Submitted:
05 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Indicator Selection
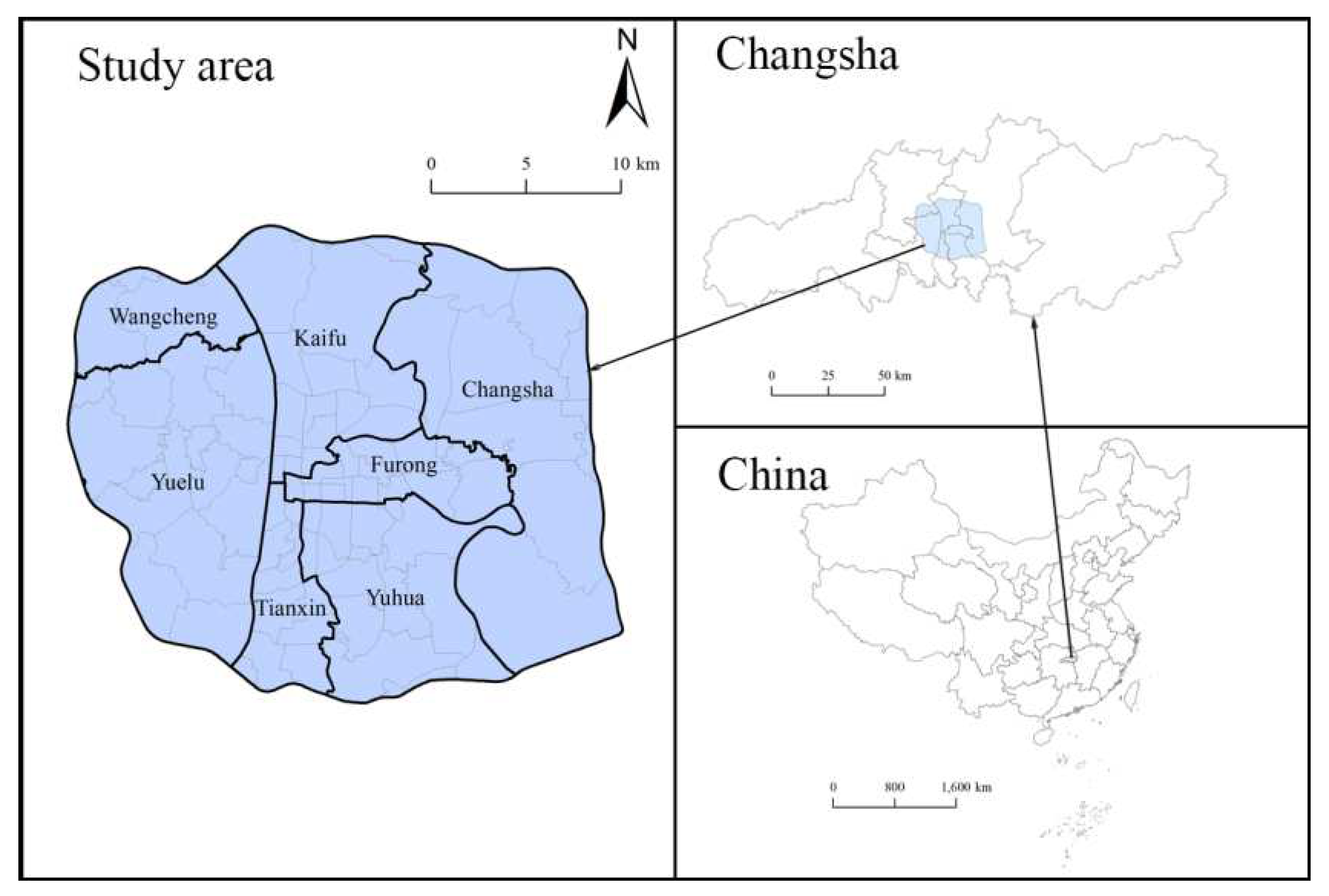
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Selection of Indicators
2.2.1. Indicators of urban vitality
| Theme | Variable | Explanation | 2013 Mean/STD |
2017 Mean/STD |
2021 Mean/STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban vitality | CW | Point density of Weibo check-ins | 1.169/2.088 | 2.062/3.630 | 1.676/2.289 |
| NLI | Night Light Index | 16.213/18.312 | 20.474/43.664 | 56.18/111.71 |
2.2.2. Influencing elements of urban vitality
3. Methodology
3.1. Entropy Weight Method
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
3.2.1. Global spatial autocorrelation
3.2.2. Local spatial autocorrelation
3.3. Geodetector model
3.4. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression
4. Characteristics of Urban vitality Evolution in Changsha
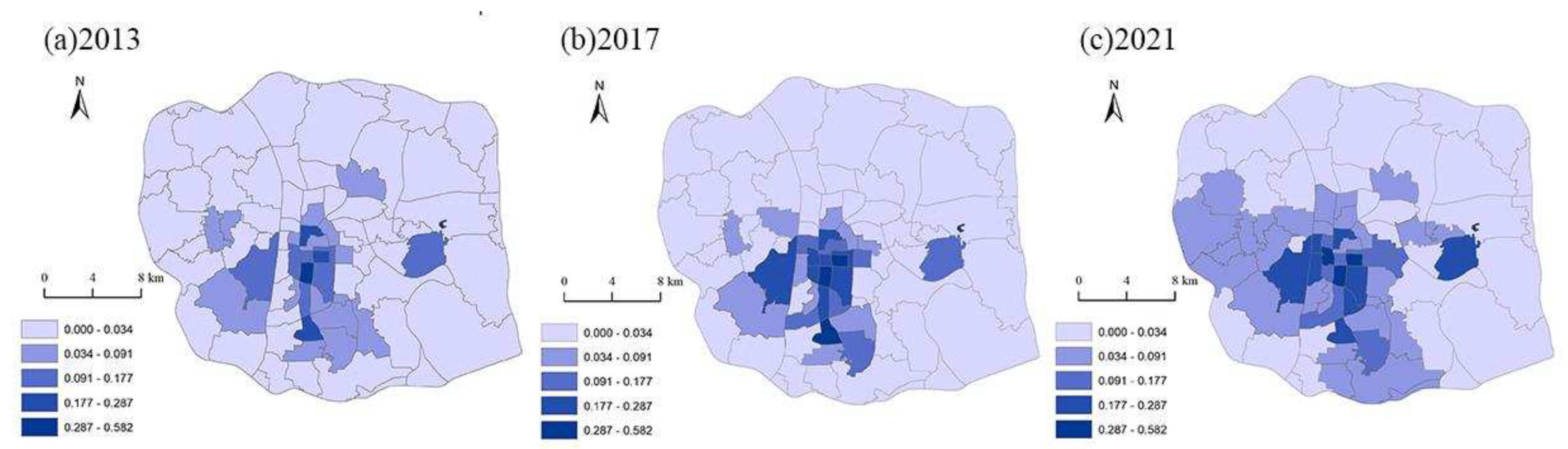
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Changes in Urban vitality
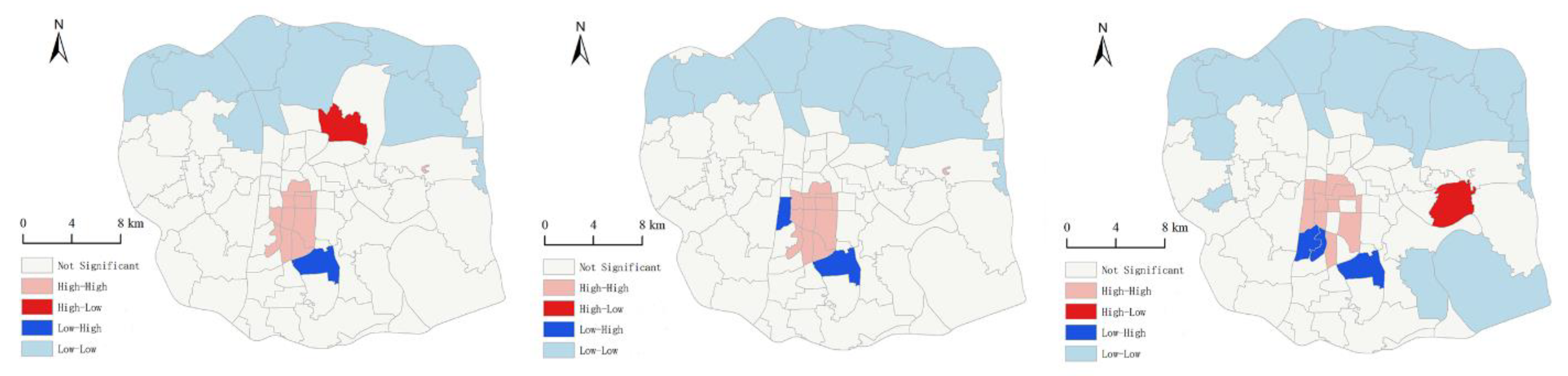
4.2. Spatial Clustering Characteristics and Changes in Urban vitality
5. An analysis of the driving factors of urban vitality within the subdistrict space
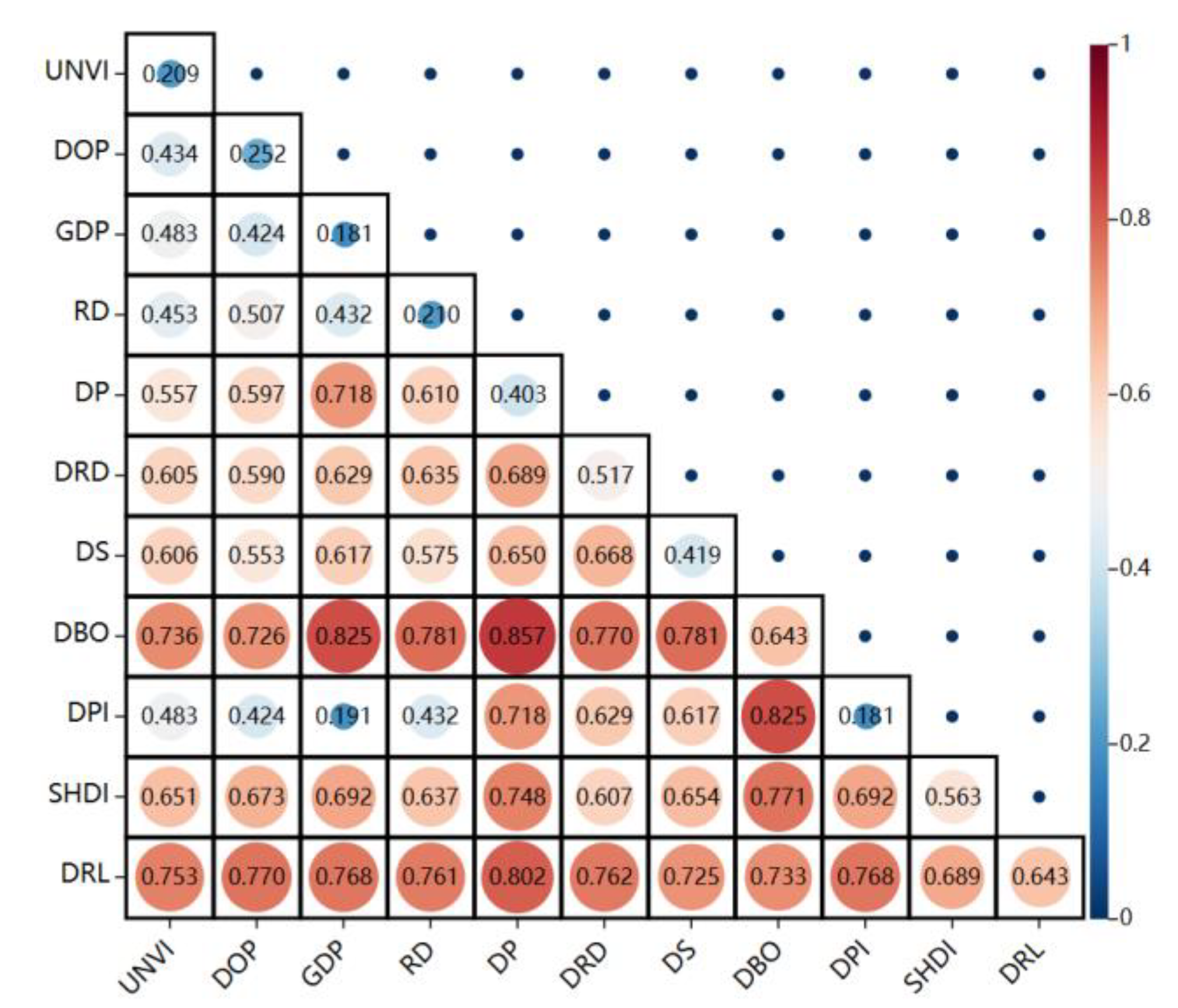
5.1. Geodetection results of driving factors
5.2. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity in spatial driving factors of subdistricts
5.2.1. Model Diagnostics and Validity Estimation Impact Analysis
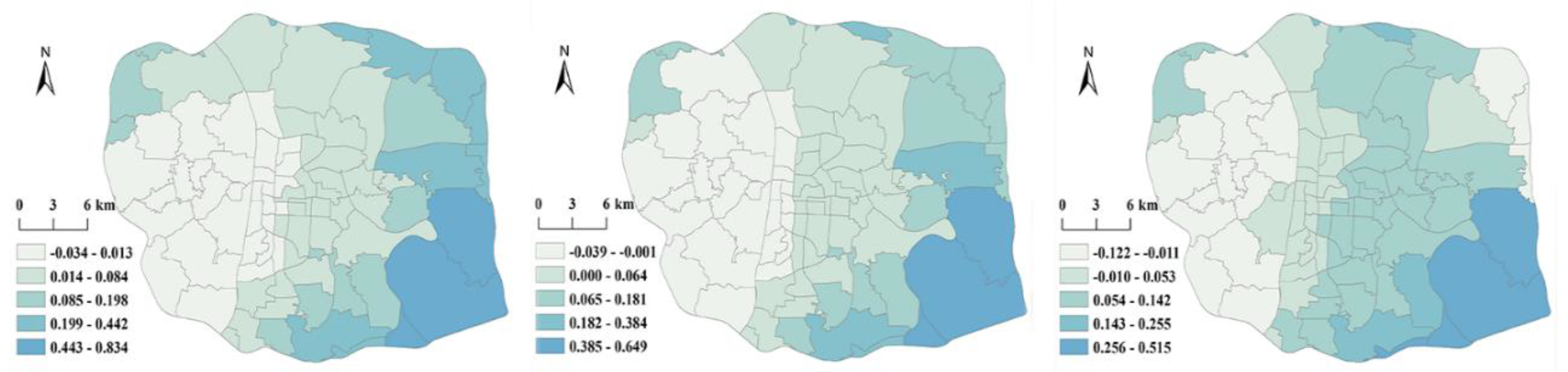
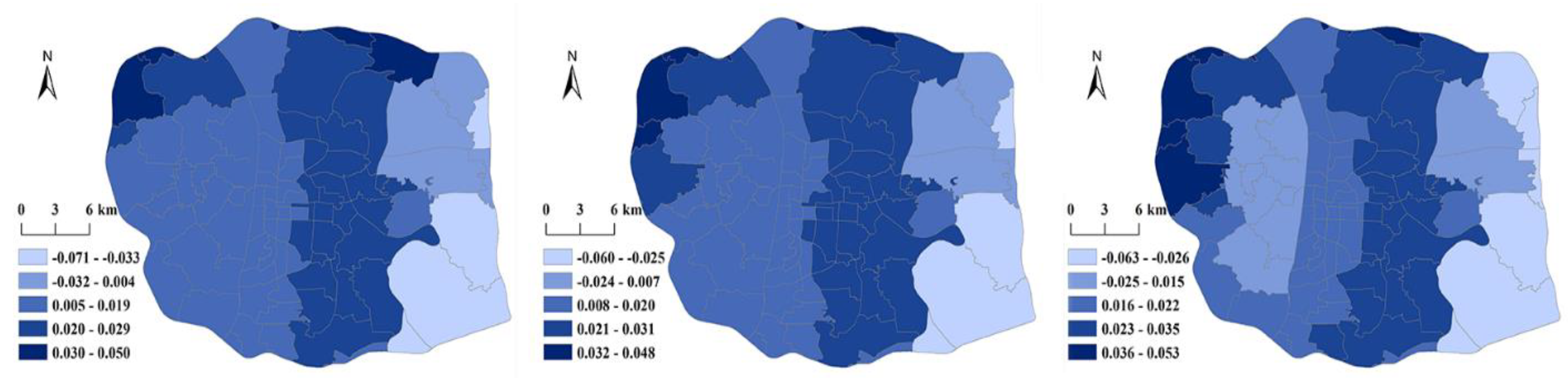
5.2.2. Spatial and Temporal Differences in the Impact of Subdistrict Morphology Aspects
5.2.3. Spatial and Temporal Differences in the Impact of Functional Aspects of the Subdistrict.
6. Discussion
6.1. Policy implications
6.2. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, H.W.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Song, Y.; Sun, B.; Hong, J. Neighborhood sustainability in urban renewal: An assessment framework. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2017, 44, 903–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shach-Pinsly, D.; Bindreiter, S.; Porat, I.; Sussman, S.; Forster, J.; Rinnerthaler, M. Multiparametric analysis of urban environmental quality for estimating neighborhood renewal alternatives. Urban Planning, 2021, 6, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Long, Y. Measuring visual quality of street space and its temporal variation: Methodology and its application in the Hutong area in Beijing. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2019, 191, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Schmid, C. Towards a new epistemology of the urban? City 2015, 19, 151–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Varo, I.; Delclòs-Alió, X.; Miralles-Guasch, C. Jane Jacobs reloaded: A contemporary operationalization of urban vitality in a district in Barcelona. Cities 2022, 123, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.D. Effects of the human and built environment on neighborhood vitality: Evidence from Seoul, Korea, using mobile phone data. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2020, 146, 05020024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, T.; Zhou, L.; Hijazi, I.H. The six dimensions of the built environment on urban vitality: Fusion evidence from multi-source data. Cities, 2022, 121, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Yeh, A.G.O.; Zhang, A. Analyzing spatial relationships between urban land use intensity and urban vitality at street block level: A case study of five Chinese megacities. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2020, 193, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Shu, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, R. Exploring the spatiotemporal patterns and correlates of urban vitality: Temporal and spatial heterogeneity. Sustainable Cities and Society 2023, 91, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Chu, J.; Xia, C. How can the urban landscape affect urban vitality at the street block level? A case study of 15 metropolises in China. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2021, 48, 1245–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.N.; Camanho, A.S. Public green space use and consequences on urban vitality: An assessment of European cities. Social Indicators Research, 2013, 113, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.L. Seoul's Wi-Fi hotspots: Wi-Fi access points as an indicator of urban vitality. Computers, Environment, and Urban Systems 2018, 72, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Duke, Y. High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ye, Y.; Gao, F.; Ye, X. Using street view images to examine the association between human perceptions of locale and urban vitality in Shenzhen, China. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2023, 88, 104291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kang, J.E. Impact of particulate matter and urban spatial characteristics on urban vitality using spatiotemporal big data. Cities, 2022, 131, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y. The relationship between urban vibrancy and the built environment: An empirical study from an emerging city in an Arid Region. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2021, 18, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, A. How Diversity and Accessibility Affect Street Vitality in Historic Districts? Land, 2023, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Liu, C.; Mu, T.; Xu, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, G. Spatiotemporal fluctuations in urban park urban vitality determined by on-site observation and behavior mapping: A case study of three parks in Zhengzhou City, China. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2021, 64, 127246. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Duan, J.; Luo, M.; Zhan, H.; Liu, M.; Peng, W. How did the built environment affect urban vitality in urban waterfronts? A case study in Nanjing Reach of Yangtze River. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2021, 10, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung. H.; Lee, S. Residential built environment and walking activity: Empirical evidence of Jane Jacobs’ urban vitality. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2015, 41, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, P. Urban Shrinkage and Urban Vitality Correlation Research in the Three Northeastern Provinces of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue W, Chen Y, Thy P T M, et al. Identifying urban vitality in metropolitan areas of developing countries from a comparative perspective: Ho Chi Minh City versus Shanghai. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 65, 102609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paköz, M.Z.; Yaratgan, D.; Şahin, A. Re-mapping urban vitality through Jane Jacobs’ criteria: The case of Kayseri, Turkey. Land Use Policy, 2022, 114, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chodron Drolma, S.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, J.; Ni, T. An investigation of the visual features of urban street vitality using a convolutional neural network. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2020, 23, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y. Characteristic Vibrant District Construction--An Important Strategy for Urban Renewal. Journal of Urban Planning, 2016, 232, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pipa, H.; de Brito, J. , Oliveira Cruz, C. Sustainable rehabilitation of historical urban areas: Portuguese case of the urban rehabilitation societies. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2017, 143, 05016011. [Google Scholar]
- Paköz, M.Z.; Işık, M. Rethinking urban density, vitality and healthy environment in the post-pandemic city: The case of Istanbul. Cities, 2022, 124, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoch, M.; Monsuur, F.; Palaiologou, G.; Quddus, M.A.; Ellis-Chadwick, F.; Morton, C.; Rayner, R. When COVID-19 came to town: Measuring the impact of the coronavirus pandemic on footfall on six high streets in England. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2022, 49, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkazei, A.; Matsubara, K. Post-conflict reconstruction and the decline of urban vitality in Downtown Beirut. International Planning Studies, 2021, 26, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yang, C.; Quan, L.; Liao, L. A new insight into understanding urban vitality: A case study in the Chengdu-Chongqing area twin-city economic circle, China. Sustainability, 2021, 13, 10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikirya, B.; He, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, C. Urban food takeaway vitality: a new technique to assess urban vitality. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, M.; Ye, Y. Measuring urban nighttime vitality and its relationship with urban spatial structure: A data-driven approach. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2023, 50, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathansohn, R.; Lahat, L. From urban vitality to urban vitalization: Trust, distrust, and citizenship regimes in a Smart City initiative. Cities, 2022, 131, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dong, B.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of urban vitality and urban density on innovation: Evidence from China's Greater Bay Area. Habitat International 2022, 119, 102490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Qi, J.; Li, S. Investigating the spatiotemporal pattern of urban vibrancy and its determinants: Spatial big data analyses in Beijing, China. Land use policy, 2022, 119, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving mechanism of urbanization in small cities: A case study from Guangxi. Land, 2022, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuofu, H.; Qingyun, H.; Xiao, O. The Capitalization Effect of Natural Amenities on Housing Price in Urban China: New Evidence From Changsha. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10, 833831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Qin, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K. Analysis of Urban Park Accessibility Based on Space Syntax: Take the Urban Area of Changsha City as an Example. Land 2023, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, F. Effect of human settlements on the urban thermal environment and factor analysis based on multi-source data: A case study of Changsha city. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2021, 31, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zheng, B.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, N. The Changsha Historic Urban Area: A Study on the Changing Accessibility of the Road Network. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Y. Investigating the spatiotemporal pattern between the built environment and urban vibrancy using big data in Shenzhen, China. Computers, Environment, and Urban Systems 2022, 95, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Guan, P.; Ren, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, N. The cause and evolution of urban street vitality under the time dimension: Nine cases of streets in Nanjing City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ye, X.; Ren, F.; Du, Q. Check-in behavior and spatio-temporal vibrancy: An exploratory analysis in Shenzhen, China. Cities, 2018, 77, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Wan, W.; Cervantes, O.; Gwiazdzinski, L. Using location-based social media data to observe check-in behavior and gender difference: Bringing Weibo data into play. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hui, E.C.M.; Lang, W.; Tao, L. People, recreational facility and physical activity: New-type urbanization planning for the healthy communities in China. Habitat International, 2016, 58, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, S.; Xiao, T.; Hemminger, B.M.; Yang, S. Global science discussed in local altmetrics: Weibo and its comparison with Twitter. Journal of Informetrics 2017, 11, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Long, Y.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, J. Evaluating cities' vitality and identifying ghost cities in China with emerging geographical data. Cities, 2017, 63, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.J.; Yao, Y. Accurate estimation of the proportion of mixed land use at the street-block level by integrating high spatial resolution images and geospatial big data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59, 6357–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H. Optimisation of building and road network densities in terms of variation in plot sizes and shapes. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2021, 48, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilford, R.J.; Oyebode, O.; Satterthwaite, D.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; Chen, Y.F.; Mberu, B.; Watson, I.S.; Sartori, J.; Ndugwa, R.; Caiaffa, P.W.; Haregu, T.; Capon, P.A.; Saith, R.; Ezeh, A. Improving the health and welfare of people who live in slums. The Lancet, 2017, 389, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégué, A.; Vintrou, E.; Ruelland, D.; Claden, M.; Dessay, N. Can a 25-year trend in Soudano-Sahelian vegetation dynamics be interpreted in terms of land use change? A remote sensing approach. Global environmental change, 2011, 21, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Mauricio, D.J. Análisis temporal del NDVI del humedal de Purrumpampa en Huamachuco y su relación con la expansión urbana. Revista Geográfica de América Central, 2023, 70, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemp, S.; Stauffacher, M.; Lang, D.J.; Scholz, R.W. Classifying railway stations for strategic transport and land use planning: Context matters! Journal of transport geography, 2011, 19, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Liu, S.; Lai. S. Q.; Liu, C.; Jiang, L. What influenced the vitality of the waterfront open space? A case study of Huangpu River in Shanghai, China. Cities 2021, 114, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, A. The contribution of local parks to neighborhood social ties. Landscape and urban planning, 2013, 109, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pei, T.; Wang, W.; Guo, S.; Song, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, C. Roles of locational factors in the rise and fall of restaurants: A case study of Beijing with POI data. Cities, 2021, 113, 103185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Sobolevsky, S.; Bautista Hobin, J.N.; Ratti, C.; Blat, J. Urban association rules: uncovering linked trips for shopping behavior. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2018, 45, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, J.; Bernhardt, T.; De Montigny, L. Computer-simulated pedestrian behavior in shopping environment. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2005, 131, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Lo, S.M. Events as community function of shopping centers: A case study of Hong Kong. Cities, 2018, 72, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celińska-Janowicz, D.; Smętkowski, M.; Wojnar, K. Behavioural Aspects of Office Space Structures in the City: The Case of Warsaw’s Business Districts. Urban Planning 2021, 6, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobker, S.; Grotz, R. Everyday mobility of elderly people in different urban settings: The example of the city of Bonn, Germany. Urban Studies, 2006, 43, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Chen, S.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J. The influence of Community Sports Parks on residents’ subjective well-being: A case study of Zhuhai City, China. Habitat International, 2021, 117, 102439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. The influence of state policy and proximity to medical services on health outcomes. Journal of Urban Economics, 2014, 80, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indaco, A. From Twitter to GDP: Estimating economic activity from social media. Regional Science and Urban Economics 2020, 85, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansel, D. Local decentralization and local economic growth: A cross-sectional examination of US metropolitan areas. Journal of Urban Economics, 2005, 57, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Zhu, T.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q. Exploring metro vibrancy and its relationship with built environment: a cross-city comparison using multi-source urban data. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2022, 25, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, J.; Pei, X. Measurement Method and Influencing Mechanism of Urban Subdistrict Vitality in Shanghai Based on Multisource Data. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; L., Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Coupling relationship between urbanization and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt and its socio-ecological driving forces: A county-level perspective. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 146, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, A.; Ni, Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of rural settlements in low hilly region—A case study of 17 cities in Hubei Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gong, Z. Spatiotemporal characteristics of urban air quality in China and geographic detection of their determinants. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2018, 28, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Al Kindi, A.; Al-Said, A.; Al-Said, A.; Atkinson, P. Sociodemographic determinants of COVID-19 incidence rates in Oman: Geospatial modeling using multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Sustainable cities and society, 2021, 65, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Exploring the spatial and temporal driving mechanisms of landscape patterns on habitat quality in a city undergoing rapid urbanization based on GTWR and MGWR: The case of Nanjing, China. Ecological Indicators 2022, 143, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. Analysis on land ecological security change and affect factors using RS and GWR in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area, China. Applied Geography, 2019, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, G.; Tang, C.; Fan, S.; Guo, X. The spatial organization pattern of urban-rural integration in urban agglomerations in China: An agglomeration-diffusion analysis of the population and firms. Habitat International, 2019, 87, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Qiu, H. Using urban landscape pattern to understand and evaluate infectious disease risk. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2021, 62, 127126. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, D. Optimizing road network density considering automobile traffic efficiency: Theoretical approach. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2022, 148, 04021062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanis, A.; Botzoris, G.; Eliou, N. Pedestrian road safety in relation to urban road type and traffic flow. Transportation research procedia 2017, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xiang, L.; Gong, J. Updating road networks by local renewal from GPS trajectories. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2016, 5, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, T.; Van de Voorde, T. Are social media data and survey data consistent in measuring park visitation, park satisfaction, and their driving factors? A case study in Shanghai. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2023, 81, 127869. [Google Scholar]
- Chiesura, A. The role of urban parks for the sustainable city. Landscape and urban planning, 2004, 68, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F. Greener urbanization? Changing accessibility to parks in China. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2017, 157, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Kellar, I.; Conner, M.; Gidlow, C.; Kelly, B.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; McEachan, R. Associations between park features, park satisfaction, and park use in a multi-ethnic deprived urban area. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening 2019, 46, 126485. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, B.K.L.; Jim, C.Y. Linking park users' socio-demographic characteristics and visit-related preferences to improve urban parks. Cities 2019, 92, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminani-Ghasrodashti, R. , Hamidi, S. Online shopping as a substitute or complement to in-store shopping trips in Iran? Cities, 2020, 103, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z. The geography of online shopping in China and its key drivers. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2022, 49, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Cao, X.; Zhen, F. How does same-day-delivery online shopping reshape social interactions among neighbors in Nanjing? Cities, 2021, 114, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.A.; Ponce, H.R. Personality traits influencing young adults' conspicuous consumption. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 2021, 45, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal Incera, A.; Kitsos, A.; Posada, D.G. Universities, students and regional economies: a symbiotic relationship? Regional Studies 2022, 56, 892–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wash, P.M.; Omar, S.I.; Mohamed, B.; Isa, M.I. Recreation as a Social Factor in Urban Development: A Response to Covid-19 Pandemic in Greater Jos, Nigeria. International Journal of Built Environment and Sustainability, 2022, 9, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Chen, L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, X. How effective is a traffic control policy in blocking the spread of COVID-19? A case study of Changsha, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19, 7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaraguruparan, S.V.; Ramaraj, A.; Venkatavaradan, S. A Review on Office Space Management Post Pandemic COVID-19. International Journal of Built Environment and Sustainability, 2022, 9, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Sohn, D.W. An analysis of the relationship between land use density of office buildings and urban street configuration: Case studies of two areas in Seoul by space syntax analysis. Cities, 2002, 19, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Theme | Variable | Explanation | 2013 Mean/STD |
2017 Mean/STD |
2021 Mean/STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdistrict Form | SHDI | Shannon's Diversity Index | 0.373/0.400 | 0.500/0.402 | 1.012/0.449 |
| RD | Road density | 2.880/2.209 | 5.003/2.702 | 6.849/3.943 | |
| UNVI | Urban Normalized Vegetation Index | 4455.808/1462.664 | 5391.162/1344.464 | 5574.558/1327.430 | |
| MSD | Metro station density | -/- | 0.881/2.566 | 1.240/2.547 | |
| NH | Neighborhood hydrophilic | 0.701/0.482 | 0.736/0.508 | 0.806/0.522 | |
| Subdistrict Function | DP | The density of park facilities | 0.820/1.746 | 2.711/4.629 | 6.849/3.943 |
| DRD | Dining room density | 25.256/42.980 | 142.550/187.261 | 1.012/0.449 | |
| DS | The density of shopping facilities | 56.383/100.326 | 250.027/281.288 | 3.406/5.036 | |
| DBO | The density of business office facilities | 30.205/89.556 | 104.054/196.502 | 197.486/273.150 | |
| DRL | The density of recreational and leisure facilities | 8.047/14.820 | 20.553/33.906 | 125.612/168.580 | |
| DH | The density of health facilities | 3.179/3.769 | 5.546/4.953 | 7.206/5.320 | |
| Subdistrict Economy | GDP | Gross Domestic Product | 810.971/251.924 | 1153.451/295.777 | 1520.181/445.961 |
| DPI | Disposable personal income | 3.263/0.462 | 4.666/0.498 | 6.400/0.562 | |
| DOP | The density of the resident population | 4.592/3.964 | 4.325/3.326 | 4.546/2.787 |
| code | Geodetector factor | q-value | p-value | significance | sort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | SHDI | 0.563 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 3 |
| X2 | RD | 0.497 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 5 |
| X3 | UNVI | 0.209 | 0.031 | 0.05% | - |
| X4 | DP | 0.403 | 0.002 | 0.01% | 7 |
| X5 | DRD | 0.517 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 4 |
| X6 | DS | 0.419 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 6 |
| X7 | DBO | 0.642 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 2 |
| X8 | DRL | 0.643 | 0.000 | 0.01% | 1 |
| X9 | DH | 0.357 | 0.051 | 0.05% | - |
| X10 | GDP | 0.181 | 0.042 | - | - |
| X11 | DPI | 0.181 | 0.042 | 0.05% | - |
| X12 | DOP | 0.252 | 0.008 | 0.01% | - |
| X13 | MSD | 0.285 | 0.255 | - | - |
| X14 | NH | 0.058 | 0.774 | - | - |
| covariance test | Modified covariance test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| variant | VIF value | variant | VIF value |
| DRL | 8.793 | DRL | 4.579 |
| DBO | 2.110 | DBO | 1.797 |
| SHDI | 1.903 | SHDI | 1.802 |
| DRD | 14.283 | RD | 1.452 |
| RD | 1.469 | DS | 3.418 |
| DS | 4.443 | DP | 2.843 |
| DP | 2.861 |
| OLS | TWR | GWR | GTWR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.588 | 0.614 | 0.668 | 0.681 |
| R2Adjusted | 0.577 | 0.604 | 0.631 | 0.672 |
| AICc | 490.830 | -668.756 | 477.808 | 1579.8 |
| 2013 | 2017 | 2021 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | mean | STD | min | max | mean | STD | min | max | mean | STD | ||
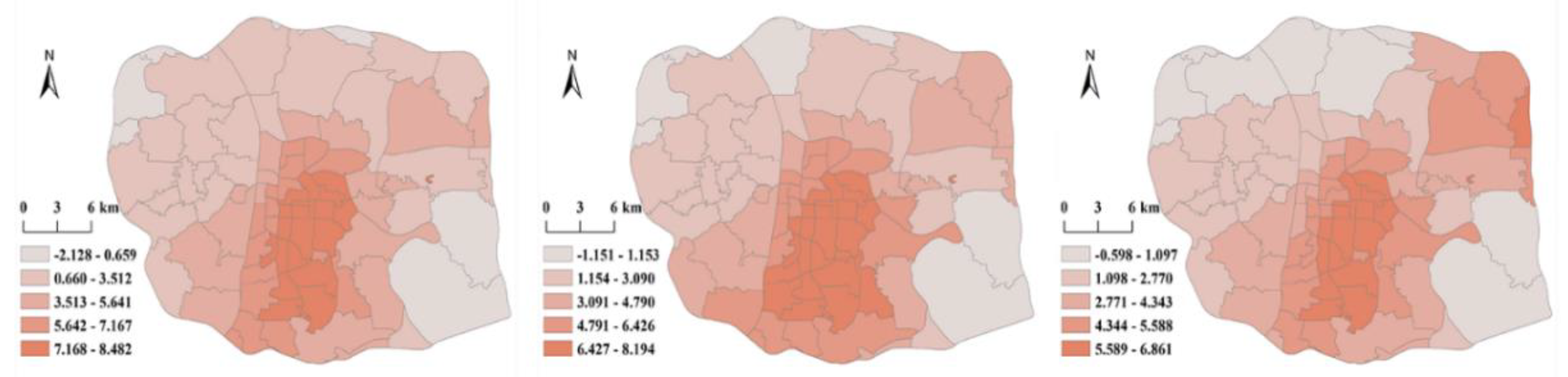
| subdistrict form | SHDI | -2.128 | 0.620 | 4.824 | 2.618 | -1.151 | 8.194 | 4.585 | 2.412 | -0.598 | 6.861 | 3.718 | 2.021 |
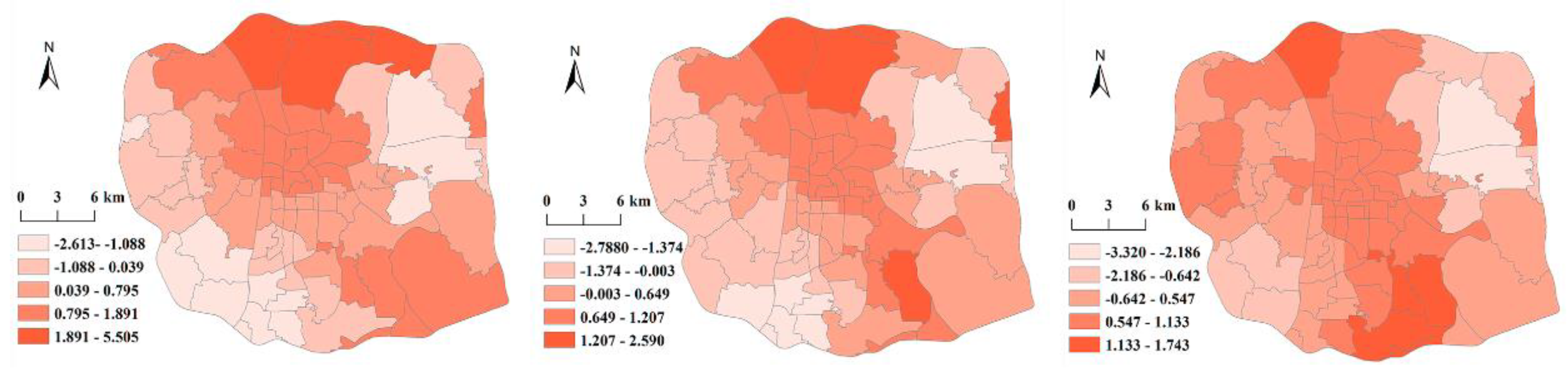
| RD | -1.179 | 0.620 | -0.424 | 0.439 | -1.291 | 0.460 | -0.428 | 0.428 | -0.984 | 0.486 | 3.718 | 0.337 | |
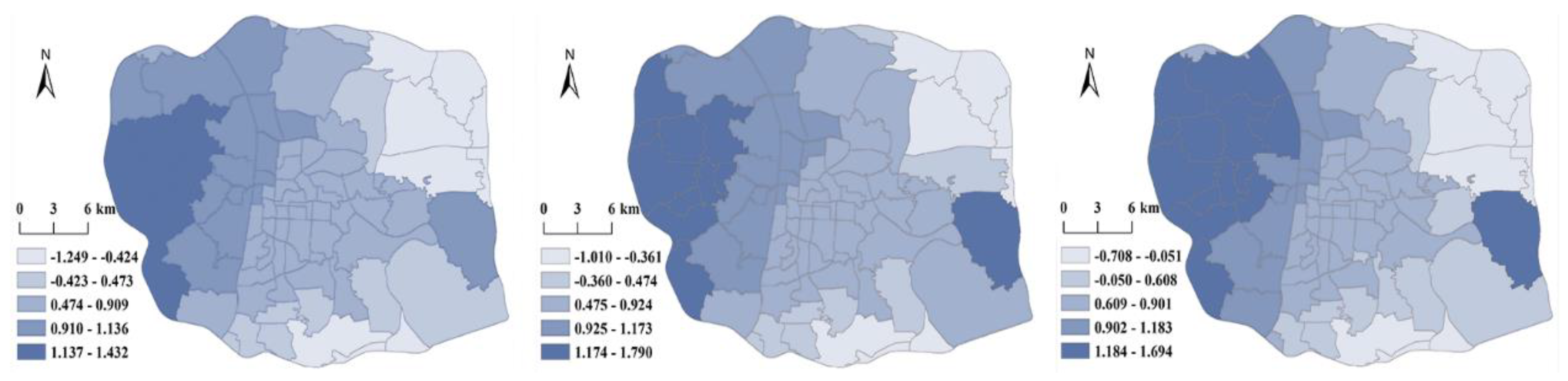
| subdistrict function | DP | -1.249 | 1.432 | 0.665 | 0.560 | -1.010 | 1.790 | 0.751 | 0.528 | -0.708 | 1.694 | 0.750 | 0.531 |
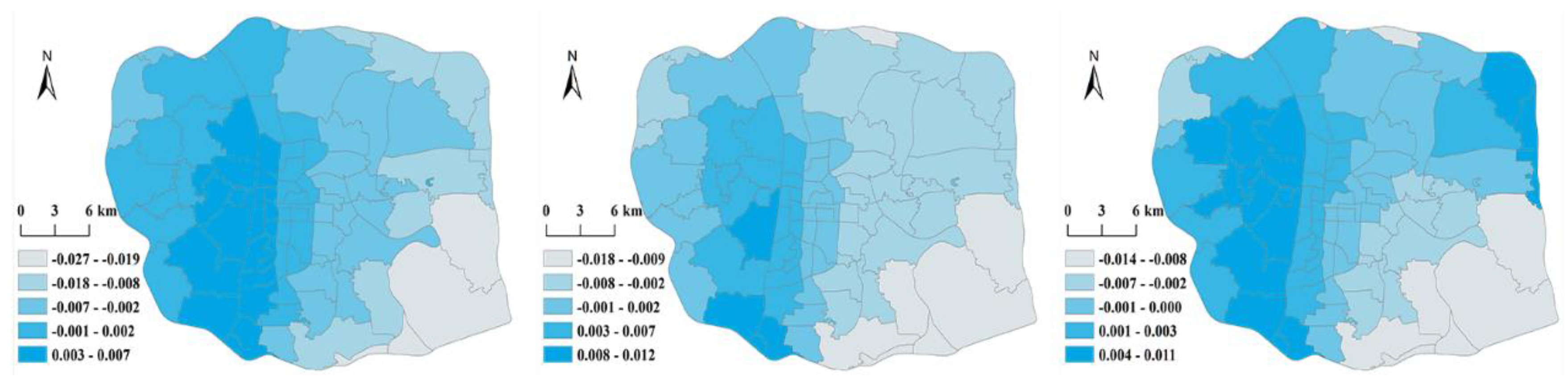
| DS | -0.027 | 0.007 | -0.002 | -0.002 | -0.018 | 0.012 | -0.001 | 0.006 | -0.014 | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.004 | |
| DRL | 0.084 | 0.834 | 0.084 | 0.084 | -0.039 | 0.649 | 0.058 | 0.132 | -0.122 | 0.515 | 0.063 | 0.108 | |
| DBO | -0.071 | 0.050 | 0.015 | 0.018 | -0.060 | 0.048 | 0.018 | 0.016 | -0.063 | 0.053 | 0.018 | 0.020 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




