Submitted:
07 September 2023
Posted:
11 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
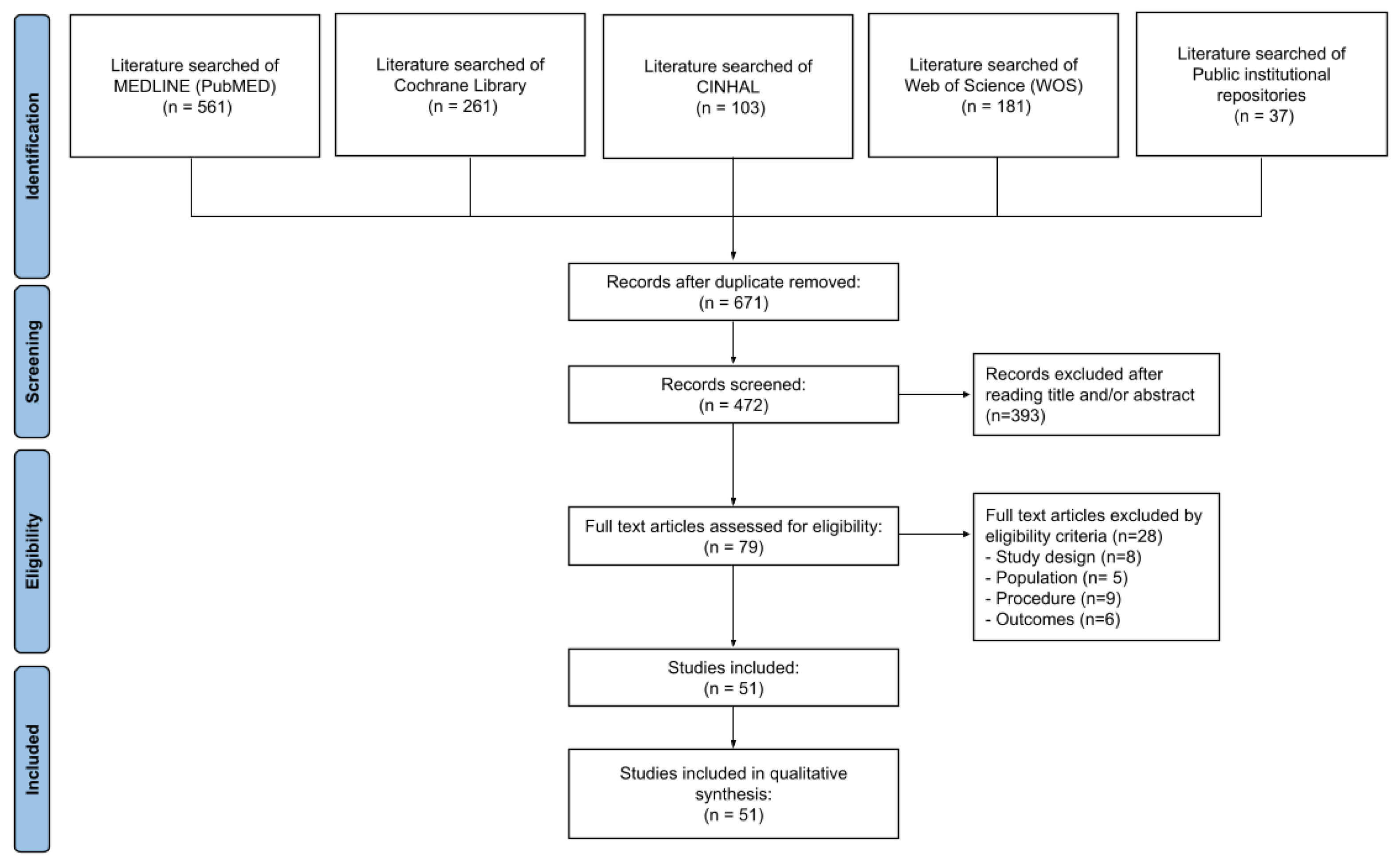
2.2. Search strategy
2.3. Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological quality assessment
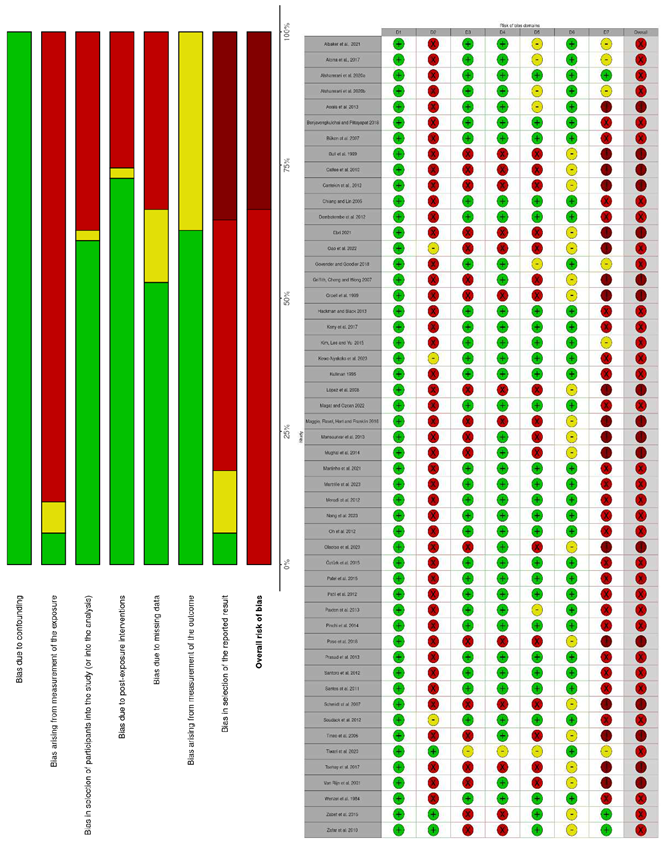
2.5. Risk of bias assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of included studies
3.3. Methodological quality assessment (NOS)
3.4. Risk of bias assessment (ROBINS-E)
3.5. Data synthesis
3.5.1. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among Caucasian ethnicities Children
3.5.1.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.1.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.1.3. Sensitivity and specificity of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.1.4. Precision of radiographic skeletal methods Tanner-Whitehouse 2 and 3 (TW2 and TW3)
3.5.1.5. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal methods Tanner-Whitehouse 2 and 3 (TW2 and TW3)
3.5.1.6. Sensitivity and specificity of radiographic skeletal methods Tanner-Whitehouse 2 and 3 (TW2 and TW3)
3.5.1.7. Precision of radiographic dental method of Demirjian
3.5.1.8. Accuracy of radiographic dental method of Kullman
3.5.2. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among Asian ethnicities Children
3.5.2.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.2.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.2.3. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3)
3.5.2.4. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3)
3.5.2.5. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Korean Standard Chart (KS)
3.5.2.6. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Korean Standard Chart (KS)
3.5.2.7. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal methods RUS-CHN (China 05)
3.5.3. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among Indian ethnicities Children
3.5.3.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.3.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.3.3. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3)
3.5.3.4. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Fishman
3.5.3.5. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method McKay’s Method (MK)
3.5.3.6. Precision of radiographic dental method of Demirjian
3.5.3.7. Precision of radiographic dental method of Willem
3.5.3.8. Precision of other of radiographic methods
3.5.4. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among Arab ethnicities Children
3.5.4.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.4.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.4.3. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3)
3.5.4.4. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3)
3.5.4.5. Precision of other of radiographic methods
3.5.4.6. Precision of radiographic dental method of Demirjian
3.5.5. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among Hispanic ethnicities Children
3.5.5.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.5.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.5.3. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3
3.5.5.4. Precision of radiographic dental method of Demirjian
3.5.6. Precision and Accuracy of Skeletal Method for BA Assessment Among African ethnicities Children
3.5.6.1. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.6.2. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Greulich and Pyle Atlas (GPA)
3.5.6.3. Precision of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3
3.5.6.4. Accuracy of radiographic skeletal method Tanner-Whitehouse 3
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin DD, Calder AD, Ranke MB, Binder G, Thodberg HH. Accuracy and self-validation of automated bone age determination. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Mughal AM, Hassan N, Ahmed A. Bone age assessment methods: A critical review. Pak J Med Sci 2014, 30. [CrossRef]
- Płudowski P, Lebiedowski M, Lorenc RS. Evaluation of practical use of bone age assessments based on DXA-derived hand scans in diagnosis of skeletal status in healthy and diseased children. Journal of Clinical Densitometry 2005, 8. [CrossRef]
- Makkad R, Balani A, Chaturvedi S, Tanwani T, Agrawal A, Hamdani S. Reliability of panoramic radiography in chronological age estimation. J Forensic Dent Sci. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee BD, Lee MS. Automated Bone Age Assessment Using Artificial Intelligence: The Future of Bone Age Assessment. Korean J Radiol. 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Chaumoitre K, Saliba-Serre B, Adalian P, Signoli M, Leonetti G, Panuel M. Forensic use of the Greulich and Pyle atlas: prediction intervals and relevance. Eur Radiol. 2017, 27. [CrossRef]
- Prokop-Piotrkowska M, Marszałek-Dziuba K, Moszczyńska E, Szalecki M, Jurkiewicz E. Traditional and new methods of bone age assessment-an overview. JCRPE Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology. 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Vignolo M, Milani S, Cerbello G, Coroli P, Di Battista E, Aicardi G. FELS, Greulich-Pyle, and Tanner-Whitehouse bone age assessments in a group of Italian children and adolescents. American Journal of Human Biology. 1992, 4. [CrossRef]
- Nahhas RW, Sherwood RJ, Chumlea WC, Duren DL. An update of the statistical methods underlying the FELS method of skeletal maturity assessment. Ann Hum Biol. 2013, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumela WC, Roche AF, Thissen D. The FELS method of assessing the skeletal maturity of the hand-wrist. American Journal of Human Biology. 1989, 1. [CrossRef]
- Alshamrani K, Messina F, Offiah AC. Is the Greulich and Pyle atlas applicable to all ethnicities? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2019, 29. [CrossRef]
- Mansourvar M, Ismail MA, Raj RG, et al. The applicability of Greulich and Pyle atlas to assess skeletal age for four ethnic groups. J Forensic Leg Med. 2014, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao F, Huang HK, Pietka E, Gilsanz V. Digital hand atlas and web-based bone age assessment: System design and implementation. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. 2000, 24. [CrossRef]
- Grave KC, Brown T. Skeletal ossification and the adolescent growth spurt. Skeletal ossification and the adolescent growth spurt. Am J Orthod. 1976, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizawa K, Asami T, Anzo M, et al. Standard RUS skeletal maturation of Tokyo children. Ann Hum Biol. 1996, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed RB, Krishnamraju P V., Prasanth PS, Sanghvi P, Reddy MAL, Jyotsna S. Dental age estimation using Willems method: A digital orthopantomographic study. Contemp Clin Dent. 2014, 5. [CrossRef]
- Garamendi PM, Landa MI, Ballesteros J, Solano MA. Reliability of the methods applied to assess age minority in living subjects around 18 years old: A survey on a Moroccan origin population. Forensic Sci Int. 2005, 154. [CrossRef]
- Mughal AM, Hassan N, Ahmed A. The applicability of the Greulich & Pyle Atlas for bone age assessment in primary school-going children of Karachi, Pakistan. Pak J Med Sci. 2014, 30. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Zhou B, Gong P, et al. Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Bone Age Assessment to Improve the Accuracy and Consistency of Physicians With Different Levels of Experience. Front Pediatr. 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology: A Proposal for Reporting - Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) Group B. JAMA Neurol 2000, 283.
- Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. (Available from: URL: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp) Published online. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Bero L, Chartres N, Diong J, et al. The risk of bias in observational studies of exposures (ROBINS-E) tool: Concerns arising from application to observational studies of exposures. Syst Rev. 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Keny SM, Sonawane D V., Pawar E, et al. Comparison of two radiological methods in the determination of skeletal maturity in the Indian pediatric population. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics Part B. 2018, 27. [CrossRef]
- 24. Patel P, Chaudhary A, Dudhia B, Bhatia P, Jani Y, Soni N. Accuracy of two dental and one skeletal age estimation methods in 6-16 year old Gujarati children. J Forensic Dent Sci. 2015, 7. [CrossRef]
- Patil ST, Parchand MP, Meshram MM, Kamdi NY. Applicability of Greulich and Pyle skeletal age standards to Indian children. Forensic Sci Int. 2012, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Prasad CMS, Reddy VN, Sreedevi G, Ponnada SR, Padma Priya K, Raveendra Naik B. Objective evaluation of cervical vertebral bone age-its reliability in comparison with hand-wrist bone age: By TW3 method. Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice. 2013, 14. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari PK, Gupta M, Verma A, Pandey S, Nayak A. Applicability of the Greulich–Pyle Method in Assessing the Skeletal Maturity of Children in the Eastern Utter Pradesh (UP) Region: A Pilot Study. Cureus Published online. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Büken B, Şafak AA, Yazici B, Büken E, Mayda AS. Is the assessment of bone age by the Greulich-Pyle method reliable at forensic age estimation for Turkish children? Forensic Sci Int. 2007, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantekin K, Celikoglu M, Miloglu O, Dane A, Erdem A. Bone Age Assessment: The Applicability of the Greulich-Pyle Method in Eastern Turkish Children. J Forensic Sci. 2012, 57. [CrossRef]
- Magat G, Ozcan S. Assessment of maturation stages and the accuracy of age estimation methods in a Turkish population: A comparative study. Imaging Sci Dent. 2022, 52. [CrossRef]
- Öztürk F, Karataş OH, Mutaf HI, Babacan H. Bone age assessment: comparison of children from two different regions with the Greulich–Pyle method In Turkey. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences. 2016, 48. [CrossRef]
- Awais M, Nadeem N, Husen Y, Rehman A, Beg M, Khattak YJ. Comparison between greulich-pyle and girdany-golden methods for estimating skeletal age of children in Pakistan. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan. 2014, 24.
- Zafar AM, Nadeem N, Husen Y, Ahmad MN. An appraisal of greulich-pyle atlas for skeletal age assessment in Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc. 2010, 60.
- Albaker AB, Aldhilan AS, Alrabai HM, et al. Determination of Bone Age and its Correlation to the Chronological Age Based on the Greulich and Pyle Method in Saudi Arabia. J Pharm Res Int. Published online 2021. [CrossRef]
- Alshamrani K, Hewitt A, Offiah AC. Applicability of two bone age assessment methods to children from Saudi Arabia. Clin Radiol. 2020, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao C, Qian Q, Li Y, et al. A comparative study of three bone age assessment methods on Chinese preschool-aged children. Front Pediatr. 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Griffith JF, Cheng JCY, Wong E. Are western skeletal age standards applicable to the Hong Kong Chinese population? A comparison of the Greulich and Pyle method and the tanner and whitehouse method. Hong Kong Medical Journal. 2007, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kim JR, Lee YS, Yu J. Assessment of bone age in prepubertal healthy korean children: Comparison among the korean standard bone age chart, greulich-pyle method, and tanner-whitehouse method. Korean J Radiol. 2015, 16. [CrossRef]
- Oh Y, Lee R, Kim HS. Evaluation of skeletal maturity score for Korean children and the standard for comparison of bone age and chronological age in normal children. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang KH, Chou AS Bin, Yen PS, et al. The reliability of using Greulich-Pyle method to determine children’s bone age in Taiwan. Tzu Chi Med J. 2005, 17.
- Moradi M, Sirous M, Morovatti P. The reliability of skeletal age determination in an Iranian sample using Greulich and Pyle method. Forensic Sci Int. 2012, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudack M, Ben-Shlush A, Jacobson J, Raviv-Zilka L, Eshed I, Hamiel O. Bone age in the 21st century: UIs Greulich and Pyle’s atlas accurate for Israeli children? Pediatr Radiol. 2012, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamrani K, Offiah AC. Applicability of two commonly used bone age assessment methods to twenty-first century UK children. Eur Radiol. 2020, 30. [CrossRef]
- Bull RK, Edwards PD, Kemp PM, Fry S, Hughes IA. Bone age assessment: A large scale comparison of the Greulich and Pyle, and Tanner and Whitehouse (TW2) methods. Arch Dis Child. 1999, 81. [CrossRef]
- Hackman L, Black S. The reliability of the greulich and pyle atlas when applied to a modern scottish population. J Forensic Sci. 2013, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcina M, Lucea A, Salicrú M, Turbón D. Reliability of the Greulich and Pyle method for chronological age estimation and age majority prediction in a Spanish sample. Int J Legal Med. 2018, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrí, B. Comparative study between bone ages: Carpal, Metacarpophalangic, Carpometacarpophalangic Ebrí, Greulich and Pyle and Tanner Whitehouse2. Med Res Arch. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho D, V. , Coelho-e-Silva MJ, Valente-dos-Santos J, et al. Assessment of skeletal age in youth female soccer players: Agreement between Greulich-Pyle and Fels protocols. American Journal of Human Biology. 2022, 34. [CrossRef]
- Santos C, Ferreira M, Alves FC, Cunha E. Comparative study of Greulich and Pyle Atlas and Maturos 4.0 program for age estimation in a Portuguese sample. Forensic Sci Int. 2011, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchi V, De Luca F, Ricciardi F, et al. Skeletal age estimation for forensic purposes: A comparison of GP, TW2 and TW3 methods on an Italian sample. Forensic Sci Int. 2014, 238. [CrossRef]
- Santoro V, Roca R, De Donno A, et al. Applicability of Greulich and Pyle and Demirijan aging methods to a sample of Italian population. Forensic Sci Int. 2012, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martrille L, Papadodima S, Venegoni C, et al. Age Estimation in 0–8-Year-Old Children in France: Comparison of One Skeletal and Five Dental Methods. Diagnostics. 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Zabet D, Rérolle C, Pucheux J, Telmon N, Saint-Martin P. Can the Greulich and Pyle method be used on French contemporary individuals? Int J Legal Med. 2015, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groell R, Lindbichler F, Riepl T, Gherra L, Roposch A, Fotter R. The reliability of bone age determination in central European children using the Greulich and Pyle method. British Journal of Radiology. 1999, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt S, Koch B, Schulz R, Reisinger W, Schmeling A. Comparative analysis of the applicability of the skeletal age determination methods of Greulich-Pyle and Thiemann-Nitz for forensic age estimation in living subjects. Int J Legal Med. 2007, 121. [CrossRef]
- van Rijn RR, Lequin MH, Robben SGF, Hop WCJ, van Kuijk C. Is the Greulich and Pyle atlas still valid for Dutch Caucasian children today? Pediatr Radiol. 2001, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullman, L. Accuracy of two dental and one skeletal age estimation method in Swedish adolescents. Forensic Sci Int. 1995, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel A, Droschl H, Melsen B. Skeletal maturity in austrian children assessed by the GP and the TW-2 methods. Ann Hum Biol. 1984, 11. [CrossRef]
- Dembetembe KA, Morris AG. Is Greulich-Pyle age estimation applicable for determining maturation in male Africans? S Afr J Sci. 2012, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender D, Goodier M. Bone of contention: The applicability of the Greulich- Pyle method for skeletal age assessment in South Africa. South African Journal of Radiology. 2018, 22. [CrossRef]
- Kowo-Nyakoko F, Gregson CL, Madanhire T, et al. Evaluation of two methods of bone age assessment in peripubertal children in Zimbabwe. Bone 2023, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaotse B, Norma PG, Kaone PM, et al. Evaluation of the suitability of the Greulich and Pyle atlas in estimating age for the Botswana population using hand and wrist radiographs of young Botswana population. Forensic Science International: Reports. 2023, 7. [CrossRef]
- Tsehay B, Afework M, Mesifin M. Assessment of Reliability of Greulich and Pyle (GP) Method for Determination of Age of Children at Debre Markos Referral Hospital, East Gojjam Zone. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2017, 27. [CrossRef]
- Maggio A, Flavel A, Hart R, Franklin D. Assessment of the accuracy of the Greulich and Pyle hand-wrist atlas for age estimation in a contemporary Australian population. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences. 2018, 50. [CrossRef]
- Paxton ML, Lamont AC, Stillwell AP. The reliability of the Greulich-Pyle method in bone age determination among Australian children. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013, 57. [CrossRef]
- Nang KM, Ismail AJ, Tangaperumal A, et al. Forensic age estimation in living children: how accurate is the Greulich-Pyle method in Sabah, East Malaysia? Front Pediatr. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjavongkulchai S, Pittayapat P. Age estimation methods using hand and wrist radiographs in a group of contemporary Thais. Forensic Sci Int. 2018, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee RP, Sutter M, Steffen JA, Goldfarb CA. Skeletal and chronological ages in American adolescents: Current findings in skeletal maturation. J Child Orthop. 2010, 4. [CrossRef]
- Tineo F, Espina de Fereira A, Barrios F, Ortega A, Fereira J. Estimación de la edad cronológica con fines forenses, empleando la edad dental y la edad ósea en niños escolares en maracaibo, estado zulia. Acta Odontol Venez. 2006, 44.
- López P, Morón A, Urdaneta O. Maduración ósea de niños escolares (7-14 años) de las etnias Wayúu y Criolla del Municipio Maracaibo, Estado Zulia. Estudio Comparativo. Ciencia Odontológica. 2020, 5, 99–111. Available online: https://produccioncientificaluz.org/index.php/cienciao/article/view/33940 (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Pose Lepe G, Villacrés F, Fuente-Alba CS, Guiloff S. Correlation in radiological bone age determination using the Greulich and Pyle method versus automated evaluation using BoneXpert software. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, JF. Musculoskeletal complications of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2011, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis V, Di Maio S, Soliman A, Raiola G, Elalaily R, Millimaggi G. Hand X-ray in pediatric endocrinology: Skeletal age assessment and beyond. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014, 18. [CrossRef]
- Grave, K. The use of the hand and wrist radiograph in skeletal age assessment; and why skeletal age assessment is important. Aust Orthod J. 1994, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wingerd J, Peritz E, Sproul A. Race and stature differences in the skeletal maturation of the hand and wrist. Ann Hum Biol. 1974, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder RT, Estle DT, Morrison K, et al. Applicability of the Greulich and Pyle Skeletal Age Standards to Black and White Children of Today. American Journal of Diseases of Children. 1993, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontell FK, Ivanovic M, Ablin DS, Barlow TW. Bone age in children of diverse ethnicity. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1996, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Search Data | Database | Search equation |
|---|---|---|
| 10/01/2023 | MEDLINE (PubMED) |
“Reproducibility of results” [Mesh] OR “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic imaging” [Mesh] OR “Radiography” [Mesh] OR “Age Determination by Skeleton” [Mesh] OR “Bone matrix” [Mesh] OR “Carpal bones” [Mesh] OR “Radius” [Mesh] OR “Wrist” [Mesh] OR “Racial Groups” [Mesh] OR “Race factors” [Mesh] OR “White people” [Mesh] OR “Black people” [Mesh] OR “Hispanic or Latino” [Mesh] OR “Asian people” [Mesh] OR “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”[Mesh] OR “American Indian or Alaska Native”[Mesh] OR “Pacific Island People”[Mesh] OR “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander”[Mesh] OR “Bone Maturity” [tw] “Skeletal Maturation” [tw] OR “Skeletal Age” [tw] OR “Age Measurement” [tw] OR radiograp*[tw] OR radiol *[tw] |
| 10/01/2023 | MEDLINE (PubMED) |
“Reproducibility of results” [Mesh] OR “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic imaging” [Mesh] OR “Radiography” [Mesh] OR “Radiography, panoramic” [Mesh] OR “Age Determination by Teeth” [Mesh] OR “Dentition” [Mesh] OR “Teeth” [Mesh] OR “Tooth” [Mesh] OR “Molar, Third” [Mesh] OR “Incisor” [Mesh] OR “Racial Groups” [Mesh] OR “Race factors” [Mesh] OR “White people” [Mesh] OR “Black people” [Mesh] OR “Hispanic or Latino” [Mesh] OR “Asian people” [Mesh] “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”[Mesh] OR “American Indian or Alaska Native”[Mesh] OR “Pacific Island People”[Mesh] OR “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander”[Mesh] OR “bone age measurement” [tw] OR “Orthopantomography” [tw] OR “Bone Maturity” [tw] “Skeletal Maturation” [tw] OR “Skeletal Age” [tw] OR “Age Measurement” [tw] OR radiograp*[tw] OR radiol *[tw] |
| 12/01/2023 | Cochrane Library | ([mh “Reproducibility of results” ] OR [mh “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy] OR [mh “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures”] OR [mh “Diagnostic imaging”] OR [mh “Radiography”] OR [mh “Age Determination by Skeleton”] OR [mh “Bone matrix”] OR [mh “Carpal bone”] OR [mh “Radius”] OR [mh “Wrist”] OR [mh “Racial Groups”] OR [mh “Race factors”] OR [mh “White people”] OR [mh “Black people”] OR [mh “Hispanic or Latino”] OR [mh “Asian people”] OR [mh “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”] OR [mh “American Indian or Alaska Native”] OR [mh “Pacific Island People”] OR [mh “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”] OR Bone Matur*:ti,ab,kw OR Skeletal Age:ti,ab,kw OR Age Measurement:ti,ab,kw) |
| 12/01/2023 | Cochrane Library | ([mh “Reproducibility of results” ] OR [mh “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy] OR [mh “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures”] OR [mh “Diagnostic imaging”] OR [mh “Radiography, panoramic”] OR [mh “Age Determination by Skeleton”] OR [mh “Dentition”] OR [mh “Teeth”] OR [mh “Tooth”] OR [mh “Molar, third”] OR [mh “Incisor”] OR [mh “Racial Groups”] OR [mh “Race factors”] OR [mh “White people”] OR [mh “Black people”] OR [mh “Hispanic or Latino”] OR [mh “Asian people”] OR [mh “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”] OR [mh “American Indian or Alaska Native”]OR [mh “Pacific Island People”] OR [mh “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander”] OR Orthopantomography:ti,ab,kw OR Bone Matur*:ti,ab,kw OR Skeletal Age:ti,ab,kw OR Age Measurement:ti,ab,kw) |
| 14/01/2023 | CINAHL | (MH “Reproducibility of results” OR MH “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy OR MH “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” OR MH “Diagnostic imaging” OR MH “Radiography” OR MH “Age Determination by Skeleton” OR MH “Bone matrix” OR MH “Carpal bones” OR MH “Radius” OR MH “Wrist” OR MH “Racial Groups” OR MH “Race factors” OR MH “White people” OR MH “Black people” OR MH “Hispanic or Latino” OR MH “Asian people” OR MH “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander” OR MH “American Indian or Alaska Native” OR MH “Pacific Island People” OR MH “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander” OR bone matur* OR Skeletal Matur* OR Skeletal Age OR Age Measurement) |
| 14/01/2023 | CINAHL | (MH “Reproducibility of results” OR MH “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy OR MH “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” OR MH “Diagnostic imaging” OR MH “Radiography, panoramic” OR MH “Age Determination by Skeleton” OR MH “Dentition” OR MH “Teeth” OR MH “Tooth” OR MH “Molar, Third” OR MH “Incisor” OR MH “Racial Groups” OR MH “Race factors” OR MH “White people” OR MH “Black people” OR MH “Hispanic or Latino” OR MH “Asian people” OR MH “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander” OR MH “American Indian or Alaska Native” OR MH “Pacific Island People” OR MH “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander” OR “Orthopantomography” OR bone matur* OR Skeletal Matur* OR Skeletal Age OR Age Measurement) |
| 20/01/2023 | Web of Science (WOS) | “Reproducibility of results” [Mesh] OR “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic imaging” [Mesh] OR “Radiography” [Mesh] OR “Age Determination by Skeleton” [Mesh] OR “Bone matrix” [Mesh] OR “Carpal bones” [Mesh] OR “Radius” [Mesh] OR “Wrist” [Mesh] OR “Racial Groups” [Mesh] OR “Race factors” [Mesh] OR “White people” [Mesh] OR “Black people” [Mesh] OR “Hispanic or Latino” [Mesh] OR “Asian people” [Mesh] OR “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander” [Mesh] OR “American Indian or Alaska Native” [Mesh] OR “Pacific Island People” [Mesh] OR “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander” [Mesh] OR Bone Maturity [tw] OR Skeletal Maturation [tw] OR Skeletal Age [tw] OR Age Measurement [tw] |
| 28/01/2023 | Web of Science (WOS) | “Reproducibility of results” [Mesh] OR “Dimensional Measurements Accuracy” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures” [Mesh] OR “Diagnostic imaging” [Mesh] OR “Radiography, panoramic” [Mesh] OR “Age Determination by Skeleton” [Mesh] OR “Dentition” [Mesh] OR “Teeth” [Mesh] OR “Tooth” [Mesh] OR “Molar, Third” [Mesh] OR “Incisor” [Mesh]OR “Racial Groups” [Mesh] OR “Race factors” [Mesh] OR “White people” [Mesh] OR “Black people” [Mesh] OR “Hispanic or Latino” [Mesh] OR “Asian people” [Mesh] OR “Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander” [Mesh] OR “American Indian or Alaska Native” [Mesh] OR “Pacific Island People” [Mesh] OR “Asian American Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander” [Mesh] OR Bone Maturity [tw] OR Skeletal Maturation [tw] OR Skeletal Age [tw] OR Age Measurement [tw] |
| Authors (yrs.) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albaker et al. (2021) (34) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | 7 | ||
| Alcina et al. (2017) (46) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Alshamrani et al. (2020) (43) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Alshamrani et al. (2020) (35) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Awais et al. (2014) (32) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Benjavongkulchai and Pittayapat (2018) (67) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Büken et al. (2007) (28) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | 7 | ||
| Bull et al. (1999) (44) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Calfee et al. (2010) (68) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Cantekin et al. (2012) (29) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Chiang and Lin (2005) (40) | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | |||
| Dembetembe et al. (2012) (59) | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | |||
| Ebri (2021) (47) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Gao et al. (2022) (36) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Govender and Goodier (2018) (60) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Griffith, Cheng and Wong (2007) (37) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Groell et al. (1999) (54) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Hackman and Black (2013) (45) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Keny et al. (2017) (23) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Kim, Lee and Yu (2015) (38) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Kowo-Nyakoko et al. (2023) (61) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 8 | |
| Kullman (1995) (57) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| López et al. (2008) (70) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | 7 | ||
| Magat and Ozcan (2022) (30) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Maggio, Flavel, Hart and Franklin (2016) (64) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Mansourvar et al. (2014) (12) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Martinho et al. (2021) (48) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | 7 | ||
| Martrille et al. (2023) (52) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 8 | |
| Moradi et al. (2012) (41) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Mughal et al. (2014) (18) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Nang et al. (2023) (66) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 8 | |
| Oh et al. (2012) (39) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Olaotse et al. (2023) (62) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Öztürk et al. (2015) (31) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Patel et al. (2015) (24) | * | * | * | * | ** | * | 7 | ||
| Patil et al. (2012) (25) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Paxton et al. (2013) (65) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Pinchi et al. (2014) (50) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Pose et al. (2018) (71) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Prasad et al. (2013) (26) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Santoro et al. (2012) (51) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Santos et al. (2011) (49) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Schmidt et al. (2007) (42,55) | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 7 | ||
| Soudack et al. (2012) 55 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 |
| Tineo et al. (2006) (69) | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Tiwari et al. (2020) (27) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Tsehay et al. (2017) (63) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Van Rijn et al. (2001) (56) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Wenzel et al. (1984) (58) | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Zabet et al. (2015) (53) | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Zafar et al. (2010) (33) | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




