Submitted:
05 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Preparation of organo clay
2.2.2. Preparation of melamine formaldehyde pre polymer (MF) and hybrid composites
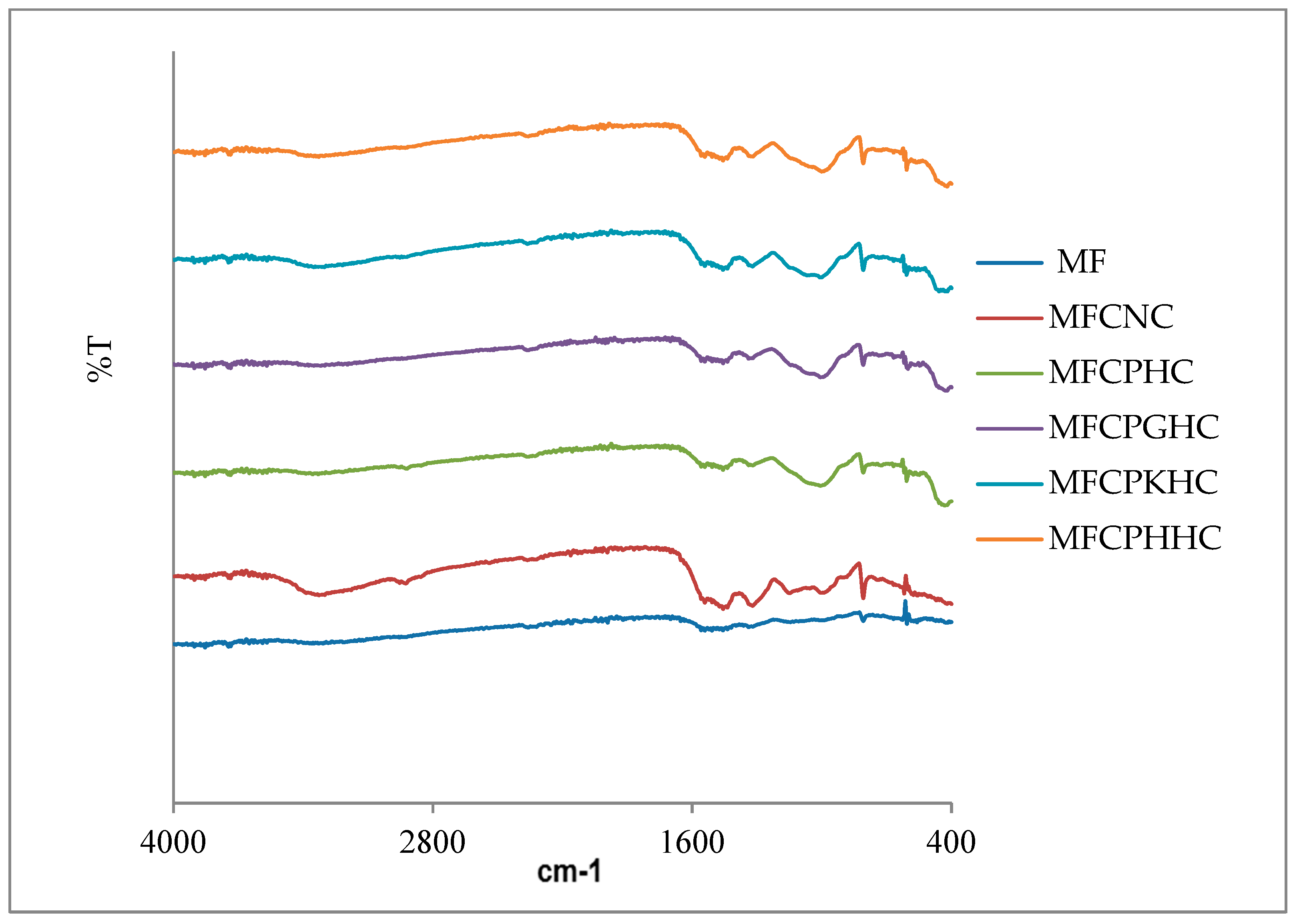
2.2.3. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis
2.2.4. X-ray powder diffraction spectroscopy (XRD) analysis
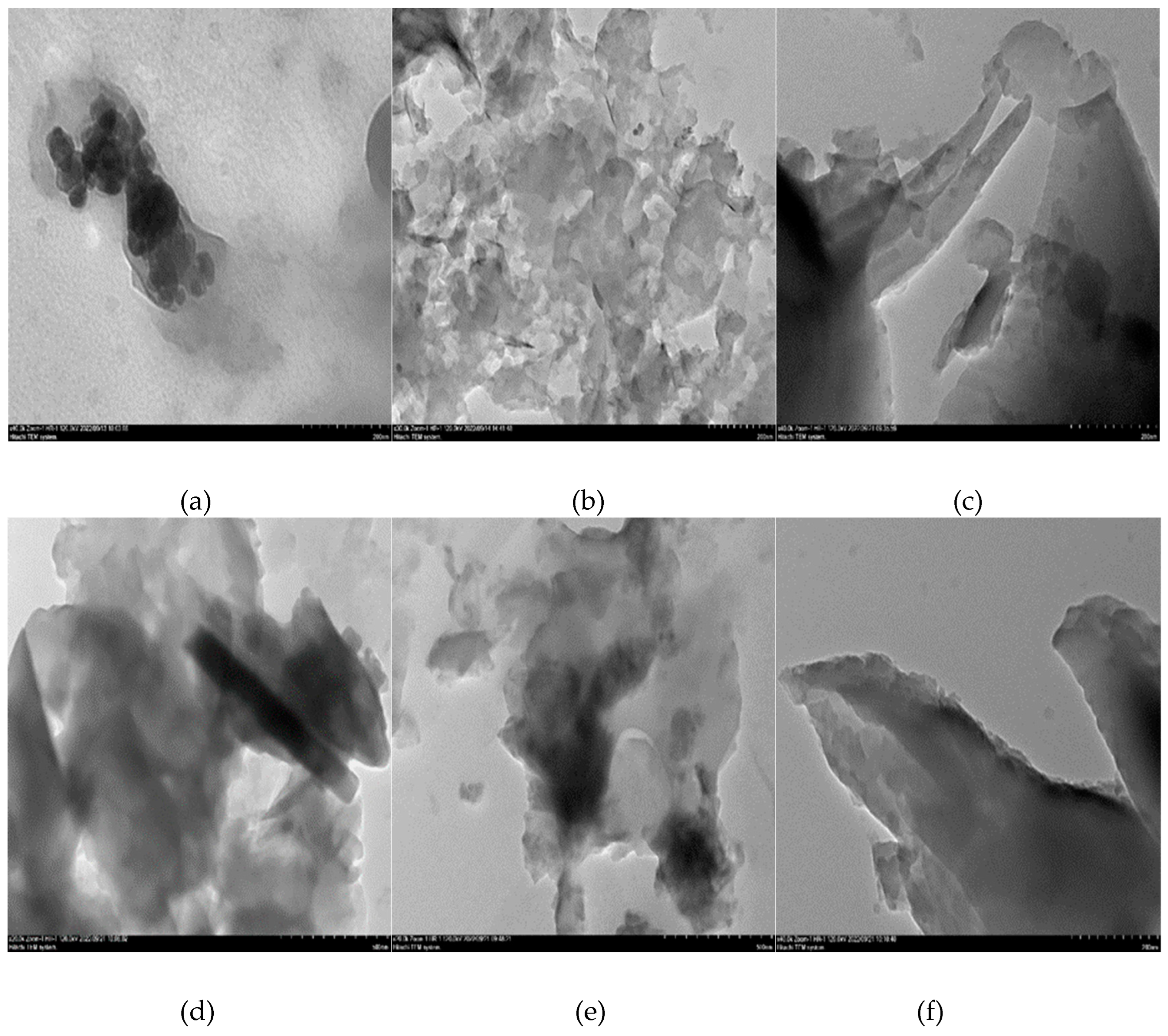
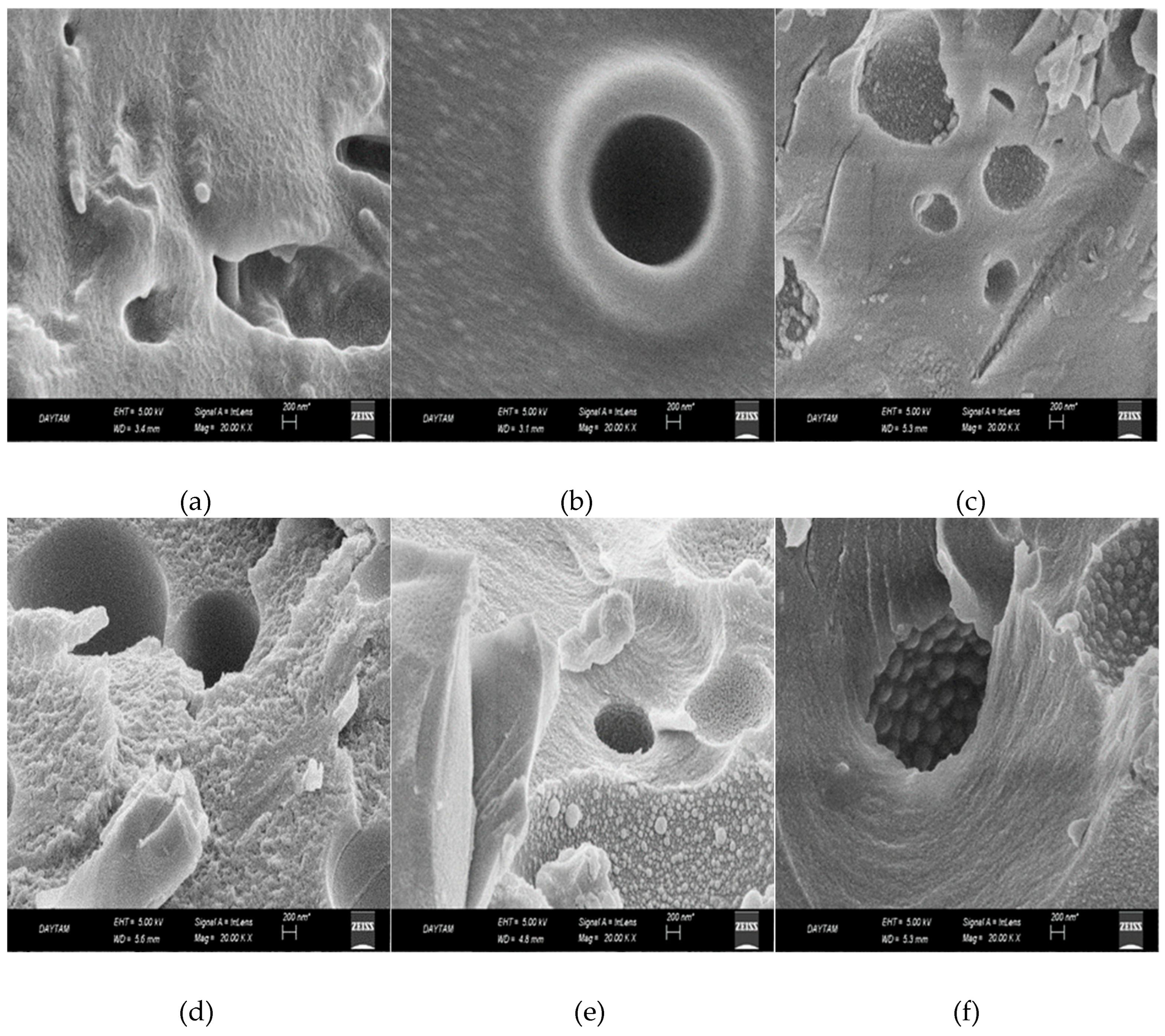
2.2.5. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
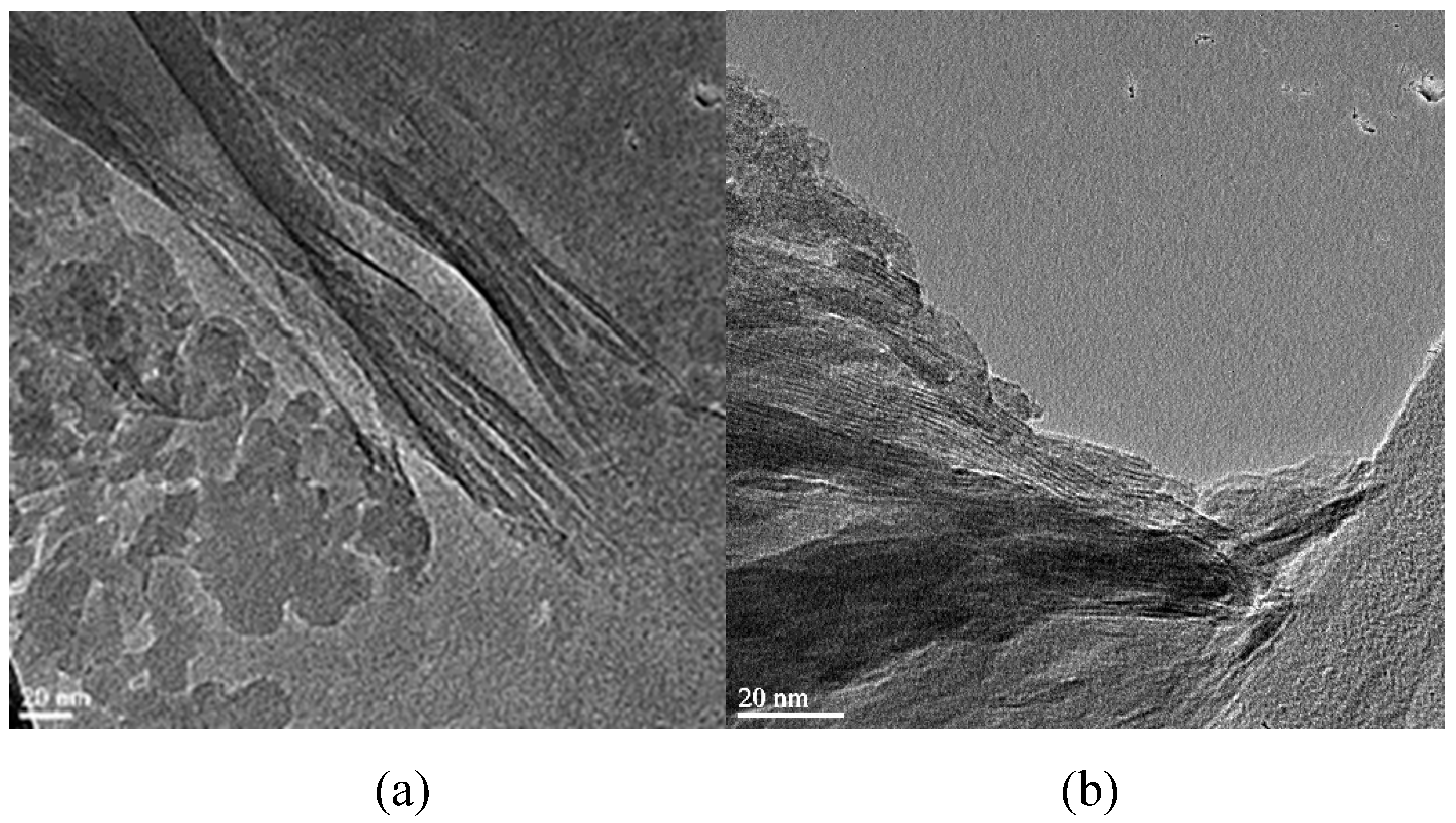
2.2.6. High resolution transmittance electron microscopy (HRTEM) analysis
2.2.7. Mechanical tests and thermal conductivity measurements
3. Results
3.1. Textural characterization of raw montmorillonite (MMT), organo-montmorillonite (OMMT), melamine formaldehyde resin (MF), melamine formaldehyde orgono clay nanocomposite (MFCNC) and hybrid composites
3.2. Surface morphological characterization of melamine formaldehyde resin (MF), melamine formaldehyde orgono clay nanocomposite (MFCNC) and hybrid composites
3.3. Analysis of FT-IR Spectra of raw montmorillonite (MMT), organo-montmorillonite (OMMT), melamine formaldehyde resin (MF), melamine formaldehyde organo-clay nanocomposite (MFCNC) and hybrid composites
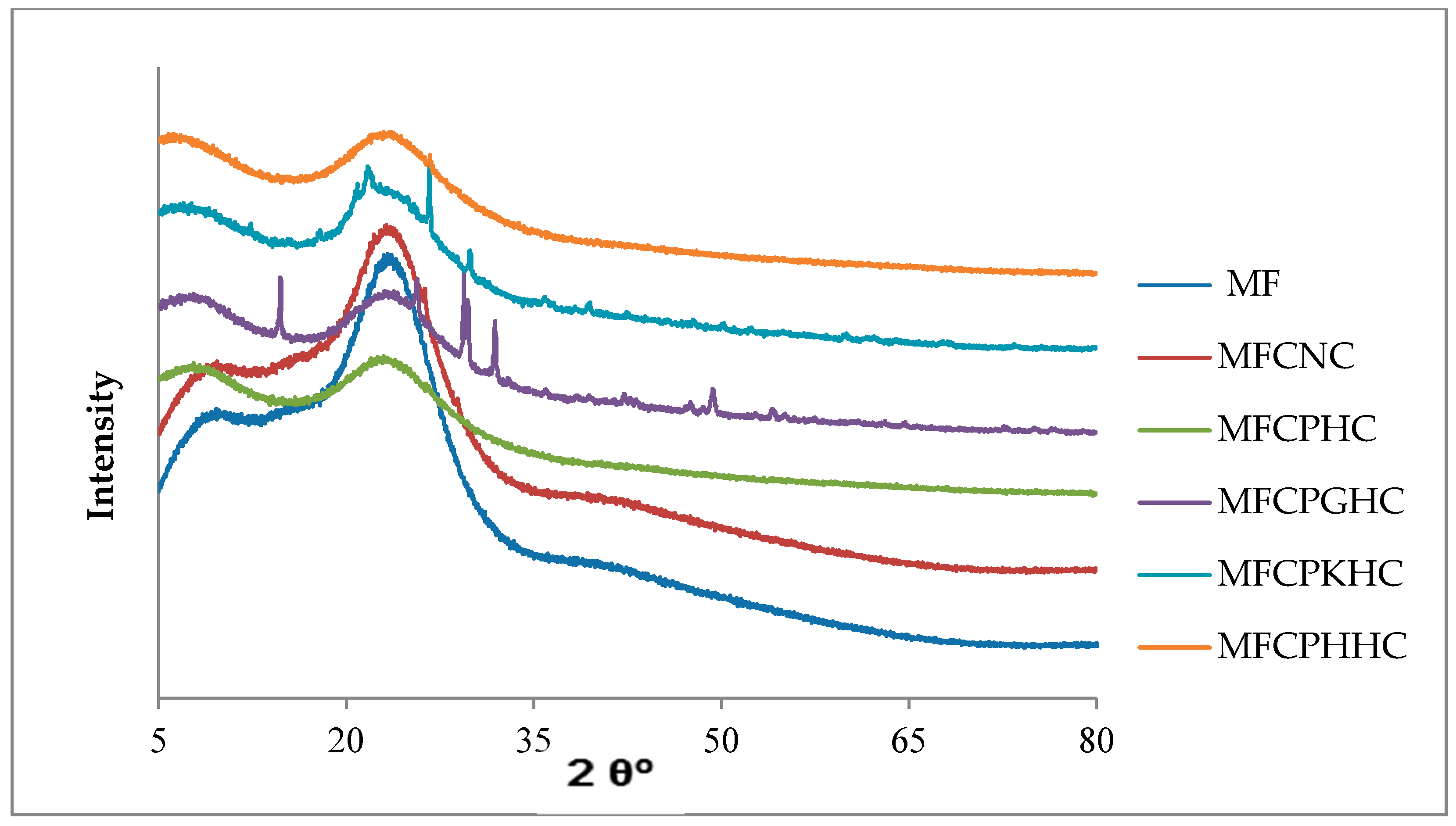
3.4. Characterization of mineralogical structures of raw montmorillonite (MMT), organo-montmorillonite (OMMT), melamine formaldehyde resin (MF), melamine formaldehyde orgono-clay nanocomposite (MFCNC) and hybrid composites
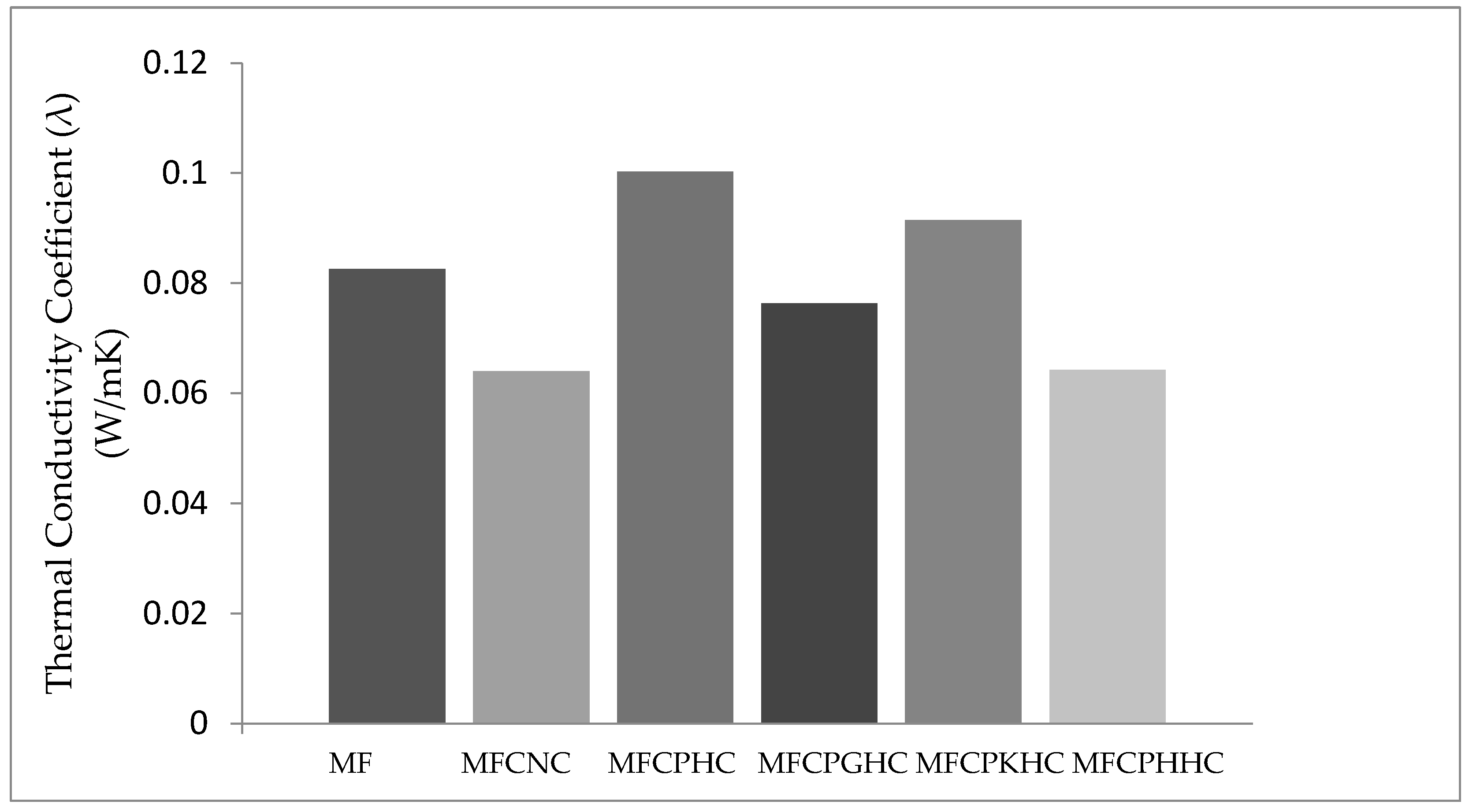
3.5. Thermal conductivities of raw montmorillonite (MMT), organo-montmorillonite (OMMT), melamine formaldehyde resin (MF), melamine formaldehyde orgono-clay nanocomposite (MFCNC) and various hybrid composites
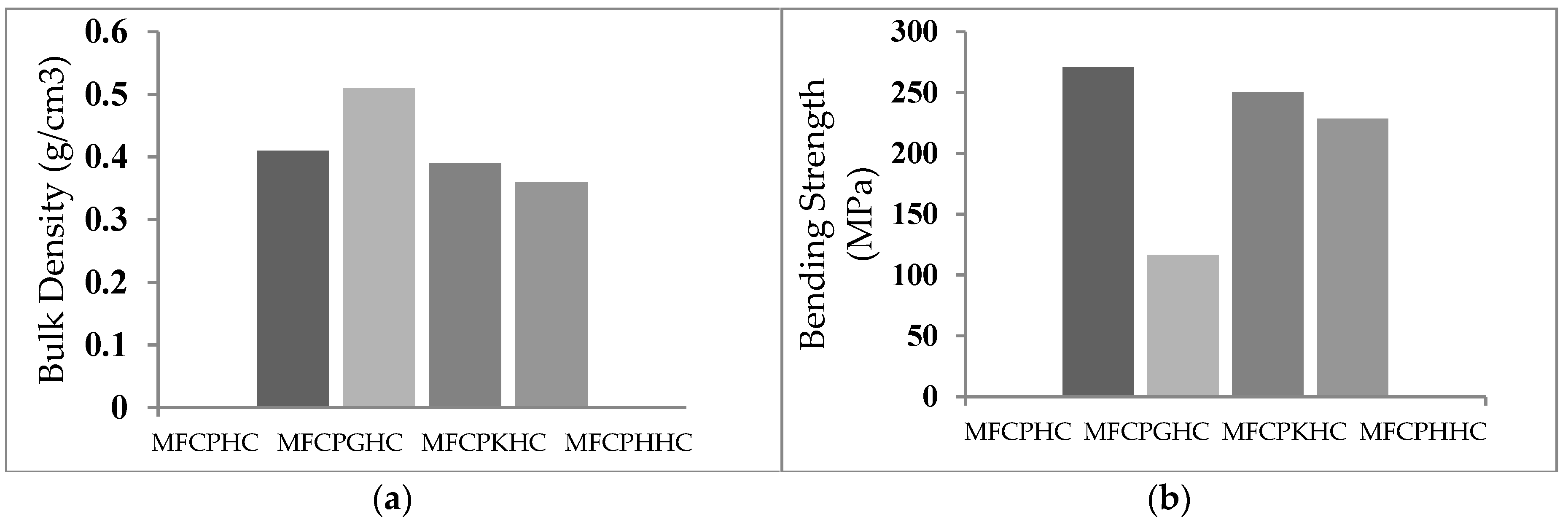
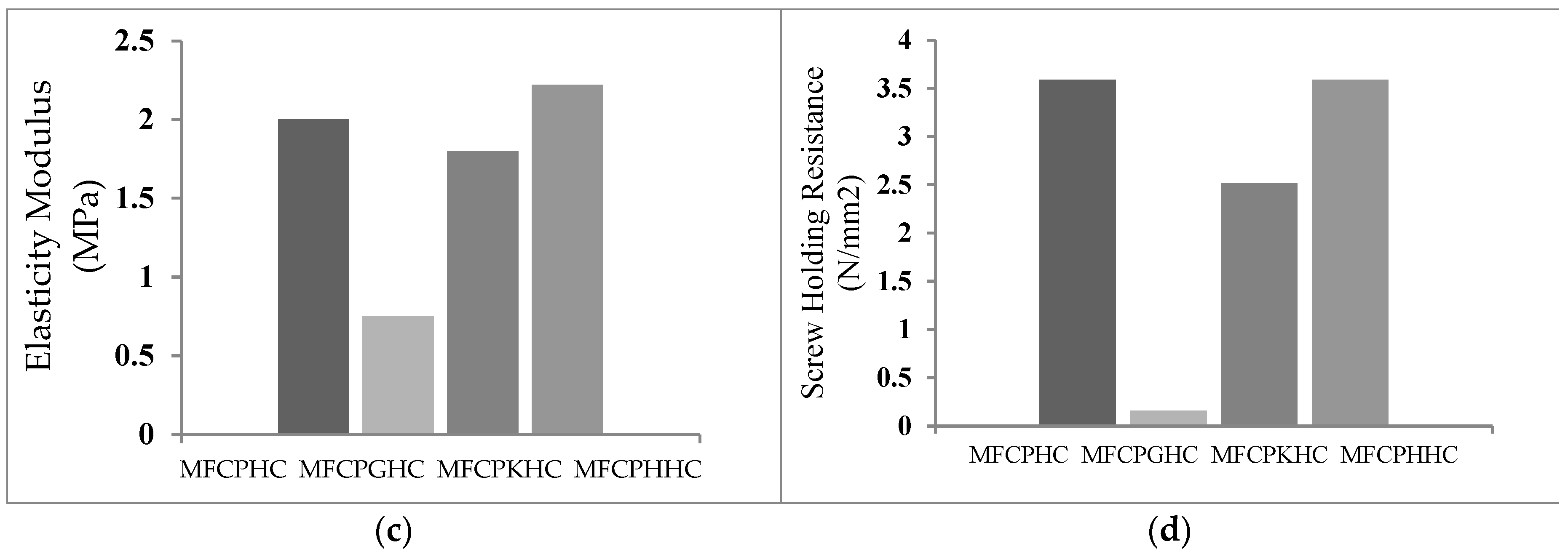
3.6. Dependence of densities, flexural strengths, modulus of elasticity and screw holding strengths of hybrid composites on their composition
Acknowledgments
References
- Kaboorani, A.; Riedl, B.; Blanchet, P.; Fellin, M.; Hosseinaei, O.; Wang, S. Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC): A renewable nano-material for polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesive. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.F.; Khanjanzadeh, H.; Dorieh, A.; Kiamahalleh, M.V.; Hoseini, K.D. Utilization of phenol formaldehyde/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as microwave preheating amplifier in laminated veneer lumber (LVL) structure. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 46, 103809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.F.; Mehdinia, M.; Kiamahalleh, M.V.; Hoseini, K.D.; Hatefnia, H.; Dorieh, A. Biological durability of particleboard: fungicidal properties of Ag and Cu nanoparticles against Trametes versicolor white-rot fungus. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 17, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, B.; McQueen, D.H.; Pelišková, M.; Rozhkova, N. Electrical and mechanical properties of melamine-formaldehyde-based laminates with shungite filler. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimidis, W.G.G. , Wood pulp fiber reinforced melamine-formaldehyde composites. Journal of Materials Science 2004. 39: p. 3245-3247.
- Hagstrand, P.-O.; Oksman, K. Mechanical properties and morphology of flax fiber reinforced melamine-formaldehyde composites. Polym. Compos. 2001, 22, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.M.; Afra, E.; Tajvidi, M.; Bousfield, D.W.; Dehghani-Firouzabadi, M. Application of cellulose nanofibril (CNF) as coating on paperboard at moderate solids content and high coating speed using blade coater. Prog. Org. Coatings 2018, 122, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.K.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, A. Studies on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy-Silicon Oxide Hybrid Materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 4440–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.; Kinloch, A.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.; Sprenger, S.; Hsieh, T.; Kinloch, A.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.; Sprenger, S. The mechanisms and mechanics of the toughening of epoxy polymers modified with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2010, 51, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.; Ramazani, A. Perlite–SO3H nanoparticles: very efficient and reusable catalyst for three-component synthesis of N-cyclohexyl-3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-amine derivatives under ultrasound irradiation. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calebrese, C.; Hui, L.; Schadler, L.S.; Nelson, J.K. A review on the importance of nanocomposite processing to enhance electrical insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, A.R., M.; Joo, S. W. , Silica nanoparticles from rice husk ash: a green catalyst for the one-pot three-component synthesis of benzo [B] furan derivatives. Advanced Materials Research, 2014. 875: p. 202-207.
- Bittmann, B.H., F.; Schlarb, A. K. , Ultrasonic dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles in epoxy resin. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2009. 16: p. 622-628.
- Johnsen, B.; Kinloch, A.; Mohammed, R.; Taylor, A.; Sprenger, S.; Johnsen, B.; Kinloch, A.; Mohammed, R.; Taylor, A.; Sprenger, S.; et al. Toughening mechanisms of nanoparticle-modified epoxy polymers. Polymer 2006, 48, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelis, E.P. , Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Advanced Materials, 1996. 8(1): p. 29-35.
- Pavlidou, S.P., C. D., A review on polymer–layered silicate nanocomposites. Progress in Polymer Science, 2008. 33(12): p. 1119-1198.
- Pol, M.H.L., G.; Zamani, E.; Ordys, A. , Investigation of the ballistic impact behavior of 2D woven glass/epoxy/nanoclay nanocomposites. Journal of Composite Materials, 2015. 49(12): p. 1449-1460.
- Pol, M.H.L., G. H., Studies on the mechanical properties of composites reinforced with nanoparticles. Polymer Composites, 2017. 38(1): p. 205-212.
- Fiedler, B.; Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.; Nolte, M.C.; Schulte, K. Fundamental aspects of nano-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Annappa, S.B., J. R. Annappa, S.B., J. Paulo Davim, Effect of organoclays on mechanical properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy nanocomposite. Polymer Bulletin, 2022. 79: p. 5085-5103.
- Zhao, Q.; Bahadur, S. The mechanism of filler action and the criterion of filler selection for reducing wear. Wear 1999, 225-229, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Non-destructive evaluation (NDE) of polymer matrix composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agubra, V.A.; Owuor, P.S.; Hosur, M.V. Influence of Nanoclay Dispersion Methods on the Mechanical Behavior of E-Glass/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.M.-C., S.; Carbonnier, B.; Di Tommaso, D.; Naili, S. , From atomistic structure to thermodynamics and mechanical properties of epoxy/clay nanocomposites: Investigation by molecular dynamics simulations. Computational Materials Science, 2017. 139: p. 191-201.
- Nguyen, V.H.M.-C., S.; Carbonnier, B.; Naili, S. , Estimation of effective elastic properties of polymer/clay nanocomposites: A parametric study. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018. 152: p. 139-150.
- Vijayan, P.P.; Puglia, D.; Pionteck, J.; Kenny, J.M.; Thomas, S. Liquid-rubber-modified epoxy/clay nanocomposites: effect of dispersion methods on morphology and ultimate properties. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 1703–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.F., X.; Thitsartarn, W.; He, C. , Rheological and mechanical properties of epoxy/clay nanocomposites with enhanced tensile and fracture toughnesses Polymer, 2015. 58: p. 43-52.
- Chen, J.L.-R., A.; Trevarthen, J.; Gizewski, T.; Lukawski, D.; Hazra, K.; Rahatekar, S., S.; Koziol, K. K. , Carbon nanotube films spun from a gas phase reactor for manufacturing carbon nanotube film/carbon fibre epoxy hybrid composites for electrical applications. Carbon, 2020. 158: p. 282-290.
- Nayak, S.K.M., S.; Nayak, S. K. , Thermal, electrical and mechanical properties of expanded graphite and micro-SiC filled hybrid epoxy composite for electronic packaging applications. Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, 2020. 49(1): p. 212-225.
- Suresha, B.; Divya, G.S.; Hemanth, G.; Somashekar, H.M. Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nano Silica-Filled Epoxy-Based Mono and Hybrid Composites for Structural Applications. Silicon 2020, 13, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, M. , & Erkliğ, A., Effects of clay and silica nanoparticles on the Charpy impact resistance of a carbon/aramid fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Journal Materials Testing, 2019. 61(1): p. 65-70.
- Toorchi, D.T., E.; Khosravi, H. , Enhanced flexural and tribological properties of basalt fiber-epoxy composite using nano-zirconia/graphene oxide hybrid system. Journal of Indusrtrial Textiles, 2022. 51(2S): p. 238S–3252S.
- Gowda, T.Y.; Sanjay, M.; Bhat, K.S.; Madhu, P.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Yogesha, B. Polymer matrix-natural fiber composites: An overview. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Arikan, V. Low-velocity impact response of E-glass reinforced thermoset and thermoplastic based sandwich composites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2017, 127, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S. , Composites manufacturing: materials, product, and process engineering. CRC Press, 2001: p. 416 page.
- Acikbas, G.Y., B. , Wear response of glass fiber and ceramic tile-reinforced hybrid epoxy matrix composites Iranian Polymer Journal, 2019. 28: p. 21-29.
- Rudresh, B.M. , Ravi Kumar, B.N., Madhu, D., Combined effect of micro- and nano-fillers on mechanical, thermal, and morphological behavior of glass–carbon PA66/PTFE hybrid nano-composites. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2019. 2: p. 176-188.
- Rudresh, B.M.R.K., B. N.; Lingesh, B. V., Fibridization effect on the mechanical behavior of PA66/PTFE blend based fibrous composites. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals 2017. 70(10): p. 2683-2694.
- Rudresh, B.M.R.K., B. N.; Lingesh, B. V., Hybridization Effect on the Mechanical Behavior of Monophase Reinforced PA66/Teflon Blend Based Hybrid Thermoplastic Composites. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2017. 70(9): p. 2335–2346.
- Osman, A.F.; Alakrach, A.M.; Kalo, H.; Azmi, W.N.W.; Hashim, F. In vitro biostability and biocompatibility of ethyl vinyl acetate (EVA) nanocomposites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 31485–31495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolonen, H.S., S. G., Effect of mineral fillers on properties of composite matrix material. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 1996. 31(4): p. 317-324.
- Shojaei, A.K., S. S., Self-healing and self-sensing smart polymer composites. Composite Materials, 2021: p. 307-357.
- Murtaja, Y.L., L.; Sepetcioglu, H.; Vlček, J.; Lapčíková, B.; Ovsík, M.; Staněk, M. , Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior. journal Nanotechnology Reviews, 2022. 11: p. 312-320.
- Usuki, A.K., Y.; Kawasumi, M.; Okada, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. , Synthesis of nylon 6-clay hybrid. Journal of Materials Research, 1993. 8(5): p. 1179-1184.
- Adesakin, A.O.A., O. O.; Imosili, P. E.; Attahdaniel, B. E.; Olusunle, S. O. O., Characterization and Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Dolomite as Filler in Polyester. Chemistry and Materials Research, 2013. 3(8).
- Chong, L.K.; Osman, A.F.; Fauzi, A.A.A.; Alrashdi, A.A.; Halim, K.A.A. The Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) (PECoVA) Composites with Pristine Dolomite and Organophilic Microcrystalline Dolomite (OMCD). Polymers 2021, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, A.F.; Siah, L.; Alrashdi, A.A.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Ibrahim, I. Improving the Tensile and Tear Properties of Thermoplastic Starch/Dolomite Biocomposite Film through Sonication Process. Polymers 2021, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morreale, M.; Liga, A.; Mistretta, M.C.; Ascione, L.; La Mantia, F.P. Mechanical, Thermomechanical and Reprocessing Behavior of Green Composites from Biodegradable Polymer and Wood Flour. Materials 2015, 8, 7536–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsissou, R.S., R.; Benzekri, Z.; Hilali, M.; Rafik, M.; Elharfi, A. , Polymer composite materials: A comprehensive review. Composite Structures, 2021. 262.
- Alakrach, A.M. , Osman, A. F., Noriman, N. Z., Betar, B. O., & Dahham, O. S., Thermal properties of ethyl vinyl acetate (EVA)/montmorillonite (MMT) nanocomposites for biomedical applications. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2016. 78.
- Hamid, A.R.A.; Osman, A.F.; Mustafa, Z.; Mandal, S.; Ananthakrishnan, R. Tensile, fatigue and thermomechanical properties of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) nanocomposites incorporating low and high loadings of pre-swelled organically modified montmorillonite. Polym. Test. 2020, 85, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.F.; Fitri, T.F.M.; Rakibuddin; Hashim, F. ; Johari, S.A.T.T.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Ramli, R. Pre-dispersed organo-montmorillonite (organo-MMT) nanofiller: Morphology, cytocompatibility and impact on flexibility, toughness and biostability of biomedical ethyl vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Fan, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. Modified nano Fe2O3-epoxy composite with enhanced mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, S. Experimental study of mechanical and electrical properties of carbon nanofiber/epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoman, T.S.; Džunuzović, J.V.; Jeremić, K.B.; Grgur, B.N.; Miličević, D.S.; Popović, I.G.; Džunuzović, E.S. Improvement of epoxy resin properties by incorporation of TiO2 nanoparticles surface modified with gallic acid esters. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Krug, H.; Schmidt, H. Tailoring of Thermomechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Nanocomposites by Surface Modification of Nanoscale Silica Particles. MRS Proc. 1996, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, G.; Her, Y.-S.; Matijević, E. Preparation and Characterization of Nanocomposite Thin Films for Optical Devices. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 2929–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Wetzel, B.; Friedrich, K. Microstructure and tribological behavior of polymeric nanocomposites. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2001, 53, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Anant, R.; Kumar, K.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Anticorrosive and electromagnetic shielding response of a graphene/TiO2–epoxy nanocomposite with enhanced mechanical properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113405–113414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of conductive polyaniline/nanosilica particle composites through ultrasonic irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.R. , Bhamidipati, V., Zhong, W., H.,Li, J., Lukehart, C.,M., Mechanical Property Characterization of a Polymeric Nanocomposite Reinforced by Graphitic Nanofibers with Reactive Linkers. Journal of Composite Materials, 2004. 38(18): p. 1563-1582.
- Gürses, A. , Güneş, K., Mindivan, F., Korucu, M. E., Açıkyıldız, M., & Doğar, Ç., The investigation of electrokinetic behaviour of micro-particles produced by CTA+ ions and Na-montmorillonite. Applied Surface Science, 2014. 318: p. 79-84.
- Singla, P.; Mehta, R.; Upadhyay, S.N. Clay Modification by the Use of Organic Cations. Green Sustain. Chem. 2012, 02, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, E.C.; Bandeira, R.M.; Vega, M.L.; Junior, J.R.d.S. Poly(melamine-formaldehyde-silica) Composite Hydrogel for Methylene Blue Removal. Mater. Res. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Gu, Z.; Hong, S.; Lian, H. Preparation and characterization of microencapsulated LDHs with melamine-formaldehyde resin and its flame retardant application in epoxy resin. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaia, R.A.; Giannelis, E.P. Lattice Model of Polymer Melt Intercalation in Organically-Modified Layered Silicates. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7990–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GÜNİSTER CANBAZ, E. , Synthesis and characterization of biopolymer/clay nanocomposites, in INSTITUTE OF NATURAL SCIENCES. 2008, ISTANBUL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY.
- International, A.S.T.M. , ASTM 1037 16, in Standard Test Method for Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel Materials. 2007, Annual book of ASTM standards.
- International, A.S.T.M. , ASTM D790, in Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and electrical insulating materials. 2007, Annual book of ASTM standards.
- Naresh, R.; Parameshwaran, R.; Ram, V.V. Microcapsules of n-dodecanoic acid/melamine-formaldehyde with enhanced thermal energy storage capability for solar applications. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, A.; Barın, T.B. Preparation, Structural Characterization and Evaluation of Some Dynamic and Rheological Properties of a New Type of Clay Containing Mastic Material, Clay-Mastic. Minerals 2023, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, A.; Güneş, K.; Şahin, E.; Açıkyıldız, M. Investigation of the removal kinetics, thermodynamics and adsorption mechanism of anionic textile dye, Remazol Red RB, with powder pumice, a sustainable adsorbent from waste water. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1156577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhu, G.; Legg, B.A.; Guan, B.; De Yoreo, J.J. Bassanite Grows Along Distinct Coexisting Pathways and Provides a Low Energy Interface for Gypsum Nucleation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 6582–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Churchman, G.J.; Gu, Y.; Yin, K.; Wang, C. Kaolinite–smectite mixed-layer clays in the Jiujiang red soils and their climate significance. Geoderma 2012, 173-174, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Richards, R.M. General strategy for one-pot synthesis of metal sulfide hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2012, 125, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. , Liu, S., Wang, Q., & Wang, G., Preparation of melamine–formaldehyde resin grafted by (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane for high-performance hydrophobic materials. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020: p. 10.
- Nemanič, V.; Zajec, B.; Žumer, M.; Figar, N.; Kavšek, M.; Mihelič, I. Synthesis and characterization of melamine–formaldehyde rigid foams for vacuum thermal insulation. Appl. Energy 2014, 114, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaghi, K.M. , Hasankhani, H., & Koukabi, M., Improvement in physical and mechanical properties of butyl rubber with montmorillonite organo-clay. Iranian Polymer Journal, 2007. 16(10): p. 671-679.
- Sever, K.; Atagür, M.; Tunçalp, M.; Altay, L.; Seki, Y.; Sarıkanat, M. The effect of pumice powder on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 32, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, A.; Nagalli, A.; de Carvalho, K.Q.; Mymrin, V.; Passig, F.H.; Mazer, W. Properties of recycled gypsum from gypsum plasterboards and commercial gypsum throughout recycling cycles. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, G.K.; Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Removal of hazardous basic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto kaolinite and acid-treated kaolinite: kinetics, isotherm and mechanistic study. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhangsun, X.; Tao, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of Red 2G on the suspended TiO2-hollow glass sphere. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2021, 134, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide-modified poly(melamine-formaldehyde) microcapsules containing phase change material n-dodecanol for thermal energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11624–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, A.; Doğar. ; Köktepe, S.; Mindivan, F.; Güneş, K.; Aktürk, S. Investigation of Thermal Properties of PUF/colored Organoclay Nanocomposites. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2015, 127, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyika, H. , Maina, E., Gachanja, A. and Marika, D., Instrumental characterization of montmorillonite clays by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and uv/visible spectrophotometry. Journal of Agriculture, Science and Technology, 2016. 17(1): p. 224-239.
- Khorzughy, S.H.; Eslamkish, T.; Ardejani, F.D.; Heydartaemeh, M.R. Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by pumice and nano-pumice. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 32, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Chaker, Y.; Belarbi, E.H.; Abbas, O.; Chotard, J.; Abassi, H.; Van Nhien, A.N.; El Hadri, M.; Bresson, S. XRD and ATR/FTIR investigations of various montmorillonite clays modified by monocationic and dicationic imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1173, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Lingfa, P. Sodium bentonite and kaolin clays: Comparative study on their FT-IR, XRF, and XRD. Mater. Today: Proc. 2019, 22, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tironi, A.; Trezza, M.; Irassar, E.; Scian, A. Thermal Treatment of Kaolin: Effect on the Pozzolanic Activity. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M. Effects of the reaction degree of melamine-formaldehyde resin on the structures and properties of melamine-formaldehyde/polyvinyl alcohol composite fiber. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S. , & Ahmed, S., Synthesis of nano-crystallite gypsum and bassanite from waste Pila globosa shells: crystallographic characterization. RSC Advances, 2022. 12: p. 25096–25105.
- Sakae, T.; Sato, Y.; Numata, Y.; Suwa, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kuwada, T.; Hayakawa, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Thermal ablation of FEL irradiation using gypsum as an indicator. Lasers Med Sci. 2006, 22, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, U.A.; Sarioglu, M. Removal of tetracycline from wastewater using pumice stone: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 79–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, M.N.; Amrane, A.; Karimaian, K.A.; Zarrabi, M.; Ghaffari, H.R. Potential of waste pumice and surface modified pumice for hexavalent chromium removal: Characterization, equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 45, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardolinski, J.E.F.C.; Lagaly, G. Grafted organic derivatives of kaolinite: II. Intercalation of primary n-alkylamines and delamination. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinger, L.; Lehmann, S.; Zielbauer, L.; Scharfe, B.; Gerdes, T. Aluminum Coated Micro Glass Spheres to Increase the Infrared Reflectance. Coatings 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.; Vicente, R.; Ferreira, V.; Silva, T. Polyurethane foams with microencapsulated phase change material: Comparative analysis of thermal conductivity characterization approaches. Energy Build. 2017, 153, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontini, P., M. and Pouzada, A., S., Chapter 6 - Trends in the multifunctional performance of polyolefin/clay nanocomposite injection moldings. Multifunctionality of Polymer Composites, 2015: p. 213-244.
- Wang, X. , Li, C., & Zhao, T., Fabrication and characterization of poly (melamine- formaldehyde)/silicon carbide hybrid microencapsulated phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity and light-heat performance. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018. 1836: p. 82-91.
- Șova, D.; Stanciu, M.D.; Georgescu, S.V. Design of Thermal Insulation Materials with Different Geometries of Channels. Polymers 2021, 13, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y. Strategies for enhancing thermal conductivity of polymer-based thermal interface materials: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 1064–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuallim, B.; Harun, W.S.W.; Al Rikabi, I.J.; Mohammed, H.A. Thermally conductive polymer nanocomposites for filament-based additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 3993–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, H. , Demirboğa, R., Şahin, R., & Gül, R., The effects of different cement dosages, slumps, and pumice aggregate ratios on the thermal conductivity and density of concrete Cement and Concrete Research, 2004. 34(5): p. 845-848.
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Silva, R.; Costa-Pereira, M.; Flores-Colen, I. Thermal and mechanical performance of gypsum composites with waste cellulose acetate fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, A.; Smith, D.S.; Degot, S.; Gault, C. Thermal conductivity and specific heat of kaolinite: Evolution with thermal treatment. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorda J, K.G. , Barbu MC, Petutschnigg A, Král P., Influence of Adhesive Systems on the Mechanical and Physical Properties of Flax Fiber Reinforced Beech Plywood. Polymers (Basel). Polymers, 2021. 13.
- Kwon, Y.-M.; Chang, I.; Cho, G.-C. Consolidation and swelling behavior of kaolinite clay containing xanthan gum biopolymer. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 3555–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, R.; Cheng, H.; Zou, M.; Wang, H.; Zheng, K. Hollow glass microspheres/phenolic syntactic foams with excellent mechanical and thermal insulate performance. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1216706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Shen, Q. Compound Effects of Sodium Chloride and Gypsum on the Compressive Strength and Sulfate Resistance of Slag-Based Geopolymer Concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyadi; Tamai, H. Enhancing the Performance of Porous Concrete by Utilizing the Pumice Aggregate. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gibson, L. Elastic moduli of a composite of hollow spheres in a matrix. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1993, 41, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component (%) | |||||||||||
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | MnO | SrO | SO3 | Other |
| 73.35 | 12.88 | 0.77 | 0.08 | 1.10 | 4.40 | 3.82 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 3.02 |
| Components (%) | |||||||||
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | Cr2O3 | Other |
| 71.00 | 20.00 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 7.93 |
| Components (%) | |||||||||
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | SO3 | Other |
| 59.32 | 17.19 | 5.95 | 3.63 | 2.21 | 1.68 | 0.97 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 7.81 |
|
Density (15 0C), kg/m3 |
Calorific value MJ/kg |
Flash point 0C |
Water by distillation, wt. % |
C | H | N | S | Ash |
| 990.7 | 42.74 | 105.8 | 0.1 | 83.4 | 11.9 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.03 |

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





