1. Introduction
In human life activities and industrial production, fossil fuels occupy a large amount of share. According to the World Energy Council, the world will need twice as much energy in 2050 as it consumes today.[
1] Therefore, there is a need for a new energy source that can replace fossil fuels. Replacing conventional energy systems by implementing renewable energy systems is considered a crucial step towards sustainable development.[
2,
3]
Renewable energy requires an environmentally friendly and efficient energy storage device. The energy technologies that can be selected include solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, geothermal energy, etc. These new energy sources must consider the influence of factors such as geographical location and climatic conditions.[
4,
5,
6] After decades of development, supercapacitors have attracted extensive attention due to their high power density, fast charge and discharge speed, and long-term cycle stability compared with traditional secondary batteries.[
7] These outstanding properties make supercapacitors a promising carrier for use in portable electronics, hybrid electric vehicles, etc., helping to build renewable energy systems.[
8,
9,
10,
11]
However, a significant reason currently limiting supercapacitors is their low energy density.[
12,
13,
14] Some researchers have pointed out that using new materials, such as nanoscale metal oxides,[
15,
16] conductive polymers,[
17] and heteroatom doping (B, N, S, P, O) carbon, etc.[
18,
19,
20,
21,
22] could improve the energy density. For example, nitrogen enrichment is an effective way to achieve the N-doping of supercapacitor carbon materials. The nitrogen functional group in the supercapacitor carbon materials can improve the electron transfer rate and stability, reduce the equivalent series resistance, and thus improve the electrochemical performance of the material.[
23,
24] Many reports have also pointed out that supercapacitor carbon materials have considerable advantages in many industrial applications due to their large specific surface area and porous structure. High porosity is an important parameter that can provide adsorption sites for ion storage and promote ion transport.[
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]
There are many kinds of raw materials for the preparation of supercapacitor carbon materials, among which biomass has become a hot spot for its advantages of high yield, renewable, low pollution, zero carbon dioxide emission and so on. At present, the conversion of biomass to supercapacitor carbon materials is mainly achieved by a thermochemical method [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35], among which hydrothermal carbonization(HTC) shows much promise as it can directly use wet biomass and produce high economic benefits[
36]. During the HTC process, the hydrogen bond force between water molecules is weakened, and both the ionization constant and the concentration of H
+ in the liquid phase will increase.[
37] At the same time, the pH value of the liquid phase will also increase with the addition of organic acids, which will promote the hydrolysis of oligosaccharides and other substances, thereby further promoting the growth of oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the resulting hydrochar.[
38] However, the doping sources or the organic acids produced during the HTC process of the biomass are limited, and additional organic acids need to be added.
There have been a large number of reports on improving the performance of carbon materials prepared in various aspects by adding additives. For example, Susanti et al. added a small amount of citric acid in the HTC of salacca peel to increase the specific surface area of carbon materials.[
39] Deng et al. added an N source to activated carbon to prepare electrodes with high spectral surface area and dense nanopores.[
40] Guo et al. removed heavy metals through HTC by adding urea as a nitrogen source.[
41] Huang et al. prepared carbon materials for supercapacitor use by adding melamine as a nitrogen source during the HTC of bamboo shoot shells[
42]. Wu et al. used urea as a nitrogen source during the HTC of carboxymethyl cellulose to prepare spherical carbonaceous adsorbents (CSn) with micro-porosity used for carbon dioxide capture capacity.[
43]
The type of doping source has a great influence on the electrochemical properties of the material. Among the doping sources, boric acid is widely used as an important doping source of B, which could improve the electrochemical performance of supercapacitor carbon, and the co-doping of B and N could further improve the electrochemical properties of the material. Zhao et al. proposed a low-cost and simplified strategy for the prepration of B,N-codoped porous C using freeze-drying chitosan-boric acid aerogel beads followed by a tube furnace carbonization. The B doping significantly affected the distribution of N species in the carbon material. The resulting doped carbon presented a good wettability and is conducive to the diffusion of electrolytes and the transport of ions.[
44] Liang et al. developed an efficient strategy to carbonize the chitosan in the presence of boric acid, and the resulting carbon showed a high specific capacitance, large operation voltage and excellent cycle stability for supercapacitors.[
45]
Therefore, in this present study, HTC of cellulose was examined with the addition of an inorganic N source (ammonium sulfate) or organic N source (thiourea) for the production of supercapacitor carbon. The effect of B addition on the specific surface area, pore structure, and electrochemical performance of the resulting carbon materials prepared by adding organic and inorganic nitrogen sources was elaborated in detail. Finally, the electrochemical performances of the activated carbon material were characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) test, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cycle life measurement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
ɑ-Cellulose powder (CL) was purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.(Shanghai, China). Thiourea (TU), ammonium sulfate (AS), and boric acid (BA) were purchased from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (Tianjin, China). Deionized water was prepared in the lab, which has a conductivity of less than 10 μs/cm. Potassium hydroxide (KOH), hydrochloric acid (HCL), and acetylene black BP2000 were purchased from Tianjin Kermel Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd.(Tianjin, China). The polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) binder was provided by Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd.(Shanghai, China).
The HTC reaction was performed using a mechanical reactor MSG100-P5-T3-SS1-SV-R (Anhui CHEMᴺ Instrument Co., Ltd., China) with a volume of 100 mL. This reactor is equipped with a stirrer. The heating power of the reactor was 1.1 kW. The rated temperature and pressure of the reactor are 300°C and 20.7 MPa, respectively.
2.2. HTC
5 g CL, 0.5 g TU or AS, 0.5 g BA(when needed), and 40 mL deionized water were loaded into a 100 mL beaker and mixed uniformly to form a paste. This paste was transferred into the 100 mL stainless-steel reactor and sealed. The switch was turned on to start the heating. About 30 min later(depending on the reaction temperature), the temperature inside the reactor reached 240 °C, and the reaction time was counted at this point. After 1 h reaction time was completed, the reactor was placed into a water bath. Once the temperature inside the reactor reached room temperature, it was taken out of the water bath. If there were gas products formed in the reactor, the valve needed to be opened to release the gas products first. The solid (hydrochar) and the aqueous phase were transferred into a büchner funnel for separation. The hydrochar was dried in an oven at 105 °C for 12 h. The yield of hydrochar was equal to the mass of hydrochar divided by the total mass of the material initially added into the reactor. The hydrochar (HC) produced from HTC of CL, CL+TU, CL+AS, CL+TU+ BA, CL+AS+BA were named HC-CL, HC-CL-TU, HC-CL-AS, HC-CL-TU-BA, and HC-CL-AS-BA, respectively.
2.3. Activation of HC
0.5 g HC and 1.5 g KOH were loaded into a 250 mL beaker, and 200 mL deionized water was added into the beaker and subjected to ultrasonication for 20 min. The HC was soaked in the KOH solution for 24 h. The soaked HC was separated by a büchner funnel and dried at 105 ℃ for 12 h. The soaked HC was loaded into a porcelain boat and placed into a tube furnace, which was heated to 800℃ at a heating rate of 3℃ min-1 under an Ar environment at a flow rate of 20 mL min-1 and stayed at 800℃ for 1 h. After the activation, the activated hydrochar (AHC) was cooled to room temperature under an Ar atmosphere and soaked in 100 mL 1M HCL solution for 12 h. Subsequently, the ACH was washed with deionized water until the pH of the filtrate reached 7 and dried at 105 ℃ for 12 h. The activated hydrochar (AHC) produced HC-CL, HC-CL-TU, HC-CL-AS, HC-CL-TU-BA, and HC-CL-AS-BA were named AHC-CL, AHC-CL-TU, AHC-CL-AS, AHC-CL-TU-BA, and AHC-CL-AS-BA, respectively.
2.4. Characterizaiton of AHC
The specific surface area (SSA) and pore size distribution of AHCs were determined by N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm at 77 K through an JW-BK100 equipment (Beijing JWGB Instruments Co., Ltd.). The morphology and microstructure of samples were obtained by a Gemini SEM 500 scanning electron microscopy (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany). X-ray diffraction was obtained by XRD-6100(Shimadzu Corporation, Nakagyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan). The infrared spectrum was obtained by Nicolet iS50(ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The thermogravimetric analysis was obtained by STA449F5 (Netzsch, Selb, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was acquired on ESCALAB 250Xi (Thermo Scientific, USA). Elemental analysis was obtained by Vario EL cube (Elementar Americas Inc., Ronkonkoma, NY, USA).
2.5. Electrochemical performance test of AHC
The electrochemical performances of individual electrodes were evaluated by an electrochemical workstation model CHI1030B (Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Co. Ltd, Shanghai, China). A three-electrode device was used as the test system under an ambient atmosphere, where the platinum sheet electrode served as the counter electrode and Hg/HgO for the reference electrode.
The AHC, acetylene black, and PTFE were mixed at a mass ratio of 16:3:1 and dissolved in ethanol. The mixture was subjected to sonication at a power of 120 W for 20 min and dried at 105°C for 5 h to totally remove the ethanol. The dried mixture was pressed into flakes at uniform mass under a pressure of 2 MPa and cut into circular flakes with a diameter of 10 mm. Cut two pieces of nickel foam into circular slices with a diameter of 15 mm. The 10 mm diameter electrode disc and a nickel sheet were placed between the two pieces of nickel foam discs and extruded by a tablet press at a pressure of 4 Mpa to make a working electrode. The electrolyte used in the testing process was 6 M KOH. Electrochemical tests included cyclic voltammetry (CV) at scan rates ranging from 10 to 200 mV s
-1 for CV curves, galvanostatic charge/discharge (GCD) at current densities between 1 and 20 A g
-1 for GCD curves, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) at scan frequencies between 0.01 Hz and 100 kHz. On the Land cell test program, the cycling stability was examined through 20,000 cycles at 10 A g
-1. As shown in Equation (1), the specific capacitance based on GCD measurements was determined.
where C is the gravimetric specific capacitance of electrodes (F g
-1), I is the discharge current (A), ∆t is the discharge time (s), m is the mass of the active material (g), ∆V is the voltage range (V).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Yield of the HC and elemental anlaysis of the HC and AHC
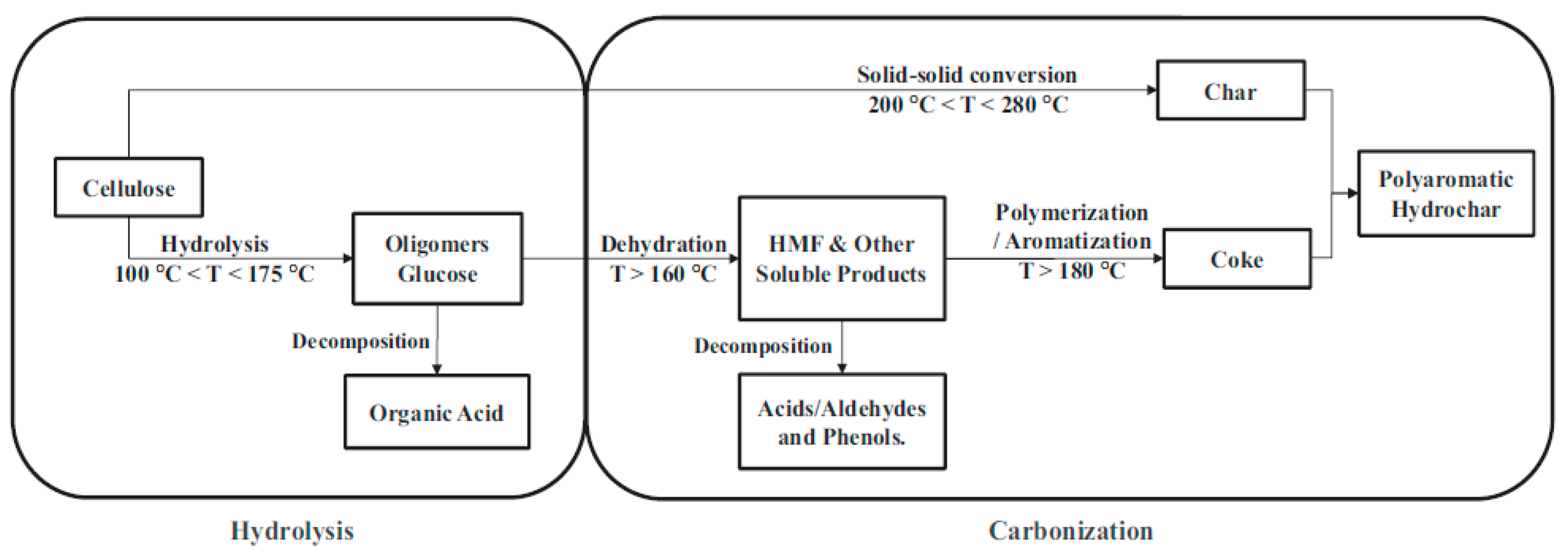
The HC yield obtained by direct HTC of CL was 52.8 wt%. Whether AS or TU was added, the HC yield obtained after HTC of CL was slightly increased, and was maintained at about 53.5 wt%. The reactions occurred between CL and AS or TU, and the addition of BA slightly reduced the hydrochar yield to about 53 wt%. Figrue 1 shows the reaction path of CL carbonization under hydrothermal conditions.[
46] The aqueous solution of BA is acidic, which is not conducive to the carbonization reaction of CL or its hydrolysates. In addition, a acidic condition also facilitated the hydrolysis of oligosaccharides into organic acids and the decomposition of HMF into acids/aldehydes and phenols, and thus reduce the hydrochar yield.
Table 1 lists the elemental composition of HC and AHC produced from different reaction feedstocks. Compared with CL, the hydrochar obtained from the HTC of CL has
higher C content (71.14 wt%) and lower H(4.35 wt%) and O(24.07 wt%) contents,indicating that the dehydration reaction occured during the carbonization process of CL, as described in the reaction path in
Figure 1. This is also illustrated by the low H/C and O/C of the hydrochar obtained from the HTC of CL. The addition of AS or TU promoted the HTC of CL because the resulting hydrochar has a higher C content than that of pure CL. Compared with CL, AS and TU have a higher H content, so the resutling hydrochar has a higher H content after adding AS and TU. The reaction between CL and AS or TU resulted in higher contents of N and S in the hydrochar, and the higher the N and S in the additive, the higher the N and S in the hydrochar. It should be noted that the S content of hydrochar obtained by the reaction of CL and AS is only 0.35 wt%, while the content of hydrochar and S obtained by TU is 4.54 wt%, indicating that organic sulfur is more likely to react with CL. Since the contents of C, H, N and S of the obtained hydrochar increased after adding AS or TU, the responding O content decreased. The addition of BA promoted the reaction of CL with AS or TU, which further increased the N and S contents of the obtained hydrochar. The H/C of hydrochar is reduced, which also shows that BS promoted the carbonization reaction of CL with AS or TU. At the same time, BA also participated in the reaction, resulting in an increased O content of hydrochar and a small amount of boron.
Since the activation was carried out in a high temperature and inert atmosphere, all activated hydrochar have a higher C content and a lower H and O contentS than hydrochar. The H/C ratio of all activated hydrochar was also as low as 0.26-0.29. The contents of N and S in the activation process of hydrochar also has different degrees of loss, resulting in the contents of N and S in the activated hydrochar were lower than that of hydrochar.
3.2. BET Analysis of the AHC
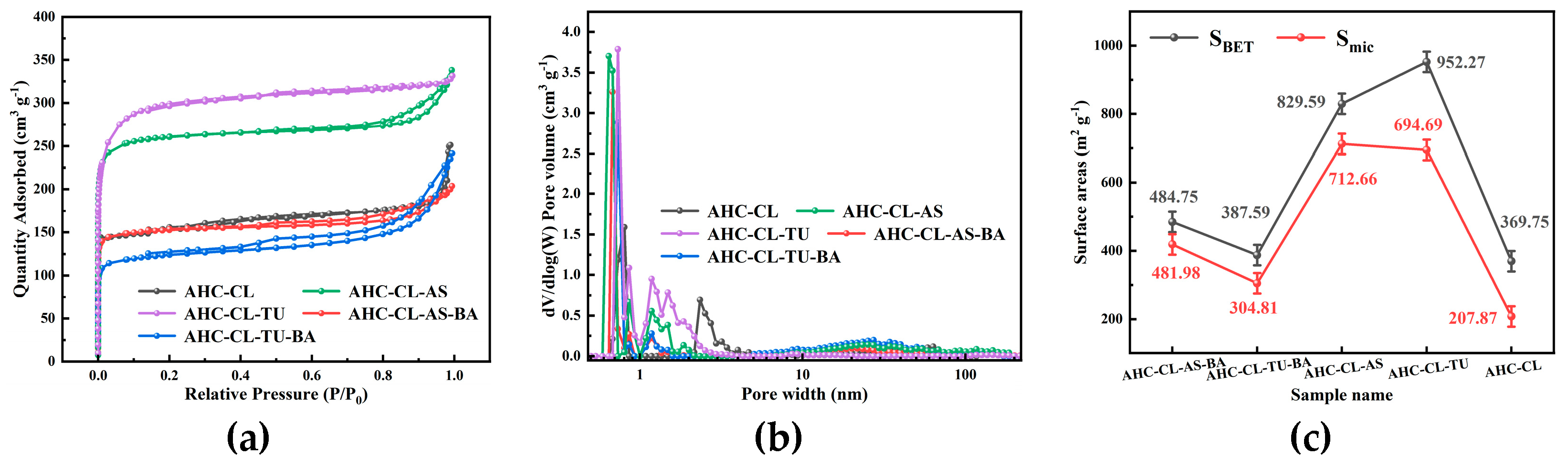
The porosity of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA was investigated using N
2 adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K. From
Figure 2(a), it can be seen that none of the isotherms of AHC-CL+TU has obvious hysteresis loops, showing typical I-type behavior. But AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS showed obvious hysteresis loops. At lower relative pressures P/P
0 (P/P
0<0.1), nitrogen uptake increased dramatically, indicating that the as-prepared AHC has typical microporous properties. When the relative pressure P/P
0 was increased to 0.2, the uptake of nitrogen gradually increased, which was partly due to the micro/mesoporosity. Compared with AHC-CL+AS+BA and AHC-CL+TU+BA, AHC-CL+AS and AHC-CL+TU obviously have better adsorption capacity, which indicates that AAM and AAT have a higher SSA. This may be because the boron element hinders the generation of pore structure during the HTC process, resulting in the reduction of SSA. At the same time, it can be seen that the effect of boron doping on doping TU is significantly higher than that on AS. The addition of BA would reduce the specific surface area of AHC doped with TU and AS, and the specific surface area of the experimental group doped with TU would be more obvious. It can be seen from
Figure 2(b) that the number of micropores in the AHC after doping with boron is significantly reduced, which further illustrates that the doping of boron occupied the pores of the AHC, resulting in a decrease in the SSA of the AHC. As shown in
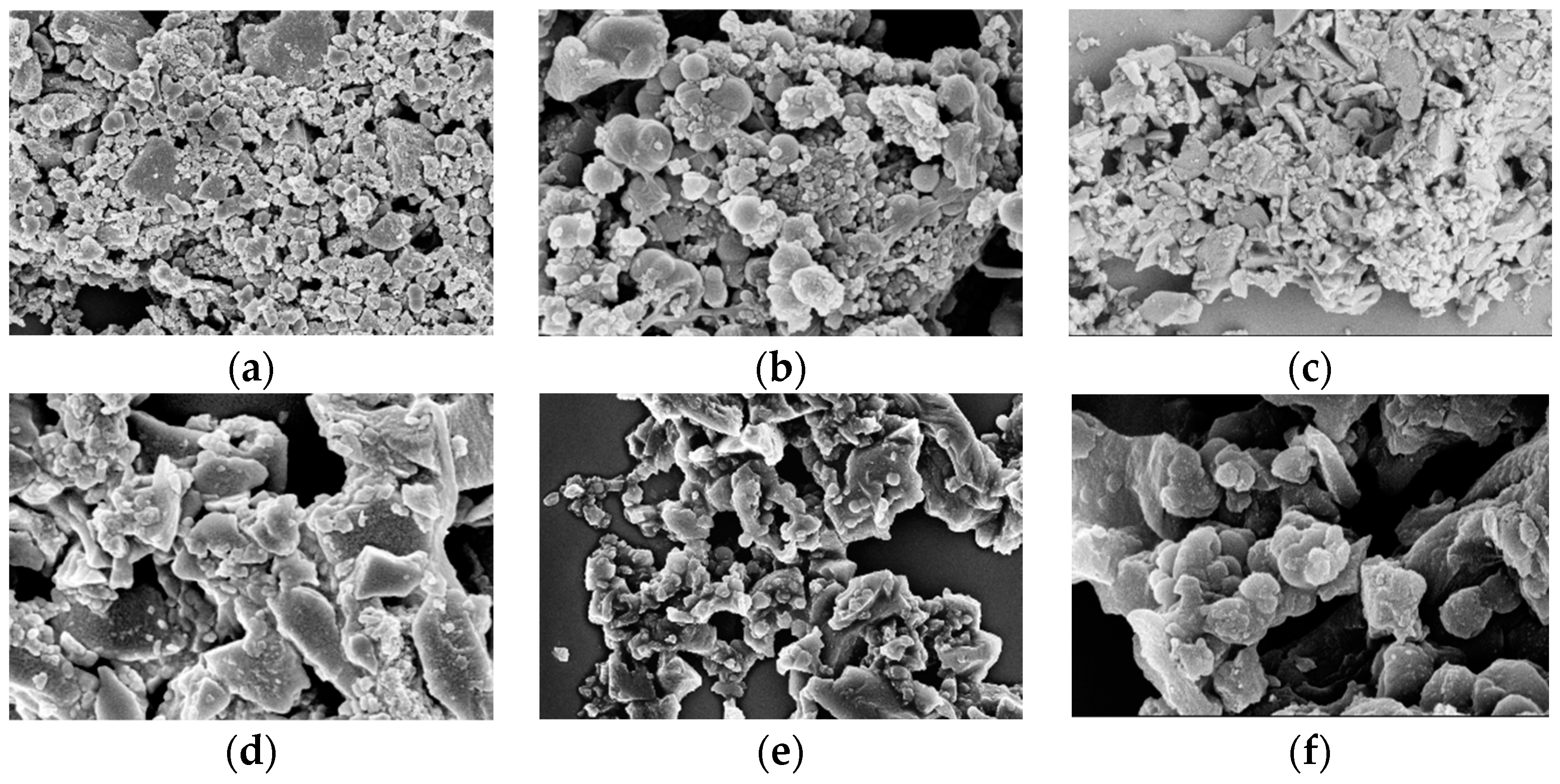
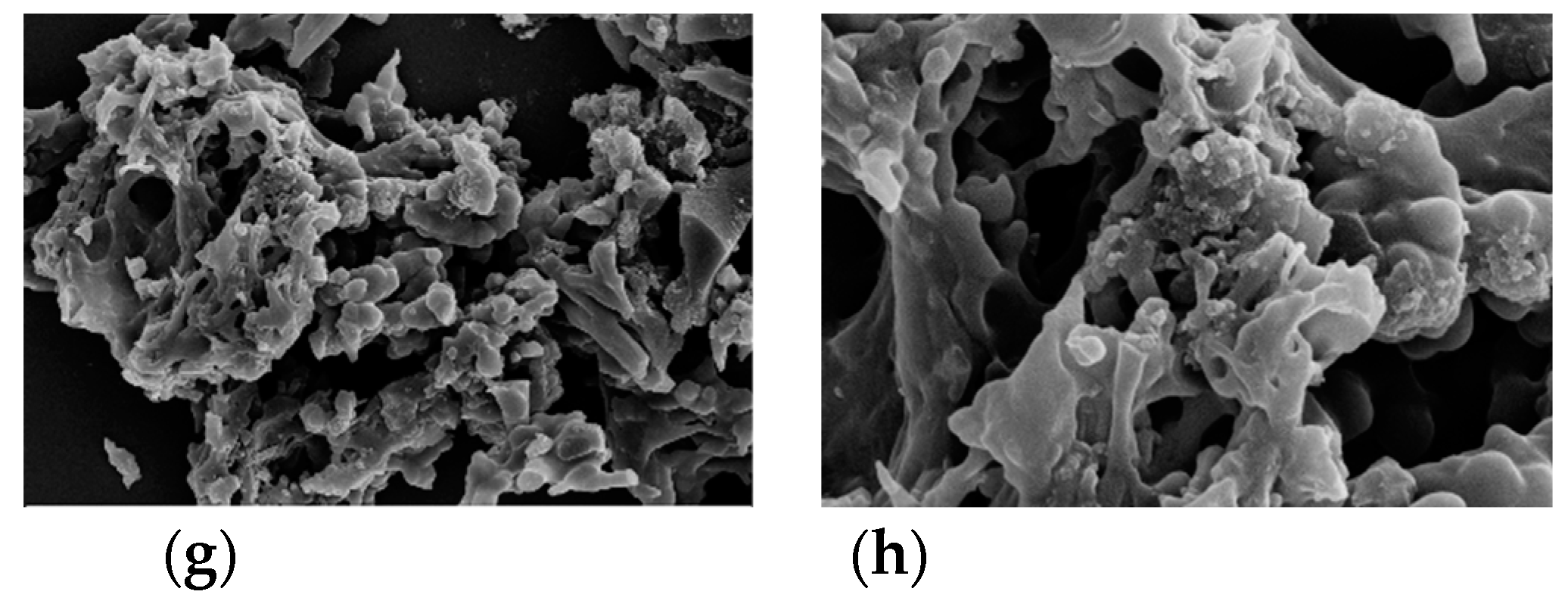
Figure 3, the SEM images show that AHC-CL+TU and AHC-CL+AS have more pore structures than those of AHC-CL+TU-BA and AHC-CL+AS-BA.
As indicated in
Figure 2(c), we can see that the SSA and micropore area of AHC are suppressed when boron is doped, especially when BA and TU were co-carbonized, the SSA and micropore area of the obtained AHC are was significantly inhibited. When only TU acts, the SSA of the AHC reached 952.27 m
2 g
-1, and the micropore area reaches 694.69 m
2 g
-1. Under the action of only CL, the SSA of the AHC reached 829.59 m
2 g
-1, and the micropore area reaches 712.66 m
2 g
-1. When boron was added, the specific surface area of AHC-CL+AS+BA was reduced to 484.76 m
2 g
-1, and its micropore area was reduced to 418.99 m
2 g
-1; the specific surface area of AHC-CL+TU+BA was reduced to 397.59 m
2 g
-1, and its micropore area was reduced to 304.81 m
2 g
-1. This may be because the addition of BA occupied the micropore sites during the HTC process, resulting in a decrease in the micropore area of the HC sample. It can be seen that after boron doping, both the SSA and the micropore area were affected, and the most affected group was the group doped with TU. And when no boron is doped, the specific surface area of the AHC added with AS was much smaller than that of the AHC added with TU, and the prepared micropore area was almost the same, which proved that the addition of AS had a better ability to manufacture micropores ability. While removing the interference of boron, the AHC with AS addition also showed a stronger ability to create micropores.
3.3. XPS Analysis of the AHC
To further probe the chemical state of the elements on the surface of the AHC, the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of the AHC was used.
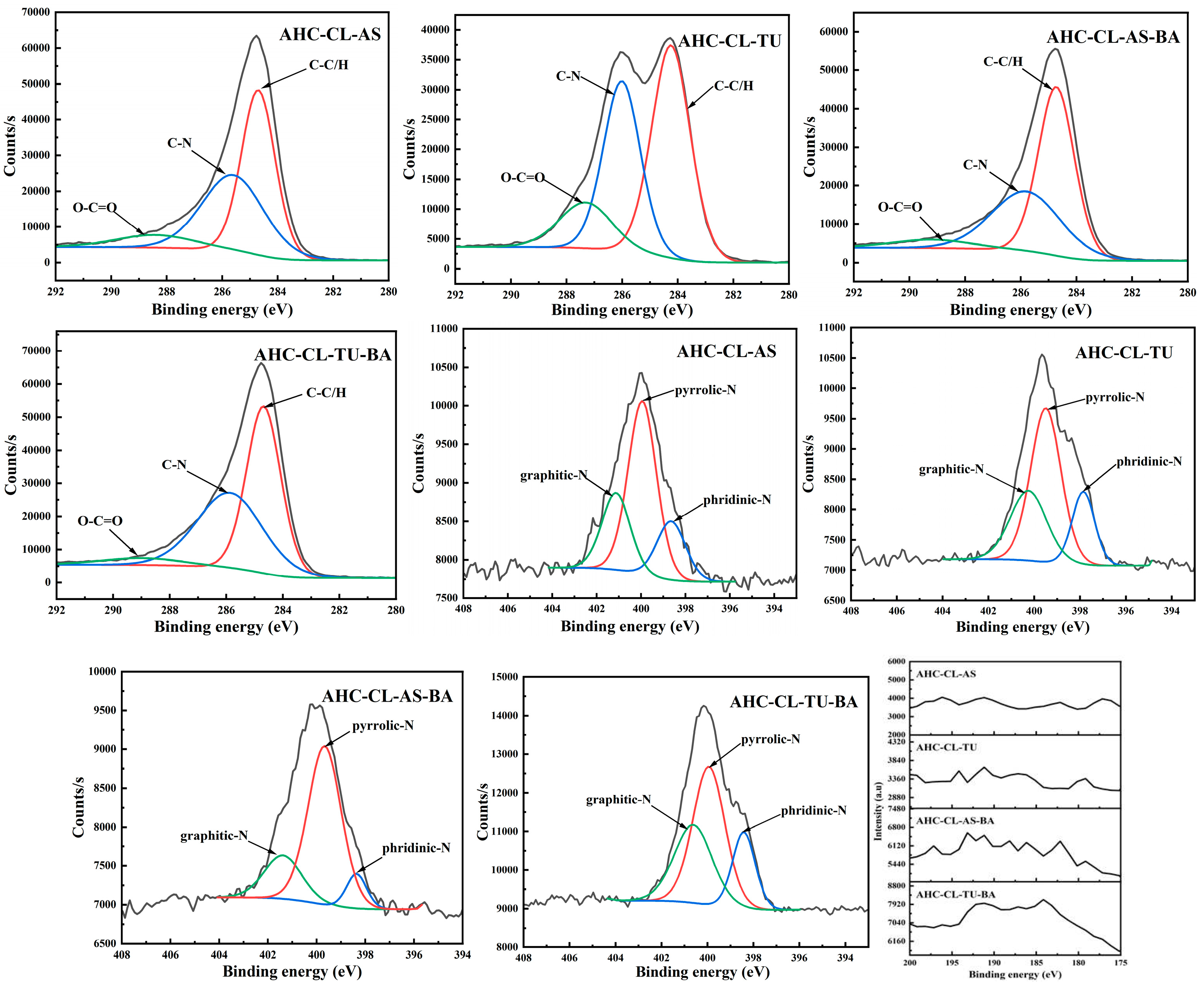
Figure 3 shows all the results. The peaks around 286.1 eV and 287.6 eV represent C-N and O-C=O. Compared with AS, the C-N/C-O peak intensity of the TU-doped experimental group increased significantly. Moreover, the peak intensity of C=O in the experimental group doped with TU is obviously higher than that of doped with AS. It shows that compared with doped AS, AHC doped with TU would undergo a certain degree of decarboxylation reaction in the HTC reaction. It is further proved that the addition of TU could make the prepared AHC have more oxygen-containing functional group (OFGs), which could improve the wettability of AHC pores and make it easier for ions to enter the pores.
The main peaks appear at 399.1 eV and 398.3 eV correspond to pyrrole-N and pyridine-N, respectively. The increase in pyrrole-N in the AHC would prompt to generate more electrochemically active sites, thereby improving the faradaic capacitance by changing the electron distribution on the surface of the AHC. As shown in
Table 1, TU-doped AHC has a higher N content, but the pyrrole-N peak intensity of AHC-CL+TU is smaller than that of AHC-CL+AS, indicating that not all N was converted into pyrrole-N during the HTC process. Instead, it existed in the AHC as other N form. AHC-CL+AS has more pyrrole-N, which indicates that this kind of carbon may has a better charge transfer performance and electron supply performance.
Figure 3.
XPS spectra of AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA.
Figure 3.
XPS spectra of AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA.
When the nitrogen and boron doping sources were added at the same time, the C-N peak intensity of AHC-CL+TU+BA is significantly higher than that of AHC-CL+AS+BA, indicating that B-assisted TU synergistic carbonization was more conducive to the formation of C-N. At the same time, the peak intensity of O-C=O in the B-assisted TU synergistic carbonization process was better than that in the B-assisted CL synergistic carbonization process, indicating that the B-assisted TU synergistic carbonization process could promote the decarboxylation reaction during the HTC process. During the process of CL/TU synergistic carbonization assisted by B addition, the increase of pyrrole-N content would induce more electrochemically active sites in the AHC, thereby improving the faradaic capacitance by changing the electron distribution on the surface of the AHC. The pyrrole-N peak intensity of AHC-CL+AS+BA is similar to that of AHC-CL+TU+BA. Although the AHC-CL+AS+BA and AHC-CL+TU+BA have similar N content, however, the intensity of the pyridine-N peak of AHC-CL+TU+BA was significantly higher than that of AHC-CL+AS+BA. During the process of adding TUas the N source, after adding B as the doping source at the same time, the C-N peak intensity of the TU-doped experimental group was significantly reduced. It shows that the addition of B would inhibit the formation of C-N. Moreover, after adding B, the peak intensity of C=O also decreased significantly. It shows that the addition of B assists the process of TU synergistic carbonization, which would inhibit the decarboxylation reaction of this process. This would reduce the OFGs of AHC and reduce the wettability of AHC pores, and thus prevent ions from entering the pores. After adding B as a dopant source, the intensity of the pyrrole-N peak of AHC decreased. As indicated
Table 1, the N contents of the two groups of AHCs are similar, indicating that not all N were converted into pyrrole-N during the HTC or activation process, but exists in the AHC in the other form of N. The pyrrole-N content of AHC-CL+TU was higher, indicating that this sample may have better charge transfer performance and electron supply performance.
In the process of adding AS as N source, after adding B as doping source, the C-N peak intensity of the AS-doped experimental group was significantly reduced. It shows that the addition of B would inhibit the formation of C-N during the HTC and /or activation process. Moreover, after adding B, the peak intensity of C=O also decreased. It shows that the process of synergistic carbonization by adding B to assist TU will inhibit the decarboxylation reaction in this process, which is not conducive to the carbonization process. This process will reduce the OFGs of AHC, reduce the wettability of AHC pores, and thus prevent ions from entering the pores. After adding B as the doping source, the pyrrole-N peak intensity of AHC is similar. As shown
Table 1, the N content of AHC-CL+AS+BA is significantly higher than that of AHC-CL+ASA, indicating that not all N were converted into pyrrole-N during HTC and /or activation process, but existed in AHC in the other form of N.
3.4. Electrochemical Analysis of the AHC
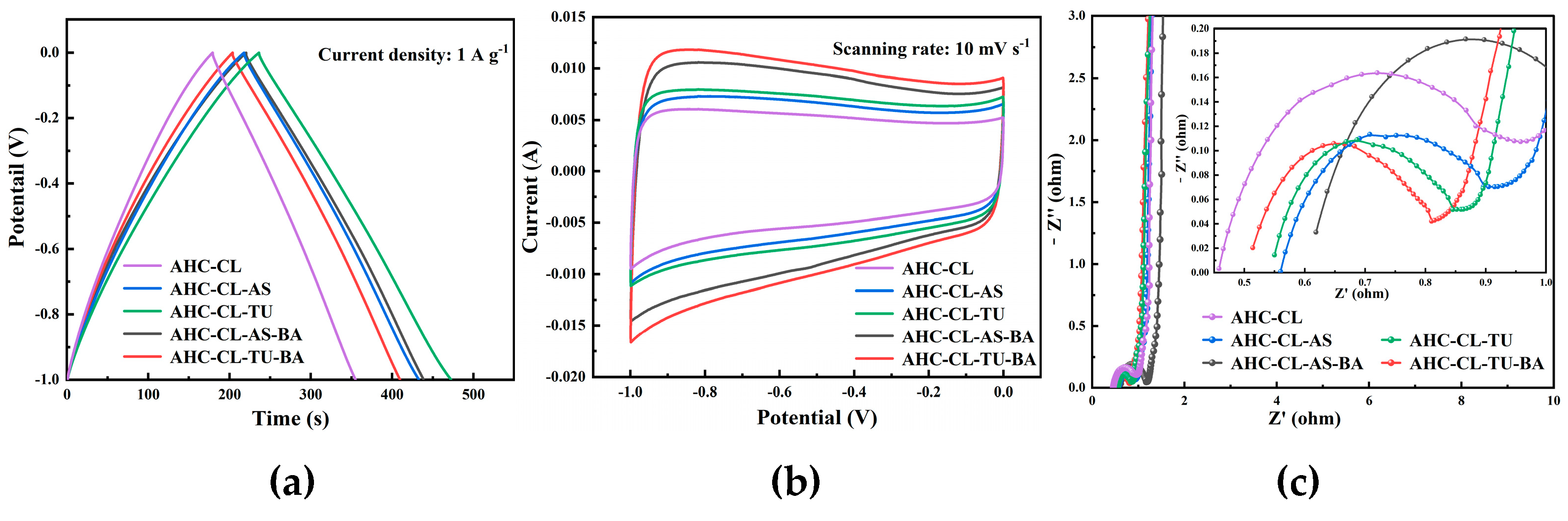
In the three-electrode system, the electrochemical performance of AHC in 6 M KOH electrolyte was obtained by testing CV, GCD and EIS. In order to explore the change of electrochemical performance of AHC after the addition of B assisted TU and A S synergistically carbonized cellulose, the GCD and CV of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA were tested, respectively. As shown in
Figure 4(a), all the AHC have good symmetrical triangular distributions, indicating good electric double layer capacitance and electrochemical reversibility. The AHC-CL+TU takes longer to charge and discharge. At a current density of 1 A g
-1, the mass specific capacitance of AAT reaches 236.25 F g
-1. This indicates that AHC-CL+TU has a higher energy storage capacity.
Figure 4(b) shows the CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 10 mV s
-1. It can be seen that the CV curves of AHC-CL+TU+BA and AHC-CL+AS+BA have a larger quasi-rectangular area, slightly protruding, and less deformation, indicating that the electric double layer capacitor sample contains a small amount of oxygen, which is the redox reaction of the surface functional groups during the rapid charge and discharge process caused behavior. AHC-CL+TU and AHC-CL+AS have more regular quasirectangular shapes, indicating that electrolyte ions undergo rapid ionic reactions in these two samples.
As shown in
Figure 4(c), it is the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA. The Nyquist plots of the four groups of samples (AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA) present a small quasi-semicircle in the high-frequency region, followed by a linear transition in the low-frequency region, which is characteristic of carbon materials. And all exhibit good electrical conductivity and ion diffusion properties. A semicircle on the real axis is approximately equal to the charge transfer resistance. And observing the semicircle section connected to the x-axis, it can be seen that with the addition of B, the charge transfer resistance of the electrode doped with AS as the N source increases. However, the charge transfer resistance of electrodes doped with TU as N source decreases. At the same time, the Nyquist curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA are almost straight lines in the low frequency region, and the slope is almost infinite, indicating that the ion diffusion resistance of the four electrode materials is high.
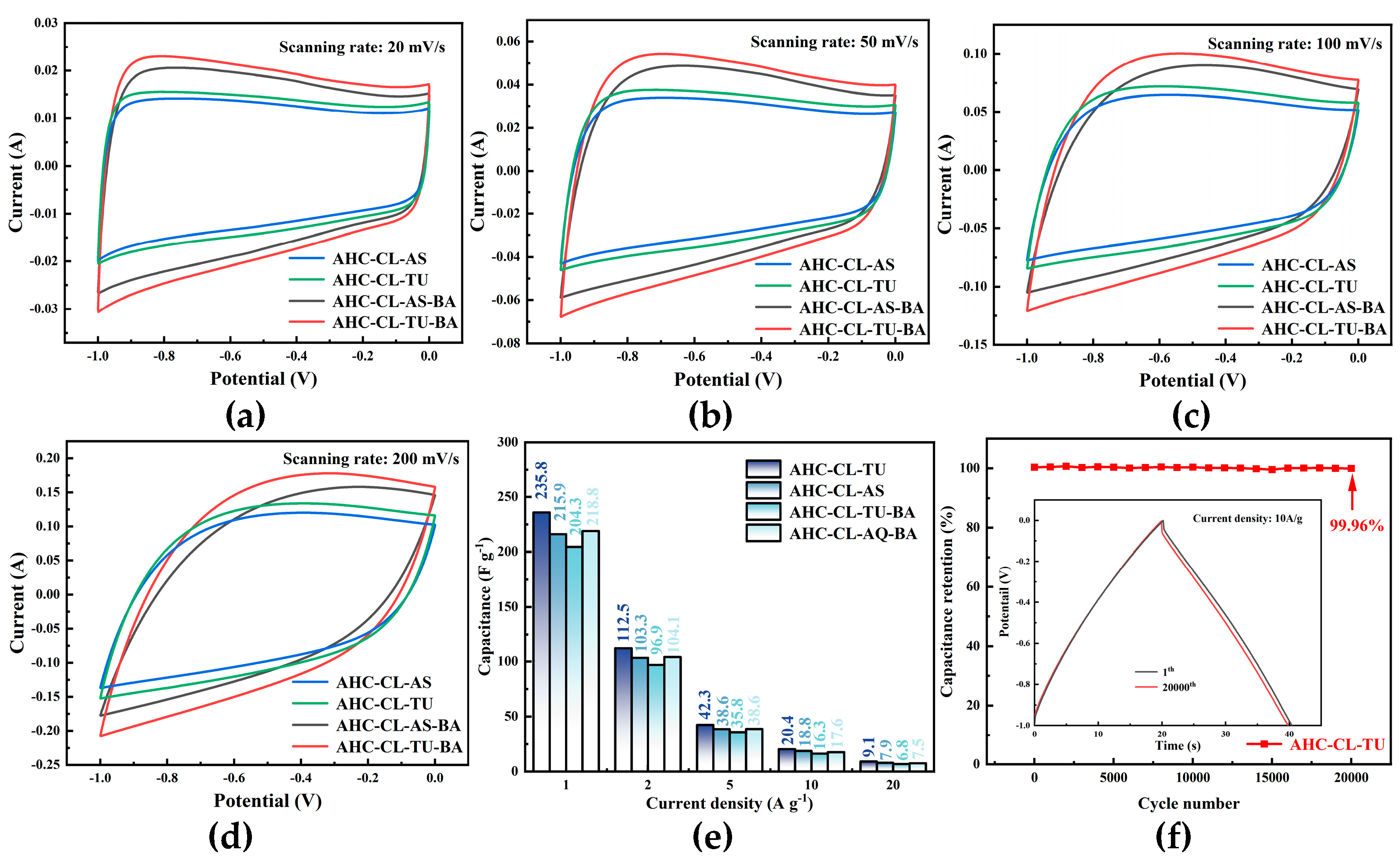
Figure 5(a, b, c, d) shows the CV curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at scan rates of 20 mV s
-1, 50 mV s
-1, 100 mV s
-1 and 200 mV s
-1, respectively. As shown in Figure 7(a), it can be seen that the CV curves of AHC-CL+TU+BA and AHC-CL+AS+BA have larger quasi-rectangular regions with slight protrusions and less deformation, indicating that the samples of electric double layer Behavior induced by redox reactions of surface functional groups during discharge. AAT and AHC-CL+AS have more regular quasi-rectangular shapes, indicating that electrolyte ions underwent rapid ionic reactions in these two samples. As the scan rate increases, the quasi-rectangular shape of the CV curve starts to change. At a high-speed scan rate of 100 mV s
-1, AHC-CL+AS and AHC-CL+TU still maintain a relatively stable quasi-rectangular structure. It shows that AHC has typical double-layer capacitance characteristics and good reversible capacitance characteristics.
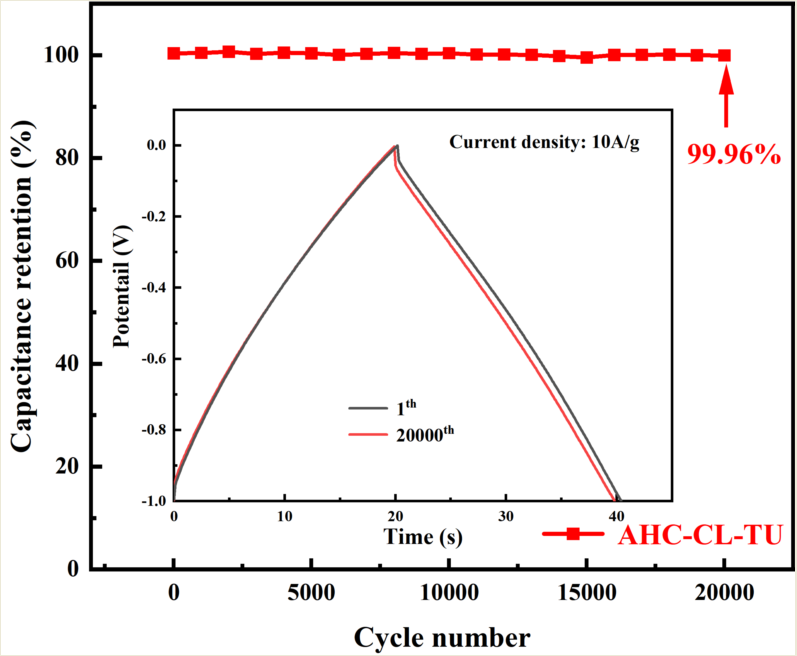
The specific capacity data of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA were calculated according to the GCD curves, as shown in Figure 7(e). As shown in Figure 7(f), the cycle durability of AHC-CL+TU was investigated by GCD measurement for 20,000 cycles at a charge-discharge current density of 10.0 A g-1. AHC-CL+TU exhibits good cycling stability and high capacitance retention of 99.96%.
5. Conclusion
The doping of nitrogen and sulfur in the process of hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose could be realized. The doping effect of organic nitrogen and sulfur compounds was better than that of inorganic compounds. The addition of boric acid had a negative effect on the carbon materials prepared by the co-carbonization of both nitrogen sources and cellulose, most notably when thiourea acted as an organic nitrogen source. Boric acid will reduce the specific surface area of porous materials and inhibit the pore-forming process of micropores. The electrochemical performance of the doped thiourea sample was significantly reduced, and the influence of boric acid on the experimental sample could be eliminated by cycling. In the carbonization experiment of doping N and B elements at the same time, boric acid has a more obvious inhibitory effect. Compared with AHC-CL-AS (829.59 m2 g-1) and AHC-CL-TU (952.27 m2 g-1), the specific surface area of AHC-CL-AS-BA (484.76 m2 g-1) and AHC-CL-TU-BA (397.59 m2 g-1) has obvious decline. At a current density of 1 A g-1, the specific capacitance of AHC-CL-AS-BA (219.3 F g-1) and AHC-CL-AS (216.4 F g-1) has no obvious difference, and AHC-CL-TU-BA (205.8 F g-1) was compared with AHC-CL-TU (236.25 F g-1) decreased significantly. Therefore, boric acid has a certain inhibitory effect on carbonization experiments doped with nitrogen. Nevertheless, we view that supercapacitor carbon materials with good properties can be prepared by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose and nitrogen and sulfur compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptu-alization, Pei-Gao Duan and Naveed Ramzan; methodology, Kun Wang; software, Chang Liu; validation, Chang Liu, Kun Wang and Yu-Han Du; formal analysis, Chang Liu; investigation, Chang Liu; resources, Pei-Gao Duan; data curation, Chang Liu; writing—original draft preparation, Chang Liu and Yu-Han Du.; writing—review and editing, Pei-Gao Duan and Naveed Ramzan; visualization, Ya-Qi Shan; supervision, Pei-Gao Duan and Naveed Ramzan; project administration, X.X.; funding acquisition, Pei-Gao Duan. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52370150).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgements
We thank Zijun Ren from the Instrument Analysis Center of Xi'an Jiaotong University for his help with the SEM tests. We thank Anhui CHEMᴺ Instrument Co., Ltd. for their help with the experimental equipment. We thank Beijing JWGB Instruments Co., Ltd. for their help with the BET testing equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gao, P.; Yue, S.; Chen, H. Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: From the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 283, 124655. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu, China's renewable energy law and policy: A critical review, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2019, 99, 212-219. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Ma, C.; Su, B. Investment efficiency of the new energy industry in China. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 536–544. [CrossRef]
- F.E. Ahmed, R. Hashaikeh, N. Hilal, Solar powered desalination – Technology, energy and future outlook, Desalination 2019, 453, 54-76. [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.F.; Lopez, M.C.; Moore, N.; Müller, N.; Hyndman, D.W. Sustainable hydropower in the 21st century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11891–11898. [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.K. Wind energy developments and policies in China: A short review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1393–1405. [CrossRef]
- Abouelamaiem, D.I.; He, G.; Parkin, I.; Neville, T.P.; Jorge, A.B.; Ji, S.; Wang, R.; Titirici, M.-M.; Shearing, P.R.; Brett, D.J.L. Synergistic relationship between the three-dimensional nanostructure and electrochemical performance in biocarbon supercapacitor electrode materials. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 772–785. [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Kong, Q.; Cao, Y.; Sun, G.; Su, F.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Ahmad, A.; Xie, L.; Chen, C.-M. Biomass-derived porous carbon materials with different dimensions for supercapacitor electrodes: a review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16028–16045. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, W. Ou-Yang, X. Xu, M. Wang, S. Hou, T. Lu, Y. Yao, L. Pan, Micro-/mesoporous carbon nanofibers embedded with ordered carbon for flexible supercapacitors, Electrochimica Acta 2018, 271, 591-598. [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Chen, X.; Tan, Z.; Chi, M.; Xie, W.; Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Hu, H.; Dong, H.; et al. Synthesis of Porous Carbon Material with Suitable Graphitization Strength for High Electrochemical Capacitors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6601–6610. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.; Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H. KCl-assisted activation: Moringa oleifera branch-derived porous carbon for high performance supercapacitor. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 5712–5719. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Arora, A.; Tripathi, S.K. Review of supercapacitors: Materials and devices. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 801–825. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L. Recent progress of biomass-derived carbon materials for supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2020, 451, 227794. [CrossRef]
- L. Yao, J. Lin, Y. Chen, X. Li, D. Wang, H. Yang, L. Deng, Z. Zheng, Supramolecular-mediated ball-in-ball porous carbon nanospheres for ultrafast energy storage, InfoMat 2021, 4, e12278. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Yuan, C.; Lou, X.W. Recent Advances in Metal Oxide-based Electrode Architecture Design for Electrochemical Energy Storage. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5166–5180. [CrossRef]
- C. Sassoye, C. Laberty, H. Le Khanh, S. Cassaignon, C. Boissière, M. Antonietti, C. Sanchez, Block-Copolymer-Templated Synthesis of Electroactive RuO2-Based Mesoporous Thin Films, Advanced Functional Materials 2009 19, 1922-1929. [CrossRef]
- Ramya, R.; Sivasubramanian, R.; Sangaranarayanan, M. Conducting polymers-based electrochemical supercapacitors—Progress and prospects. Electrochimica Acta 2013, 101, 109–129. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Lee, S.; Oh, J.; Lee, K.S.; Potts, J.R.; Ji, J.; Zhao, X.; Ruoff, R.S.; Park, S. Generation of B-Doped Graphene Nanoplatelets Using a Solution Process and Their Supercapacitor Applications. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 19–26. [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.V.; Leng, M.; Li, M.; Huang, X.L.; Xue, J.M. Sulphur-functionalized graphene towards high performance supercapacitor. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 250–257. [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Piñero, E.; Cadek, M.; Béguin, F. Tuning Carbon Materials for Supercapacitors by Direct Pyrolysis of Seaweeds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1032–1039. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wen, B. Wang, C. Huang, L. Wang, D. Hulicova-Jurcakova, Synthesis of phosphorus-doped graphene and its wide potential window in aqueous supercapacitors, Chemistry 2015, 21, 80-5. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Guan, G.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H. Recent Advancement of Nanostructured Carbon for Energy Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5159–5223. [CrossRef]
- Lota, G.; Grzyb, B.; Machnikowska, H.; Machnikowski, J.; Frackowiak, E. Effect of nitrogen in carbon electrode on the supercapacitor performance. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 404, 53–58. [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Torres, D.; Shiraishi, S.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D. Improvement of carbon materials performance by nitrogen functional groups in electrochemical capacitors in organic electrolyte at severe conditions. Carbon 2015, 82, 205–213. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Kohandehghan, A.; Li, Z.; Cui, K.; Tan, X.; Stephenson, T.J.; King’ondu, C.K.; Holt, C.M.B.; Olsen, B.C.; et al. Interconnected Carbon Nanosheets Derived from Hemp for Ultrafast Supercapacitors with High Energy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5131–5141. [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Cao, C.; Idrees, F.; Ma, X. Hierarchical Porous Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanosheets Derived from Silk for Ultrahigh-Capacity Battery Anodes and Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2556–2564. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.J.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.P. Camellia pollen-derived carbon for supercapacitor electrode material. J. Power Sources 2018, 394, 9–16. [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Lv, J.; Lian, S.; Hu, B.; Mai, L.; Zhou, L. Tailoring porous carbon spheres for supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21604–21616. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhu, H.; Meng, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, F.; Hu, Z.-A. Graphene covalently functionalized with 2,6-diaminoanthraquinone (DQ) as a high performance electrode material for supercapacitors. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 16821–16830. [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Gao, J.; Wu, F.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Xie, M.; Mi, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J. Dictyophora-derived N-doped porous carbon microspheres for high-performance supercapacitors. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 15415–15425. [CrossRef]
- Jahirul, M.I.; Rasul, M.G.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Ashwath, N. Biofuels Production through Biomass Pyrolysis —A Technological Review. Energies 2012, 5, 4952–5001. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, R. Effects of pyrolysis temperature and heating time on biochar obtained from the pyrolysis of straw and lignosulfonate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 176, 288–291. [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.E.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Satrio, J.A.; Brown, R.C. Characterization of biochar from fast pyrolysis and gasification systems. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 386–396. [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. Biomass-derived carbon: synthesis and applications in energy storage and conversion. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4824–4854. [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H. Preparation of High-Performance Porous Carbon Materials by Citric Acid-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Bamboo and Their Application in Electrode Materials. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 9303–9312. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. A review of the hydrothermal carbonization of biomass waste for hydrochar formation: Process conditions, fundamentals, and physicochemical properties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 223–247. [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Balasubramanian, R.; Srinivasan, M. Hydrothermal conversion of biomass waste to activated carbon with high porosity: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 789–805. [CrossRef]
- Susanti, R.F.; Arie, A.A.; Kristianto, H.; Erico, M.; Kevin, G.; Devianto, H. Activated carbon from citric acid catalyzed hydrothermal carbonization and chemical activation of salacca peel as potential electrode for lithium ion capacitor’s cathode. Ionics 2019, 25, 3915–3925. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zou, K.; Ji, X. Review on recent advances in nitrogen-doped carbons: preparations and applications in supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 4, 1144–1173. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Peng, P.; Xiao, B.; Yang, Y. Urea/ZnCl2 in situ hydrothermal carbonization of Camellia sinensis waste to prepare N-doped biochar for heavy metal removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30365–30373. [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Cai, J. High-performance hierarchical N-doped porous carbons from hydrothermally carbonized bamboo shoot shells for symmetric supercapacitors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 96, 672–680. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Jin, C. Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped spherical carbon from carboxymethylcellulose for CO2 capture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 101–107. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Xi, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, L. B,N-Codoped Porous C with Controllable N Species as an Electrode Material for Supercapacitors. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 13252–13261. [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Fan, X.; Yu, C.; Yang, J.; Xiao, N.; Qiu, J. Boric acid-mediated B,N-codoped chitosan-derived porous carbons with a high surface area and greatly improved supercapacitor performance. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5120–5125. [CrossRef]
- Fakkaew, K.; Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C. Effects of hydrolysis and carbonization reactions on hydrochar production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 328–334. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The reaction path of CL carbonization under hydrothermal conditions.
Figure 1.
The reaction path of CL carbonization under hydrothermal conditions.
Figure 2.
(a). Adsorption/desorption curves of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA under N2 environment; (b). Pore size distribution curves of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA; (c). Specific surface area and micropore area of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA.
Figure 2.
(a). Adsorption/desorption curves of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA under N2 environment; (b). Pore size distribution curves of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA; (c). Specific surface area and micropore area of AHC-CL, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS+BA, AHC-CL+TU+BA.
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a, b). AAM; (c, d); AABM; (e, f). AAT; (g, h). AABT.
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a, b). AAM; (c, d); AABM; (e, f). AAT; (g, h). AABT.
Figure 4.
The electrochemical performance data of the three-electrode system using 6M potassium hydroxide solution as the electrolyte. (a). GCD curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at current density of 1A g-1; (b). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 10 mV s-1; (c). Nyquist spectra of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA.
Figure 4.
The electrochemical performance data of the three-electrode system using 6M potassium hydroxide solution as the electrolyte. (a). GCD curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at current density of 1A g-1; (b). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 10 mV s-1; (c). Nyquist spectra of AHC-CL+TU,AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA.
Figure 5.
The electrochemical performance data of the three-electrode system using 6M potassium hydroxide solution as the electrolyte. (a). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 20 mV s-1; (b). CV curves of ABM, ABT, AM, and AT at a scan rate of 50 mV s-1; (c). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 100 mV s-1; (d). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 200 mV s-1; (e). Histogram of specific capacitance at flow densities of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20A g-1 respectively. (f). Based on AHC-CL+TU supercapacitors were tested for stability of 20,000 cycles at a current density of 5A g-1.
Figure 5.
The electrochemical performance data of the three-electrode system using 6M potassium hydroxide solution as the electrolyte. (a). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 20 mV s-1; (b). CV curves of ABM, ABT, AM, and AT at a scan rate of 50 mV s-1; (c). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 100 mV s-1; (d). CV curves of AHC-CL+TU, AHC-CL+AS, AHC-CL+TU+BA, and AHC-CL+AS+BA at a scan rate of 200 mV s-1; (e). Histogram of specific capacitance at flow densities of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20A g-1 respectively. (f). Based on AHC-CL+TU supercapacitors were tested for stability of 20,000 cycles at a current density of 5A g-1.
Table 1.
Elemental analysis(wt%) of the HC and AHC.
Table 1.
Elemental analysis(wt%) of the HC and AHC.
| Sample |
C |
H |
N |
S |
O |
H/C |
O/C |
| CL |
66.61 |
4.44 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
28.55 |
0.06 |
0.43 |
| HC-CL |
70.14 |
4.35 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
24.07 |
0.06 |
0.34 |
| HC-CL-AS |
66.98 |
5.12 |
3.63 |
0.35 |
15.36 |
0.10 |
0.66 |
| HC-CL-TU |
52.34 |
6.20 |
4.67 |
2.92 |
12.94 |
0.08 |
0.37 |
| HC-CL-AS-BA |
63.21 |
4.66 |
4.92 |
4.54 |
15.81 |
0.07 |
0.34 |
| HC-CL-TU-BA |
67.54 |
4.81 |
4.31 |
0.37 |
16.14 |
0.07 |
0.35 |
| AHC-CL |
76.11 |
1.27 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
21.91 |
0.02 |
0.29 |
| AHC-CL-AS |
78.59 |
1.88 |
2.84 |
0.32 |
11.69 |
0.02 |
0.15 |
| AHC-CL-TU |
70.32 |
1.94 |
3.25 |
2.23 |
21.46 |
0.03 |
0.31 |
| AHC-CL-AS-BA |
78.56 |
1.74 |
4.02 |
3.97 |
10.27 |
0.02 |
0.13 |
| AHC-CL-TU-BA |
79.34 |
1.79 |
3.77 |
0.32 |
12.73 |
0.02 |
0.16 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).