1. Introduction
Endothelial cells (ECs) form the inner lining of blood vessels that play an important role in maintaining vascular integrity and homeostasis. They provide a physical barrier between the blood and vessel walls or tissues, essential in regulating homeostasis and coordinating responses to blood vessel injury and inflammation. As ECs are constantly exposed to mechanical, chemical and biological stresses, their plasma membrane is frequently disrupted and repaired. Failure to repair the disrupted membrane may cause endothelial cell death, which impairs the barrier function of blood-tissues or vessel walls, leading to vasculopathy, acute organ injury and initiation of atherosclerosis [
1]. The capacity and mechanisms of cells to repair wounded plasma membranes have been studied in a number of cell types, especially skeletal muscle and cardiomyocytes [2-5]. Although the exact mechanisms underlying the membrane repair or resealing in these cells are still not fully understood, shreds of evidence available so far indicate that plasma membrane resealing is an autonomous and intrinsic process. In addition, although frequent disruption and resealing are commonly observed in mechanically exposed tissues, including skeletal muscle and endothelium, the study on endothelial cell membrane repair is limited. In the review, we will discuss the recent advances in the study of endothelial cell membrane repair by focusing on the protein machinery that specifically operates in ECs. The future research direction in this area will also be highlighted.
2. A general model of cell membrane repair
The plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells is vulnerable to mechanical, chemical and biological stresses. Consequently, plasma membrane disruption is a common type of cellular injury in eukaryotic cells, and effective membrane repair mechanisms have evolved to rapidly reseal a membrane breach, restore internal homeostasis and prevent cell death [6, 7]. Although the exact mechanisms underlying the membrane repair or resealing are still not fully understood, and different cell types may have different mechanisms, a general model of cell membrane repair has been hypothesized.
2.1. Ca2+ influx as a trigger
By actively pumping Ca
2+ ions from the cytosol into the extracellular spaces, cells maintain cytosolic resting Ca
2+ concentration in the nanomolar range and extracellular Ca
2+ in the millimolar range. When the integrity of the plasma membrane is breached, a rapid influx of Ca
2+ generates localized and transient increases in the cytosolic free Ca
2+ concentration. The Ca
2+ influx is required to trigger a series of reactions that rapidly reseal the disrupted membrane [
8]. Early studies in sea urchin eggs showed that Ca
2+ influx through plasma membrane wounds triggered a rapid surface reaction followed by fully restoring the egg’s integrity, allowing subsequent fertilization and normal development. In contrast, when Ca
2+ was removed from seawater surrounding the eggs, wounding resulted in progressive loss of cytosol and cell death [
9]. These initial observations were confirmed in mammalian cells. For example, microinjection of cells in Ca
2+-free media inevitably results in cell death, suggesting that extracellular Ca
2+ as a trigger is required to effectively repair microneedle wounds [
10].
2.2. Ca2+-targeted proteins form a temporary diffusion barrier (resealing phase)
Different types of wounds may be repaired by different mechanisms. Tiny membrane injury (<1 nm), such as those created by electroporation or proteins that induce lipid disorder, may repair spontaneously by the force of the underlying membrane cytoskeleton [
11], and which will not be discussed in this article. If a large membrane injury is created, Ca
2+ influx will rapidly activate several cytosolic Ca
2+-binding proteins, such as calpain, dysferlin, annexins, S100A11 and transglutaminases. Calpain is a Ca
2+-dependent cysteine protease, which can rapidly cleave dysferlin to release a 72-KD C-terminal fragment (mini-DyaferlinC72). The mini-dysferlin can move to membrane-injured sites and bind to the exposed lipids [
12]. MG53 (also known as TRIM72) is an E3 ligase. MG53 is not a Ca
2+ binding protein, but it can rapidly move to membrane injured sites and bind to exposed membrane lipids. MG53 can interact with dysferlin and form a tight lattice-network to form a protein scaffold around the wounds, which forms the first protein barrier to reseal the wound [13-15]. Annexins are Ca
2+ and phospholipid-binding proteins that move to the membrane-injured sites and form a protein scaffold [
16]. Anexin A2 can bind to S100A11, another Ca
2+-activated protein, both of which are required for efficient cell membrane repair [
17]. The protein complex of Annexins and S00A11 may form a second protein barrier to reseal the wound. Ca
2+-activated transglutaminase has protein-linking activity, which can make the proteins cross-linking and form more intensive protein barriers at the wound sites, preventing cytosol loss while the integrity of the lipid bilayer is restored [
19]. Interestingly, dysferlin can also interact with annexins to make these two layers of protein “patch” more tightly. There may be more proteins involved in the formation of the protein barrier. In addition, the protein machinery resealing the wounds may be different in different cell types. For example, MG53 is a skeletal muscle-specific protein. In the non-skeletal muscle cells (eg. endothelial cells), there may be another protein or proteins serving an equivalent role as MG53.
2.3. Ca2+-regulated liposome exocytosis (repairing phase)
While the membrane injury is rapidly resealed, the loss of membrane at the sites of injury needs to be repaired. Experiments in sea urchin eggs and mammalian cells revealed extensive and localized fusion of intracellular vesicles with the plasma membrane, a few seconds after injury and Ca
2+ influx [
20]. Inhibiting vesicle exocytosis by interfering with the formation of SNARE complexes impaired plasma membrane repair, suggesting that upon Ca
2+ influx through the wound, pre-existing intracellular vesicles would fuse with each other to form a membrane “patch”, which would then merge with the injured plasma membrane and restore its integrity [
21]. The identity of intracellular vesicles for membrane repair was confirmed as liposomes [
22]. Exocytosis of liposomes has been extensively observed in injured cells, and plasma membrane repair is impaired after inhibition of liposome exocytosis. Impaired plasma membrane repair is also seen after inhibition of synaptotagmin 7, a member of the synaptotagmin family of Ca
2+ sensors present on the membrane of lysosomes [
23], or of the components of SNARE complexes that mediate lysosome exocytosis [
24]. Interestingly, inhibition of the lysosomal Ca
2+ channel mucolipin-1 also impairs plasma membrane repair, suggesting that Ca
2+ stored in the lumen of lysosomes may also contribute to the increase in cytosolic Ca
2+ concentration that is critical for plasma membrane resealing [
25]. Recent studies suggest that the other vesicles, such as endosomes and storage granules, may also be involved in the plasma membrane repair [26, 27].
2.4. Lesion removal by endocytosis
The final step is how to remove the repaired lesions of the cell membrane. Mammalian cells injured mechanically or by bacterial pore-forming toxins, such as streptolysin O (SLO), were found to undergo massive endocytosis after Ca
2+-triggered exocytosis of lysosomes [
28]. This unusual form of endocytosis observed after Ca
2+ influx is independent of classical endocytosis proteins such as clathrins, requires the presence of cholesterol in the plasma membrane, and can be triggered by extracellular exposure to the enzyme sphinogomylinase, which provides an important link between lysosomal exocytosis and endocytosis-mediated plasma membrane repair. Caveolae are plasma membrane invaginations with a diameter of ~80 nm that are associated with membrane microdomains enriched in cholesterol and sphingomyelin (frequently described as lipid rafts). Caveolae are present in many cell types and are particularly abundant in cells that are under significant mechanical stress in vivo, such as muscle fibers, cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells [
29]. Interestingly, electron microscopy studies have revealed a large number of internalized vesicles with the size and morphology of caveolae in the cytoplasm of injured cells or in intact cells treated with sphingomyelinase [
30]. SLO was directly visualized traveling into cells inside internalized caveolar vesicles, and inhibition of caveolae formation blocked plasma membrane repair, strongly suggesting that wounds can be removed from the plasma membrane through caveolar endocytosis [
31].
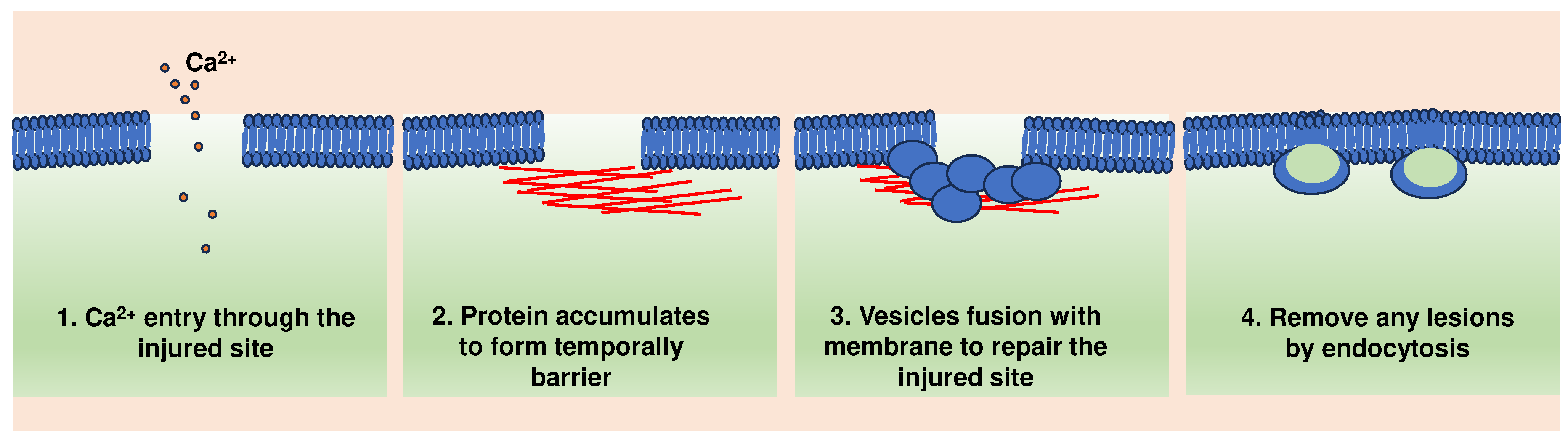
Collectively, these findings led to a multi-step model of plasma membrane repair. According to this model, plasma membrane injury triggers Ca2+ influx, formation of protein barrier and exocytosis of lysosomal hydrolases, including ASM, which in turn remodel the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. This triggers a ceramide-dependent wave of endocytosis that internalizes the lesions (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
A general model of cell membrane repair.
Figure 1.
A general model of cell membrane repair.
3. Endothelial cell membrane repair
The ECs in vivo are constantly exposed to mechanical, chemical and biological stresses generated by the hemodynamic forces, toxic environmental substances and metabolites and pathogen-derived pore-forming toxins under physiological and pathological conditions. Earlier studies found that on average, 6.5% of the endothelial cells of the rat aorta show transient and resealable plasma membrane disruption [
1]. Interestingly, these wounded endothelial cells were particularly abundant around vascular bifurcation characterized by turbulent and disturbed flow, which is the area prone to atherosclerosis. These results suggest that the disruption and reseal of the endothelial plasma membrane may frequently happen, and failure to repair the wounded cells may be an important mechanism leading to the formation of early atherosclerotic lesions [
1]. However, despite the fundamental importance of membrane repair for cell survival and tissue integrity, the studies on endothelial cell membrane repair are limited. Current studies suggest that endothelial cell membrane repair may share some general mechanisms with other cell types, such as skeletal muscle, but also have specific components to fulfill the specific situations that endothelial cells encounter.
3.1. Dysferlin and myoferlin
All known mammalian ferlin gene products (dysferlin, myoferlin and otoferlin) are essential for the trafficking of intracellular vesicles and may be involved in cell membrane repair. Both dysferlin and myoferlin are abundantly expressed in skeletal muscles and are important components of repairing machinery for muscles [
32]. Loss of dysferlin or myoferlin activity causes limb-girdle muscular dystrophy through impaired skeletal muscle repair after physical injury [33, 34]. Otoferlin is a specific member strongly expressed in the auditory inner hair cells that are responsible for transmitting auditory information to central nervous system. Mutations of otoferlin cause autosomal recessive deafness in humans, and genetic inactivation of the otoferlin gene impairs Ca
2+-dependent exocytosis in mouse auditory inner hair cells and causes profound deafness [
35]. Proteomic profiling showed that both dysferlin and myoferlin are localized at the endothelial membrane and lipid rafts [
36]. Western blot confirmed their expression in human primary endothelial cells. Moreover, recent studies showed that dysferlin may participate in endothelial cell membrane repair by mediating lysosome fusion with endothelial cell membrane [
37], and myoferlin is required for efficient endothelial membrane repair after mechanical injury [
38]. Nevertheless, the importance and mechanisms of dysferlin and myoferlin in endothelial cell membrane repair in vitro and in vivo need to be further determined.
3.2. Annexins and S100A10/11
Annexins constitute a multigene family of Ca
2+-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins, with members of the family being expressed in animals, plants, fungi and protists. This family can be divided into five classes (A-E) based on their biological origins. In vertebrates, the class A is composed of 12 members AnxA1-AnxA13 (Anx12 is currently unassigned). Annexins have two structural domains: a conserved C-terminal domain with 4 repeats of 70-80 amino acids (8 in the case of AnxA6) and a variable N-terminal domain. Each repeat contains a Ca
2+ binding motif, allowing the annexins to rapidly translocate to the plasma membrane or intracellular membranes by binding to negatively charged phospholipids [
39]. The functions of annexins include Ca
2+-regulated endocytic and exocytic events, the maintenance and regulation of membrane-cytoskeleton contacts and membrane domain organization [
40]. AnxA2 is the most abundant member in endothelial cells [
41]. A1 and A5 are also expressed in endothelial cells as well. Recent studies showed that AnxA1, A2, A5 and A6 all rapidly moved to the wounded sites after injury in endothelial cells. They can form a protein complex with S100A11, which is an EF hand-type Ca2+-binding protein. Knocking down of AnxA2 or S100A11 proved that both of them are required for efficient repair of endothelial cell membrane wounds. Further studies showed that S100A11 C-terminal extension (residues 93-105) can interact with AnxA1 and AnxA2 in a Ca
2+-dependent manner. In addition, synaptotagmin-1 also binds to S100A11 in the presence of Ca
2+ and depletion of synaptotagmin-1 interferes with wound site recruitment of S100A11 and proper membrane resealing in endothelial cells [
42].
3.3. Caveolins
Caveolins are major components associated with caveolar lipid rafts in the plasma membrane and implicated in many aspects of cellular functions. There are three members of caveolins: caveolin-1, caveolin-2 and caveolin-3. Caveolin-1 is the primary member of caveolins and is ubiquitously expressed in all tissues, including endothelial cells. Caveolin-3 (Cav3) is restricted expressed in skeletal muscles. Mutation of Caveolin-3 is linked to muscular dystrophy in patients [
43]. Cav3 is essential for the repair of muscle membrane damage. Cav3 can form a protein complex with MG53 and dysferlin. Cav3 mutants that cause retention of Cav3 in the Golgi apparatus result in aberrant localization of MG53 and dysferlin in a dominant-negative fashion, leading to defective membrane repair [
44]. These results suggest that Cav3 at the membrane is required for correct localization and retention of MG53 and dysferlin on muscle membranes. While Cav3 is specifically expressed in muscles, Cav1 is expressed in many tissues, including endothelial cells. Cav1 forms a protein complex with myoferlin in endothelial cells. Both Cav1 and myoferlin are critical for efficient endothelial membrane repair after injury [
45].
3.4. Weibel-Palade bodies
Weibel-Palade bodies (WPB) are unique secretory organelles in endothelial cells that undergo evoked exocytosis following intracellular Ca
2+ or cAMP elevation, thereby supplying the vasculature with factors controlling hemostasis. The major components stored within WPB are the multimeric glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) and the adhesion receptor P-selectin. WPBs move to the endothelial cell membrane when blood vessel injury and fuse with the plasma membrane. VWF was released into the lumen of the blood vessel and provided platelet adhesion sites. Low levels of VWF can lead to a bleeding tendency, such as in von Willebrand disease, and elevated levels of VWF are associated with an increased risk for thrombosis and associated with cardiovascular disease [
46]. A recent study observed that complement-mediated endothelial membrane injury can be mitigated by the mobilization of WPBs along with the secretion of VWF. Endothelial cells lacking WPBs were not resistant to complement-mediated damage but became resistant when transfected to express VWF. This study suggests that WPB exocytosis in response to endothelial plasma membrane damage may be an essential mechanism for endothelial cell membrane repair [
47]. Interestingly, several other studies showed that annexin A2 and S100A10 complex is required for WPB exocytosis [48, 49]. In a recent study, the Annexin A2/S100A10 was confirmed to be required for efficient endothelial cell membrane repair after mechanical injury [
50]. How WPB repairs the endothelial cell membrane still needs further study.
3.5. Other proteins
Theoretically, any proteins that regulate the processes such as cytoskeleton, exocytosis, endocytosis may affect cell membrane repair. For example, Rab3a, Rab10, myosin 11A, 11B, SNARE and ESCRT III are reported to be involved in the regulation of cell membrane repair [51-55]. However, whether they are also involved in endothelial cell membrane repair needs to be determined. Anoctamin 5 (ANO5, also known as TMEM16E) is a member of the transmembrane 16 (TMEM16) family of Ca2+-activated ion channels and phospholipid scramblases. Human mutations of ANO5 cause adult onset limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2L (LGMD2L) and Miyoshi Muscular Dystrophy (MMD3). In mouse, ANO5 is implicated in muscle differentiation and membrane repair [
56]. ANO5 is primarily expressed in muscle and bone. It is also expressed in endothelial cells. However, its role in endothelial cells remains unclear. Endophylin-A2, which participates in membrane vesiculation during receptor-mediated endocytosis, is a ∼40 kDa SH3 domain-containing protein that binds to the proline/arginine-rich domain of dynamin 2, a ∼100 kDa GTPase that is essential for endocytic membrane scission. Both endophilin-A2 and dynamin 2 are involved in the regulation of cell membrane repair [
57]. However, whether those proteins are also involved in endothelial cell membrane repair remains to be studied. MG53 (also known as TRIM72) is a member of the TRIM-family protein that acts as a key component of cell membrane repair machinery in muscles [
58]. However, MG53 is not expressed in human endothelial cells. The role of MG53 may be fulfilled by another TRIM protein or non-TRIM protein in endothelial cells needs to be determined.
4. The diseases linked with defective endothelial membrane repair
Failure to rapidly reseal the damaged endothelial membrane may result in endothelial cell death, which may link with acute or chronic vascular diseases such as disruption of blood-tissue barrier or atherosclerosis.
4.1. Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that causes vascular remodeling and is associated with local inflammation and oxidative stress. Disruption of endothelial cell homeostasis is an early step in the atherosclerosis process, as it can lead to vascular permeability, impaired clotting function and lipid infiltration into perivascular intima, which causes stress injuries to the vascular wall. It was established that dysferlin, myoferlin, annexins and caveolins are actively involved in the process of endothelial membrane repair and other functions in endothelial cells. It may be expected that loss of function of those proteins may promote the development of atherosclerosis. Despite high dysferlin expression in mouse and human atheromatous plaques, loss of dysferlin did not affect atherosclerotic burden as measured in the aortic root, arch, thoracic and abdominal aortic regions in ApoE-/- mice [
59]. These results may be due to myoferlin compensate the role of dysferlin in endothelial cells. In addition, genetic ablation of caveolin-1, a principal structural protein component of caveolae, which are small invaginations in the plasma membrane, was proven to protect against the development of atherosclerosis, with an about 65% reduction in the atherosclerotic lesion area [
60]. Annexin A1 is a 37kDa protein that plays an important role in the cardiovascular system. Annexin A1 is found in different locations, including the plasma membrane, endosomes, secretory vesicles, cytoskeleton and nucleus. It also can be secreted into the outside of cells when the cells are activated. Several studies have demonstrated that annexin A1 protects from atherogenesis and atheroprogression in mice [
61]. Annexin A2 expression is markedly upregulated in atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE knockout mice [
62]. However, germline deletions of Annexin A2 did not reduce atherosclerotic burden in ApoE-deficient mice [
63].
4.2. Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Vascular injury arising from hyperglycemia is considered a major contributor to the growing morbidity and mortality rates associated with diabetes. In diabetic patients, oxidative stress, reduced nitric oxide (NO) levels, and inflammation all can contribute to the disruption of endothelial integrity, leading to abnormal blood fluidity and vascular tone. Instant cell membrane resealing (ICMR) is a crucial mechanism that helps to maintain endothelial integrity. Annexin A5 can form two-dimensional bandage at the torn membrane edges to prevent the expansion of the membrane wound and promote the final step of membrane resealing. However, more retarded ICMR was observed in mouse aortic endothelial cells exposed to high glucose, which is because high glucose decreased the association of membrane ceramide with annexin A5 [
64]. The high glucose-induced impairment of membrane resealing could be prevented by sphingomyelin or C24-ceramide pretreatment [
65]. Additionally, hyperglycemia also elevates lysosome exocytosis, ceramide production, and membrane raft clustering. Overall, high glucose impairs endothelial membrane resealing and makes the cells more vulnerable to secondary membrane damage.
4.3. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
Cell injury and death play a critical role in lung-injurious diseases. In ARDS and IPF, the lung is exposed to various insults such as infection, oxidative stress, and mechanical stress, highly susceptible to plasma membrane wounding. Cell death always occurs through apoptosis, necrosis, necroptosis, and other undefined mechanisms, following plasma membrane wounding. Lung injury and repair are involved in the pathogenesis of ARDS and IPF. Prolonged cell wounding and aberrant repair make it difficult to maintain cell membrane integrity, resulting in the release of intracellular contents and subsequent immune response. Proinflammatory cytokines also can activate downstream signaling, which either produces membrane-injury productions or direct compromised plasma membrane integrity as part of the cell death mechanism. Quick and effective plasma membrane repair can restore the injurious cells and preserve cellular homeostasis. In type I alveolar epithelial cells, MG53 improves cellular integrity through its interaction with caveolin 1 [
66]. However, the link between MG53 and caveolar endocytosis or other protein-binding partners at the plasma membrane in the context of repairing wounding of lung endothelial cells is not well understood.
5. The resealing agents for endothelial membrane repair
When the endothelial cell membrane is damaged, it may lead to cell death and have various adverse consequences. Therefore, treatment targeting membrane repair may help to maintain the integrity of endothelial cells and benefit for the patients with membrane repair defects.
5.1. Recombinant MG53
MG53, also known as TRIM72, has been identified as an essential component of the cell membrane repair machinery in striated muscles. The recombinant human MG53 can specifically be transported to the membrane wounding sites and prevent the expansion of the rupture. Several studies demonstrated that treatment with recombinant human MG53 protein increased membrane integrity and protect organ injury in mice, such as muscles, heart, lungs, kidney, brain and liver [67-72].
5.2. Recombinant annexins
Several annexins can be secreted outside of cells. The recombinant human annexins exhibit many effects on cells, including membrane repair, anti-inflammation and promote fibrinolysis etc. In numerous studies, treatment with recombinant human annexins and annexin analog peptides have consistently found positive outcomes in animal models of sepsis, myocardial infarction, and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Annexins A1 and A5 improve organ function and reduce mortality in animal sepsis models, inhibit inflammatory processes, reduce inflammatory mediator release, and protect against ischemic injury. The mechanisms of action and demonstrated efficacy of annexins in animal models support the development of annexins and their analogs for the treatment of sepsis. The safety and efficacy of recombinant human annexin A5 are currently being studied in clinical trials in septic patients [
73].
5.3. Poloxamer 188
Poloxamer 188 (P188) is a stable amphiphilic polymer localized in lipid monolayers and damaged regions of membranes. The FDA approved it as a therapeutic reagent to reduce blood viscosity for transfusions. It has been shown to increase the structural stability and resealing of the plasma membrane, making it a potential therapeutic agent for various conditions that involve membrane damage. For example, administration of P188 can reduce the loss of muscle mass in dysferlin-deficient SJL mice, which could provide a basis for potential therapeutic strategies for dysferlinopathy [
74]. In addition, P188 can instantly improve ventricular geometry and block the development of acute cardiac failure in dystrophic mice during a dobutamine-mediated stress protocol [
75]. P188 pretreatment could restore BBB integrity, suppress TBI-induced neural cell death, and improve neurological function [
76]. Notably, a recent study demonstrated that P188 could prolong endothelial cell survival in bovine corneas stored at 4 ℃ by lowering the surface tension of cell membranes [
77]. The safety and non-toxicity of P188 in human was confirmed, but high doses may be toxic for long-term use. Therefore, more research is needed to understand the potential benefits and risks of P188.
5.4. Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) or Sphingomyelin or ceramide
The plasma membrane repair requires Ca2+-dependent endocytosis to remove membrane lesions. Membrane rafts are specialized domains in the plasma membrane that are enriched in certain lipids, such as sphingomyelin and glycosphingolipids, as well as cholesterol. The clustering of membrane rafts can be mediated by the translocation of acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) to these domains. In response to certain stimuli, such as cell injury or stress, ASM can translocate to the site of injury and become activated to facilitate repair. The local ASM activation and ceramide production is an important step that mediates membrane raft clustering. Ceramide-mediated endocytosis could repair membrane wounding quickly. Exogenously added recombinant ASM restores endocytosis and membrane resealing in ASM-depleted cells [
78]. Chen et al. also suggested that ceramide-mediated instant cell membrane repair in endothelial cells was impaired during diabetes, and this impairment could be prevented by sphingomyelin and ceramide pretreatment [
79]. In addition, caspase-7 could enhance endocytic membrane repair of GSDMD and MLKL pore opening by activating ASM to produce ceramide [
80].
6. Future directions
ECs are constantly exposed to mechanical, chemical and biological stresses generated by the hemodynamic forces, toxic environmental substances and metabolites and pathogen-derived pore-forming toxins under physiological and pathological conditions. A complex reparative/regeneration system is required to repair the wounded membrane to keep cells surviving. However, despite the fundamental importance of membrane repair for cell survival and vascular integrity, studies on endothelial cell membrane repair are limited. Current studies suggest that endothelial cell membrane repair may share some general mechanisms with other cell types, such as skeletal muscle, but also have specific components to fulfill the specific challenges/stimuli that endothelial cells encounter. The core machinery for endothelial cell membrane repair remains to be determined along with injury-specific (sepsis, shear stress, metabolic insults) repair mechanisms. Some of the proteins identified as playing a role in endothelial plasma membrane repair include dysferlin, myoferlin, annexins, and caveolins, as described above. There may be other proteins involved in this process. In the future, 1) the importance of cell membrane repair in the pathogenesis of endothelial cell-related diseases needs to be evaluated; 2) the core machinery and its working mechanisms of endothelial cell membrane repair needs to be identified; 3) the follow-up effect of endothelial cell injury and repair on the endothelial function needs to be further studied. Identifying the mechanisms might enable future application of recombinant molecular therapy to reconstitute the EC membrane and attenuate progress of diseases.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approve it for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by UMKC internal grant FFE2023 to M.F.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data availability Statement: Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
EC: endothelial cells; CVD: Cardiovascular diseases; ASM: Acid sphingomyelinase; GSDMD: gasdermin D; MLKL: mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase; ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; ICMR: Instant cell membrane resealing; NO: nitric oxide; ANO5: Anoctamin 5; LGMD2L: limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2L; MMD3:miyoshi muscular dystrophy; WPB: Weibel-Palade bodies; and VWF: von Willebrand factor.
References
- Yu, Q.C.; McNeil, P.L. Transient disruptions of aortic endothelial cell plasma membranes. Am J Pathol. 1992, 141, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McNeil, P.L.; Steinhardt, R.A. Plasma membrane disruption: repair, prevention, adaptation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003, 19, 697–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K.; McNeil, P.L. Mechanical injury and repair of cells. Crit Care Med. 2003, 31 8 Suppl, S496–S501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.W.; Almeida, P.E.; Corrotte, M. Damage control: cellular mechanisms of plasma membrane repair. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demonbreun, A.R.; Quattrocelli, M.; Barefield, D.Y.; Allen, M.V.; Swanson, K.E.; McNally, E.M. An actin-dependent annexin complex mediates plasma membrane repair in muscle. J Cell Biol. 2016, 213, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, A.D.; Paleo, B.J.; Weisleder, N. Plasma Membrane Repair: A Central Process for Maintaining Cellular Homeostasis. Physiology (Bethesda). 2015, 30, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, N.R.; Sonnemann, K.J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Bement, W.M. Membrane dynamics during cellular wound repair. Mol Biol Cell. 2016, 27, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, H. Calcium signaling in membrane repair. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015, 45, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Dominguez, A.N.M.; Decker, J.R.; Hull, A.J.; Verboon, J.M.; Parkhurst, S.M. Into the breach: how cells cope with wounds. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draeger, A.; Schoenauer, R.; Atanassoff, A.P.; Wolfmeier, H.; Babiychuk, E.B. Dealing with damage: plasma membrane repair mechanisms. Biochimie 2014, 107 Pt A, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.W.; Almeida, P.E.; Corrotte, M. Damage control: cellular mechanisms of plasma membrane repair. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, A.; Evesson, F.J.; Lemckert, F.A.; Redpath, G.M.; Lueders, A.K.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; North, K.N.; Cooper, S.T. Calpains, cleaved mini-dysferlinC72, and L-type channels underpin calcium-dependent muscle membrane repair. J Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5085–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, M.; Ko, J.K.; Weisleder, N.; Takeshima, H.; Ma, J. Redox-dependent oligomerization through a leucine zipper motif is essential for MG53-mediated cell membrane repair. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C106–C114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.R.; Campbell, K.P.; Glass, D.J. MG53's new identity. Skelet Muscle 2013, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Masumiya, H.; Weisleder, N.; Matsuda, N.; Nishi, M.; Hwang, M.; Ko, J.K.; Lin, P.; Thornton, A.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Z.; Komazaki, S.; Brotto, M.; Takeshima, H.; Ma, J. G53 nucleates assembly of cell membrane repair machinery. Nat Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, C.; Carmeille, R.; Brévart, C.; Bouter, A. Annexins and Membrane Repair Dysfunctions in Muscular Dystrophies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvanpour, A.; Santamaria-Kisiel, L.; Shaw, G.S. The S100A10-annexin A2 complex provides a novel asymmetric platform for membrane repair. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286, 40174–40183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, R.; Matsuki, M.; Yamada, K.; Morishima, Y.; Shen, S.C.; Kuramoto, N.; Yasuno, H.; Takahashi, K.; Miyachi, Y.; Yamanishi, K. Facilitated wound healing by activation of the Transglutaminase 1 gene. Am J Pathol. 2000, 157, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittel, D.C.; Chandra, G.; Tirunagri, L.M.S.; Deora, A.B.; Medikayala, S.; Scheffer, L.; Defour, A.; Jaiswal, J.K. Annexin A2 Mediates Dysferlin Accumulation and Muscle Cell Membrane Repair. Cells 2020, 9, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, J.K.; Andrews, N.W.; Simon, S.M. Membrane proximal lysosomes are the major vesicles responsible for calcium-dependent exocytosis in nonsecretory cells. J Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.K.; Huynh, C.; Proux-Gillardeaux, V.; Galli, T.; Andrews, N.W. Identification of SNAREs involved in synaptotagmin VII-regulated lysosomal exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 20471–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.; Caler, E.V.; Andrews, N.W. Plasma membrane repair is mediated by Ca(2+)-regulated exocytosis of lysosomes. Cell. 2001, 106, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakrabarti, S.; Kobayashi, K.S.; Flavell, R.A.; Marks, C.B.; Miyake, K.; Liston, D.R.; Fowler, K.T.; Gorelick, F.S.; Andrews, N.W. Impaired membrane resealing and autoimmune myositis in synaptotagmin VII-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.K.; Huynh, C.; Proux-Gillardeaux, V.; Galli, T.; Andrews, N.W. Identification of SNAREs involved in synaptotagmin VII-regulated lysosomal exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 20471–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Q.; Ali Samie, M.; Azar, M.; Tsang, W.L.; Dong, L.; Sahoo, N.; Li, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Garrity, A.G.; Wang, X.; Ferrer, M.; Dowling, J.; Xu, L.; Han, R.; Xu, H. The intracellular Ca²⁺ channel MCOLN1 is required for sarcolemma repair to prevent muscular dystrophy. Nat Med. 2014, 20, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Greune, L.; Kahms, M.; Mildner, K.; Franzkoch, R.; Psathaki, O.E.; Zobel, T.; Zeuschner, D.; Klingauf, J.; Gerke, V. Early Endosomes Act as Local Exocytosis Hubs to Repair Endothelial Membrane Damage. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023, 10, e2300244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manneville, J.B.; Etienne-Manneville, S.; Skehel, P.; Carter, T.; Ogden, D.; Ferenczi, M. Interaction of the actin cytoskeleton with microtubules regulates secretory organelle movement near the plasma membrane in human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 19, 3927–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idone, V.; Tam, C.; Goss, J.W.; Toomre, D.; Pypaert, M.; Andrews, N.W. Repair of injured plasma membrane by rapid Ca2+-dependent endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrotte, M.; Almeida, P.E.; Tam, C.; Castro-Gomes, T.; Fernandes, M.C.; Millis, B.A.; Cortez, M.; Miller, H.; Song, W.; Maugel, T.K.; Andrews, N.W. Caveolae internalization repairs wounded cells and muscle fibers. Elife. 2013, 2, e00926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idone, V.; Tam, C.; Goss, J.W.; Toomre, D.; Pypaert, M.; Andrews, N.W. Repair of injured plasma membrane by rapid Ca2+-dependent endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrotte, M.; Almeida, P.E.; Tam, C.; Castro-Gomes, T.; Fernandes, M.C.; Millis, B.A.; Cortez, M.; Miller, H.; Song, W.; Maugel, T.K.; Andrews, N.W. Caveolae internalization repairs wounded cells and muscle fibers. Elife. 2013, 2, e00926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, D.; Campbell, K.P. Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, D.; Miyake, K.; Vogel, S.S.; Groh, S.; Chen, C.C.; Williamson, R.; McNeil, P.L.; Campbell, K.P. Defective membrane repair in dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy. Nature. 2003, 423, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatchez, P.N.; Acevedo, L.; Fernandez-Hernando, C.; Murata, T.; Chalouni, C.; Kim, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Shah, V.; Gratton, J.P.; McNally, E.M.; Tempst, P.; Sessa, W.C. Myoferlin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 stability and function. J Biol Chem. 2007, 282, 30745–30753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, M.; Akcayoz, D.; Incesulu, A. A novel missense mutation in a C2 domain of OTOF results in autosomal recessive auditory neuropathy. Am J Med Genet A. 2005, 138, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Massey, K.; Witkiewicz, H.; Schnitzer, J.E. Systems analysis of endothelial cell plasma membrane proteome of rat lung microvasculature. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.Q.; Xia, M.; Xu, M.; Boini, K.M.; Ritter, J.K.; Li, N.J.; Li, P.L. Lysosome fusion to the cell membrane is mediated by the dysferlin C2A domain in coronary arterial endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 5, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, P.N.; Sharma, A.; Kodaman, P.; Sessa, W.C. Myoferlin is critical for endocytosis in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C484–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häger, S.C.; Nylandsted, J. Annexins: players of single cell wound healing and regeneration. Commun Integr Biol. 2019, 12, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerdt, S.N.; Ashraf, A.P.K.; Gerke, V. Annexins and plasma membrane repair. Curr Top Membr. 2019, 84, 43–65. [Google Scholar]
- Koerdt, S.N.; Gerke, V. Annexin A2 is involved in Ca2+-dependent plasma membrane repair in primary human endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.P.K.; Gerke, V. Plasma membrane wound repair is characterized by extensive membrane lipid and protein rearrangements in vascular endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrotte, M.; Almeida, P.E.; Tam, C.; Castro-Gomes, T.; Fernandes, M.C.; Millis, B.A.; Cortez, M.; Miller, H.; Song, W.; Maugel, T.K.; Andrews, N.W. Caveolae internalization repairs wounded cells and muscle fibers. Elife. 2013, 2, e00926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Weisleder, N.; Ko, J.K.; Komazaki, S.; Sunada, Y.; Nishi, M.; Takeshima, H.; Ma, J. Membrane repair defects in muscular dystrophy are linked to altered interaction between MG53, caveolin-3, and dysferlin. J Biol Chem. 2009, 284, 15894–15902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatchez, P.N.; Sharma, A.; Kodaman, P.; Sessa, W.C. Myoferlin is critical for endocytosis in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C484–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligorsky, M.S.; Patschan, D.; Kuo, M.C. Weibel-Palade bodies--sentinels of acute stress. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2009, 5, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl Khursigara, M.; Schlam, D.; Noone, D.G.; Bruno, V.; Ortiz-Sandoval, C.G.; Pluthero, F.G.; Kahr, W.H.A.; Bowman, M.L.; James, P.; Grinstein, S.; Licht, C. Vascular endothelial cells evade complement-mediated membrane injury via Weibel-Palade body mobilization. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehab, T.; Santos, N.C.; Holthenrich, A.; Koerdt, S.N.; Disse, J.; Schuberth, C.; Nazmi, A.R.; Neeft, M.; Koch, H.; Man, K.N.M.; Wojcik, S.M.; Martin, T.F.J.; van der Sluijs, P.; Brose, N.; Gerke, V. A novel Munc13-4/S100A10/annexin A2 complex promotes Weibel-Palade body exocytosis in endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2017, 28, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthenrich, A.; Gerke, V. Regulation of von-Willebrand Factor Secretion from Endothelial Cells by the Annexin A2-S100A10 Complex. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerdt, S.N.; Gerke, V. Annexin A2 is involved in Ca(2+)-dependent plasma membrane repair in primary human endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017, 1864, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, O.V. Rab3a and Rab10 are regulators of lysosome exocytosis and plasma membrane repair. Small GTPases. 2018, 9, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encarnação, M.; Espada, L.; Escrevente, C.; Mateus, D.; Ramalho, J.; Michelet, X.; Santarino, I.; Hsu, V.W.; Brenner, M.B.; Barral, D.C.; Vieira, O.V. A Rab3a-dependent complex essential for lysosome positioning and plasma membrane repair. J Cell Biol. 2016, 213, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togo, T.; Steinhardt, R.A. Nonmuscle myosin IIA and IIB have distinct functions in the exocytosis-dependent process of cell membrane repair. Mol Biol Cell. 2004, 15, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.K.; Huynh, C.; Proux-Gillardeaux, V.; Galli, T.; Andrews, N.W. Identification of SNAREs involved in synaptotagmin VII-regulated lysosomal exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 20471–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, L.; Stock, S.; Kobold, S. ESCRT machinery: role of membrane repair mechanisms in escaping cell death. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022, 7, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.A.; Johnson, R.W.; Whitlock, J.M.; Pozsgai, E.R.; Heller, K.N.; Grose, W.E.; Arnold, W.D.; Sahenk, Z.; Hartzell, H.C.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R. Defective membrane fusion and repair in Anoctamin5-deficient muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2016, 25, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrotte, M.; Cerasoli, M.; Maeda, F.Y.; Andrews, N.W. Endophilin-A2-dependent tubular endocytosis promotes plasma membrane repair and parasite invasion. J Cell Sci. 2020, 134, jcs249524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Masumiya, H.; Weisleder, N.; Matsuda, N.; Nishi, M.; Hwang, M.; Ko, J.K.; Lin, P.; Thornton, A.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Z.; Komazaki, S.; Brotto, M.; Takeshima, H.; Ma, J. MG53 nucleates assembly of cell membrane repair machinery. Nat Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, Z.; Milad, N.; Sellers, S.L.; Bernatchez, P. Effect of Dysferlin Deficiency on Atherosclerosis and Plasma Lipoprotein Composition Under Normal and Hyperlipidemic Conditions. Front Physiol. 2021, 12, 675322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Hernando, C.; Yu, J.; Suárez, Y.; Rahner, C.; Dávalos, A.; Lasunción, M.A.; Sessa, W.C. Genetic evidence supporting a critical role of endothelial caveolin-1 during the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, M.; de Jong, R.; Rossaint, J.; Viola, J.R.; Leoni, G.; Wang, J.M.; Grommes, J.; Hinkel, R.; Kupatt, C.; Weber, C.; Döring, Y.; Zarbock, A.; Soehnlein, O. Annexin A1 counteracts chemokine-induced arterial myeloid cell recruitment. Circ Res. 2015, 116, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, Q.; Han, L.; Cao, K.; Lan, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xue, J.; Shan, F.; Feng, J.; Xie, X. Tenascin-c renders a proangiogenic phenotype in macrophage via annexin II. J Cell Mol Med. 2018, 22, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedhli, N.; Falcone, D.J.; Huang, B.; Cesarman-Maus, G.; Kraemer, R.; Zhai, H.; Tsirka, S.E.; Santambrogio, L.; Hajjar, K.A. The annexin A2/S100A10 system in health and disease: emerging paradigms. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 406273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Bhat, O.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.L. Impairment of Ceramide-Mediated Endothelial Instant Membrane Resealing During Diabetes Mellitus. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 910339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.C.; McNeil, A.K.; Xiong, F.; Xiong, W.C.; McNeil, P.L. A novel cellular defect in diabetes: membrane repair failure. Diabetes. 2011, 60, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, P.; Lieber, G.; Nishi, M.; Yan, R.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Whitson, B.A.; Duann, P.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, H.; Takeshima, H.; Hunter, J.C.; McLeod, R.L.; Weisleder, N.; Zeng, C.; Ma, J. Treatment of acute lung injury by targeting MG53-mediated cell membrane repair. Nat Commun. 2014, 5, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagre, N.; Cong, X.; Ji, H.L.; Schreiber, J.M.; Fu, H.; Pepper, I.; Warren, S.; Sill, J.M.; Hubmayr, R.D.; Zhao, X. Inhaled TRIM72 Protein Protects Ventilation Injury to the Lung through Injury-guided Cell Repair. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018, 59, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, P.; Han, L.; Han, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, G.; Zheng, M.; Weisleder, N.; Xiao, R.P.; Takeshima, H.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H. Cardioprotection of ischemia/reperfusion injury by cholesterol-dependent MG53-mediated membrane repair. Circ Res. 2010, 107, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchina, L.V.; Bhattacharya, S.; McElhanon, K.E.; Choi, J.H.; Manring, H.; Beck, E.X.; Alloush, J.; Weisleder, N. Treatment with Recombinant Human MG53 Protein Increases Membrane Integrity in a Mouse Model of Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy 2B. Mol Ther. 2017, 25, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Huang, T.; Wang, X.; Xing, Q.; Gumpper, K.; Li, P.; Song, J.; Tan, T.; Yang, G.L.; Zang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Ma, J.; Ma, S. The TRIM protein Mitsugumin 53 enhances survival and therapeutic efficacy of stem cells in murine traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duann, P.; Li, H.; Lin, P.; Tan, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Gumpper, K.; Zhu, H.; Ludwig, T.; Mohler, P.J.; Rovin, B.; Abraham, W.T.; Zeng, C.; Ma, J. MG53-mediated cell membrane repair protects against acute kidney injury. Sci Transl Med. 2015, 7, 279ra36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tai, W.L.; Xia, Z.; Hei, Z. MG53 anchored by dysferlin to cell membrane reduces hepatocyte apoptosis which induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2017, 21, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Barbero, N.; San Sebastian-Jaraba, I.; Blázquez-Serra, R.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. Annexins and cardiovascular diseases: Beyond membrane trafficking and repair. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022, 10, 1000760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, R.; Dai, D.K.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.Z.; Qin, Z.H.; Chen, X.P.; Tao, L.Y. Poloxamer-188 attenuates TBI-induced blood-brain barrier damage leading to decreased brain edema and reduced cellular death. Neurochem Res. 2012, 37, 2856–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhardt, R.A.; Alderton, J.M. Poloxamer 188 enhances endothelial cell survival in bovine corneas in cold storage. Cornea. 2006, 25, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloughney, J.G.; Weisleder, N. Poloxamer 188 (p188) as a membrane resealing reagent in biomedical applications. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.; Townsend, D.; Michele, D.E.; Favre, E.G.; Day, S.M.; Metzger, J.M. Dystrophic heart failure blocked by membrane sealant poloxamer. Nature. 2005, 436, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.; Idone, V.; Devlin, C.; Fernandes, M.C.; Flannery, A.; He, X.; Schuchman, E.; Tabas, I.; Andrews, N.W. Exocytosis of acid sphingomyelinase by wounded cells promotes endocytosis and plasma membrane repair. J Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Bhat, O.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.L. Impairment of Ceramide-Mediated Endothelial Instant Membrane Resealing During Diabetes Mellitus. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 910339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K.; Maltez, V.I.; Rayamajhi, M.; Tubbs, A.L.; Mitchell, J.E.; Lacey, C.A.; Harvest, C.K.; Li, L.; Nash, W.T.; Larson, H.N.; McGlaughon, B.D.; Moorman, N.J.; Brown, M.G.; Whitmire, J.K.; Miao, E.A. Caspase-7 activates ASM to repair gasdermin and perforin pores. Nature. 2022, 606, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).