1. Introduction
Periodontal disease is a frequent inflammatory disorder within the oral cavity, affecting the teeth and tooth-supporting tissues, and it is caused primarily by
P. gingivalis, a major gram-negative anaerobic periodontal pathogen [
1,
2]. Growing evidence indicates that periodontal disease has an adverse impact on several systemic diseases, including diabetes, Alzheimer's, colorectal cancer, and atherosclerosis [
3].
P. gingivalis and its LPS can cause periodontitis and directly lead to systemic inflammation by invading the bloodstream, which may trigger or exacerbate vascular inflammatory processes, especially atherosclerosis [
4].
Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic compounds with various beneficial effects in relieving the initiation and progression of periodontal disease [
5]. Administration of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the major flavonoid in green tea, to apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-knockout mice injected with
P. gingivalis decreased atherosclerotic plaque formation and serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and atherosclerotic risk factors [
6]. Hispidulin (4’,5,7-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone) is a natural phenolic flavonoid present in various plants, including
Saussurea involucrata, Arrabidaea chica, Salvia involucrata, and
Grindelia argentina, and it has various pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, antifungal, anti-osteoporotic, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Hispidulin alleviates skin, airway, and allergic inflammation by downregulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [
11,
12]. More recently, hispidulin has been shown to block the angiogenic properties of endothelial cells, such as vascular endothelial growth factor-induced proliferation, migration, and tubular formation [
13]. However, little attention has been given to the inhibitory effect of hispidulin on vascular inflammation.
The aim of this study was to determine whether hispidulin prevented P. gingivalis LPS-induced endothelial inflammation and propose possible anti-inflammatory mechanisms of hispidulin in endothelial cells.
2. Results
2.1. Hispidulin decreases P. gingivalis LPS-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in vascular endothelial cells
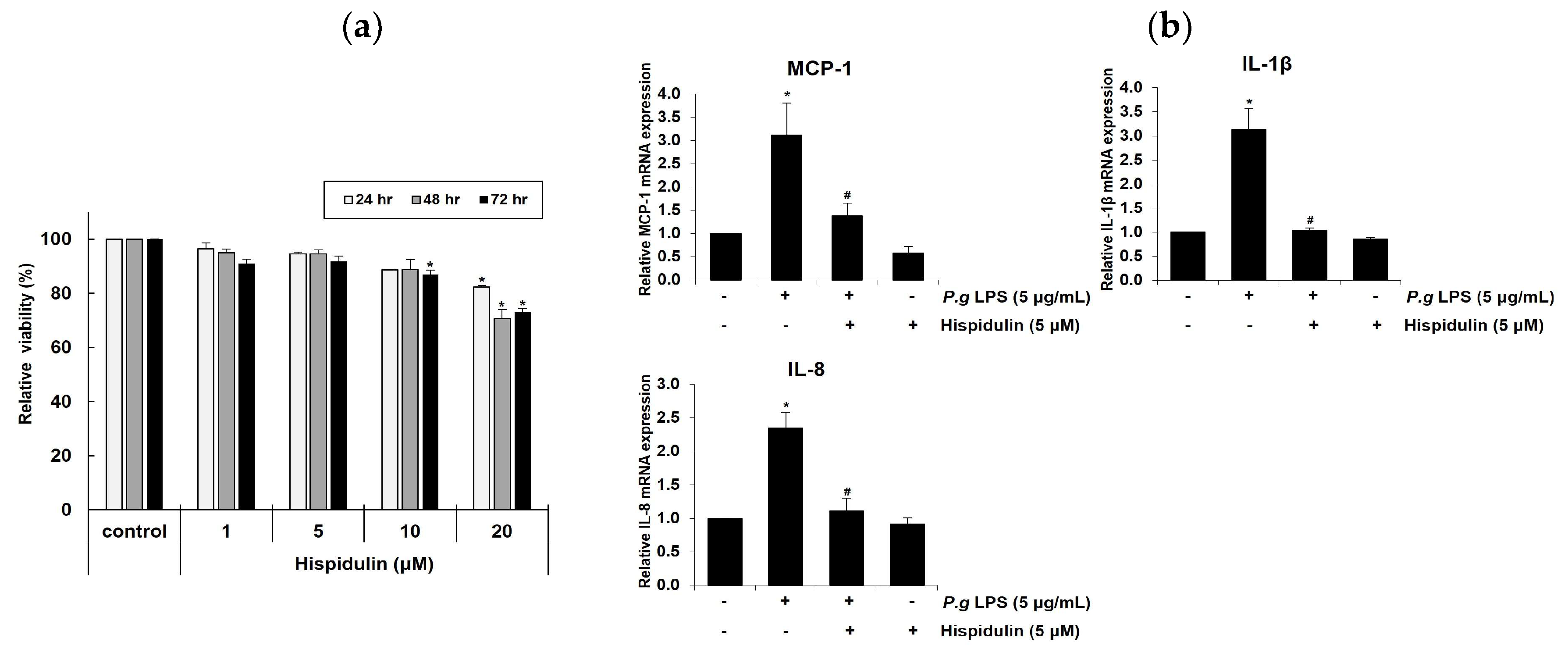
To determine the optimal concentration of hispidulin for
in vitro experiments, we assessed the viability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) HUVECs treated with different concentrations of hispidulin (1, 5, 10, or 20 μM) for 1–3 days using the methylthiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay (MTT) assay. No cytotoxicity was observed when cells were treated with 1 μM hispidulin. At 5 μM or 10 μM, hispidulin slightly decreased the relative viability over 3 days. After 2–3 days of treatment with 20 μM hispidulin, the proliferation of HUVECs was significantly reduced (approximately 20 %) compared to that in the control group (
Figure 1a). During vascular inflammation, pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Interleukin-1 β (IL-1β), and Interleukin-8 (IL-8), play critical roles in the recruitment of monocytes to endothelial cells at inflammation sites [
14]. Hispidulin treatment decreased the mRNA levels of MCP-1, IL-1β, and IL-8 upregulated by
P. gingivalis LPS (
Figure 1b)
2.2. Hispidulin decreases P. gingivalis LPS-induced expression of ICAM-1 in endothelial cells
Vascular endothelial cells express the cell adhesion molecules such as ICAM-1 in response to injury or inflammation, thereby allowing for the adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium [
15]. To determine the potential role of hispidulin in endothelial dysfunction, we examined its effect on
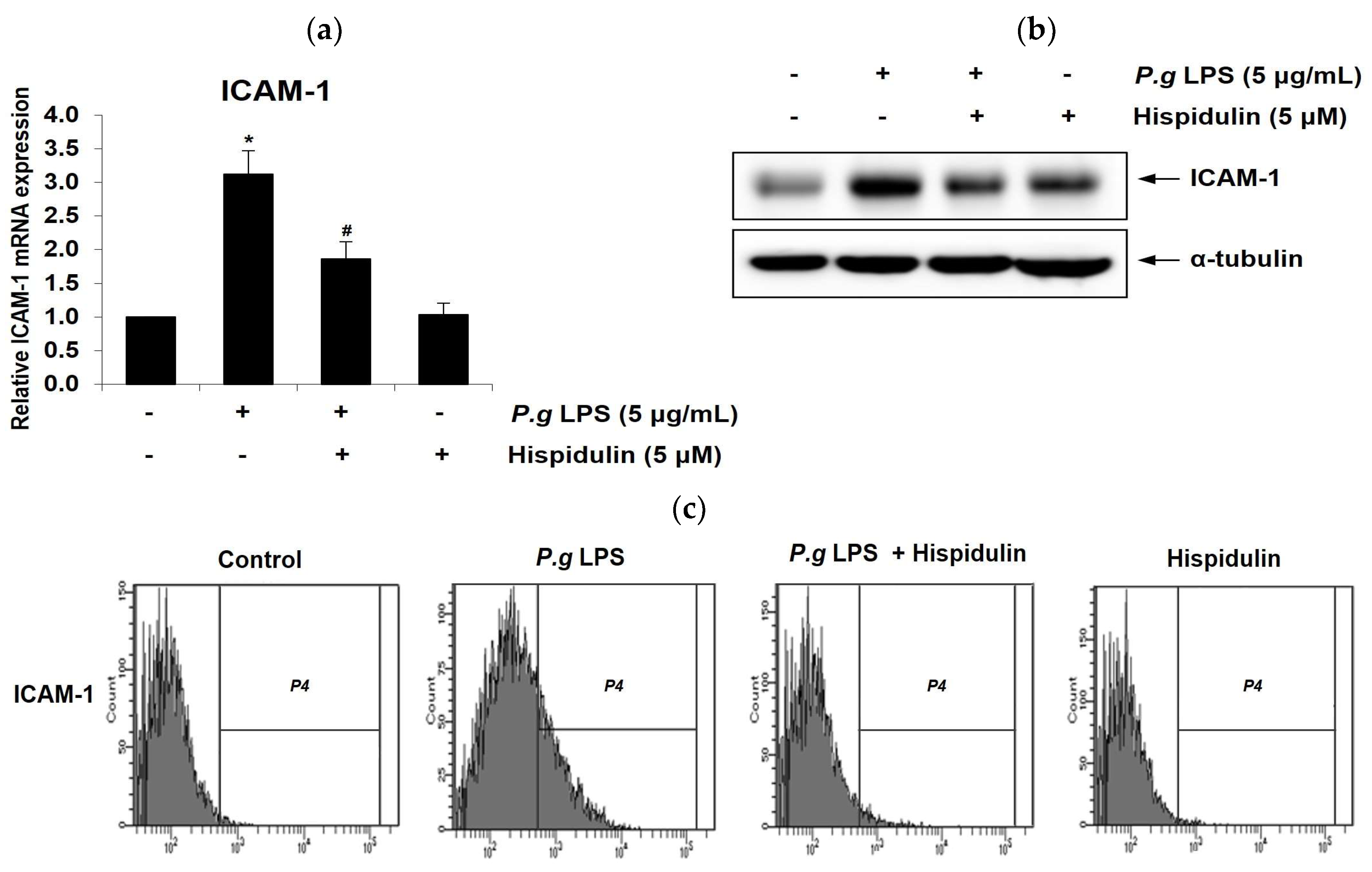
P. gingivalis LPS-induced ICAM-1.
P. gingivalis LPS significantly increased ICAM-1 mRNA levels in HUVECs; however, treatment with hispidulin reduced their expression (
Figure 2a). As shown in
Figure 2b, western blot showed hispidulin decreases the ICAM-1 protein levels induced by
P. gingivalis LPS. In addition, surface expression of ICAM-1 protein was evaluated using flow cytometry. Hispidulin reduced
P. gingivalis LPS-induced cell surface expression of ICAM-1 protein (
Figure 2c).
2.3. Hispidulin inhibits monocyte adhesion to P. gingivalis LPS-stimulated vascular endothelial cells
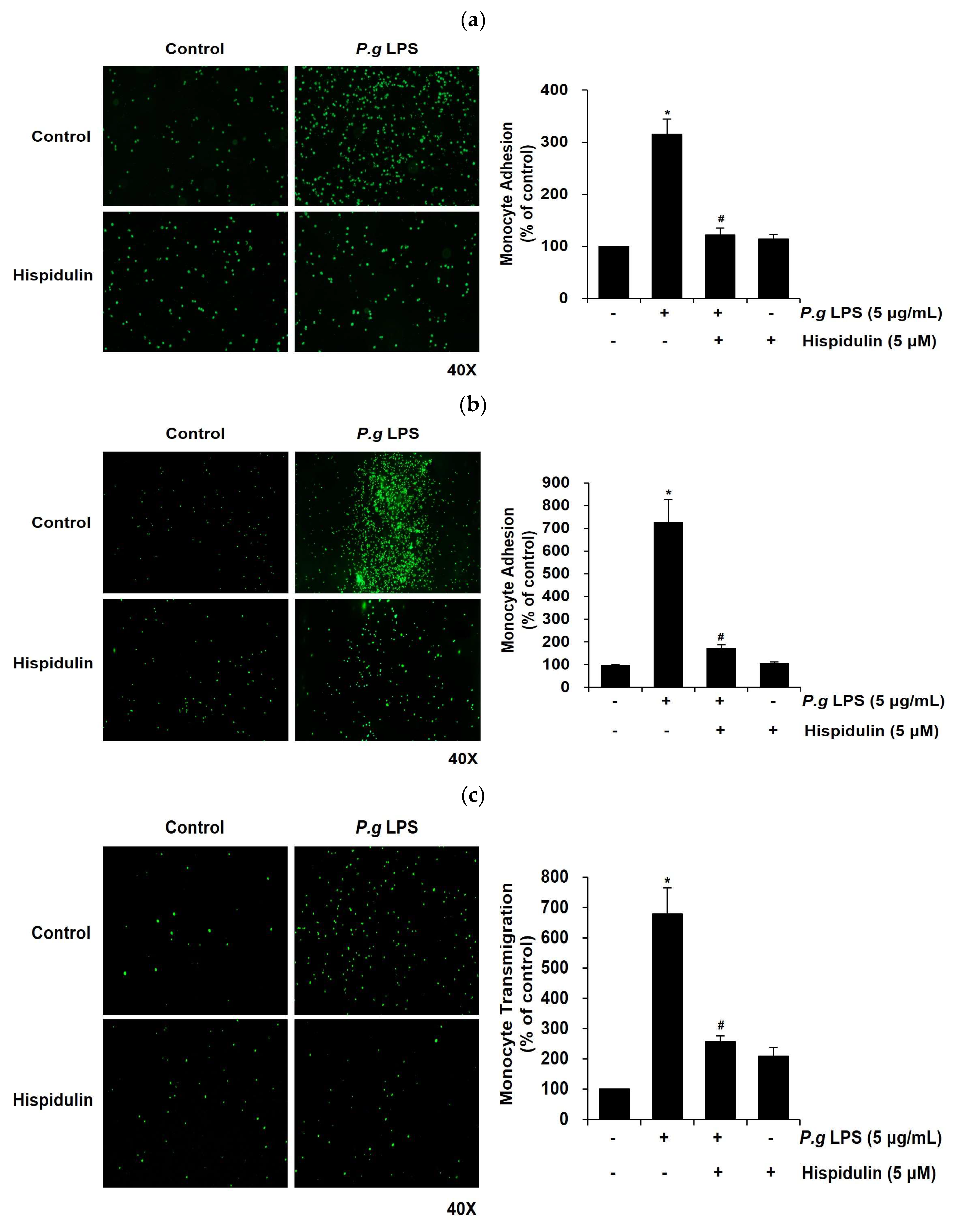
Next, we investigated whether hispidulin affected the adhesion of monocytes to
P. gingivalis LPS-stimulated endothelial cells, which is a critical step in vascular inflammation [
16].
P. gingivalis LPS stimulated the adhesion of THP-1 cells to HUVECs; however, this effect decreased significantly upon treatment of HUVECs with hispidulin (
Figure 3a). Next, we conducted an
ex vivo endothelial-monocyte adhesion assay using fluorescently labeled THP-1 cells and the aorta isolated from a Sprague-Dawley rat. The number of fluorescently-labeled monocytes adhering to the aortic endothelium increased significantly following
P. gingivalis LPS treatment relative to the untreated control (
Figure 3b); however, it dropped significantly upon hispidulin addition.
2.4. Hispidulin decreases the P. gingivalis LPS-induced transendothelial migration of monocytes
Once monocytes adhere to the endothelium, they transmigrate through the endothelial layer as a subsequent progressive step in atherosclerotic lesion formation [
17,
18]. We used a transmigration assay to assess whether the migration of
P. gingivalis LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells through the endothelial cell layer was modulated by hispidulin treatment. We observed that
P. gingivalis LPS increased significantly (by 7-fold) the transmigration of THP-1 cells across HUVEC monolayers relative to control cells (
Figure 3c); however, it was markedly retarded by hispidulin (
Figure 3c).
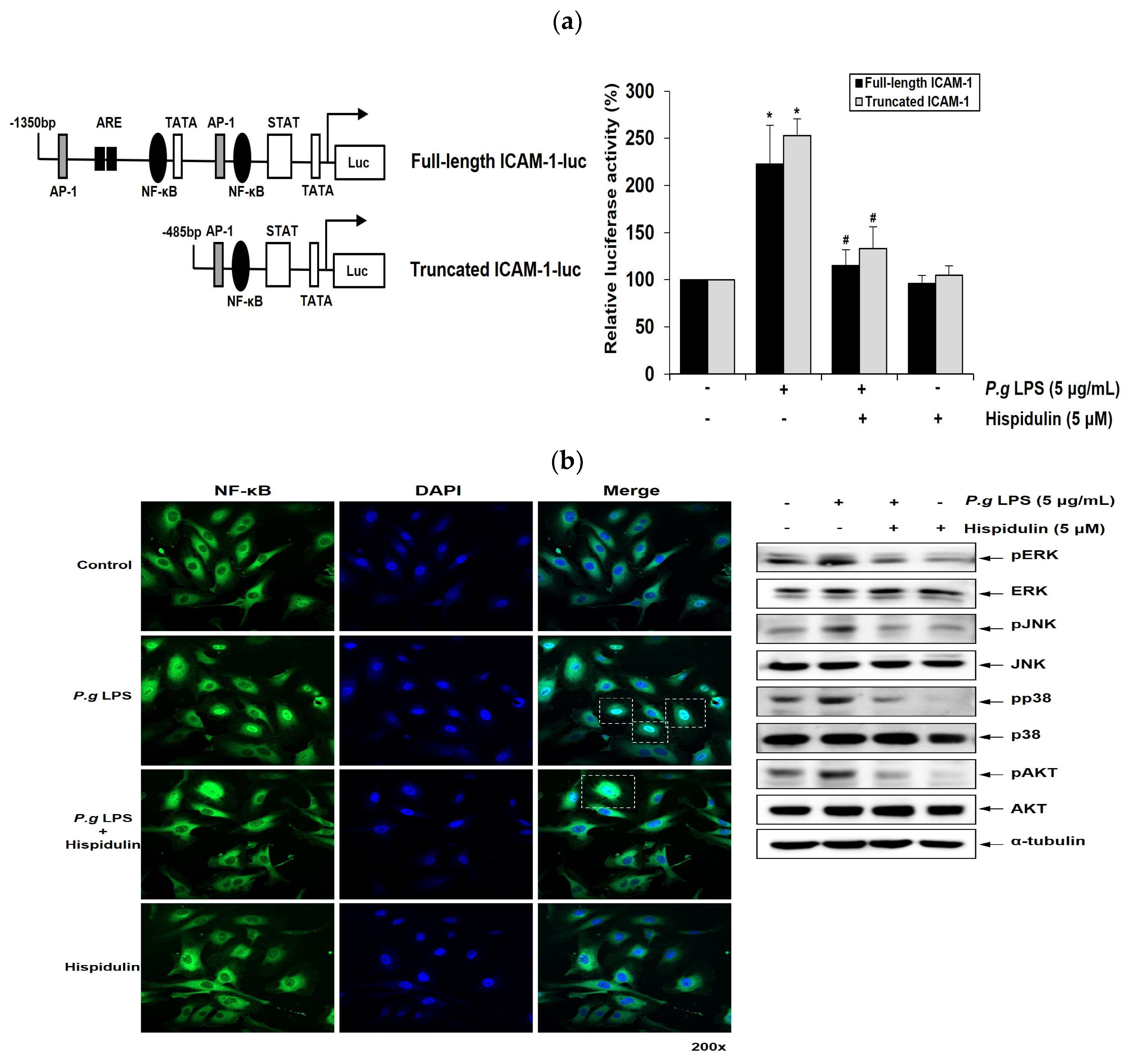
2.5. Hispidulin downregulates P. gingivalis LPS-induced transcriptional activation of ICAM-1 through NF-κB activation
NF-κB mediates the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules, thereby leading to pro-inflammatory responses in vascular endothelial cells [
19]. ICAM-1 promoter has binding sites for NF-κB. We performed luciferase promoter assays to determine whether hispidulin regulated ICAM-1 1 transcriptional activity. The full-length promoter regions of ICAM-1 (1.3 kb) in the luciferase reporter construct contained the NF-κB, TRE, and GATA binding sites [
20]. ICAM-1 truncated promoter construct contained a proximal NF-κB binding motif (
Figure 4a). Whereas
P. gingivalis LPS enhanced the reporter activity of truncated ICAM-1 promoter; this increase was attenuated by hispidulin treatment (
Figure 4a). These results were similar to those obtained with the full-length ICAM-1 promoter, indicating that NF-κB binding site played an essential role in mediating the effect of hispidulin on
P. gingivalis LPS-activated promoters. Inflammatory stimuli promote the translocation of the p65 subunit of NF-κB into the nucleus and its subsequent binding to cognate DNA-binding sites to upregulate several inflammation-related genes [
21]. Immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated the localization of p65 within the nucleus of HUVECs after
P. gingivalis LPS stimulation. In contrast, exposure to
P. gingivalis LPS and hispidulin decreased nuclear p65 accumulation (
Figure 4b).
2.6. Hispidulin downregulates P. gingivalis LPS-induced MAPKs and AKT in vascular endothelial cells
P. gingivalis LPS triggers MAPKs signaling, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38MAPK in human gingival fibroblasts, leading to increased cytokine production [
22]. The AKT signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating the survival of human gingival epithelial cells [
23]. We examined the impact of hispidulin on the MAPKs and AKT pathways in
P. gingivalis LPS-stimulated endothelial cells. The addition of hispidulin reduced the
P. gingivalis LPS-stimulated phosphorylation of ERK, p38MAPK, and JNK and significantly inhibited that of AKT in HUVECs (
Figure 4c).
3. Discussion
Hispidulin is a natural flavonoid with appealing anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, anticancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-microbial activities and exerts beneficial effects in various inflammatory diseases, including allergic inflammation, atopic dermatitis, and neuroinflammation [
24,
25,
26]. Hispidulin has been reported to downregulate LPS-induced inflammatory responses
in vitro and
in vivo. Hispidulin inhibits the LPS-induced production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-1β, and IL-6 in microglial cells by suppressing the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway [
27]. Additionally, it attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury in mice by reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and by modulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways [
28]. TLR4 signaling plays a crucial role in the recognition of
P. gingivalis LPS by endothelial cells, leading to the activation of downstream signaling pathways that ultimately produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [
29]. Additionally, we observed that hispidulin downregulates
P. gingivalis LPS-induced mRNA expression of TLR4 in endothelial cells (data not shown). Additionally, we show that hispidulin inhibits the NF-қB, AKT, and MAPKs (ERK, p38 MAPK, and JNK) signaling pathways activated by
P. gingivalis LPS, along with downstream production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecule in vascular endothelial cells. Thus, our results suggest that the negative effect of hispidulin on the inflammatory response triggered by
P. gingivalis LPS may be due to inhibition of TLR4-dependent signaling pathway.
Recently, natural phenolic compounds capable of modulating host inflammatory responses have received attention as effective tools for managing periodontal disease [
5]. Myricetin and apigenin inhibit the expression of inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in different types of cells in the periodontium, such as gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells [
30,
31]. Curcumin and quercetin alleviated experimental periodontitis in animal models by reducing gingival inflammation and attenuating alveolar bone loss [
32,
33]. More recently, oral hygiene products containing
Scutellaria baicalensis extract or catechins have been shown to decrease the depth and number of bacteria in the periodontal pockets of patients with periodontal disease [
34]. Our preliminary results suggest that hispidulin lowers the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human gingival fibroblasts (data not shown), hinting at its anti-inflammatory role in periodontitis. This possibility is currently under investigation.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall, leading to plaque formation within the arteries [
35]. Vascular endothelial cells, which line the inner surface of blood vessels, are essential for the development and progression of atherosclerosis [
36]. Once the endothelial barrier is compromised, inflammatory cells enter the arterial wall and contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques [
37]. In this study, we demonstrate that hispidulin reduces monocyte adhesion to
P. gingivalis LPS-activated endothelial cells and their transmigration across the endothelial layer. The presence of
P. gingivalis or
P. gingivalis LPS may be an additional risk factor that exacerbates the progression of atherosclerosis [
38].
P. gingivalis LPS-accelerated atherosclerosis typically progresses through several stages, including foam cell formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation/migration, plaque rupture, and endothelial dysfunction [
39]. Further investigations are ongoing to determine whether hispidulin inhibits several atherosclerotic properties in an established
P. gingivalis LPS-accelerated atherosclerosis model in ApoE-/- mice.
In conclusion, our results show that hispidulin suppresses P. gingivalis LPS-induced adhesion and transmigration of monocytes through the vascular endothelium and the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecule. This is achieved by inhibiting NF-κB and blocking MAPKs and AKT activations. Our findings indicate that hispidulin has beneficial effects in managing and treating periodontal pathogen-associated atherosclerosis.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and antibodies
Hispidulin and MTT were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Antibodies against human ICAM-1 and tubulin were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) and Bioworld Technology (St. Louis Park, MN, USA), respectively. Antibodies against human ERK, phospo-ERK, AKT, phospo-AKT, p38MAPK, phospo-p38MAPK, JNK, and phospo-JNK were acquired from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA).
4.2. Cell culture and osteogenic induction
HUVECs were purchased from CLONETICS (Basel, Switzerland), plated on 0.2 % gelatin-coated dishes, and grown in endothelial cell basal medium-2 (EBM-2; Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) supplemented with EGM-2 SingleQuots™ (Lonza) at 37 °C in humidified air with 5 % CO2. HUVECs from passage 2 were seeded at passages 4–7 for subsequent experiments. Human THP-1 monocytes were purchased from the Korea Cell Line Bank and grown in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 (Gibco, Billings, MT, USA) with 10 % fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 1 % penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco), and 5 μg/mL Plasmocin® (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
4.3. Cell proliferation assay
HUVECs were seeded in 48-well plates and incubated at 37 °C for 24, 48, or 72 h. At the end of the culture period, the cells were placed in 500 μL fresh medium containing 0.5 mg/mL MTT and incubated for 4 h. The medium was then replaced with 200 μL dimethyl sulfoxide (Sigma-Aldrich) for 3 min. The resulting blue formazan product was measured at 540 nm with a microplate reader (Allsheng, Hangzhou, China).
4.4. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
Total RNA was isolated using a RiboEx kit (GeneAll, Seoul, Korea), and reverse-transcribed with a reverse transcription kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), followed by real-time PCR with SYBR Green premix (Enzynomix, Daejeon, Korea). The following oligonucleotide primers were used: β-actin 5′-ACTCTTCCAGCCTTCCTTCC-3′ and 5′-TGTTGGCGTACAGGTCTTTG-3′; monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) 5′-ACTCTCGCCTCCAGCATGAA-3′ and 5′-TTGATTGCATCTGGCTGAGC-3′; interleukin (IL)-1β 5'-GACCTGGACCTCTGCCCTCT-3' and 5'-CTGCCTGAAGCCCTTGCTGT-3'; IL-8 5′-CTGGCCGTGGCTCTCTTG-3′ and 5′- CCTTGGCAAAACTGCACCTT-3′; ICAM-1 5′-CCCCACCATGAGGACATACA-3′ and 5′-GTGTGGGCCTTTGTGTTTTG-3′. Cycling parameters included one cycle at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by amplification for 40 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 60 s, and 72 °C for 7 s. The process was carried out using an Applied Biosystems thermocycler (Foster City, CA, USA).
4.5. Western immunoblot analysis
Proteins were separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electropho-resis and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden). The membrane was blocked with 5 % skim milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1 % Tween-20 for 1 h at room temperature and probed with the appropriate antibodies. The signal was developed using an enhanced chemiluminescence solution (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) and visualized on a LAS4000 imager (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA).
4.6. Flow cytometry analysis
HUVECs (1 × 106) were seeded in a 60-mm dish and incubated with P. gingivalis LPS (10 µg/mL) alone or in combination with hispidulin (5 µM) for 16 h. HUVECs were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and incubated in PBS with phyco-erythrin-conjugated anti-human CD54 (ICAM-1; BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA, USA) at 4 ℃. After 1 h, the cells were washed twice with PBS and analyzed using flow cytometry with a fluorescence-activated cell sorter (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
4.7. In vitro monocyte adhesion assay
HUVECs were plated in 24-well plates (5 × 104 cells/well) and incubated with P. gingivalis LPS (5 µg/mL) alone or in combination with hispidulin (5 µM) for 16 h. Before their addition, THP-1 cells were stained with 5 g/mL calcein-AM (Invitrogen) for 30 min. THP-1 cells were then added (1 × 105 cells/well) to confluent monolayers of HUVECs and incubated for 1 h. Non-adherent monocytes were removed by washing twice with PBS. Adherent cells were counted in three separate fields in each well under a microscope (Korea Lab Tech, Seungnam, Korea).
4.8. Ex vivo monocyte adhesion assay
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (6 weeks of age) were obtained from Koatech (Pyeongtaek, Korea). The aortas were opened longitudinally and incubated with P. gingivalis LPS (5 µg/mL) alone or in combination with hispidulin (5 µM) for 16 h. The aortas were then incubated for 1 h with 5 × 105 calcein-AM-labeled THP-1 cells. After incubation, unbound monocytes were rinsed twice with PBS. In contrast, adherent cells were counted in three random fields using a fluorescence microscope (Korea Lab Tech).
4.9. Transmigration assay
HUVECs (5 × 104) were added in the upper chamber of transwells with 8-µm pore-size membrane inserts (Costar, Corning, NY, USA) and cultured for 24 h to form a confluent monolayer. After incubation, calcein-AM-labeled THP-1 cells were added to the upper chamber and allowed to migrate through the HUVEC monolayer to the lower chamber for 24 h. These cells were treated with P. gingivalis LPS (5 g/mL) alone or in combination with hispidulin (5 µM) in EBM-2 medium supplemented with EGM-2 SingleQuots™. The lower chamber was filled with RPMI 1640 medium. Images were captured using a fluorescence microscope (Korea Lab Tech). Each experiment was performed in duplicate, and three separate experiments were performed for each group.
4.10. Transient transfection and reporter gene analysis
HUVECs were transfected with 3 μg of the plasmid DNA using Amaxa Nucleofector II (Lonza). After transfection, HUVECs were incubated with
P. gingivalis LPS (5 µg/mL) alone or in combination with hispidulin (5 µM) for 16 h. The cell extracts were analyzed using a β-galactosidase enzyme assay (Promega) for the luciferase activity using a luminometer (Turner Biosystems, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The relative luciferase activity was calculated as RLU/β-galactosidase at least three times. The ICAM-1 luciferase reporter constructs with the full-length (-1350 to +45 bp) and truncated forms (-485 to +45 bp) were used as previously described [
20].
4.11. Immunocytochemistry
HUVECs were pretreated with hispidulin (5 µM) for 30 min, incubated for 1 h with P. gingivalis LPS (5 g/mL), and fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde. After blocking with 0.5 % Triton X-100/PBS and 5 % normal goat serum (Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA), the cells were reacted with primary antibody against NF-κB p65 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and Alexa® 488-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h. Coverslips were mounted with DAPI-containing Vectastain (Vector Laboratories). Cells were analyzed using a confocal microscope (LSM900; Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
4.12. Statistical analysis
Data represent the mean and standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s honest significant difference post-hoc test and Student’s t-test.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-K.B.; methodology, H.-J.P., M.-K.K. and Y.K.; resources, H.-J.K., H.L. and Y.-I. K.; investigation, H.-J.P., Y.K., H.L. and M.-K.K.; data curation, H.-J.P. and Y.K.; formal analysis, H.L. and S.-K.B.; writing—original draft, Y.K. and M.-K.B.; writing—review and editing, H.L., Y.-J.K. and M.-K.B.; funding acquisition, M.-K.B.; project administration, Y.-J.K. and M.-K.B.; supervision, Y.-J.K. and M.-K.B.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Korean government (MSIT, NRF-2018R1A5A2023879) and (No. 2021R1A2C1003687).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors deny any conflict of interest related to this study.
References
- Sharaf, S.; Hijazi, K. Modulatory Mechanisms of Pathogenicity in Porphyromonas gingivalis and Other Periodontal Pathobionts. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysak, J.; Podzimek, S.; Sommerova, P.; Lyuya-Mi, Y.; Bartova, J.; Janatova, T.; Prochazkova, J.; Duskova, J. Porphyromonas gingivalis: Major Periodontopathic Pathogen Overview. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 476068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Zhi, A.; Lai, P.F.H.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Che, N.; Ai, L. The oral microbiota – a mechanistic role for systemic diseases. Br. Dent. J. 2018, 224, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontology 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rojas, B.; Gutiérrez-Venegas, G. Flavonoids exert multiple periodontic benefits including anti-inflammatory, periodontal ligament-supporting, and alveolar bone-preserving effects. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Kurita-Ochiai, T.; Hashizume, T.; Yamamoto, M. Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuatesPorphyromonas gingivalis-induced atherosclerosis. Pathog. Dis. 2012, 67, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, F.; Yan, J.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, D.; Ma, P. Hispidulin: A promising flavonoid with diverse anti-cancer properties. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaq, A.; Maqbool, M.F.; Maryam, A.; Khan, M.; Shakir, H.A.; Irfan, M.; Qazi, J.I.; Li, Y.; Ma, T. Hispidulin: A novel natural compound with therapeutic potential against human cancers. Phytotherapy Res. 2020, 35, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Patel, D.K. Medicinal importance, pharmacological activities, and analytical aspects of hispidulin: A concise report. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 7, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, Z.; Ma, C. Hispidulin Exerts Anti-osteoporotic Activity in Ovariectomized Mice via Activating AMPK Signaling Pathway. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 69, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.E.; Min, K.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, T.K. Hispidulin Inhibits Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation through Down-Regulation of Histamine Release and Inflammatory Cytokines. Molecules 2019, 24, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Choi, Y.-A.; Lee, B.; Kwon, T.K.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, S.-H. Hispidulin alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation by inhibiting splenic Th1/Th17 cell population and keratinocyte activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wu, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Pang, X. Hispidulin, a small flavonoid molecule, suppresses the angiogenesis and growth of human pancreatic cancer by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2010, 102, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, S. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 109, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Gordon, J.L.; Gearing, A.J.H.; Pigott, R.; Woolf, N.; Katz, D.; Kyriakopoulos, A. The expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, PECAM, and E-selectin in human atherosclerosis. J. Pathol. 1993, 171, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jeong, S.K.; Kim, S.R.; Bae, S.K.; Kim, W.S.; Jin, S.D.; Koo, T.H.; Jang, H.Y.; Yun, I.; Kim, K.W.; Bae, M.K. Resveratrol Inhibits Porphyromonas Gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Adhesion Molecule Expression by Suppressing NF-kappaB Activation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriuchi, K.; Kihara, T.; Aoki, H.; Kakita, H.; Takeshita, S.; Ueda, H.; Inoue, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Shimono, Y.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Monocyte-Derived miRNA-1914-5p Attenuates IL-1β–Induced Monocyte Adhesion and Transmigration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyo, I.M.; Gafencu, A.V. The involvement of the monocytes/macrophages in chronic inflammation associated with atherosclerosis. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.M. Nuclear factor (NF)- B proteins: therapeutic targets. Rheumatology 2004, 63, ii57–ii61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-R.; Bae, Y.-H.; Bae, S.-K.; Choi, K.-S.; Yoon, K.-H.; Koo, T.H.; Jang, H.-O.; Yun, I.; Kim, K.-W.; Kwon, Y.-G.; et al. Visfatin enhances ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression through ROS-dependent NF-κB activation in endothelial cells. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cynader, M.S.; Jia, W. TDP-43 Inhibits NF-κB Activity by Blocking p65 Nuclear Translocation. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0142296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, C.-X.; Li, M.-Z.; Zheng, W.-Y.; He, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Z.-M.; Fan, Q.-S.; Hu, Y.-H.; Li, C.-J. Tormentic acid inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts via inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, O.; Jungas, T.; Verbeke, P.; Ojcius, D.M. Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway Contributes to Survival of Primary Epithelial Cells Infected with the Periodontal Pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Xie, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiu, X.; Li, L.; Tang, M. Hispidulin exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaghi-Barbosa, P.; Rocha, A.M.; Lima, A.F.d.C.; de Oliveira, B.H.; de Oliveira, M.B.M.; Carnieri, E.G.S.; Cadena, S.M.; Rocha, M.E.M. Hispidulin: Antioxidant properties and effect on mitochondrial energy metabolism†. Free. Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.; Dhakal, H.; Choi, Y.-A.; Kwon, T.K.; Khang, D.; Kim, S.-H. Hispidulin alleviates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and house dust mite extract-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-I.; Cheng, C.-I.; Kang, Y.-F.; Chang, P.-C.; Lin, I.-P.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Jhou, A.-J.; Lin, M.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Hispidulin Inhibits Neuroinflammation in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated BV2 Microglia and Attenuates the Activation of Akt, NF-κB, and STAT3 Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Leem, J. Hispidulin Ameliorates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nativel, B.; Couret, D.; Giraud, P.; Meilhac, O.; D’Hellencourt, C.L.; Viranaïcken, W.; Da Silva, C.R. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharides act exclusively through TLR4 with a resilience between mouse and human. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Venegas, G.; Luna, O.A.; Ventura-Arroyo, J.A.; Hernández-Bermúdez, C. Myricetin suppresses lipoteichoic acid-induced interleukin-1β and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human gingival fibroblasts. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, S.-N.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, E.-C. Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin on nicotine- and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells via heme oxygenase-1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, Z.Y.; Bakır, B.; Bozkurt, B.; Kayis, S.A.; Hakki, S.S. Positive effect of curcumin on experimental peridontitis via suppression of IL-1-beta and IL-6 expression level. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2022, 92, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-C.; Huang, R.-Y.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-K.; Liu, C.-H.; Chu, C.-L.; Fu, E. Ameliorative effect of quercetin on the destruction caused by experimental periodontitis in rats. J. Periodontal Res. 2010, 45, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Zhuoneng, L.; Guangxun, Z. Protective role of flavonoid baicalin from Scutellaria baicalensis in periodontal disease pathogenesis: A literature review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 38, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; García-Cardeña, G.; Owens, G.K. Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dri, E.; Lampas, E.; Lazaros, G.; Lazarou, E.; Theofilis, P.; Tsioufis, C.; Tousoulis, D. Inflammatory Mediators of Endothelial Dysfunction. Life 2023, 13, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Leducq Transatlantic Network On Atherothrombosis. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: From Pathophysiology to Practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bian, T.; Lyu, J.; Cui, D.; Lei, L.; Yan, F. Human β-defensin-3 alleviates the progression of atherosclerosis accelerated by Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Links between atherosclerotic and periodontal disease. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).