1. Introduction
The learning method is often employed in education to enhance knowledge and skills during the teaching and learning process between teachers and students. This approach has been reported to have the ability to increase intelligence levels and improve the quality of human resources for the nation and state [
1].
The education of children by teachers aligns with Law 20 of 2003, which pertains to the Indonesian National Education System. Furthermore, the primary objective is to cultivate abilities and foster a sense of honorable national character and civilization, fear of God Almighty, noble character, health, knowledge, creativity, and independence, to produce democratic and responsible citizens [
2].
Junior High School is an educational stage designed for male and female adolescents aged 12-15 years old. The teaching and learning methods employed in this stage differ from those utilized in tertiary institutions, high schools, elementary schools, and kindergartens. Furthermore, the distinction in educational levels is largely determined by age, and this influences the diverse learning approaches at each level [
3].
The learning method is a teaching model developed by the teacher to facilitate the acquisition of new knowledge and skills among junior high school students. This approach plays a crucial role in nurturing human resources through comprehensive education across various fields of human life. Furthermore, it involves the introduction of students to the realm of science, socialization, mental and moral development, as well as character building, within a broad environment [
4,
5].
Although diligent teaching is undoubtedly important, it cannot solely guarantee an increase in students' learning achievement. Adequate nutrition also plays a crucial role, as it provides the body with the necessary physical and mental resilience to support the learning process [
6]. A study on junior high school students in Ghana (2019) showed that nutritious food consumption improved learning achievement [
7]. Based on observations, the problems found in Papua Province included low academic achievement due to the lack of access to nutritious food, which caused difficulty in concentrating at school and poor examination performance. This was exemplified by the high rate of anemia (57.1%) among young females aged 10-14 years at Kelila Public Junior High School in Mamberamo Tengah Regency in 2018 [
8]. Low students’ achievement in Jayapura City was also observed among families who could not afford nutritious food and school fees, leading to poor nutritional status due to the low intake of vegetables and fruits [
9].
Jayapura, the capital of Papua Province, is widely recognized as the City of Education, hosting a wide range of educational institutions. These include Kindergarten, Junior High School, Public/Private High School, Vocational High School, and Higher institutions [
10]. In Jayapura, there are 38 Junior High Schools, which are distributed across different districts, with 7, 10, 9, 9, and 3 of them being located in Abepura, North Jayapura, South Jayapura, Heram, and Muara Tami, respectively [
11].
Nutrition plays a vital role in the overall development of intellectual abilities and growth, including the increase in the number of cells and body tissues. The age, weight gain, and height of Junior High School students can be determined using basal metabolic index (BMR). Therefore, this study aims to improve learning achievement through nutrition among students in Jayapura City.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
This was a quantitative study with a cross-sectional design, which was carried out to measure the effect of nutrition on improving the learning achievement of students. The study locations included all junior high schools in Jayapura City, Papua Province, Indonesia, totaling 38. Furthermore, samples were selected using the accidental sampling method, with inclusion criteria of students aged 12-16 years old, male and female, strata VII-IX, parents living in Jayapura City, and parents' occupations were civil servants and non-civil servants. Students from public and private junior high schools as well as those with parents living outside Jayapura City were excluded.
The study population consisted of Junior High School students in Jayapura City. The sample size was determined based on the difference in proportion test formula (
n) [
12]:
Where:
n = sample size
= degree of significance at α = 0.05; Zα = 1.96
= test strength at β = 0.10; Zβ = 1.28
Po = the proportion of students who have learning achievement (P1 = 0.35)
Pa = the proportion of students who do not have learning achievement (P2 = 0.05)
The sample was 350 junior high school students in Jayapura City.
2.2. Data Collection
This study used both primary and secondary data, where the secondary data contained demographics and the population of Jayapura City, which were collected from the Central Bureau of Statistics in 2022. Meanwhile, the primary data included Knowledge of Nutrition, Balanced diet, physical activity, interest in learning, nutritional status (Basal Metabolic Index), and academic achievement, which were obtained from students of the Faculty of Public Health living in Jayapura City.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The data obtained on this study were analyzed using descriptive and path analyses. The descriptive analysis was carried out to assess students’ BMR, gender, class VII-IX, and Junior High School within the districts of Jayapura City (Ordinal data form). Meanwhile, the path analysis was used to evaluate multivariate data sets to form a causal model of student achievement in Jayapura City in 2022 (Interval data form). This study was conducted thorough Ethics Review and was granted approval by the Ethics Committee of Cenderawasih University, the registry number of 114/KEPK-FKM UC/2022 on 9th May 2022.
3. Results
3.1. Jayapura City Demographics
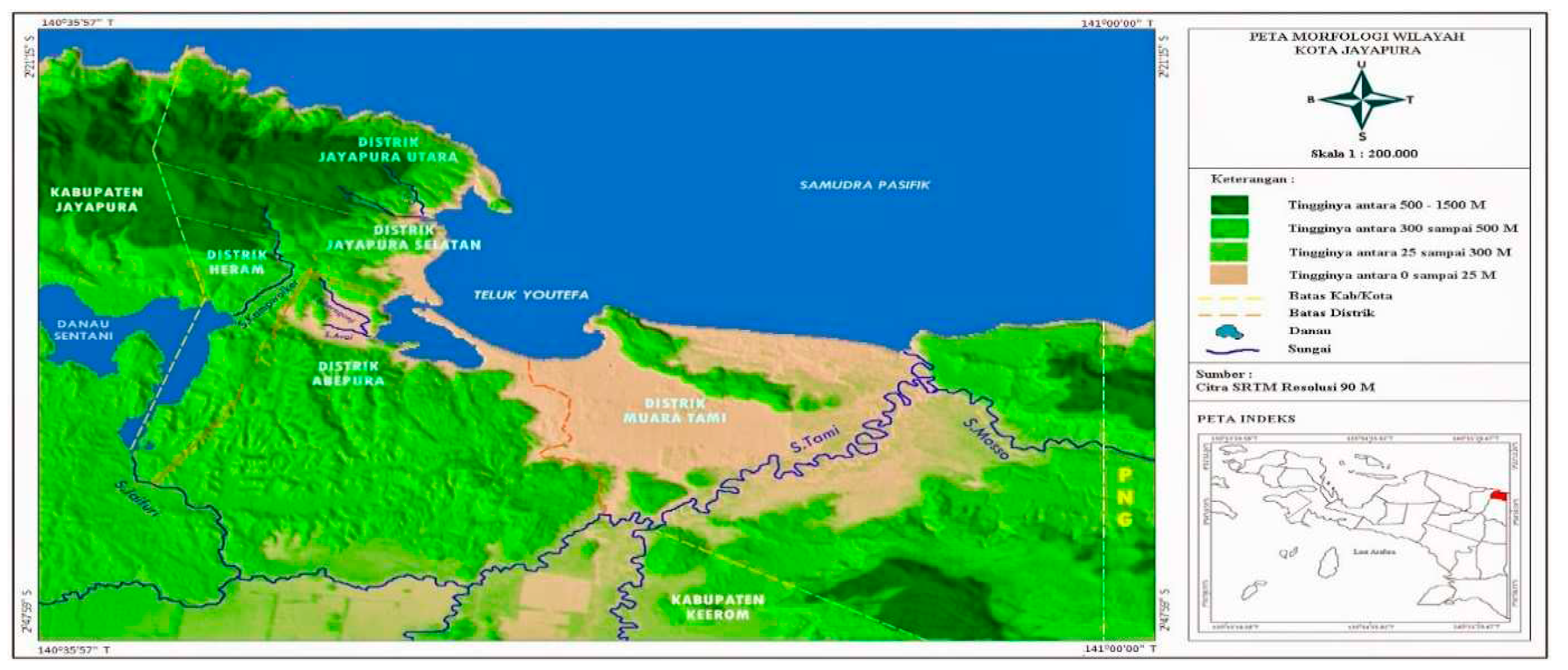
Jayapura was the capital city of Papua Province with an area of 940 Km2. Furthermore, Muara Tami was the district with the largest area of 626.7 Km2, while South Jayapura was the smallest with 43.4 Km2. Based on astronomical findings, Jayapura was located at 1370271–1410411 East Longitude and 10271–30491 South Latitude, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 1.
Map of Jayapura City, Papua Province, Indonesia.
Figure 1.
Map of Jayapura City, Papua Province, Indonesia.
The northern part of Jayapura City was bounded by the Pacific Ocean, to the east by the State of Papua New Guinea, to the south by Arso District (Keerom Regency), and to the west by Depapre District (Jayapura Regency). Furthermore, it consisted of 5 districts, namely Abepura, North Jayapura, South Jayapura, Heram, and Muara Tami Districts. Muara Tami was the district with the largest area of 626.7 Km
2, while South Jayapura had the smallest of 43.4 Km
2 (10). Based on districts, Abepura, North Jayapura, South Jayapura, Heram, and Muara Tami had a total of 7, 10, 9, 9, and 3 Junior High Schools, respectively, totaling 38 in Jayapura City [
12].
3.2. Resident
Table 1 presents the diverse population of Jayapura City, which comprises both native residents and individuals who have migrated from other cities across Indonesia.
In 2021, the residents in Jayapura City experienced a 33% increase to 404,004 compared to the population in 2020. A total of 271,586 people were in the productive age group of 15-64 years, while those aged 0-14 and 65+ years were 132,418. Previous reports showed that the population density was 429.79 people/Km
2, with South Jayapura and Muara Tami Districts having the highest and lowest densities, respectively [
11].
3.3. Basal Metabolic Index (BMI)
BMI obtained from the weight and height of Junior High School students was divided into five categories, namely underweight (BMI < 17.0), mild underweight (BMI 17.0–18.5), severe normal weight (BMI 18.5–25.0), lighter weight (BMI 25.0–27.0), and more severe body weight (BMI > 27.0).
BMI further showed multiple nutritional differences among students. Among the Abepura District male students, 16.92% were underweight in class VII, 9.09% had normal weight in class VII, and 14.55% had normal weight in class IX. Furthermore, a total of 10.77% of female students in Class VII had normal weight, 14.55% in Class VIII were underweight, and 9.09% in Class IX were underweight. Based on the results, the number of students with nutritional status of severely underweight, overweight, and obese was low in Abepura District in 2022 [
13].
Students in South Jayapura District showed a BMI with different nutritional statuses. A total of 7.69% of males in Class VII had normal weight, 7.27% in Class VIII were underweight, and 9.09% in Class IX had normal weight. Furthermore, 9.23% of females in Class VII were underweight, 9.09% in Class VIII were underweight, and 3.64% in Class IX were found to be severely underweight, underweight, normal-weight, and overweight [
14]. Nutritional status varied widely among students due to their different family consumption patterns [
15].
The results of the BMI of nutritional status found that 9.23% of Class VII male students in North Jayapura District were overweight, 9.09% in Class VIII were underweight, and 7.27% in Class IX were underweight and normal weight. However, 10.77% of females in Class VII had normal weight, 7.27% in Class VIII were underweight, and 9.09% in Class IX were overweight. The results showed that the number of students in North Jayapura District with severely underweight and obese conditions was low.
Based on the results, 6.15% of Class VII male students in Muara Tami District had normal weight, 7.27% in Class VIII were severely underweight and underweight, and 9.09% in class IX were underweight. Meanwhile, 4.62% of females in class VII were severely underweight and underweight, 7.27% in class VIII were underweight, and 3.64% in class IX were severely underweight, underweight, and normal weight. The number of students with obese nutritional status in Muara Tami District was low
Table 2.
Students’ Body Mass Index (BMI) by Gender in Jayapura City in 2022 (n = 350).
Table 2.
Students’ Body Mass Index (BMI) by Gender in Jayapura City in 2022 (n = 350).
| Junior High School in Jayapura City |
Boys |
Girls |
Information |
| Class VII |
Class VIII |
Class IX |
Class VII |
Class VIII |
Class IX |
|
| BMI < 17.0 |
2 (3.08%) |
1 1.82%) |
- |
4 (6.15%) |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Severely underweight |
| BMI 17.0–18.5 |
11 (16.92%) |
3 (5.45%) |
7 (12.73%) |
4 (6.15%) |
8 (14.55%) |
5 (9.09%) |
Underweight |
| BMI 18.5–25.0 |
4 (6.15%) |
5 (9.09%) |
8 (14.55%) |
7 (10.77%) |
5 (9.09%) |
3 (5.45%) |
Normalweight |
| BMI 25.0–27.0 |
1 (1.54%) |
2 (3.64%) |
- |
2 (3.08%) |
2 (3.64%) |
1 (1.82%) |
Overweight |
| BMI > 27.0 |
2 (3.08%) |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
1 (1.82%) |
Obese |
| BMI < 17.0 |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
2 (3.08%) |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Severely underweight |
| BMI 17.0–18.5 |
3 (4.62%) |
4 (7.27%) |
2 (3.64%) |
6 (9.23%) |
5 (9.09%) |
2 (3.64%) |
Underweight |
| BMI 18.5–25.0 |
5 (7.69%) |
3 (5.45%) |
5 (9.09%) |
4 (6.15%) |
2 (3.64%) |
2 (3.64%) |
Normalweight |
| BMI 25.0–27.0 |
2 (3.08%) |
3 (5.45%) |
- |
- |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Overweight |
| BMI > 27.0 |
- |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
Obese |
| BMI < 17.0 |
1 (1.54%) |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
3 (4.62%) |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
Severely underweight |
| BMI 17.0–18.5 |
2 (3.08%) |
5 (9.09%) |
4 (7.27%) |
2 (3.08%) |
4 (7.27%) |
1 (1.82%) |
Underweight |
| BMI 18.5–25.0 |
1 (1.54%) |
1 (1.82%) |
4 (7.27%) |
7 (10.77%) |
3 (5.45%) |
1 (1.82%) |
Normalweight |
| BMI 25.0–27.0 |
6 (9.23%) |
3 (5.45%) |
- |
1 (1.54%) |
- |
5 (9.09%) |
Overweight |
| BMI > 27.0 |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
1 (1.82%) |
2 (3.08%) |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
Obese |
| BMI < 17.0 |
2 (3.08%) |
4 (7.27%) |
3 (5.45%) |
3 (4.62%) |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Severely underweight |
| BMI 17.0–18.5 |
2 (3.08%) |
4 (7.27%) |
5 (9.09%) |
3 (4.62%) |
4 (7.27%) |
2 (3.64%) |
Underweight |
| BMI 18.5–25.0 |
4 (6.15%) |
2 (3.64%) |
1 (1.82%) |
1 (1.54%) |
2 (3.64%) |
2 (3.64%) |
Normalweight |
| BMI 25.0–27.0 |
2 (3.08%) |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
1 (1.54%) |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
Overweight |
| BMI > 27.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Obese |
| BMI < 17.0 |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
2 (3.64%) |
1 (1.54%) |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Severely underweight |
| BMI 17.0–18.5 |
5 (7.69%) |
4 (7.27%) |
4 (7.27%) |
6 (9.23%) |
7 (12.73%) |
9 (16.36%) |
Underweight |
| BMI 18.5–25.0 |
7 (10.77%) |
3 (5.45%) |
8 (14.55%) |
5 (7.69%) |
4 (7.27%) |
3 (5.45%) |
Normalweight |
| BMI 25.0–27.0 |
3 (4.62%) |
2 (3.64%) |
- |
- |
3 (5.45%) |
1 (1.82%) |
Overweight |
| BMI > 27.0 |
- |
1 (1.82%) |
- |
1 (1.54%) |
- |
2 (3.64%) |
Obese |
| Total Sample |
65 |
55 |
55 |
65 |
55 |
55 |
350 Students |
Students in Heram District showed multiple BMI nutritional status. A total of 10.77% of males in Class VII had normal weight, 7.27% in Class VIII were underweight, and 14.55% in Class IX had normal weight. Meanwhile, 9.23% of females in Class VII were underweight, 12.73% in class VIII were underweight, and 16.36% in Class IX were underweight. Male and female students with nutritional status of overweight, obese, and severely underweight were rarely found in Junior High Schools in Heram District.
3.4. Univariate Analysis
Junior High School was typically established for male and female students aged 12-15 years. At this stage, adolescents were very vulnerable during their growth and development, which had a relationship with nutritional knowledge, balanced diet, physical activity, interest in learning, nutritional status, and academic achievement. The average of the data obtained as well as the normality test were presented in
Table 3.
Univariate mean and normality tests of Junior High School students were conducted in Jayapura City in 2022. The results showed that the mean nutritional knowledge was 2.22% of the minimum and maximum values. Furthermore, the standard deviation was 1.14, and the nutritional knowledge variable was normally distributed, as indicated by the skewness value (p-value 2.08 ≤ 2). The mean balanced diet was 1.96% of the minimum and maximum daily consumption values of students, with a standard deviation of 0.88. The skewness value (p-value 0.60 ≤ 2) indicated that data on balanced diet variables were normally distributed.
The average number of students engaging in physical activity (sports) at school or home was 17.61% of the minimum and maximum value. Furthermore, the standard deviation was 2.31 and the skewness value (p-value 0.73 ≤ 2) indicated normally distributed data. The mean of the variable interest in learning was 2.22% of the minimum and maximum values, with a standard deviation of 1.14. The data on interest in learning were normally distributed based on the skewness value (p-value 2.08 ≤ 2).
The mean nutritional status was 20.33% of BMI obtained from the threshold value for the minimum and maximum. The standard deviation was 3.95 and the variable data measured by the QQ Plot graph were normal, but not shown by the skewness value. The mean students' achievement was 68.94% of the minimum and maximum scores recorded, with a standard deviation of 17.75. The skewness value (p-value was 1.9 ≤ 2) obtained indicated normal data distribution [
9,
16].
3.5. Path Analysis Diagrams
Path analysis could be elucidated through the theory of planned behavior developed by Azjen (1985) concerning school students and the study by Ingram, Cope, Harju, and Wuensch (2000). The results of nutritional status effect on the students’ learning achievement investigated in Jayapura City could be explained as follows:
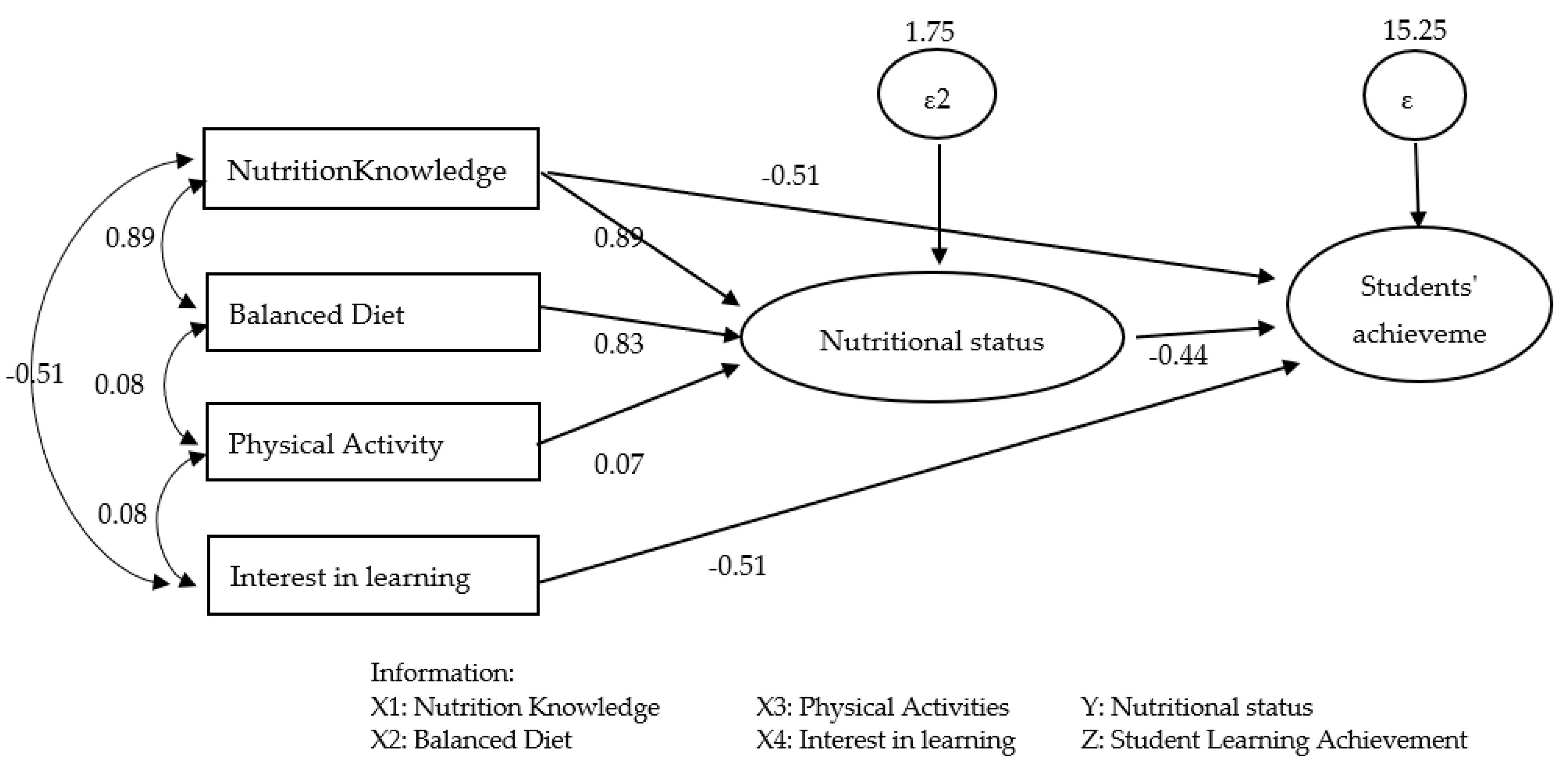
Figure 2.
Path analysis diagram.
Figure 2.
Path analysis diagram.
The path correlation coefficients of students' achievement were summarized in the following model:
Correlation coefficients of cause and effect (knowledge of nutrition and balanced diet = 0.89, balanced diet and physical activity = 0.08, physical activity and interest in learning = 0.08, as well as nutrition knowledge and interest in learning = -0.51). The total effect on students was 0.003 from the formed path analysis.
Indirect effect correlation coefficients (nutrition knowledge and nutritional status = 0.89, balanced diet and nutritional status = 0.83, and physical activity and nutritional status = 0.07). The total effect was 0.06, indicating an indirect effect on the students’ learning achievement.
Direct effect correlation coefficients (nutrition knowledge and students' achievement = -0.51, nutritional status and students' achievement = -0.44, and interest in learning and students' achievement = 0.51). The total effect was -0.11, which had a direct effect on students' learning achievement.
The indirect residual variable (ε2 = 1.75) was a combination of nutrition knowledge, balanced diet, physical activity, and other variables outside the measured analysis model, as well as measurement errors. Meanwhile, the direct residual variable (ε3 = 15.25) was a combination of nutritional knowledge, nutritional status, other variables outside the measured analysis model, and measurement errors.
The path analysis model formed, namely the direct variable, showed that students’ achievement was majorly influenced by nutrition knowledge (-0.51) and interest in learning (-0.51), while the indirect variables with the greatest effect on student achievement were nutrition knowledge and nutritional status (0.89).
3.6. Multivariate Analysis
Junior High School students of Class VII to IX in Jayapura City in 2022 were analyzed through exogenous and endogenous variables with an indirect influence. The nutritional status was assessed based on BMI, which was found to be in the normal range (B* = 3.09, SE = 0.08, and B** = 0.89). Furthermore, the results showed that the students' nutrition knowledge affected their nutritional status (p-value = 0.001).
Table 4.
Path Analysis (n = 350).
The nutritional status could be improved through the consumption of a balanced diet (B* = 3.72, SE = 0.13, and B** = 0.83). The significant results showed that the balanced diet consumed affected this variable (p count = 0.001). BMI was an anthropometric assessment of the students' nutritional status through physical activity (B* = 0.12, SE = 0.09, and B** = 0.07). Based on the results, students' physical activity through sports at school or home had no effect (p-value = 0.167).
Analysis was carried out on Class VII to IX Junior High School students in Jayapura City in 2022 using exogenous and endogenous variables, which directly had an effect on learning achievement. The increase in achievement was caused by an improvement in nutrition knowledge (B* = -8.03, SE = 0.71, and B** = -0.51). Furthermore, the results showed that nutrition knowledge had a significant effect on learning achievement (p-value = 0.001). Achievement was also improved through an interest in learning (B* = -8.03, SE = 0.71, and B** = -0.51), where students with a high interest had a higher value of this variable (p-value = 0.001). Students' achievement was accomplished through optimal nutritional status (B* = -1.99, SE = .21, and B** = -0.44) and the consumption of nutritious food provided enormous benefits.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Nutrition Knowledge on Students' Nutritional Status
The nutritional status of students was evaluated through measurements of body weight for age, weight for height, or height for age [
17]. This measurement was a standard assessment designed by WHO and UNICEF to generally determine the status of all individuals in the world [
18]. Improving the [
11,
19] of adolescents aged 12-15 years old was crucial. This was because the age group was very rapid growth and development, where the body parts increased in size in terms of height and weight [
20].
The results showed the effect of nutrition knowledge on the nutritional status of Junior High School students in Jayapura City (
p-value = 0.001). The nutrition knowledge of the male and female students was also found to be useful since it influenced the pattern of balance diet consumption. The positive impact observed was the fulfillment of nutritious food intake during puberty among students in classes VII-IX [
21]. This indicated that good nutrition [
4,
22] helped them to maintain a normal nutritional status.
This current study was in line with previous studies, such as concerning the relationship between knowledge of balanced nutrition and the nutritional status of young females in class XI Accounting 2 at PGRI 2 Vocational High School, Kediri City [
2,
11,
23]. The results showed a relationship between the variable observed in the analysis (
p-value = 0.003).
Several previous studies obtained similar results as this current study, including [
16], which assessed the relationship between knowledge and attitudes with the nutritional status of Medan MAN students during the Covid-19 pandemic [
4,
22]. A relationship was discovered between the knowledge and nutritional status of students at MAN 1 and 2 (
p-value = 0.007). Furthermore, examined the relationship between knowledge of balanced nutrition, body image, adequacy level of energy, and macronutrients with the nutritional status of students [
24]. A significant relationship was found between knowledge of balanced nutrition and nutritional status (
p-value = 0.0001) [
17].
Other studies on food intake, such as which assessed the role of nutritional knowledge, energy intake, nutritional status, and attitudes toward adolescent nutrition, found a relationship between nutrition knowledge and students' nutritional status (
p-value = 0.003) [
19]. Also examined the relationship between knowledge, attitudes, balanced nutrition, and the nutritional status of Class IV and V students at Tarakanita Gading Serpong Elementary School [
25]. The results showed a relationship between the level of knowledge about balanced nutrition and the nutritional status (
p-value = 0.032).
4.2. The Effect of a Balanced Diet on Students' Nutritional Status
The purpose of a balanced diet was explained in “
INI PIRINGKU” as a message for improving nutrition in Indonesia [
26]. The children, adolescents, adults, and elderly population must concentrate on a balanced diet consumption pattern, which was beneficial for the normal nutritional status of the population [
27,
28,
29].
The undernourished and poor nutritional status of female or male adolescent students was detected in the group with bad eating habits, unhealthy dietary patterns, and lack of hygiene [
15,
30,
31]. Malnutrition was often found in students whose parents did not have a fixed monthly income [
32,
33,
34]. Meanwhile, normal and overweight nutritional status (obesity) was commonly found in male and female students with good eating habits supported by healthy and hygienic eating patterns [
9,
35].
In this study, the young males and females were Junior High School students in Jayapura City. The results showed that the consumption of a balanced diet during puberty was crucial to maintain their normal nutritional status [
36]. Furthermore, the statistical test results indicated that the normal nutritional status found in students was caused by the consumption of a balanced diet according to the Nutrition Adequacy Rate (
p-value = 0.001). Based on these findings, the normal nutritional status was diverse and based on balanced diet intake.
The results of this study were consistent with previous reports, such as, which examined the relationship between knowledge of balanced nutrition, body image, energy adequacy levels and macronutrients, and nutritional status in students [
26]. The results showed a significant relationship between energy (
p-value = 0.0001), fat (
p-value = 0.019), and carbohydrate adequacy levels (
p-value = 0.044), as well as nutritional status [
37]. Furthermore, examined the factors affecting the nutritional status of adolescents aged 16-18 years [
16,
20]. The results showed a significant relationship between energy consumption and nutritional status (
p-value = 0.000) [
38].
This current study was supported by previous reports studies, such as concerning the correlation of eating behavior and nutritional status to students' achievement in the accelerated program in Junior High School Negeri 1 Malang [
21]. The results showed a significant relationship between eating behavior and nutritional status (
p-value = 0.000). Furthermore, examined the relationship between diet and physical activity on the nutritional status of Al-Azhar Pontianak Junior High School students. The results revealed an association between diet and nutritional status (
p-value = 0.016) investigated the relationship between diet and physical activity with the nutritional status of Class VII students of Public Junior High Schools (Full Day Schools) [
23,
39]. A significant relationship was discovered between diet and the nutritional status of the female students (
p-value = 0.000 and correlation coefficient = 0.406).
4.3. The Effect of Physical Activity on Students' Nutritional Status
Physical activity referred to routines carried out by an individual or group of people either in the form of sports or other engagements by moving the arms, legs, head, stomach, or the whole body [
13]. Based on previous reports, physical activity was largely determined by body fitness and nutritious food intake [
40]. The consumption of nutritious food could improve normal nutritional status, but excessive intake often led to obesity [
41]. However, excessive physical activity without the consumption of nutritious food did not often lead to normal nutritional status [
28,
42,
43].
The study on Junior High School students in Jayapura City in 2022 showed that the sports carried out at school or home by female and male adolescents were physical activities, but did not affect their nutritional status [
28]. The statistical test results revealed that the nutritional status of students in Jayapura City, namely malnutrition, poor, normal, or obesity was not found among physically active students (
p-value = 0.167) [
44]. This current study was consistent with concerning the consumption of energy and protein, physical activity, and nutrition knowledge with the nutritional status of Dukuhsari State Elementary School students, Sidoarjo Regency [
21,
45,
46,
47]. The analysis results showed that there was no relationship between physical activity and students' nutritional status (
p-value = 0.926 and r = 0.018). Furthermore, evaluated the association between physical activity and eating patterns with nutritional status in class 1 High School Girls in North Denpasar, and the results showed the absence of a significant relationship (
p-value = 0.541) [
29].
A study on Junior High Schools students in Jayapura City was inversely proportional to previous studies. Investigated the relationship between diet and physical activity with nutritional status in children at Public Elementary School 47/IV in Jambi City [
48,
49]. The results showed a relationship between physical activity and nutritional status (
p-value = 0.033). Furthermore, examined the factors influencing the nutritional status of adolescents aged 16-18 years and the results revealed a significant relationship with physical activity (
p-value = 0.004) [
41,
50,
51]. explored the association between diet and physical activity on the nutritional status of Al-Azhar Pontianak Middle School students. The results showed that physical activity and nutritional status were associated (
p-value = 0.020). (27) evaluated the relationship between diet and physical activity with the nutritional status of class VII students in Public Junior High Schools (Full Day Schools) [
2,
5,
23,
51]. A significant relationship was reported between physical activity and female students' nutritional status (
p-value = 0.000 and correlation coefficient = 0.348).
4.4. The Effect of Nutrition Knowledge on Students' Achievement
Nutrition knowledge referred to the information possessed by Junior High School students about food and drink, which served as energy, builders and regulators [
22]. This indicated that these foods and drinks could maintain health status during the teaching and learning process at school [
4,
29,
31]. Foods containing sufficient nutrition were the best for students' achievements (33). Furthermore, achievement at school was largely determined by the consumption of good food that was not contaminated with infectious diseases or harmful chemicals, and usually of various kinds [
21].
The results showed that one of the factors influencing students' achievement was nutrition knowledge (
p-value = 0.001). The learning achievement was improved through diligent teaching at school [
21]. However, the nutrition knowledge possessed by students indirectly influenced their consumption patterns [
46]. These results indicated that a good achievement was often caused by an increase in nutrition knowledge.
Explored the relationship between nutritional knowledge and breakfast habits on student achievement at State Senior High School 12 Bekasi City, which was in line with this current study [
47]. The results showed a significant relationship between nutrition knowledge and learning achievement (
p-value = 0.001, OR = 5.174, CI = 1.810–14.790). This indicated that students with good nutrition knowledge were 5.1 times more at risk of increasing learning achievement compared to those with poor knowledge [
9,
52].
4.5. The Effect of Nutritional Status on Students' Achievement
Anthropometric assessment revealed that excessive feeding led to obesity, while undernourishment was caused by low food intake. Furthermore, low food intake caused low learning achievement, and balanced diet consumption promoted normal nutritional status [
53]. A study in Ethiopia found that female Junior High School students with normal nutritional status in Bahir Dar Amhara City experienced a direct effect of increasing learning achievement by 72%.
The current results obtained in Jayapura City showed that the nutritional status of students directly affected their achievement, and those with a good nutritional status experienced a significantly increase in this variable (
p-value = 0.001). This was supported by concerning the influence of adolescents' breakfast habits and nutritional status on learning achievement [
54]. The results revealed that students with normal nutritional status had the opportunity to improve learning achievement by 1.56 times better (
p-value = 0.045).
Explored the correlation of eating behavior and nutritional status to students' achievement in acceleration programs in Junior High School [
54]. Based on the results, there was a significant relationship between nutritional status and achievement. Students with good nutritional status found it easier to concentrate while learning to achieve maximum satisfactory achievement [
55].
A previous study by showed a significant relationship between nutritional status and learning achievement of Junior High School students at Al-Manar Private Middle School, Hamparan Perak District (
p-value = 0.017) [
9,
52]. Report an association between nutritional status and learning achievement (
p-value = 0.02). Furthermore, similar findings were obtained by, where there was a significant relationship between these two variables among class IX students in Junior High School 2 Kumelembai [
7,
47].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the consumption of various foods according to the Nutrition Adequacy Rate (RDA) was a crucial aspect in increasing Human Resources (HR). Furthermore, the results showed that energy, building materials, and regulators improved the learning achievement of Junior High School students in Jayapura City.
The indirect effect of exogenous variables on endogenous variables showed that nutrition knowledge and a balanced diet affected nutritional status, but physical activity had no effect. The direct effect of exogenous variables on endogenous variables further revealed that nutrition knowledge, interest in learning, and nutritional status directly influenced achievement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.I., F.E. and A.Z.; methodology, S.P.I.; software, R.R.H; validation, E.S., R.R.H. and M.F.P.P.; formal analysis, A.Z.; investigation, F.E.; resources, S.P.I.; data curation, S.P.I.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P.I; writing—review and editing, E.S.; visualization, E.S.; supervision, M.F.P.P.; project administration, E.S.; funding acquisition, S.P.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Cenderawasih University (protocol code 114/KEPK-FKM UC/2022 and 9th May 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting presented results can be found by directly asking the correspondence.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Cenderawasih University and Faculty of Public Health students for assisting in the collection of study data in 38 Junior High schools in Jayapura City.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mustafa, S.; Haque, C.E.; Baksi, S.; Valentino, C. Low Daily Intake of Fruits and Vegetables in Rural and Urban Bangladesh: Influence of Socioeconomic and Demographic Factors, Social Food Beliefs and Behavioural Practices. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollwein, J.; et al. Nutritional status according to the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA®) and frailty in community dwelling older persons: A close relationship. Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging 2013, 17, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ghwass, M.M.E.; Halawa, E.F.; Sabry, S.M.; Ahmed, D. Iron deficiency anemia in an Egyptian pediatric population: A cross-sectional study. Ann Afr Med 2015, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Webb, M.C.; Beckford, S.E. Nutritional knowledge and attitudes of adolescent swimmers in Trinidad and Tobago. J Nutr Metab 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmare, B.; Taddele, M.; Berihun, S.; Wagnew, F. Nutritional status and correlation with academic performance among primary school children, northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes 2018, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Jayapura. Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Jayapura. Jayapura City. 1 January 2020. Available online: https://jayapurakota.bps.go.id/indicator/23/71/1/jumlah-penduduk-miskin-menurut-kabupaten-kota-di-provinsi-papua.html (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Krause, C.; Sommerhalder, K.; Beer-Borst, S.; Abel, T. Just a subtle difference? Findings from a systematic review on definitions of nutrition literacy and food literacy. Health Promot Int 2018, 33, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Truswell, A.S. Essentials of human nutrition, 5th ed.; Oxford University Pres: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 1, Available online: https://books.google.com/books/about/Essentials_of_Human_Nutrition.html?hl=id&id=a6t0DgAAQBAJ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Fanzo, J. Ethical issues for human nutrition in the context of global food security and sustainable development. Glob Food Sec 2015, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossfeld, H.-P.; Buchholz, S.; Skopek, J.; Triventi, M. Models of secondary education and social inequality: An international comparison, 5th ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northamton, USA, 2016; Volume 1, Available online: https://books.google.com/books/about/Models_of_Secondary_Education_and_Social.html?hl=id&id=0fR-DQAAQBAJ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Akseer, N.; Al-Gashm, S.; Mehta, S.; Mokdad, A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Global and regional trends in the nutritional status of young people: a critical and neglected age group. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2017, 1393, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; et al. General scientific guidance for stakeholders on health claim applications (Revision 1)1. EFSA Journal 2021, 19, e06553. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.; McAuley, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Despres, J.P.; Arena, R.; Kokkinos, P. Physical Activity and Cardiorespiratory Fitness as Major Markers of Cardiovascular Risk: Their Independent and Interwoven Importance to Health Status. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2015, 57, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aris, I.M.; et al. Association of Weight for Length vs Body Mass Index During the First 2 Years of Life With Cardiometabolic Risk in Early Adolescence. JAMA Netw Open 2018, 1, e182460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.G.; Davies, I.G.; Richardson, L.D.; Stevenson, L. Determinants of takeaway and fast food consumption: a narrative review. Nutr Res Rev 2018, 31, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitkeviciute, R.; Ball, L.E.; Harris, N. The relationship between food literacy and dietary intake in adolescents: a systematic review. Public Health Nutr 2015, 18, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, N.; Aslam, M.; Petersen, J.H.; Mustafa, G. The 2022 Pakistani references from birth to 60 months for length/height, weight and body mass index. Acta Paediatr 2023, 112, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisnana, I.; Azizah, R.; Kusumaningrum, T.; Has, M.; Mishbahatul, E. Feeding Patterns of Children with Stunting Based on WHO (World Health Organization) Determinant Factors of Behaviours Approach. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development 2019.
- Rossi, F.E.; Landreth, A.; Beam, S.; Jones, T.; Norton, L.; Cholewa, J.M. The Effects of a Sports Nutrition Education Intervention on Nutritional Status, Sport Nutrition Knowledge, Body Composition, and Performance during Off Season Training in NCAA Division I Baseball Players. J Sports Sci Med 2017, 16, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. Weight-for-length/height growth curves for children and adolescents in China in comparison with body mass index in prevalence estimates of malnutrition. 2016, 44, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geaney, F.; et al. The effect of complex workplace dietary interventions on employees’ dietary intakes, nutrition knowledge and health status: a cluster controlled trial. Prev Med (Baltim) 2016, 89, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Stewart, D.; Chang, C.; Shi, Y. Effect of a school-based nutrition education program on adolescents’ nutrition-related knowledge, attitudes and behaviour in rural areas of China. Environ Health Prev Med 2015, 20, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, A.M.; Smith, S. Body composition and morphological assessment of nutritional status in adults: a review of anthropometric variables. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics 2016, 29, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustino, V.; Parroco, A.M.; Gennaro, A.; Musumeci, G.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G. Physical Activity Levels and Related Energy Expenditure during COVID-19 Quarantine among the Sicilian Active Population: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey Study. Journal Of Sustainability 2021, 12, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shen, J.; Krenn, H.Y.; Hu, S.; Yuan, J. A Meta-Analysis of the Relationship Between Learning Outcomes and Parental Involvement During Early Childhood Education and Early Elementary Education. Educ Psychol Rev 2016, 28, 771–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K. Rehabilitation Nutrition for Injury Recovery of Athletes: The Role of Macronutrient Intake. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.; Hou, G.G. Whole wheat noodle: Processing; quality improvement, and nutritional and health benefits. Cereal Chem 2019, 96, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, Z.; et al. Relationship between physical activity, healthy lifestyle and COVID-19 disease severity; a cross-sectional study. Journal of Public Health 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahia, N.; Brown, C.A.; Rapley, M.; Chung, M. Level of nutrition knowledge and its association with fat consumption among college students. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Halder, H.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Parvez, M. Poverty and childhood malnutrition: Evidence-based on a nationally representative survey of Bangladesh. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Kliemann, N.; Wardle, J.; Johnson, F.; Croker, H. Reliability and validity of a revised version of the General Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2016, 70, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Berkley, J.A.; Bandsma, R.H.J.; Kerac, M.; Trehan, I.; Briend, A. Severe childhood malnutrition. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2017, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, T.; Kabir, Z.N.; Wahlin, Å.; Streatfield, K.; Cederholm, T. The multidimensional background of malnutrition among rural older individuals in Bangladesh—a challenge for the Millennium Development Goal. Public Health Nutr 2009, 12, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septriliyana, R.N.; Aryanti, D.; Septriliyana, R.N. The Realtionship Between Feeding Patterns And Stunting Incidence In Toddlers Aged 0-24 Months At The Cicangkang Girang Primary Health Care. Science Midwifery 2022, 10, 4286–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manillaturrochmah, M.; Fatmaningrum, W.; Setyoningrum, R.A.; Utomo, B. Relationship of Nutritional Status with Tuberculosis Lungs of Children Aged 0-5 Years in Surabaya. Asian Journal of Social and Humanities 2023, 1, 110–117. Available online: http://jsh.peloporpublikasi.com/index.php/jsh/article/view/15 (accessed on 15 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Depauw, E.; Oxley, D. Toddlers; teenagers, and terminal heights: the importance of puberty for male adult stature. Econ Hist Rev 2019, 72, 925–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyatman, B.; Fatimah, S.; Peminatan, D.; Ibu, K.; Anak, D.; Kesehatan, F. Faktor Risiko Kejadian Gizi Kurang Pada Balita: (Studi Kasus di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Bandarharjo Kota Semarang). Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat 2017, 5, 778–787. [Google Scholar]
- Taklual, W.; Baye, S.; Mekie, M.; Andualem, T. Double Burden of Malnutrition among Female Adolescent Students in Bahir Dar City, Amhara, Ethiopia. Biomed Res Int 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.R.M.; Luiz, R.R.; Monteiro, L.S.; Ferreira, M.G.; Gonçalves-Silva, R.M.V.; Pereira, R.A. ‘Adolescents’ unhealthy eating habits are associated with meal skipping. Nutrition 2017, 42, 114–120e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadvand, P.; et al. Green spaces and General Health: Roles of mental health status, social support, and physical activity. Environ Int 2016, 91, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Maroto-Sánchez, B.; Luzardo-Socorro, R.; Palacios, G.; Gil-Antuñano, N.P.; González-Gross, M. Evaluation of nutritional status and energy expenditure in athletes. Nutr Hosp 2015, 31, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kielgast, L.V.K.; et al. Towards More Physical Activity in Cities—Tranforming public spaces to promote Physical Activity. World Health Organization 2018.
- Foster, C.; Moore, J.B.; Singletary, C.R.; Skelton, J.A. Physical activity and family-based obesity treatment: a review of expert recommendations on physical activity in youth. Clin Obes 2018, 8, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zach, S.; Bar-eli, M.; Morris, T.; Moore, M. Measuring motivation for physical activity: An exploratory study of PALMS - the physical activity and leisure motivation scale Article. Journal Of Athletic Insight 2012, 4, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrenholtz, I.L.; et al. Effects of a 16-Week Digital Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge and Behavior in Female Endurance Athletes with Risk of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (REDs). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katenga-Kaunda, L.Z.; et al. Enhancing nutrition knowledge and dietary diversity among rural pregnant women in Malawi: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.M.S.; Cassady, D.L. The effects of nutrition knowledge on food label use. A review of the literature. Appetite 2015, 92, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, G.; et al. Socio-economic determinants of physical activity across the life course: A “DEterminants of DIet and Physical Activity. (DEDIPAC) umbrella literature review. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0190737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zach, S.; Bar-Eli, M.; Morris, T.; Moore, M. Measuring motivation for physical activity: An exploratory study of PALMS - the physical activity and leisure motivation scale. Athletic Insight’s Writings of 2012 2013, 4, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.G.; et al. Environmental influences on helminthiasis and nutritional status among Pacific schoolchildren. Int J Environ Health Res 2004, 14, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.M.; Chiang, B.L.; Wang, L.C. Maternal Nutritional Status and Development of Atopic Dermatitis in Their Offspring. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology 2020, 61, 128–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.D. Food Insecurity and Mental Health Status: A Global Analysis of 149 Countries. Am J Prev Med 2017, 53, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowitz, C.K.; Yoder, A.B.B.; Schoeller, D.A. School Gardens Enhance Academic Performance and Dietary Outcomes in Children. Journal of School Health 2015, 85, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaga, E.; et al. Fluid Intake and Hydration Status among Sports Science Students at Cenderawasih University. ACTIVE: Journal of Physical Education, Sport, Health and Recreation 2022, 11, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Aji, K.W.; Rekreasi, J.P.J.K.D.; Keolahragaan, F.I. Survei Bakat Olahraga Pada Siswa Kelas VII Dan Kelas VIII Di SMP Negeri 2 NGadirejo Kabupaten Temanggung Tahun 2020. Indonesian Journal for Physical Education and Sport 2020, 1, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).