Submitted:
22 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
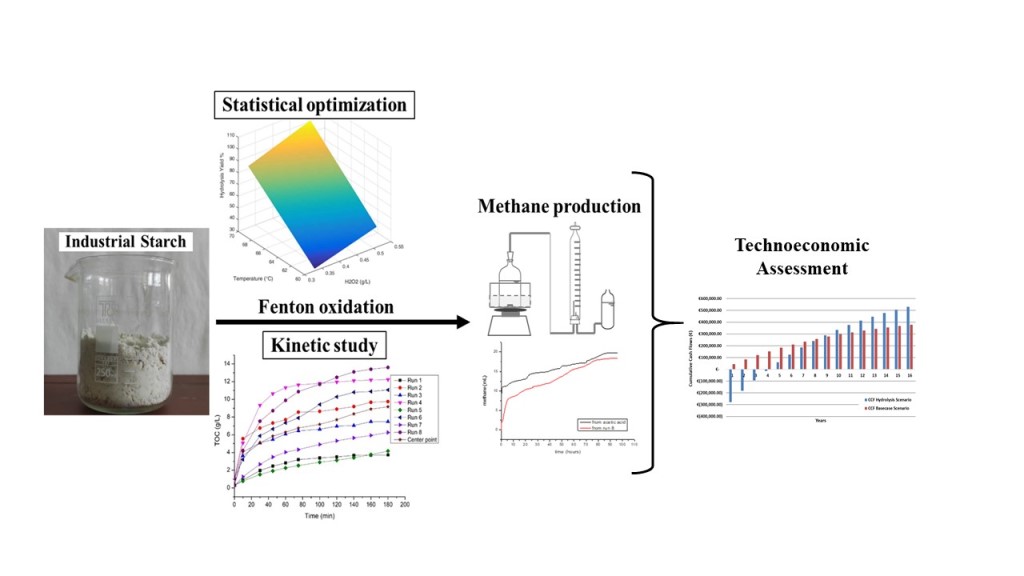
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrolysis of starch
2.3. Experimental design
2.4. Biomethane production from starch hydrolysates
2.5. Analytical procedures
2.6. Cost analysis
2.6.1. Calculation of CAPEX
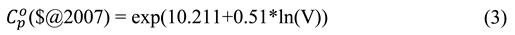
2.6.2. Profitability indicators
3. Results and discussion
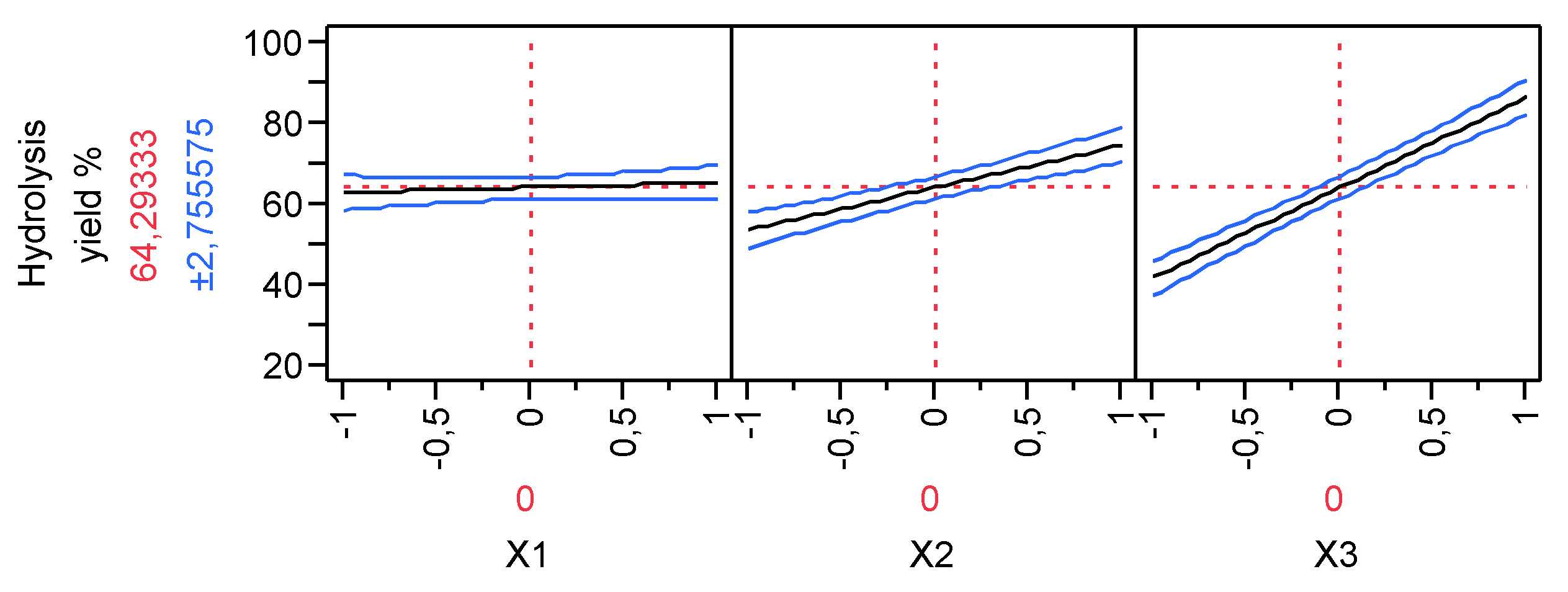
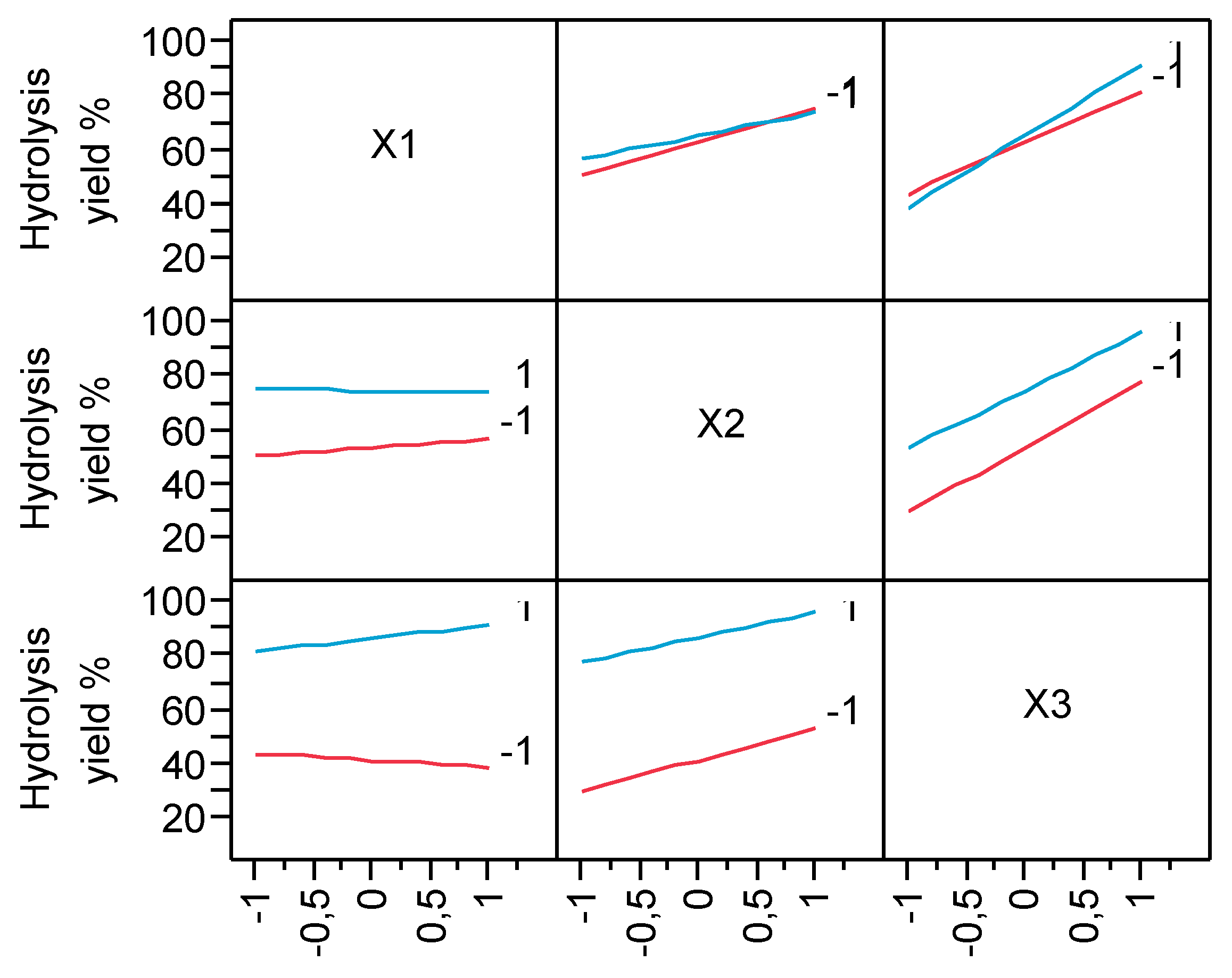
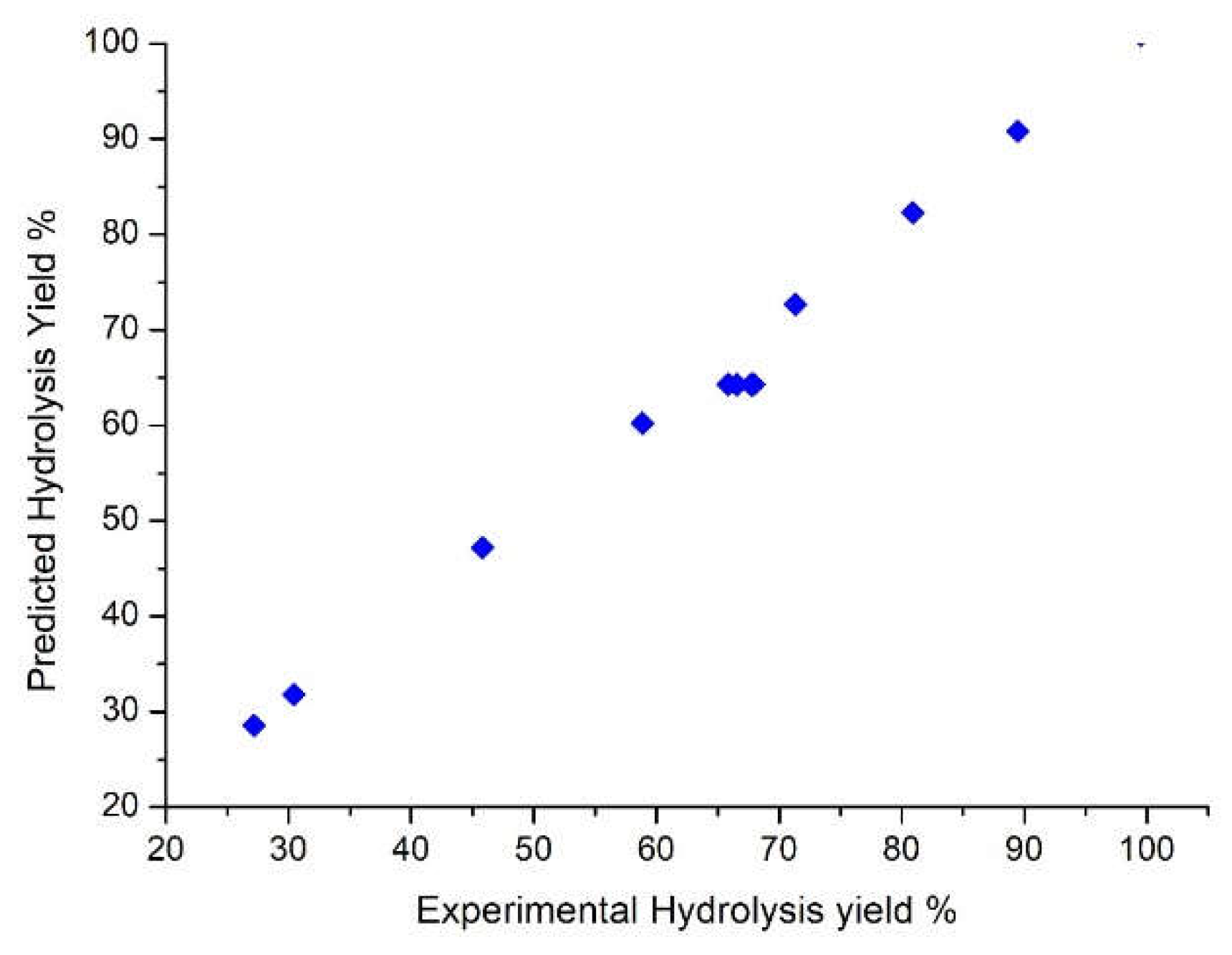
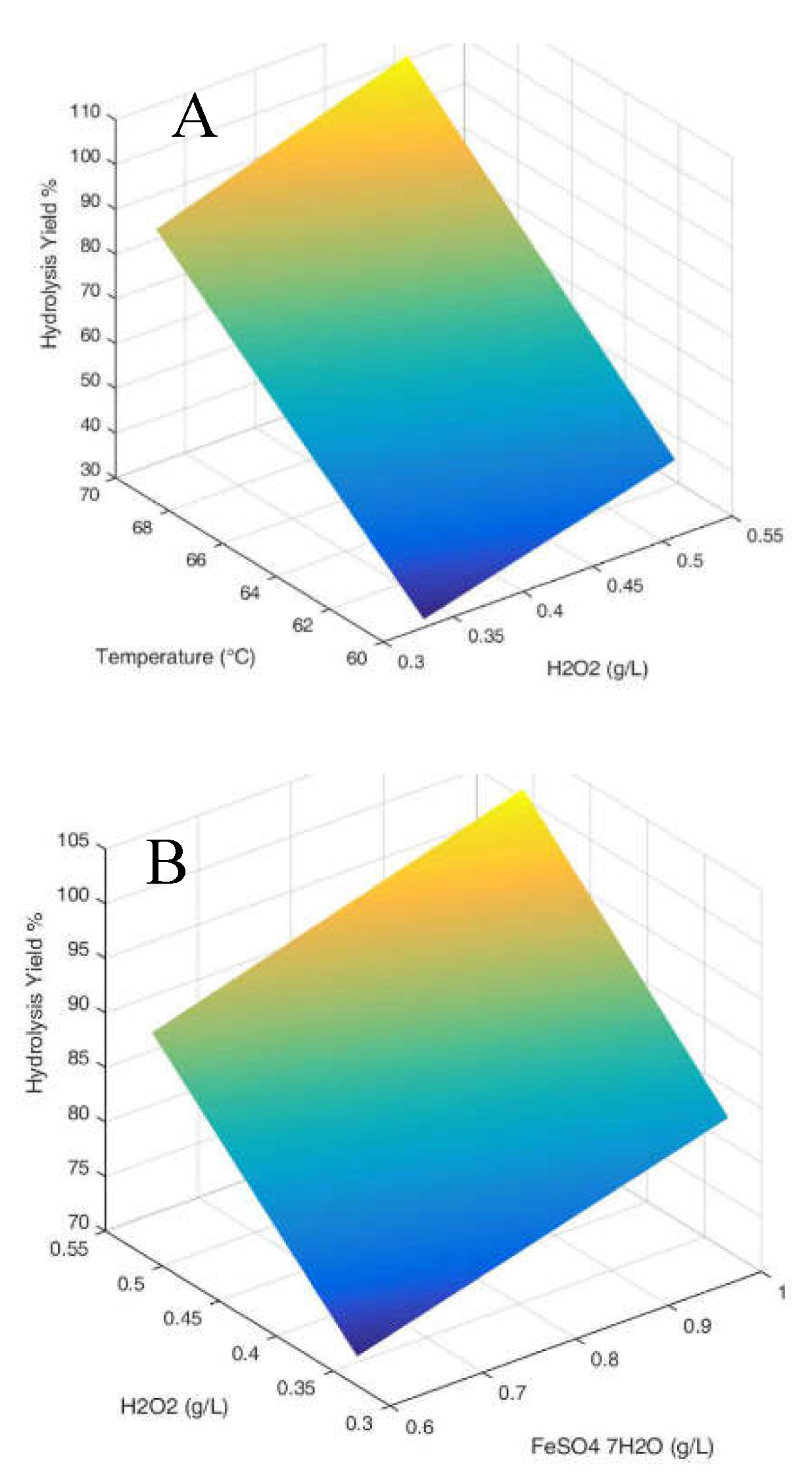
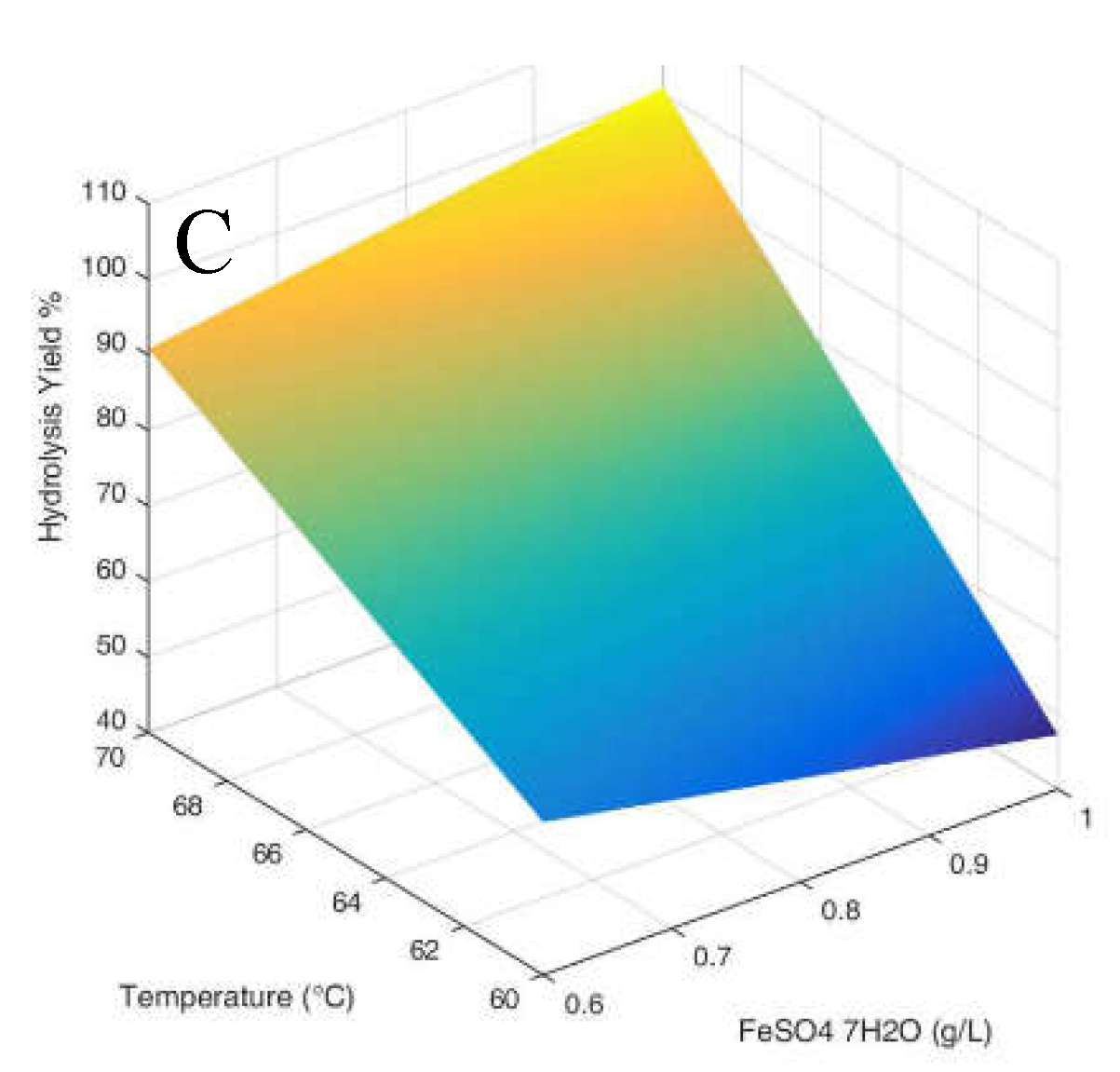
3.1. Hydrolysis yield results
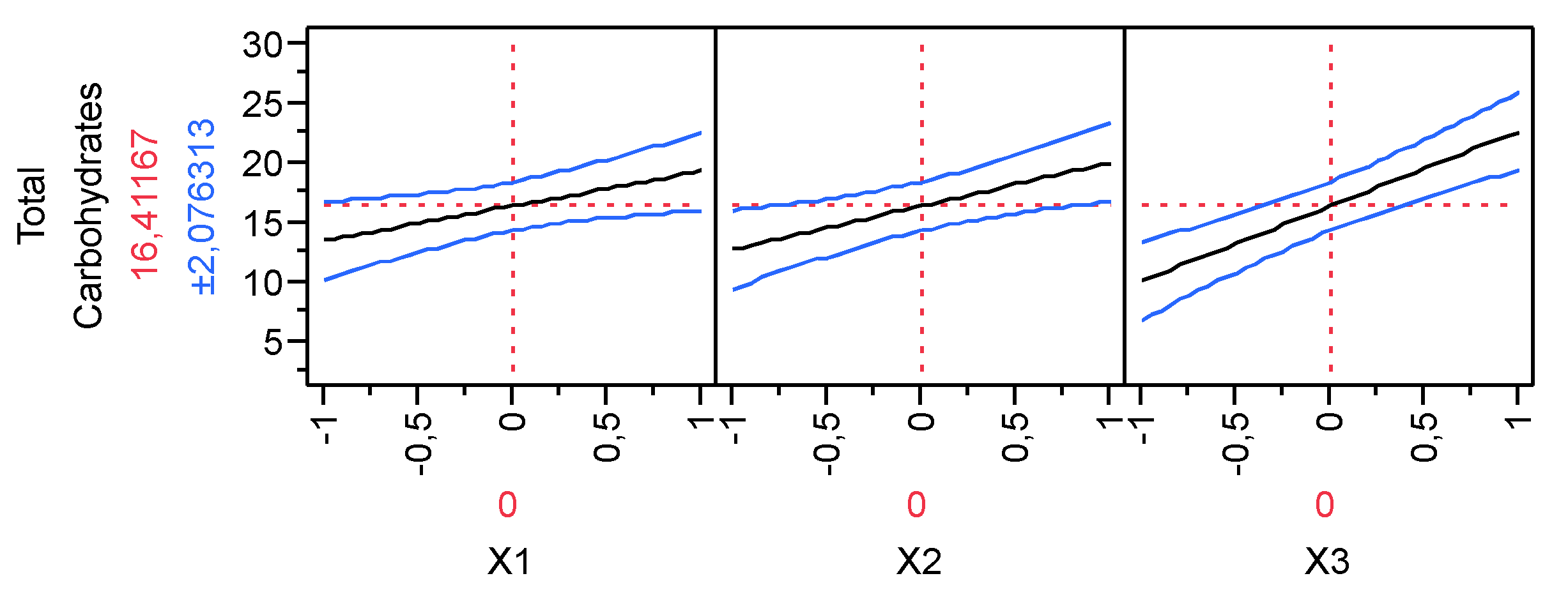
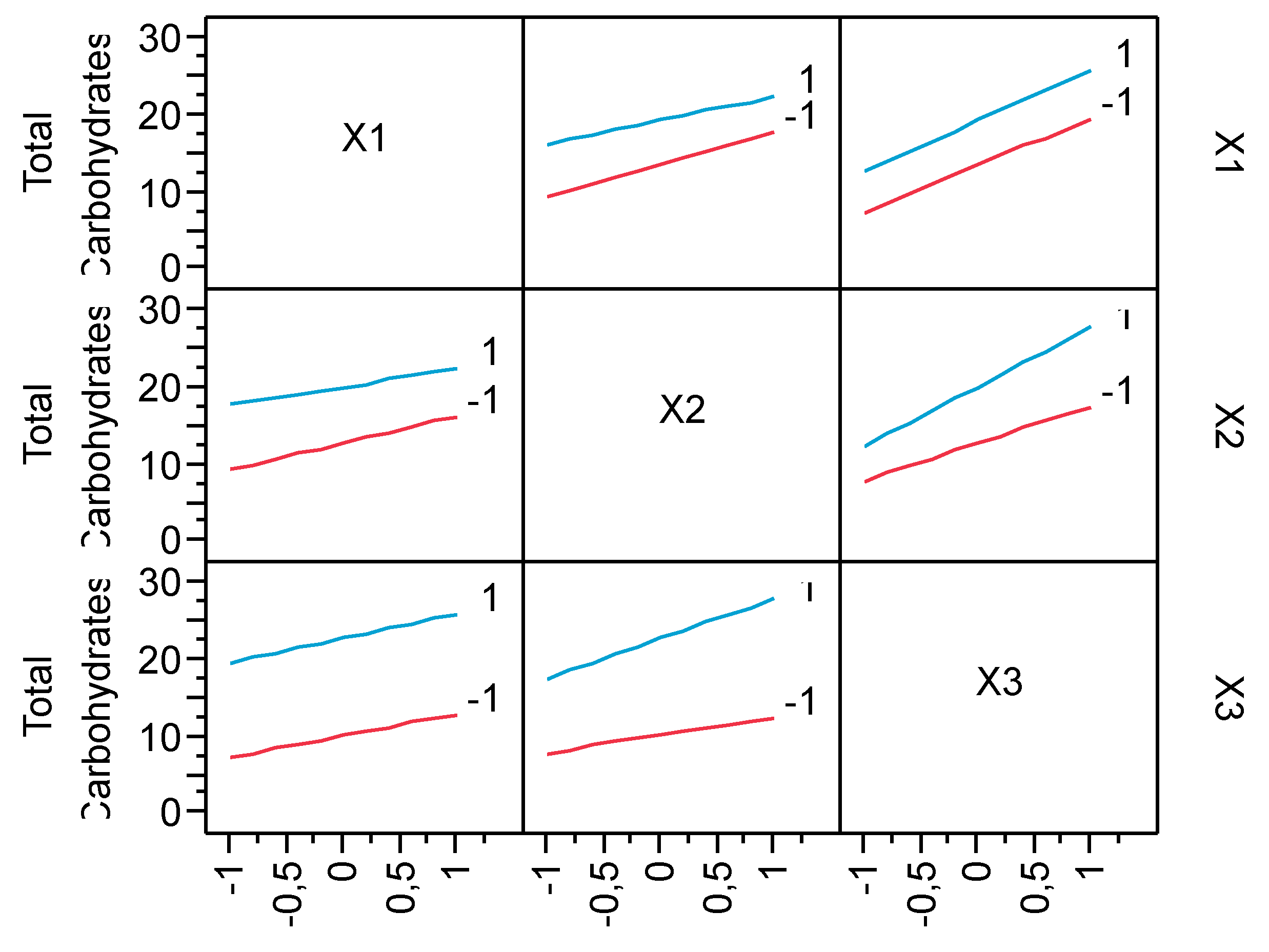
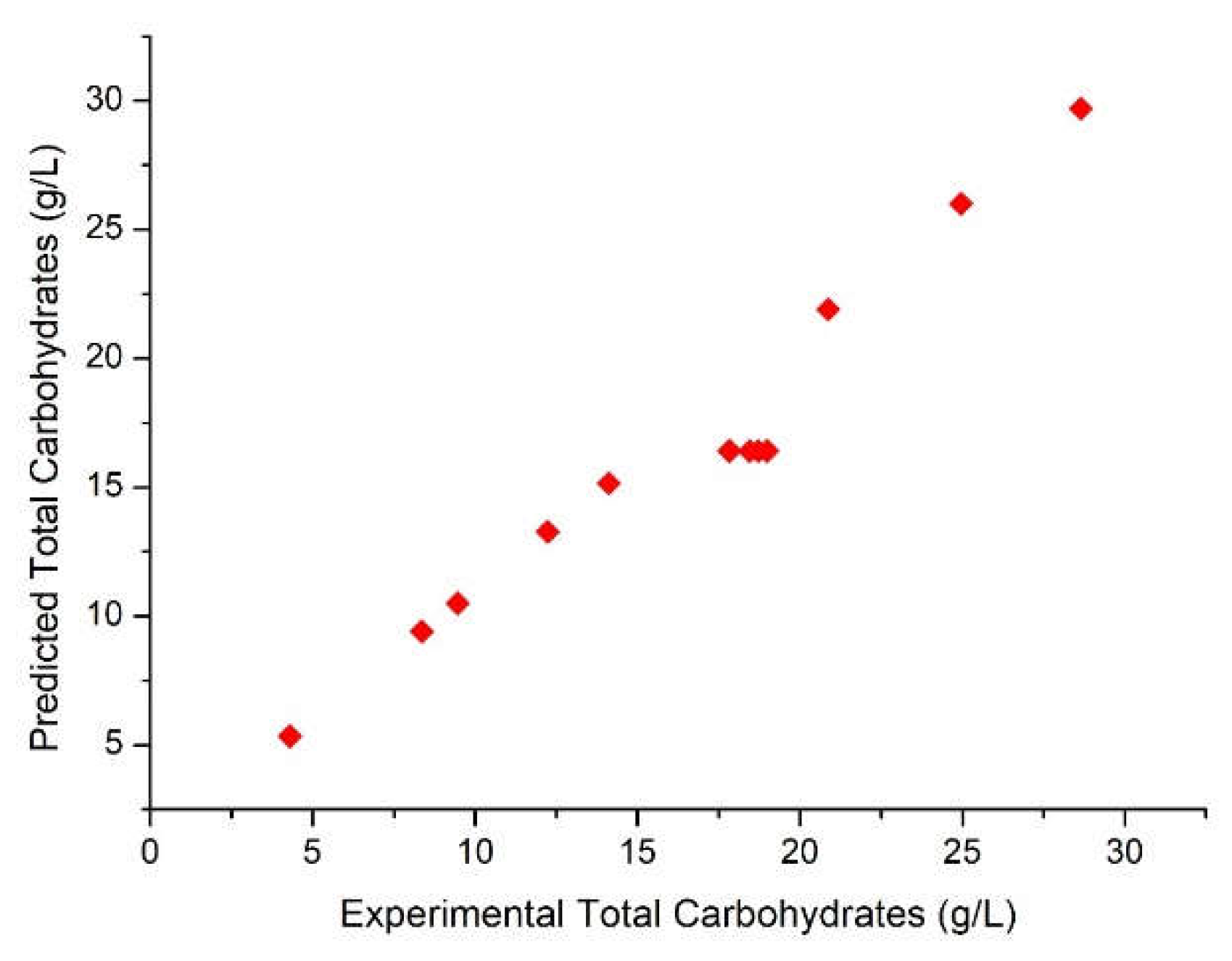
3.2. Production of Total Carbohydrates during the hydrolysis process
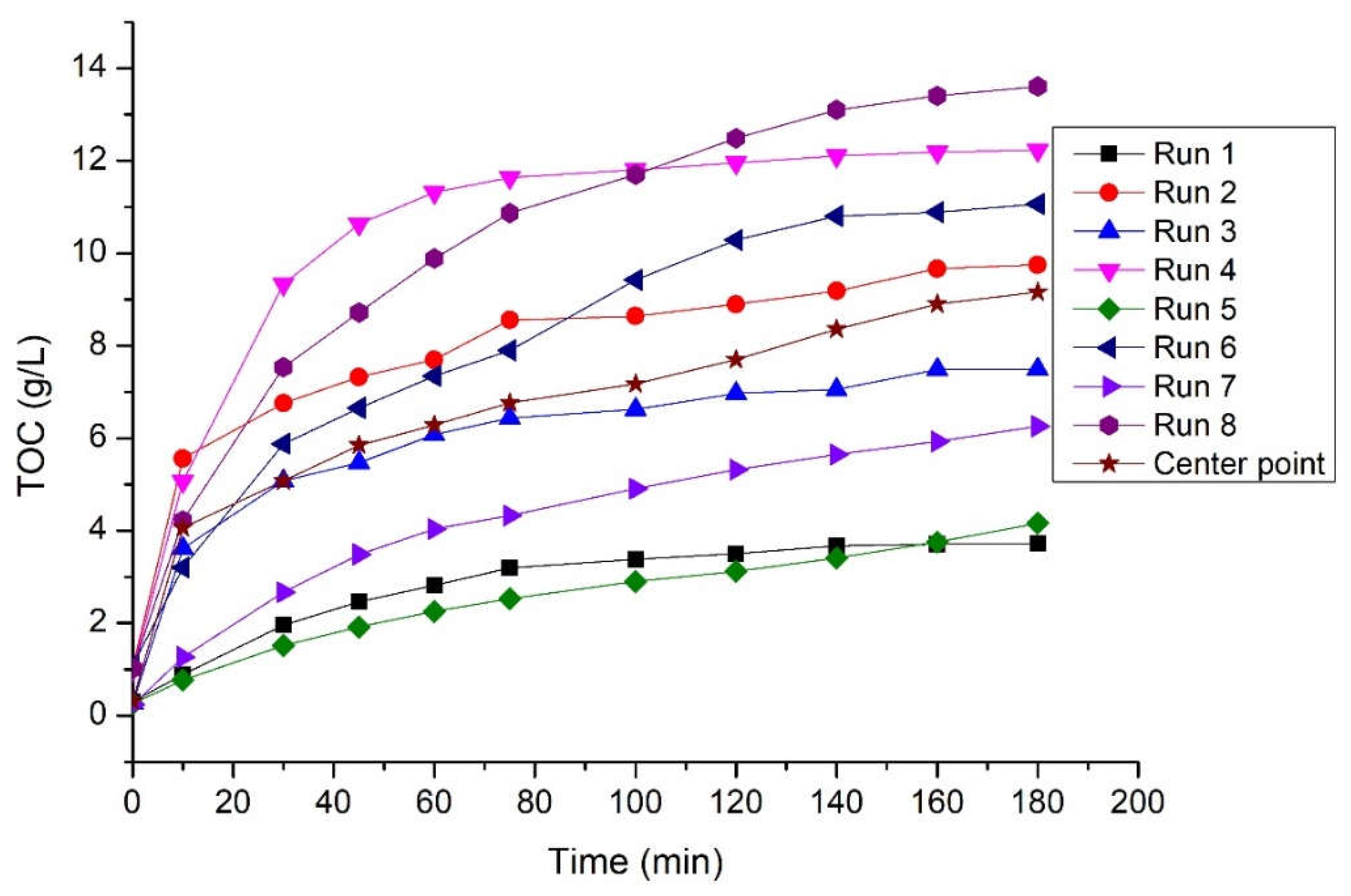
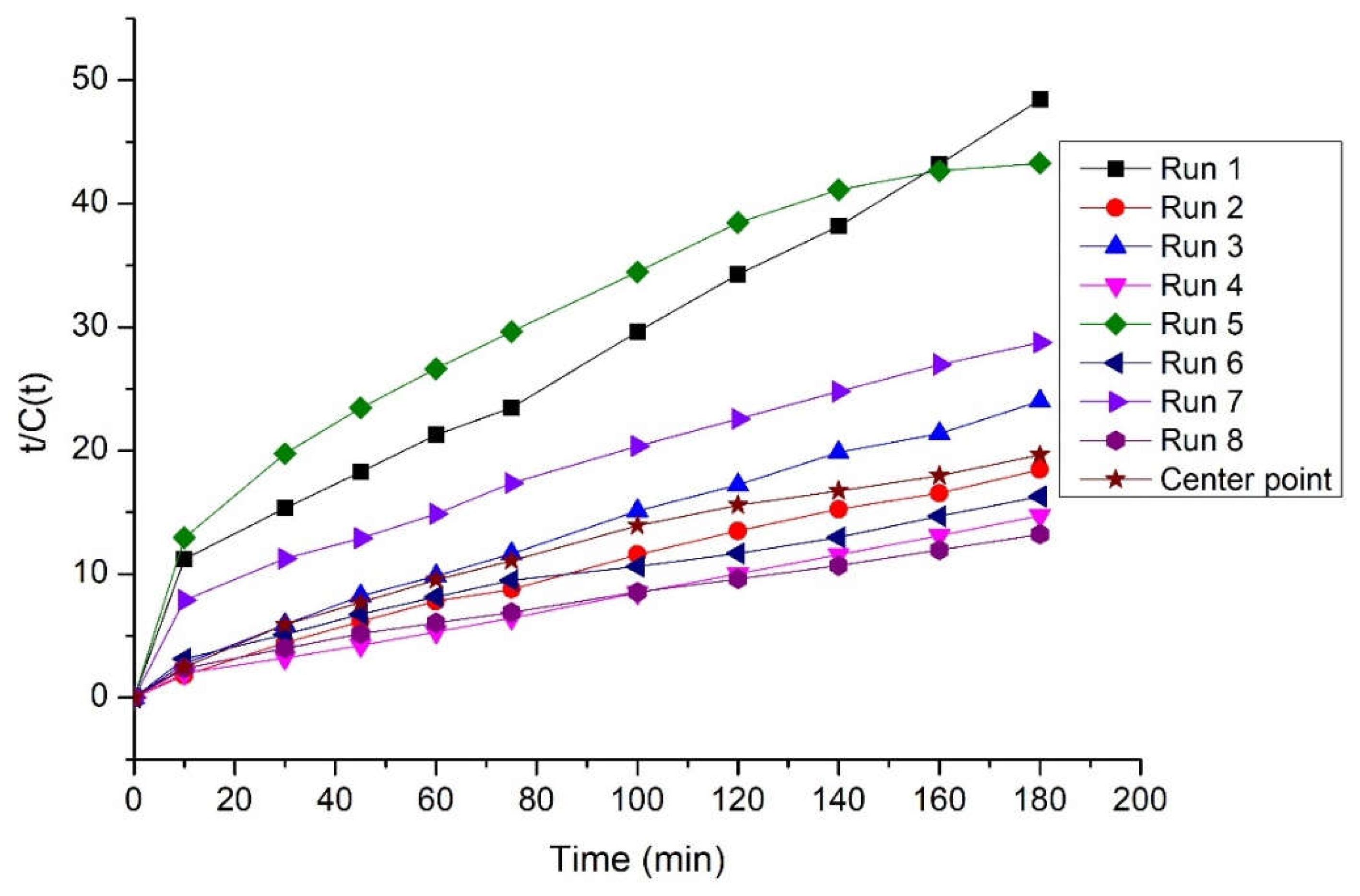
3.3. Kinetic study on starch hydrolysis with Fenton oxidation
3.4. Biodegradability tests
3.5. Plain cost analysis of starch hydrolysis and biomethane production
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caldeira C, De Laurentiis V, Corrado S, van Holsteijn F, Sala S. Quantification of food waste per product group along the food supply chain in the European Union: a mass flow analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2019; 149: 479-488. [CrossRef]
- Chavan S, Yadav B, Atmakuri A, Tyagi RD, Wong JWC, Drogui P. Bioconversion of organic wastes into value-added products: A review. Bioresour Technol. 2022, 344. [CrossRef]
- Caldeira C, Vlysidis A, Fiore G, De Laurentiis V, Vignali G, Sala S. Sustainability of food waste biorefinery: A review on valorisation pathways, techno-economic constraints, and environmental assessment. Bioresour Technol. 2020, 312, 123–575. [CrossRef]
- Pathak PD, Mandavgane SA, Puranik NM, Jambhulkar SJ, Kulkarni BD. Valorization of potato peel: a biorefinery approach. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2018, 38(2), 218-230. [CrossRef]
- Catarino J, Mendonça E, Picado A, Anselmo A, Nobre da Costa J, Partidário P. Getting value from wastewater: by-products recovery in a potato chips industry. J Clean Prod. 2007, 15(10), 927-931. [CrossRef]
- Vlyssides A, Barampouti EM, Mai S, Stamatoglou E, Rigaki K. Hydrolysis of starch using Fenton’s reagents as a key for waste integrated management in a potato processing industry, Chem Eng Trans. 2009, 18, 165–170. [CrossRef]
- Yokoi H, Maki R, Hirose J, Hayashi S. Microbial production of hydrogen from starch-manufacturing wastes. Biomass and Bioenergy. 2002, 22(5), 389-395. [CrossRef]
- Khongkliang P, Kongjan P, O-Thong S. Hydrogen and Methane Production from Starch Processing Wastewater by Thermophilic Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion. Energy Procedia. 2015, 79, 827–832. [CrossRef]
- Lu X, Zhen G, Estrada AL, Chen M, Ni J, Hojo T, Kubota K, Li Y. Operation performance and granule characterization of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating wastewater with starch as the sole carbon source. Bioresour Technol. 2015, 180, 264–273. [CrossRef]
- Farmanbordar S, Karimi K, Amiri H. Municipal solid waste as a suitable substrate for butanol production as an advanced biofuel. Energy Convers Manag. 2018, 157. [CrossRef]
- Poe N E, Yu D, Jin Q, Ponder M A, Stewart A C, Ogejo J A, Wang H, Huang H. Compositional variability of food wastes and its effects on acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation. Waste Manag. 2020, 107. [CrossRef]
- Su G, Chan C, He J. Enhanced biobutanol production from starch waste via orange peel doping. Renew Energy. 2022, 193. [CrossRef]
- Drosg B, Neubauer M, Marzynski M, Meixner K. Valorisation of starch wastewater by anaerobic fermentation. Appl Sci. 2021, 11(21). [CrossRef]
- Vanier NL, El Halal SLM, Dias ARG, da Rosa Zavareze E. Molecular structure, functionality and applications of oxidized starches: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1546–1559. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Copeland L. Effect of acid hydrolysis on starch structure and functionality: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015, 55(8), 1081-1097. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Ma X, Yan L, et al. Ultrasound assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of starch catalyzed by glucoamylase: Investigation on starch properties and degradation kinetics. Carbohydr Polym. 2017, 175, 47–54. [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, P. Specific Physical and Chemical Properties of Potato Starch. Global science books, Food. 2009; 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dhital S, Shrestha AK, Hasjim J, Gidley MJ. Physicochemical and structural properties of maize and potato starches as a function of granule size. J Agric Food Chem. 2011, 59(18), 10151–10161. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Zhou M, Cheng F, Lin Y, Shi L, Zhu PX. Preparation of oxidized corn starch with high degree of oxidation by fenton-like oxidation assisted with ball milling. Mater Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100–793. [CrossRef]
- Maniglia BC, Castanha N, Le-Bail P, Le-Bail A, Augusto PED. Starch modification through environmentally friendly alternatives: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021, 61(15). [CrossRef]
- Isbell HS, Frush HL. Mechanisms for hydroperoxide degradation of disaccharides and related compounds. Carbohydr Res. 1987, 161(2), 181–193. [CrossRef]
- Chong WT, Uthumporn U, Karim AA, Cheng LH. The influence of ultrasound on the degree of oxidation of hypochlorite-oxidized corn starch. LWT - Food Sci Technol. 2013, 50(2), 439-443. [CrossRef]
- Sangseethong K, Termvejsayanon N, Sriroth K. Characterization of physicochemical properties of hypochlorite- and peroxide-oxidized cassava starches. Carbohydr Polym. 2010, 82(2), 446-453. [CrossRef]
- Pirt SJ, Whelan WJ. The determination of starch by acid hydrolysis. J Sci Food Agric. 1951, 2(5), 224–228. [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh MA, Ramadan MA, El-Shafie A. Photo-oxidation of rice starch. Part I: Using hydrogen peroxide. Carbohydr Polym. 2010, 80(1), 266-269. [CrossRef]
- Hoover R, Hughes T, Chung HJ, Liu Q. Composition, molecular structure, properties, and modification of pulse starches: A review. Food Res Int. 2010, 43(2), 399-413. [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk S, Fortuna T, Raś Ł. The influence of pH and Fe(II) ions on physicochemical properties of oxidized potato starch, EJPAU. 2007, 10(4).
- Dang X, Chen H, Shan Z, Zhen W, Yang M. The oxidation of potato starch by Electro-Fenton system in the presence of Fe(II) ions. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019, 121, 113–119. [CrossRef]
- Lamprou GK, Vlysidis A, Tzathas K, Vlyssides AG. Statistical optimization and kinetic analysis of the extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2020, 95(2), 457–465. [CrossRef]
- Miller TL, Wolin MJ. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 27(5), 985–987.
- Soto M, Méndez R, Lema J M. Methanogenic and non-methanogenic activity tests. Theoretical basis and experimental set up. Water Res. 1993, 27(8), 1361-1376. [CrossRef]
- Hussain A, Dubey SK. Specific methanogenic activity test for anaerobic degradation of influents. Appl Water Sci. 2017, 7(2), 535–542. [CrossRef]
- Tran, T. Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23nd edition.
- Tuller EF, Keiding NR. Determination of Protein-Bound Carbohydrates by Anthrone Reaction. Anal Chem. 2002; 26(5), 875-878. [CrossRef]
- Jacob S, Chintagunta A D, Banerjee R, Selective digestion of industrial potato wastes for efficient biomethanation: a sustainable solution for safe environmental disposal. Int. J. of En. Sc. and Tech., 2016, 13(10), 2363-2374. [CrossRef]
- Arapoglou D, Varzakas T, Vlyssides A, Israilides C. Ethanol production from potato peel waste (PPW). Waste Manag. 2010, 30(10). [CrossRef]
- Perry RH, Green DW, Maloney JO. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook 7th Edition. 1997, 38.
- Psaki O, Maina S, Vlysidis A, Papanikolaou S. , Machado A., Freire D.M.G., Dheskali E., Kookos I., Koutinas A., Optimisation of 2,3-butanediol production by Enterobacter ludwigii using sugarcane molasses. Biochem Eng J. 2019, 152, 107–370. [CrossRef]
- Maina S, Stylianou E, Vogiatzi E, Vlysidis A. , Mallouchos A., Nychas G-J E., Machado A., Dheskali E., Kookos I.K., Koutinas A., Improvement on bioprocess economics for 2,3-butanediol production from very high polarity cane sugar via optimisation of bioreactor operation. Bioresour Technol. 2019, 274, 343–352. [CrossRef]
- Vlysidis A, Binns M, Webb C, Theodoropoulos C. A techno-economic analysis of biodiesel biorefineries: Assessment of integrated designs for the co-production of fuels and chemicals. Energy. 2011, 36(8), 4671-4683. [CrossRef]
- Suhartini S, Lestari Y. P. and Nurika I. Estimation of methane and electricity potential from canteen food waste. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ Sci. 2019; 230(1), 012-075. [CrossRef]
- Personal communication with Tasty Foods, SA. January 2023. www.pepsico.com.gr.
- Vasquez-Medrano R, Prato-Garcia D, Vedrenne M. Ferrioxalate-Mediated Processes. Adv Oxid Process Wastewater Treat Emerg Green Chem Technol. February 2018, 1, 89–113. [CrossRef]
- Mahtab MS, Islam DT, Farooqi IH. Optimization of the process variables for landfill leachate treatment using Fenton based advanced oxidation technique. Eng Sci Technol an Int J. 2021, 24(2), 428–435. [CrossRef]
- Li Z, Cai L, Gu Z, Shi YC. Effects of granule swelling on starch saccharification by granular starch hydrolyzing enzyme. J Agric Food Chem. 2014, 62(32), 8114–8119. [CrossRef]
- Uthumporn U, Zaidul ISM, Karim AA. Hydrolysis of granular starch at sub-gelatinization temperature using a mixture of amylolytic enzymes. Food Bioprod Process. 2010, 88(1), 47-54. [CrossRef]
- Kong, H. , Yang X., Gu Z., Li Z.,Cheng L., Hong Y., Li C., Heat pretreatment improves the enzymatic hydrolysis of granular corn starch at high concentration. Process Biochemistry, 2018; 64, 193-199.
- Pietrzyk S, Juszczak L, Fortuna T, Łabanowska M, Bidzińska E, Błoniarczyk K. The influence of Cu(II) ions on physicochemical properties of potato starch oxidised by hydrogen peroxide. Starch - Stärke. 2012, 64(4), 272-280. [CrossRef]
- Łabanowska M, Kurdziel M, Bidzińska E. Influence of metal ions on thermal generation of carbohydrate radicals in native and modified starch studied by EPR. Starch - Stärke. 2013, 65(5-6), 469-482. [CrossRef]
- Yu D, Li C, Wang L, Zhang J, Liu J, Wei Y. Multiple effects of trace elements on methanogenesis in a two-phase anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating starch wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016, 100(15), 6631-6642. [CrossRef]
- Sun Y, Wang M, Liang L, Sun C, Wang X, Wang Z, Zhanget Y. Continuously feeding fenton sludge into anaerobic digesters: Iron species change and operating stability. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119–283. [CrossRef]
- Personal communication with ENBIO, 06/03/2023, www.enbio.gr.
- Eurostat. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Natural_gas_price_statistics, assessed in 12/04/2023.
- Eurostat. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Electricity_price_statistics, assessed in 20/04/2023.
- Dimou, C. , Vlysidis A. , Kopsahelis N., Papanikolaou S., Koutinas A., Kookos I.K., Techno-economic evaluation of wine lees refining for the production of value-added products, Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 116, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Level | FeSO4 7H2O (g/L) | H2O2 (g/L) | Temperature (°C) |
| -1 | 0.60 | 0.329 | 60 |
| 0 | 0.80 | 0.419 | 65 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 0.509 | 70 |
| Run | X1 | X2 | X3 | pH after oxidation | Experimental Hydrolysis Yield % | Predicted Hydrolysis Yield % | Experimental Total Carbohydrates (g/L) | Predicted Total Carbohydrates (g/L) |
| 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 2.82 | 27.19 | 28.55 | 4.3 | 5.34 |
| 2 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 3.02 | 71.32 | 72.68 | 12.23 | 13.27 |
| 3 | -1 | 1 | -1 | 2.9 | 58.86 | 60.22 | 8.36 | 9.4 |
| 4 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 2.66 | 89.46 | 90.82 | 24.96 | 26.00 |
| 5 | 1 | -1 | -1 | 2.83 | 30.43 | 31.79 | 9.46 | 10.50 |
| 6 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 2.68 | 80.90 | 82.26 | 20.87 | 21.91 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 2.99 | 45.81 | 47.17 | 14.12 | 15.16 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2.59 | 99.50 | 100.86 | 28.65 | 29.69 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.75 | 65.84 | 64.29 | 17.83 | 16.41 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.98 | 67.92 | 64.29 | 18.99 | 16.41 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.78 | 66.56 | 64.29 | 18.72 | 16.41 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.76 | 67.73 | 64.29 | 18.45 | 16.41 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Ratio | P > F |
| Model | 7 | 5077.776 | 725.397 | 61.369 | <0.0007 |
| Error | 4 | 47.281 | 11.820 | ||
| Lack Of Fit | 1 | 44.362 | 14.415 | 45.612 | 0.0066 |
| Pure Error | 3 | 2.918 | 2.624 | ||
| Total Error | 4 | 47.281 | 0.973 | ||
| Parameter Estimates | Estimate | Std Error | t Ratio | Prob>|t| | |
| β0 | 64.292 | 0.992 | 64.78 | <.0001 | |
| β1 | 1.226 | 1.216 | 1.01 | 0.3701 | |
| β2 | 10.474 | 1.216 | 8.62 | 0.0010 | |
| β3 | 22.361 | 1.216 | 18.40 | <.0001 | |
| β1*β2 | -1.979 | 1.216 | -1.63 | 0.1789 | |
| β1*β3 | 3.679 | 1.216 | 3.03 | 0.0389 | |
| β2*β3 | -1.289 | 1.216 | -1.06 | 0.3488 | |
| β1*β2*β3 | 2.094 | 1.216 | 1.72 | 0.1601 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Ratio | P > F |
| Model | 7 | 516.611 | 73.802 | 10.997 | 0.018 |
| Error | 4 | 26.844 | 6.711 | ||
| Lack Of Fit | 1 | 26.104 | 26.104 | 105.846 | 0.002 |
| Pure Error | 3 | 0.740 | 0.247 | ||
| Total Error | 4 | 26.844 | |||
| Parameter Estimates | Estimate | Std Error | t Ratio | Prob>|t| | |
| β0 | 16.412 | 0.748 | 21.950 | <.0001 | |
| β1 | 2.90625 | 0.916 | 3.170 | 0.0338 | |
| β2 | 3.65375 | 0.916 | 3.990 | 0.0163 | |
| β3 | 6.30875 | 0.916 | 6.890 | 0.0023 | |
| β1*β2 | -0.544 | 0.916 | -0.590 | 0.5847 | |
| β1*β3 | 0.176 | 0.916 | 0.190 | 0.8568 | |
| β2*β3 | 1.47375 | 0.916 | 1.610 | 0.1829 | |
| β1*β2*β3 | -0.694 | 0.916 | -0.760 | 0.4910 |
| Runs | Ce (g/L) | k (L/g min) | R2 |
| 1 | 4.246 | 9.162 10-3 | 0.974 |
| 2 | 10.040 | 8.621 10-3 | 0.991 |
| 3 | 7.831 | 9.719 10-3 | 0.991 |
| 4 | 12.804 | 9.298 10-3 | 0.997 |
| 5 | 4.721 | 4.197 10-3 | 0.894 |
| 6 | 12.531 | 2.757 10-3 | 0.961 |
| 7 | 7.179 | 3.583 10-3 | 0.944 |
| 8 | 14.993 | 2.856 10-3 | 0.978 |
| Center point | 9.597 | 4.831 10-3 | 0.967 |
| Substrate | Maximum specific rate (mL CH4/min) | SMA (g CODCH4/gVSS d) | mL CH4 | mL CH4 (acetic acid as feed) | Normalization % |
| Run 5th | 0.375 | 0.388 | 16.3 | 18.95 | 86.02 |
| Run 8th | 0.650 | 0.669 | 18.4 | 19.80 | 92.93 |
| Run 9th | 0.416 | 0.428 | 17.7 | 20.10 | 88.06 |
| Run 1st | 0.078 | 0.080 | 13.4 | 18.80 | 71.28 |
| native starch | 0.075 | 0.077 | 9.2 | 19.05 | 48.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





