1. Introduction
Ischemic cardiomyopathy (CMP) after acute myocardial infarction (MI) is the most common cause of heart failure and therefore the leading cause of death worldwide [
1,
2]. While in the acute phase of MI percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTCA) is the most important means to restore coronary perfusion ("time is muscle“) [
3], lifestyle modification as well as the drug regimes of anti-platelet therapy, cholesterol lowering and heart failure therapy [
4,
5] play a crucial role for recurrence prevention, maintenance of cardiac functional performance as well as prevention of adverse ventricular remodeling.
At the present time, the risk with respect to the development of ischemic CMP depends, among other factors, on the infarct location and on the duration of complete reperfusion of the affected coronary vessel [
6,
7,
8,
9]. The irreversible destruction of cardiomyocytes leads to the development of a corresponding infarct area with loss of myocardial contractility due to scarring [
10,
11]. All current drug therapy options aim at preserving the remaining myocardial functional capacity. Therapeutic options to prevent or reduce cell death of cardiomyocytes or even to regenerate them after cell death are still lacking.
The broad research field of microRNAs (miRs) could offer potential new therapeutic approaches to prevent ischemic CMP by acting on the post-transcriptional regulation of corresponding gene expressions [
12,
13,
14]. Despite their small size of approximately 20 nucleotides, miRs, as small non-coding RNAs, have a significant impact on cell proliferation and differentiation as well as apoptosis regulation. In particular, miRs play a relevant role in the development of blood vessels, the contractility and regeneration of cardiomyocytes, the development and stabilization of arteriosclerosis, and the regulation of the basic cardiac rhythm in the context of various underlying cardiovascular diseases [
15,
16,
17].
In the setting of acute MI, miRs may not only be considered biomarkers for improved early diagnosis [
18,
19,
20], but also act as clinical prognostic markers for the occurrence of major cardiovascular events (MACE) or mortality [
21]. However, miRs can not only be quantified but also modified to increase (agomir/mimic) or decrease (antagomir) expression [
22].
Based on these considerations, miRs have also been used therapeutically in previous work in both in-vivo and in-vitro studies. For example, myocardial ischemia was induced using animal models and then agomirs/mimics of miR-21 [
23,
24], miR-199a or miR-590 [
25,
26], respectively, were administered, which stimulated a cardiac repair. The use of antagomirs of miR-1 [
27], miR-24 [
28] and miR-132 [
29,
30] in comparable animal models also improved cardiac functional performance after induced ischemia.
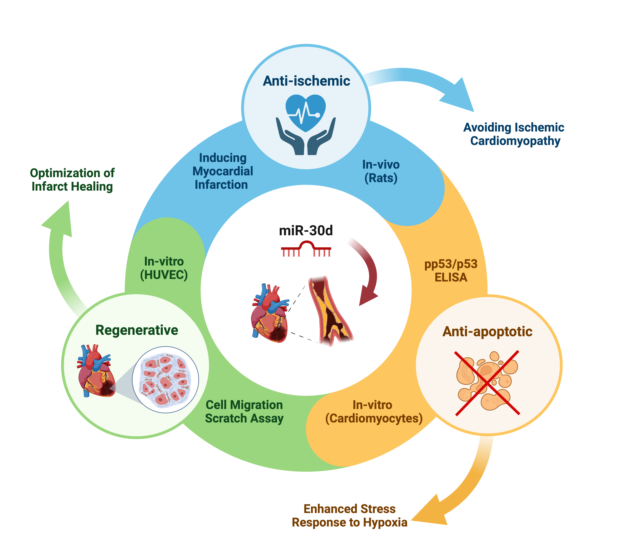
The aim of this experimental work was to establish a miR expression profile of ischemic vs. healthy myocardium using an animal model as a first step. Based on these results, miR-30d, which was significantly down-regulated in the setting of acute MI, was considered as a potential therapeutic target. In a second step, in-vivo and in-vitro studies were used to investigate the effect of "drug" stimulation of miR-30d on the development of ischemic CMP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental rat model
2.1.1. Inducing of acute myocardial infarction
The animal experiment described in this publication was approved by the Committee for Animal Research of the Medical University of Vienna 66.009/0122-WF/V/3b/2017 and was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996).
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were used for the animal model and were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of xylazine (4 mg/kg; Bayer, Germany) and ketamine (100 mg/kg; Dr. E. Gräub AG, Switzerland). Ventilation with a 14-gauge tube was performed at 9 ml/kg body weight and a respiratory rate of 75-85 stroke/min. Adequate analgesia was provided by intraperitoneally injected piritramide (0.1 ml/kg body weight). Rectal temperature was monitored and maintained at 37.5 – 38.5°C by a heated operating table and the heart rhythm was monitored by electrocardiogram (ECG). Myocardial infarction was induced by coronary artery ligation as described previously, [
31,
32]. To induce myocardial ischemia, the heart was exposed via a left thoracotomy and a permanent ligation of the left coronary artery (LCA) 2-3 mm away from the origin using a 6-0 prolene was induced. Myocardial ischemia was documented by ECG through the development of ST-segment elevations. For postoperative analgesia, piritramide was administered via drinking water (2 ampules of Piritramide with 30 ml of Glucose 5% in 250 ml water). In order to obtain the respective histological samples of the hearts, rats were sacrificed after six weeks under deep anesthesia by opening the inferior vena cava.
2.1.2. MiR expression with next generation sequencing (NGS)
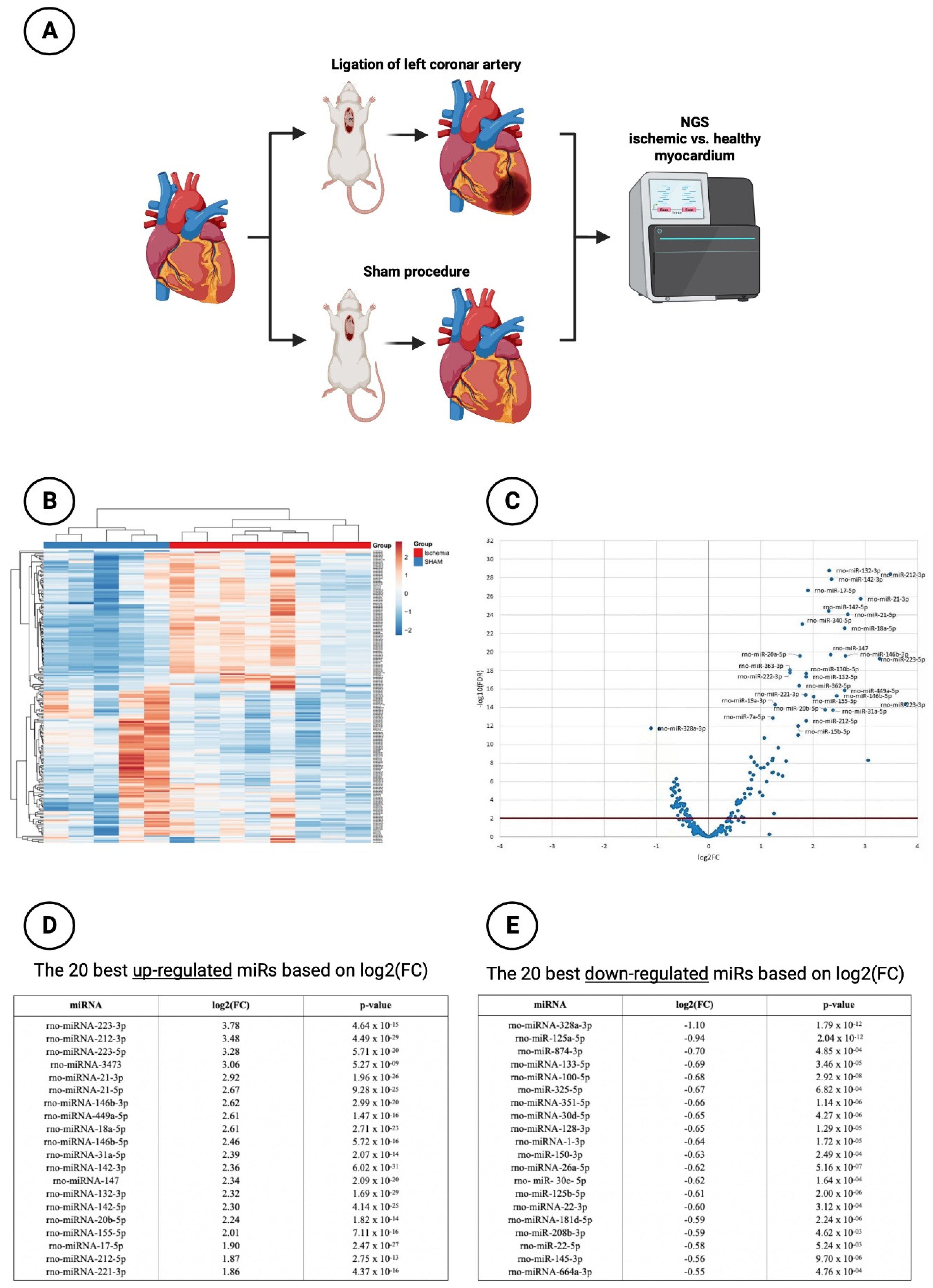
MiR profiling was performed by NGS to assess differences in miR expression in ischemic vs. healthy myocardium in the animal model mentioned above (
Figure 1A). A total of 13 animals were subjected to surgical intervention. 8 of them underwent ischemia injury via ligation of the LCA, whereas 5 sham-operated animals without ligation of LCA served as control group. Six weeks after the induction of MI, rats were sacrificed and hearts were explanted and immediately deep frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at -80°C.
2.1.2.1. Total RNA extraction from tissue
Total RNA from frozen tissues was extracted using miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). In the first step fresh frozen tissue was weighed and subsequently 350 µL Qiazol were added. Subsequent steps were performed at room temperature. TissueRuptor homogenizer (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was applied to each tissue for 30s at full speed until no visible tissue parts were observed. After an incubation at room temperature for 5 minutes 140 µl chloroform were added to the lysates followed by vigorous mixing on a vortex, incubation at room temperature for 3 minutes and cooled centrifugation at 12,000g for 15 minutes at 4°C. Exactly 350 µL of the upper aqueous phase were mixed with 525 µL ethanol and RNA was precipitated on a miRNeasy mini column followed by automated washing with RPE and RWT buffer in a Qiacube liquid handling robot (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Finally, total RNA was eluted in 30 µL nuclease free water. Total RNA integrity and concentration were checked using the RNA6000 Nano Bioanalyzer assay (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) as well as spectrophotometric RNA quantification (Nanodrop; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.1.2.2. Small RNA-sequencing
Equal amounts of total RNA (230 ng) were used for small RNA library preparation using NEBNext small RNA library preparation kit (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacture’s declarations. Adapter-ligated libraries were amplified using barcoded Illumina reverse primers in combination with the Illumina forward primer. Libraries were pooled equimolar on the basis of DNA 1000 Bioanalyzer quantification (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and gel-based size selection was performed on the pooled library to enrich for insert sizes between 18 and 36 basepairs. The library pool(s) were quantified using the qPCR KAPA Library Quantification Kit (KAPA Biosystems; Roche Holding, Basel, Switzerland). The library pool(s) were then sequenced on a NextSeq500 sequencing instrument (50 bp single-end) according to the manufacturer instructions yielding an average of 11.9 million reads per sample (10.6M to 12.8M). Raw data was de-multiplexed and FASTQ files for each sample was generated using the bcl2fastq software (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). FASTQ data were checked using the FastQC tool (
http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/).
2.1.2.3. Small RNA-sequencing data analysis
Cutadapt (1.11) was used to extract trim and remove adapters. Bowtie2 (2.2.2) was used for mapping the reads requiring a perfect match to the reference miR-base sequences, and allowing for one mismatch in the first 32 bases of the read for the respective genome mapping is allowed.
2.1.3. Histology and planimetry
Once miR-30d was established as a promising target and thus a potential cardioprotective agent, the infarct model of rat was used.
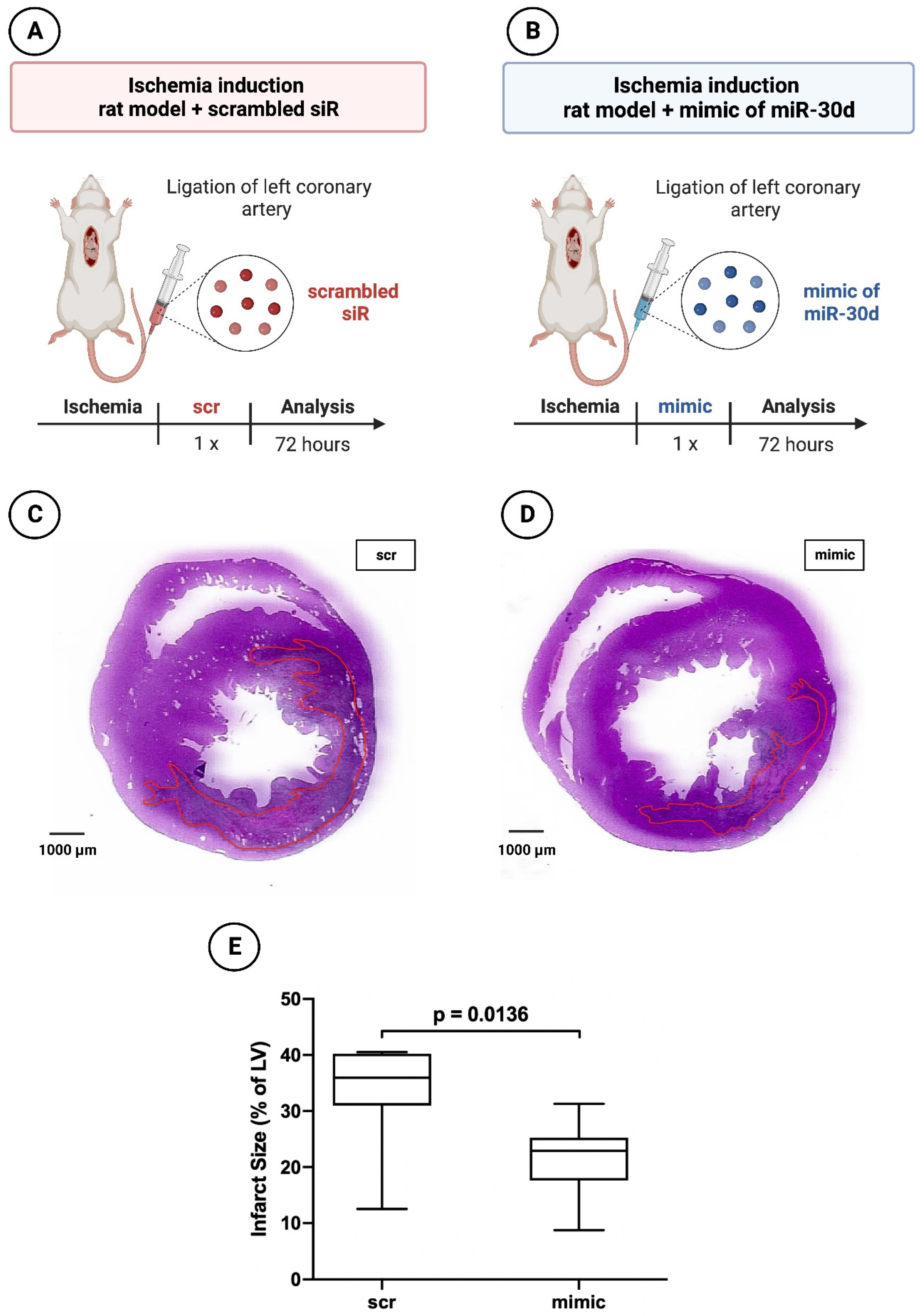
To assess the effect of miR-30d on the acute ischemic response, 17 rats were subjected to myocardial infarction. Ten rats received a miR-30d mimic (Dharmacon, Lafayette, LA, USA) intraperitoneally, whereas 7 rats were administered a non-functional scrambled siR (Dharmacon, Lafayette, LA, USA) also intraperitoneally (
Figure 2A,B). Rats were sacrificed 72 hours after the coronary artery ligation.
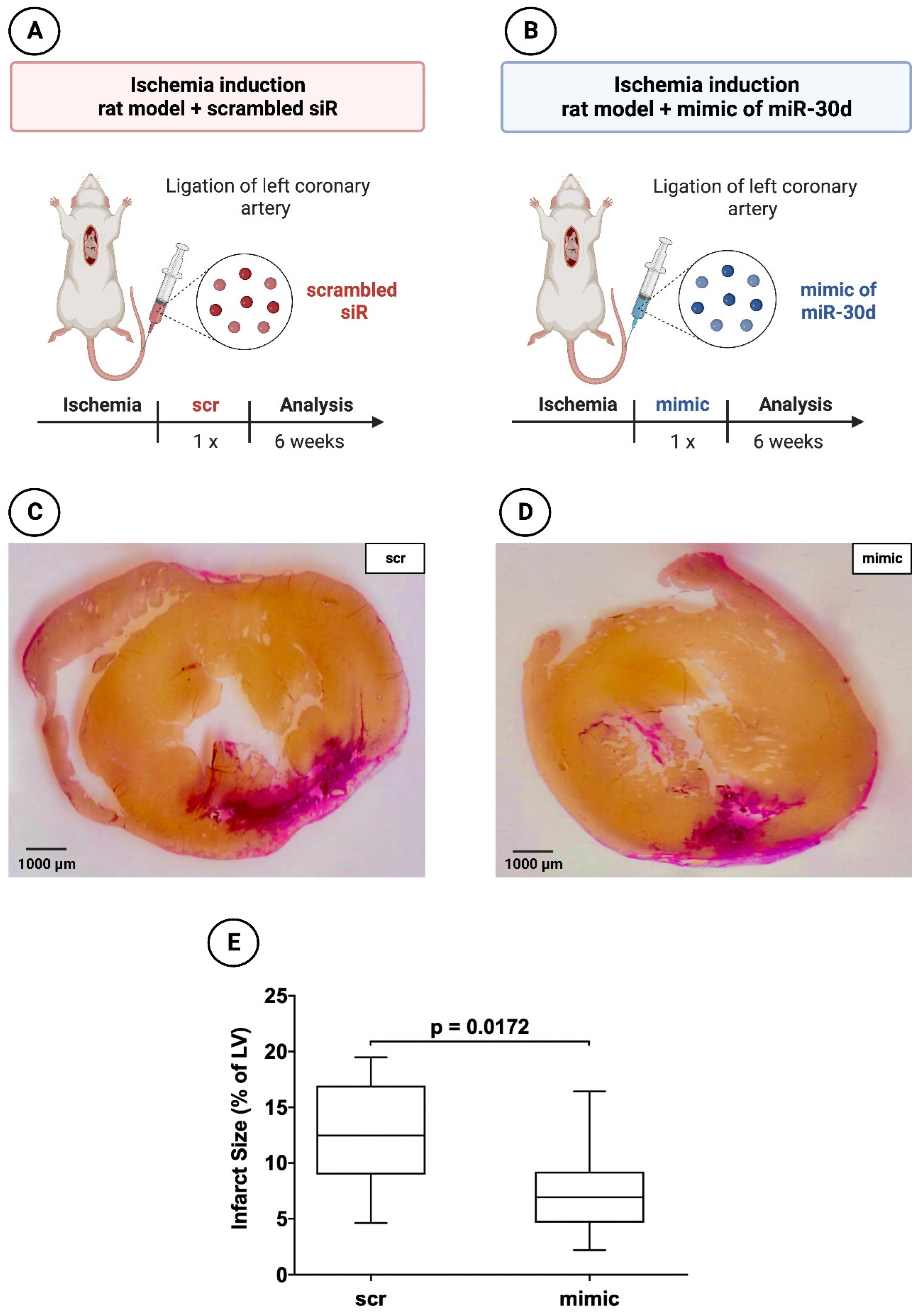
In addition, 19 animals (9 with application of miR-30d mimic and 10 with application of scrambled siR) were used to evaluate the myocardial infarct area 6 weeks after MI induction (
Figure 3A,B). The necessary miR/siR was packaged into appropriate nanoparticles as described in the study of Borchardt et al. [
33]. 17.7 µg (6.65 µl of a 200 µM stock solution) miR mimic or scrambled siR were dissolved in 200 µl HN buffer (10 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) and incubated for 10 min. In parallel, 133 µg PEI F25-LMW was diluted in 200 µl HN buffer and incubated for 10 min, prior to mixing with the miR solution and complexation for 15 min. The nanoparticles were stored at -80°C. For injection, aliquots were thawed and kept at room temperature for 30 min prior to use.
After 6 weeks hearts were explanted and the organs were sliced at three layers at the level of the largest extension of infarcted area. Sections were fixed in 10% neutral buffered paraformaldehyd, embedded in paraffin and sliced into 5 µm sections. Subsequently, both hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and van Gieson (VG) staining were performed. An inverted microscope with 200x and 400x magnification was applied to evaluate the tissue specimen. Image J planimetry software (Rasband, W.S., Image J, U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA) was utilized to assess the extent of the necrosis/fibrotic area after 6 weeks. Infarction size was expressed as a percentage of the total left ventricular area as described previously [
34].
2.2. Human umbilical cord endothelial cells (HUVEC)
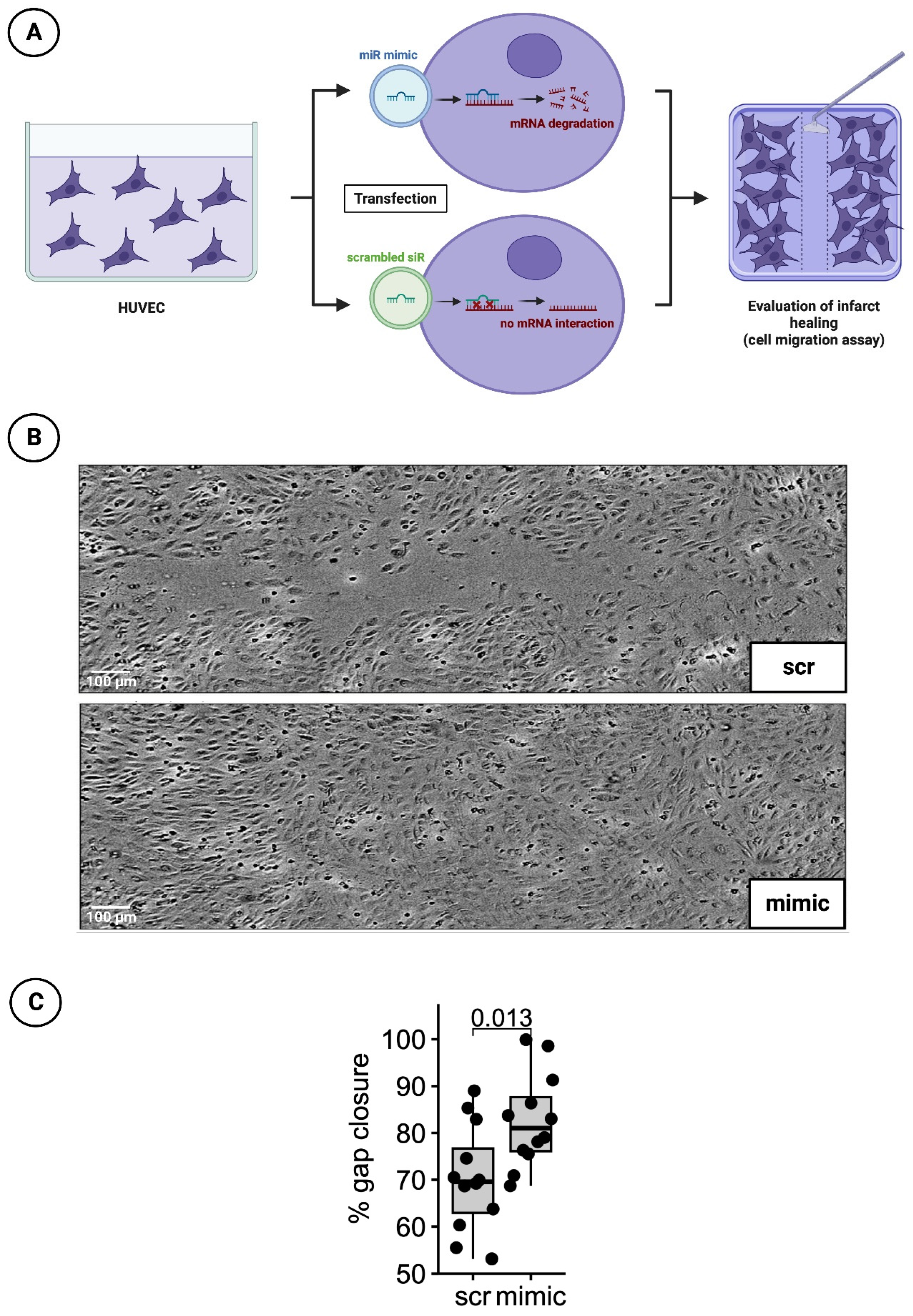
2.2.1. Cultivation and transfection with nanoparticles of miR mimic or scrambled siR
HUVEC (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were cultivated in T75 flasks using endothelial cell growth medium 200 (M200500, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Afterwards, 1.5 x 105 cells in 500 µl cultivation medium were seeded in Costar® 24-well plates (CLS3527, Corning Costar, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and incubated for 24 hour at 37°C. The corresponding HUVEC were subjected to a transfection process when a confluence of nearly 80% was reached. HUVEC transfection protocol on 24-well plate was carried out on the basis of the manufacturer's instructions by means of XfectTM RNA Transfection Reagent Protocol. Therefore, an Xfect polymere (631450, Takara Bio Inc., Kusatsu, Japan) was used mixed with either the aforementioned nanoparticles of miR-30d mimic or a scrambled siR. Mimic miR and scrambled siR were brought to a concentration of 50 nM and applied to the respective wells. The total incubation time with the transfection medium was 4h. This was then replaced with normal endothelial growth medium and incubated for a further 44 h at 37°C with 5% CO2. The growth medium was changed every 24 h.
2.2.2. Detection of infarct healing via cell migration scratch assay
48 h after treatment with the transfection medium, a 100 µl pipette tip was used to manually obtain a cell-free gap for cell migration scratch assay. The growth processes over the scratch was monitored every hour for 24 h by measuring cell confluence in a pre-defined, constant area including the gap using a Tecan Spark® 10M multimode microplate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). Percentage of gap closure was assessed 20 hrs after scratch initiation (t = 0) using image analysis software (ImageJ, version 1.53c, NIH, USA) to determine gap area normalized to gap area at timepoint t = 0 (
Figure 4A).
2.3. Human cardiomyocytes (HCMs)
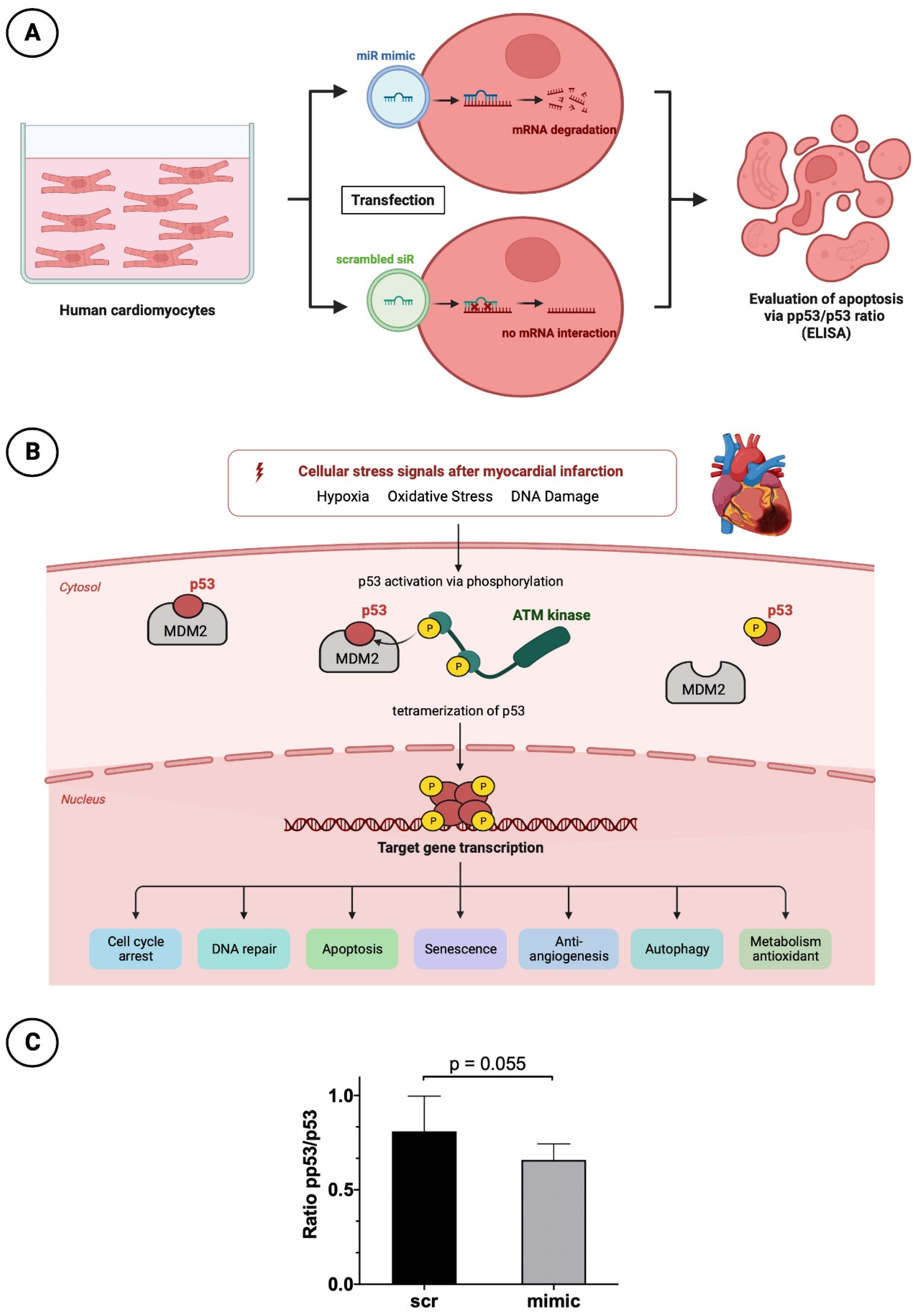
2.3.1. Cultivation and transfection with nanoparticles of miR mimic or scrambled siR
The cultivation of HCMs (PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany) was based on a myocyte growth medium supplemented with supplement mix (PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany), 1% L-glutamine and 1% PenStrep in T75 flasks. For the following enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), cells were seeded at a concentration of 1x10
4 cells in a 96-well plate (Greiner Bio-One; Frickenhausen, Germany) with 150 µl cultivation medium. Confluence was achieved at a cell density of slightly 4 x 10
4 cells per well after 24 hours. If confluence was not visually achieved, the culture medium was replaced with fresh 150 µl cultivation medium. When confluence was satisfactory, the basal medium was removed and starvation medium (supplemented only with 1% PenStrep and 1% L-glutamine) was applied for 3 h instead. HCMs were further treated for transfection with the same protocol as used in HUVEC cells (
Figure 5A). Again, nanoparticles including miR-30d-mimic and a scrambled siR was applied in a concentration of 50 nM for 15 minutes.
2.3.2. Apoptosis testing by p53 and pp53 ELISA
P53 plays a relevant key role in controlled cell death. Due to numerous stimuli in the context of acute myocardial infarction and associated ischemic injury, hypoxia, oxidative stress and damage to cardiomyocyte DNA occur. Among other things, this leads to increased activation of the enzyme Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase, a serine protein kinase, that initiates phosphorylation of p53. This phosphorylation causes the conformational state of p53 to change such that the inactive form originally bound to its regulator and proto-oncogen Mouse Double Minute 2 Homolog (MDM2) is released and thus activated. Through tetramerization, p53 reaches the configuration to finally initiate cell death at the nucleus level by means of increased transcription of corresponding genes. For better understanding the molecular processes is shown by a schematic overview in
Figure 5B.
To investigate the anti-apopteutic and thus simultaneously cardioprotective effect of miR-30d, above-mentioned prepared HCMs were subjected to p53 (DuoSet® IC ELISA – Human Total p53, R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK) and pp53 ELISA analysis (DuoSet® IC ELISA – Human Phospho-p53, R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK). Accordingly, conclusions about the apoptosis rate of cells treated with and without mimic of miR-30d can be drawn from the ratio between phosphorylated and total p53. For this purpose, a 96-well plate was split and one side was incubated with p53-capture antibody and the other with pp53-capture antibody according to the manufacturer's instructions at room temperature over night. Afterwards, the pretreated HCMs were detached from the 96-well plate in several washings and application of a lysis buffer containing 0.5% Triton X-100. The obtained solution was centrifuged and the cell supernatant was transferred to the prepared 96-well plate containing capture antibody. After the incubation time was observed, the supernatant was removed and either the biotinylated p53 or pp53 detection antibody was added. Finally, in two additional steps streptavidin-Horseradish peroxidase and tetramethylbenzidine was added to achieve a color reaction. Subsequently, the analysis was performed using a microplate reader set to a wavelength of 450 nm.
2.4. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of NGS data was done with with Statistical Software R (version 4.2.0). To identify microRNAs that are significantly regulated between ischemia and control animals, differential expression analysis was performed using the edgeR package v3.28 (Bioconductor,
http://bioconductor.org/) and, in this case, specific log2-transformed fold change (log2(FC)). The log2(FC) describes the fold-difference in microRNA levels between controls and treatment groups. Positive log2(FC) describes up-regulation, negative log2(FC) describes down-regulation in the treatment group.
The further statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0, GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA,
www.graphpad.com) and SPSS 25 (IBM Corp. Released 2017. IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 25.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.) with again use of R (version 4.2.0). Normally distributed data are given as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and non-normally distributed data as median ± interquartile range (IQR). Categorical variables are expressed as percentage. In the case of a normal distribution, an unpaired student t-test was performed, and in the case of a non-normal distribution, a Wilcoxon signed-rank test was conducted. All tests were two-sided. A p-value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. miR-30d with significant down-regulation in animal model of induced iCMP
In the context of NGS sequencing, 202 miRs were analyzed with respect to their expression between healthy myocardium and ischemic myocardium. An overview of all analyzed miRs is provided in
Figure 1B. It can be shown that a large number of miRs were significantly regulated between sham-operated and LCA-ligated rats. Therefore, a vulcano plot was created for a better overview (
Figure 1C). Here, it could be demonstrated that the majority of miRs in the ischemia group were significantly up-regulated (log2(FC) values > 1), again with the top 20 up-regulated miRs shown in
Figure 1D. The highest log2(FC) value was achieved by miR-223-3p (3.78) and miR-212-3p (3.48) with a highly significant p-value < 0.001 each. An additional, artificial increase of these already up-regulated miRs after myocardial ischemia by drug delivery would therefore not lead to any additional benefit, so that the focus of this study was rather on the down-regulated miRs with a negative log2(FC) value < -0.5).
In this regard,
Figure 1E shows the top 20 down-regulated miRs. Here, miR-328a-3p with a log2(FC) of -1.10 ranks as the most significantly down-regulated miR of the entire cohort studied followed by miR-125a-5p (log2(FC): -0.94). Like the other miRs, miR-30d-5p, which was further investigated in this work, provided highly significant down-regulation with a log2(FC) value of -0.65. Preliminary studies or experiments performed by our own research group [
35,
36] demonstrated that in both in vivo and in vitro studies, stimulation with anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) leads to an induced upregulation of miR-30d-5p. Thus, miR-30d-5p was shown to be down-regulated in myocardial ischemia but could also be increased in secretion by ATG stimulation. Based on these findings in combination with an extensive literature search in known scientific databases (PubMed, Scopus, etc.), miR-30d-5p was chosen to be evaluated as a new therapeutic target for the prevention of ischemic CMP after myocardial infarction.
3.2. Significant reduction of infarct areal size in animals treated with mimic of miR-30d after 72 hours and after 6 weeks
As described in the section of material & methods, experimental rat model of myocardial infarction (ligation of LCA) was used to evaluate a potential therapeutic benefit of a mimic of miR-30d regarding a potential reduction of myocardial scar size in comparison to the administration of a scrambled siR.
In the 72-hours animals, those treated with miR-30d showed a volumetric infarct size of 22.89 ± 7.66% on average, whereas those rats treated with scrambled siR presented an infarct extent of 35.96 ± 9.27%. Here, a statistically significant difference was found with a p = 0.0136.
Rat hearts 6 weeks after induced MI administered a mimic of miR-30d showed a volumetric infarct area of 6.93 ± 4.58%, whereas scrambled siR treated animals demonstrated an infarct size of 12.48 ± 7.09%. This revealed a statistically significant difference between the two groups with a p-value of 0.0172.
Representative images can be seen in
Figure 2C,D for the 72-hours animals and in
Figure 3C,D for the 6-weeks animals; Figures 2E and 3E represent the respective boxplot diagrams as a summary.
3.3. Significantly faster gap closure in cell migration scratch assay of HUVECs transfected with mimic of miR-30d
To investigative the healing process after myocardial infarction under the influence of a mimic of miR-30d, cell migration scratch assay mentioned above was performed. In total, 3 independent experiments with 4 wells per experimental group and run were conducted. A difference in % gap closure was evaluated with an unpaired, two-sided non-parametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test on gap areas merged from all wells of all independent experiments. The results indicates that cells treated with mimic for 48h were closing the gap significantly faster by 12.4% at 20h post scratching (p-value = 0.013). Representative images are shown in
Figure 4B, whereas a boxplot diagram sums up the results of the unpaired Wilcoxon test (
Figure 4C).
3.4. Reduced apoptotic rate in HCMs transfected with mimic of miR-30d
To understand the cardioprotective mechanism of miR-30d also at the cellular level, after appropriate cultivation of HCMs and transfection with again a mimic of miR as well as a scrambled siR, a p53/pp53 ELISA was performed to determine the apoptosis rate. HCMs treated with the mimic showed a higher p53/pp53 ratio of 0.81 ± 0.17 than cells transfected with the scrambled siR, as the latter had a reduced ratio of 0.66 ± 0.08 (
Figure 5C). Although the result was not statistically significant with a p-value of 0.055, it showed a clear tendency towards a reduced apoptosis rate in the presence of increased miR-30d.
4. Discussion
Myocardial ischemia in the context of MI leads to a significant restructuring of the miR expression profile. As shown in this work, cardiomyocytes stressed by hypoxia respond in particular with a marked upregulation of miRs measuring approximately 18-25 nucleotides in contrast to vital cardiomyocytes. A significantly lower number of miRs are downregulated in ischemic myocardial territory, but definitely not to the same extent as other miRs are upregulated (compare corresponding logFC values of this study). Nevertheless, the focus in this experimental work was on the downregulated miRs to compensate for the resulting deficiency by therapeutic delivery. Based on the miR expression profile as well as the current literature, miR-30d was chosen for further experimental study.
4.1. Anti-remodeling therapy – therapeutic option to reduce the extent of ischemia
After surviving a myocardial infarction with successful recanalization of the coronary vessel, the prevention of early and late complications plays a relevant role. The most frequent complication is the development of ischemic CMP with loss of myocardial contractility. Therefore, close echocardiographic follow-up is crucial to assess LVEF and to initiate drug therapy. In myocardial infarction patients, in addition to dual anti-platelet therapy and the use of statins, a drug combination therapy of beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors or AT1 antagonists is established irrespective of the LVEF in order to improve cardiac perfusion and simultaneously avert ventricular remodeling [
37]. Ventricular remodeling is the term used to describe reactive remodeling processes of the non-infarcted ventricular myocardium as a late complication of myocardial infarction, which can manifest as fibrosis, hypertrophy and ventricular dilatation [
38]. The exact pathomechanism is not clear at the present time; however, it is thought to be related to an exaggerated function of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This at least explains the cardioprotective effect of the use of ACE inhibitors or AT1 antagonists. Also miRs seem to play a significant role in post-myocardial infarction remodeling [
39,
40]. Maries et al. [
41] showed in a review that numerous miRs (miR-1, -21, -29, -30, -34, -92, -133, -146a, etc.) were essential regulators of cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. miRs, however, not only offer therapeutic approaches with regard to successful anti-remodeling, but also have much more to offer at the molecular level.
4.2. What do miRs offer regarding other therapeutic options in the course of MI?
Since their discovery in the 1990s, miRs could open up a broad field of treatment for patients after myocardial infarction. An appealing compilation of the potential mechanisms of action or repair is provided by the reviews of Boon et al. [
42] and Wang et al. [
43]. These papers demonstrate that miRs have additional therapeutic docking sites for the prevention of ischemic CMP besides the aforementioned anti-remodeling. For example, significant anti-apoptotic potential and thus increased cardiomyocyte survival could be achieved by both regular, pathophysiological changes in miR expression profile and drug-induced up- or downregulation of specific miRs. Stimulation of cardiomyocyte proliferation and neovascularization of the infarct area by induced angiogenesis are also relevant mechanisms for the cardioprotective effect of different miRs. Finally, it should also be noted that a certain cardiac regenerative capacity could be achieved in in vitro studies by stimulation of pluripotent stem cells with certain miRs.
4.3. MiR-30d and its role in ischemic CMP
MiR-30d plays a role in underlying cardiovascular diseases that should not be underestimated. Xiao et al. [
44] demonstrated in patients with acute heart failure that subjects with low serum levels of miR-30d had a significantly higher 1-year mortality. Similarly, in a publication by Melman et al. [
45], low circulating levels of miR-30d were shown to be associated with a poorer response to cardiac resychronization therapy.
In the context of acute MI and its sequelae such as ischemic CMP, the current number of studies is scarce. Jia et al. [
46] described a significant increase in serum concentration of miR-30d in the initial phase of MI (0-6 hours) in infarcted patients in contrast to healthy subjects and even suggested a diagnostic superiority over the clinically used troponin I. After 4-6 hours, the peak of miR-30d plasma level manifested itself with subsequently declining values. Bukauskas et al. [
47] demonstrated in a direct comparison of serum levels of miR-30d that ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients had significantly decreased levels 24 hours after the event compared to healthy subjects. Regarding the expression of miR-30d in the acute phase of MI, no conclusion could be drawn in our study because the animal model was deliberately designed for the development of ischemic CMP or ventricular remodeling.
However, it could be shown that after 6 weeks of "conservative therapy" of a myocardial infarction in the animal model, a significant reduction of miR-30d occurred in the myocardium. This was also demonstrated in an experimental work by Li et al. from 2021 [
48], who associated decreased expression of miR-30d with a significantly higher risk of adverse cardiac remodeling, fibrosis and inflammation. In another work by Li et al. from 2022 [
49], the results could be applied to hypertrophic CMP.
4.4. Resistance to ischemia, anti-apoptosis and proliferation – mechanisms of action through therapeutic increase of miR-30d
In the present study, serum concentrations were therapeutically increased by transfection of a mimic of miR-30d in animal models (induction of ischemic CMP by ligation of LCA) and in different cell cultures (HCMs, HUVECs), and complex processes were investigated in vivo and in vitro. Finally, clinically relevant mechanisms of action could be deduced, which might be causative for a possible prevention of ischemic CMP after MI.
In particular, in the animal model of induced ischemic CMP, a significant reduction of the infarct area could be demonstrated by increasing the serum concentration of miR-30d, suggesting an increased stress resistance of cardiomyocytes regarding hypoxia. This statement confirmed the observations of Li et al. in 2021 [
48], who also described a cardioprotective function against hypoxic stress in their animal models of ischemic CMP by increased accumulation of miR-30d in cardiomyocytes.
A major mechanism behind this may lie in the regulation of autophagic and apoptotic processes, as miR-30d has already demonstrated its potential in several previous ischemia studies in both the heart and brain. For example, Jiang et al. [
50] demonstrated that in a rat model of induced acute cerebral ischemia, administration of exosomes of miR-30d could significantly reduce the infarct area by suppressing autophagy. A reduction of autophagic processes by administration of an agomir of miR-30d was observed in developing rat brains after induction of hypoxic-ischemic injury by Zhao and colleagues [
51]. A similar constellation manifested in the heart, where in a MI-induced animal model, overexpression of miR-30d decreased autophagy processes by reducing the activity of downstream autophagy related 5 (ATG5) protein [
52]. A definitive reduction of pro-apoptotic factors such as caspase 3 by miR-30d was demonstrated in an in vitro work by Kim et al. [
53] in ventricular cardiomyocytes. In this current work, the anti-apoptotic effect of miR-30d was demonstrated once again, as HCMs treated with a mimic of miR-30d already showed a significantly reduced apoptotic rate in the physiological state in contrast to HCMs transfected with scrambled siR.
Finally, the proliferation- and migration-inducing mechanism of miR-30d should not be ignored. In contrast to numerous cancers such as renal cell, pancreatic or colorectal carcinoma [
54,
55,
56], in which an increase in miR-30d causes suppression of proliferation, migration and invasion of cancer cells, the situation in the heart is not entirely clear. Li et al. [
48] described an inhibition of cardiac fibroblast activity by increased miR-30d expression in their animal model and thus a reduction of cardiac fibrosis after induced MI. However, this contrasts with the findings of our HUVEC experiments with the cell migration scratch assays performed, in which cells with transfection of miR-30d exhibited significantly faster gap closure and thus migration/proliferation. The extent to which miR-30d acts in a cell-specific manner and is inductive for the migration of cardiomyocytes or endothelial cells into the newly formed infarct area in case of MI will have to be clarified in further in vitro and in vivo studies.
5. Limitation
Here, in this study we sought to analyze the pattern of miR-alterations caused by myocardial ischemia. We furthermore sought to determine possible targets of therapeutic intervention and selected miR-30d as a possible target. We are aware of the fact that myocardial ischemia affects miR-signalling in a very broad fashion and that hundreds of miRs are affected by ischemia. Our intention was to focus on the effects of one single miR in this pathophysiological condition and to determine possible mechanistic effects in in vitro experiments. We want to propose miR-30d an interesting target molecule in myocardial ischemia, though, we know that the this study can just give hints for possible mechanisms and further in vitro and in vivo studies are necessary to gain more insight into cellular mechanisms in order to gain more knowledge for possible therapeutic use.
6. Conclusions
Using a mimic of miR-30d underlines the cardioprotective effects of miR-30d in MI/IR and could reduce the risk for iCMP development. Further investigations regarding its therapeutic potential in humans should be considered, as miR treatments are gaining more and more clinical applicability today.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization M.L., B.W.; Methodology B.W., A.K., V.P., A.A., E.A., S.W., B.K.P., R.Z., V.W., M.H., M.L.; Software M.H.; Formal analysis M.L.; Resources B.K.P., U.C.H.; Writing—original draft preparation E.B.; Writing—review and editing E.B., A.E.B., U.C.H., M.L.; Visualization M.L.; Advice on experiments A.A., M.H.; Project administration M.L.; Funding acquisition M.L.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research fund of the Paracelsus Medical University Salzburg (PMU-FFF), grant number E-141201104-LIC.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal experiment described in this publication was approved by the Committee for Animal Research of the Medical University of Vienna 66.009/0122-WF/V/3b/2017 and was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Figures were created and compiled with BioRender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bhandari, B., Quintanilla Rodriguez, B. S., & Masood, W. (2022). Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Nowbar, A. N., Gitto, M., Howard, J. P., Francis, D. P., & Al-Lamee, R. (2019). Mortality From Ischemic Heart Disease. Circulation. Cardiovascular quality and outcomes, 12(6), e005375. [CrossRef]
- Abreu L. M. (2019). Time is Muscle. Arquivos brasileiros de cardiologia, 112(4), 408–409. [CrossRef]
- Brinks, J., Fowler, A., Franklin, B. A., & Dulai, J. (2016). Lifestyle Modification in Secondary Prevention: Beyond Pharmacotherapy. American journal of lifestyle medicine, 11(2), 137–152. [CrossRef]
- Yarnell, J. W., Sweetnam, P. M., Rumley, A., & Lowe, G. D. (2000). Lifestyle and hemostatic risk factors for ischemic heart disease : the Caerphilly Study. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 20(1), 271–279. [CrossRef]
- Çitaku, H., Miftari, R., Stubljar, D., & Krasniqi, X. (2021). Size of Acute Myocardial Infarction Correlates with Earlier Time of Initiation of Reperfusion Therapy with Cardiac Perfusion Scintigraphy: A National Single-Center Study. Medical Science Monitor Basic Research, 27, e933214-1–e933214-6. [CrossRef]
- Wagdy, H. M., & Christian, T. F. (1996). Determinants of infarct size in acute myocardial infarction in patients treated with reperfusion therapy. Current opinion in cardiology, 11(4), 369–377. [CrossRef]
- Simonis, G., Strasser, R. H., & Ebner, B. (2012). Reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction. Critical Care, 16(Suppl 2), A22. [CrossRef]
- Hausenloy, D. J., & Yellon, D. M. (2013). Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. The Journal of clinical investigation, 123(1), 92–100. [CrossRef]
- Jenča, D., Melenovský, V., Stehlik, J., Staněk, V., Kettner, J., Kautzner, J., Adámková, V., & Wohlfahrt, P. (2021). Heart failure after myocardial infarction: incidence and predictors. ESC heart failure, 8(1), 222–237. [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, H., Qi, X., & Rouleau, J. L. (1998). Correlation between cardiac remodelling, function, and myocardial contractility in rat hearts 5 weeks after myocardial infarction. Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 76(1), 53–62.
- Kong, A. S., Lai, K. S., Lim, S. E., Sivalingam, S., Loh, J. Y., & Maran, S. (2022). miRNA in Ischemic Heart Disease and Its Potential as Biomarkers: A Comprehensive Review. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(16), 9001. [CrossRef]
- Song, M. A., Paradis, A. N., Gay, M. S., Shin, J., & Zhang, L. (2015). Differential expression of microRNAs in ischemic heart disease. Drug discovery today, 20(2), 223–235. [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A., Cardillo, M. T., Galea, R., & Biasucci, L. M. (2013). Potential therapeutic role of microRNAs in ischemic heart disease. Journal of cardiology, 61(5), 315–320. [CrossRef]
- Colpaert, R. M. W., & Calore, M. (2019). MicroRNAs in Cardiac Diseases. Cells, 8(7), 737. [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, A., Počivavšek, K., Petrovič, D., & Peterlin, B. (2020). The Role of microRNAs in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 7, 161. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S. S., Jin, J. P., Wang, J. Q., Zhang, Z. G., Freedman, J. H., Zheng, Y., & Cai, L. (2018). miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges. Acta pharmacologica Sinica, 39(7), 1073–1084. [CrossRef]
- Sun, T., Dong, Y. H., Du, W., Shi, C. Y., Wang, K., Tariq, M. A., Wang, J. X., & Li, P. F. (2017). The Role of MicroRNAs in Myocardial Infarction: From Molecular Mechanism to Clinical Application. International journal of molecular sciences, 18(4), 745. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C., Li, R., Hou, K., Chen, J., Alzogool, M., Hu, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, R. et al. (2020). Value of Blood-Based microRNAs in the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in physiology, 11, 691. [CrossRef]
- Scărlătescu, A. I., Micheu, M. M., Popa-Fotea, N. M., & Dorobanțu, M. (2021). MicroRNAs in Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction-A New Tool for Diagnosis and Prognosis: Therapeutic Implications. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(9), 4799. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Du, X., Ma, K., Li, G., Liu, Z., Rong, W., Miao, H., Zhu, F., Cui, Q., Wu, S. et al. (2021). Circulating miRNAs Related to Long-term Adverse Cardiovascular Events in STEMI Patients: A Nested Case-Control Study. The Canadian journal of cardiology, 37(1), 77–85. [CrossRef]
- Diener, C., Keller, A., & Meese, E. (2022). Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends in genetics : TIG, 38(6), 613–626. [CrossRef]
- Bejerano, T., Etzion, S., Elyagon, S., Etzion, Y., & Cohen, S. (2018). Nanoparticle Delivery of miRNA-21 Mimic to Cardiac Macrophages Improves Myocardial Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Nano letters, 18(9), 5885–5891. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Tang, X., Liu, X., Cui, X., Lian, M., Zhao, M., Peng, H., & Han, X. (2020). Targeted miR-21 loaded liposomes for acute myocardial infarction. Journal of materials chemistry. B, 8(45), 10384–10391. [CrossRef]
- Eulalio, A., Mano, M., Dal Ferro, M., Zentilin, L., Sinagra, G., Zacchigna, S., & Giacca, M. (2012). Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature, 492(7429), 376–381. [CrossRef]
- Lesizza, P., Prosdocimo, G., Martinelli, V., Sinagra, G., Zacchigna, S., & Giacca, M. (2017). Single-Dose Intracardiac Injection of Pro-Regenerative MicroRNAs Improves Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation research, 120(8), 1298–1304. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y., Peng, S., Wu, M., Sachidanandam, R., Tu, Z., Zhang, S., Falce, C., Sobie, E. A., Lebeche, D., & Zhao, Y. (2014). Multifaceted roles of miR-1s in repressing the fetal gene program in the heart. Cell research, 24(3), 278–292. [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, J., Jazbutyte, V., Kirchmaier, B. C., Gupta, S. K., Lorenzen, J., Hartmann, D., Galuppo, P., Kneitz, S., Pena, J. T., Sohn-Lee, C. et al. (2011). MicroRNA-24 regulates vascularity after myocardial infarction. Circulation, 124(6), 720–730. [CrossRef]
- Foinquinos, A., Batkai, S., Genschel, C., Viereck, J., Rump, S., Gyöngyösi, M., Traxler, D., Riesenhuber, M., Spannbauer, A., Lukovic, D. et al. (2020). Preclinical development of a miR-132 inhibitor for heart failure treatment. Nature communications, 11(1), 633. [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, R., Batkai, S., Bähr, A., Bozoglu, T., Straub, S., Borchert, T., Viereck, J., Howe, A., Hornaschewitz, N., Oberberger, L. et al. (2021). AntimiR-132 Attenuates Myocardial Hypertrophy in an Animal Model of Percutaneous Aortic Constriction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 77(23), 2923–2935. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I. F., Acar, E., Costantino, S., Szabo, P. L., Hamza, O., Tretter, E. V., Klein, K. U., Trojanek, S., Abraham, D., Paneni, F. et al. (2019). Epigenetic modulation of tenascin C in the heart: implications on myocardial ischemia, hypertrophy and metabolism. Journal of hypertension, 37(9), 1861–1870. [CrossRef]
- Pilz, P. M., Hamza, O., Gidlöf, O., Gonçalves, I. F., Tretter, E. V., Trojanek, S., Abraham, D., Heber, S., Haller, P. M., Podesser, B. K. et al. (2019). Remote ischemic perconditioning attenuates adverse cardiac remodeling and preserves left ventricular function in a rat model of reperfused myocardial infarction. International journal of cardiology, 285, 72–79. [CrossRef]
- Borchardt, H., Kogel, A., Kalwa, H., Weirauch, U., & Aigner, A. (2022). Therapeutic miR-506-3p Replacement in Pancreatic Carcinoma Leads to Multiple Effects including Autophagy, Apoptosis, Senescence, and Mitochondrial Alterations In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomedicines, 10(7), 1692. [CrossRef]
- Lichtenauer, M., Schreiber, C., Jung, C., Beer, L., Mangold, A., Gyöngyösi, M., Podesser, B. K., & Ankersmit, H. J. (2014). Myocardial infarct size measurement using geometric angle calculation. European journal of clinical investigation, 44(2), 160–167. [CrossRef]
- Lichtenauer, M., Mildner, M., Werba, G., Beer, L., Hoetzenecker, K., Baumgartner, A., Hasun, M., Nickl, S., Mitterbauer, A., Zimmermann, M. et al. (2012). Anti-thymocyte globulin induces neoangiogenesis and preserves cardiac function after experimental myocardial infarction. PloS one, 7(12), e52101. [CrossRef]
- Wernly, B., Paar, V., Aigner, A., Pilz, P. M., Podesser, B. K., Förster, M., Jung, C., Hofbauer, J. P., Tockner, B., Wimmer, M. et al. (2020). Anti-CD3 Antibody Treatment Reduces Scar Formation in a Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction. Cells, 9(2), 295. [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, M., & Roubina, E. (2005). Drugs for left ventricular remodeling in heart failure. The American journal of cardiology, 96(12A), 10L–18L. [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A. S., Ambrosy, A. P., & Velazquez, E. J. (2017). Adverse Remodeling and Reverse Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction. Current cardiology reports, 19(8), 71. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C., Ponnusamy, M., Liu, C., Gao, J., Wang, K., & Li, P. (2017). MicroRNA as a Therapeutic Target in Cardiac Remodeling. BioMed research international, 2017, 1278436. [CrossRef]
- Topkara, V. K., & Mann, D. L. (2010). Clinical applications of miRNAs in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. Personalized medicine, 7(5), 531–548. [CrossRef]
- Maries, L., Marian, C., Sosdean, R., Goanta, F., Sirbu, I. O., & Anghel, A. (2021). MicroRNAs-The Heart of Post-Myocardial Infarction Remodeling. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland), 11(9), 1675. [CrossRef]
- Boon, R. A., & Dimmeler, S. (2015). MicroRNAs in myocardial infarction. Nature reviews. Cardiology, 12(3), 135–142. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W., & Zheng, H. (2021). Myocardial Infarction: The Protective Role of MiRNAs in Myocardium Pathology. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 8, 631817. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J., Gao, R., Bei, Y., Zhou, Q., Zhou, Y., Zhang, H., Jin, M., Wei, S., Wang, K., Xu, X. et al. (2017). Circulating miR-30d Predicts Survival in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, 41(3), 865–874. [CrossRef]
- Melman, Y. F., Shah, R., Danielson, K., Xiao, J., Simonson, B., Barth, A., Chakir, K., Lewis, G. D., Lavender, Z., Truong, Q. A. et al. (2015). Circulating MicroRNA-30d Is Associated With Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Heart Failure and Regulates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis: A Translational Pilot Study. Circulation, 131(25), 2202–2216. [CrossRef]
- Jia, K., Shi, P., Han, X., Chen, T., Tang, H., & Wang, J. (2016). Diagnostic value of miR-30d-5p and miR-125b-5p in acute myocardial infarction. Molecular medicine reports, 14(1), 184–194. [CrossRef]
- Bukauskas, T., Mickus, R., Cereskevicius, D., & Macas, A. (2019). Value of Serum miR-23a, miR-30d, and miR-146a Biomarkers in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research, 25, 3925–3932. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Salvador, A. M., Li, G., Valkov, N., Ziegler, O., Yeri, A., Yang Xiao, C., Meechoovet, B., Alsop, E., Rodosthenous, R. S. et al. (2021). Mir-30d Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Intracellular and Paracrine Signaling. Circulation research, 128(1), e1–e23. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Sha, Z., Zhu, X., Xu, W., Yuan, W., Yang, T., Jin, B., Yan, Y., Chen, R., Wang, S. et al. (2022). Targeting miR-30d reverses pathological cardiac hypertrophy. EBioMedicine, 81, 104108. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M., Wang, H., Jin, M., Yang, X., Ji, H., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Wu, F., Wu, G., Lai, X. et al. (2018). Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs Reverse Acute Ischemic Stroke-Induced, Autophagy-Mediated Brain Injury by Promoting M2 Microglial/Macrophage Polarization. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, 47(2), 864–878. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F., Qu, Y., Zhu, J., Zhang, L., Huang, L., Liu, H., Li, S., & Mu, D. (2017). miR-30d-5p Plays an Important Role in Autophagy and Apoptosis in Developing Rat Brains After Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury. Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology, 76(8), 709–719. [CrossRef]
- Tang, S., Wang, Y., Ma, T., Lu, S., Huang, K., Li, Q., Wu, M., Yang, H., & Zhong, J. (2020). MiR-30d inhibits cardiomyocytes autophagy promoting ferroptosis after myocardial infarction. Panminerva medica, 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03979-8. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. O., Park, J. H., Kim, T., Hong, S. E., Lee, J. Y., Nho, K. J., Cho, C., Kim, Y. S., Kang, W. S., Ahn, Y. et al. (2018). A novel system-level approach using RNA-sequencing data identifies miR-30-5p and miR-142a-5p as key regulators of apoptosis in myocardial infarction. Scientific reports, 8(1), 14638. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H., Lin, X., Wang, F., Zhang, B., Wang, W., Shi, H., Zou, B., & Zhao, J. (2014). Proliferation inhibition and the underlying molecular mechanisms of microRNA-30d in renal carcinoma cells. Oncology letters, 7(3), 799–804. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., Zong, K., Wang, X., Dou, D., Lv, P., Zhang, Z., & Li, H. (2021). miR-30d suppresses proliferation and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer by targeting the SOX4/PI3K-AKT axis and predicts poor outcome. Cell death & disease, 12(4), 350. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R., Xu, J., Zhao, J., & Bai, J. (2017). Mir-30d suppresses cell proliferation of colon cancer cells by inhibiting cell autophagy and promoting cell apoptosis. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine, 39(6), 1010428317703984. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).