Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
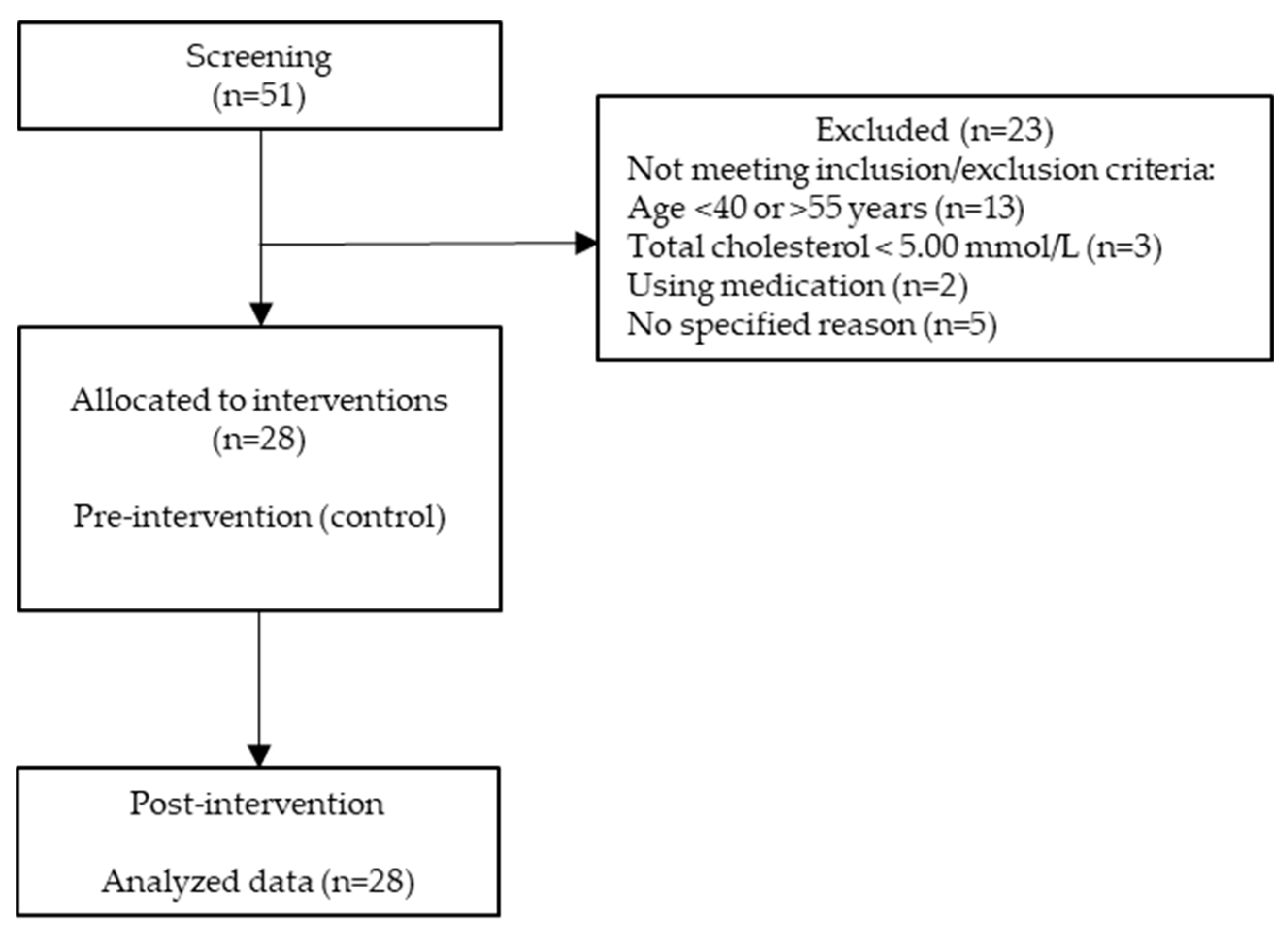
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Dietary Intervention
2.3. Anthropometric Data
2.4. Blood Sample Collection and Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Clinical Trial Participants
3.2. Effect of Sea Buckthorn Juice Consumption on Anthropometric Characteristics and Blood Pressure
3.3. Effect of Sea Buckthorn Juice Consumption on Biochemical Characteristics
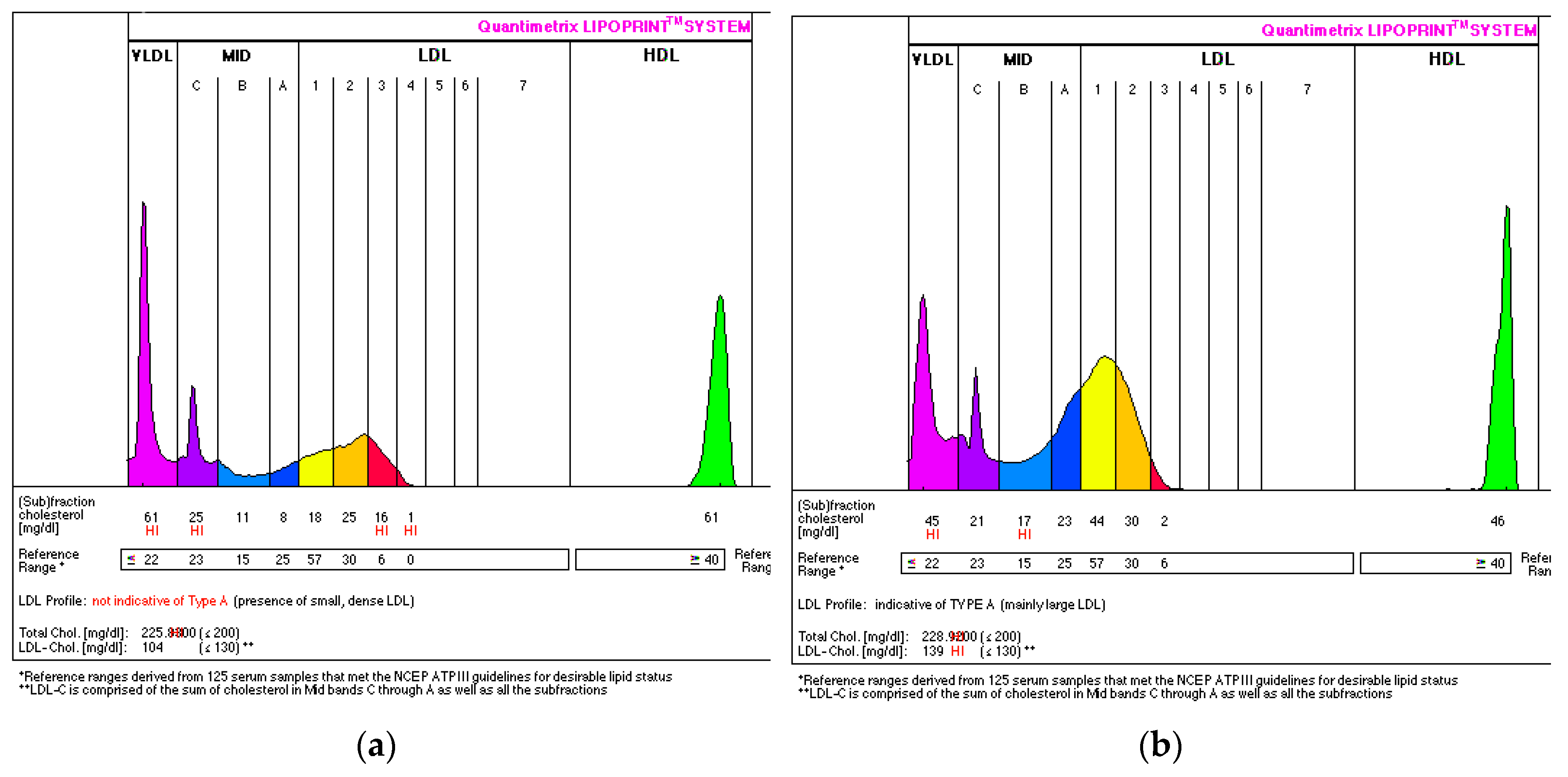
3.4. Effect of Sea Buckthorn Juice Consumption on LDL Subfractions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soppert, J.; Lehrke, M.; Marx, N.; Jankowski, J.; Noels, H. Lipoproteins and lipids in cardiovascular disease: from mechanistic insights to therapeutic targeting. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, S.; Longo, V.D. Dietary Restrictions and Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2019, 124, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M. The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Medicine. 2018, 46, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, N.; Kazakiewicz, D.; Lucy Wright, F.; Timmis, A.; Huculeci, R.; Torbica, A.; Gale, C.P.; Achenbach, S.; Weidinger, F.; Vardas, P. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022, 19, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharjee, S.; Boden, W.E. , Hartigan, P.M.; Teo, K.K.; Maron, D.J.; Sedlis, S.P. Low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and increased risk of cardiovascular events in stable ischemic heart disease patients: A post- hoc analysis from the COURAGE Trial (Clinical Outcomes Utilizing Revascularization and Aggressive Drug Evaluation). Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1826–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, J.G.; O'Dea, K.; Walker, K.Z. Evidence for low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Australian indigenous peoples: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2014, 2, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Bagherniya, M.; Atkin, S.L.; Askari, G.; Orafai, H.M.; Sahebkar, A. The beneficial effects of nutraceuticals and natural products on small dense LDL levels, LDL particle number and LDL particle size: a clinical review. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Puganen, A.; Alakomi, H.L.; Uusitupa, A.; Saarela, M.; Yang, B. Antioxidative and antibacterial activities of aqueous ethanol extracts of berries, leaves, and branches of berry plants. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascot, A.; Lemieux, I.; Prud’homme, D.; Tremblay, A.; Nadeau, A.; Couillard, C.; Bergeron, J.; Lamarche, B.; Després, J. P. Reduced HDL Particle Size as an Additional Feature of the Atherogenic Dyslipidemia of Abdominal Obesity. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, R.; Qin, X.; Liu, D.; Lin, F.; Feng, Q. Isorhamnetin inhibits IL-1β-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2017, 16, 4253–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernáez, Á.; Soria-Florido, M.T.; Schröder, H.; Ros, E.; Pintó, X.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Serra-Majem, L.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; Elosua, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Fitó, M. Role of HDL Function and LDL Atherogenicity on Cardiovascular Risk: A Comprehensive Examination. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14, e0218533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevjer, M.; Saether, J.C.; Vesterbekkmo, E.; Giskeoedegaard, G.; Bathen, T.; Gigante, B.; Gjaere, S.; Myhra, M.; Wiseth, R.; Madssen, E.; Bye, A. Lipoprotein subfraction LDL-5 and the presence of coronary atherosclerosis. European Heart Journal 2020, 41, ehaa946.1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K.; Corrado, E.; Novo, S. The significance of low-density lipoproteins size in vascular diseases. Int Angiol. 2006, 25, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Higashioka, M.; Sakata, S.; Honda, T.; Hata, J.; Yoshida, D.; Hirakawa, Y.; Shibata, M.; Goto, K.; Kitazono, T.; Osawa, H.; Ninomiya, T. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in a Japanese Community. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020, 27, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellsworth, D.; Costantino, N.; Blackburn, H.; Engler, R.; Kashani, M.; Vernalis, M. Lifestyle modification interventions differing in intensity and dietary stringency improve insulin resistance through changes in lipoprotein profiles. Obes Sci Pract. 2016, 2, 282–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiuve, S.E.; Cook, N.R.; Shay, C.M.; Rexrode, K.M.; Albert, C.M.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B. Lifestyle-based prediction model for the prevention of CVD: the healthy heart score. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboota, R.K.; Bishnoi, M.; Ambalam, P.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Sarma, S.M.; Boparai, R.K.; Podili, K. Functional food ingredients for the management of obesity and associated co-morbidities—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolori, P.; Setaysh, L.; Rasaei, N.; Jarrahi, F.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Mirzaei, K. Adherence to a healthy plant diet may reduce inflammatory factors in obese and overweight women—A cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. J. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Drozińska, E.; Kanclerz, A.; Kurek, M.A. Microencapsulation of sea buckthorn oil with _-glucan from barley as coating material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Laaksonen, O.; Heinonen, J.; Sainio, T.; Kallio, H.; Yang, B. Sensory profile of ethyl _-D-glucopyranoside and its contribution to quality of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.). Food Chem. 2017, 233, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, F.; Salim, R.; Bashir, M. Chemical and antioxidant properties of of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides). Pharma Innov. 2017, 6, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, S.; Kuang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, E.H. Network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation to explore the mechanism of sea buckthorn flavonoids on hyperlipidemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gallegos, J.L.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.; Lodge, J.K. Effects of Blueberry Consumption on Cardiovascular Health in Healthy Adults: A Cross-Over Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sytařová, I.; Orsavová, J.; Snopek, L.; Mlˇcek, J.; Byczy´ nski, Ł.; Mišurcová, L. Impact of phenolic compounds and vitamins C and E on antioxidant activity of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries and leaves of diverse ripening times. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesarová, Z.; Murkovic, M.; Cejpek, K.; Kreps, F.; Tobolková, B.; Koplík, R.; Belajová, E.; Kukurová, K.; Daško, Ľ.; Panovská, Z.; Revenco, D.; Burčová, Z. Why is sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) so exceptional? A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Gong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Advanced Research on the Antioxidant Activity and Mechanism of Polyphenols from Hippophae Species-A Review. Molecules. 2020, 25, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E. Hippophae rhamnoides L. (Sea Buckthorn): a potential source of nutraceuticals. Food Public Health 2012, 2, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, S.; Garg, P.; Dviwedi, A.; Ali, A.; Kapoor, V.K.; Kapoor, D.; Kulshrestha, S.; Lal, U.R.; Negi, P. Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and dermatological effects of Hippophae rhamnoides L.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Jang, H.; Lee, M.; Kang, H.; Heo, H. J.; Kim, D.O. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaf extracts protect neuronal PC-12 cells from oxidative stress. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaśniewska, A.; Diowksz, A. Wide spectrum of active compounds in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) for disease prevention and food production. Antioxidants. 2021, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Kondo, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Meng, X.; Umemura, K. Inhibitory effects of total flavones of Hippophae Rhamnoides L on thrombosis in mouse femoral artery and in vitro platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejcarová, J.; Straková, E.; Suchý, P.; Herzig, I.; Karásková, K. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) as a potential source of nutraceutics and its therapeutic possibilities - A review. Acta Veterinaria Brno. 2015, 84, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.F.F.; Macdonald, R.; Lovegrove, J.A. Fruit polyphenols and CDV risk: a review of human intervention studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, S28–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, C.A.; Divakar, K.; Santani, D. , Solanki, H.K.; Thakkar, J.H. Remedial Prospective of Hippophae rhamnoides Linn. (Sea Buckthorn). ISRN Pharmacol. 2012, 2012, 436857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, S.; Chen, N.; Bai, X.; Ke, Q.; Shen, J.; Xia, M. Small dense LDL cholesterol is associated with metabolic syndrome traits independently of obesity and inflammation. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Puganen, A.; Alakomi, H.L.; Uusitupa, A.; Saarela, M.; Yang, B. Antioxidative and antibacterial activities of aqueous ethanol extracts of berries, leaves, and branches of berry plants. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Franquesa, A.; Saldo, J.; Juan, B. Potential of sea buckthorn-based ingredients for the food and feed industry – a review. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition 2020, 2, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleszko, M.; Wojdyło, A.; Rudzińska, M.; Oszmiański, J.; Golis, T. Analysis of Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Bioactive Compounds Content in Sea Buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) Berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4120–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kallio, H. 2002. Supercritical Co-extracted sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides) oils as new food ingredients for cardiovascular health. Proc. Health Ingred. 2002, 17, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. .; Wu, R..; Qin, X.; Liu, D.; Lin, F.; Feng, Q. Isorhamnetin inhibits IL-1β-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2017, 16, 4253–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.C.; Li, X.H.; Li, Q.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Jiang-Yong, S.L.; Meng, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.F. Total flavonoids from sea buckthorn ameliorates lipopolysaccharide/cigarette smoke-induced airway inflammation. Phytother Res. 2019, 33, 2102–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmo, P.S.; Yang, B.; Hurme, S.A.; Alin, J.A.; Kallio, H.P.; Salminen, E.K.; Tahvonen, R.L. Effect of a low dose of sea buckthorn berries on circulating concentrations of cholesterol, triacylglycerols, and flavonols in healthy adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2009, 48, 277–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B.; Kontek, B.; Szczesna, M.; Grabarczyk, L.; Stochmal, A.; Zuchowski, J. Inhibition of blood platelet adhesion by phenolics' rich fraction of Hippophae rhamnoides L. fruits. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.; Chaudhary, A. Unexplored therapeutic treasure of Himalayan sea buckthorn berry: An opportunity for rejuvenation applications in Ayurveda. International Journal of Green Pharmacy. 2016, 4, S164. [Google Scholar]
- Mulati, A.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Kamanova, S.; Sair, A.T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Sea-Buckthorn Flavonoids Alleviate High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Inhibiting Insulin Resistance and Neuroinflammation. J Agric Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5835–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.P.; Ahmad, F.; Gore, D.D.; Tikoo, K.; Bansal, A.; Jachak, S.M.; Jena, G. Therapeutic potential of seabuckthorn: a patent review (2000-2018). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2019, 29, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Cui, X.; Su, Z.; Hu, P. A Comparative Study on Polyphenolic Composition of Berries from the Tibetan Plateau by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS System. Chem Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenkowski, S. , Yakimishen, R., Przybylski, R., & Muir, W. E. Quality of extracted SB seed and pulp oil. Canadian Biosystems Engineering. 2006, 48, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, B.; Akhtar, N.; Mahmood, T. A Comprehensive Review of a Magic Plant, Hippophae rhamnoides. Pharmacognosy Journal. 2010, 16, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. , Yang B., Cai W., et al., Effect of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) on blood lipid profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis from 11 independent randomized controlled trials. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2016, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Drossard, C.; Frohling, B.; Bolzenius, K.; Dietrich, H.; Kunz, C.; Kersting, M. Liking of anthocyanin-rich juices by children and adolescents. Appetite. 2012, 58, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.L.; Nandal, U.; Pal, A.; Jain, S. Bioactive compounds and medicinal properties of fruit juices. Fruits. 2014, 69, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.M.; Micha, R.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Shi, P.; Lim, S.; Andrews, K.G.; Engell, R.E.; Ezzati, M.; Mozaffarian, D. Global Burden of Diseases Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert Group (NutriCoDE). Global, Regional, and National Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, Fruit Juices, and Milk: A Systematic Assessment of Beverage Intake in 187 Countries. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0124845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Zafar, R.; Pradeep Dwivedi, LP Shinde and Borkar Prita. Pharmacological and nutritional importance of sea buckthorn (Hippophae). The Pharma Innovation Journal. 2018, 7, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Roque, M.J.; Rojas-Grau, M.A.; Elez-Martinez, P.; Martin-Belloso, O. In vitro bioaccessibility of health-related compounds as affected by the formulation of fruit juice- and milk-based beverages. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Hamouz, K.; Čepl, J.; Pivec, V.; Šulc, M.; Dvořák, P. The Effect of Selected Factors on Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Activity in Potato Tubers. Chem. Listy. 2006, 100, 522–527. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriele, M.; Pucci, L.; Árvay, J.; Longo, V. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of fermented whole wheat on TNFα-stimulated HT-29 and NF-κB signaling pathway activation. Journal of Functional Foods. 2018, 45, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedüsova, A.; Mezeyová, I.; Andrejiová, A. Metódy stanovenia vybraných biologicky aktívnych látok, 1st ed.; Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita: Nitra, Slovak Republic, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald,W. T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, Without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopčeková, J.; Kolesárová, A.; Schwarzová, M.; Kováčik, A.; Mrázová, J.; Gažarová, M.; Lenártová, P.; Chlebo, P.; Kolesárová, A. Phytonutrients of Bitter Apricot Seeds Modulate Human Lipid Profile and LDL Subfractions in Adults with Elevated Cholesterol Levels. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022, 19, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Prasad, R.; Jayamurthy, P.; Pal, K.; Arumughan, C.; Sawhney, R.C. Antiatherogenic effects of seabuckthorn (Hippophaea rhamnoides) seed oil. Phytomedicine. 2007, 14, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng,T. Acute toxicity of flesh oil of Hippophae rhamnoides and its protection against experimental hepatic injury. J. Trad. Chin. Med. 1990, 15, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston, C.; Baoru, Y.; Tahvonen, R.; Kallio, H.; Rimbach, G.H.; Minihane, A.M. Effects of an antioxidant-rich juice (sea buckthorn) on risk factors for coronary heart disease in humans. J. Nutr. Bioch. 2002, 13, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Kłapcińska, B.; Podgórski, T.; Szade, B.; Tyl, K.; Hadzik, A. Effects of supplementation with acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) berry-based juice blend on the blood antioxidant defence capacity and lipid profile in junior hurdlers. A pilot study. Biol. Sport. 2015, 32, 161–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiitinen, K.M.; Yang, B.; Haraldsson, G.G.; Jonsdottir, S.; Kallio, H.P. Fast analysis of sugars, fruit acids, and vitamin C in SB (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) varieties. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2006, 54, 2508–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbravă, D.G.; Moldovan, C.; Raba, D.N.; Popa, M.V.; Drugă, M. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, polyphenols and vitamin C content of some exotic fruits. Journal of Pharmacy and BioAllied Sciences. 2016, 22, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.W.; Lee, J.E.; Park, K.M. Diets containing Sophora japonica L. prevent weight gain in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 819–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Jouyandeh, Z.; Abdollahi, M. A systematic review of anti-obesity medicinal plants - an update. J Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2013, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-McGrievy, G.; Mandes, T.; Crimarco, A. A plant-based diet for overweight and obesity prevention and treatment. Journal of Geriatric Cardiology. 2017, 14, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Paraíso, A.F.; Sousa, J.N.; Andrade, J.M.O.; Mangabeira, E.S.; Lelis, D.F.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Martins, A.M.E.B.; Lima, W.J.N.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Melo, G.A.; Schwarz, M.; Santos, S.H.S. Oral gallic acid improves metabolic profile by modulating SIRT1 expression in obese mice brown adipose tissue: A molecular and bioinformatic approach. Life Sci. 2019, 237, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, M.; Fan, P.; Lei, D.; Du, J.; Gale, M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y. Ellagic acid promotes browning of white adipose tissues in high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats through suppressing white adipocyte maintaining genes. Endocr. J. 2019, 66, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Tang, Q.; Gao, Z.C.; Yu, Z.P.; Song, H.Z.; Zheng, X.D.; Chen, W. Blueberry and mulberry juice prevent obesity development in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8, e77585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noratto, G.; Martino, H.; Simbo, S.; Byrne, D.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Consumption of polyphenol-rich peach and plum juice prevents risk factors for obesity-related metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease in Zucker rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.S.; Saccon, T.D.; da Silva, T.M.; Costa, M.Z.; Dutra, F.; de Vasconcelos, A.; Lencina, C.L.; Stefanello, F.M.; Barschak, A.G. Green juice as a protector against reactive species in rats. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Dupak, R.; Hrnkova, J.; Simonova, N.; Kovac, J.; Ivanisova, E.; Kalafova, A.; Schneidgenova, M.; Prnova, M.S.; Brindza, J.; Tokarova, K.; Capcarova, M. The consumption of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) effectively alleviates type 2 diabetes symptoms in spontaneous diabetic rats. Res Vet Sci. 2022, 152, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body Mass Index: Obesity, BMI, and Health: A Critical Review. Nutr Today. 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtonen, H.M.; Suomela, J.P.; Tahvonen, R.; Yang, B.; Venojärvi, M.; Viikari, J.; Kallio, H. Different berries and berry fractions have various but slightly positive effects on the associated variables of metabolic diseases on overweight and obese women. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2011, 65, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmo, P.S.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Lehtonen, H.M.; Suomela, J.P.; Yang, B.; Viikari, J.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Kallio, H.P. Effects of sea buckthorn and bilberry on serum metabolites differ according to baseline metabolic profiles in overweight women: a randomized crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013, 98, 941–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Effects and Mechanisms of Fruit and Vegetable Juices on Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, G.; Liao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, X. Effects of berries consumption on cardiovascular risk factors: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, L.M.; Meda, V.; Naik, S.; Satya, S. Sea buckthorn berries: A potential source of valuable nutrients for nutraceuticals and cosmoceuticals. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, M.; Miglio, C.; Ray, S. Potential cardiovascular implications of Sea Buckthorn berry consumption in humans. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.J.; Kaur, M.; Dhillon, R.S.; Tappia, P.S.; Dhalla, N.S. Health benefits of sea buckthorn for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. J. Funct. Foods. 2011, 3, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, B.; Cai, W.; Li, D. Effect of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) on blood lipid profiles: A systematic review and meta-analysis from 11 independent randomized controlled trials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomela, J.P.; Ahotupa, M.; Yang, B.; Vasankari, T.; Kallio, H. Absorption of flavonols derived from sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) and their effect on emerging risk factors for cardiovascular disease in humans. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 7364–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexel, H.; Aczel, S.; Marte, T.; Benzer, W.; Langer, P.; Moll, W.; Saely, C.H. Is atherosclerosis in diabetes and impaired fasting glucose driven by elevated LDL cholesterol or by decreased HDL cholesterol? Diabetes Care. 2005, 28, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.J. The potential role of HDL-and LDL-cholesterol modulation in atheromatous plaque development. Cur. Med. Res. Opin. 2005, 21, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Castillo, K.P.; Lin, S.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Vizmanos, B.; López-Quintero, A.; Márquez-Sandoval, F. Functional Food and Bioactive Compounds on the Modulation of the Functionality of HDL-C: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccleston, C.; Baoru, Y.; Tahvonen, R.; Kallio, H.; Rimbach, G.H.; Minihane, A.M. Effects of an antioxidant-rich juice (sea buckthorn) on risk factors for coronary heart disease in humans. J. Nutr. Bioch. 2002, 13, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.K.; Korte, H.; Yang, B.; Stanley, J.C.; Kallio, H.P. Sea buckthorn berry oil inhibits platelet aggregation. J. Nutr Biochem. 2000, 11, 491–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokanson, J.E.; Austin, M.A. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J. Cardiovasc. Risk. 1996, 3, 213–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. , A clinical study of reducing fat and anti-oxidation of dried Hippoplae emulsion. Hippophae. 1995, 8, 33–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kunutsor SK, Zaccardi F, Karppi J, Kurl S, Laukkanen JA. Is High Serum LDL/HDL Cholesterol Ratio an Emerging Risk Factor for Sudden Cardiac Death? Findings from the KIHD Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou Y, Zhong L, Hu C, Zhong M, Peng N, Sheng G. LDL/HDL cholesterol ratio is associated with new-onset NAFLD in Chinese non-obese people with normal lipids: a 5-year longitudinal cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, J.J.; van der Steeg, W.A.; Holme, I.; Gaffney, M.; Cater, N.B.; Barter, P.; Deedwania, P.; Olsson, A.G.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Demicco, D.A.; Szarek, M.; LaRosa, J.C.; Pedersen, T.R.; Grundy, S.M. Lipids, apolipoproteins, and their ratios in relation to cardiovascular events with statin treatment. Circulation 2008, 117, 3002–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habanova, M.; Holovicova, M.; Scepankova, H.; Lorkova, M.; Gazo, J.; Gazarova, M.; Pinto, C.A.; Saraiva, J.A.; Estevinho, L.M. Modulation of Lipid Profile and Lipoprotein Subfractions in Overweight/Obese Women at Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases through the Consumption of Apple/Berry Juice. Antioxidants, 2022, 11, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.O.; Earnest, C.P.; Tinsley, G.M.; Izidoro, L.F.M.; Macedo, R.C.O. Small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (sdLDL-C): Analysis, effects on cardiovascular endpoints and dietary strategies. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020, 63, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, E.K.; Aday, A.W.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Pradhan, A.D. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Small Dense LDL Cholesterol, and Incident Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanonidou, C. Small dense low-density lipoprotein: Analytical review. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2021, 520, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Fu, D.X.; Wilkinson, M.; Simmons, B.; Wu, M.; Betts, N.M.; Du, M.; Lyons, T.J. Strawberries decrease atherosclerotic markers in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Res. 2010, 30, 462–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Betts, N.M.; Nguyen, A.; Newman, E.D.; Fu, D.; Lyons, T.J. Freeze-dried strawberries lower serum cholesterol and lipid peroxidation in adults with abdominal adiposity and elevated serum lipids. J Nutr. 2014, 144, 830–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habanova, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Holovicova, M.; Moreira, S.A.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Haban, M.; Gazo, J.; Schwarzova, M.; Chlebo, P.; Bronkowska, M. Effect of berries/apple mixed juice consumption on the positive modulation of human lipid profile. Journal of Functional Foods. 2019, 60, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, S.J.; Parelman, M.A.; Freytag, T.L.; Stephensen, C.B.; Kelley, D.S.; Mackey, B.E.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Bonnel, E.L. Effects of dietary strawberry powder on blood lipids and inflammatory markers in obese human subjects. Br J Nutr. 2012, 108, 900–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunino, S.J.; Peerson, J.M.; Freytag, T.L.; Breksa, A.P.; Bonnel, E.L.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Storms, D.H. Dietary grape powder increases IL-1beta and IL-6 production by lipopolysaccharide-activated monocytes and reduces plasma concentrations of large LDL and large LDL-cholesterol particles in obese humans. Br J Nutr. 2014, 112, 369–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein as Biomarker for Atherosclerotic Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017, 1273042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berneis, K.K.; Krauss, R.M. Metabolic origins and clinical significance of LDL heterogeneity. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ding, X.; Gu,W. Radical-scavenging proanthocyanidins from sea buckthorn seed. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Kwon, S.; Zheng, D. Effects of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes on lipoprotein subclass particle size and concentration determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. Diabetes. 2003, 52, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, B.J.; Lemieux, I.; Després, J.P.; Gagnon, P.; Wareham, N.J.; Stroes, E.S.; Kastelein, J.J.; Khaw, K.T.; Boekholdt, S.M. HDL particle size and the risk of coronary heart disease in apparently healthy men and women: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Atherosclerosis. 2009, 206, 276–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitnanova, I.; Oravec, S.; Janubova, M.; Konarikova, K.; Dvorakova, M.; Laubertova, L.; Kralova, M.; Simko, M.; Muchova, J. Gender differences in LDL and HDL subfractions in atherogenic and nonatherogenic phenotypes. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 79, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oravec, S.; Dukat, A.; Gavornik, P.; Kucera, M.; Gruber, K.; Gaspar, L.; Rizzo, M.; Toth, P.P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Atherogenic versus non-atherogenic lipoprotein profiles in healthy individuals. Is there a need to change our approach to diagnosing dyslipidemia? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 2892–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlstrøm, H.; Mjøen, G.; März, W. Neopterin is associated with cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in renal transplant patients. Clin Tranplant. 2014, 28, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancalon, P.F.; King, D. Health benefits of polyphenol-rich orange and grapefruit juices. XII Int. Citrus Congr. Int. Soc. Citric. 2015, 1065, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- O'Morain, V.L.; Ramji, D.P. The Potential of Probiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, R.; Castro-Barquero, S.; Estruch, R.; Sacanella, E. Nutrition and Cardiovascular Health. J Mol Sci. 2018, 19, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Broncel, M.; Markowicz, M.; Chałubiński, M.; Wojdan, K.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E. Short-term supplementation with Aronia melanocarpa extract improves platelet aggregation, clotting, and fibrinolysis in patients with metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Bridgeman, M.B.; Brunetti, L. Evaluation of alterations in serum immunoglobulin concentrations in components of metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders. 2019, 19, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, B.M.; Erlund, I.; Koli, R.; Puukka, P.; Hellström, J.; Wähälä, K.; Mattila, P.; Jula, A. Consumption of chokeberry (Aronia mitschurinii) products modestly lowered blood pressure and reduced low-grade inflammation in patients with mildly elevated blood pressure. Nutr Res. 2016, 36, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffey, K.J.; Sutherland, L.A. Adult consumers of cranberry juice cocktail have lower C-reactive protein levels compared with nonconsumers. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Chang, Y.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Yang, M.D.; Chao, P.M. Tomato juice supplementation in young women reduces inflammatory adipokine levels independently of body fat reduction. Nutrition. 2015, 31, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codoner-Franch, P.; Betoret, E.; Betoret, N.; Lopez-Jaen, A.B.; Valls-Belles, V.; Fito, P. Dried apples enriched with mandarin juice by vacuum impregnation improve antioxidant capacity and decrease inflammation in obese children. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buscemi, S.; Rosafio, G.; Arcoleo, G.; Mattina, A.; Canino, B.; Montana, M.; Verga, S.; Rini, G. Effects of red orange juice intake on endothelial function and inflammatory markers in adult subjects with increased cardiovascular risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, E.J.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nijveldt, R.J.; van Nood, E.; van Hoorn, D.E.; Boelens, P.G.; van Norren, K.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 418–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.; Schijlen, E.; Kooistra, T.; Herbers, K.; Verschuren, L.; Hall, R.; Sonnewald, U.; Bovy, A.; Kleemann, R. Transgenic flavonoid tomato intake reduces C-reactive protein in human C-reactive protein transgenic mice more than wild-type tomato. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2331–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Lowe, G.D.; Rumley, A.; Bruckdorfer, K.R.; Whincup, P.H. Associations of vitamin C status, fruit and vegetable intakes, and markers of inflammation and hemostasis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 567–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Units | Quantity | Parameter | Units | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | mg GAE/g | 1.56 ± 0.03 | Palmitic acid | (%) | 35.91 ± 0.62 |
| Rutin | mg/L | 18.26 ± 0.21 | Palmitoleic acid | (%) | 29.77 ± 0.65 |
| Benzoic acid | mg/L | 142.47 ± 1.12 | Stearic acid | (%) | 0.93 ± 0.08 |
| Caffeic acid | mg/L | 7.13 ± 0.34 | Oleic acid | (%) | 22.01 ± 1.35 |
| Coumaric acid | mg/L | 6.23 ± 0.03 | Linoleic acid | (%) | 2.87 ± 0.01 |
| Ferulic acid | mg/L | 18.14 ± 0.21 | α-linolenic acid | (%) | 0.82 ± 0.01 |
| Myricetin | mg/L | 12.28 ± 0.38 | Arachidic acid | (%) | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Resveratrol | mg/L | 2.48 ± 0.08 | SFA | (%) | 3.69 ± 0.01 |
| Neochlorogenic acid | mg/L | 1.03 ± 0.06 | MUFA | (%) | 51.91 ± 0.69 |
| Cryptochlorogenic acid | mg/L | 5.53 ± 0.15 | PUFA | (%) | 37.23 ± 0.54 |
| Vitamin C | mg/100g | 385.41 ± 0.38 | |||
| Total carotenoids | mg/100g | 64.79 ± 5.27 | |||
| AA (inhibition of DPPH) | % | 42.5 ± 0.43 |
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 50.58 ± 5.76 | 40 | 55 |
| BW (kg) | 72.89 ± 13.95 | 49.20 | 100.80 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.30 ± 5.01 | 19.56 | 38.41 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 6.02 (6.58-5.66) | 5.06 | 8.33 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.70 ± 0.23 | 1.15 | 2.01 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.86 (4.71-3.43) | 2.84 | 5.83 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.97 (1.12-0.85) | 0.53 | 3.15 |
| GLU (mmol/L) | 4.80 ± 0.35 | 4.20 | 5.40 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 127.76 ± 17.40 | 85 | 159 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 86.00 ± 10.43 | 73 | 110 |
| Parameter | Baseline | Week 8 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BW (kg) | 72.89 ± 13.95 | 72.49 ± 13.98 | 0.0221 |
| BFM (kg) | 25.16 ± 10.37 | 24.22 ± 10.40 | < 0.001 |
| BFM (%) | 33.21 ± 8.07 | 32.07 ± 8.37 | < 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.30 ± 5.01 | 26.07 ± 4.93 | 0.0389 |
| VFA (cm2) | 102.31 ± 37.82 | 98.63 ± 38.55 | < 0.001 |
| SMM (kg) | 26.20 ± 2.89 | 26.54 ± 3.01 | 0.0183 |
| FFM (kg) | 47.73 ± 4.92 | 48.26 ± 5.09 | 0.0268 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 127.96 ± 13.87 | 127.27 ± 17.23 | > 0.05 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 85.77 ± 10.29 | 85.26 ± 8.31 | > 0.05 |
| Parameter | Baseline | Week 8 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT (µkat/L) | 0.24 (0.20-0.32) | 0.27 (0.22-0.36) | > 0.05 |
| AST (µkat/L) | 0.31 (0.27-0.36) | 0.32 (0.27-0.38) | > 0.05 |
| GGT (µkat/L) | 0.28 (0.24-0.34) | 0.28 (0.23-0.38) | > 0.05 |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 8.60 (7.05-11.40) | 8.55 (6.55-10.72) | > 0.05 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 4.68 ± 1.29 | 4.75 ± 1.22 | > 0.05 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 65.90 ± 9.31 | 68.30 ± 8.70 | > 0.05 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | 275.29 ± 61.05 | 284.71± 67.07 | > 0.05 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 49.11 ± 2.62 | 48.65 ± 2.68 | > 0.05 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.40 (4.00-5.70) | 4.05 (3.50-5.05) | < 0.001 |
| IL-6 (ng/L) | 7.84 ± 0.95 | 7.36 ± 0.79 | 0.0387 |
| ORM (g/L) | 0.86 ± 0.21 | 0.55 ± 0.18 | < 0.001 |
| IgA (g/L) | 1.70 ± 0.62 | 1.55 ± 0.62 | < 0.001 |
| IgG (g/L) | 10.97 ± 2.78 | 10.43 ± 2.62 | < 0.001 |
| IgM (g/L) | 1.22 ± 0.54 | 1.12 ± 0.52 | < 0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 6.02 (6.58-5.66) | 6.06 (6.85-5.23) | > 0.05 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.70 ± 0.23 | 1.77 ± 0.28 | 0.0051 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.86 (4.71-3.43) | 3.73 (4.60-3.31) | 0.0335 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.97 (1.12-0.85) | 1.07 (1.33-0.77) | > 0.05 |
| LDL/HDL ratio | 2.44 ± 0.57 | 2.31 ± 0.58 | 0.0070 |
| Parameter | Baseline | Week 8 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 5.98 (7.42-5.85) | 6.35 (7.14-5.96) | NS |
| LDL | 3.21 (4.64-3.18) | 3.93 (4.59-3.62) | NS |
| HDL | 1.62 ± 0.32 | 1.49 ± 0.33 | NS |
| TG | 1.49 (2.26-1.01) | 1.44 (1.86-1.14) | NS |
| VLDL | 1.14 ± 0.35 | 0.99 ± 0.21 | NS |
| IDL-A | 0.59 ± 0,25 | 0.87 ± 0.30 | 0.0058 |
| IDL-B | 0.36 (0.52-0.29) | 0.50 (0.68-0.42) | 0.0241 |
| IDL-C | 0.53 (0.64-0.33) | 0.66 (0.72-0.56) | NS |
| LDL1 | 1.21 ± 0.58 | 1.34 ± 0.39 | NS |
| LDL2 | 0.79 ± 0.26 | 0.52 ± 0.32 | NS |
| LDL3-7 | 0.13 (0.36-0.08) | 0 (0.04-0) | 0.0321 |
| Mean LDL particle size | 267.17 ± 5.27 | 271.67 ± 4.13 | 0.0053 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





