1. Introduction
Maxillary canines show eruption abnormalities characterized by frequent ectopic eruptions or impactions because they are between teeth that erupt later than other teeth in the dental arch and follow a long and difficult eruption pathway higher than the other teeth during the eruption. Knowing the basic concepts of development and eruption will help to understand the cause of malposition and choose the appropriate treatment [
1,
2] (p. 12).
Impaction of maxillary canines is quite common; after the third mandibular molars, maxillary canines are the most frequently impacted teeth in the dental arch. Dachi and Howell conducted a study on 3874 routine full-mount radiographs from patients over 20 years of age and found the incidence of maxillary canines to be impacted at 0.92%. They stated that these cases were mostly unilateral and saw twice as many women (1.17%) as men (0.51%). The incidence of mandibular canines was approximately 0.09% [
3] (p. 12).
Two major theories explain the cause of the ectopic persistence of permanent maxillary canines. These are guidance theory and genetic theory. In the guidance theory, it is believed that the roots of the lateral incisor guide the eruption of the permanent canine in the dental arch in the appropriate direction. In cases such as hypoplasia or lateral incisor aplasia, the canine crown cannot continue in its proper place and becomes palatal dysplasia. According to genetic theory, ectopic eruption or impaction of the canine in the palatal direction is due to genetic reasons [
1,
4,
5] (p. 12).
The mesiodistal localization and angulation of the canines are important regarding their eruption potential. Ericson and Kurol reported that permanent canine crowns positioned mesially are less likely to erupt after the extraction of deciduous canines. The proportion of impacted canines in the buccal/labial direction is less than that of impacted canines in the palatal direction. Impacted maxillary canines are 85% palatal and 15% labial/buccal [
6] (p. 12). During their normal development, canines tend to erupt in the palatal direction between the ages of 5 and 9, while they move more in the buccal direction between the ages of 10 and 12 [
7] (p. 12). Space and crowding in the maxillary dental arch are often the main causes of buccally located canines, while excess space and lateral deficiency cause palatal-located canines [
8] (p. 12). In cases of excess space in the maxillary dental arch, lateral deficiency or shape anomaly, and Angle Class II, Division 2, palatal-positioned ectopic canines are observed more frequently [
9] (p. 12). Becker found in his study that 5.5 percent of palatally displaced canines did not have maxillary lateral incisors. This was 2.4 times higher than in the general population [
10] (p. 12).
Although the initial radiographic examination of impacted canines includes periapical and panoramic films, CBCT (cone beam computerized tomography) is a very useful method to more accurately define the position of the impacted canine in three dimensions and to analyze whether there is root resorption [
8] (p. 12). CBCTs are very useful in determining root resorption compared to other radiographic methods. In addition, CBCTs are very good at analyzing follicle size, the buccal and palatal position of the tooth, the inclination of the long axis of the tooth, the amount of bone in the tooth, the condition of adjacent teeth, root resorption, and dental development mechanisms in dental follicle research [
11] (p. 12).
Treatment of impacted canines often involves a complex multidisciplinary approach that requires surgery, periodontology, restorative treatment, and orthodontic applications. In a patient with an impacted canine, the existing malocclusions and the prognosis of orthodontic treatment must be fully evaluated for the location of the impacted tooth. Factors affecting the prognosis include age, cooperation, oral hygiene, skeletal variation, gaps or crowding in the dental arch, and the canine crown or root's vertical, anteroposterior, and transverse positions. The prognosis is poor if the canine is placed close to the midline and at an angle of more than 45° to the midline. Furthermore, for successful treatment, the root should not have ankylosis or dilaceration and should be carefully examined to determine any resorption of the incisive roots. The more the tooth is moved, the poorer the prognosis. A good buccal overjet-overbite relationship and a correct root position are essential to ensuring a stable outcome [
12] (p. 13).
The position of the impacted tooth in three directions should be evaluated with a clinical and radiological examination. Angulation of the teeth in buccopalatal, vertical, or horizontal positions affects the difficulty of treatment [
13] (p. 13). In canines that are too inclined towards the midline, it is more appropriate to extract these teeth rather than treat them. Furthermore, the bucco-palatal position of the canine affects the treatment decision. Canines with palatal positions are usually treated by exposure, whereas ones with buccal positions may require extraction due to difficulties in the attached gingiva [
14] (p. 13).
Furthermore, if the canine is above the occlusal level, the prognosis for treatment is not good. In the rule that McSherry defined as the 'vertical rule of thirds,' he said that if the apex of the canine tubercle is at the level of the enamel-cementum junction of the adjacent incisor, it has a good prognosis. It has a moderate prognosis at half the length of the incisor root and a poor prognosis at 1/3 of the apical. If the canine apex is 14 mm above the occlusal plane, treatment takes an average of 24 months; if it is more than 14 mm, treatment can take up to 31 months [
15] (p. 13).
Pitt et al. investigated the factors affecting the difficulty of treatment. They found that the ectopic canines' horizontal position, the patient's age, the bucco-palatal position, or the vertical height of the ectopic tooth are among the factors affecting orthodontic treatment [
16]. The current study’s null hypothesis is that no statistically significant differences in morphological characteristics exist between the unilaterally impacted maxillary canines and the nonimpacted canines.
In the study by Ericson and Kurol, root resorption was observed in 38% of the laterals and 9% of the central incisors due to ectopically located canines, and only 3% of normal erupting canines were observed to have root resorption in the lateral incisors. Once resorption occurs, it progresses quite rapidly. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment decisions should be made very quickly. According to Ericson and Kurol, resorption occurs more frequently in palatal canines [
17] (p. 13). When impacted canines are not treated, they can cause external root resorption, internal resorption, cyst formation, migration of adjacent teeth, crown resorption of the ectopic tooth, and labial or lingual malposition of the ectopic tooth [
13] (p. 13).
Knowing some of the characteristic features of impacted teeth according to their location at the beginning of treatment may increase the effectiveness of treatment and shorten the duration. This study aims to explore the effects of vertical, horizontal, and transversal positions and dentoalveolar morphological characteristics of impacted maxillary canines on the prognosis of orthodontic treatment, as well as detect the presence of crown root anomalies or resorption that may occur in impacted teeth or adjacent teeth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
The project was approved by the ethics committee of Ankara Yildirim Beyazit University, Ankara, Turkey (ref: 08.12.2022/19-1272).
2.2. Calculation of the Sample Size and Participants
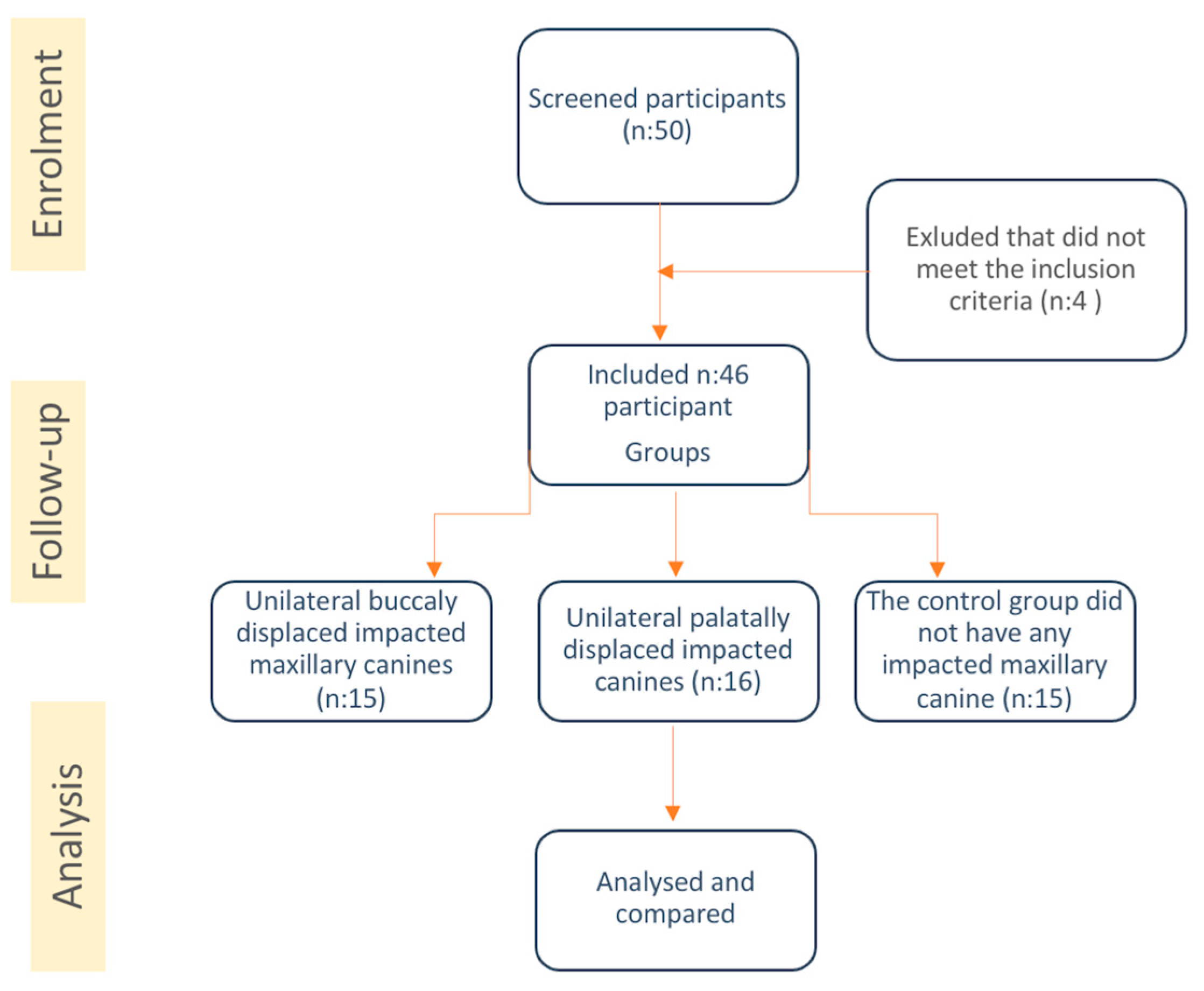
This study was planned as a retrospective cross-sectional study. CBCT images of 46 patients with impacted canines who applied to the Faculty of Dentistry of Ankara Yildirim Beyazit University were used as the study material. All CBCT images were obtained standing, using a Promax 3D Mid machine (Planmeca, Helsinki, Finland). Exposure parameters were 94 kVp, 14 mA, and 27 s. A single orthodontist evaluated the CBCT images in all three planes (sagittal, axial, and coronal) on a flat-screen monitor. All angular and dimensional measurements were made using the Planmeca Romexis 3D Imaging Program (Planmeca Romexis 3D Imaging Software, Helsinki, Finland).
The sample size was calculated using the G*power software (version 3.1.9; Franz Faul Universitat, Kiel, Germany). Al-Tawachi’s study [
18] was taken into consideration for the power analysis. According to the power analysis, the total sample size was determined to be 27, with a desired power (1-b) of 0.95 at the conventional a level (0.05) and an effect size of 0.84.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria: adolescents aged >10 years, unilateral impaction of permanent maxillary canines, presence and eruption of the maxillary lateral incisors, and CBCT images with good image quality. Exclusion criteria: no systemic or dentofacial deformities; non-syndromic and non-cleft patients without previous orthodontic treatment; no contributing history of trauma; no multiple missing teeth; and no presence of cysts or other pathology.
2.4. Study Design and Definitions of the Variables Used in the Study
The samples were divided into 3 groups according to the location of the impacted canine: the “no impaction group (CC, control group)”, “the group with unilateral buccal impaction (BC)”, and “the group with unilateral palatal impaction (PC)”.
The demographic characteristics (age, sex) of the participants were recorded. The following unilaterally impacted canine-related variables were analyzed in the CBCT images: impaction side (left side or right side); location (buccal, central or palatal); rotation (mesiobuccal, distobuccal, mesiopalatal, distopalatal); level of contact relationship with the adjacent tooth (crown, cervical, middle, apical); impacted canines with the sagittal view (sectors 1-5); root resorption levels and number of adjacent teeth (Grade 1-3).
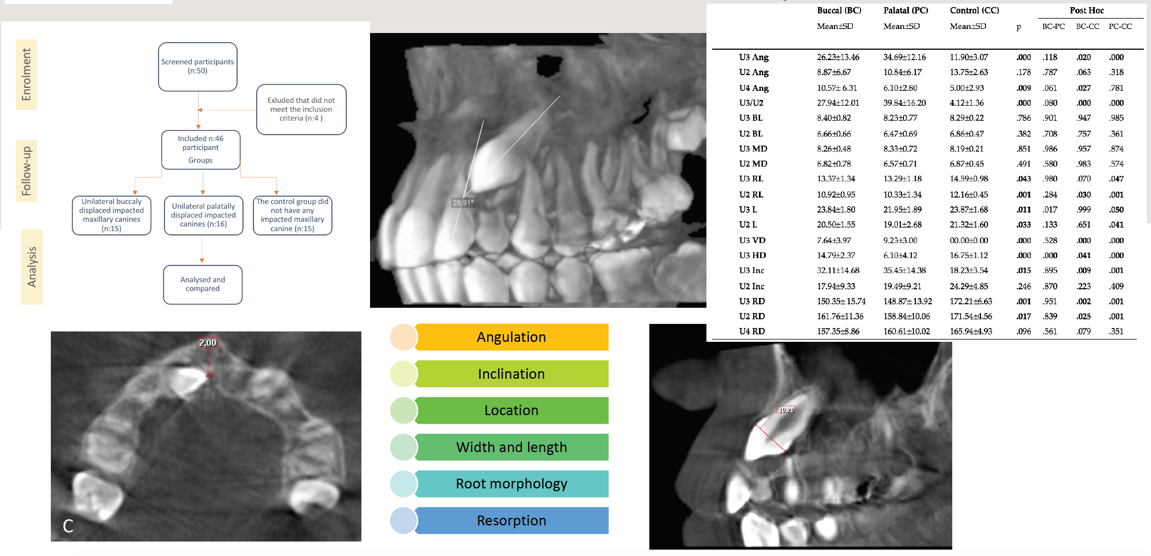
Figure 1.
Flow chart showing the methodology of the study.
Figure 1.
Flow chart showing the methodology of the study.
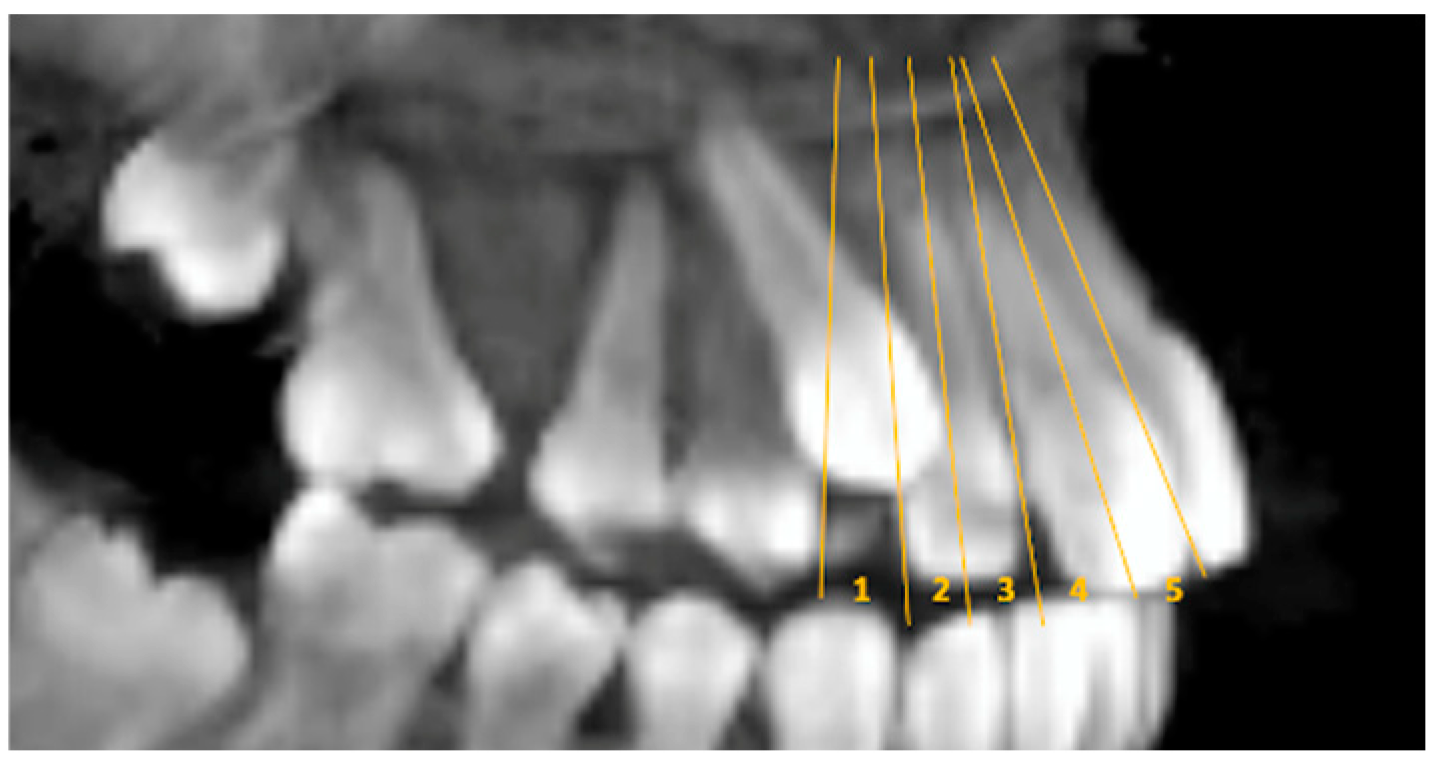
Sector; sagittal view illustrating reference lines of canine overlap (sectors) assigned to one of five categories: 1 = normal position; 2 = distal to the long axis of the lateral incisor; 3 = mesial to the long axis of the lateral incisor; 4 = distal to the long axis of the central incisor; 5 = mesial to the long axis of the central incisor [
19] (p. 13) (
Figure 2).
Resorption; the resorption caused by the impacted canine in the adjacent teeth was evaluated with axial CBCT images. The severity of resorption was graded according to the Ericson and Kurol classification. According to this, grade 0 (no resorption): intact root surface except for cement loss. Grade 1 (mild resorption): mild resorption of the pulp up to half the thickness of the dentin. Grade 2 (moderate resorption): Half or more of the pulp is covered with pulp dentin. Grade 3 (severe resorption): the pulp is exposed [
20] (p. 13).
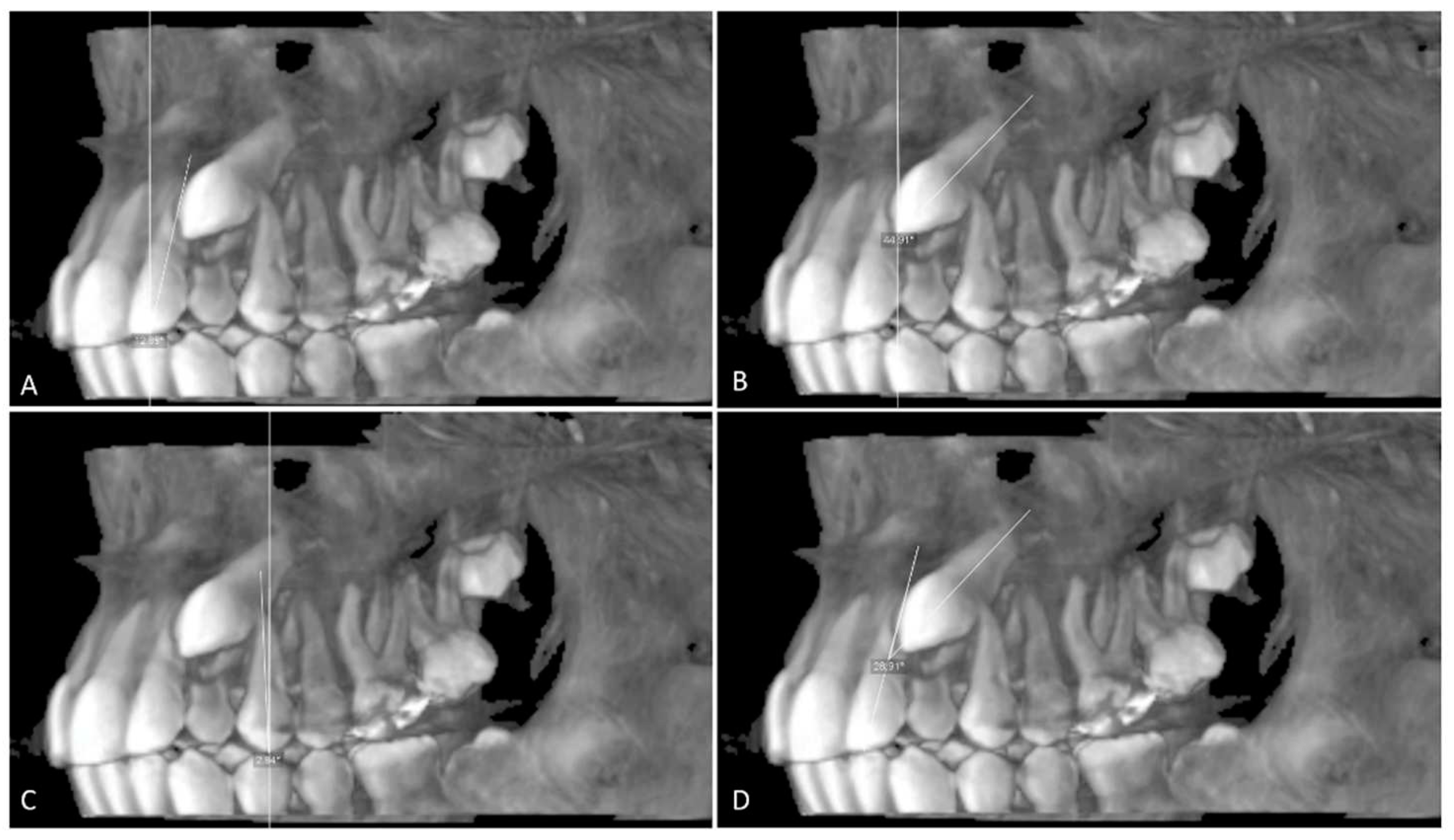
The angulation of the maxillary impacted canine (U3Ang), the lateral incisor (U2Ang), and the first premolar (U4Ang) to the vertical line is determined from the sagittal section by the resulting angle between a line parallel to the midline and a line on the long axis of the lateral incisor, the canine, and the first premolar. The angle between the long axes of the impacted canine and the adjacent lateral incisor (U3/U2) (
Figure 3).
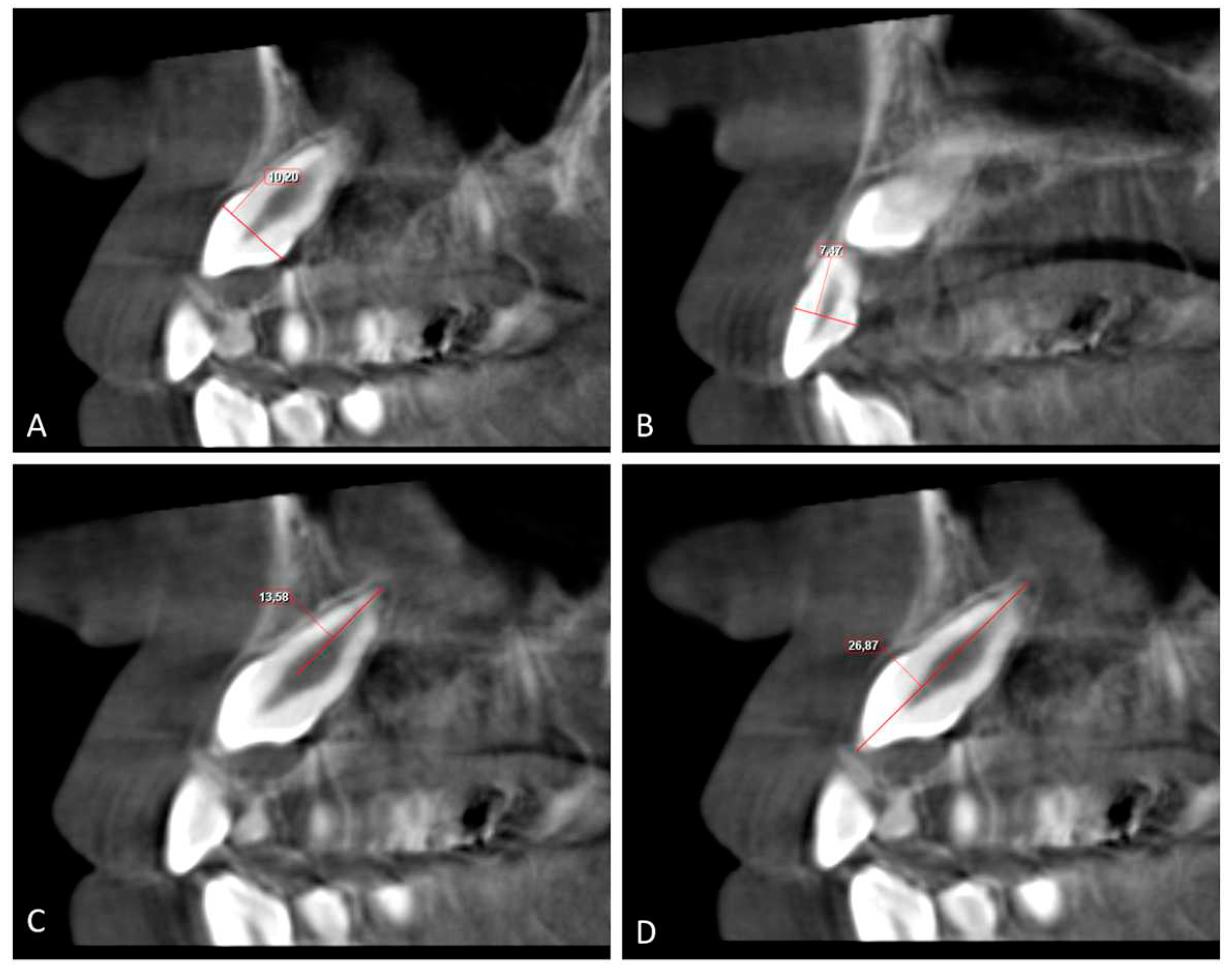
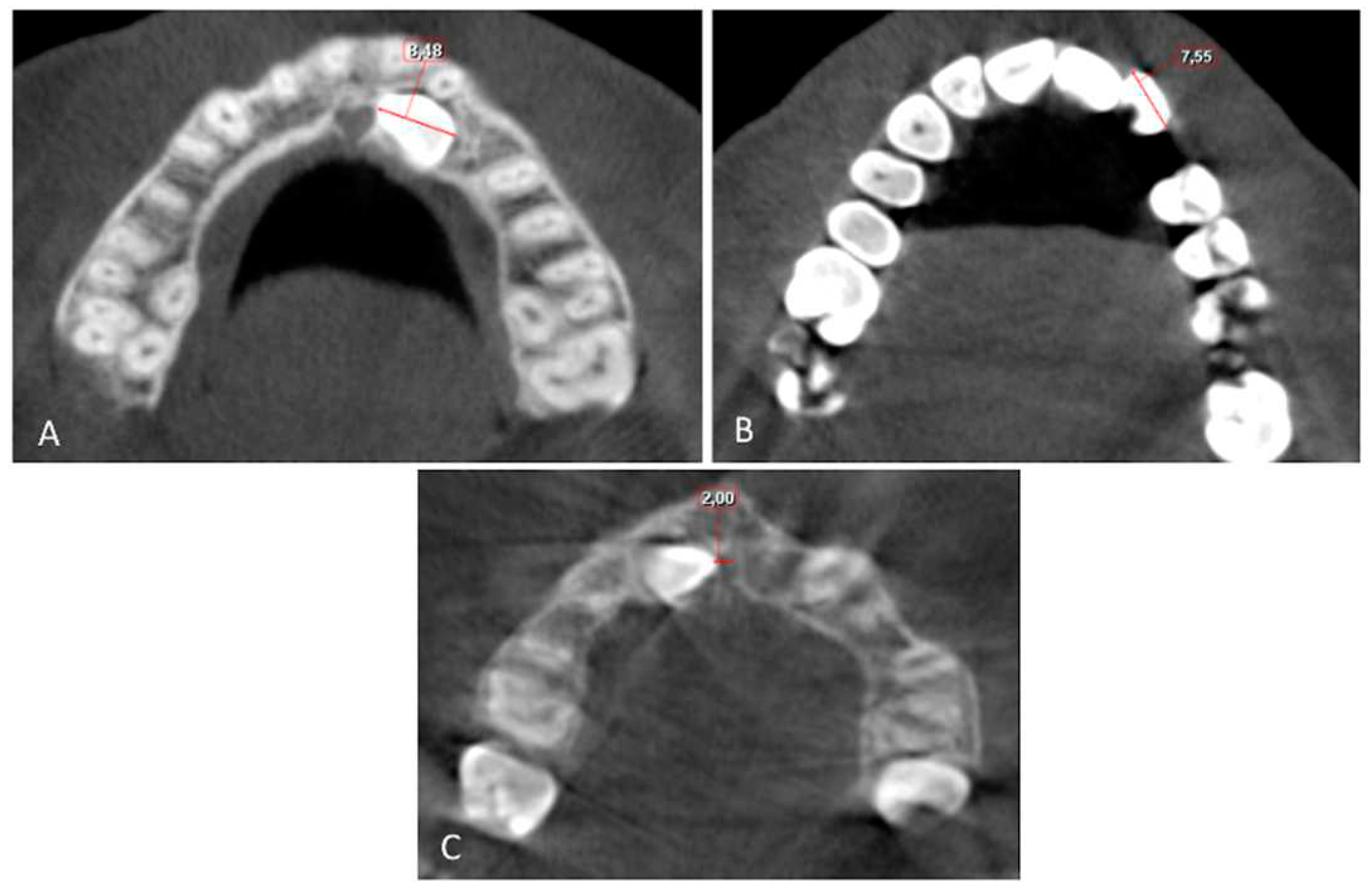
The buccolingual (BL) and mesiodistal (MD) widths of the crowns of the lateral incisor (U2) and canine (U3) were measured from the widest point of the crown perpendicular to the long axis on the sagittal and coronal sections, respectively (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
Root length (RL) was measured from the lowest level of the buccal cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to the root apex, and the total length (L) of the lateral incisor was measured from the incisal tip to the root apex on the sagittal section (
Figure 5). The horizontal distance of the maxillary impacted canine (U3 HD) from the tip of the canine cusp to the midline was measured in the axial section. The vertical distance of the maxillary impacted canine (U3 VD) from the tip of the canine cusp to the occlusion plane was measured in the sagittal plane (
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6).
Figure 5.
A. Buccolingual width of the canine crown (U3 BL) and B. Buccolingual width of lateral crown (U2 BL); the distance between widest points of the crown on the sagittal section; C. Length of the root canine (U3 RL) and length of the root lateral incisor (U2 RL); the length from lowest buccal CEJ level to the root apex on the sagittal section. D. Total length of the canine (U3 L) and total length of the lateral incisor (U2 L); the length from the incisal tip to the root apex on the sagittal section. CEJ: Cementoenamel junction.
Figure 5.
A. Buccolingual width of the canine crown (U3 BL) and B. Buccolingual width of lateral crown (U2 BL); the distance between widest points of the crown on the sagittal section; C. Length of the root canine (U3 RL) and length of the root lateral incisor (U2 RL); the length from lowest buccal CEJ level to the root apex on the sagittal section. D. Total length of the canine (U3 L) and total length of the lateral incisor (U2 L); the length from the incisal tip to the root apex on the sagittal section. CEJ: Cementoenamel junction.
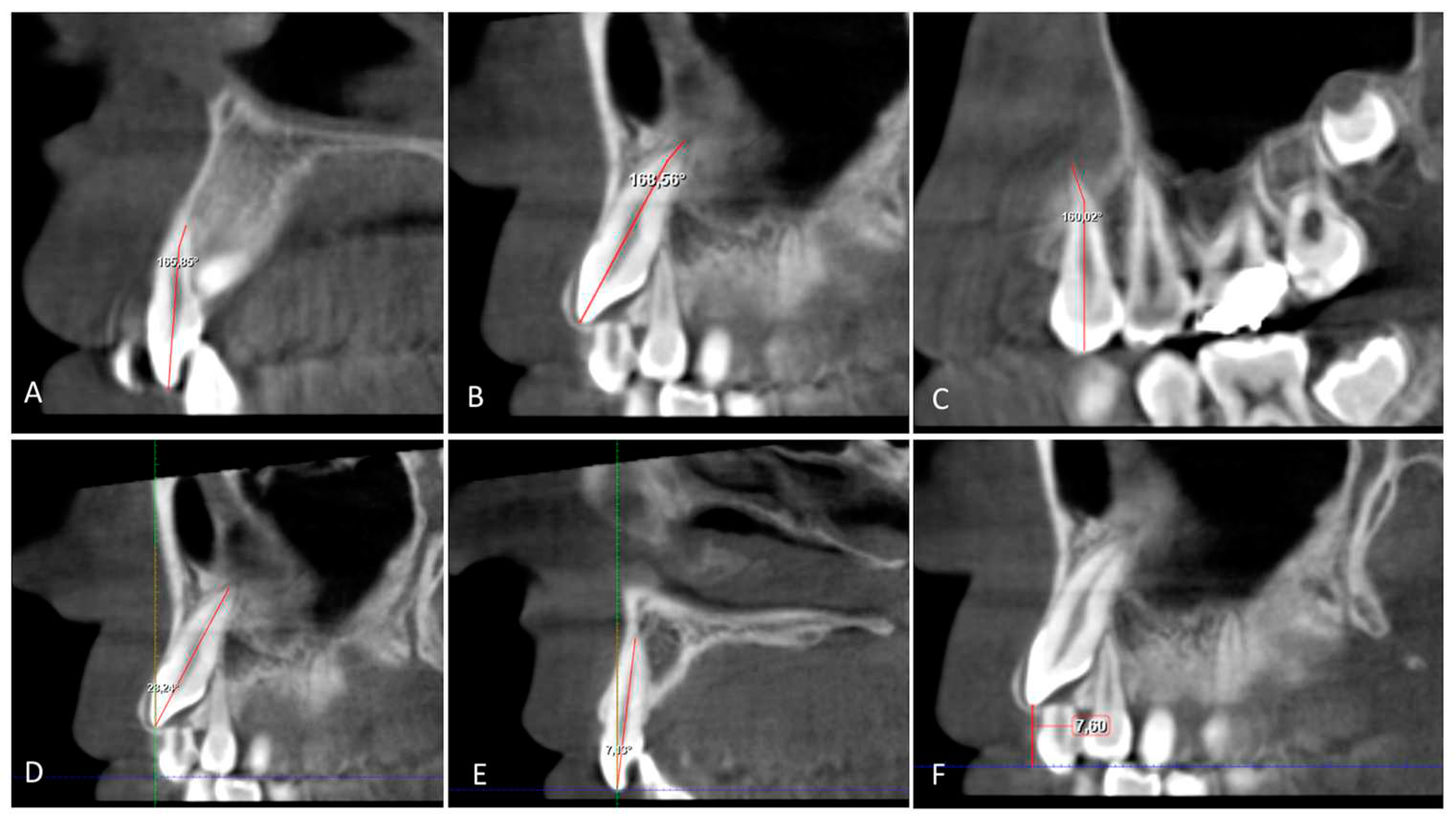
Figure 6.
A. B. C. The angle root dilaceration of canine (U3 RD), lateral incisor (U2 RD) and 1.premolar (U4 RD); the angle between a line to long axis of tooth and a line of the root apex on the sagittal section. D. E. Inclination of canine (U3 Inc) and lateral incisor (U2 Inc); the angle between a line 90° to the occlusal plane and a line to the long axis of the canine and lateral incisor on the sagittal section. F. Vertikal Distance to occlusal plane from canine crown (U3 VD); distance from cusp tip of canine crown to the occlusal plane on the sagittal section.
Figure 6.
A. B. C. The angle root dilaceration of canine (U3 RD), lateral incisor (U2 RD) and 1.premolar (U4 RD); the angle between a line to long axis of tooth and a line of the root apex on the sagittal section. D. E. Inclination of canine (U3 Inc) and lateral incisor (U2 Inc); the angle between a line 90° to the occlusal plane and a line to the long axis of the canine and lateral incisor on the sagittal section. F. Vertikal Distance to occlusal plane from canine crown (U3 VD); distance from cusp tip of canine crown to the occlusal plane on the sagittal section.
The inclination of the maxillary impacted canine (U3Inc) and lateral incisor (U2Inc) is determined from the sagittal section by the resulting angle between a line parallel to the midline and a line to the long axis of the lateral incisor and canine (
Figure 6). The angle of dilaceration of the root (RD) between the long axis of the tooth and the apex of the root of the impacted canine, the lateral incisor, and the first premolar in the sagittal section (
Figure 6).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using the SPSS program (Version 29; Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). In the study, the normality distribution analysis of the measurements was performed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Mean ± SD and median values, which are descriptive statistical data for the variables, are given in
Table 1 and
Table 3. The demographic characteristics of the participants were analyzed using the chi-square test (Fisher’s exact test). The percentages of location, rotation, sectors, contact point, and resorption of impacted canines in the groups were analyzed using the chi-square test (Fisher-Freeman-Halton exact test). Differences in linear and angular measurements between the groups were evaluated using a one-way ANOVA test for values with a normal distribution and the Kruskal-Wallis test for nonnormally distributed values. Tukey and Tamhane post hoc tests were used to determine between groups statistically different values. A p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
The sample size of this study, which consisted of 46 subjects, consisted of 22 males (47.8%) and 24 females (52.2%). The mean age of the included subjects was 14.58 ± 2.29 years. The side of impaction showed that 23 (50%) of the impacted canines were located on the left and 23 (50%) on the right side (
Table 1). The demographic characteristics of the participants were analyzed using the chi-square test (Fisher’s exact test). No statistically significant association was found (
Table 1).
In general, 42 (91.3%) of the 46 impacted canines were vertical, while 4 (8.7%) were horizontal. A statistically significant positive association (χ2 = 6.02, p < 0.05) was found between the groups. The impacted canine rotation was found to have the highest percentage of mesiopalatal rotation (54.3%). Distobuccal and distopalatal rotations were not observed. Distributions of contact relations, location, rotations, sectors, and severity of resorption are analyzed by the chi-square test (Fisher-Freeman-Halton exact test) and are presented in
Table 2. A statistically significant positive association (χ2 = 48.08, p < 0.01) was found between the groups (
Table 2).
The highest percentage was observed in Sector 1 (45.7%), the lowest percentage in Sector 4 (0%), and Sector 3 (13.3%), and Sector 5 (13%). Although sectors 1 and 2 had a higher percentage in the buccal-impacted group, sectors 3 and 5 were found to have a higher percentage in the palatal-impacted group. A statistically significant positive association (χ2 = 35.32, p < 0.01) was found between the groups (
Table 2).
The contact relationship was highest at the crown level (32.6%) and lowest at the apical level (17.4%). A statistically significant positive association (χ2 = 48.80, p < 0.001) was found between the groups. The overall prevalence of root resorption was 56.5%, as presented in
Table 2. The severity of resorption between canine and lateral incisors was observed to be highest in grade 1 (32.6%) and lowest in grade 3 (2.2%). A statistically significant positive association (χ2 = 33.84, p < 0.001) was found between the groups (
Table 2).
Descriptive statistics and comparisons for linear and angular measurements between the groups are shown in
Table 3. Comparison of mean values of the measured characteristics in the three groups of patients using the variance method (one-way ANOVA) showed statistically significant differences in all characteristics.
The mean values of the angles of U3Ang and U3/U2 showed statistically significant higher values in the BC and PC groups compared to the CC group (p < 0.001). The mean values of the angulation of U4 were significantly higher in the BC group than in the CC group (p < 0.05) (
Table 3).
Table 3.
The mean values and standart deviation of measurements and comparison between groups.
Table 3.
The mean values and standart deviation of measurements and comparison between groups.
| |
Buccal (BC) |
Palatal (PC) |
Control (CC) |
|
Post Hoc |
| |
Mean ± SD |
Mean ± SD |
Mean ± SD |
p |
BC-PC |
BC-CC |
PC-CC |
| U3 Ang |
26.23
±
13.46
|
34.69
±
12.16
|
11.90
±
3.07
|
.000 |
.118
|
.020 |
.000 |
| U2 Ang |
8.87
±
6.67
|
10.84
±
6.17
|
13.75
±
2.63
|
.178
|
.787
|
.063
|
.318
|
| U4 Ang |
10.57
±
6.31
|
6.10
±
2.80
|
5.00
±
2.93
|
.009 |
.061
|
.027 |
.781
|
| U3/U2 |
27.94
±
12.01
|
39.84
±
16.20
|
4.12
±
1.36
|
.000 |
.080
|
.000 |
.000 |
| U3 BL |
8.40
±
0.82
|
8.23
±
0.77
|
8.29
±
0.22
|
.786
|
.901
|
.947
|
.985
|
| U2 BL |
6.66
±
0.66
|
6.47
±
0.69
|
6.86
±
0.47
|
.382
|
.708
|
.757
|
.361
|
| U3 MD |
8.26
±
0.48
|
8.33
±
0.72
|
8.19
±
0.21
|
.851
|
.986
|
.957
|
.874
|
| U2 MD |
6.82
±
0.78
|
6.57
±
0.71
|
6.87
±
0.45
|
.491
|
.580
|
.983
|
.574
|
| U3 RL |
13.37
±
1.34
|
13.29
±
1.18
|
14.59
±
0.98
|
.043 |
.980
|
.070
|
.047 |
| U2 RL |
10.92
±
0.95
|
10.33
±
1.34
|
12.16
±
0.45
|
.001 |
.284
|
.030 |
.001 |
| U3 L |
23.84
±
1.80
|
21.95
±
1.89
|
23.87
±
1.68
|
.011 |
.017
|
.999
|
.050 |
| U2 L |
20.50
±
1.55
|
19.01
±
2.68
|
21.32
±
1.60
|
.033 |
.133
|
.651
|
.041 |
| U3 VD |
7.64
±
3.97
|
9.23
±
3.00
|
00.00
±
0.00
|
.000 |
.528
|
.000 |
.000 |
| U3 HD |
14.79
±
2.37
|
6.10
±
4.12
|
16.75
±
1.12
|
.000 |
.000 |
.041 |
.000 |
| U3 Inc |
32.11
±
14.68
|
35.45
±
14.38
|
18.23
±
3.54
|
.015 |
.895
|
.009 |
.001 |
| U2 Inc |
17.94
±
9.33
|
19.49
±
9.21
|
24.29
±
4.85
|
.246
|
.870
|
.223
|
.409
|
| U3 RD |
150.35
±
15.74
|
148.87
±
13.92
|
172.21
±
6.63
|
.001 |
.951
|
.002 |
.001 |
| U2 RD |
161.76
±
11.36
|
158.84
±
10.06
|
171.54
±
4.56
|
.017 |
.839
|
.025 |
.001 |
| U4 RD |
157.35
±
8.86
|
160.61
±
10.02
|
165.94
±
4.93
|
.096
|
.561
|
.079
|
.351
|
There were no statistically significant differences between the groups in comparing the mean values of the measured U3, U2, BL, and MD widths. However, in the mean values of U3L, U2L, U3RL, and U2RL, significant differences were found between the PC and CC groups. The mean values of U2RL were statistically significantly shorter in the BC group (p < 0.05) and PC group (p < 0.001) than in the CC group. The mean values of U3L were found to be statistically significantly shorter in the PC groups compared to the BC group (p < 0.05) (
Table 3).
In the mean values of U3VD and U3HD, statistically significant differences were found between the BC and CC groups, the PC group, and the CC group (p < 0.001). The mean values of U3HD were found to be statistically significantly shorter in the PC group compared to the BC group (p < 0.001) (
Table 3).
The mean values of U3Inc were found to be statistically significantly higher in BC (p < 0.01) and PC groups (p < 0.001), compared to CC groups. The mean values of U3RDA and U2RDA were found to be statistically significantly lower in the BC (p < 0.05) and PC groups (p < 0.001) compared to the CC group. However, no significant differences were observed for mean U4 RD angle values between the groups (
Table 3).
4. Discussion
During the planning of orthodontic treatment for impacted canines, some factors should be considered when deciding which of the treatment plans to follow. These are the angulation of the maxillary impacted canine, inclination, horizontal and vertical location, age, malocclusion, surrounding tissue pathologies, and the amount of resorption in the root of the adjacent tooth [
15,
17,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25] (p. 13).
The most valuable information about the location and angulation of the maxillary impacted canine tooth and the detection of resorption and pathology in the surrounding tissues can be obtained with CBCT. It is beneficial for treatment planning to be done correctly. In a study, it was determined that 43.7% of the orthodontic treatment plan could change if CBCT was used for orthodontic treatment planning in cases with impacted canines. According to a report, the detection of resorption in the incisor roots through CBCT could lead to a 53.8% change in the treatment plan [
26] (p. 13). Therefore, we preferred to use CBCT images in this study. In addition, while planning this study, we selected unilaterally impacted canine cases and canines from the nonimpacted side of these cases as the control group to achieve more accurate and reliable results and to eliminate the differences between individuals.
Because radiographic examination before the age of 10 has been shown to not provide a reliable basis for the prognosis of a future unfavorable eruption path of the maxillary canines, patients between the ages of 10 and 16 were eligible to participate in this study [
22] (p. 13).
Warford et al. conducted a study on panoramic radiographs to determine whether the combination of impacted tooth angulation values and sector location could predict greater impaction risk than sector location alone. Consequently, the location of the unerupted canine was found to be the most important contributor to impaction. There is a greater than 0.87 possibility of impaction when the canine overlaps the midline of the lateral incisor [
23] (p. 13).
In this study, while sectors 1 and 2 had a higher percentage in the buccal-impacted group, sectors 3 and 5 had a higher percentage in the palatal-impacted group. The impacted canines in the palatal impacted group were located mesially closer to the midline. In addition, the vertical distance of the impacted canine was found to be greater in the palatal impacted group, while the midline distance was found to be greater in the buccal impacted group (
Table 2 and
Table 3). At the same time, a study has shown that when impacted canines are positioned more mesially and closer to the midline, they are less passively eruption and more difficult to treat [
22] (p. 13).
If the angle of the impacted canine with the midline is more than 31 degrees, the possibility of eruption of the impacted tooth is considerably reduced [
27] (p. 13). At the same time, the increase in lateral incisor angulation with the impacted canine is also thought to be related to the impacted canine [
25] (p. 13). Ericson et al. stated that if the angulation of the impacted canine with the midline exceeds 25 degrees and with the lateral incisor exceeds 28 degrees, the possibility of resorption increases by 50% [
28] (p. 13). According to these results, it would be useful to evaluate the angulation of the impacted canine and its relationship with the lateral incisor on CBCT images taken in the mixed dentition period and to take precautions in the early period before resorption.
In this study, the angulation of the lateral incisor on the impacted side was lower than on the non-impacted side. Canine angulation was higher on the impacted side than on the non-impacted side. In the palatal-impacted canine group of this study, the canine angulation value (34.69°) was higher than the buccal-impacted canine group (26.23°) (
Table 3). In terms of resorption rate and canine angulation, the severe resorption rate was found to be higher in the palatal group (Grades 2 and 3) (
Table 2). Long-term follow-up of teeth with root resorption in the adjacent region due to ectopically erupted canines showed no problems. In most of these cases, either the resorption regresses spontaneously or after surgery. Resorption decreases when the ectopically erupted canine is removed or its position is changed by orthodontic treatment [
29] (p. 13).
Al-Tawachi et al. reported that the root lengths of the lateral incisors in the palatal-impacted canine group were shorter than in the buccal-impacted and control groups, while the mesiodistal and labiopalatal widths were similar in all groups. In addition, they said that the lateral incisors were inclined distally and palatally [
18] (p. 13). Koral et al. reported that the width of the BL and MD of the lateral incisor crown, the total length of the lateral incisor, the length of the root, the angulation of the midline of the lateral incisor, and the angle of the lateral incisor with the canine tooth are among the strong predictor factors of maxillary canine impaction [
30] (p. 13).
Although the BL and MD width of the lateral incisors in the PC group was smaller than in the other groups, there were no significant differences between the BC, PC, and CC groups. However, the U2RL and U2L were smaller by 0.82-2.31 mm compared to those in the CC group and smaller in the PC group compared to the BC group, and the study's hypothesis was rejected (
Table 3). These findings are also consistent with previous research indicating that the length of the lateral incisors is shorter on the impacted side [
18,
24,
30] (p. 13).
As described in the eruption guidance theory, the roots of the lateral incisors guide the erupting permanent canines. In this study, it is clearly seen that the lateral incisor length and lateral incisor root length were found to be short in the BC and PC groups, which supports this theory. In other words, it should be considered that lateral incisors with shorter root lengths may be a potential cause for the maxillary canine to remain impacted.
The lateral root length adjacent to the impacted canine was shorter, and the root dilaceration angle was smaller [
24] (p. 13). Similarly, this study found that adjacent lateral incisor roots were shorter, and canine and lateral roots were more dilasere in the impacted groups. These problems during eruption also cause root development problems.
The fact that this study was planned retrospectively created some limitations. In this study, we could only include CBCT images that fully captured the maxillary region. The findings of this study may be helpful in facilitating the diagnosis of maxillary impacted canines, preventing problems, and planning effective treatment. More research is needed to evaluate the angular and linear measurements on CBCT images in a wider population.
5. Conclusions
Buccally maxillary impacted canines are positioned further from the midline and vertically lower. Palatally impacted canines are located closer to the midline and vertically higher. In addition, canine angulations are higher in the palatal group, making them more difficult to treat and increasing the degree of root resorption.
The buccolingual and mesiodistal widths of the lateral incisors were smaller in the palatally impacted canine group, but there were no statistically significant differences. Maxillary impacted canines mostly show mesiopalatal rotation.
The fact that the U2RL and U2L values in the palatally impacted group were shorter than those in the buccally impacted group suggests that the reduced dimensions of the maxillary lateral incisors and shorter roots may be a potential factor in the impaction of the maxillary canine.
Author Contributions
Study design: Conceptualization, K.E.; methodology, K.E.; data analyses, K.E.; writing, K.E. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Ankara Yildirim Beyazit University, (19-1272/08 December 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
This was a retrospective archive study however the patients' consent to treatment is available
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Becker, A. The orthodontic treatment of impacted teeth, 2nd ed.; UK Martin Dunitz Publisher: London, UK, 1998; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Coulter, J.; Richardson, A. Normal eruption of the maxillary canine quantified in three dimensions. Eur J Orthod. 1997, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dachi, S.F.; Howel, F.V. A survey of 3,874 routine full-month radiographs. II. A study of impacted teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1961, 14, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, S.; Peck, L.; Kataja, M. The palatally displaced canine as a dental anomaly of genetic origin. Angle Orthod. 1994, 64, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B. The influence of congenitally missing teeth on the eruption of the upper canine. Dental Practitioner. 1963, 13, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Radiographic examination of ectopically erupting maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987, 91, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.H. Diagnosis and prevention of maxillary cuspid impaction. Angle Orthod. 1981, 51, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, H. The etiology of maxillary canine impactions. Am J Orthod. 1983, 84, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nimri, K.; Gharaibeh, T. Space conditions and dental and occlusal features in patients with palatally impacted maxillary canines: An aetiological study. Eur J Orthod. 2005, 27, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A. Etiology of maxillary canine impactions. Am J Orthod. 1984, 86, 437–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.; Enciso, R.; Mah, J. Three-dimensional localization of maxillary canines with cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005, 128, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSherry, P.F. The ectopic maxillary canine: A review. Br J Orthod. 1998, 25, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, S.E. Clinical management of impacted maxillary canines. Semin Orthod. 1998, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stivaros, N.; Mandall, N.A. Radiographic factors affecting the management of impacted upper permanent canines. J Orthod. 2000, 27, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.A.; Heo, G.; Glover, K.E.; Williamson, P.C.; Lam, E.W.; Major, P.W. Factors that relate to treatment duration for patients with palatally impacted maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001, 119, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, S.; Hamdan, A.; Rock, P. A treatment difficulty index for unerupted maxillary canines. Eur J Orthod. 2006, 28, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Incisor resorption caused by maxillary cuspids. A radiographic study. Angle Orthod. 1987, 57, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Tawachi, A.; Abu Alhaija, E.S.; Al-Jamal, G.A. Evaluation of maxillary canine root and maxillary bone thickness and density in patients with displaced maxillary canines: A cone-beam tomography study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022, 162, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Early treatment of palatally erupting maxillary canines by extraction of the primary canines. Eur J Orthod. 1988, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Incisor root resorptions due to ectopic maxillary canines imaged by computerized tomography: A comparative study in extracted teeth. Angle Orthod. 2000, 70, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Chaushu, S. Success rate and duration of orthodontic treatment for adult patients with palatally impacted maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003, 124, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Radiographic assessment of maxillary canine eruption in children with clinical signs of eruption disturbance. Eur J Orthod. 1986, 8, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warford, J.H.; Grandhi, R.K.; Tira, D.E. Prediction of maxillary canine impaction using sectors and angular measurement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003, 124, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchor-Soto, M.E.; Arriola-Guillen, L.E.; Aliaga-DelCastillo, A.; Ruiz-Mora, G.A.; Rodriguez-Cardenas, Y.A. Root morphology of lateral incisors adjacent to impacted maxillary canines: A cone-beam computed tomography retrospective cross-sectional study. Int Orthod. 2022, 20, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqerban, A.; Jacobs, R.; Fieuws, S.; Williems, G. Radiographic predictors for maxillary canine impaction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015, 147, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerklin, K.; Ericson, S. How a computerized tomography examination changed the treatment plans of 80 children with retained and ectopically positioned maxillary canines. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Power, S.M.; Short, M.B. An investigation into the response of palatally displaced canines to the removal of deciduous canines and an assessment of factors contributing to favourable eruption. Br J Orthod. 1993, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Resorption of maxillary lateral incisors caused by ectopic eruption of the canines. A clinical and radiographic analysis of predisposing factors. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988, 94, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahat, B.; Ericson, S.; Mak D’Amico, R.; Bjerklin, K. Incisor root resorption due to ectopic maxillary canines: A long-term radiographic follow-up. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koral, S.; Arman Özçırpıcı, A.; Tunçer, N. Association Between Impacted Maxillary Canines and Adjacent Lateral Incisors: A Retrospective Study with Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Turk J Orthod. 2021, 34, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).