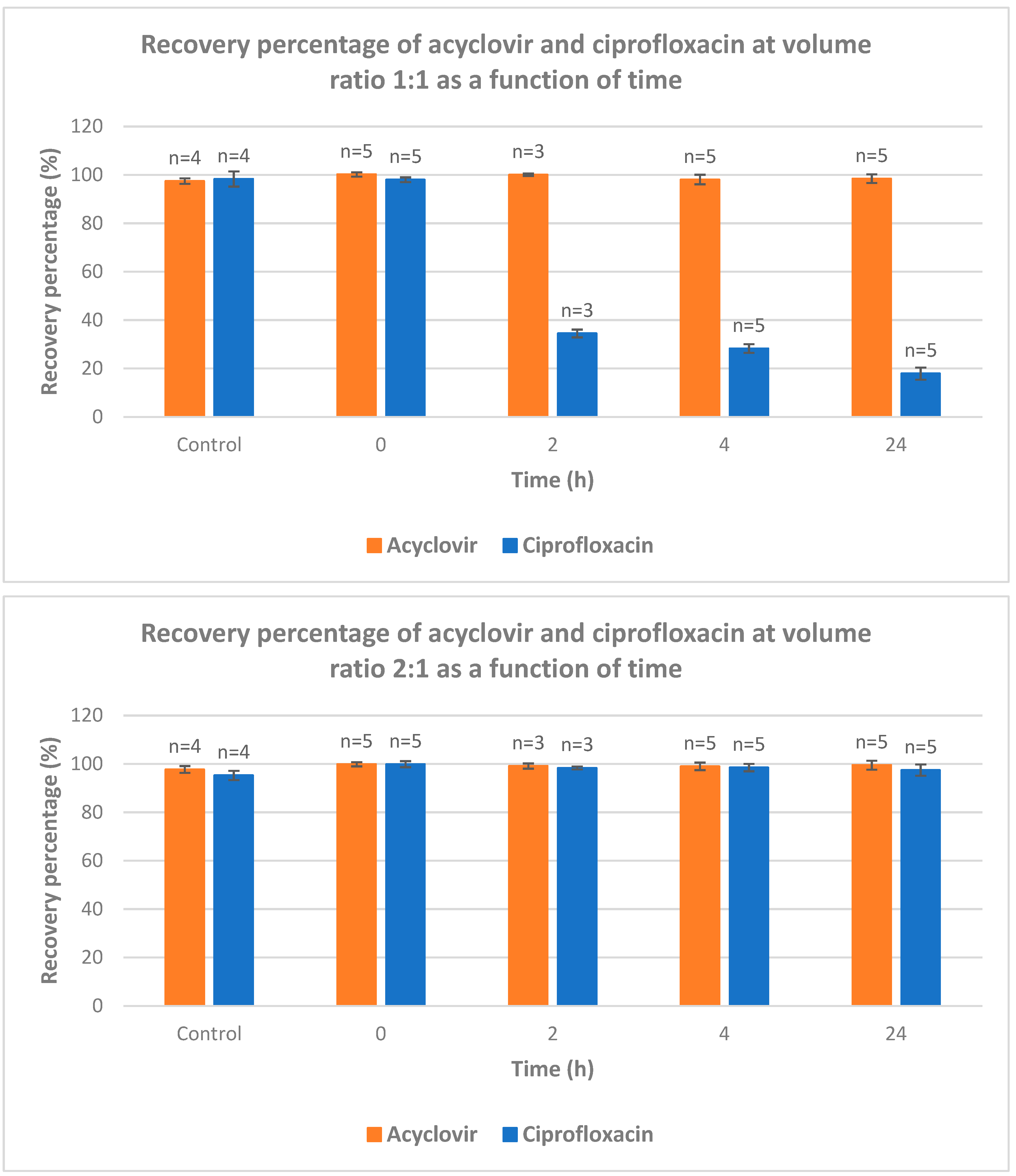
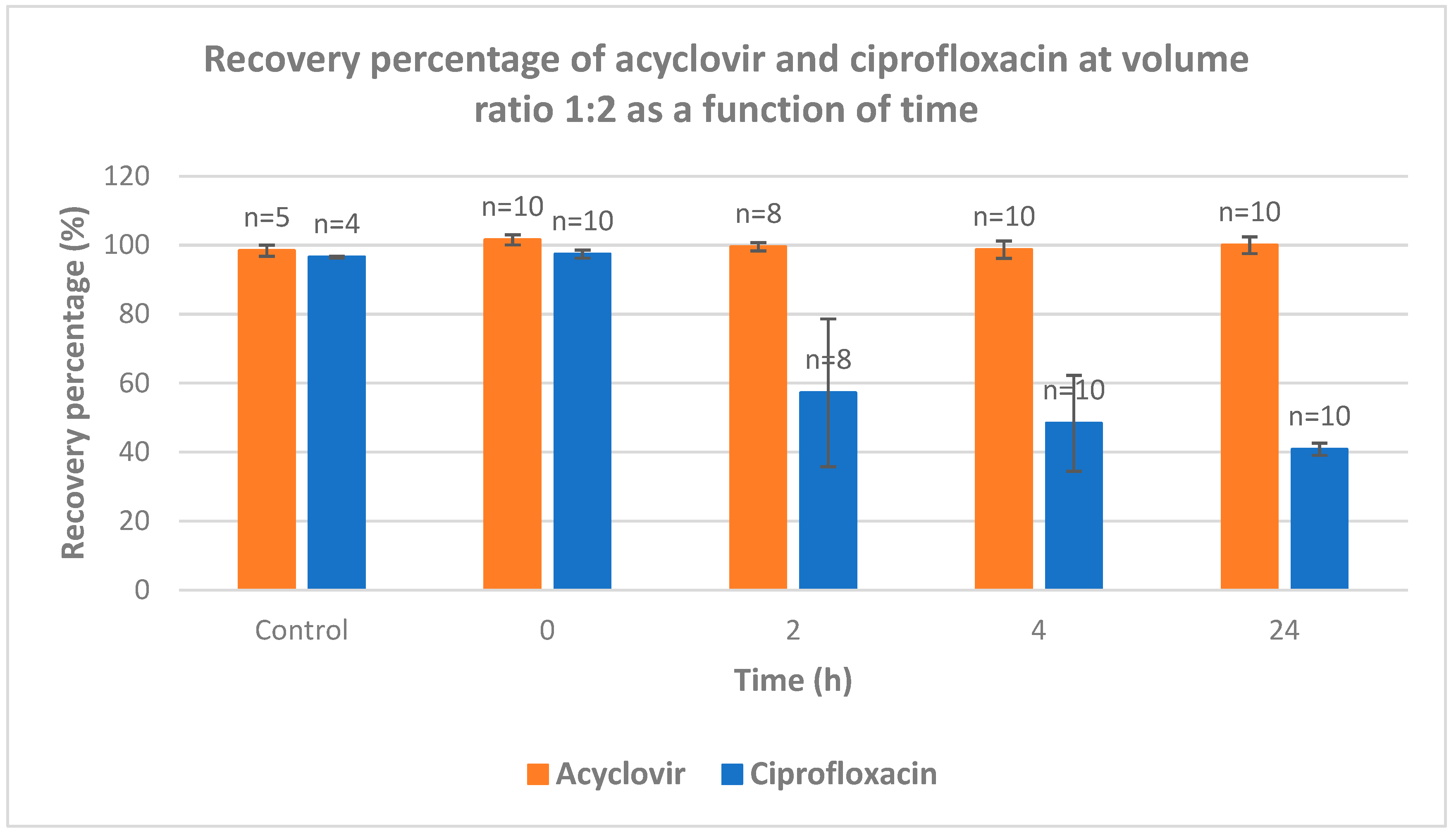
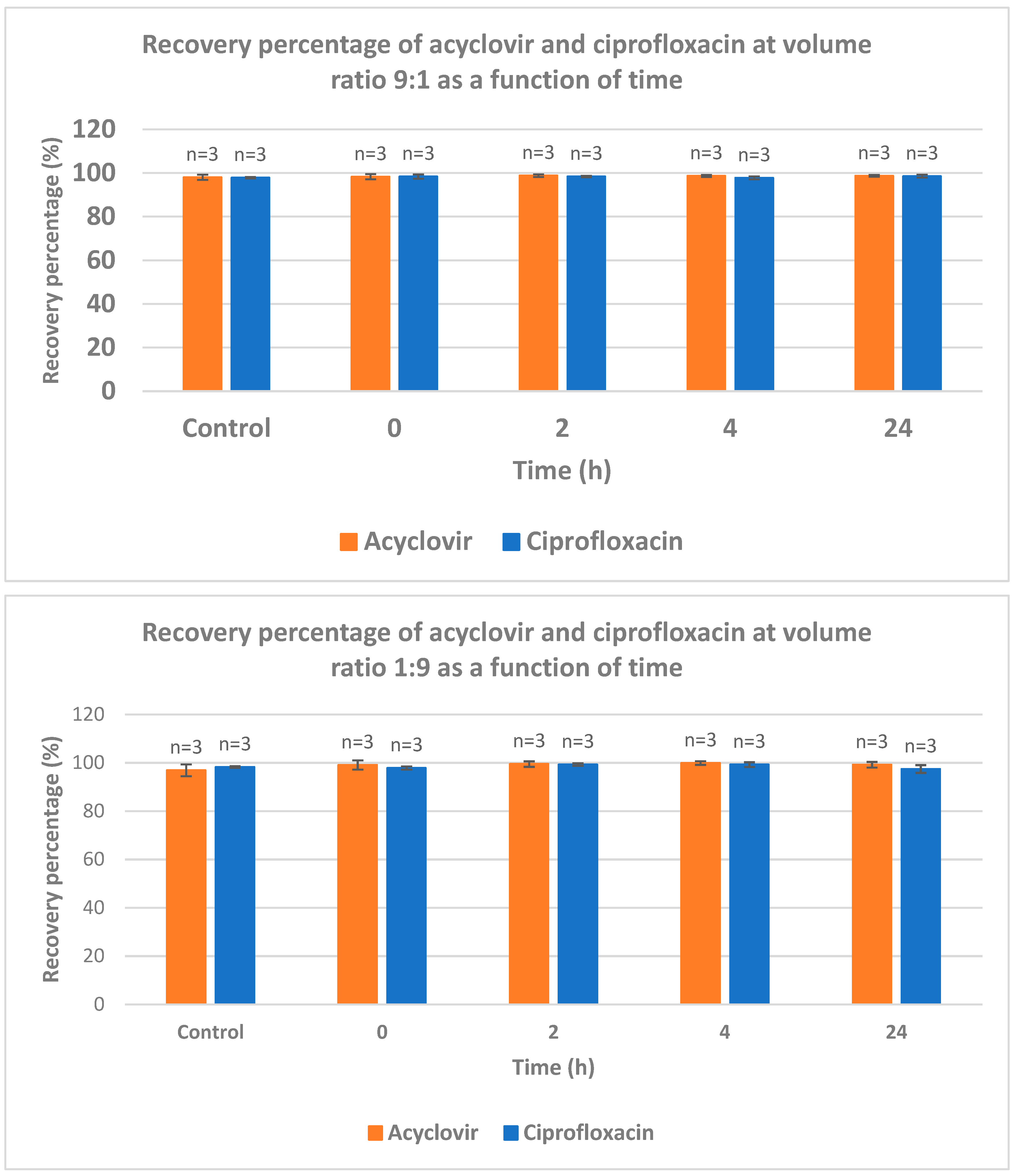
The recovery of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin was measured by RP-HPLC at five different ratios (1/1; 2/1; 1/2; 9/1 and 1/9) and time intervals (from 0 to 24 h) (
Figure 4). At ratio 1/1, the recovery of ciprofloxacin is severely dropped after 2 hours of contact. After 24 h, less than 20% of ciprofloxacin was recovered. At 2/1 ratio, a total recovery of both drugs is measured. When the latter ratio was inversed (from 2/1 to 1/2), the recovery of acyclovir was total whereas the recovery percentage of ciprofloxacin was around 35, 30 and 18% after 2, 4 and 24 intervals, respectively. When the acyclovir is present in large excess (ratio 9/1), the recovery of both drugs is almost quantitative which is in agreement with what observed with ratio 2/1. The ratio 1/9 gave the same results as ratio 9/1 with both compounds recovered almost quantitatively.
The consequences of IPCs can be multiple. First of all, an IPC can result in a loss of active ingredient (following precipitation or degradation) and therefore an incorrect dose delivered to the patient. Catheters could become clogged due to the formation of a precipitate in them, preventing the medication from being administered to the patient. In addition, the precipitates can cause embolism if they reach the general circulation, crystals could be deposited in the organs and cause inflammation. Following gas release, gas bubbles could reach the patient's systemic circulation, thereby creating a risk of gas embolism. Finally, the secondary derivatives that can be produced can turn out to be toxic. All of these problems are likely to lead to a reduction in the effectiveness of medications, therapeutic failure or even jeopardize the patient's vital prognosis.
Interactions between acyclovir and ciprofloxacin is not documented. However, this does not necessarily mean that no interactions exists. Our study highlight clearly that caution should be taken when these drugs are concomitantly taken, via Y-site administration. Particularly, two parameters must be monitored, the pH and the ratio of the two drugs. These tow parameters are tightly linked to the amphoteric characters of drugs.
4. Conclusions
This study intends to fill the existing knowledge gap and contribute to the optimization of IV drug therapy, enhancing patient care and promoting rational prescribing practices. By systematically evaluating the compatibility of these commonly used medications, we can ensure safer and more effective treatment options, thereby improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of pharmacotherapy. The most striking information deals with the ratio acyclovir/ciprofloxacin used for Y-site IV administration. An equal ratio leads to bad recovery of ciprofloxacin. Excess of acyclovir versus ciprofloxacin (ratio 2/1 and higher) leads to almost full recovery of both drugs. When one of the drugs is present in large excess (ratios 1/9 and 9/1), a full recovery of both drugs was observed.
The results obtained from this investigation provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals, empowering them to make informed decisions about the co-administration of acyclovir and ciprofloxacin via IV infusion.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Volumes of stock solutions used to prepare the mixtures; System suitability testing for RP-HPLC method; Regression analysis; Compatibility data for acyclovir and ciprofloxacin
Author Contributions
D.L. performed the experiments. T.B. performed a part of the experiments, supervised the HPLC studies, participated in the project conceptualization and participated in the manuscript writing. L.F. Participated in the project conceptualization. A.B. Supervised the study and wrote the original draft of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was equally funded by University Grenoble Alpes and DrugOptimal to whom authors are thankful.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Dr. Edwige NICOLLE (Faculty of Pharmacy of Grenoble) for the instructive discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Castells, L.G.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Roura, T.J.; Prat, D.M.; Soy, M.D. López, C.C. Compatibility of drugs administered as Y-site infusion in intensive care units: A systematic review. Med. Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2020, 44, 80-87. [CrossRef]
- Oduyale, M.S.; Patel, N.; Borthwick, M.; Claus, S. Co-administration of multiple intravenous medicines: Intensive care nurses' views and perspectives. Nurs. Crit. Care 2020, 25, 156-164. [CrossRef]
- Allwood, M.C.; Kearney, M.C. Compatibility and stability of additives in parenteral nutrition admixtures. Nutrition 1998, 14, 697-706. [CrossRef]
- Trissel, L.A. Handbook on injectable drugs. 20th ed. 2018, Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists.
- Begum, S.G.; Reddy, Y.D.; Divya, B.S.; Kiranmai, S.Y.; Sushmitha, P.K.K.; Ruksar, S. Pharmaceutical incompatibilites: a review. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Devel (AJPRD). 2018, 6, 56-61. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.A.F.; Neininger, M.P.; Hensen, J.; Zube, O.; Bertsche, T. Avoiding incompatible drug pairs in central-venous catheters of patients receiving critical care: an algorithm-based analysis and a staff survey. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 1081-1089. [CrossRef]
- Maiguy-Foinard, A.; Genay, S.; Lannoy, D.; Barthélémy, C.; Lebuffe, G.; Debaene, B.; Odou, P.; Décaudin, B. Criteria for choosing an intravenous infusion line intended for multidrug infusion in anaesthesia and intensive care units. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2017, 36, 53-63. [CrossRef]
- Manallack, D.T.; Prankerd, R.J.; Yuriev, E.; Oprea, T.I.; Chalmers, D.K. The Significance of acid/base properties in drug discovery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 485–496. [CrossRef]
- Elion, G.B.; Furman, P.A.; Fyfe, J.A.; De Miranda, P.; Beauchamp, L.; Schaeffer, H.J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1977, 74, 5716−5720. [CrossRef]
- Kristl, A. Estimation of aqueous solubility for some guanine derivatives using partition coefficient and melting temperature. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 109−110. [CrossRef]
- Bergström, C.A.S; Norinder, U.; Luthman, K.; Artursson, P. Experimental and computational screening models for prediction of aqueous drug solubility. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 182−188. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Gruninger, R.P.; Nelson, S.M.; Klicker, R.E. Comparative in vitro activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366) and ten other oral antimicrobial agents against urinary bacterial isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 848–851. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Grundmann, O. The utilization and development of viral vectors in vaccines as a prophylactic treatment against Ebola virus as an emerging and zoonotic infectious disease. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wilder, A.J.; Foushee, J.A.; Fox, L.M.; Navalle, J.; Wright, A.M.; Greer, M.A. Physical compatibility of medications used in critically Ill patients with balanced fluid solutions. Int. J. Pharm. Compd. 2020, 24, 238-241.
- Kim, L.K.; Compatibility of ciprofloxacin lactate with other drugs. during simulated Y-site administration. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 1999, 56, 1730-1733. [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, S.; Bois-Maublanc, J.; Hocqueloux, L.; Bret, L.; Francia, T.; Eleout-Da Violante, C.; Billaud, E.M.; Barbier, F.; Got, L. A simple ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry assay for the simultaneous quantification of 15 antibiotics in plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1065-1066, 50-58. [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, S., Silimbani, P.; Gaggeri R.; Rossi, R.; Elviri, L.; Maltoni, M.; Masini, C. Validation of RP-HPLC method to assess the compatibility of metoclopramide and midazolam intravenous mixture used in patients with cancer. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2019, 26, 323-328. [CrossRef]
- Tietje, C.; Brouder, A. « International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use », in Handbook of Transnational Economic Governance Regimes, Brill | Nijhoff, 2010, 1041-1053. [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, M.; Indrayanto, G. « Validation of chromatographic methods of analysis », in Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology, Elsevier, 2005, 243-259. [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Kelley, S.P.; Bica, K.; Wallace, S.P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Acyclovir as an ionic liquid cation or anion can improve aqueous solubility. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3483-3493. [CrossRef]
- Babic, S.; Horavt, A.J.M.; Pavolvic, D.M.; Kastelan-Macan, M. Determination of pKa values of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 1043-1061. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).