1. Introduction
The Covid-19 pandemic that emerged in the year 2019 has impacted current people’s health status, the economy, and the growth of the built environment in general. The disease has been identified as the worst pandemic experienced by people for decades; thus addressing the impacts from built environment viewpoints will be important for the urban regeneration drives. Consequently, researchers are attempting to find the most constructive and productive means of managing the epidemic and limiting its negative impacts across the globe [
1,
2,
3]. Therefore, the relationship between human interaction, built environments, and Covid-19 infectious disease are paramount given the ongoing debate [
2,
4,
77].
The built environment, according to [
2,
4] refers to the human-made physical surroundings in which people live, work, and interact. It encompasses all the structures, spaces, and systems that have been created by humans, such as buildings, roads, parks, transportation networks, utilities, and other infrastructure elements. The built environment is a result of human planning, design, construction, and development activities, and it plays a significant role in shaping the quality of life, social interactions, and overall well-being of individuals and communities. In view of the Covid-19 pandemic, resilience which is an important tool for evaluating urban ecosystems’ capacity to adjust to shifting circumstances and meet social standards of environmental targets is important. The notion of resilience has garnered attention across diverse fields since the early 1900s, yet its exploration within the built environment remains limited [
5,
77]. Within the context of this research, resilience in the built environment is construed in terms of the capacity of a neighborhood, to recover from various stresses, and pressures to simultaneously foster constructive adaptation and evolution toward sustainability. The theoretical idea of built-environmental resilience has grown in popularity in recent years, owing to the growing frequency and severity of global disasters [
6,
77,
82]. This has resulted in the necessity for a more thorough and holistic method for comprehending the numerous aspects that contribute to built-environmental resilience [
7,
8].
A handful of research has documented the significance of resilience in the built environment, as well as the relevance of human social capital in recovering from catastrophes, after the Covid-19 pandemic [
9,
10,
39]. Studies have iterated built-environmental resilience as the capacity of communities and structures to endure, recover, and adapt to numerous hazards such as natural catastrophes, climate change, and social-economic disturbances, and Covid-19 [
12,
53,
80]. Other urban hazards that call for resilience include, the increasing urban population, which has adversely affected both the environment and the residents [
11,
12,
77]. The recent global Covid-19 pandemic has been the major contributor challenge [
13,
14].
Human social capital encompasses the assets and values that emerge from interactions between the people and interactions with the built environment. Meanwhile, human social capital’s function of enabling resilience building has attracted a great deal of interest in recent years [
7,
15,
20]. Resilience, in particular, is crucial for a successful community response to the problems posed by Covid-19. The significance of the interactions between Covid-19 cum the built environment cannot be overemphasized. The fact remains that the Covid-19 epidemic has broadened the human horizon by altering people’s behavior and use of the built environment [
16,
17]. To foster the potential adaptive construction of cities, the linkage between both the built environment and the Covid-19 epidemic must be given appropriate attention.
Despite increased awareness of the relevance of social capital for resilience, little is known about how it may be quantified and integrated into the built environment. This research tries to fill the vacuum by providing a comprehensive assessment of existing comprehension of the inter-relationships among the social capital as well as the urban landscape’s resilience. In Nigeria’s context, little research has been done in the context of focusing on diverse interactions between the physical environment and human social capital for Covid-19 post-recovery [
18,
19]. As a result, this study creates a framework for documenting a resilient built environment in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic using human social capital.
The purpose of the research is to examine the impact of the resilient built environment in response to the Covid-19 pandemic, with a specific focus on the South-west Geopolitical zone of Nigeria. The objectives include the following:
- (i)
To assess the impact of the built environment capital on human social capital considering the Covid-19 pandemic.
- (ii)
To evaluate the relationship between disaster management indices and human social capital within the framework of the resilient built environment.
- (iii)
To explore the degree of understanding of the Covid-19 pandemic and its connection to human social capital and the built environment.
- (iv)
To investigate the effectiveness of built environment adaptive strategies in mitigating the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on human social capital.
- (v)
To analyze the indirect effects of built environment capitals, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness on Covid-19 pandemic indices through their influence on human social capital.
This investigation is aimed at enhancing existing knowledge by presenting a methodology that considers the pandemic’s indirect effects on built environment capital, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness via the human social capital. Thus, a framework is proposed in the research by examining the impact of the resilient built environment in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. In view of this, human social capital is a problem-solving technique that has recently become available [
7,
20,
31]. The results of the investigation have significant implications for the future built-environment development in Nigeria and can help with post-Covid 19 recovery efforts. The study advances the body of knowledge on the significance of human social capital in resilience building and provides policymakers and practitioners in Nigeria and beyond with practical insights.
This article has been structured into the following:
Section 2 comprises a review of crucial literature concerning Post-Covid-19 Recovery, Resilience, Human Social Capital, and the Built Environment. In
Section 3, we outline the research framework and formulate hypotheses, while
Section 4 details the gathering of data and analysis methods used in the research.
Section 5 offers the presentation and discussion of findings, conclusions, research implications, and reflections for potential future research endeavors.
2. Literature Review and Background
2.1. Post Covid-19 Recovery
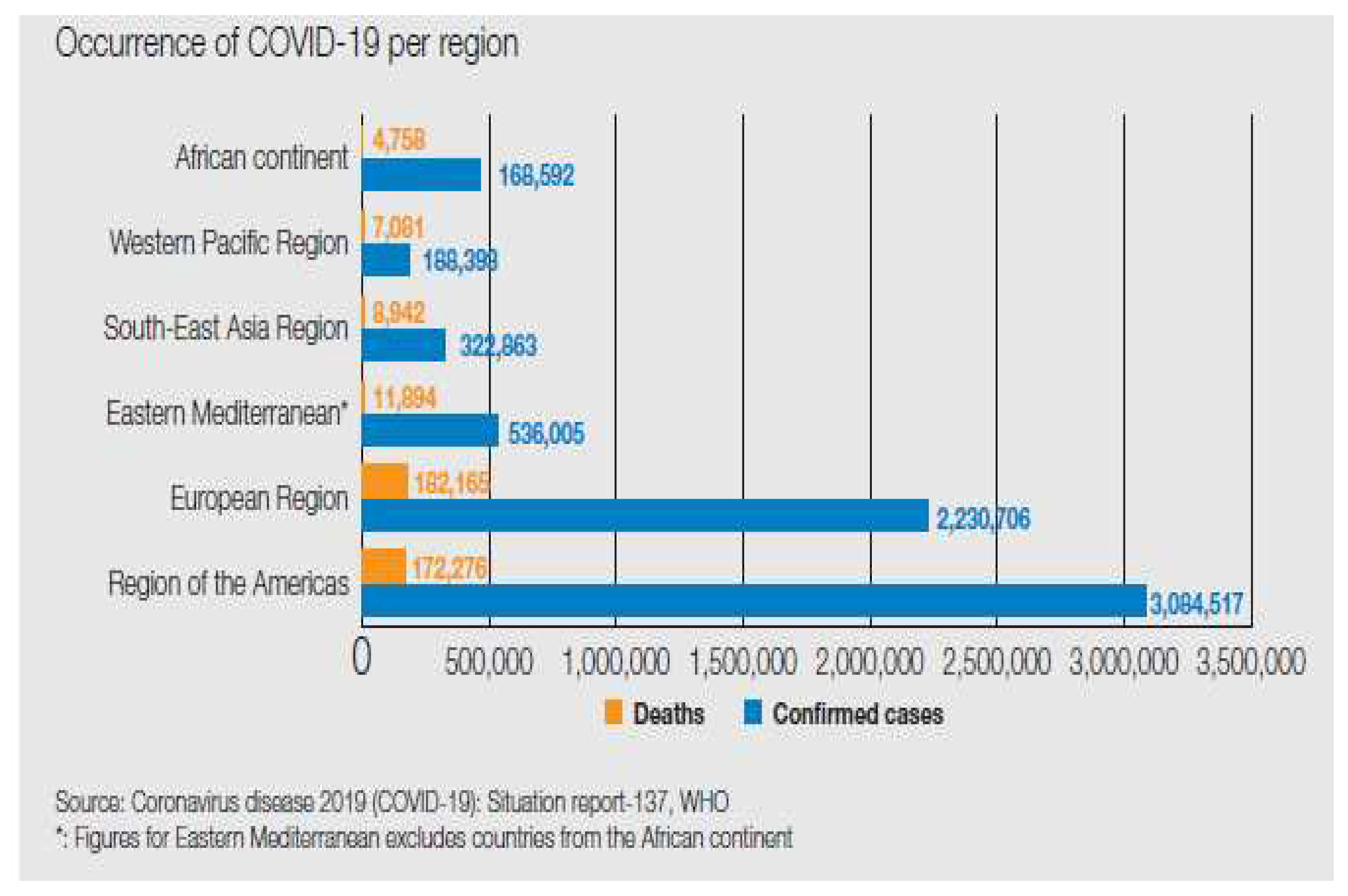
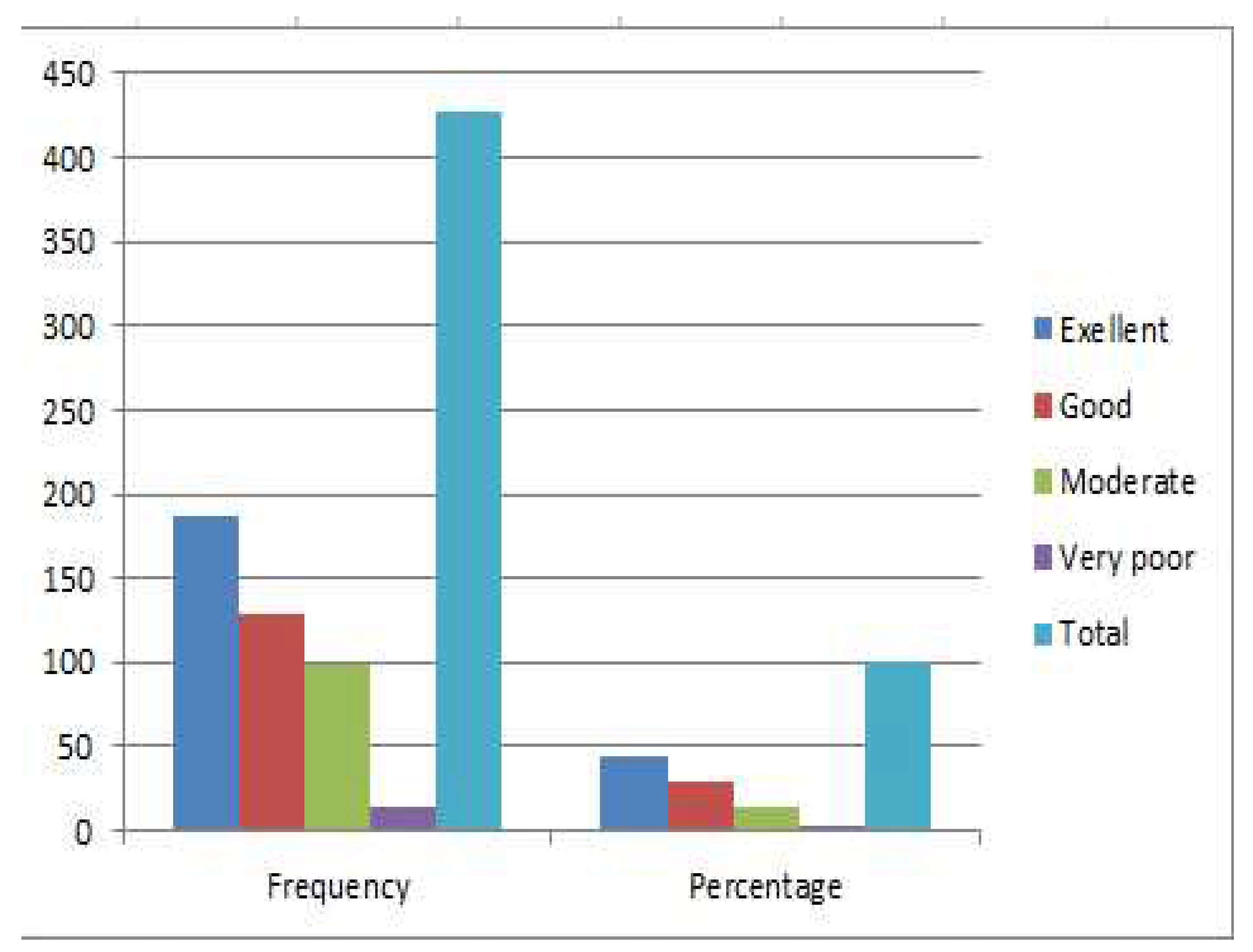
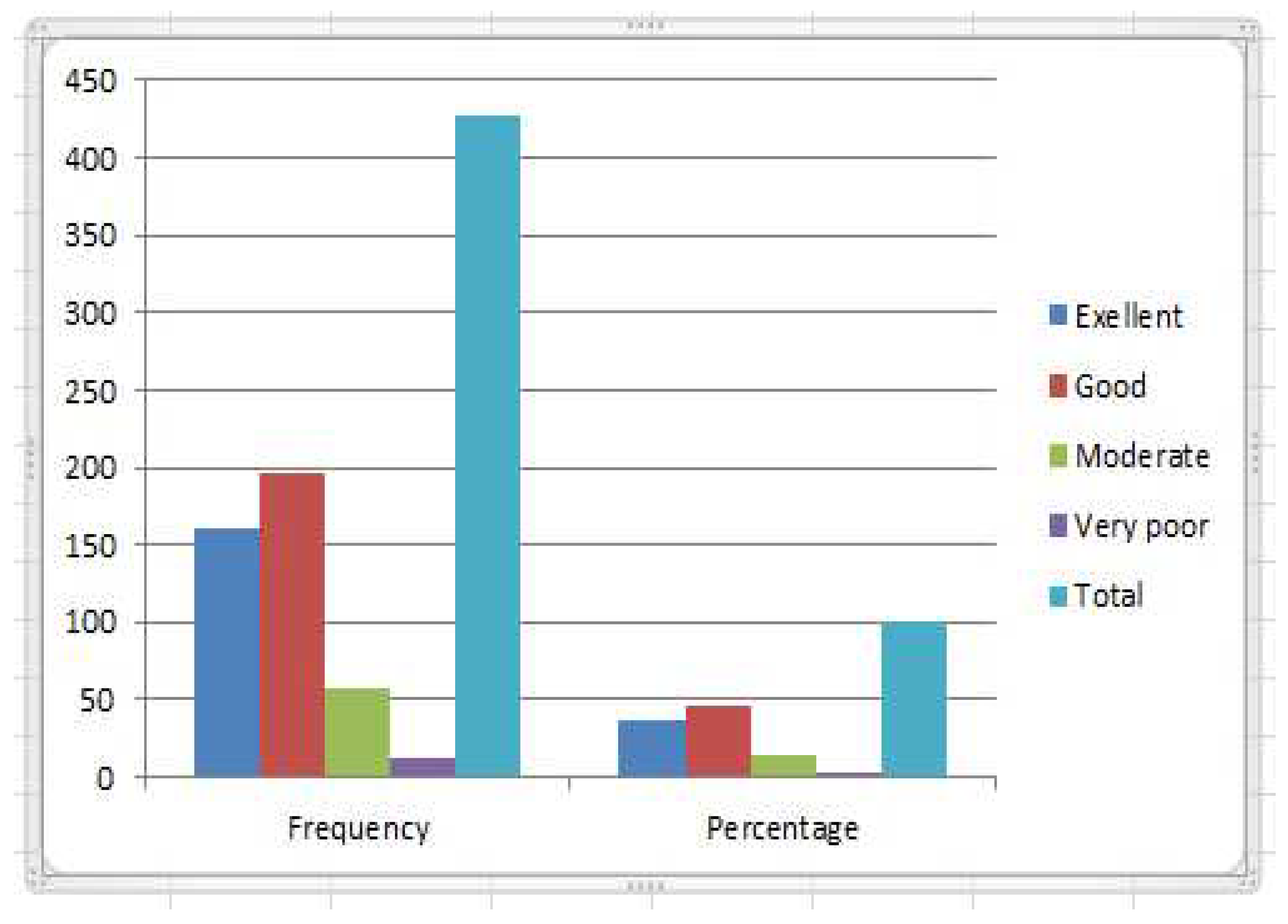
The Covid-19 pandemic deaths spreads across the globe, [
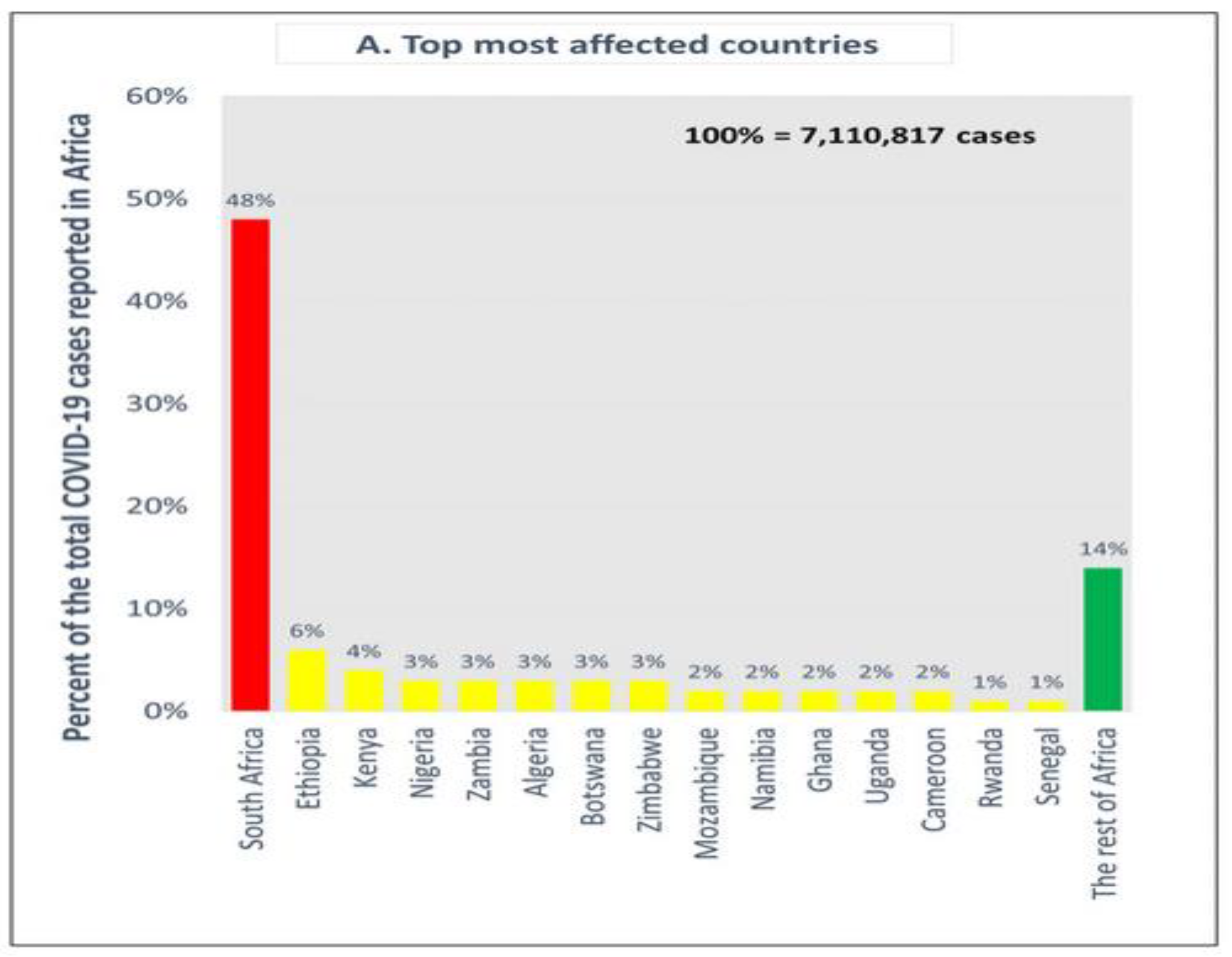
87], and African Continent as well was not spared [
88]; as shown in the
Figure 1 and
Figure 2, respectively. These had enormous consequences for communities and economies resulting in extensive social, economic, and health implications. Confronted with these constraints, the significance of social capital in facilitating recovery has grown in importance. Several research efforts have already been carried out to present the significance of social capital in connection with the cooperation among individuals and groups to overcome challenges [
15,
20,
21]. Some pieces of literature as well, substantiated that social capital can equally help in achieving resilience after the pandemic [
22,
23,
82]. The literatures revealed social capital could facilitate communities’ adaptation goals after any catastrophes. Social capital has become vital in assisting communities to cope with the pandemic’s effects and build resilience. This considers the pandemic’s social and economic effects, and the need for coordination and cooperation to assist those who have been most affected [
24,
25,
32].
In disaster and emergency research, resilience and vulnerability are progressively being researched alongside social capital [
29,
30,
33]. Before, and afterward of a crisis, social capital influences resilience and vulnerability. It was often used to assess people’s potential to recover from disasters [
34,
35,
82]. The notion as well includes social organizations that allow members of society to help one another, so boosting the urban communities and lessening dependency also on the state. Simply put, the moral codes, principles, confidence, and connections integrated with communities, in addition to their inequality and injustice. The organizations could have at their discretion that might analytics and insights for group cohesion as well as enhancing cooperation and collaboration in the face of potential consequences and disasters. The collection of potential capabilities is linked to various types of networking consisting primarily of formalized acquaintance.
2.2. Resilience, Human Social Capital and Built Environment
Resilience is described as the capacity to absorb disruptive changes while also recognizing and capitalizing on opportunities [
36,
37,
79]. In line with this assertion, [
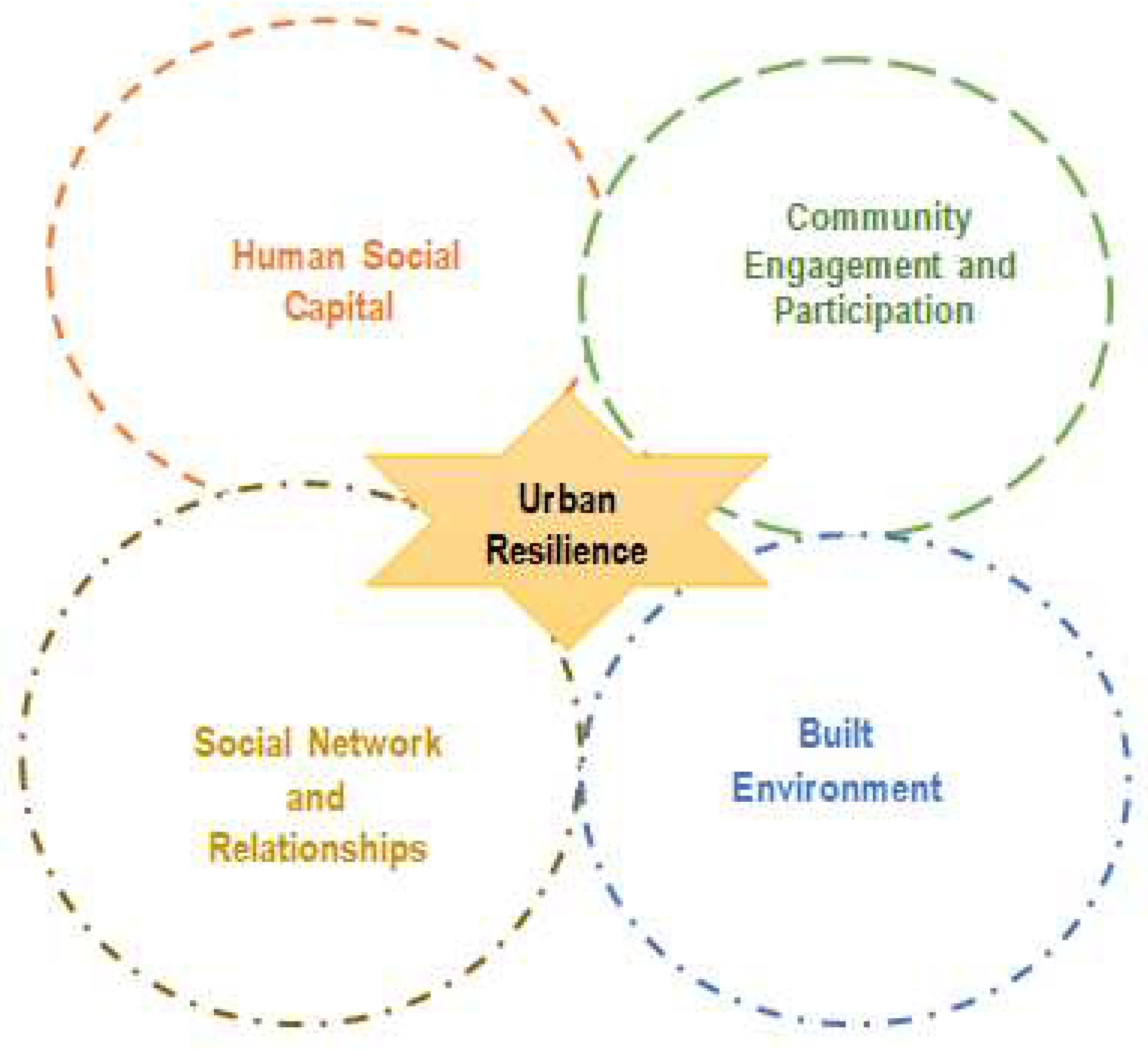
37] introduced the concept of resilience, as a series of adaptive abilities that guide a positive path of functioning following a disturbance. These inferred that resilience is not only the ultimate result, but rather the intermediary process connecting resources in the form of adaptive capacity to achieve desired results viewed as an adaptation. In the context of the built environment, resilience is considered a city’s capability to endure while recovering from natural disasters, economic shocks, and other disruptive events. Human social capital is the value that is derived from social networks, relationships, and interactions between people. Concerning the built environment, social capital is essential for building resilient communities after certain disruptive events. There are several ways in which resilience and human social capital are interconnected in the built environment namely:
- (i)
Building social networks and relationships: Social capital entails the formation and relationships between individuals and groups. These networks and relationships can be leveraged in times of crisis to provide support and resources to those who need them [
35].
- (ii)
Promoting community engagement and participation: Resilient communities are those that actively engage and participate in the planning and development of their built environment. By promoting community engagement and participation, social capital is built to enhance the community’s resilience as a whole [
23,
79].
- (iii)
Fostering trust and cooperation: Trust and cooperation are essential for building social capital and promoting resilience in the built environment. When individuals and groups trust each other and cooperate, they will recover from disruptive events [
20].
- (iv)
Encouraging knowledge sharing and learning: Resilient communities are those that can gain insight from previous encounters and adapt their approaches to potential challenges. Social capital is essential for promoting knowledge sharing and learning among individuals and groups within the neighborhood [
38].
Given the foregoing, urban resilience and the human social capital remain the subject matter and relevant in the discuss of the built environment as adapted from the study of [
20], [
36],[
38] and presented in
Figure 3. By building strong social networks and relationships, promoting community engagement and participation, fostering trust and cooperation, and encouraging knowledge sharing and learning, communities can become more resilient and adapt to disruptive events.
2.3. Consolidating Resilience Built Environment Using Human Social Capital
The structural, ecological, and socio-cultural capital comprise the built environment represented by man-made building and infrastructure stocks. The built environment’s resilience is crucial in light of the growing frequency and severity of natural catastrophes and other stressors such as climate change and social-economic disturbances. A resilient built environment is characterized by a structure’s ability to endure and adapt to a variety of shocks. This necessitates the skill and knowledge needed to take into account a variety of social, economic, and technical aspects.
The idea of resilience provides a way to manage the protracted adaptation of the built environment and to investigate the impacts of ecological changes on the effectiveness of various approaches to planning, design, and management. In consequence, resilience is a conceptual and modeling framework that identifies the processes that help or hinder the attainment of sustainable environmental objectives. The description of resilience has three components: i) the term’s core description; ii) models for translating the ambiguously defined, core concepts to specific situations; and, iii) analogies for having conversations, social as well as private assumptions, experiences, and values associated with the theoretical theory. Social capital is one major aspect that is progressively becoming recognized as important for generating resilience in the built environment. Individuals’ desire to cooperate and contribute to the collective good can be increased by trust and reciprocity rules [
23,
38].
Furthermore, social capital can improve access to resources, facilitate risk reduction and adaptation, and improve communities’ ability to respond to catastrophes [
22,
35,
84]. Despite growing recognition of the value of social capital for resilience, the incorporation of social capital into the physical environment design is still in its early stages. The difficulty in measuring and quantifying social capital, as well as the necessity to address power dynamics and inequality within communities, are some of the obstacles and limitations of employing social capital as a resilience-building method [
32,
35,
84]. Human social capital is important in fostering resilience due to the way it provides individuals with resources; and communities with the resources they need to cope with adversity. Social networks can provide emotional support, information, and access to resources that can help people overcome challenges and bounce back from setbacks. Strong social connections can also help to build trust and cooperation, which are essential for effective collaboration and problem-solving [
20]. This entails integrating social, economic, and technological aspects, as well as addressing inter-generational justice in creating resilience.
A rising corpus of research on resilience in the built environment has underlined the necessity for a systems approach that takes into account the interconnections between diverse elements. The built environment, which refers to the physical surroundings in which people live and work, also plays a significant role in promoting resilience. The design and layout of buildings, neighborhoods, and cities can influence the social interactions and relationships that occur within them. For example, mixed-use developments that combine residential and commercial spaces can promote social interaction and community engagement, while poorly designed neighborhoods with few public spaces and amenities can result in social exclusion and disengagement [
20].
Furthermore, the built environment can also impact resilience in terms of its ability to adapt to environmental disasters and other disruptions. Resilient infrastructure, such as buildings, roads, and energy systems, can help to minimize the consequences of catastrophes of nature and ensure that communities can recover more quickly after a crisis. Conclusively, the resilience concept relates to the role of human social capital and the built environment. Building strong social connections and creating resilient infrastructure may assist people as well as communities in adapting to and recovering from adversity, while poorly designed environments and weak social networks can hinder resilience and exacerbate the impact of stress and trauma.
2.4. Conceptual framework
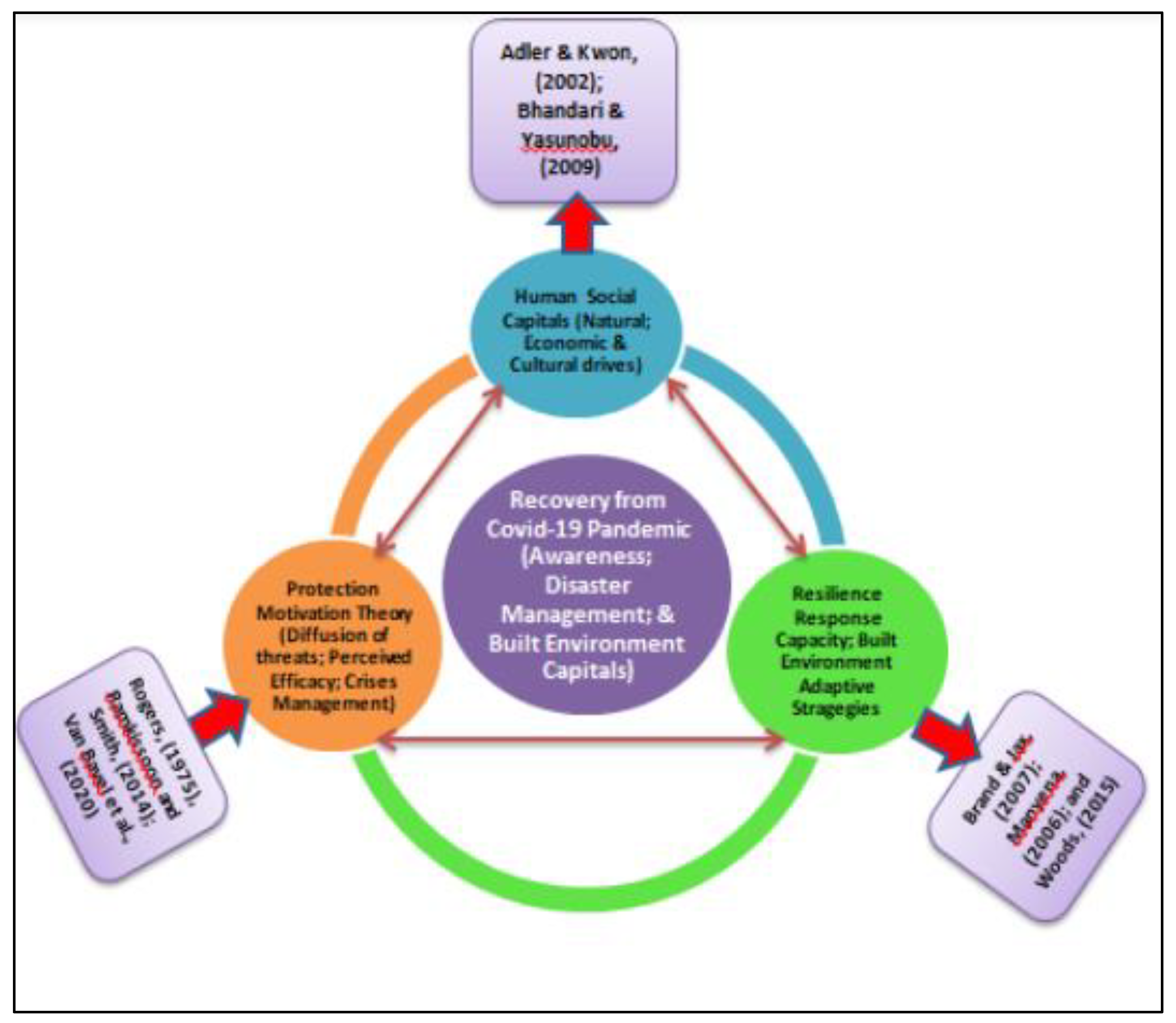
Protection Motivation Theory (PMT) was conceived as a psychological response to an emotional appeal that’s been utilized mostly in biomedical sciences to urge change in health habits [
40]. Over time, PMT has been employed by scholars in social and environmental, and psychological research works [
41]. People will take immediate action if they perceive a significant danger, such as apprehension about getting and transmitting the COVID-19 virus; and these individuals are desirous of participating in actions that could have a positive impact in curtailing the spread of the virus. In light of this, this study incorporated ’resilience’ and ’human social capital’ into PMT as a framework, as shown in
Figure 4.
Scholarly research into crises and disasters typically employs the same theories to illustrate, and evaluate societal manifestations such as: i) how communities, organizations, or individuals respond to traumatic emotions; ii) the socioeconomic or political ramifications of catastrophes; and iii) what changes in humanity’s fabric are needed to mitigate a crisis. On this premise, there exists an interaction between social capital and resilience affirmed by [
42,
43]. The two are frequently utilized during pandemics, terrorist attacks, and disasters. Similar studies by [
35,
52] affirmed the interconnections between resilience and catastrophe management. Catastrophe and disaster research have advanced our understanding of resilience, social capital, and disaster management via scientific, analytical, and investigatory studies.
2.4.1. Hypothesis Development
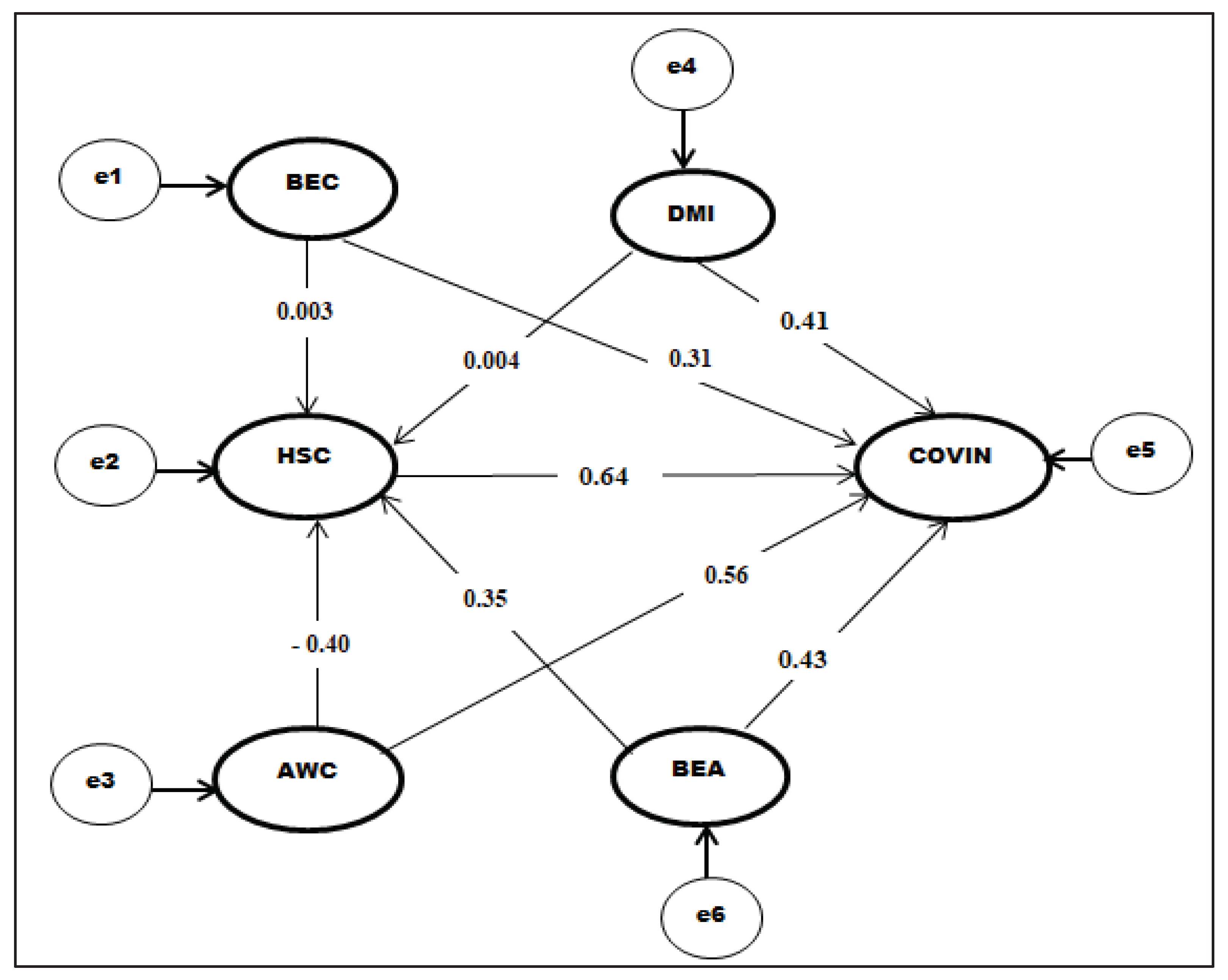
To test the proposed framework and research hypotheses, the study employs multivariate data analysis and confirmatory factor analysis of AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structures). The rationale for selecting AMOS and CFA is that they provide a powerful method for testing the validity of a theoretical model. Also, AMOS is particularly well-suited for conducting CFA because it provides a user-friendly graphical interface that allows researchers to build complex SEM models with ease. It also includes a variety of useful features for model estimation, model fit testing, and model modification. CFA is a statistical technique used to test the degree to which a group of observed variables can be accounted for by a lower amount of latent factors. In other words, CFA allows researchers to confirm whether their measures are determining what they are supposed to measure and whether they are related to the underlying constructs they are supposed to represent. The model’s reliability and validity were assessed by using the confirmatory factor analysis. Consequently, this empirical analysis documents the significant benefits of resilience built environment dimensions (built environment capitals, disaster management indices, Covid-19 awareness, and built environment adaptive methods) on ameliorating the adverse effects brought about by the Covid-19 pandemic.
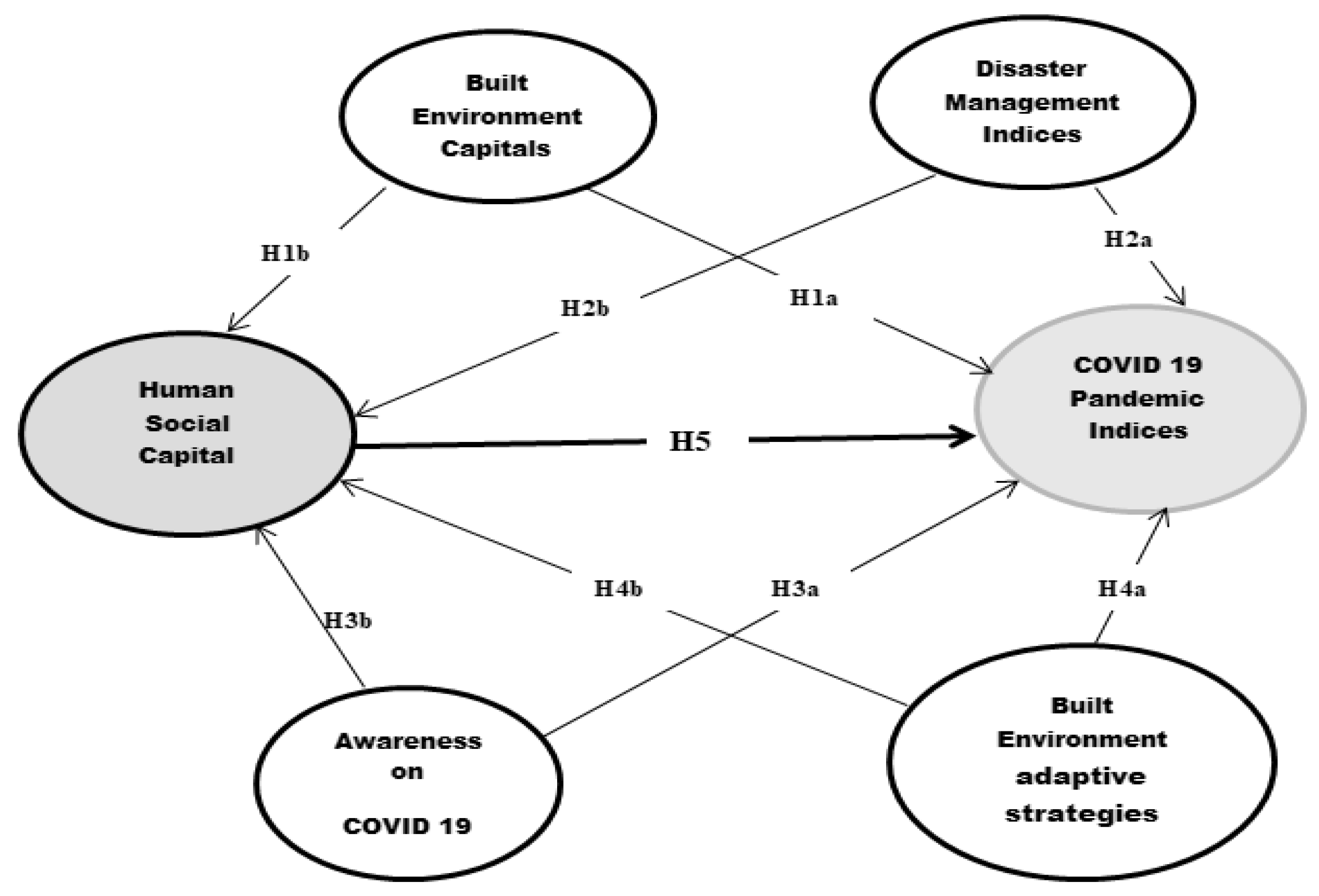
Figure 5 depicts a hypothetical analytical regression model of the effects of human social capital on COVID-19 Pandemic indicators based on the preceding premise. The goal of this research was to explore the impact of four built environments, resilience indices (Built Environment Capitals, Disaster Management Indices, Awareness of the Covid-19 Pandemic, and Built Environment Adaptive Strategies) on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices and Human Social Capital. Built environment capitals, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness, on the other hand, have an indirect effect on Covid-19 pandemic indices via Human social capital. Consequently, the following hypotheses are formulated:
Hypothesis 1a: The built environment capital has a positive impact on Covid-19 Pandemic Indicators
Hypothesis 1b: The built environment capital has a positive impact on Human Social Indicators
Hypothesis 2a: The disaster management indices have a positive impact on Covid-19 Pandemic Indicators
Hypothesis 2b: The disaster management indices have a positive impact on Human social capital indicators
Hypothesis 3a: The awareness of Covid-19 has a positive on Covid-19 Pandemic Indicators
Hypothesis 3b: The awareness of Covid-19 has a positive impact on Human social capital indicators
Hypothesis 4a: The built environment adaptive strategies have a positive impact on a Covid-19 Indicators
Hypothesis 4b: The built environment adaptive strategies have a positive impact on Human social capital
Hypothesis 5:The Human social capital has a positive impact on Covid-19 Pandemic Indicators
3. Research Design and Methods
3.1. Variables Measurement
The contents of the survey questionnaire were divided into two segments as presented in
Table 1. The first segment comprises questions about the respondent’s demographic profiles, such as their age, gender, work status, educational backgrounds, etc. While the second segment of the survey was developed to assess the various constructs included in the proposed framework, such as built environment capital, disaster management indices, Covid-19 awareness, human social capital, and Covid-19 pandemic indices. The measuring items were all drawn from established scales, and the content of some items was modified to fit the research context.
Validating a research questionnaire is an important step in ensuring that it accurately measures targeted research questions and produces reliable and meaningful data. The questionnaire’s construct (variable) is well-defined and aligns with our research variables. To ensure the content validity of the questionnaires, pilot survey was carried out in which the experts in the field were asked to review the measurement variables. The experts provided a reasonable assessment relevant to the questions. The pilot testing was accomplished with a twenty-five (25) sample of the target population. This helps identify any issues with question-wording, instructions, or response options. Participants’ feedback during the pilot test was used as guide refinements in the main questionnaire.
All the items were adjusted to positive questions rated on ‘
5 point Likert scale’. Respondents’ opinion on the research questions captured their level of either ‘
strongly disagree’ of ’1’ to a ‘
strongly agree’ of ’5’ for the measured items as previously carried out in the past studies. In view of the above, measurement of built environment capitals captured four (4) items adopted from the proposed assessment perspective of [
44,
47] in which the pieces of literature elucidate the interconnection between various capitals of natural, human, economic, and cultural for a sustainable built environment. Built environment capital (BEC) influences the kinds and degrees of services and goods necessary for satisfying social desires. This necessitates the existence of natural capital as well as the capability to prepare it to be utilized through constructed capital, thereby satisfying human wants through commodities and services needed for enhancing the natural capital properly [
44,
81]. For instance, on the Built Environment Capital; the respondents’ level of agreement was elicited on questions such as i) ‘
Human capital relates with low-energy resources and services’; ii) ‘
Human capital is a production element that interacts with constructed capital to achieve economic consequences’ amongst others.
In connection with the Disaster Management Indices (DMI) measurement were based on the seven (7) tested items and confirmed performance index items adopted from [
46]. The purpose of disaster management, according to the author, is to offer proper reaction and retroactive effect after a disaster. It is determined by the level of readiness of both the accountable institutions and the populace in its entirety. In addition, the aim was to respond effectively and properly when a threat had become a disaster. Performance indicates that the agencies engaged possess effective organizational capabilities, as well as the competence and strategies in place to deal with catastrophic repercussions. Questionnaires on this involved, i) ‘
Disaster management can be reduced through the Organization and coordination of emergency operations’; ii) ‘
Disaster management can be reduced through Hazard Monitoring and forecasting’; among others.
In addition, Awareness of Covid-19 pandemic (AWC) was measured by six (6) tested items for the study as previously measured by [
45]. Questions include: i)’
When it comes to Covid-19, I am terrified’; ii) ‘
When I think about the death scene created by Covid-19, I get nervous’ and so forth. The measurement of Covid-19 Pandemic Indicators (COVIN) was captured using previously tested five (5) items and the items conformed to the study of [
45,
82]. A sample of the question includes: i) ‘
I am helpless in the face of the Covid-19 pandemic’; ii) ‘
During Covid-19, I was concerned that I lacked sufficient immunity to adequately combat the Coronavirus’. Built environment adaptive strategies included five (5) items and were adapted from [
12,
53,
83]. Human social capital included five (5) measurement items and was adapted from [
38,
81]. This was with a view of documenting the role played by human social capital in enhancing the resilient built environment after the Covid 19 crisis.
3.2. Sampling and Data Analysis
This study’s approach entails employing an online poll instrument to gather data from a sample of Nigerian respondents via email google forms between 2nd February and 30th April 2022. In total, 427 acceptable random samples were obtained from the survey; while the demographics of respondents accurately reflected the gender and age groupings.
Table 2, indicates the results of the Measure of Sampling Adequacy. The scale’s reliability and internal consistency were assessed through the application of the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient test. Overall, the scale was established to be adequate with KMO values of 0.870. Also, the sample was deemed to be satisfactory at a Cronbach value of 0.700 or higher based on minimum standards suggested by [
48]. The Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.853 and 0.896 were obtained in this study confirms its reliability for subsequent analysis.
To show the statistical model dataset, normality tests were carried out. The normal distribution set is based on reports of skewness and kurtosis [
48]. The skewness and kurtosis Z values should be greater than 1.96, and the p-value for the Shapiro-Wilk estimate should be greater than 0.05. These were eventually achieved; as 86 percent of the skewed z-values are greater than 1.96, which was sufficient for further investigation [
48,
49]. In addition, a total of 31 outliers were, identified and eliminated.
The data analysis was evaluated in two stages, as recommended by [
50,
51]. This was carried out via measurement and structural model building [
51]. Developing a measurement model, including the first performance of a synchronized CFA, includes all variables. The second procedure took into consideration the use of structural modeling intending to examine the links between the components, as shown in
Figure 2. For the mediation effects, comparisons were made between the mediation models, while bootstrapping was used as suggested by [
54], to test for the significance of the indirect effects.
This quantitative survey uses SPSS and AMOS version 24.0, to explore the enhancement of a resilient built environment through the use of residents’ social capital in the post-COVID-19 era. This quantitative research strategy was deemed suitable for mitigating biased evaluation and discussion as supported by the works of [
55,
56]. In the meantime, a sample size of 100 or above was regarded as adequate for variance-based Structural Equation Modeling [
48]. Nevertheless, this research assesses the conceptual models in the proposed model that were validated using existing scales, and the content of some items has already been tailored to the research context. The Sample size was calculated using the Raosoft sample size calculator [
86]; by presuming a 95% confidence level, 5% margin of error, and response distribution of 50%, yielding a sample size of 427.
The screened data obtained were evaluated with multivariate data analysis and confirmatory factor analysis using AMOS software version 24. AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structures) is a popular software tool used for structural equation modeling (SEM), which is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. AMOS allows researchers to build models that depict the hypothesized relationships between variables and then test those models using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). For example, AMOS can compute a variety of goodness-of-fit indices, such as the chi-square statistic, the comparative fit index (CFI), and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), which can help researchers evaluate the overall fit of their model. The confirmatory factor analysis was used to evaluate the reliability and validity of each construct in the model, while the multivariate data analysis was used to test the research hypotheses. Before cross-validation, the exploratory factor (EF) analysis yielded a valuable model-specific algorithmic technique with confirmatory factor analysis. Confirmatory factor analyses (CFA) and exploratory factor analyses (EFA) are approaching in which the data are studied and descriptions of the many parameters required to reflect the data presented.
The EFA variables were related to the latent construct, whereas CFA researchers defined the plethora of indicators expected for the outcomes. CFA can be defined as a method for validating or rejecting an estimate [
48]. As an exploratory study, it introduces the validity of the instrument using an exploratory factor analysis approach. The data collected were analyzed using the proposed framework, and the results were used to demonstrate the indirect effects of built environment capital, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness on the pandemic through the human social capital. The contents of the survey questionnaire allowed feedback from the respondents on the impact of a resilient built environment on post-Covid 19 recoveries in Nigeria.
4. Results
The purpose of this investigation is to put the research hypotheses to the test by analyzing the data gathered from the people’s opinions on the objectives of the study. Seven hundred (500) questionnaires were sent out and 538 of them were received. Eventually, 427 valid samples were left for an 85.4% valid return rate, guaranteeing statistical validity with a 95% confidence interval and ±0.05 sampling error. Demographic statistics revealed that 57.37% of respondents were male, 42.62% were female, 13.80% were 18-35 years old, 37.00% had a Bachelor / HND degree, and 22.48% worked in Health Care Services. This study’s sample size ensures a representation of the cross-section of the population under investigation. Also, this sample adequately reflects the diversity and characteristics of the larger population to draw meaningful conclusions that allowed generalization.
Table 3 shows the demographic features.
Meanwhile,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 indicate respondents’ self-ratings of their knowledge regarding the built environment and the COVID-19 epidemic. To examine and test research hypotheses, the multivariate data analysis method was applied. The measurement model consisted of six (6) latent constructs namely built environment capital (4 items), disaster management indices (7 items), awareness on the Covid-19 (6 items), Covid-19 pandemic indices (5 items), human social capital (5-items), and built environment adaptive strategies (5-items). The results of a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) analysis that categorizes variables into components, identifies the most significant factors, and explains how much of the original data’s variation each component capture were presented in
Table 4. The factors were grouped, and then transform into components of the variables used in subsequent analyses. The results indicate that, following an assessment of 32 variables, six components converged after six rotation iterations, explaining 92.72% of the overall variance. These parameters exhibit variance percentages of 15.06%, 15.14%, 15.50%, 15.13%, 15.11%, and 15.78%, respectively. These percentages demonstrate that by using a combination of these six components, a substantial portion (92.72%) of the original data’s variability has been successfully distilled into a more compact yet informative representation. This reduction in dimensionality simplifies the data analysis process while retaining the most crucial features and patterns.
For reliability and validity; SPSS version 22.0 was used for reliability analyses, while AMOS version 24.0 was used for a validity test using the CFA results. We also conducted item reliability and the convergent validity study for each construct in the model; in addition to the overall assessment of model fit; and the results were provided in
Table 5. The measurement model fit has Chi-square/df smaller than 3, CFI, TLI, and IFI all are larger than 0.9 and RMSEA is smaller than 0.08; in line with the suggestions of [
48,
58].
The Cronbach alpha was used to determine structural dependability or internal consistency, which ranged from 0.853 to 0.896 for all constructs, above [
57] criteria of 0.7. As a result, the scales for all structures are reliable. Overall, for the model fit of the measurement model, the analysis achieved sufficient measures (χ2/df = 3.206 and RMSEA = 0.052, CFI = 0.939, GFI=0.947, TLI = 0.918 and IFI =0.937). Each construct’s standardized item loadings were statistically significant (p < 0.001). None of the items had loadings smaller than 0.50, a common factor analysis threshold [
59,
60]. For each construct, the composite reliability [
60], and the average variance retrieved [
61], were also examined. The composite dependability of a concept evaluates its unidimensionality and should, at the very least, be greater than the 0.70 cutoff standard [
62].These criteria are met by all of our structures.
The extracted average variance estimates the proportion of variation explained concerning the variance attributable to random error [
63]. All of our measures are more than 0.50, indicating that we have strong internal consistency and that the amount of variance captured by each construct is greater than the variances caused by measurement error [
61]. All of these findings indicate that the six latent components have appropriate convergent validity and item reliability. The degree to which one latent construct differs from another is referred to as discriminant validity. The AVE was used to confirm discriminant validity in this current study. This was achieved by coordinating the correlations among the latent constructs with the square roots of the retrieved average variance. As a result, the square root of the extracted average variance exceeded the correlations among latent components, indicating good discriminant validity, as shown in
Table 6.
The structural component of our stated model was analyzed in the second step of the analysis, the key results of which are shown in
Figure 8. The control variables are not shown in this diagram for clarity. Nonetheless, routes from each dependent construct were described in all structural models, as [
64] had done. The final structural model achieved a good overall fit: χ2/df = 3.345; CFI= 0.916; TLI= 0.918; IFI = 0.925; RMSEA= 0.053. The results show that hypotheses H1a, H2a, H3a, H4b, H4a, and H5 were supported, except for H1b, H2b, and H3b which were not supported.
Table 7 shown the path analysis results from the structural model.
In other words, Built Environment Capital, Disaster Management Indices, Awareness of Covid-19, and Built Environment Adaptive Strategies all positively affect Covid-19 Pandemic Indices. Awareness of Covid-19 has the highest impact of 0.567 on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices, followed by Built Environment Adaptive Strategies with an impact of 0.435. The Disaster Management Indices have an impact of 0.413; while Built Environment Capitals have the lowest impact of 0.312. Meanwhile, only Human Social Capital has a positive direct influence on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices with a path coefficient of 0.641. The Hypothesis of Built environment Adaptive Strategies on Human Social Capital was supported with an impact of 0.359. Regrettably, the hypothesis on the impacts of Built Environment Capitals, Disaster Management Indices, and Awareness of Covid-19 on Human social capital was not supported with a significant value p>0.05.
Table 8, shows that four constructs (Built Environment Capitals, Disaster Management Indices, Awareness of Covid-19, and Built Environment Adaptive Strategies have an indirect effect on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices. The indirect effect of Built Environment Capital on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices has 0.086; Disaster Management Indices has 0.043; Awareness of Covid-19 has 0.144 and Built Environment Adaptive Strategies has 0.042. Overall, the total effect of Human social capital on Covid-19 Pandemic Indices has higher than the others with an effect of 0.753.
5. Discussion
5.1. The built environment capital and the human social capital considering the Covid-19 epidemic
This study raises our knowledge and comprehension of how diverse interconnections exist between the factors of resilience built environment which includes built environment capital; disaster management; awareness on the Covid-19; and built environment adaptive strategies; and were directly and indirectly, impacted achieving Covid-19 post-recovery. Social capital contributes to increased resilience during and after the Covid-19 epidemic. Most importantly, the outcome of our analysis revealed that human social capital had the highest impact on the Covid-19 pandemic indices. The results inferred that personal capacity to tackle the pandemic was reported strong in any neighborhood as corroborated by [
65,
66].
The study recognizes the significance of resilience in the built environment and has been in tandem with various studies in fields such as urban planning, architecture, and disaster management [
38,
73,
78]. This research has shown that strong social ties can contribute to effective disaster response, community support, and recovery. This finding aligns with current literature on the function of social capital in building community resilience (e.g., Putnam’s theory of social capital). The research highlights that human social capital had the highest impact on Covid-19 pandemic indices. This finding suggests those individuals’ connections, cooperation, and shared resources played a pivotal role in responding to and recovering from the pandemic. The emphasis on human social capital resonates with research on the importance of community engagement and social cohesion in times of crisis.
5.2. The disaster management indices, human social capital, and resilient built environment framework
The results we obtained agree with a growing amount of empirical and theoretical research [
24,
27,
67]; indicating that people who live in close-knit communities for three different reasons recovered better during the outbreak. Firstly, a deeper feeling of shared conviction exists in a more coherent community [
28,
68]. Second, when groups have high social capital, they are more inclined to organize themselves to provide communal assistance and encouragement for those particularly affected by a disaster, boosting or substituting state intervention [
69]. Thirdly, in cultures with strong social capital, coping resources are more broadly available [
25,
70,
77]. According to [
70], social capital is a community-level interpersonal asset that helps to reduce the effects of the disease of pandemic confinement and seclusion.
5.3. Awareness of the Covid-19 pandemic and its connection to human social capital
This study has affirmed that communities with strong social capital will fare better during and after the pandemic in several ways, including increased compliance with public health guidelines, greater resilience to economic disruption, and better psychological well-being. These communities have been able to leverage their social networks and relationships to provide mutual support, coordinate collective action, and in the following situations, develop resilience amid disaster.
- (i)
Mutual Aid Networks: In many communities, mutual aid networks have emerged during the pandemic to provide support to vulnerable populations. These networks are typically composed of volunteers who offer to help with tasks such as grocery shopping, medication delivery, and transportation. They rely on social networks and relationships to coordinate their efforts and reach those in need. Communities with a high level of social cohesiveness have been able to mobilize these networks with greater effectiveness and ensure that support reaches those who need it most as in tandem with the studies of [
68,
71].
- (ii)
Compliance with Public Health Guidelines: Communities with strong social cohesion have generally been more compliant with public safety measures such as mask use, physical separation, and proper hand washing. This is because individuals in these communities are more likely to trust and respect each other and wellness and good health are important to their fellow residents. This has contributed to lower rates of Covid-19 transmission in these communities as supported by [
2,
72].
- (iii)
Resilience to Economic Disruption: Communities with strong social cohesion have been more resilient to economic disruption caused by the pandemic. This is because individuals in these communities are more likely to support local businesses and each other during times of economic hardship in line with the studies of [
73].
- (iv)
Psychological Well-being: Communities with strong social cohesion have also fared better in terms of psychological well-being during the pandemic. This is because individuals in these communities have a greater sense of social support, belonging, and connection to others [
68].
5.4. The adaptive strategies for mitigating the impact of the Covid-19 epidemic
This study has revealed the built environment adaptive strategies to the intentional adjustments and modifications made to the physical environment (such as buildings, public spaces, transportation systems, and infrastructure) to address and respond to changing circumstances, challenges, or threats. This is consistent with the study of [
1,
25,
85]. Adaptive methods within the context of the Covid-19 epidemic include changes to urban design, transportation systems, workplace layouts, public spaces, and housing to promote safety, hygiene, and social distancing. Additionally, communities with strong social networks, such as immigrant communities and religious groups, perhaps helped one another out during a global epidemic by providing financial assistance, food, and other essential resources. Positive actions could be made through stakeholder participation in local community initiatives to tackle the Covid-19 threat. Furthermore, social capital has a substantial influence on people’s resilience and communities’ capacity to adapt to the Covid-19 pandemic’s effects. This was corroborated by the discoveries of [
25,
26,
28].
5.5. Built environment capitals, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness
This study confirms that beneficial human activities can reduce the susceptibility of the built environment during Covid 19 catastrophes. Adapting to the Covid-19 epidemic will be simple in civilizations with strong community social connectedness [
25,
68]. That is consistent with prior research by [
70], which established that the negative health effects of quarantine during a pandemic are reduced by social capital, an asset that exists at the neighborhood level. In connection with previous findings; this study has shown that disaster response can improve connectedness among residents and such efforts can increase self-confidence and shared understanding [
71,
72,
73]. A proactive, resilient society or community, on the other hand, acknowledges the certainty of change and works to build a system that responds to adaptable management procedures [
74,
75]. In terms of social cohesion, this study in connection with past studies has shown that communities with high levels of social cohesion, such as small towns and tight-knit neighborhoods, could have had lower rates of Covid-19 transmission compared to neighborhoods that have inadequate social capital.
6. Conclusions
The impact of a resilient built environment of post-Covid 19 recoveries in Nigeria, employing human social capital as an intermediary factor has been established. The results uncovered by this study indicated that built environment capitals, disaster management indices, and Covid-19 awareness have indirect effects on the Covid-19 pandemic indices through the human social capital. The research offers valuable perspectives by revealing the significance of human social capital in enhancing adequate resilience in the built environment. The study affirms the significance of multi-disciplinary dimensions to enhance the resilience of the built environment, considering the intricate relationships among various factors, including social capital. The current study makes a substantial contribution to expanding knowledge in this area by uncovering multiple ways in which individuals, communities, and organizations are heavily reliant on social capital towards recovering from the adverse effects of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Notably, social capital often leads to effective responses compared to institutional assistance in many instances. Moreover, while discussions about resilience in the built environment usually focus on post-disaster recovery procedures, this study underscores the ongoing importance of social capital for recovery following any form of disaster. It highlights how neighborhoods rich in social connections tend to exhibit greater resilience during recovery phases. In the context of the built environment, resilience can include measures aimed to minimize the potential for transmitting infections, ensure access to essential services, and support economic recovery. Achieving resilience in the built environment during the pandemic requires a multi-disciplinary approach that involves professionals from a range of fields.
Examples of a multi-disciplinary concept to enhancing resilience in the built environment during the pandemic include, first, the collaboration between architects, engineers, and public health professionals to design buildings and public spaces that reduce the risk of infection transmission. Secondly, the involvement of urban planners, transportation experts, and public health professionals in designing transportation systems that ensure access to essential services while minimizing the risk of infection transmission. Thirdly, a collaboration between economists, public health professionals, and policymakers to develop economic recovery plans that support businesses and individuals while minimizing the risk of infection transmission.
The limitation of the study includes challenges in measuring social capital. A universally recognized approach for gauging social capital is lacking, and different approaches may yield different results. This poses challenges when assessing the influence of social capital strategies on resilience. Comprehending the relationships between adaptations in the built environment and human social capital during the pandemic has practical implications for urban planning, policy development, and public health interventions. They must prioritize the needs of vulnerable populations and ensure that they are provided with the assistance they need to build social capital. The study’s findings reveal insights for policymakers and other stakeholders in Nigeria and demonstrate the significance of taking into account human social capital in the creation and strategizing of an environment that is resilience.
Policymakers can play a role in promoting human social capital by investing in community-based programs and initiatives that foster social capital and build trust among community members. This can include supporting community organizations, promoting the utilization of communal areas for social interaction, and encouraging the development of neighborhood-based networks and partnerships. It is important to take a holistic and inclusive approach to social capital-building in the built environment. This can involve engaging with diverse stakeholders and communities, identifying and addressing existing inequalities and power structures, and adopting a flexible and adaptive approach to resilience-building that acknowledges the intricate nature of the obstacles encountered by societies.
The study’s proposed framework possesses the potential to function as a valuable instrument for policymakers and practitioners as they strive to bolster the resilience of constructed spaces against upcoming pandemics and calamities. This includes using materials and technologies that are resistant to natural disasters and other threats, as well as design buildings and public spaces that are flexible and adaptable to changing needs and circumstances. Importantly, policymakers must also prioritize equitable access to resilient infrastructure and services. This means considering the needs of vulnerable populations, including but not limited to underserved communities, senior citizens, and individuals with varying abilities; and ensuring that they have access to safe and resilient buildings, public spaces, and services. There is a strong need for a multi-disciplinary strategy to enhance resilience in the built environment during the pandemic. Future research might include investigating the long-term impacts of social capital on resilience and exploring the potential for social capital to address other environmental challenges beyond Covid-19.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O. P. and H. A.; methodology, O. P.; software, O. P.; validation, O. P., H. A.; writing—original draft preparation, O. P. and H. A.; writing—editing, H. A.; Y.A., visualization, Y.A.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Desjardins, M.; Hohl, A.; Delmelle, E. Rapid surveillance of COVID-19 in the United States using a prospective space-time scan statistic: Detecting and evaluating emerging clusters. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 118, 102202–102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franch-Pardo, I. , Napoletano, B.M., Rosete-Verges, F., & Billa, L. Exploring COVID-19 through Spatial Analysis and GIS: An In-depth Review. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 739, 140033. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. The COVID-19 pandemic: Impacts on cities and major lessons for urban planning, design, and management. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 142391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter-Wollman, N.; Jelić, A.; Wells, N.M. The impact of the built environment on health behaviours and disease transmission in social systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galderisi, A.; Limongi, G.; Salata, K.-D. Strengths and weaknesses of the 100 Resilient Cities Initiative in Southern Europe: Rome and Athens’ experiences. City, Territ. Arch. 2020, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y. M. Cheung, C. K., & Chan, A. H. Enhancing resilience of the built environment through integrating disaster risk reduction and sustainability. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2016, 21, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Donate, M.J.; Peña, I.; de Pablo, J.D.S. HRM practices for human and social capital development: effects on innovation capabilities. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2015, 27, 928–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podjed, D. Renewal of Ethnography in the Time of the COVID-19 Crisis. Sociol. i Prost. 2021, 59, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahagia, B.; Habibah, N.W.; Mangunjaya, F.M.; Wibowo, R. Religion Value and Social Capital for Resilience to Combat Covid-19 In Society Environment. EDUKATIF : J. ILMU Pendidik. 2021, 3, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amekudzi-Kennedy, A. , Labi, S., Woodall, B., Chester, M., & Singh, P. Reflections on pandemics, civil infrastructure, and sustainable development: Five lessons from COVID-19 through the lens of transportation. 2020.
- Rahbarianyazd, R. Sustainability in Historic Urban Environments: Effect of gentrification in the process of sustainable urban revitalization. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.D.; Romero-Lankao, P.; Mehrotra, S.; Dhakal, S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Bowman, T.; Bader, D.A.; Blake, R.; Grimm, A.; et al. Ibrahim. Climate change and cities: Second assessment report of the urban climate change research network. Cambridge University Press. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDRR. Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction. Our World at Risk: Transforming Governance for a Resilient Future; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gatzweiler, F.W.; Jayasinghe, S.; Siri, J.G.; Corburn, J. Towards a New Urban Health Science. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, R.D. Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community. Simon & Schuster. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hassler, U.; Kohler, N. Resilience in the built environment. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuff, S. F., Tucker, J. A., Murphy, J. G. Behavioral economics of substance use: Understanding and reducing harmful use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 29, 456–465. [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.P.; Rasidi, M.H.; Bin Said, I.; Zakka, S.D.; Shuaibu, A.-W. Residents’ Social Interactions in Market Square and Its Impact on Community Well-Being. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2018, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilesanmi, O.; Afolabi, A. Perception and practices during the COVID-19 pandemic in an urban community in Nigeria: a cross-sectional study. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Waegh, R. , House, J., Duarte, A., Fonua, M., Martins, D., Raubani, J., & Steenbergen, D. J. Social inclusion and resilience. In Islands and Resilience: Experiences from the Pandemic Era. 2023. (pp. 17-33). Springer Nature Singapore.
- Bourdieu, P. The forms of capital. In Education: Culture, Economy, and Society, AH Halsey, H Lauder, P Brown, A Stuart Wells (Eds.). Oxford University Press: Oxford; 1997. 46–58.
- Ostrom, E. Collective Action and the Evolution of Social Norms. J. Econ. Perspect. 2000, 14, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N. Social and ecological resilience: Are they related? Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2000, 24, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Kudva, A.; Shukla, R. Social capital, health, and recovery from COVID-19. Lancet Public Heal. 2020, 5, e568–E568. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reicher, S.; Stott, C. On order and disorder during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2020, 59, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samutachak, B.; Ford, K.; Tangcharoensathien, V.; Satararuji, K. Role of social capital in response to and recovery from the first wave of COVID-19 in Thailand: a qualitative study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e061647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, K.; Bigdeli, A.Z.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Raman, R. How is COVID-19 altering the manufacturing landscape? A literature review of imminent challenges and management interventions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solymosi, R.; Jackson, J.; Pósch, K.; Yesberg, J.A.; Bradford, B.; Kyprianides, A. Functional and dysfunctional fear of COVID-19: a classification scheme. Crime Sci. 2021, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Fu, Y.-C.; Hsung, R.-M. Measurement Techniques for Investigations of Social Capital. Soc. Cap. Theory Res. 2017, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickes, R.; Zahnow, R.; Taylor, M.; Piquero, A.R. Neighborhood Structure, Social Capital, and Community Resilience: Longitudinal Evidence from the 2011 Brisbane Flood Disaster*. Soc. Sci. Q. 2015, 96, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. , Han, J., & Brass, D. J.. Human capital diversity in the creation of social capital for team creativity. Journal of Organizational Behavior 2014, 35, 54–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S. , Jonas, A. E., & Davoudi, S. Resilience: A bridging concept or a dead end? Environmental Planning A 2012, 44, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Panneer, S.; Kantamaneni, K.; Pushparaj, R.R.B.; Shekhar, S.; Bhat, L.; Rice, L. Multistakeholder Participation in Disaster Management—The Case of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadri, A.M.; Ukkusuri, S.V.; Lee, S.; Clawson, R.; Aldrich, D.; Nelson, M.S.; Seipel, J.; Kelly, D. The role of social capital, personal networks, and emergency responders in post-disaster recovery and resilience: a study of rural communities in Indiana. Nat. Hazards 2017, 90, 1377–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Prayag, G.; Orchiston, C.; Spector, S. Postdisaster Social Capital, Adaptive Resilience and Business Performance of Tourism Organizations in Christchurch, New Zealand. J. Travel Res. 2018, 58, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, E.; Tagliazucchi, G.; Marchi, G. The resilient retail entrepreneur: dynamic capabilities for facing natural disasters. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2018, 24, 1222–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, F.H.; Stevens, S.P.; Pfefferbaum, B.; Wyche, K.F.; Pfefferbaum, R.L. Community Resilience as a Metaphor, Theory, Set of Capacities, and Strategy for Disaster Readiness. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2007, 41, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, F. , Ecke, M, & Stanners, D. Building resilience in urban areas: A review of the interconnections between urban planning and ecosystem services. Ecosystem Services 2015, 11, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.W. A Protection Motivation Theory of Fear Appeals and Attitude Change. J. Psychol. 1975, 91, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zomeren, M.; Leach, C.W.; Spears, R. Does group efficacy increase group identification? Resolving their paradoxical relationship. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 46, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, H.; Yasunobu, K. What is Social Capital? A Comprehensive Review of the Concept. Asian J. Soc. Sci. 2009, 37, 480–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsut, C.; Kuran, C.; Kruke, B.I.; Orru, K.; Hansson, S. Linking resilience, vulnerability, social capital and risk awareness for crisis and disaster research. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2021, 30, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.H. Indicators and information systems for sustainable development. 1998.
- Liu, Y.; Lv, X.; Tang, Z. The impact of mortality salience on quantified self behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2021, 180, 110972–110972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, M.L.; Cardona, O.D.; Barbat, A.H. A disaster risk management performance index. Nat. Hazards 2007, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throsby, D. Cultural capital. In Handbook of Cultural Economics, Third Edition. 2020. (pp. 168-173). Edward Elgar Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; da Silva Gabriel, M.L.D.; Patel, V.K. AMOS covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM): Guidelines on its application as a marketing research tool. Rev. Bras. Mark. 2014, 13, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.P.; Azizul, M.F.; Rasidi, M.H.; Said, I. The cultural sustainability of traditional market place in Africa: A new research agenda. J. Rural. Stud. 2018, 62, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Interpretational Confounding of Unobserved Variables in Structural Equation Models. Sociol. Methods Res. 1976, 5, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.J.; Goerdel, H.T.; Lovrich, N.P.; Pierce, J.C. Social capital and emergency management planning: A test of community context effects on formal and informal collaboration. Am. Rev. Public Adm. 2015, 45, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramyar, R.; Ackerman, A.; Johnston, D.M. Adapting cities for climate change through urban green infrastructure planning. Cities 2021, 117, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.R.; Mulaik, S.A.; Brett, J.M. A Tale of Two Methods. Organ. Res. Methods 2006, 9, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J. W. , & Creswell, J. D. Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage Publications. 2017.
- Fetters, M.D.; Curry, L.A.; Creswell, J.W. Achieving Integration in Mixed Methods Designs-Principles and Practices. Heal. Serv. Res. 2013, 48, 2134–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnally, J. Psychometric Theory (Vol. 2). 1978. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Hooper, D. , Coughlan, J., & Mullen, M.. Evaluating the model fits a synthesis of the structural equation modeling literature. In 7th European Conference on Research Methodology for Business and Management Studies. 2008. (pp. 195-200).
- Hulland, J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strategic Management Journal 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raykov, T. Estimation of Composite Reliability for Congeneric Measures. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1997, 21, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raykov, T. Analytic Estimation of Standard Error and Confidence Interval for Scale Reliability. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2002, 37, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, H.A.; Vandenberg, R.J. Integrating managerial perceptions and transformational leadership into a work-unit level model of employee involvement. J. Organ. Behav. 2005, 26, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Tan, T.; Guo, H.; Lu, W.; Yeh, A.G.O.; Xue, F. Role of the Built Environment in the Recovery From COVID-19: Evidence From a GIS-Based Natural Experiment on the City Blocks in Wuhan, China. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunnusi, M. , Hamma-Adama, M., Salman, H. And Kouider, T. COVID-19 pandemic: the effects and prospects in the construction industry. International journal of real estate studies [online], 2020, 14 (Special Issue 2), pages 120-128. Available online: https://www.utm.my/intrest/files/2020/11/2_Final_MS_CRES-Covid-025.pdf.
- Agboola, O.P.; Rasidi, M.H.; Said, I.; Abogan, S.O.; Adejuwon, A.S. Morphological and GIS-based land use Analysis: A Critical Exploration of a Rural Neighborhood. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2018, 2, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicher, S.; Bauld, L. From the ‘Fragile Rationalist’ to ‘Collective Resilience’: What Human Psychology Has Taught Us about the Covid-19 Pandemic and What the Covid-19 Pandemic Has Taught Us about Human Psychology. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2021, 51, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, J.; Rogers, M.B.; Marteau, T.M.; Yardley, L.; Reicher, S.; Stott, C. Re-opening live events and large venues after Covid-19 ‘lockdown’: Behavioural risks and their mitigations. Saf. Sci. 2021, 139, 105243–105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, E.D.; Cordero, M.L. Salir Adelante: Social capital and resilience during the Covid-19 pandemic in Argentina. Heal. Place 2022, 77, 102870–102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, P.T.; Shneiderman, B.; Fleischmann, K.R.; Preece, J.; Qu, Y.; Wu, P.F. Community response grids: E-government, social networks, and effective emergency management. Telecommun. Policy 2007, 31, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrayathi, P.A.; Januraga, P.P.; Pradnyani, P.E.; Gesesew, H.A.; Ward, P.R. Perceived Social Norms as Determinants of Adherence to Public Health Measures Related to COVID-19 in Bali, Indonesia. Front. Public Heal. 2021, 9, 646764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, R.L.; Mah, S.M.; Howell, N.; Larsen, M.M. Social Cohesion and Community Resilience During COVID-19 and Pandemics: A Rapid Scoping Review to Inform the United Nations Research Roadmap for COVID-19 Recovery. Int. J. Heal. Serv. 2021, 51, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, D.P.; Meyer, M.A. Social Capital and Community Resilience. Am. Behav. Sci. 2014, 59, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, S.L.; Barnes, L.; Berry, M.; Burton, C.; Evans, E.; Tate, E.; Webb, J. A place-based model for understanding community resilience to natural disasters. Glob. Environ. Change 2008, 18, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicher, S.; Bauld, L. Considering COVID-19 through the lens of hazard and disaster research. Social Sciences 2021, 10, 248–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comfort, L.; Wisner, B.; Cutter, S.; Pulwarty, R.; Hewitt, K.; Oliversmith, A.; Wiener, J.; Fordham, M.; Peacock, W.; Krimgold, F. Reframing disaster policy: the global evolution of vulnerable communities. Glob. Environ. Chang. Part B: Environ. Hazards 1999, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, N.; Wise, R.M.; Colloff, M.J.; Walker, B.H.; Butler, J.R.A.; Ryan, P.; Norman, C.; Langston, A.; Anderies, J.M.; Gorddard, R.; et al. Building resilient pathways to transformation when “no one is in charge”: insights from Australia’s Murray-Darling Basin. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, O.; Kajita, Y. Influences of Culture in the Built Environment; Assessing Living Convenience in Kabul City. Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.M. COVID, resilience, and the built environment. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2020, 40, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimany, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, S.; Sharifi, A. Community resilience to pandemics: An assessment framework developed based on the review of COVID-19 literature. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 80, 103248–103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, E.; Falana, B.; Solaja, S.; Yakubu, S.; Alabi, O.; Okikiola, B.; Awe, T.; Adesina, B.; Tokula, B.; Kipchumba, A.; et al. Systematic review of climate change impact research in Nigeria: implication for sustainable development. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpham, T.; Grant, E.; Thomas, E. Measuring social capital within health surveys: key issues. Heal. Policy Plan. 2002, 17, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawanson, T.; Foley, L.; Assah, F.; Mogo, E.; Mapa-Tassou, C.; Ogunro, T.; Onifade, V.; Oni, T. The urban environment and leisure physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic: a view from Lagos. Cities Heal. 2020, 5, S204–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, U.; Kohler, N. Resilience in the built environment. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, J.J.; Baicker, K.; Boggio, P.S.; Capraro, V.; Cichocka, A.; Cikara, M.; Crockett, M.J.; Crum, A.J.; Douglas, K.M.; Druckman, J.N.; et al. Using social and behavioural science to support COVID-19 pandemic response. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Song, M. What determines urban resilience against COVID-19: City size or governance capacity? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103304–103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raosoft Inc. RaoSoft Sample Size Calculator. 2004. Available online: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- UNESCO. Socio-economic and cultural impacts of COVID-19 on Africa: what responses from UNESCO? 2020. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000373903.
- Bwire, G.; Ario, A.R.; Eyu, P.; Ocom, F.; Wamala, J.F.; Kusi, K.A.; Ndeketa, L.; Jambo, K.C.; Wanyenze, R.K.; Talisuna, A.O. The COVID-19 pandemic in the African continent. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).