Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
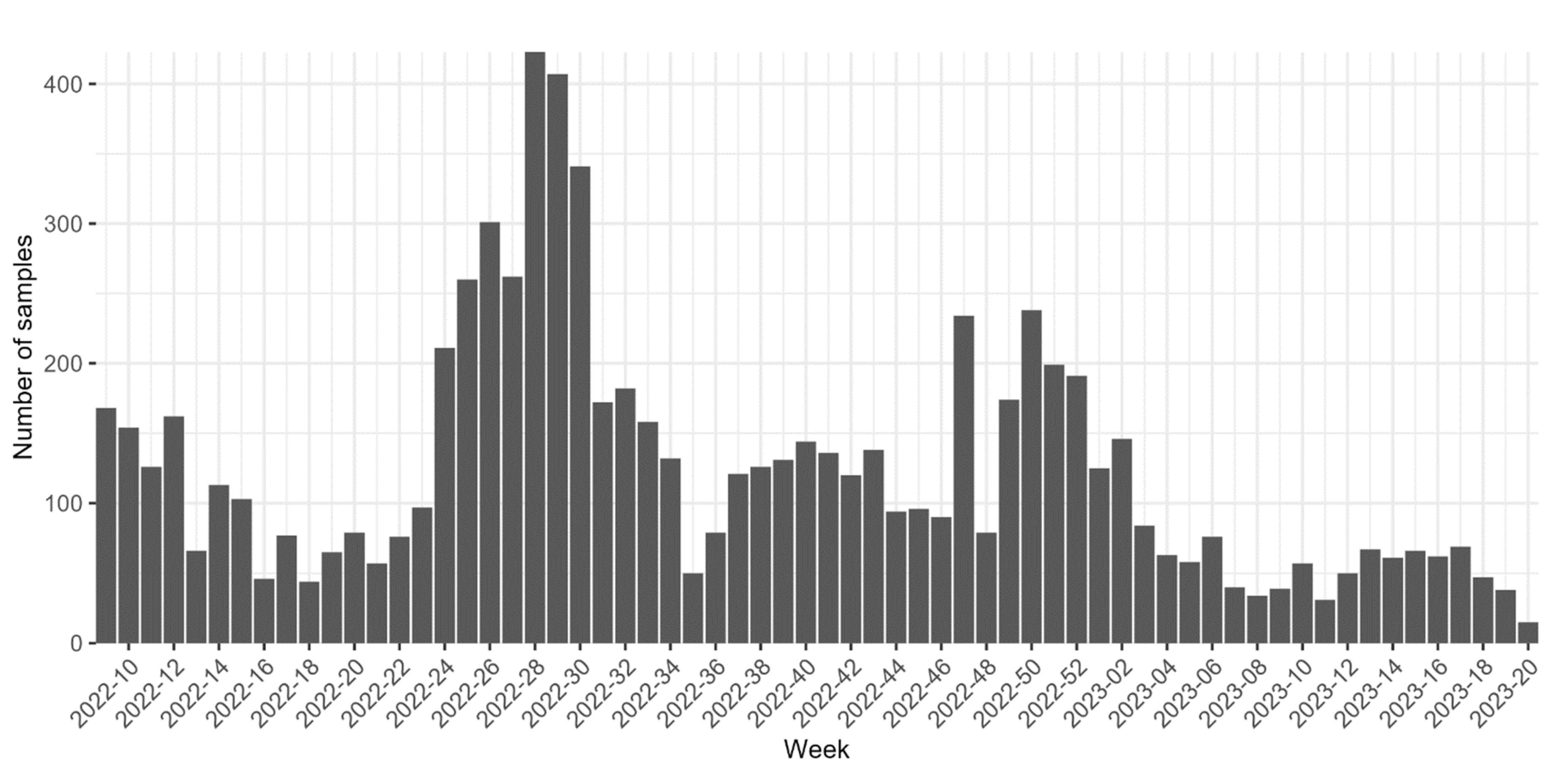
2.1. Samples collection
2.2. Viral RNA extraction and sequencing
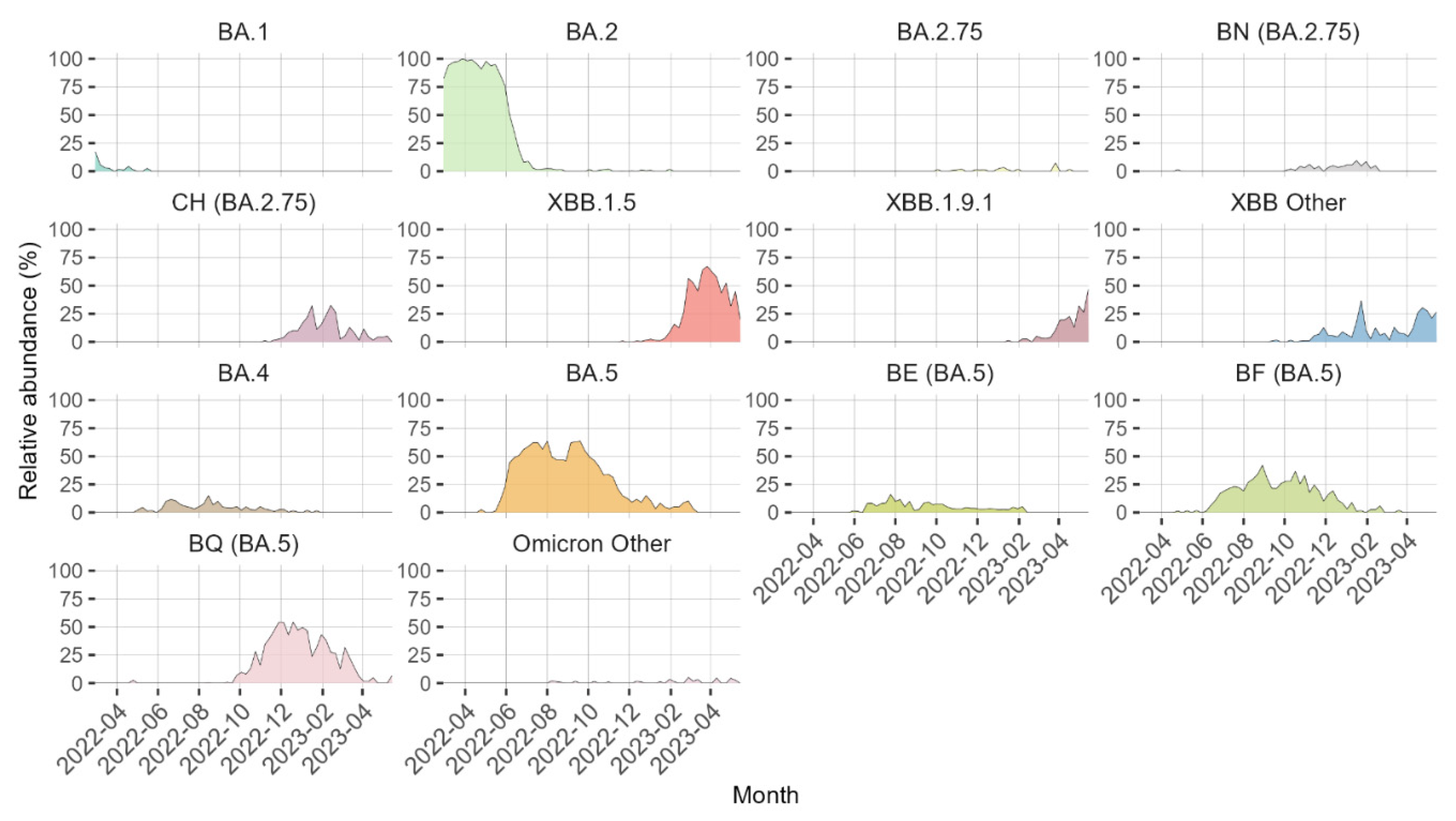
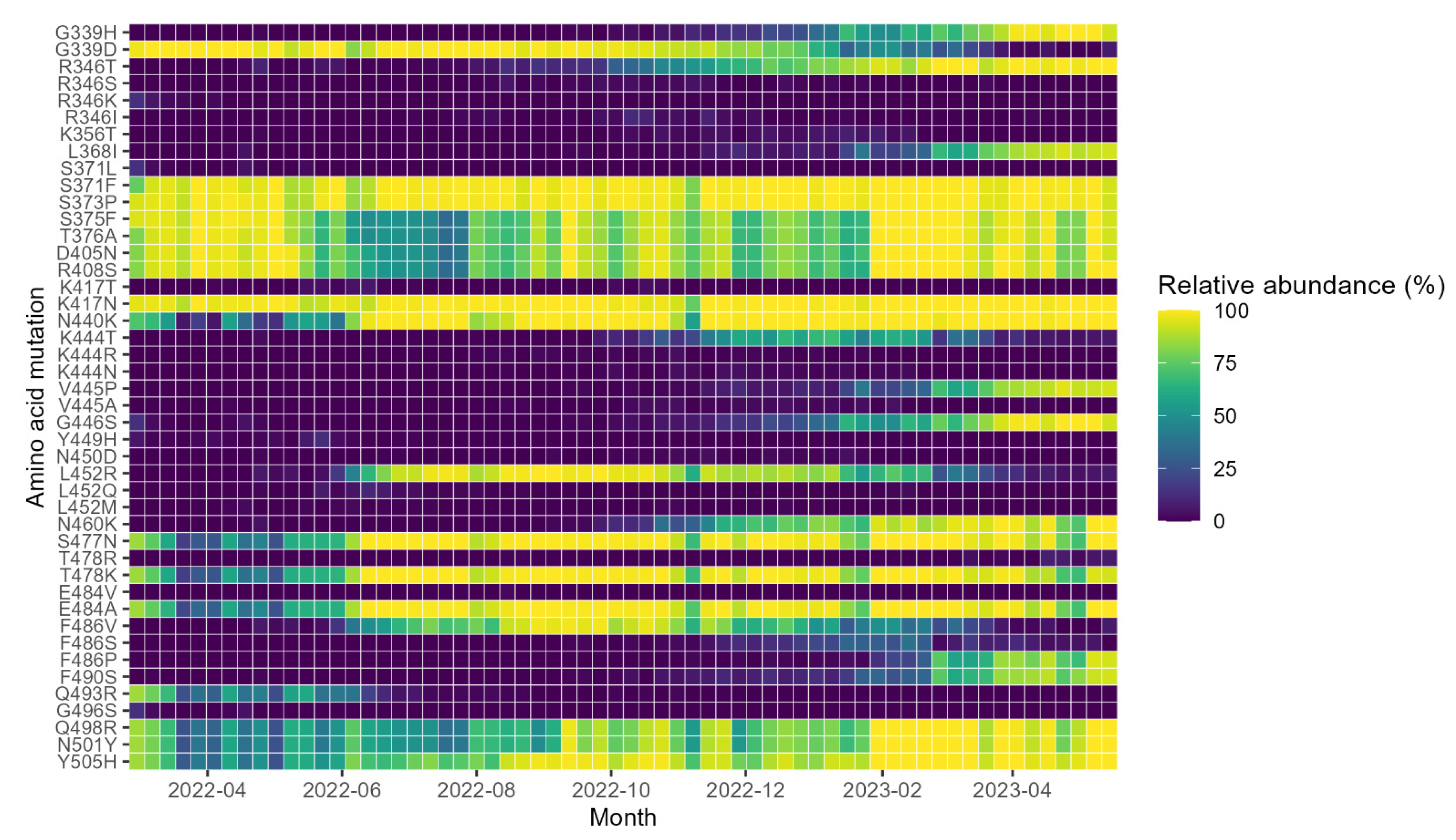
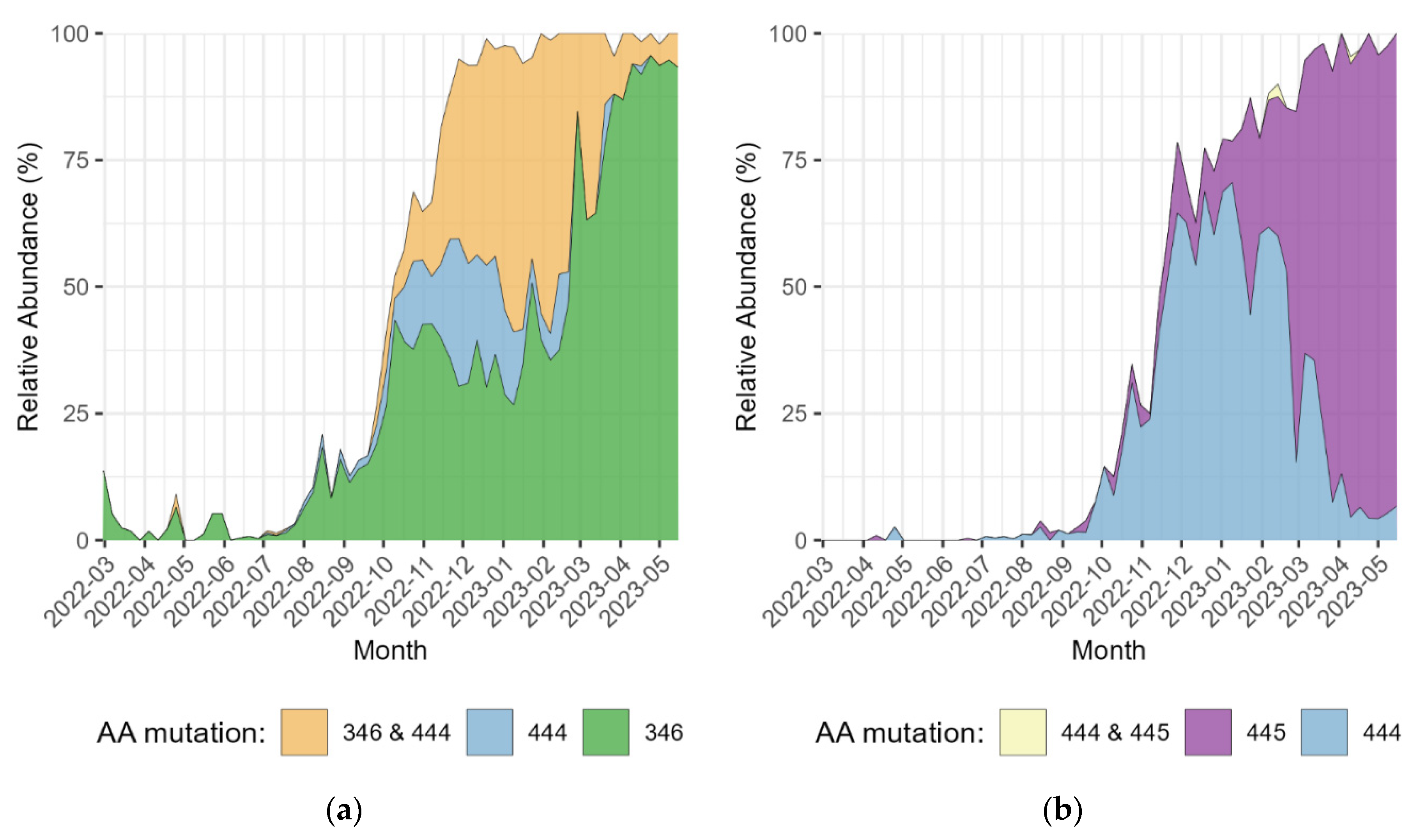
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-statement-on-ihr-emergency-committee-on-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov) (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Lyke, K.E.; Atmar, R.L.; Islas, C.D.; Posavad, C.M.; Szydlo, D.; Paul Chourdhury, R.; Deming, M.E.; Eaton, A.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; et al. Rapid Decline in Vaccine-Boosted Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Cell Rep Med 2022, 3, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An Oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 374, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, L.B.; Tedla, N.; Bull, R.A. Broadly-Neutralizing Antibodies Against Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.O.; Jette, C.A.; Abernathy, M.E.; Dam, K.-M.A.; Esswein, S.R.; Gristick, H.B.; Malyutin, A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Lee, Y.E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Structures Inform Therapeutic Strategies. Nature 2020, 588, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, T.S. Gene of the Month: The 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2 Novel Coronavirus Spike Protein. Journal of Clinical Pathology 2020, 73, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.; He, L.; Zhang, X.; Pu, J.; Voronin, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Du, L. Characterization of the Receptor-Binding Domain (RBD) of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implication for Development of RBD Protein as a Viral Attachment Inhibitor and Vaccine. Cell Mol Immunol 2020, 17, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commissioner, O. of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Monoclonal Antibody Bamlanivimab. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-monoclonal-antibody-bamlanivimab (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- EMA EMA Issues Advice on Use of Antibody Combination (Bamlanivimab / Etesevimab). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-issues-advice-use-antibody-combination-bamlanivimab-etesevimab (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- EMA Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab for COVID-19: Withdrawn Application. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/withdrawn-applications/bamlanivimab-etesevimab-covid-19 (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Emergency Use Authorization 094. Available online: https://pi.lilly.com/eua/bam-and-ete-eua-fda-authorization-letter.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- EMA Regkirona. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/regkirona (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Commissioner, O. of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Limits Use of Certain Monoclonal Antibodies to Treat COVID-19 Due to the Omicron Variant. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-limits-use-certain-monoclonal-antibodies-treat-covid-19-due-omicron (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Commissioner, O. of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19 (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Commissioner, O. of the FDA Roundup: April 5, 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-roundup-april-5-2022 (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- EMA Xevudy. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/xevudy (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Commissioner, O. of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes New Long-Acting Monoclonal Antibodies for Pre-Exposure Prevention of COVID-19 in Certain Individuals. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-new-long-acting-monoclonal-antibodies-pre-exposure (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Research, C. for D.E. and FDA Announces Evusheld Is Not Currently Authorized for Emergency Use in the U.S. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-announces-evusheld-not-currently-authorized-emergency-use-us (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- EMA Evusheld. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/evusheld (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Commissioner, O. of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes New Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19 That Retains Activity Against Omicron Variant. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-new-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19-retains (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Research, C. for D.E. and FDA Announces Bebtelovimab Is Not Currently Authorized in Any US Region. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-announces-bebtelovimab-not-currently-authorized-any-us-region (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Kaden, R. Early Phylogenetic Diversification of SARS-CoV-2: Determination of Variants and the Effect on Epidemiology, Immunology, and Diagnostics. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2020, 9, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, K.D.; Jacobs, J.L.; Mellors, J.W. The Emerging Plasticity of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2021, 371, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennerstrand, J.; Palanisamy, N. Global Prevalence of Adaptive and Prolonged Infections’ Mutations in the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Viruses 2021, 13, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming Antibody Evasion Properties of Rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB Subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jian, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Wang, J.; An, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 Humoral Immunity Induces Convergent Omicron RBD Evolution. Nature 2023, 614, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iketani, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Chu, H.; et al. Antibody Evasion Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages. Nature 2022, 604, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Dingens, A.S.; Bloom, J.D. Complete Map of SARS-CoV-2 RBD Mutations That Escape the Monoclonal Antibody LY-CoV555 and Its Cocktail with LY-CoV016. Cell Rep Med 2021, 2, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focosi, D.; Novazzi, F.; Genoni, A.; Dentali, F.; Gasperina, D.D.; Baj, A.; Maggi, F. Emergence of SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein Escape Mutation Q493R after Treatment for COVID-19. Emerg Infect Dis 2021, 27, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffot, A.; Andréani, J.; Le Maréchal, M.; Caporossi, A.; Epaulard, O.; Germi, R.; Poignard, P.; Larrat, S. SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Immunocompromised Patient Given Antibody Monotherapy. Emerg Infect Dis 2021, 27, 2725–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, A.; Focosi, D. SARS-CoV-2 Variants Resistant to Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunocompromised Patients Constitute a Public Health Concern. J Clin Invest 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Konnova, A.; Smet, M.; Berkell, M.; Savoldi, A.; Morra, M.; Averbeke, V.V.; Winter, F.H.R.D.; Peserico, D.; Danese, E.; et al. Host Immunological Responses Facilitate Development of SARS-CoV-2 Mutations in Patients Receiving Monoclonal Antibody Treatments. J Clin Invest 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellas, C.; Trémeaux, P.; Bello, A.D.; Latour, J.; Jeanne, N.; Ranger, N.; Danet, C.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Delobel, P.; Kamar, N.; et al. Resistance Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Patients Treated with Sotrovimab. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2022, 28, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, R.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Tegally, H.; Scheepers, C.; Althaus, C.L.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Bester, P.A.; Boni, M.F.; Chand, M.; et al. Rapid Epidemic Expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Southern Africa. Nature 2022, 603, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Abdullahi, A.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Goonawardane, N.; Saito, A.; Kimura, I.; Yamasoba, D.; Gerber, P.P.; Fatihi, S.; Rathore, S.; et al. Altered TMPRSS2 Usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Impacts Infectivity and Fusogenicity. Nature 2022, 603, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, L.; Peng, Z.; Chen, L.-L.; Meng, X.; Zhang, C.; Ip, J.D.; Chan, W.-M.; Chu, A.W.-H.; Chan, K.-H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Shows Less Efficient Replication and Fusion Activity When Compared with Delta Variant in TMPRSS2-Expressed Cells. Emerging Microbes & Infections 2022, 11, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Wong, L.-Y.R.; Arora, P.; Zhang, L.; Rocha, C.; Odle, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Kempf, A.; Richter, A.; Halwe, N.J.; et al. Omicron Subvariant BA.5 Efficiently Infects Lung Cells. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannsverk, S.; Bergholm, J.; Palanisamy, N.; Ellström, P.; Kaden, R.; Lindh, J.; Lennerstrand, J. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Spike Protein Mutational Dynamics in a Swedish Cohort during 2021, Studied by Nanopore Sequencing. Virol J 2022, 19, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskela von Sydow, A.; Lindqvist, C.M.; Asghar, N.; Johansson, M.; Sundqvist, M.; Mölling, P.; Stenmark, B. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing Using Tiled Amplicon Enrichment and Bait Hybridization. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünemann, S.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Prior, K.; Albersmeier, A.; John, U.; Kalinowski, J.; Mellmann, A.; Goesmann, A.; von Haeseler, A.; Stoye, J.; et al. Updating Benchtop Sequencing Performance Comparison. Nat Biotechnol 2013, 31, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gms-Artic. Available online: https://github.com/genomic-medicine-sweden/gms-artic (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Epi2me-Labs/Wf-Artic: ARTIC SARS-CoV-2 Workflow and Reporting. Available online: https://github.com/epi2me-labs/wf-artic (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- National Sample Collection Stored at NPC – The COVID-19 Library | Karolinska Institutet. Available online: https://ki.se/en/mtc/national-sample-collection-stored-at-npc-the-covid-19-library (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An Amplicon-Based Sequencing Framework for Accurately Measuring Intrahost Virus Diversity Using PrimalSeq and iVar. Genome Biol 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-Based Variant Detection from Short-Read Sequencing 2012.
- Töpfer, A. Cbg-Ethz/ConsensusFixer: Computes a Consensus Sequence with Wobbles, Ambiguous Bases, and in-Frame Insertions, from a NGS Read Alignment. Available online: https://github.com/cbg-ethz/consensusfixer (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Freed, N.E.; Vlková, M.; Faisal, M.B.; Silander, O.K. Rapid and Inexpensive Whole-Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 Using 1200 Bp Tiled Amplicons and Oxford Nanopore Rapid Barcoding. Biology Methods and Protocols 2020, 5, bpaa014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, J.R.; James, P.; Stoddart, D.; Sparks, N.; Wickenhagen, A.; Hall, G.; Choi, J.H.; Lapointe, H.; Kamelian, K.; Smith, A.D.; et al. Improvements to the ARTIC Multiplex PCR Method for SARS-CoV-2 Genome Sequencing Using Nanopore. bioRxiv 2020, 2020.09.04.283077. [CrossRef]
- Quick, J. nCoV-2019 Sequencing Protocol v3 (LoCost). 2020. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Can Coverage Be Improved for the BA.2 Variant? | NEB. Available online: https://international.neb.com/faqs/2022/04/28/can-coverage-be-improved-for-the-ba2-variant (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Davis, J.J.; Long, S.W.; Christensen, P.A.; Olsen, R.J.; Olson, R.; Shukla, M.; Subedi, S.; Stevens, R.; Musser, J.M. Analysis of the ARTIC Version 3 and Version 4 SARS-CoV-2 Primers and Their Impact on the Detection of the G142D Amino Acid Substitution in the Spike Protein. Microbiology Spectrum 2021, 9, e01803-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneious | Bioinformatics Software for Sequence Data Analysis. Available online: https://www.geneious.com/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- BBMap. Available online: https://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GISAID - Gisaid.Org. Available online: https://gisaid.org/.
- Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; O’Toole, Á.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Ruis, C.; du Plessis, L.; Pybus, O.G. A Dynamic Nomenclature Proposal for SARS-CoV-2 Lineages to Assist Genomic Epidemiology. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneious Wrapper Plugin for Pangolin. Available online: https://github.com/clinical-genomics-uppsala/Geneious_pangolin_wrapper (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- O’Toole, Á.; Scher, E.; Underwood, A.; Jackson, B.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Colquhoun, R.; Ruis, C.; Abu-Dahab, K.; Taylor, B.; et al. Assignment of Epidemiological Lineages in an Emerging Pandemic Using the Pangolin Tool. Virus Evol 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutz, S. Pango Lineage Translator. Available online: https://github.com/sschmutz/PangoLineageTranslator (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Mercatelli, D.; Triboli, L.; Fornasari, E.; Ray, F.; Giorgi, F.M. Coronapp: A Web Application to Annotate and Monitor SARS-CoV-2 Mutations. Journal of Medical Virology 2021, 93, 3238–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Ito, J.; Uriu, K.; Zahradnik, J.; Kida, I.; Anraku, Y.; Nasser, H.; Shofa, M.; Oda, Y.; Lytras, S.; et al. Virological Characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 XBB Variant Derived from Recombination of Two Omicron Subvariants. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Song, W.; Wang, L.; Jian, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, F.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y. ACE2 Binding and Antibody Evasion in Enhanced Transmissibility of XBB.1.5. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2023, 23, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca A Phase I/III Randomized, Double Blind Study to Evaluate the Safety, Efficacy and Neutralizing Activity of AZD5156/AZD3152 for Pre Exposure Prophylaxis of COVID 19 in Participants With Conditions Causing Immune Impairment. Sub-Study: Phase II Open Label Sub-Study to Evaluate the Safety, PK, and Neutralizing Activity of AZD3152 for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis of COVID-19; clinicaltrials.gov, 2023.
- ECCMID Poster: P2636 The SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody AZD3152 Potently Neutralises Historical and Currently Circulating Variants.
| Monoclonal antibody | Commercial name | Class | Granted emergency use by the FDA | Revised emergency use by the FDA | EMA Rolling Review Started | EMA Rolling Review Stopped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bamlanvimab | - | II | 09 November 2020[8] | 16 April 2021[8] | 11 March 2021[9] | 29 October 2021[10] |
| bamlanvimab & etesevimab | - | II & I | 09 February 2021[11] | - | 11 March 2021[9] | 29 October 2021[10] |
| regdanvimab | Regikrona | I | - | - | 12 November 2021[12] | - |
| casirivimab & imdevimab | Ronapreve/REGEN-COV | I & III | 21 November 2020[13] | 24 January 2022[13] | - | - |
| sotrovimab | Xevudy | III | 26 May 2021[14] | 05 April 2022[15] | 17 December 2021[16] | - |
| tixagevimab & cilgavimab | Evusheld | I & II | 08 December 2021[17] | 26 January 2023[18] | 25 March 2022[19] | - |
| bebtelovimab | - | III | 11 February 2022[20] | 30 November 2022[21] | - | - |
| Omicron lineage or mutants with a single RBD mutation | *Important resistance mutations in lineage | bamlanivimab | regdanvimab | casirivimab & imdevimab | sotrovimab | tixagevimab & cilgavimab | bebtelovimab | AZD3152 |
| BA 2 | S371F + T478K + E484A + Q493R | >1000 | >1000 | 387 | 21 | 8 | 1 | 0.6 |
| BA 2.75 | S371F + G446S + N460K + E484A | >1000 | 42 | >1000 | 12 | 24 | 3.1 | 1.9 |
| BA 4 | S371F + L452R + E484A + F486V | >1000 | >1000 | 25 | 22 | 25 | 1 | 0.2 |
| BA 5 | S371F + L452R + E484A + F486V | >1000 | >1000 | 25 | 22 | 25 | 1 | 0.2 |
| BE (BA.5) | S371F + L452R + E484A + F486V | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BN (BA 2.75) | R346T + S371F + G446S + N460K + E484A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BQ (BA.5) | S371F + K444T + L452R + N460K + E484A + F486V | - | - | 200 | 26 | >1000 | 900 | 0.9 |
| CH (BA 2.75) | R346T + S371F + K444T + G446S + E484A | - | - | >1000 | 16 | >1000 | >1000 | - |
| XBB | R346T + S371F + V445P + G446S + N460K + E484A + F486S | >1000 | - | 200 | 14 | 738 | >1000 | 0.3 |
| XBB 1.5 | R346T + S371F + V445P + G446S + N460K + E484A + F486P | - | - | 751 | 18 | 867 | 475 | 0.2 |
| XBB 1.9.1 | R346T + S371F + V445P + G446S + N460K + E484A + F486P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R346T | R346T | - | - | - | 1.3 | - | - | - |
| S371F | S371F | 0.9 | 21 | 0.6 | 9.7 | 0.6 | 2.2 | - |
| K444T | K444T | - | - | 6.2 | - | - | >1000 | - |
| V445A | V445A | - | - | 4.7 | 3.4 | - | 83 | - |
| G446S | G446S | 1.2 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 2 | 2 | - |
| L452R | L452R | >1000 | 35 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 0.6 | - |
| N460K | N460K | 1.5 | - | 1.3 | 1.2 | 2 | 1.2 | - |
| E484A | E484A | 697 | 7.9 | 7.8 | 0.9 | 5.1 | 1.4 | - |
| E484K | E484K | >1000 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 0.7 | - |
| F486V | F486V | 490 | - | 2.7 | 1.1 | 9.5 | 1.5 | - |
| Q493R | Q493R | >1000 | 949 | - | 1.3 | 3.4 | 1 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




