Submitted:
08 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Theoretical proof of DAS framework and its experimental validation using a DSSoC simulator [13];
- Extensive performance evaluation in the trade space of execution time, energy, and scheduling overhead over the Xilinx Zynq ZCU102 SoC based on workload scenarios composed of real-life applications;
2. Related Work
3. Dynamic Adaptive Scheduling Framework
3.1. Overview and Preliminaries
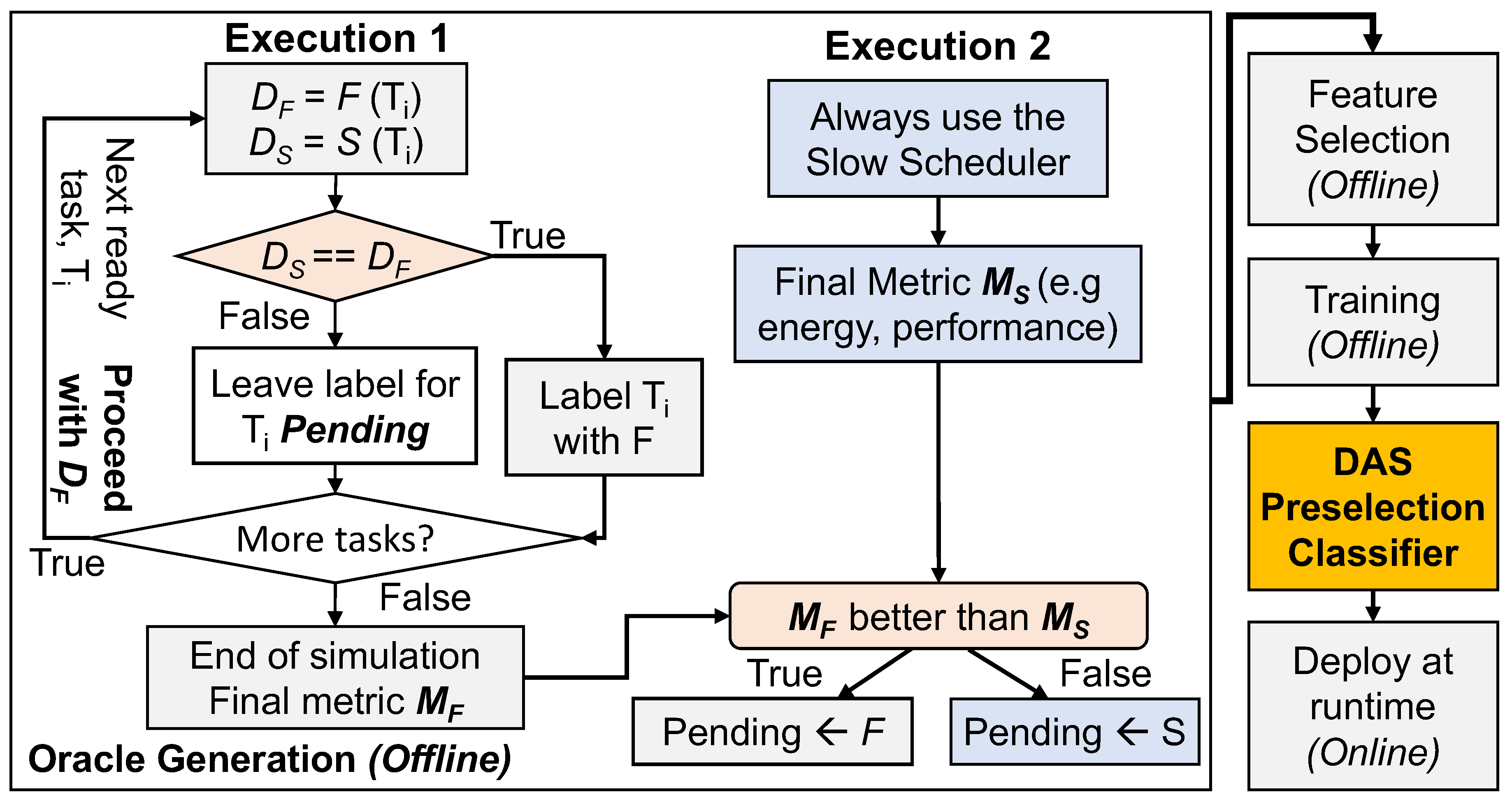
3.2. DAS Preselection Classifier
3.3. Fast & Slow (F&S) Scheduler Selection
| Algorithm 1 ETF Scheduler |
|
4. Evaluation of DAS Using Simulations
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Exploration of Machine Learning Techniques and Feature Space for DAS
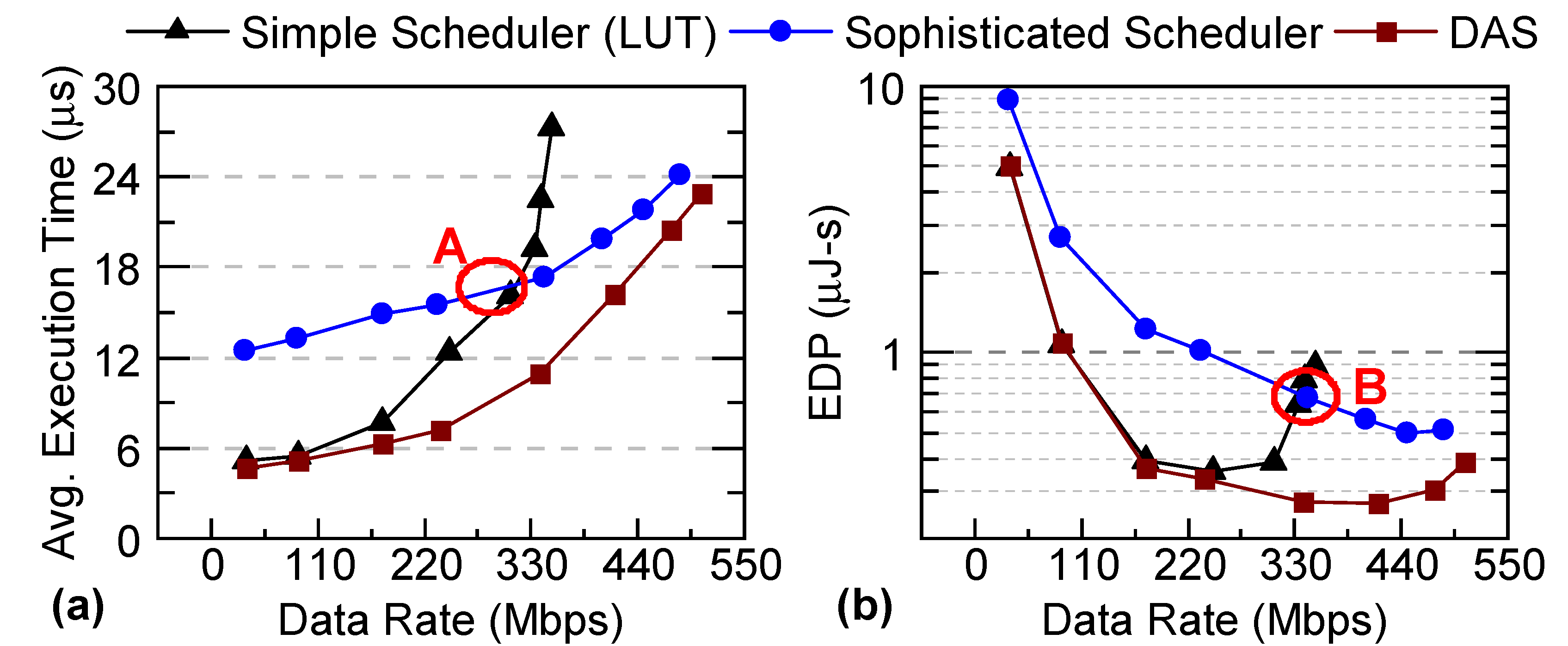
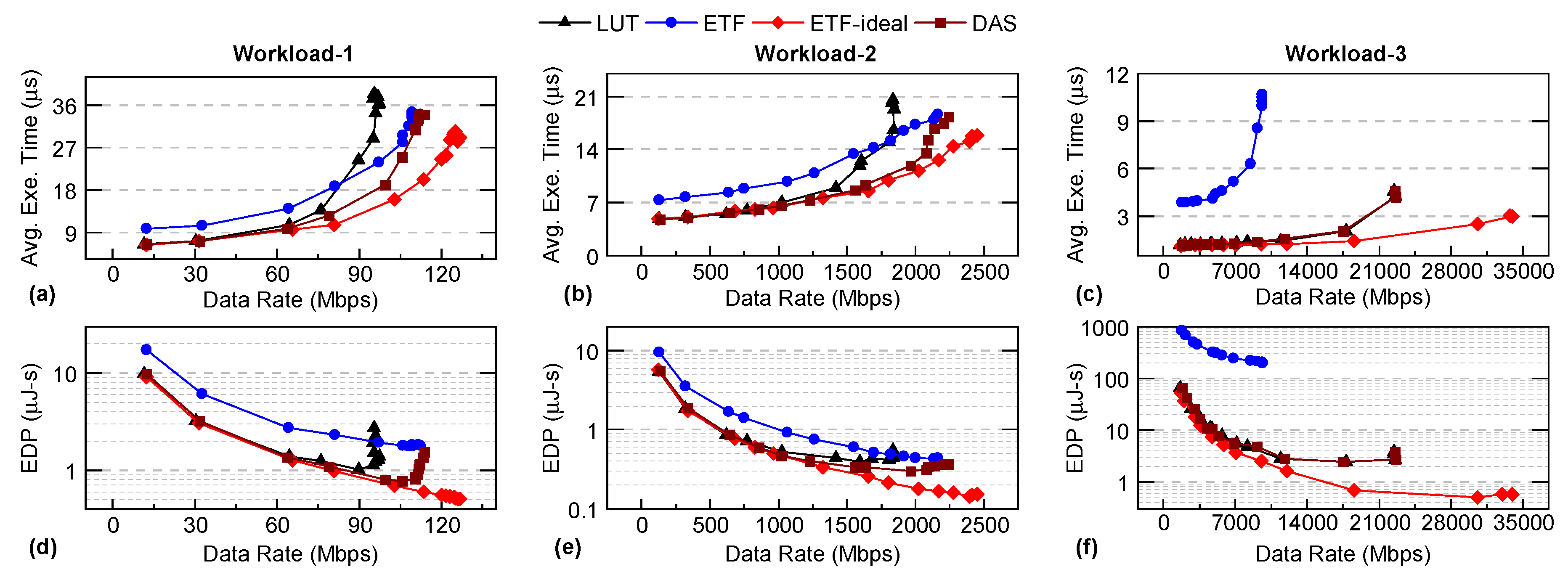
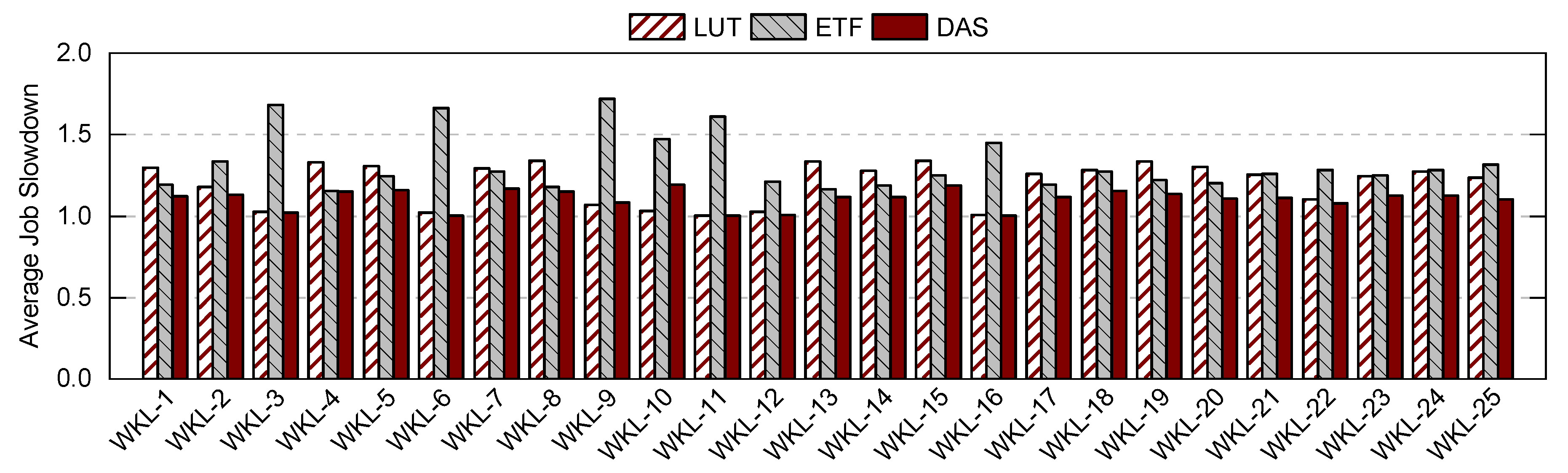
4.3. Performance Analysis for Different Workloads
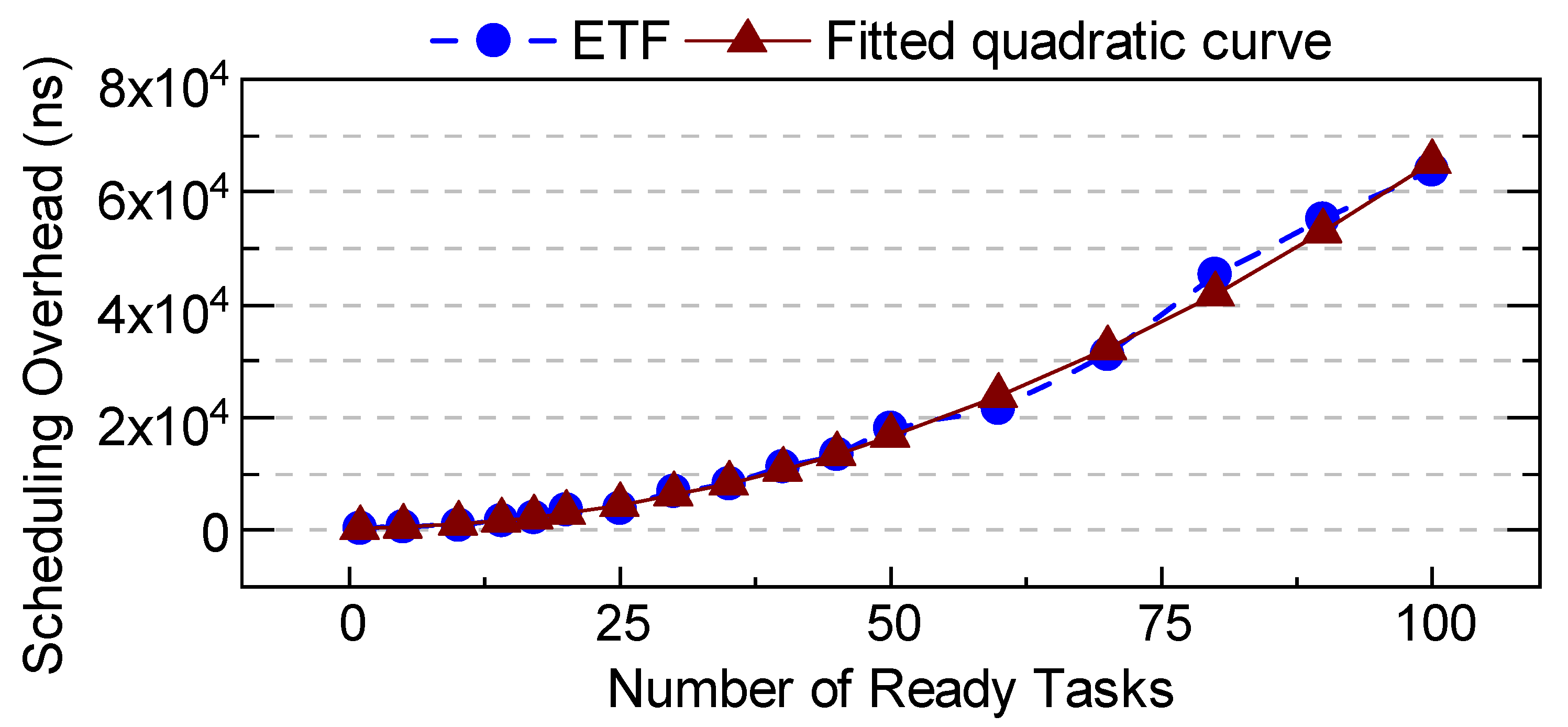
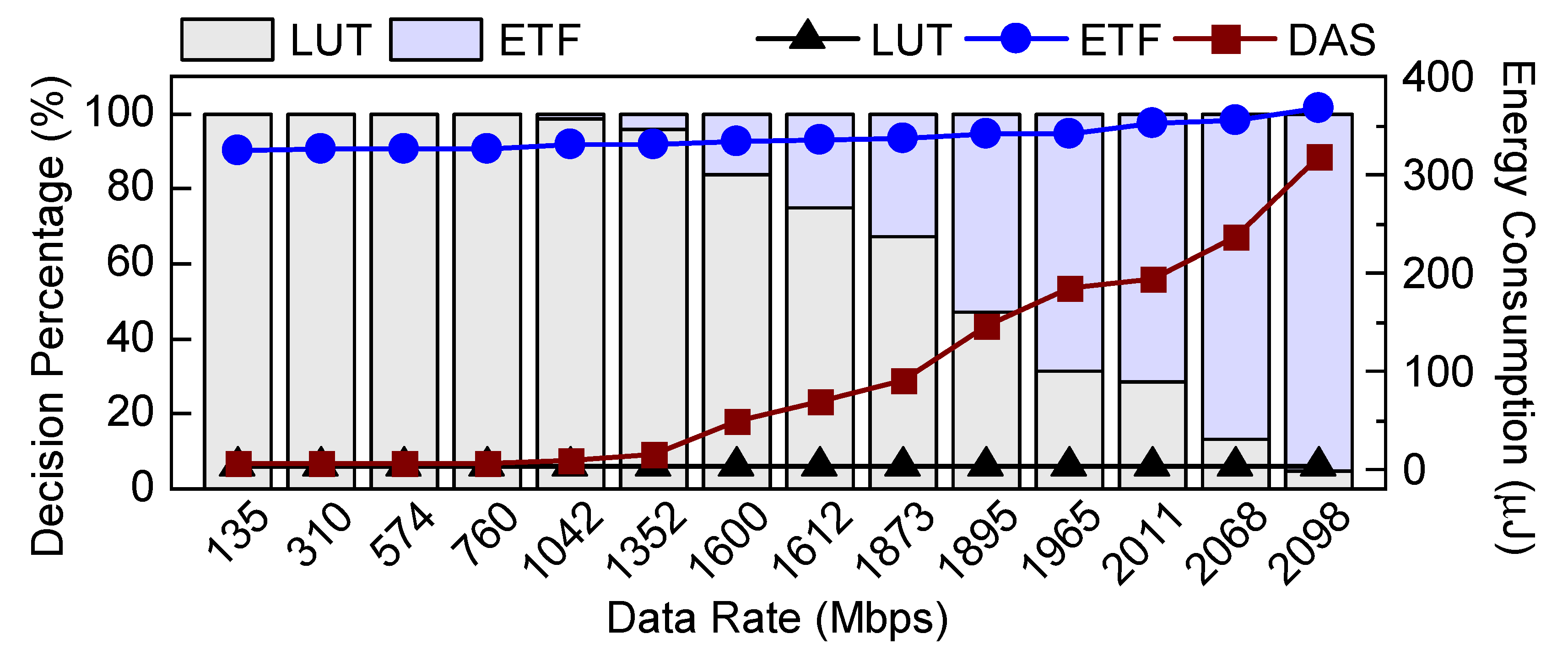
4.4. Scheduling Overhead and Energy Consumption Analysis
5. Evaluation of DAS using FPGA Emulation
5.1. Experimental Setup
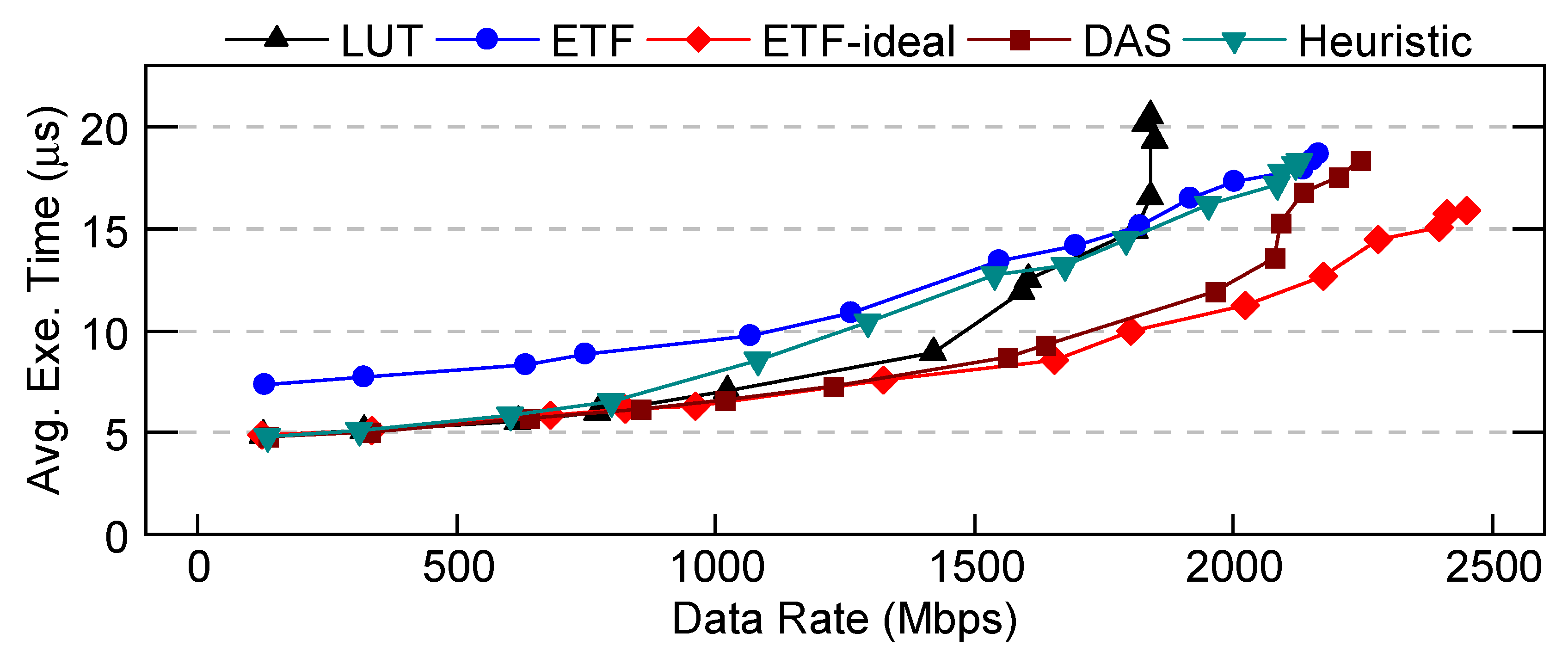
5.2. Performance Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Theoretical Proof for DAS Framework
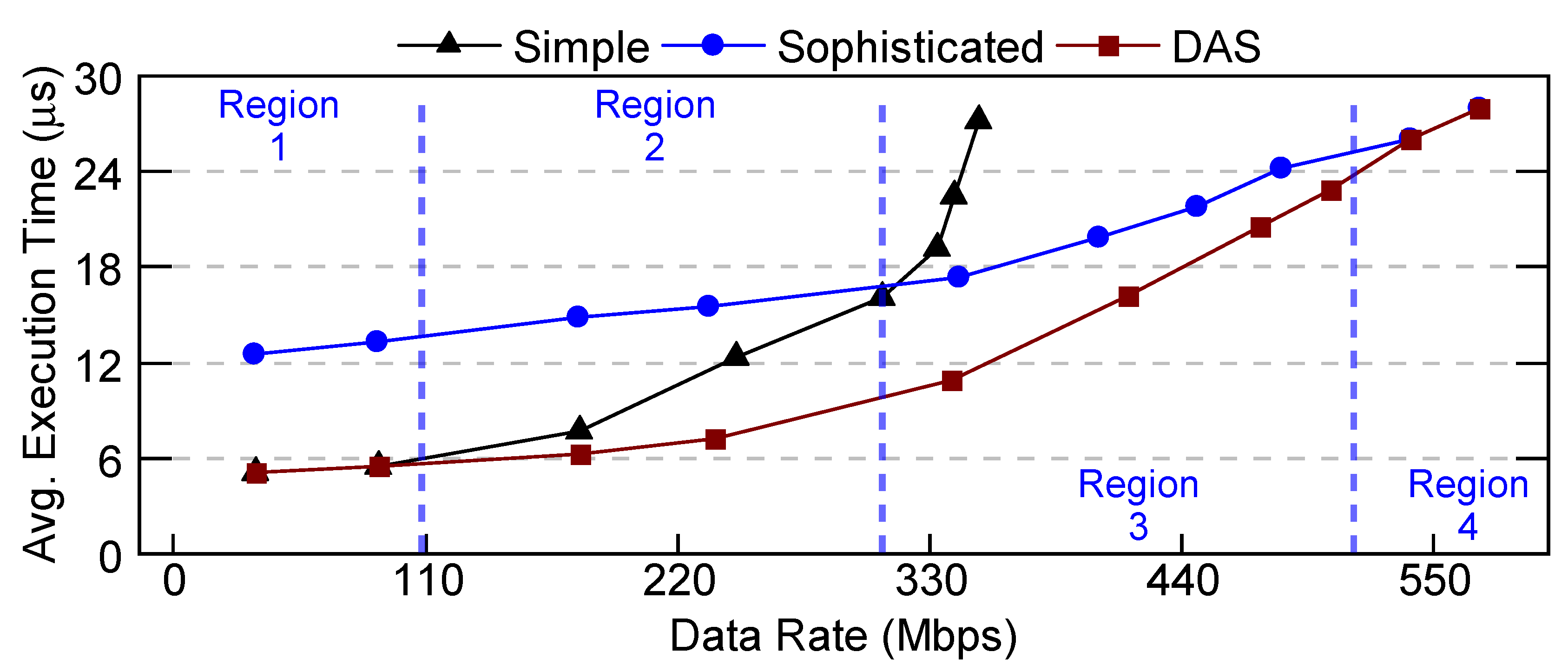
Appendix A.1. Necessary Conditions for the Superiority of DAS
| Notation | Definition |
| Ideal scheduler decision for Task-i | |
| Decision of DAS scheduler for Task-i | |
| Selecting scheduler-X when the ideal selection is Y | |
| Execution time difference for Task-i w.r.t. the fast scheduler if selecting scheduler-X when the ideal selection is Y |
|
| Total execution time difference for all tasks | |
| Execution time for simulation |
Appendix A.2. Experimental Validation of the Proof
Appendix A.2.1. Finding the Empirical Values for Δ L and Δ G
| Algorithm A1 Algorithm to find ideal decisions, , and values. |
|
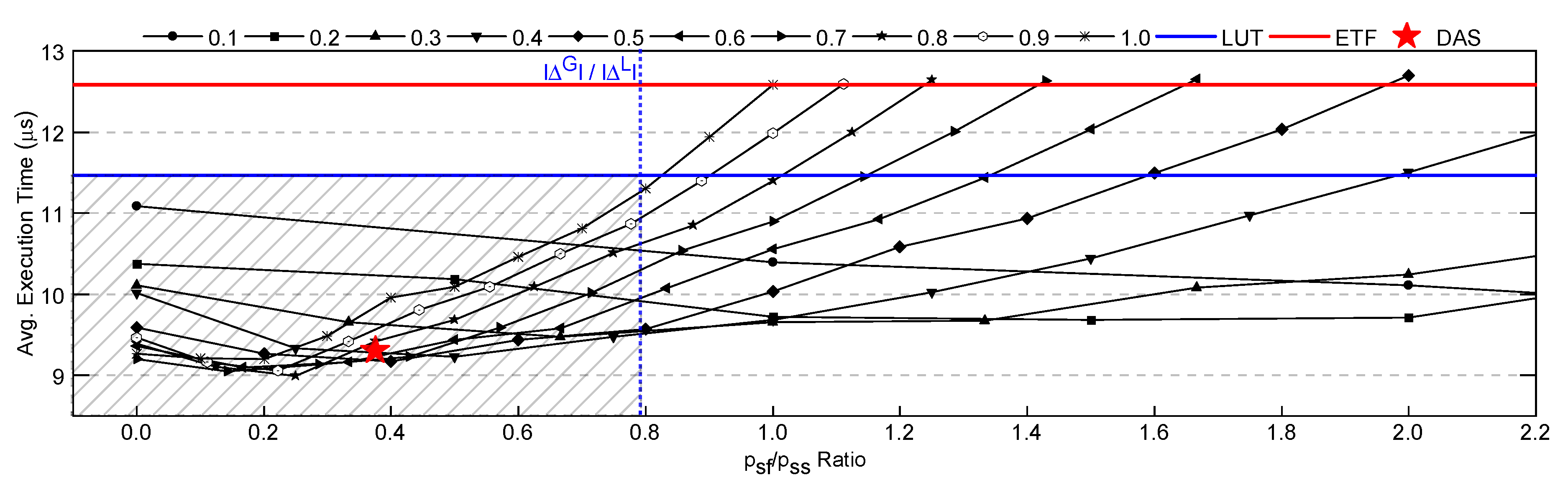
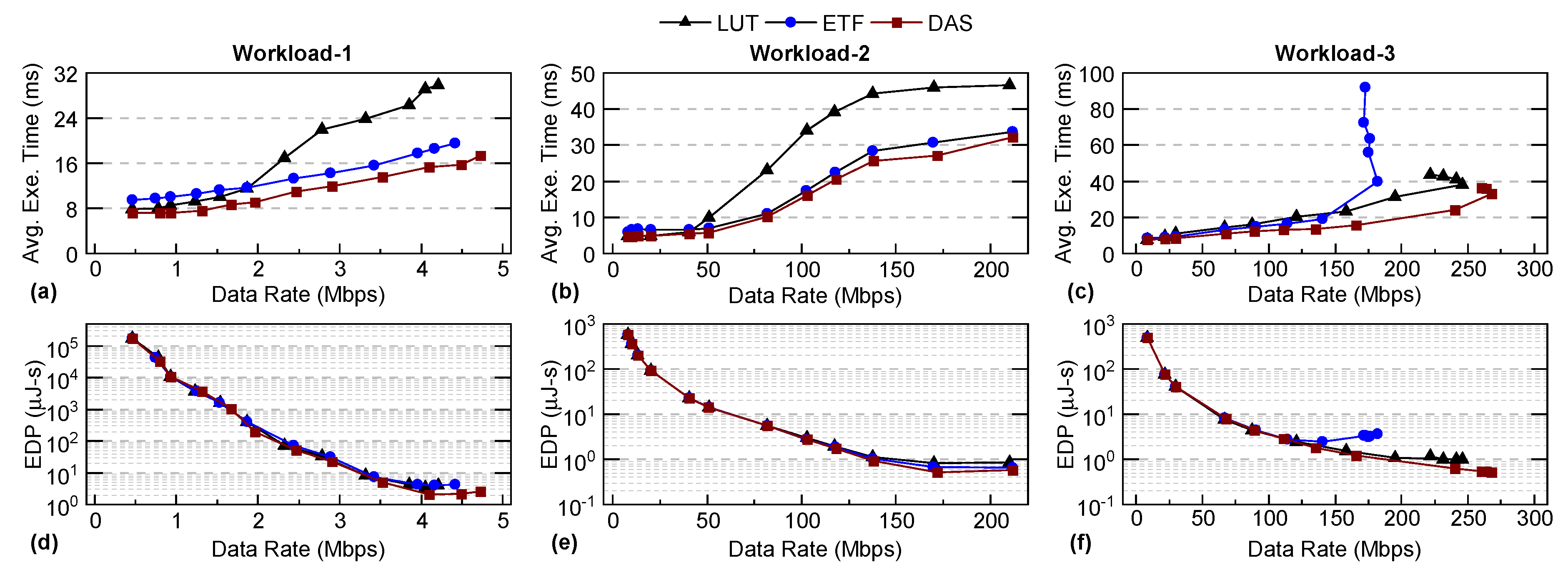
Appendix A.2.2. Validating the DAS Framework Superiority
Appendix B. DSSoC Simulator Workload Mixes
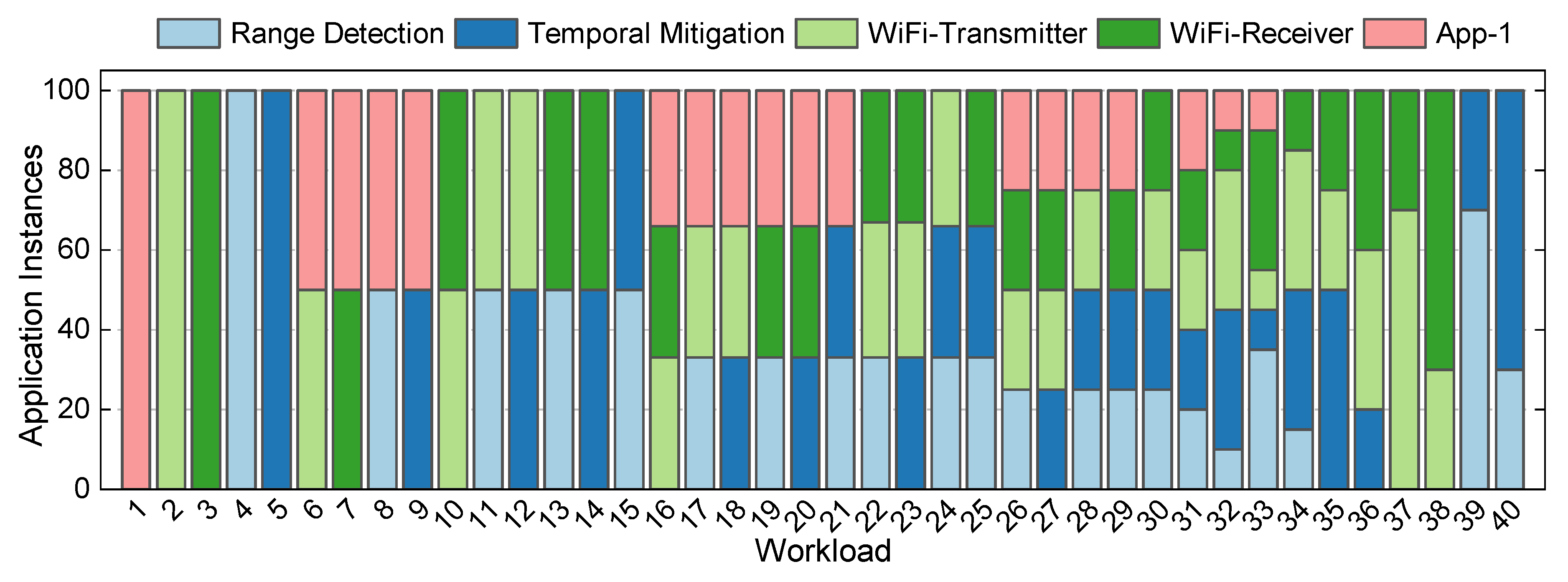
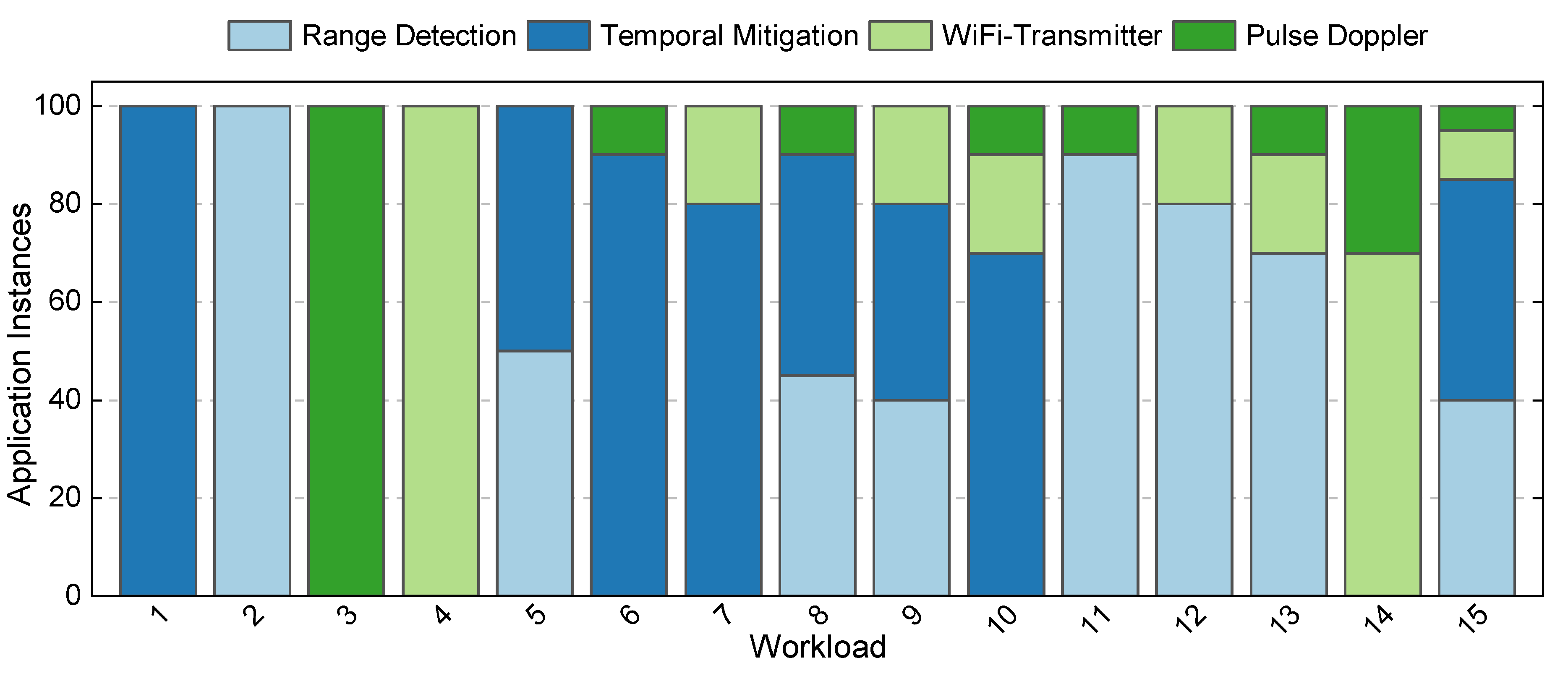
Appendix C. Runtime Framework Workload Mixes
References
- Goksoy, A.A.; Krishnakumar, A.; Hassan, M.S.; Farcas, A.J.; Akoglu, A.; Marculescu, R.; Ogras, U.Y. DAS: Dynamic adaptive scheduling for energy-efficient heterogeneous SoCs. IEEE Embedded Systems Letters 2021, 14, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, J.L.; Patterson, D.A. A New Golden Age for Computer Architecture. Commun. of the ACM 2019, 62, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; et al. Heterogeneous Integration at DARPA: Pathfinding and Progress in Assembly Approaches. ECTC, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- RF Convergence: From the Signals to the Computer by Dr. Tom Rondeau (Microsystems Technology Office, DARPA). https://futurenetworks.ieee.org/images/files/pdf/FirstResponder/Tom-Rondeau-DARPA.pdf. [Online; last accessed 19-March-2023.].
- Moazzemi, K.; Maity, B.; Yi, S.; Rahmani, A.M.; Dutt, N. HESSLE-FREE: Heterogeneous Systems Leveraging Fuzzy Control for Runtime Resource Management. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS) 2019, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, J.; Hassan, S.; Kumbhare, N.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Akoglu, A. CEDR-A Compiler-integrated, Extensible DSSoC Runtime. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS) 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarshack, P.; Paulin, P.G. System-on-chip Beyond the Nanometer Wall. In Proceedings of the Design Automation Conference; 2003; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.K.; et al. In-depth Analysis on Microarchitectures of Modern Heterogeneous CPU-FPGA Platforms. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems 2019, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, A.; Ogras, U.; Marculescu, R.; Kishinevsky, M.; Mudge, T. Domain-Specific Architectures: Research Problems and Promising Approaches. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems 2023, 22, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, A.; et al. Runtime Task Scheduling using Imitation Learning for Heterogeneous Many-core Systems. IEEE Trans. CAD Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 39, 4064–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabla, C.S. Completely Fair Scheduler. Linux Journal 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beisel, T.; Wiersema, T.; Plessl, C.; Brinkmann, A. Cooperative Multitasking for Heterogeneous Accelerators in the Linux Completely Fair Scheduler. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Application-Specific Systems, Architectures and Processors; 2011; pp. 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Arda, S.E.; et al. DS3: A System-Level Domain-Specific System-on-Chip Simulation Framework. IEEE Trans. Computers 2020, 69, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zynq ZCU102 Evaluation Kit. https://www.xilinx.com/products/boards-and-kits/ek-u1-zcu102-g.html, Accessed 10 March 2023.
- Topcuoglu, H.; Hariri, S.; Wu, M.Y. Performance-Effective and Low-Complexity Task Scheduling for Heterogeneous Computing. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distrib. Syst. 2002, 13, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, L.F.; Sakellariou, R.; Madeira, E.R. DAG Scheduling Using a Lookahead Variant of the Heterogeneous Earliest Finish Time Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Euromicro Conf. on Parallel, Distrib. and Network-based Process. 2010; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, M.A.; Pop, F.; Tutueanu, R.I.; Cristea, V.; Kołodziej, J. Resource-Aware Hybrid Scheduling Algorithm in Heterogeneous Distributed Computing. Future Generation Computer Systems 2015, 51, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ha, S. ILP based data parallel multi-task mapping/scheduling technique for MPSoC. In Proceedings of the 2008 International SoC Design Conference; 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- Benini, L.; Bertozzi, D.; Milano, M. Resource Management Policy Handling Multiple Use-Cases in MpSoC Platforms using Constraint Programming. In Proceedings of the Logic Programming: 24th International Conference, ICLP 2008, Udine, Italy, 9-13 December 2008; 2008; pp. 470–484. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, A.B.; Jette, M.A.; Grondona, M. Slurm: Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Job Scheduling Strategies for Parallel Processing; 2003; pp. 44–60. [Google Scholar]
- Thain, D.; Tannenbaum, T.; Livny, M. Distributed computing in practice: the Condor experience. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 2005, 17, 323–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronaki, K.; et al. Task Scheduling Techniques for Asymmetric Multi-core Systems. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distrib. Systems 2016, 28, 2074–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Real-time Task Scheduling and Network Device Security for Complex Embedded Systems based on Deep Learning Networks. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2020, 79, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, A.; Safari, S.; Mohammadi, S. CMV: Clustered Majority Voting Reliability-aware Task Scheduling for Multicore Real-time Systems. IEEE Trans. on Reliability 2018, 68, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zeng, G.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Li, K. Mixed Real-Time Scheduling of Multiple DAGs-based Applications on Heterogeneous Multi-core Processors. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2016, 47, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyong, T.; Li, K.; Zeng, Z.; Veeravalli, B. A Novel Security-Driven Scheduling Algorithm for Precedence-Constrained Tasks in Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. IEEE Transactions on Computers 2010, 60, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, Y.K.; Ahmad, I. Dynamic Critical-Path Scheduling: An Effective Technique for Allocating Task Graphs to Multiprocessors. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 1996, 7, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, R.; Zhao, H. A Hybrid Heuristic for DAG Scheduling on Heterogeneous Systems. In Proceedings of the Int. Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium; 2004; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Jejurikar, R.; Gupta, R. Energy-aware Task Scheduling with Task Synchronization for Embedded Real-time Systems. IEEE Trans. CAD of Integr. Circuits Syst. 2006, 25, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, P.; Navimipour, N.J. An Energy-aware Task Scheduling in the Cloud Computing using a Hybrid Cultural and Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Int. Journal of Cloud Applications and Computing 2017, 7, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskiyar, S.; Abdel-Kader, R. Energy Aware DAG Scheduling on Heterogeneous Systems. Cluster Computing 2010, 13, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, V.; Chakrabarty, K. Real-Time Task Scheduling for Energy-Aware Embedded Systems. Journal of the Franklin Institute 2001, 338, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, A. A Self-tuning Job Scheduler Family with Dynamic Policy Switching. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Job Scheduling Strategies for Parallel Process; 2002; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, M.I.; Kharma, N. A Hybrid Heuristic–genetic Algorithm for Task Scheduling in Heterogeneous Processor Networks. Journal of Parallel and Distrib. Computing 2011, 71, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeres, C.; Lima, A.; Rebello, V.E. Hybrid Task Scheduling: Integrating Static and Dynamic Heuristics. In Proceedings of the Proc. of 15th Symp. on Computer Arch. and High Perform. Computing; 2003; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, M.L. The Chi-square Test of Independence. Biochemia Medica 2013, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.J.; Chow, Y.C.; Anger, F.D.; Lee, C.Y. Scheduling Precedence Graphs in Systems with Interprocessor Communication Times. SIAM Journal on Computing 1989, 18, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZeBu server 4. https://www.synopsys.com/verification/emulation/zebu-server.html. accessed date: Jan. 2, 2020.
- Veloce2 emulator. https://www.mentor.com/products/fv/emulation-systems/veloce. accessed date: Jan. 2, 2020.
- Mack, J.; Kumbhare, N.; NK, A.; Ogras, U.Y.; Akoglu, A. User-Space Emulation Framework for Domain-Specific SoC Design. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Int. Parallel and Distrib. Process. Symp. Workshops; 2020; pp. 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xilinx - Accurate Power Measurement. https://www.xilinx.com/developer/articles/accurate-design-power-measurement.html. accessed date: Feb. 11, 2023.
- Sysfs Interface in Linux. https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/hwmon/sysfs-interface. accessed date: Feb. 11, 2023.
| Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Task | Task ID, Execution time, Power consumption, Depth of task in DFG, Application ID, Predecessor task ID and cluster IDs, Application type |
| Processing Element (PE) |
Earliest time when PE is ready to execute, Earliest availability time of each cluster, PE utilization, Communication cost |
| System | Input data rate |
| Application | Number of Tasks | Supported Clusters |
|---|---|---|
| Range Detection |
7 | big, LITTLE, FFT, SAP |
| Temporal Mitigation |
10 | big, LITTLE, FIR, SAP |
| WiFi-TX | 27 | big, LITTLE, FFT, SAP |
| WiFi-RX | 34 | big, LITTLE, FFT, FEC, FIR, SAP |
| App-1 | 10 | LITTLE, FIR, SAP |
| Processing Cluster | No. of Cores | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| LITTLE | 4 | General-purpose |
| big | 4 | General-purpose |
| FFT | 4 | Acceleration of FFT |
| FEC | 1 | Acceleration of encoding and decoding operations |
| FIR | 4 | Acceleration of FIR |
| SAP | 2 | Multi-function acceleration |
| TOTAL | 19 |
| Classifier | Tree Depth | Number of Features |
Classification Accuracy (%) |
Storage (KB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | - | 2 | 79.23 | 0.01 |
| LR | - | 62 | 83.1 | 0.24 |
| DT | 2 | 1 | 63.66 | 0.01 |
| DT | 2 | 2 | 85.48 | 0.01 |
| DT | 3 | 6 | 85.51 | 0.03 |
| DT | 2 | 62 | 85.9 | 0.01 |
| DT | 16 | 62 | 91.65 | 256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





