Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
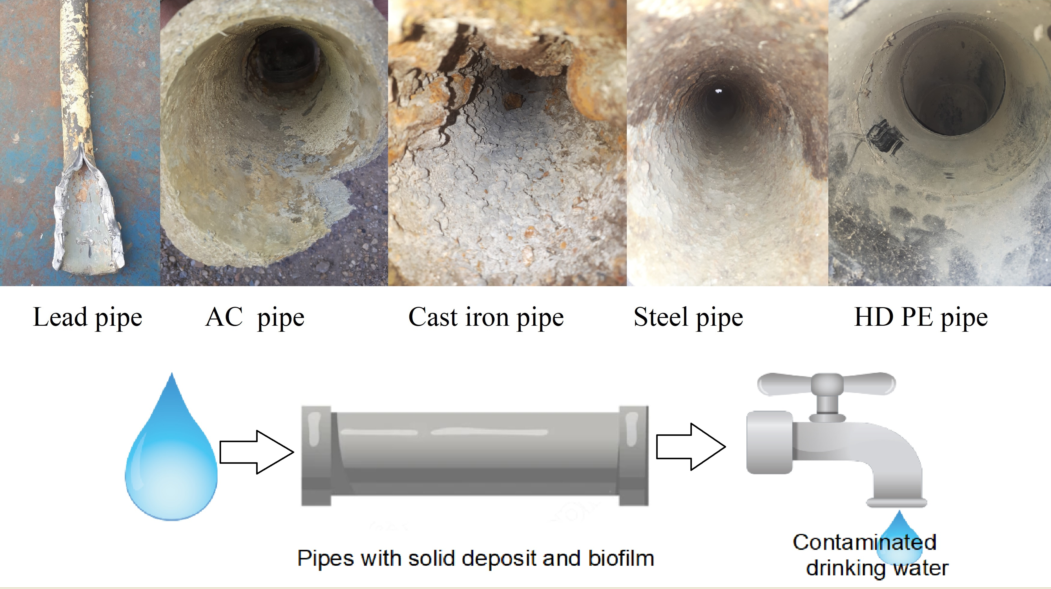
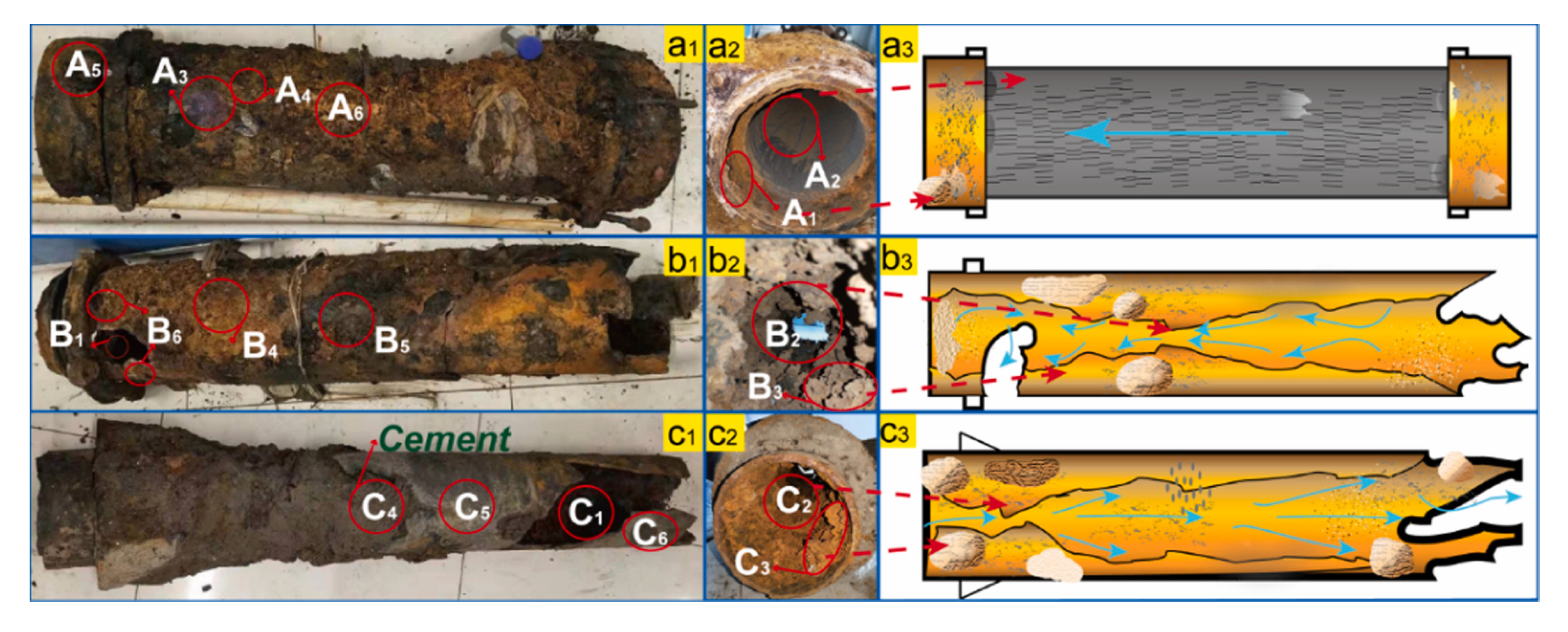
2. Materials used to manufacture the drinking water distribution pipes
- (a)
-
Water chemistry parameters:
- (i)
- pH, alkalinity
- (ii)
- the content of dissolved inorganic carbon
- (iii)
- presence of disinfectants: chlorine, chloramine, dissolved oxygen
- (iv)
- presence of corrosion inhibitors (orthophosphate, orthophosphate/polyphosphate mixture, silica)
- (v)
- Oxidation Reduction Potential
- (vi)
- Presence of organic matter
- (b)
- Flowing regime: alternate flow / stagnant regime; pipes flushing.
- (i)
- internal diffusion of liquid water through the porous wall;
- (ii)
- dissolution of the compounds;
- (iii)
- diffusion of the dissolved compounds through the pores at the surface of the pipe;
- (iv)
- external diffusion of the dissolved compounds at the wall pipe into the main water stream. The permeability of the material controls how much water diffuses through the pores of material. The leaching rate depends on if the pipe just started to be operated, the permeability of the pipe material, the softness of the drinking water, and the solubility of the leached compound. The soft water is water relatively free of dissolved ions and has a higher capacity of dissolution compared with a more saturated water in minerals.
- (a)
- compounds that crystallize directly onto tube surfaces from the flowing water (this is the case of calcium and magnesium carbonates that distribute uniformly on the inner surface of the pipe);
- (b)
- scale consisting in inorganic materials precipitated elsewhere and transported by the flowing water;
- (c)
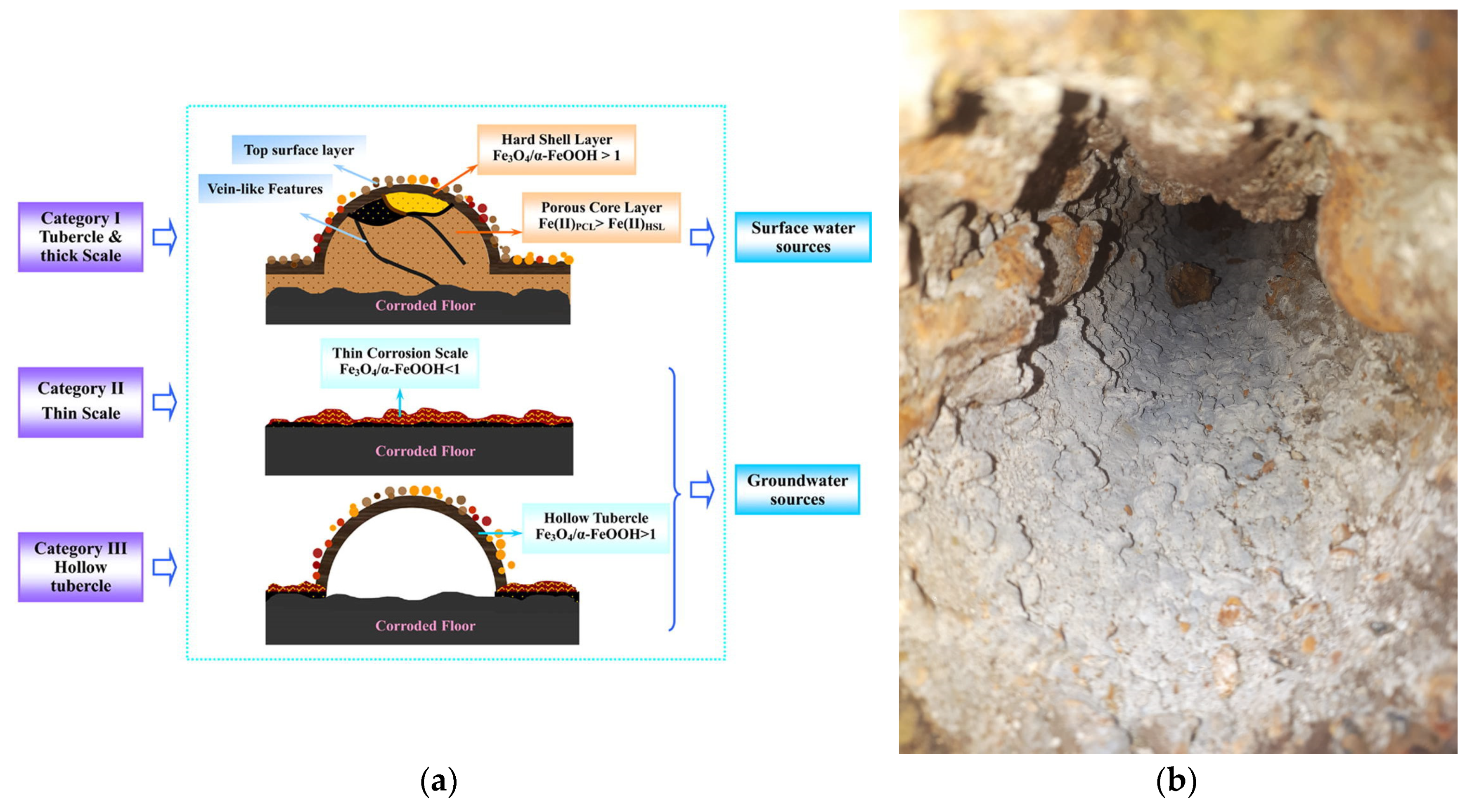
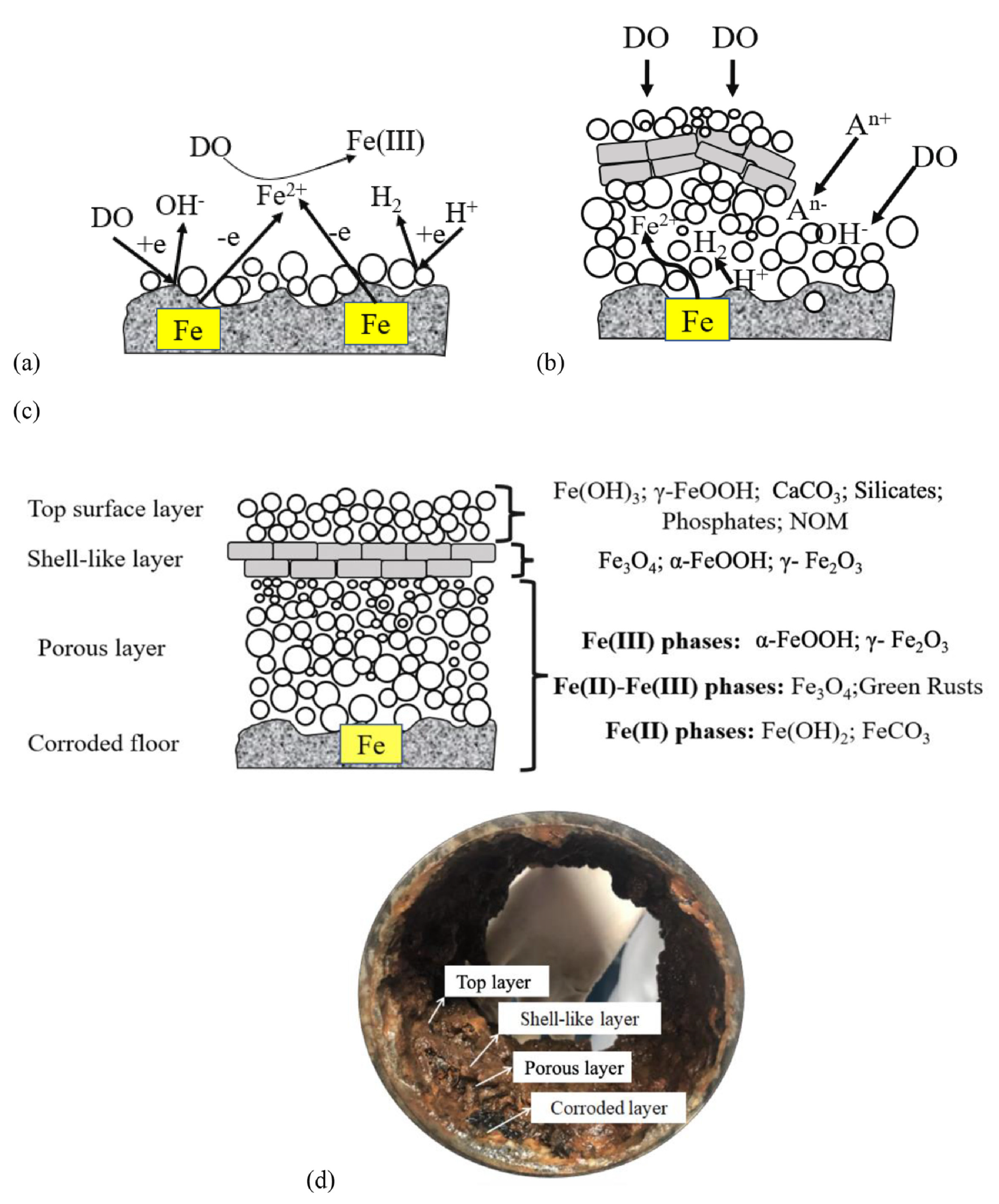
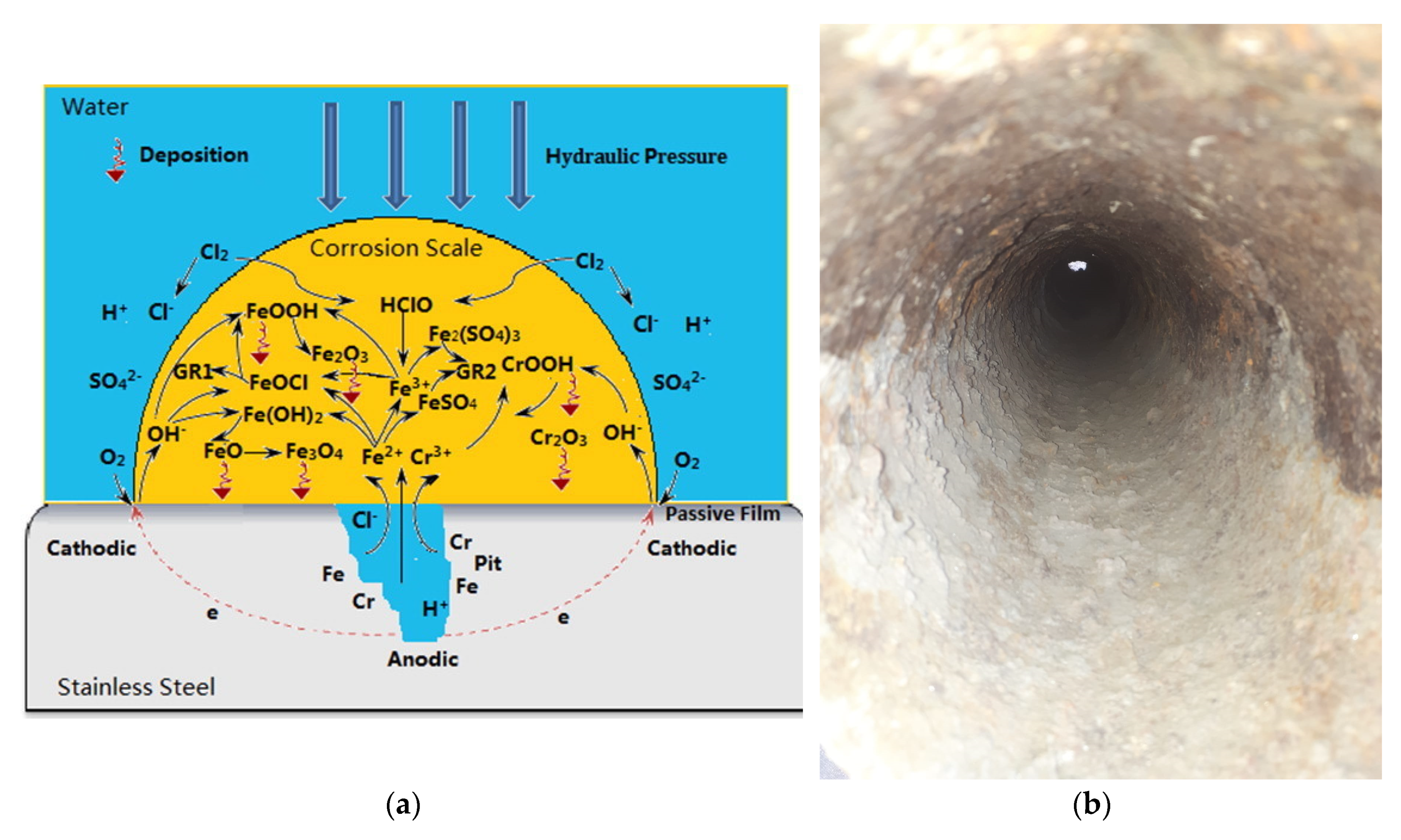
- scale formed by the corrosion products (characteristic for unlined iron cast pipes, copper pipes); the corrosion scale is a hard mineral consisting in densely distributed corrosion tubercles.
- (a)
- floor layer made of carbonates;
- (b)
- thin corrosion scale;
- (c)
- hollow tubercle.
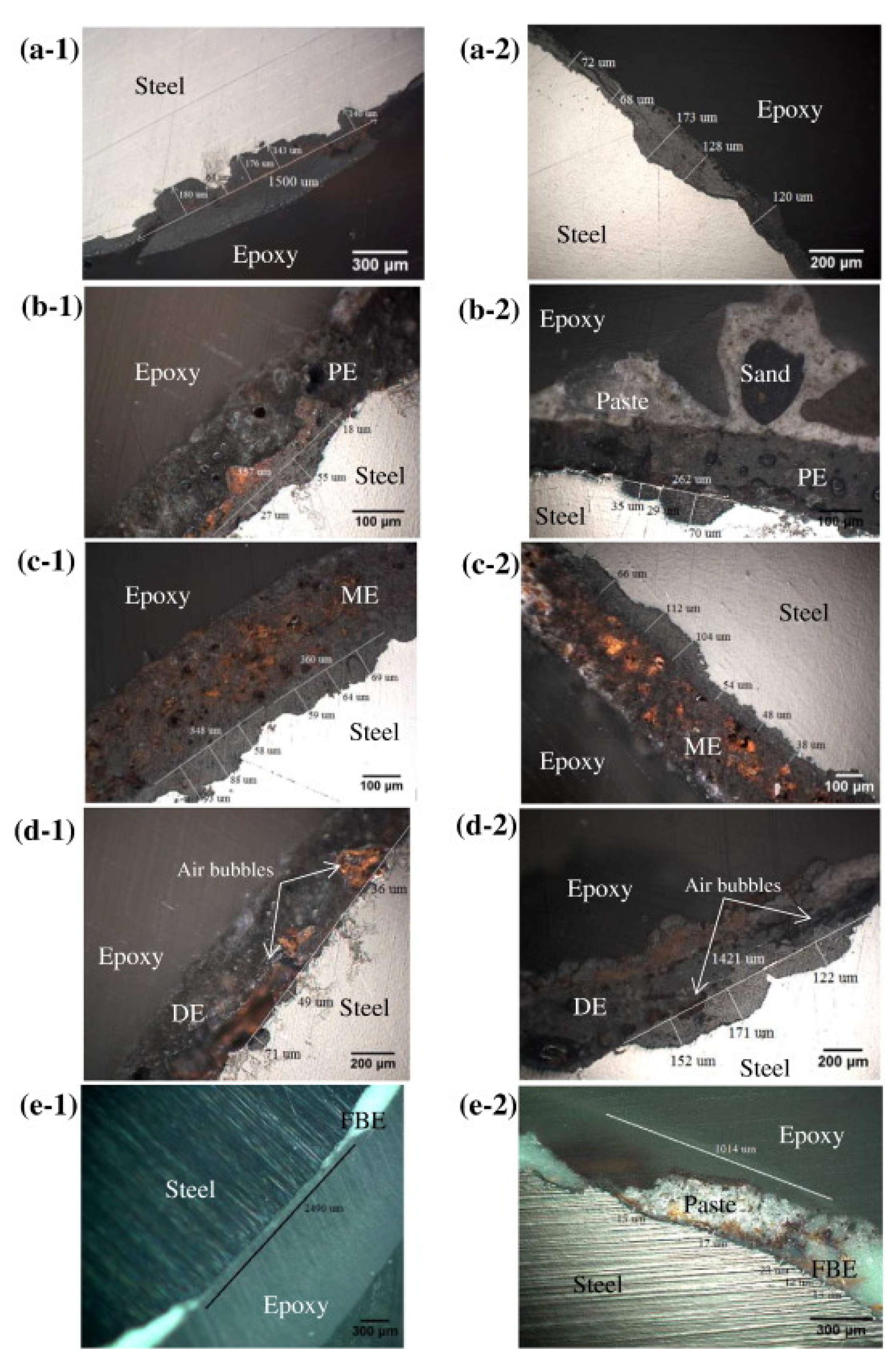
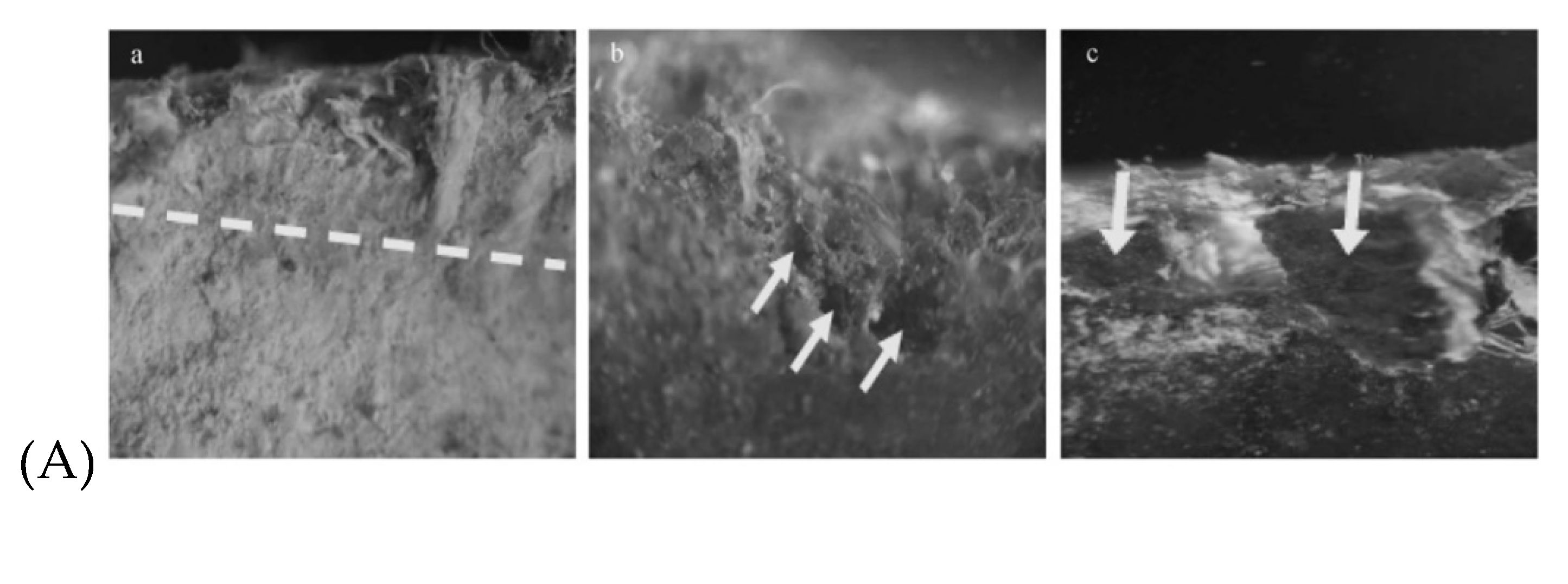
3. Biofilm formation on inner pipe wall
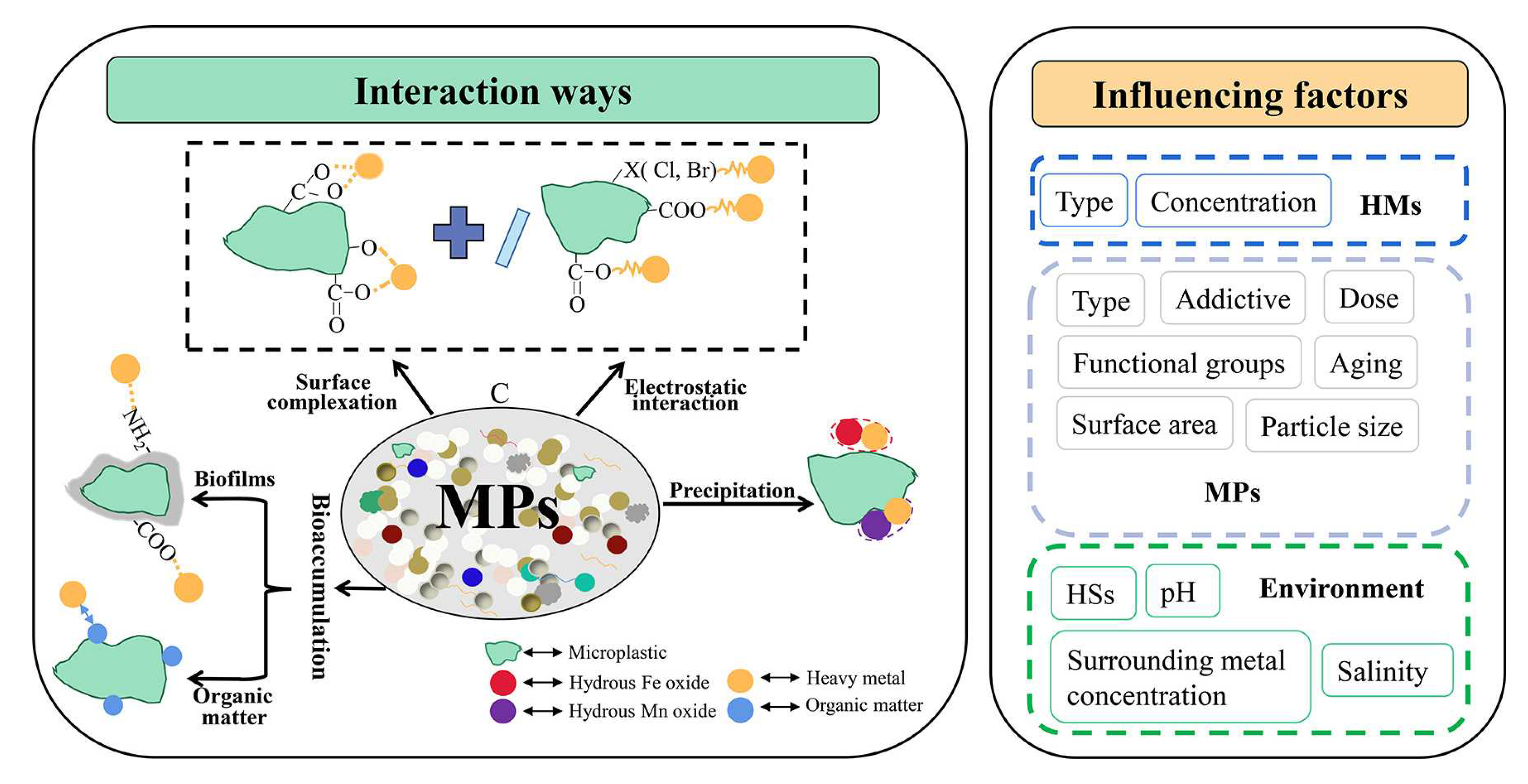
4. Microplastic (MP) fate in DWDS
5. Mathematical modelling
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DIRECTIVE (EU) 2020/2184 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 16 December 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020L2184 (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Prest, E.I.; Hammes, F.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Biological Stability of Drinking Water: Controlling Factors, Methods, and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, L.C.; Simoes, M.; Oliveira, R.; Vieira, M.J. Potential of the adhesion of bacteria isolated from drinking water to materials. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douterelo, I.; Sharpe, R.; Boxall, J. Bacterial community dynamics during the early stages of biofilm formation in a chlorinated experimental drinking water distribution system: implications for drinking water discolouration. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.-F.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, L.; Tay, J.-H. The influence of cell and substratum surface hydrophobicities on microbial attachment. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 110, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, T. Microbial diversity in biofilms on water distribution pipes of different materials. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacheus, O.M.; Iivanainen, E.K.; Nissinen, T.K.; Lehtola, M.J.; Martikainen, P.J. Bacterial biofilm formation on polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and stainless steel exposed to ozonated water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, R. The lead industry and Lead Water Pipes “A MODEST CAMPAIGN. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.M.; Yang, M. Lead in drinking water and birth outcomes: A tale of two water treatment plants. J. Health Econ. 2022, 84, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, G.; Ison, H.C.K. Corrosion and Its Prevention in Waters; Leonard-Hill: London, 1966; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Deshommes, E.; Andrews, R.C.; Gagnon, G.; McCluskey, T.; McIlwain, B.; Dore, E.; Nour, S.; Prevost, M. Evaluation of exposure to lead from drinking water in large buildings. Water Res. 2016, 99, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, E.; Deshommes, E.; Andrews, R.C.; Nour, S.; Prevost, M. Sampling in schools and large institutional buildings: Implications for regulations, exposure and management of lead and copper. Water Res. 2018, 140, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riblet, C.; Deshommes, E.; Laroche, L.; Prevost, M. True exposure to lead at the tap: Insights from proportional sampling, regulated sampling and water use monitoring. Water Res. 2019, 156, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasaee, M.A.K.; Berglund, E.; Pieper, K.J.; Ling, E.; Benham, B.; Edwards, M. Developing a framework for classifying water lead levels at private drinking water systems: A Bayesian Belief Network approach. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondeau, V.; Jacqmin-Gadda, H.; Commenges, D.; Helmer, C.; Dartigues, J.F. Aluminum and Silica in Drinking Water and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease or Cognitive Decline: Findings From 15-Year Follow-up of the PAQUID Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.L.; Varadarajulu, D.; Lewis-Michl, E.L.; Fitzgerald, E F. Cancer incidence and asbestos in drinking water, Town of Woodstock, New York, 1980–1998. Environ. Res. 2005, 98, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærheim, K.; Ulvestad, B.; Martinsen, J.I.; Andersen, A. Cancer of the gastrointestinal tract and exposure to asbestos in drinking water among lighthouse keepers (Norway). Cancer Causes Control 2005, 16, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Lagos, G. Daily intakes of copper, zinc and arsenic in drinking water by population of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.A.; Bakhshalizadeh, S.; Guerrera, M.C.; Kesbiç, O.S.; Fazio, F. Toxic effect of heavy metals on ovarian deformities, apoptotic changes, oxidative stress, and steroid hormones in rainbow trout. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 75, 127106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pan, B.; Han, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X. Toxicity risks associated with trace metals call for conservation of threatened fish species in heavily sediment-laden Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, A.; Kurrey, R.; Deb, M.K.; Patle, T.K.; Sinha, D.; Shrivas, K. Analytical approaches on some selected toxic heavy metals in the environment and their socio-environmental impacts: A meticulous review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Nazir, S.; Irshad, R.; Tahir, K.; ur Rehman, K.; Islamb, R.U.; Wahab, Z. Toxicity of heavy metals in plants and animals and their uptake by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, H.; Mehta, V.; Welter, G.J.; Giammar, D.E. Impact of galvanic corrosion on lead release from aged lead service lines. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5049–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, D.A.; Schock, M.R.; Triantafyllidou, S. Identify Lead Plumbing Sources to Protect Public Health. Opflow 2018, 44, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeyink, V.L.; Tang, M.; Lytle, D.A. Lead pipe and lead–tin solder scale formation and structure: A conceptual model. AWWA Wat. Sci. 2021, 3, e1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L. Effects of pipeline geometry, sample volume, and flow rate on Pb monitoring outcomes in copper pipe drinking water supply systems. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Lee, J.H.W.; Fung, Y.S. Prediction of lead leaching from galvanic corrosion of lead-containing components in copper pipe drinking water supply systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.Q.; Liu, S.W.; Lin, Y.P. Lead as a legendary pollutant with emerging concern: Survey of lead in tap water in an old campus building using four sampling methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, C.; Dore, E.; Laroche, L.; Nour, S.; Edwards, M.; Prevost, M. Impact of treatment on Pb release from full and partially replaced harvested Lead Service Lines (LSLs). Water Res. 2013, 47, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Edwards, M. Lead (Pb) in Tap Water and in Blood: Implications for Lead Exposure in the United States. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1297–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, M.K.; Triantafyllidou, S.; Schock, M.; Lytle, D.A. Mineralogical evidence of galvanic corrosion in drinking water lead pipe joints. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Herrera, J.E.; Huggins, D.; Braam, J.; Koshowski, S. Effect of pH on the concentrations of lead and trace contaminants in drinking water: A combined batch, pipe loop and sentinel home study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Giammar, D.E. Effect of water chemistry on the dissolution rate of the lead corrosion product hydrocerussite. Water Res. 2014, 54, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Burkhardt, J.; Tully, J.; Cahalan, K.; DeSantis, M.; Lytle, D.; Schock, M. Variability and sampling of lead (Pb) in drinking water: Assessing potential human exposure depends on the sampling protocol. Environ Int. 2021, 146, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, A.; Abokifa, A.; Gudi, R.D.; Biswas, P. Optimization of disinfectant dosage for simultaneous control of lead and disinfection-byproducts in water distribution networks. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 276, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stets, E.G.; Lee, C.J.; Lytle, D.A.; Schock, M.R. Increasing chloride in rivers of the conterminous U.S. and linkages to potential corrosivity and lead action level exceedances in drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Schock, M.R.; Formal, C.; Bennett-Stamper, C.; Harmon, S.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Williams, D.; DeSantis, M.K.; Tully, J.; Pham, M. Lead Particle Size Fractionation and Identification in Newark, New Jersey’s Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13672–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Herrera, J.E. Characteristics of Lead Corrosion Scales Formed during Drinking Water Distribution and Their Influence on the Release of Lead and Other Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6054–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, T.L.; Scheckel, K.G.; Schock, M.R. Identification and Distribution of Vanadinite (Pb5(V5+O4)3Cl) in Lead Pipe Corrosion By-Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4412–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schock, M.R.; Cantor, A.F.; Triantafyllidou, S.; Desantis, M.K.; Scheckel, K.G. Importance of pipe deposits to Lead and Copper Rule compliance. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2014, 106, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, S.M.; Tully, J.; DeSantis, M.K.; Schock, M.R.; Triantafyllidou, S.; Lytle, D.A. A holistic approach to lead pipe scale analysis: Importance, methodology, and limitations. AWWA Wat. Sci. 2022, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradham, K.D.; Nelson, C.M.; Sowers, T.D.; Lytle, D.A.; Tully, J.; Schock, M.R.; Li, K.; Blackmon, M.D.; Kovalcik, K.; Cox, D.; et al. A national survey of lead and other metal(loids) in residential drinking water in the United States. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Schock, M.R.; DeSantis, M.K.; White, C. Low Contribution of PbO2-Coated Lead Service Lines to Water Lead Contamination at the Tap. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3746–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/water/lead/lead-and-water.htm (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Bisogni, J.J.; Nassar, I.S.; Menegaux, A.M. Effect of calcium on lead in soft-water distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, B.F.; Gagnon, G.A. A new analytical approach to understanding nanoscale lead-iron interactions in drinking water distribution systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 311, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, M.K.; Schock, M.R.; Tully, J.; Bennett-Stamper, C. Orthophosphate Interactions with Destabilized PbO2 Scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14302–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvinen, O.H.; Button, K.S.; Vuorinen, A.; Carlson, L.; Mair, D.M.; Yut, L.A. Bacterial, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics of tubercles in distribution pipelines. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1980, 72, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katner, A.; Pieper, K.; Brown, K.; Lin, H.Y.; Parks, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.Y.; Masters, S.; Mielke, H.; Edwards, M. Effectiveness of Prevailing Flush Guidelines to Prevent Exposure to Lead in Tap Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, J.; DeSantis, M.K.; Schock, M.R. Water quality–pipe deposit relationships in Midwestern lead pipes. AWWA Wat. Sci. 2019, 1, e1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserstrom, L.W.; Miller, S.A.; Triantafyllidou, S.; DeSantis, M.K.; Schock, M.R. Scale Formation Under Blended Phosphate Treatment for a Utility With Lead Pipes. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2017, 109, E464–E478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.rinkerpipe.com/a-complete-guide-to-reinforced-concrete-pipe/ (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Meland, I.S. Durability of mortar linings in ductile iron pipes. In: Durability of building materials and components. In Proceedings of the eighth international conference on durability of building materials and components, Vancouver, Canada, 30 May–3 June 1999; pp. 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, H.M.; Pontefract, R. Asbestos fibres in beverages and drinking water. Nature 1971, 232, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, J.S.; Syrotynski, S.; King, M.V. Asbestos-Contaminated Drinking Water: Its Impact on Household Air. Environ. Res. 1988, 46, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavasnik, J.; Sestan, A.; Skapin, S. Degradation of asbestos – Reinforced water supply cement pipes after a long-term operation. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, S.; Knopick, M.; Oddy, G. The concentration and prevalence of asbestos fibres in Christchurch, New Zealand’s drinking water supply. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindess, S.; Young, F. Concrete; Prentice-Hall: New Jersey, USA, 1981; p. 671. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmatka, S.; Panarese, W. Design and Control of Concrete Mixes; Portland Cement Association: New Jersey, USA, 1988; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Z. Binding of Cu(II) and Zn(II) in Portland cement immobilization systems: Effect of C-A-S-H composition. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI-Adeeb, A.M.; Mattit, M.A. Int. J. Cem. Compos. Lightweight Concr. 1984, 6, 233–240. [CrossRef]
- Zielina, M.; Dabrowski, W.; Radziszewska-Zielina, E. Cement Mortar Lining as a Potential Source of Water Contamination. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 8, 723–726. [Google Scholar]
- Młyńska, A.; Zielina, M. The influence of prefabricated pipe cement coatings and those made during pipe renovation on drinking water quality. E3S web of conferences, 9th conference on interdisciplinary problems in environmental protection and engineering EKO-DOK, Boguszów-Gorce, Poland, 23–25 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Młyńska, A.; Zielina, M. A comparative study of Portland cements CEM I used for water pipe renovation in terms of pollutants leaching from cement coatings and their impact on water quality. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2018, 67, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achternbosch, M.; Brautigam, K.R.; Hartlieb, N.; Kupsch, C.; Richers, U.; Stemmermann, P. Heavy metals in cement and concrete resulting from the co-incineration of wastes in cement kilns with regard to the legitimacy of waste utilisation. Umweltforschungsplan Des Bundesministeriums Für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit, Förderkennzeichen (UFOPLAN No.) 200 33 335. Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe; 2003.
- Husillos Rodríguez, N.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Blanco-Varela, M.T.; Donatello, S.; Guillem, M.; Puig, J.; Fos, C.; Larrotcha, E.; Flores, J. The effect of using thermally dried sewage sludge as an alternative fuel on Portland cement clinker production. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, C.; Emmert, M.H.; Sakulich, A. Influence of alternative fuels on trace element content of ordinary portland cement. Fuel 2016, 184, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, S.; Xu, Y.; Qian, G. Effects of phosphorus and iron on the composition and property of Portland cement clinker utilized incinerated sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynska, A.; Zielina, M.; Bielski, A. Contamination of drinking water soon after cement mortar lining renovation depending on the disinfectant doses. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, T. Leaching of concrete: Experiments and Modelling, Licentiate Thesis, Lund University, Division of Building Materials, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Toumi, A.; François, R.; Gagné, R. Effect of crack opening on the local diffusion of chloride in inert materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, B.; Guo, C.; Du, J.; Xiaosuo, Wu. Time dependence and service life prediction of chloride resistance of concrete coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Fu, C.; Guo, J. Effect of pore structures on gas permeability and chloride diffusivity of concrete. Constr Build Mater. 2018, 163, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.S.; Asadollahfardi, G.; Saghravani, S.F.; Sahar Jafari, S.; Peighambarzadeh, F.S. The difference in chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete made with drinking water and wastewater. Constr Build Mater. 2020, 231, 117182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, K.; Li, O.; Wang, Y. Experimental studies on the chloride ion permeability of concrete considering the effect of freeze–thaw damage. Constr Build Mater. 2020, 236, 117556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setunge, S.; Nguyen, N.; Alexander, B.L.; Dutton, L. Leaching of Alkali from Concrete in Contact with Waterways. Water Air Soil Pollut.: Focus 2009, 9, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, N.A. Concrete filled PVC tube: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Qu, F.; Wang, B.; Peng, J.; Li, W. Effects of pipe diameter, curing age and exposure temperature on chloride diffusion of concrete with embedded PVC pipe. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Smith, K.; Hu, H.; Tang, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, K. Stainless steel corrosion scale formed in reclaimed water: Characteristics, model for scale growth and metal element release. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.H.; Pehkonen, S.O. General corrosion of copper in domestic drinking water installations: scientific background and mechanistic understanding. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Roomi, Y.M.; Hussain, K.F.; Al-Rifaie, M. Performance of inhibitors on CaCO3 scale deposition in stainless steel & copper pipe surface. Desalination 2015, 375, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, C. Study on electrochemical reduction mechanisms of iron oxides in pipe scale in drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schock, M.R.; Lytle, D.A.; Clement, J.A. Effect of pH, DIC, Orthophosphate and Sulfate on Drinking Water Cuprosolvency. EPA/600/R-95/085. USEPA, Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, I.T.; Alsina, M.A.; Pastén, P.A.; Pizarro, G.E. Influence of solid corrosion by-products on the consumption of dissolved oxygen in copper pipes. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, H.M.; Al-Kharafi, F.M.; Gouda, V.K. .A Morphological Study of Pitting Corrosion of Copper in Soft Tap Water. Corros. 1989, 45, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartmann, J.; Sadlowsky, B.; Dorsch, T.; Johannsen, K. Copper corrosion in drinking water systems – effect of pH and phosphate-dosage. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, N.; Edwards, M. Role of temperature, chlorine, and organic matter in copper corrosion by-product release in soft water. Water Res. 2001, 35, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Dudi, A. Role of chlorine and chloramine in corrosion of lead bearing plumbing materials. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2004, 96, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Hidmi, L.; Gladwell, D. Phosphate inhibition of soluble copper corrosion by-product release. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Schock, M.R.; Leo, J.; Barnes, B. A Model for Estimating the Impact of Orthophosphate on Copper in Water. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2018, 110, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.T.; Dowsett, A.B.; Dennis, P.J.L.; Keevil, C.W. Continuous culture studies of biofilm associated with copper corrosion, Int. Biodeter. 1991, 27, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Chamberlain, A.H.L. Microbiologically influenced copper corrosion in potable water with emphasis on practical relevance. Biodegradation 1997, 8, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keevil, C.W. The physico-chemistry of biofilm-mediated pitting corrosion of copper pipe supplying potable water. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Letelier, M.V.; De la Iglesia, R.; Gonzalez, B.; Lagos, G. Microbiologically induced corrosion of copper pipes in low-pH water. Int. biodeterior. biodegrad. 2008, 61, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, T.E.; Cienfuegos, R.; Vargas, I.T.; Pizarro, G.E. Experimental evidence for enhanced copper release from domestic copper plumbing under hydrodynamic control. Corros. Sci. 2014, 80, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.Q.; Lin, Y.P. Evaluation of Lead Release in a Simulated Lead-Free Premise Plumbing System Using a Sequential Sampling Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, K.E. An experimental approach to corrosion control, J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1980, 72, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, L.J.; Vik, E.A.; Bjornson-Langen, A. Water treatment to reduce internal corrosion in the drinking water distribution system in Oslo. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2001, 1, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hong, S.; Xiao, W.; Taylor, J. Characteristics of iron corrosion scales established under blending of ground, surface, and saline waters and their impacts on iron release in the pipe distribution system. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 322–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbricino, M.; Korshin, G.V. Changes of the corrosion potential of iron in stagnation and flow conditions and their relationship with metal release. Water Res. 2014, 62, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Niu, Z.; Lu, P.; Wang, J.; Gu, J.; Chen, C. A red water occurrence in drinking water distribution systems caused by changes in water source in Beijing, China: mechanism analysis and control measures. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, Y.; Sun, H.; Lytle, D.A.; Wang, D. Effect of sulfate on the transformation of corrosion scale composition and bacterial community in cast iron water distribution pipes. Water Res. 2014, 59, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhuang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Shi, B. Impact of initial chlorine concentration on water quality change in old unlined iron pipes. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Internal Corrosion of Water Distribution Systems, second ed., AWWA Research Foundation, DVGW-Technologiezentrum Wasser, Denver, USA, 1996; pp. 430.
- Oh, S.J.; Kwon, S.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yoo, J.-Y.; Choo, W.-Y. Oxidation of Fe2+ ions in sulfate- and chloride-containing aqueous medium. Corros. 2002, 58, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, L.S.; Edwards, M. Iron pipe corrosion in distribution systems. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2001, 93, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Ferguson, J.F.; Korshin, G.V. Effects of chloride, sulfate and natural organic matter (NOM) on the accumulation and release of trace-level inorganic contaminants from corroding iron. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5257–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, R.; Singh, A.K.; Negi, Y.S. Study of Microbially Influenced Corrosion in the Presence of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria (Strain DASEWM2). J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2020, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, R.; Huang, J. Accumulation of vanadium and arsenic by cast iron pipe scales under drinking water conditions: A batch study. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuch, A. Investigations of the reduction and re-oxidation kinetics of iron (III) oxide scales formed in waters. Corros. Sci. 1988, 28, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Qiang, Z. Modeling iron release from cast iron pipes in an urban water distribution system caused by source water switch. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Li, W.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Y. Variations regularity of microorganisms and corrosion of cast iron in water distribution system. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 74, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Peng, Z.; Liua, Y.; Jia, S.; Shen, H.; Zhao, W. Characteristics of vanadium release from layered steel pipe scales to bulk, steady, and occluded water in drinking water distribution systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerke, T.L.; Scheckel, K.G.; Maynard, J.B. Speciation and distribution of vanadium in drinking water iron pipe corrosion by-products. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5845–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, T.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, W. Cr release after Cr(III) and Cr(VI) enrichment from different layers of cast iron corrosion scales in drinking water distribution systems: the impact of pH, temperature, sulfate, and chloride. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18778–18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shan, J.; Liu, R. Manganese release from corrosion products of cast iron pipes in drinking water distribution systems: Effect of water temperature, pH, alkalinity, concentration and disinfectants. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Shi, B.; Gu, J.; Dongsheng Wang, D.; Yang, M. Morphological and physicochemical characteristics of iron corrosion scales formed under different water source histories in a drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5423–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Review on corrosion and corrosion scale formation upon unlined cast iron pipes in drinking water distribution systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 117, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Early period corrosion and scaling characteristics of ductile iron pipe for ground water supply with sodium hypochlorite disinfection. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z. Formation of known and unknown disinfection by-products from natural organic matter fractions during chlorination, chloramination, and ozonation. Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 587–588, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, C.; Emiliano, P.; Barceló, D.; Valero, F. Chemical characterization and relative toxicity assessment of disinfection byproduct mixtures in a large drinking water supply network. J. Hazard. Mater., 2018, 359, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukura, N.; Marais, S.S.; Moyo, W.; Mbali, N.; Thakalekoala, L.C.; Ingwani, T.; Mamba, B.B.; Jarvis, P.; Nkambule, T.T.I. Contemporary issues on the occurrence and removal of disinfection byproducts in drinking water - A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Plewa, M.J. To regulate or not to regulate? What to do with more toxic disinfection by-products? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Li, T.; Hu, C.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Su, Z.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; et al. Effects of cast iron pipe corrosion on nitrogenous disinfection by-products formation in drinking water distribution systems via interaction among iron particles, biofilms, and chlorine. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer, H.; Kolle, W.; Snoeyink, V.L. Siderite model of the formation of corrosion-resistant scales. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1981, 73, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hai, Y. Characteristics of iron corrosion scales and water quality variations in drinking water distribution systems of different pipe materials. Water Res. 2016, 106, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.C.B.; Nissen, E.; Arvin, E.; Albrechtsen, H.-J. Distribution of Asellus aquaticus and microinvertebrates in a non-chlorinated drinking water supply system–Effects of pipe material and sedimentation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, M. Identification and characterization of steady and occluded water in drinking water distribution systems. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Jia, S.; Zhao, W. Co-release potential and human health risk of heavy metals from galvanized steel pipe scales under stagnation conditions of drinking water. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyliev, G.; Chyhryn, O. Improving mild steel corrosion resistance in tap water: Influence of water flow and supply rates. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 50, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, G.; Brow, R.K. Chloride-induced corrosion mechanism and rate of enamel- and epoxy-coated deformed steel bars embedded in mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 82, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; He, Y.; Ren, S.; Huang, W.; Lu, F. The application of life cycle assessment for the optimization of pipe materials of building water supply and drainage system. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, C.; Guyen, N.; Bruchet, A.; Mallevialle, J. Characterization of low molecular weight products desorbed from polyethylene tubings. Sci. Total Environ. 1985, 47, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denberg, M.; Mosbæk, H.; Hassager, O.; Arvin, E. Determination of the concentration profile and homogeneity of antioxidants and degradation products in a cross-linked polyethylene type A (PEXa) pipe. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Lin, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, K. Effects of pipe materials on the characteristic recognition, disinfection byproduct formation, and toxicity risk of pipe wall biofilms during chlorination in water supply pipelines. Water Res. 2022, 210, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corfitzen, C.B. Investigation of aftergrowth potential of polymers for use in drinking water distribution: Factors affecting migration of bioavailable compounds investigated by batch set-ups and continuous flow model systems. DTU Environment 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ryssel, S.T.; Arvin, E.; Holten Lützhøft, H.–C.; Olsson, M.E.; Prochazkova, Z.; Albrechtsen, H.-J. Degradation of specific aromatic compounds migrating from PEX pipes into drinking water. Water Res. 2015, 81, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Xin, K.; Tao, T. Iron stability on the inner wall of prepared polyethylene drinking pipe: Effects of multi-water quality factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.S.; Filion, Y. The interplay of suspended sediment concentration, particle size and fluid velocity on the rapid deposition of suspended iron oxide particles in PVC drinking water pipes. Water Res. 2022, X 15, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, J.M.; Reyes, L.P.; Alvarado, C.N.; Dietrich, A.M. Effect of PVC and iron materials on Mn(II) deposition in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Laxander, M.; Miettinen, I.T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. The effects of changing water flow velocity on the formation of biofilms and water quality in pilot distribution system consisting of copper or polyethylene pipes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-O. Degradation analysis of polymeric pipe materials used for water supply systems under various disinfectant conditions. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Weerasekara, A.; Bond, P.L.; Weynberg, K.D.; Guo, J. Characterizing the premise plumbing microbiome in both water and biofilms of a 50-year-old building. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Knibbe, W.-J.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Potential impacts of changing supply-water quality on drinking water distribution: A review. Water Res. 2017, 116, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, W.; Tan, Q.; Sheng, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W. Effect of disinfectant exposure and starvation treatment on the detachment of simulated drinking water biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, M.M.; Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. Integration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Legionella pneumophila in drinking water biofilms grown on domestic plumbing materials. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C. Biofilms in drinking water and their role as reservoir for pathogens. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kooij, D.; Veenendaal, H.R.; Italiaander, R. Corroding copper and steel exposed to intermittently flowing tap water promote biofilm formation and growth of Legionella pneumophila. Water Res. 2020, 183, 115951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Cao, C.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, F.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Z.; Fu, J. Pilot investigation on formation of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole via microbial O-methylation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in drinking water distribution system: An insight into microbial mechanism. Water Res. 2018, 131, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, T.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Impact of pipe material and chlorination on the biofilm structure and microbial communities. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Hu, C.; Liao, L. Characteristics of corrosion scales and biofilm in aged pipe distribution systems with switching water source. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 60, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Zhang, K.; Cen, C.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, X. Characteristics of biostability of drinking water in aged pipes after water source switching: ATP evaluation, biofilms niches and microbial community transition. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learbuch, K.L.G.; Smidt, H.; van der Wielen, P.W.J.J. Water and biofilm in drinking water distribution systems in the Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Hu, J.Y. Interaction between phosphorus and biodegradable organic carbon on drinking water biofilm subject to chlorination. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Masters, S.; Edwards, M.A.; Falkinham, J.O.; Pruden, A. Effect of disinfectant, water age, and pipe materials on bacterial and eukaryotic community structure in drinking water biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, Q.T.; Krishna, K.C.B.; Salih, A.; Listowski, A.; Sathasivan, A. Biofilm growth on PVC and HDPE pipes impacts chlorine stability in the recycled water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liduino, V.S.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Noel, C.; Carbon, A.; Duran, R.; Lutterbach, M.T.; Camporese Sérvulo, E.F. Comparison of flow regimes on biocorrosion of steel pipe weldments: Community composition and diversity of biofilms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lian, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.R.; Tao, G.L.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, J.C. Impacts of hydraulic conditions on microplastics biofilm development, shear stresses distribution, and microbial community structures in drinking water distribution pipes. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 325, 116510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allion, A.; Lassiaz, S.; Peguet, L.; Boillot, P.; Jacques, S.; Peultier, J.; Bonnet, M.-C. A long term study on biofilm development in drinking water distribution system: comparison of stainless steel grades with commonly used materials. Revue de Métallurgie 2011, 108, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, H.Y.; Lu, J.; Lu, X.; Mou, X.; Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial diversities (16S and 18S rRNA gene pyrosequencing) and environmental pathogens within drinking water biofilms grown on the common premise plumbing materials unplasticized polyvinylchloride and copper. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2014, 88, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Lou, L.; Cheng, D.; He, X.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, S.; Fu, L.; et al. Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial communities in biofilms from different pipe materials in a city drinking water distribution system of East China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10713–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Nguyen, T.H.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Shen, C. Occurrence and quantification of culturable and viable but non-culturable (VBNC) pathogens in biofilm on different pipes from a metropolitan drinking water distribution system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraj, W.; Pytlak, A.; Kowalska, B.; Kowalski, D.; Grządziel, J.; Szafranek-Nakonieczna, A.; Galazka, A.; Stępniewska, Z.; Stępniewski, W. Influence of pipe material on biofilm microbial communities found in drinking water supply system. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learbuch, K.L.G.; Smidt, H.; van der Wielen, P.W.J.J. Influence of pipe materials on the microbial community in unchlorinated drinking water and biofilm. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Calendo, G.; Kopec, K.; Henry, R.; Coutts, S.; McCarthy, D.; Murphy, H.M. The Impact of Pipe Material on the Diversity of Microbial Communities in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 779016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Siyang Xu, S.; Pei, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Yixing Yuan, Y. Effect of domestic pipe materials on microbiological safety of drinking water: Different biofilm formation and chlorination resistance for diverse pipe materials. Process Biochem. 2023, 129, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Du, M. A review: microbiologically influenced corrosion and the effect of cathodic polarization on typical bacteria. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Jia, R.; Unsal, T.; Xu, D. Toward a better understanding of microbiologically influenced corrosion caused by sulfate reducing bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, S. Iron release and characteristics of corrosion scales and bacterial communities in drinking water supply pipes of different materials with varied nitrate concentrations. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fan, E.; Jia, J.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Corrosion mechanism of nitrate reducing bacteria on X80 steel correlated to its intermediate metabolite nitrite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryachko, Y.; Hemmingsen, S.M. The role of localized acidity generation in microbially influenced corrosion. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosvetsky, J.; Starosvetsky, D.; Pokroy, B.; Hilel, T.; Armon, R. Electrochemical behaviour of stainless steels in media containing iron-oxidizing bacteria (IOB) by corrosion process modeling. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Guan, Y.T.; Zhu, W.P. Effect of biofilm on cast iron pipe corrosion in drinking water distribution system: Corrosion scales characterization and microbial community structure investigation. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Han, X.; Zhu, L.; Bai, X. The role of pipe biofilms on dissemination of viral pathogens and virulence factor genes in a full-scale drinking water supply system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grengg, C.; Mittermayr, F.; Baldermann, A.; Böttcher, M.E.; Leis, A.; Koraimann, G.; Grunert, P.; Dietzel, M. Microbiologically induced concrete corrosion: A case study from a combined sewer network. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 77, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulikowski, J.; Kozubal, J. The Durability of a Concrete Sewer Pipeline Under Deterioration by Sulphate and Chloride Corrosion. Procedia Eng. 2016, 153, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cullimore, R. Bacteriological challenges to asbestos cement water distribution pipelines. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Cullimore, R.; Hu, Y.; Chowdhury, R. Biodeterioration of asbestos cement (AC) pipe in drinking water distribution systems. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2011, 65, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Chu, X.; Zheng, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W. Field study on the characteristics of scales in damaged multi-material water supply pipelines: Insights into heavy metal and biological stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang¸, M. Effects of microbial redox cycling of iron on cast iron pipe corrosion in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2014, 65, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wanga, H.; Hu, C.; Yang, M.; Hu, H.; Niu, J. Characteristics of biofilms and iron corrosion scales with ground and surface waters in drinking water distribution systems. Corros. Sci. 2015, 90, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Hu, C.; Yang, M.; Qu, J. Characterization of biofilm and corrosion of cast iron pipes in drinking water distribution system with UV/Cl2 disinfection. Water Res. 2014, 60, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, C.; Gu, T.; Zhang, G.; Lv, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in the presence of sulfate reducing bacteria and iron oxidizing bacteria cultured in oilfeld produced water. Corros. Sci. 2015, 100, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gu, T.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. The effect of magnetic field on biomineralization and corrosion behavior of carbon steel induced by iron-oxidizing bacteria. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun-Jung, J.; Choi, Y.-J.; Ka, J.-O. Effects of Diverse Water Pipe Materials on Bacterial Communities and Water Quality in the Annular Reactor. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Deng, Y.; Bond, T.; Fang, C.; Cao, Z.; Chu, W. Disinfection byproduct formation during drinking water treatment and distribution: A review of unintended effects of engineering agents and materials. Water Res. 2019, 160, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douterelo, I.; Fish, K.E.; Boxall, J.B. Succession of bacterial and fungal communities within biofilms of a chlorinated drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2018, 141, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginige, M.P.; Garbin, S.; Wylie, J.; Krishna, K.C.B. Effectiveness of Devices to Monitor Biofouling and Metals Deposition on Plumbing Materials Exposed to a Full-Scale Drinking Water Distribution System. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0169140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, S.N.; Falkinham, J.O., III. Adherence and biofilm formation of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium abscessus to household plumbing materials. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Miettinen, I.T.; Lampola, T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. Pipeline materials modify the effectiveness of disinfectants in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z. Impacts of antibiotics on biofilm bacterial community and disinfection performance on simulated drinking water supply pipe wall. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Qi, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y. Impact of biofilm formation and detachment on the transmission of bacterial antibiotic resistance in drinking water distribution systems. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhong, X. Occurrence and identification of microplastics in tap water from China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Gomiero, A.; Jes Vollertsen, J. Microplastic pollution in drinking water. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 28, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E. Microplastics in drinking water? Present state of knowledge and open questions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 41, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, X.; Chen, M.; Yi, H. Removal of microplastics via drinking water treatment: Current knowledge and future directions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radityaningrum, A.D.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Mar’atusholihah; Soedjono, E.S.; Herumurti, W. Microplastic contamination in water supply and the removal efficiencies of the treatment plants: A case of Surabaya City, Indonesia. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 43, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, S.; Ghosal, A.; Nadda, A.K.; Jose, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P. Prevalence and implications of microplastics in potable water system: An update. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhib, Md.I.; Uddin, Md.K.; Rahman, Md.M.; Malafaia, G. Occurrence of microplastics in tap and bottled water, and food packaging: A narrative review on current knowledge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, H.; Ghayebzadeh, M.; Ganji, F.; Mousavi, S.; Azizi, N. Tracking microplastics contamination in drinking water in Zahedan, Iran: From source to consumption taps. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Zhou, L.; Qi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, Z.; Lin, T. Variation of microplastics and biofilm community characteristics along the long-distance raw water pipeline. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete Velasco, A.; Ramseier Gentile, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Le Coustumer, P.; Serge Stoll, S. Contamination and removal efficiency of microplastics and synthetic fibres in a conventional drinking water treatment plant in Geneva, Switzerland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Kerpen, J.; Wolff, S.; René Langer, R.; Eschweiler, V. Investigation of microplastics contamination in drinking water of a German city. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Adu, F.A.; Oyebamiji, A.K.; Bamisaye, A.; Adigun, R.A.; Olasoji, S.O.; Ogunjinmi, O.E. Microplastics toxicity, detection, and removal from water/wastewater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ma, X.; Song, Y.; Zuo, S.; Li, H.; Deng, W. A critical review on the interactions of microplastics with heavy metals: Mechanism and their combined effect on organisms and humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wu, H. Adsorption behavior of aged polystyrene microplastics (PSMPs) for manganese in water: Critical role of hydrated functional zone surrounding the microplastic surface. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 109040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Yu, B.; Cheng, X.; Hao, T.; Yuanyuan Dou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Effects of chlorination on microplastics pollution: Physicochemical transformation and chromium adsorption. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmala, K.; Rangasamy, G.; Ramya, M.; Shankar, V.U.; Rajesh, G. A critical review on recent research progress on microplastic pollutants in drinking water. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Ren, S.Y.; Ni, H.G. Effects of microplastic sorption on microbial degradation of halogenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerlein, P.S.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Pieke, E.N.; ter Laak, T.L. Fate of microplastics in the drinking water production. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau-Soler, J.; Ballesteros-Cano, R.; Ferrer, N.; Boleda, M.R.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics throughout a tap water supply network. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, P. The effect of adsorption on the fate of colloidal polystyrene microplastics in drinking water distribution system pipe scales. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zheng, B.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, P.; Tian, Y. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in water supply systems: In water and pipe scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lian, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.R.; Tao, G.L.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, J.C. Impacts of hydraulic conditions on microplastics biofilm development, shear stresses distribution, and microbial community structures in drinking water distribution pipes. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 325, 116510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Yang, M.; Qu, J. Effects of disinfectant and biofilm on the corrosion of cast iron pipes in a reclaimed water distribution system. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, H.R.; Hu, G.; Hewage, K.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Sadiq, R. Prioritization of unregulated disinfection by-products in drinking water distribution systems for human health risk mitigation: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 147, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhijith, G.R.; Ostfeld, A. Examining the Longitudinal Dispersion of Solutes Inside Water Distribution Systems. J. Water. Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielski, A.; Zielina, M.; Mlynska, A. Analysis of heavy metals leaching from internal pipe cement coating into potable water. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielina, M.; Bielski, A.; Mlynska, A. Leaching of chromium and lead from the cement mortar lining into the flowing drinking water shortly after pipeline rehabilitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punurai, W.; Davis, P. Prediction of Asbestos Cement Water Pipe Aging and Pipe Prioritization using Monte Carlo Simulation. Eng. J. 2017, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
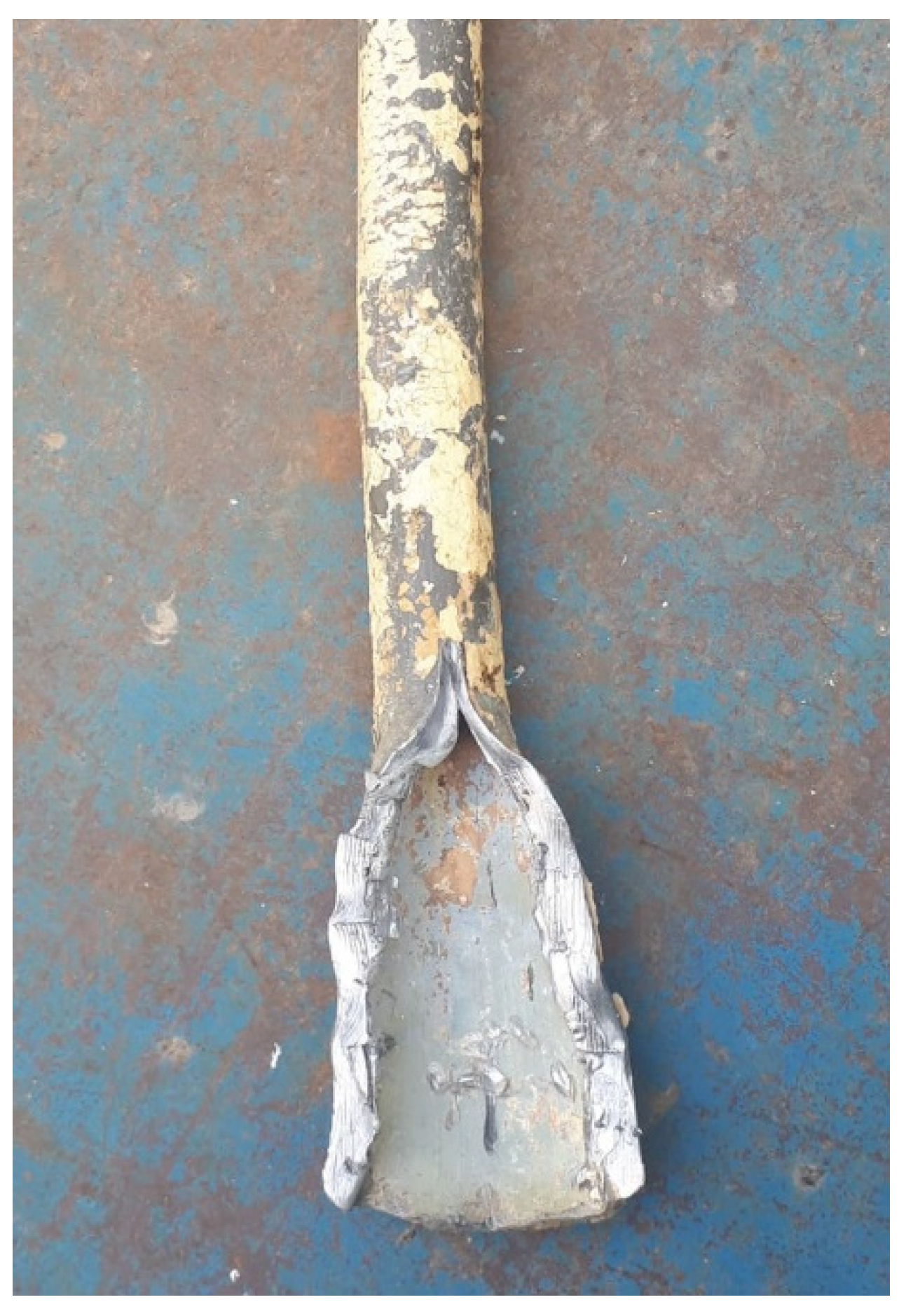
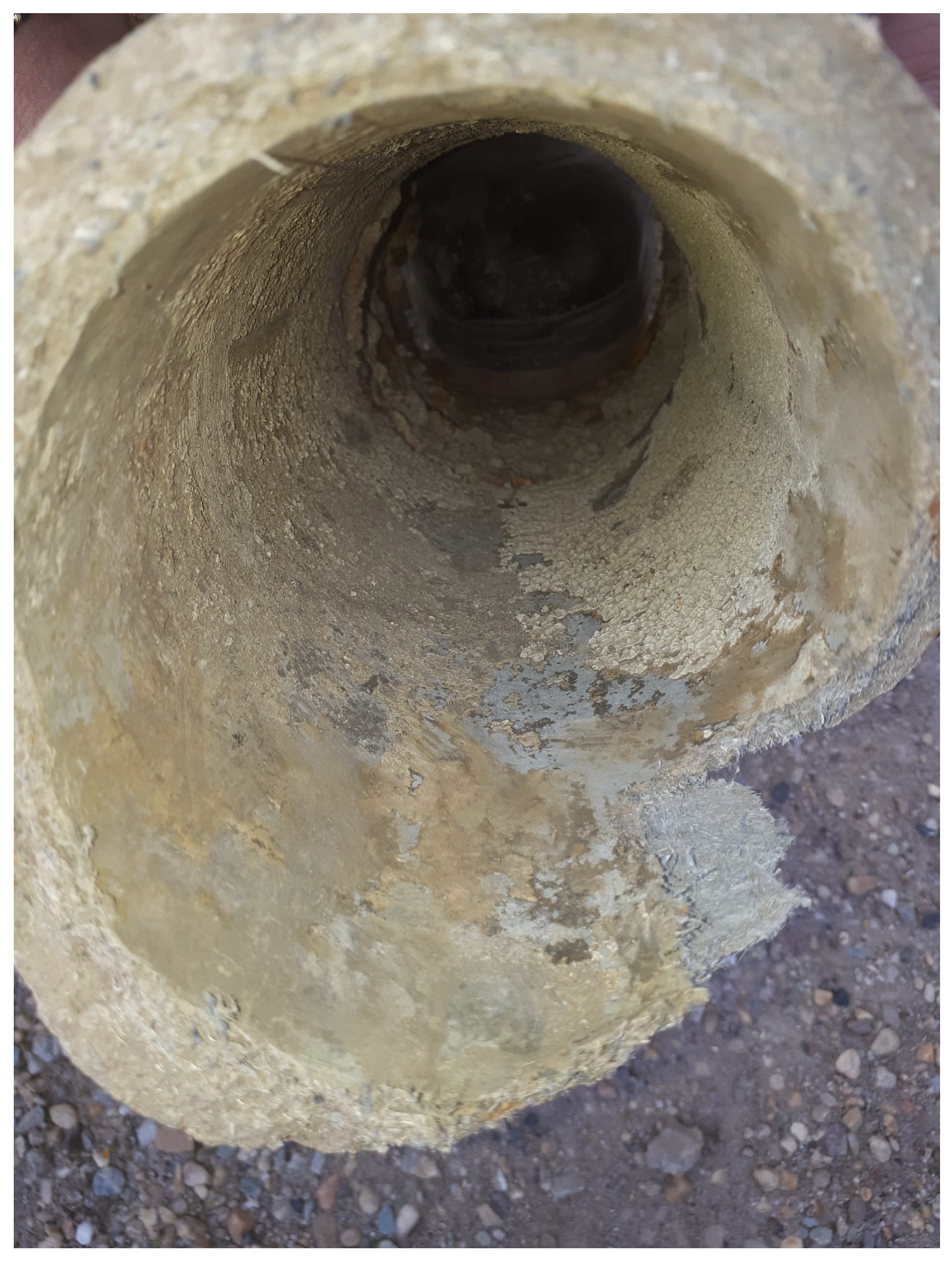
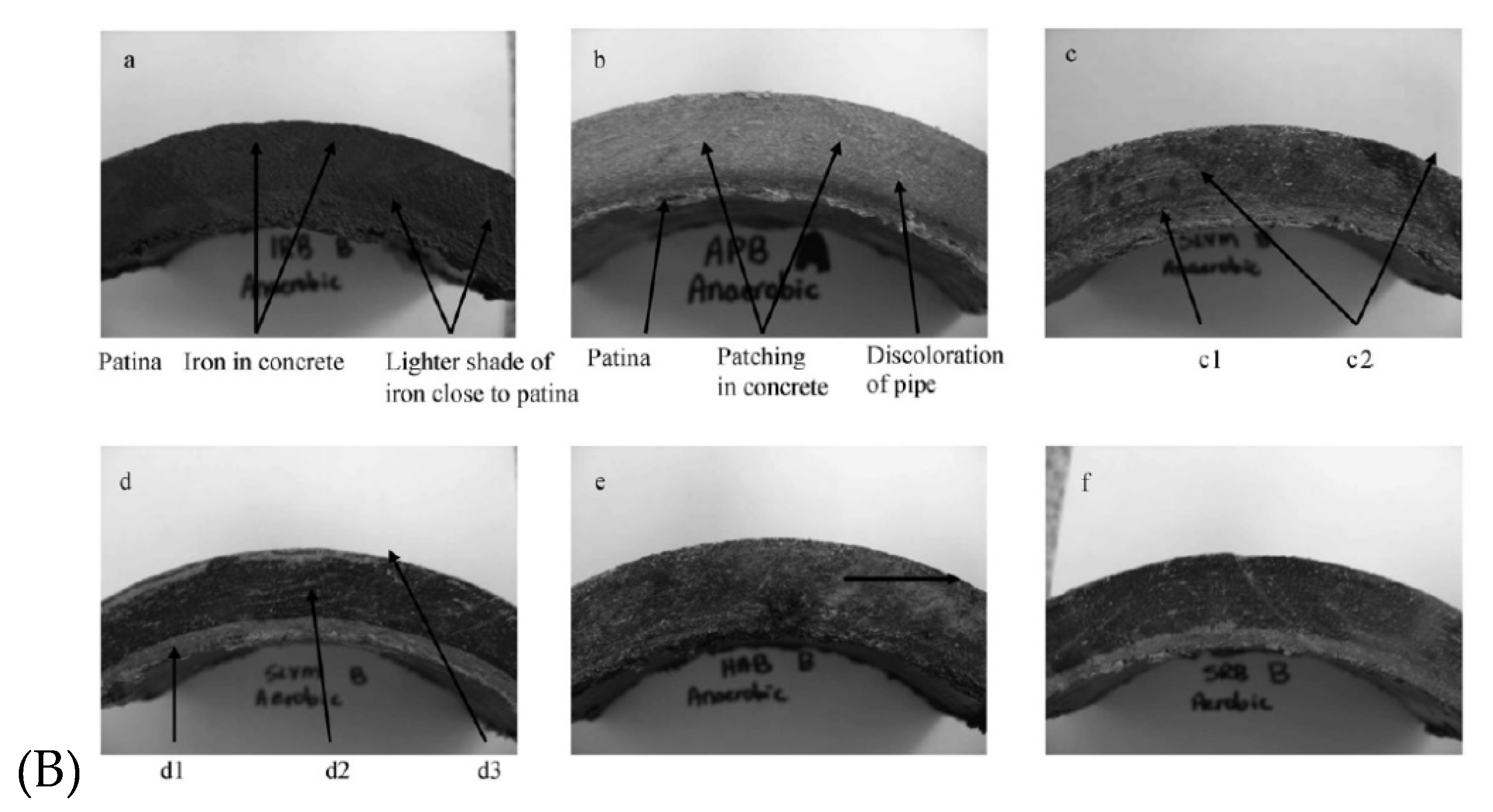





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



