1. Introduction
Opioids are important agents in the field of palliative medical treatment because of their powerful analgesic properties [
1]. In the management of pain in particular, including cancer pain, opioids are key to improving patient quality of life. Although opioids are an important class of drugs in palliative care worldwide, opioid sales in the United States increased fourfold between 1999 and 2010 [
2], causing a social problem known as the opioid crisis. In response, the World Health Organization (WHO) published the guidelines “Ensuring Balance in National Policies on Controlled Substances” in 2011 and “WH Guidelines on the Availability and Accessibility of Controlled Substances” in 2012 [
3]. Regulation of controlled substance prescriptions has consequently been thoroughly enforced in the USA, and the prescribing and use of opioids have declined.
In contrast, Japan has yet to experience such an opioid crisis. On the contrary, the current situation is one in which the quantity of opioids prescribed is not commensurate with patients' pain due to doctors’ reluctance to prescribe opioids. This situation has been called into question by those who point out that opioid use in Japan tends to be low, both in general and in comparison to use in other countries [
4].
Japan lags behind the USA not only in the prescription and use of opioids but also in the approval of opioid drugs. For example, tapentadol was approved for prescription in the USA in November 2008 [
5] but was approved in Japan only in August 2014 [
6]. Hydromorphone was approved in the USA in 1984 [
7] but remained unapproved in Japan for over thirty years. Finally, after forceful requests from the Japanese Society for Palliative Medicine and others, the brand name Nalrapide® was approved in Japan in June 2017 [
8]. Because the approval of opioids in Japan is slower than in the USA, studies on adverse events tend to accumulate fewer cases in Japan than in the USA.
For these reasons, it is difficult to secure sufficient cases for robust analysis either in opioid case studies or using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database (JADER), a large database in Japan. Although opioid prescription availability and guidelines vary from country to country as described above, Japanese guidelines for palliative medicine specify clearly how to respond to opioid side effects. [
9] In clinical practice, coping therapies are used to deal with various symptoms of opioid side effects [
9].
Known adverse events to opioids from a pharmacological point of view include nausea and vomiting, which are believed to be caused by chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) stimulation due to μ-receptor stimulation [
10], and constipation, which is believed to be influenced by the peristaltic inhibitory effect unique to opioids. Respiratory depression, drowsiness, delirium, and somnolence have been observed due to the inhibitory effect on the medullary respiratory control center [
11,
12]. Although the involvement of μ-receptors has been pointed out in these side effects, the details of the mechanism of occurrence of each of these symptoms have not been elucidated [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. Therefore, for this study, we conducted an adverse event analysis of opioids using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28], a large database in the United States, because of the problem of opioid use in Japan and the relatively new drug and number of cases.
We conducted a comprehensive analysis of USA-based palliative care data on adverse events due to μ-receptor stimulation by opioids approved in Japan in order to compare the incidence of adverse events among opioids. We hope that our findings will assist in drug selection, opioid switching, and the appropriate use of opioids.
2. Results
2.1. Number of Reported Adverse Events
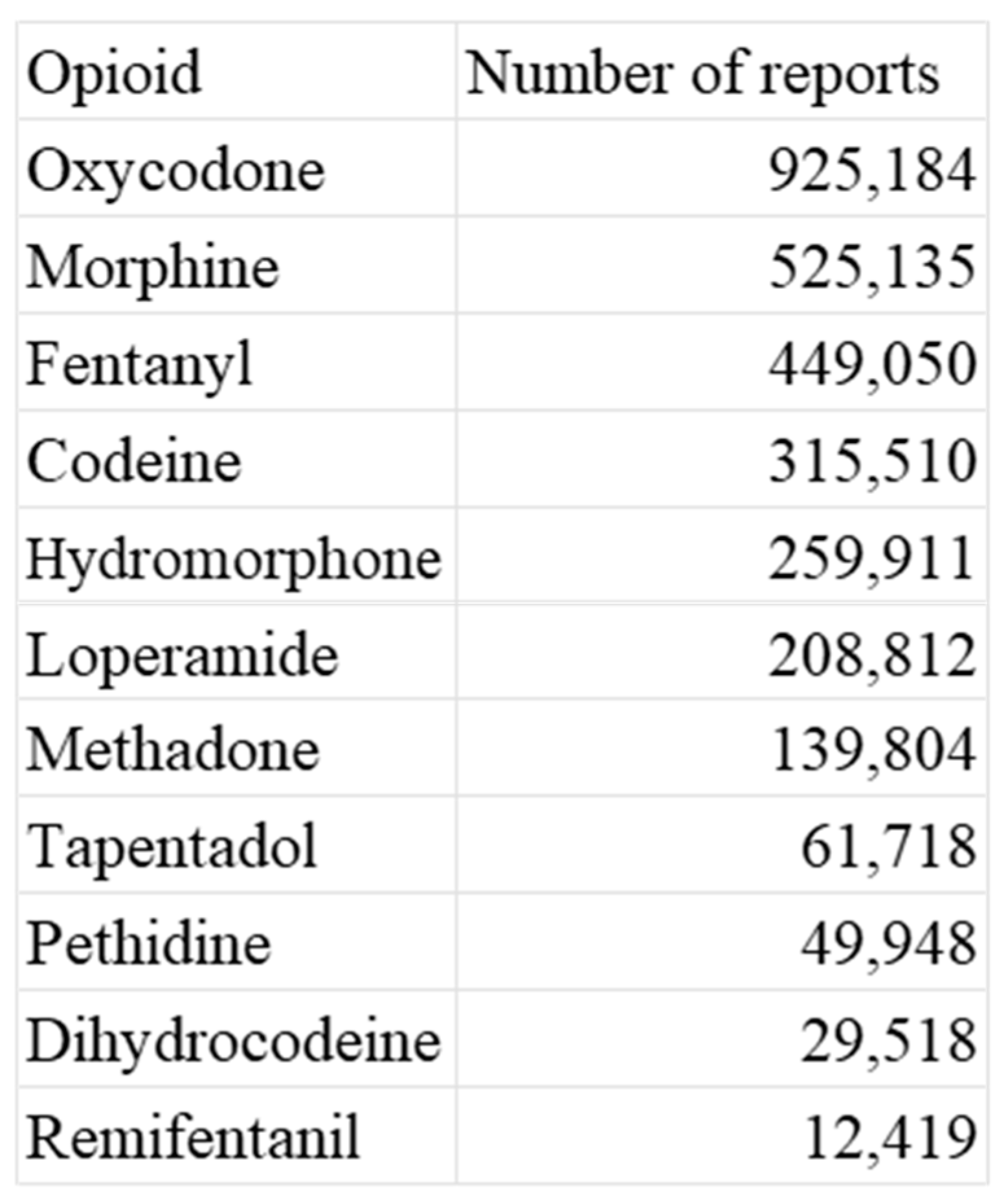
According to the data from FAERS, the opioids oxycodone, morphine, and fentanyl exhibited the highest number of reported adverse events. It is worth noting that these drugs are commonly used in palliative care settings [
30,
31]. Please refer to
Table 1 and
Table S1 for more information.
2.2. Top of the Adverse Event
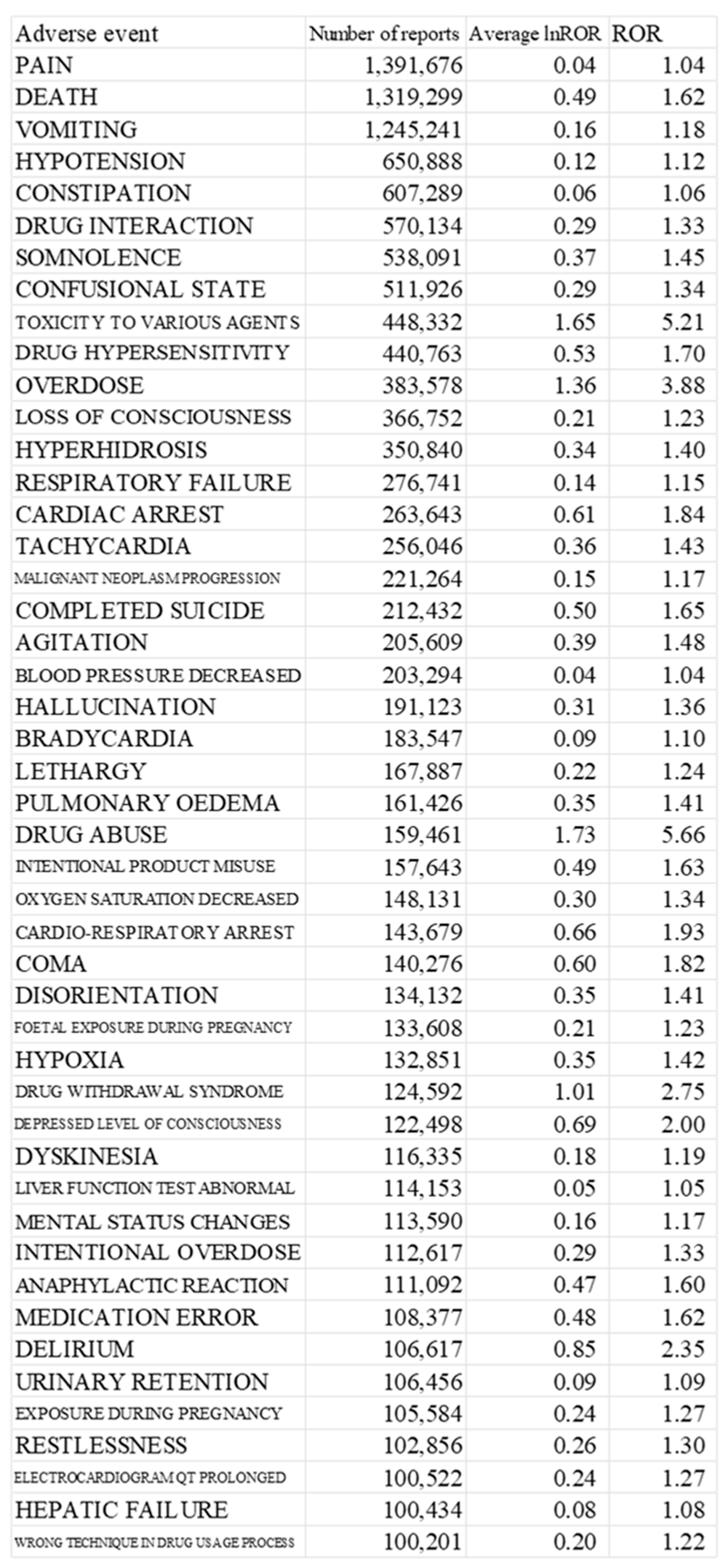
We identified 47 preferred terms for adverse events based on the mean lnROR of the target opioids. Frequently observed side effects, such as somnolence, delirium, and constipation, which are known to be associated with µ receptor stimulation, were common among them. We extracted the top 26 adverse events that had been reported in >150,000 cases (
Table 2). The ROR and 95% confidence interval for each target opioid concerning the 47 adverse event terms with a positive average ROR are presented in the supplementary data. The table presents the top 26 adverse events with >150,000 reported cases, including columns for adverse event, number of reports, average lnROR, and ROR. The ROR and 95% confidence interval for each target opioid concerning the 47 adverse event terms with a positive average ROR are presented in the supplementary data.
Top 47 Adverse Events with >150,000 Reported Cases and Associated Reporting Odds Ratio Values for Target Opioids
2.3. Hierarchical Cluster Classifications
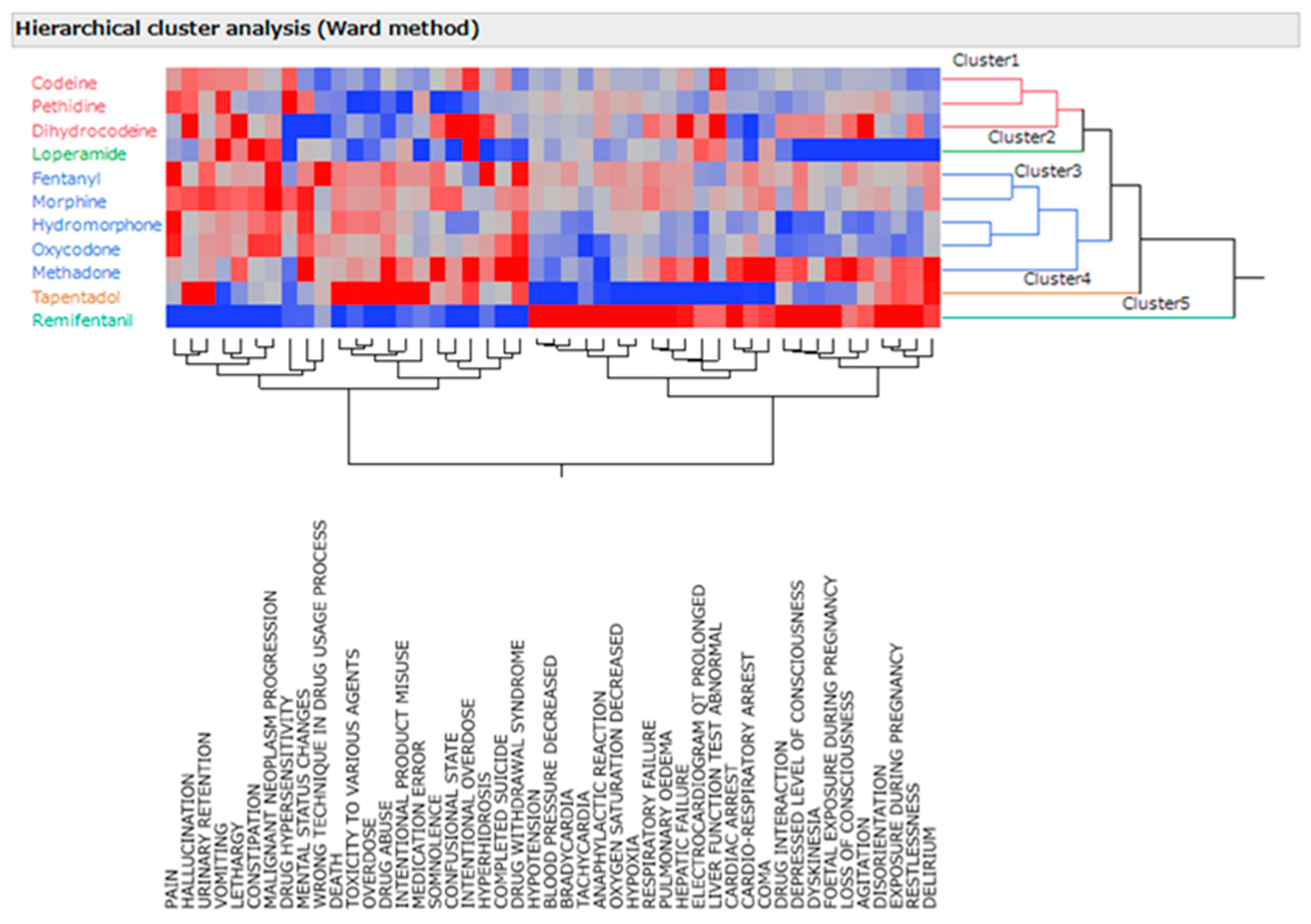
In this study, the 11 analyzed opioids were classified into five distinct groups using hierarchical cluster analysis (Ward’s method) based on the adverse event names and lnROR (
Figure 1). The clusters comprised two primary groups of opioids, including loperamide, tapentadol, and remifentanil. Cluster 1 included codeine, pethidine, and dihydrocodeine. In Cluster 2, loperamide was identified. Cluster 3 included fentanyl, morphine, hydromorphone, oxycodone, and methadone. Cluster 4 contained tapentadol, and Cluster 5 contained remifentanil. Meanwhile, adverse effects were clustered into seven types. Cluster 1 included pain, malignant neoplasm progression, urinary retention, vomiting, constipation, hallucinations, altered mental status, lethargy, and the wrong technique in the drug usage process. Cluster 2 comprised death, drug toxicity, overdose, drug abuse, intentional misuse, and medical malpractice. Cluster 3 comprised somnolence, confusion, intentional overdose, hyperhidrosis, suicide, and drug withdrawal symptoms. Cluster 4 contained hypotension, bradycardia, tachycardia, an anaphylactic reaction, desaturation of oxygen, and hypoxia. Cluster 5 featured liver failure and abnormal liver function tests. Cluster 6 included echocardiographic (ECG) QT prolongation, cardiac arrest, and cardio–respiratory arrest. Cluster 7 encompasses disorientation, restlessness, and delirium.
The vertical axis represents the 11 µ-opioid receptor agonists, and the horizontal axis represents the names of reported adverse events. Red indicates a high log odds ratio and a high incidence of adverse events, whereas blue indicates a low log odds ratio and a low incidence of relevant adverse events.
We extracted primary and secondary suspect drugs from the drug table, removing duplicates. We then combined the reaction, demographic, and indication tables to create an analysis table.
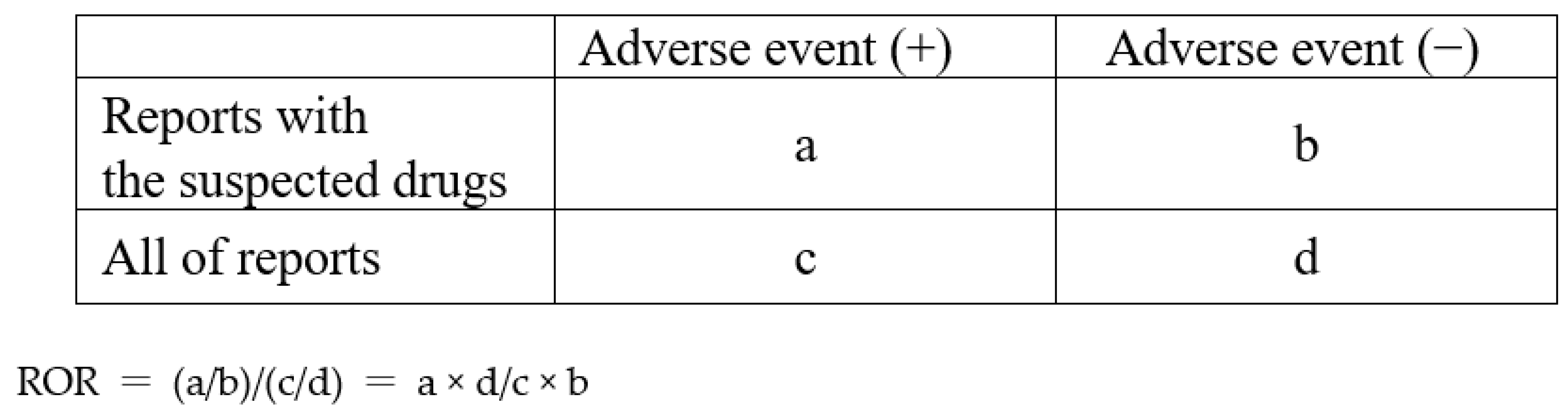
The study utilized a 2 × 2 contingency table to investigate the association between reported adverse events and target opioids. The reporting odds ratios were computed to determine the magnitude of this association.
3. Discussion
This study analyzed the adverse event reports for target opioids using the FAERS database, which collects reports from public institutions in the United States. Although the focus was on opioids used in Japan, a larger number of cases were reported in FAERS compared with the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database, which is constructed by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency. This could be due to the reluctance of Japanese medical professionals to use opioids [
32]. To enhance comparative validation among opioid drugs, the US side effect database was used.
As FAERS primarily reports adverse reactions from both inside and outside the United States, there are many cases of hydromorphone and tapentadol usage for which there is still limited information available in Japan. Consequently, FAERS analysis may contribute to palliative care in Japan. Of the adverse events extracted using the ROR, those with a positive lnROR value were highly related to the target opioid. Adverse events such as somnolence, delirium, and constipation [
9,
10,
11] were frequently reported in 47 diseases that were related to opioids (
Table 2). We believe that the ROR of FAERS has a relationship with the side effects owing to the stimulation of the μ-opioid receptors.
While it is generally not recommended to interpret ROR quantitatively in the analysis of side effect databases, we assumed that a highly reliable ROR that can withstand quantitative verification can be extracted using the number of reported adverse events and the p-value in Fischer’s exact test. A cluster analysis of the 11 target opioids and reported adverse events with significant RORs classified them into remifentanil, tapentadol, loperamide, and two other groups.
Cluster 1 included codeine, pethidine, and dihydrocodeine. This group tends to be less associated with adverse events such as overdose, substance abuse, and drug withdrawal symptoms compared with other groups. The reason is that drugs other than pethidine are clinically used for purposes other than narcotism and pain relief. Pethidine is used for purposes such as preanesthetic administration, adjunctive general anesthesia, and pain relief [
33]. Adverse events such as overdose and substance abuse are classified into relatively small categories because they are often used under close supervision for purposes related to anesthesia.
Cluster 2 comprised loperamide, an over-the-counter drug commonly used to treat diarrhea symptoms. It is speculated that loperamide is closely related to diarrhea adverse events owing to its stimulation of peripheral nerve μ receptors. Moreover, loperamide has a lower central nervous system μ-receptor stimulating effect compared with other opioids, which suggests that it is less associated with central nervous system adverse events such as loss of consciousness and disorientation [
34].
Cluster 3 comprised fentanyl, morphine, hydromorphone, oxycodone, and methadone, all classified as strong opioids used to manage cancer pain and chronic pain. These opioids have many reports of adverse events related to pain, and their association with malignant neoplasm progression and drug withdrawal syndrome was strongly classified. Methadone, also included in the same group, was associated with substance abuse, overdose, and drug withdrawal syndrome. This background is thought to be related to its use for heroin addiction treatment in the United States [
35]. Methadone replacement therapy involves gradually withdrawing from the symptoms of addiction by administering methadone as a substitute for heroin.
Cluster 4 included tapentadol, which is expected to expand its efficacy range to include nervous system pain owing to its dual-acting mechanism that involves μ-opioid receptor agonistic action and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitory action [
36]. Hence, it was clustered into a group distinct from other strong opioids. Tapentadol tends to be highly associated with overdoses and drug abuse [
37], and its prescription for moderate or severe pain is approved, suggesting that it contributes significantly to improving the quality of life. The trend of other reported adverse events alludes to the fact that it is necessary to pay attention to delirium when using it, but it is possible that it is an opioid that can be used with relatively little effect on respiratory failure.
Cluster 5 contained remifentanil, which tends to cause fewer gastrointestinal adverse events, such as vomiting and constipation. A substantial tendency to develop respiratory failure, hypotension, and other adverse events was confirmed, which was different from that of other opioids. Remifentanil is used in the field of anesthesia and is dose- and rate-controlled for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia. This characteristic of remifentanil might have led to cluster classifications that differ from those of other opioids used for pain management [
38].
The adverse effects were clustered into seven types, each with specific characteristics and associated opioids:
Cluster 1: Pain, progression of malignant neoplasms, urinary retention, vomiting, constipation, hallucinations, altered mental status, lethargy, errors in the drug use process. The above adverse events tended to be reported more frequently with morphine and less frequently with remifentanil. Frequent occurrences of vomiting and constipation are known as adverse events attributed to μ-receptor stimulation of opioids [
9]. Based on these results, morphine increases the risk of adverse effects due to decreased renal function, which leads to decreased elimination of the metabolite M6G [
39]. This finding strongly confirms the strong association of morphine with vomiting and constipation, which was observed in many patients with deteriorated renal function.
Cluster 2: Death, various drug toxicities, overdose, drug abuse, intentional misuse, medical malpractice. Among opioids, tapentadol was reported more frequently and remifentanil less frequently in this cluster, and tapentadol tended to be more involved in these adverse events than other strong opioids used in palliative care. The stronger association of tapentadol with drug abuse and overdose suggests that while tapentadol shows great promise for ease of use and efficacy in pain management, it should be used with caution due to its enhanced risks of illicit use.
Cluster 3: Somnolence, confusion, intentional overdose, hyperhidrosis, suicide, and drug withdrawal symptoms. The above adverse events were found to cluster with a high incidence of methadone. An analytical study using the Australian database found that fentanyl and methadone were more frequently involved in unintentional intoxication than other opioids [
40]. Our results seem to support the above studies.
Cluster 4: Hypotension, bradycardia, tachycardia, anaphylactic reactions, decreased oxygen saturation, hypoxia. We observed a trend, indicating higher incidence for remifentanil and lower incidence for tapentadol. As noted above, remifentanil is highly associated with intraoperative hypotension and elevation of blood pressure; hence, its use in anesthesiology. Remifentanil is an opioid used in an environment where it is prone to producing fluctuating circulatory dynamics that affect the supply–demand balance of oxygen supplied to the myocardium [
41].
Cluster 5: Liver failure, abnormal liver function tests. These adverse events comprised a cluster with a high incidence of dihydrocodeine and codeine. Codeine and dihydrocodeine tended to have higher incidence of reported adverse events, including abnormal liver function tests and liver failure. These opioids are metabolized by the liver metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6 or CYP3A [
42,
43,
44]. Our results suggest that codeine and dihydrocodeine affect liver function more intimately than other opioids. This distinction may explain their classification in the cluster of abnormal liver function tests and liver failure. Prior studies support this finding [
42,
43].
Cluster 6: ECG QT prolongation, cardiac arrest, cardiac arrest – respiratory arrest. This cluster had a high incidence of methadone, and methadone tended to ave a higher incidence of ECG QT prolongation, cardiac arrest, and cardiac arrest – respiratory arrest compared to other μ-receptor stimulating opioids. The cluster was high in methadone, and methadone tended to have a higher incidence of ECG QT prolongation, cardiac arrest, and cardiac arrest – respiratory arrest compared to other μ-receptor stimulated opioids. In addition, a previous study of methadone reported a stronger association with the adverse event of ECG QT prolongation [
45]. The package insert [
46] includes warnings for ECG QT prolongation and ventricular tachycardia (including torsades de pointes) [
47]. However, the details of the causal mechanism for these events remain unknown [
47]. Currently, guidelines also specify doses to be used with caution in the event of ECG QT prolongation [
48].
Cluster 7: Disorientation, restlessness, and delirium
These adverse events were clusters that were more frequently associated with methadone and tapentadol than with other strong opioids used in palliative care. The hypothesis that delirium, the name of the adverse event, is caused by an imbalance of substances in the brain has been proposed, but no clear mechanism is known [
49]. Future research on the relationship between methadone, tapentadol, and delirium is warranted.
As to why side effects differ among opioids despite being mediated by opioid receptors, as well as differences in selectivity for opioid receptor subtypes (μ, κ, and δ receptors), we note the findings in previous studies [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. Furthermore, differences in metabolism and excretion mechanisms among drugs [
50] and individual genetic factors for opioids [
51] may be the causes of differences in adverse drug reaction trends among the patient populations using the various opioids.
These analyses indicate that cluster analysis using a large database can be effectively used to compare adverse effect propensities among opioids. We believe that such comparisons will facilitate effective drug switching to avoid the risk of adverse events. The association of particular adverse event names with particular opioids may lead to a better understanding of the aforementioned differences in characteristics among opioids. Clearer associations may also help prompt the naming of diseases for which associations of particular symptoms with particular opioids would otherwise remain to be confirmed.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Table Creation
To extract data on adverse reactions associated with opioid drugs, we used 153,673,177 records of reported data from the FAERS database spanning the years 2004–2020 [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
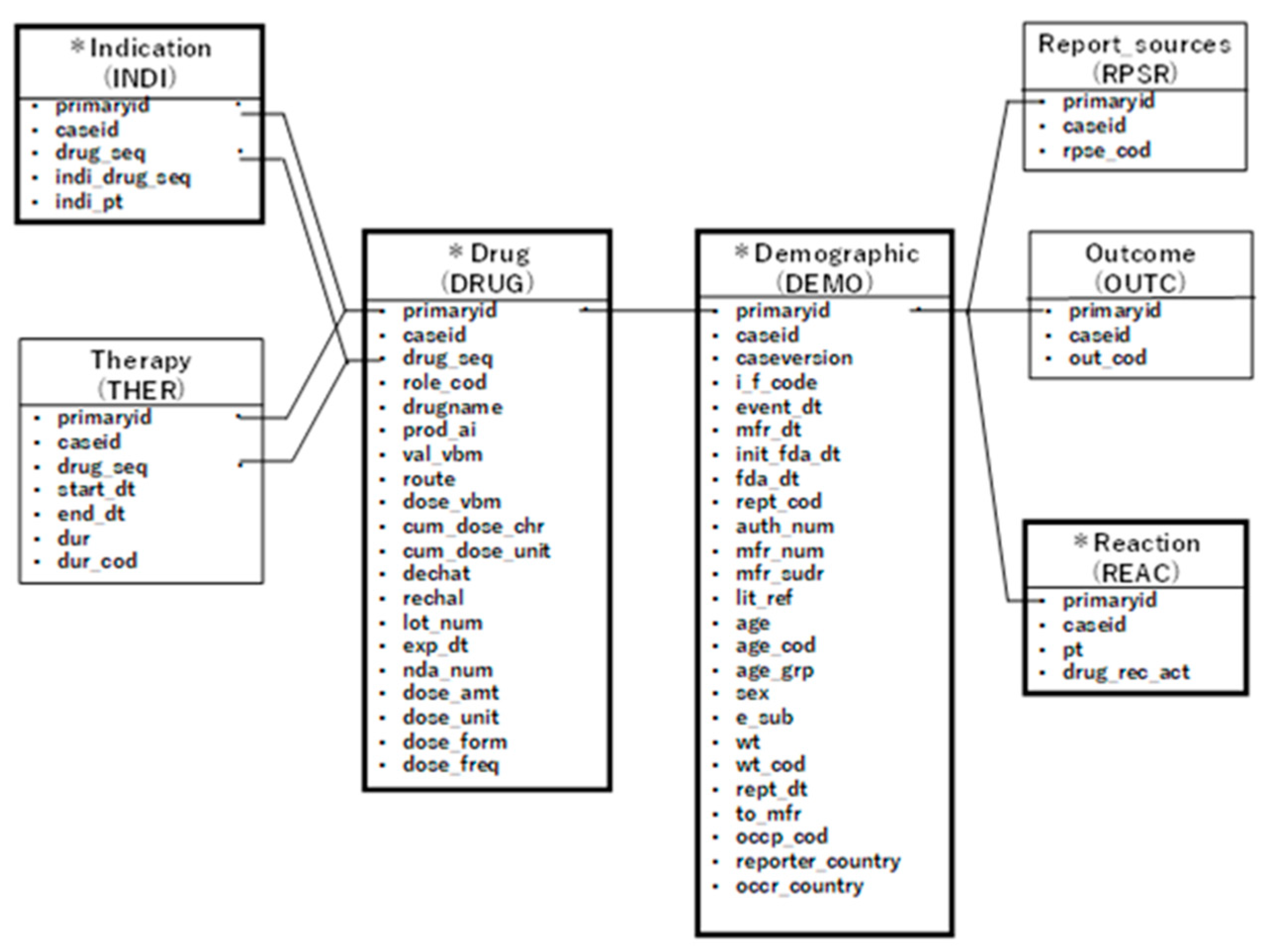
29]. The data tables were categorized based on their characteristics, including a case information table (demographic), a drug information table (drug), an adverse event information table (reaction), and an underlying disease information table (indication). Information across these tables was linked using registration IDs.
The drug table classified the reported drugs into four categories: primary suspect drug, secondary suspect drug, concomitant drugs, and interactions. For this study, we extracted drugs reported as primary or secondary suspect drugs. Each data table was linked by its registration ID to create a data table for analysis for each opioid (see
Figure 2).
To selectively extract opioids, we examined target drugs based on their μ receptor affinity, as reported in previous studies [
43,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59]. We selected 11 opioids, which are μ receptor agonists used in Japan, including morphine, fentanyl, oxycodone, codeine, dihydrocodeine, hydromorphone, methadone, tapentadol, pethidine, loperamide, and remifentanil. Each opioid extraction case was extracted as the total opioid, including drug names such as hydrate and hydrochloride. For morphine, the drug name excluding apomorphine was extracted as the relevant morphine. For fentanyl, drug names excluding remifentanil were extracted as fentanyl.
To determine the number of adverse event reports for each opioid, we extracted the report counts from the reaction table (see
Table 1).
4.2. MedDRA
The Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) is an international medical terminology developed by the International Conference on Harmonization of Drug Regulations to facilitate international information exchange and regulatory harmonization. In this study, we used the preferred terms of MedDRA ver22.0 for the disease names of reported adverse events.
From the analysis data table, we created a 2 × 2 contingency table to determine whether all reported adverse events and each suspected opioid were present. This contingency table allowed us to estimate the relationship between the adverse event of interest and the drug of interest (see
Figure 3). In this study, we employed a combination of the reporting odds ratio (ROR) and
p-value in Fischer’s exact test as indicators of signal detection. If there are any 0 cells in the contingency table, the ROR calculation cannot be performed, and if the frequency is low, the estimation becomes unstable. To rectify bias, we applied the Haldane–Anscombe 1/2 correction by adding 0.5 to all cells [
60]. We then calculated the RORs and Fisher’s exact tests for various adverse events for each opioid.
4.3. Hierarchical Cluster Classification
In this study, we used the hierarchical cluster classification method to classify reported adverse events among opioids. This method creates a tree diagram based on the similarity of distinguishing features of objects. We analyzed 21,334 reported adverse events in the reaction table of FAERS and calculated the lnROR for each adverse event of the 11 target opioid drugs. We then extracted 310 adverse event names that were reported >100,000 times.
To identify adverse event names closely related to opioids, we extracted those with a positive mean lnROR value for opioids (
Table S1). Subsequently, we performed hierarchical cluster analysis (using Ward’s method) based on the adverse event names and the lnROR of the target opioids (
Figure 1).
4.4. Statistical Analysis
We performed all statistical analyses using JMP Pro 14.2.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and set the level of statistical significance at 0.05.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study utilized the FAERS database to investigate the adverse events of opioids used in Japan and conducted a cluster analysis to enhance our understanding of the relationships between opioids and their side effects. We identified five distinct clusters of opioids, each with specific patterns of adverse events, and seven clusters of adverse effects. The clustering allowed for an in-depth comprehension of the associations between specific side effects and opioids. The findings of this study can facilitate better decision-making in clinical practice regarding the use of opioids in Japan. The results emphasize the need for cautious prescribing of certain opioids, especially in cases where patients may be at higher risk for specific adverse events. For instance, clinicians should be careful when using methadone owing to its association with somnolence, confusion, intentional overdose, hyperhidrosis, suicide, and drug withdrawal symptoms. Moreover, the study highlights the potential benefits of specific opioids, such as tapentadol, which could offer improved quality of life for patients with moderate to severe pain. However, caution is still recommended owing to its association with delirium and other adverse events. In conclusion, this study provides valuable insights into the relationships between opioids and their associated adverse events, allowing a better understanding and management of the risks and benefits associated with these drugs in Japan.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1: Positive mean lnROR value for opioids.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.U.; methodology, Y.U.; software, Y.U.; validation, R.H., and Y.U.; formal analysis, R.H. and Y.U.; investigation, R.H. and Y.U.; resources, R.H. and R.H.; data curation, R.H. and Y.U.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H.; writing—review and editing, R.H. and Y.U.; visualization, R.H. and Y.U.; supervision, R.H. and Y.U.; project administration, Y.U.; funding acquisition, Y.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received partial support from KAKENHI, granted by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (22K06707).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gaertner, J.; Boehlke, C.; Simone, C.B.; Hui, D. Early palliative care and the opioid crisis: ten pragmatic steps towards a more rational use of opioids. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2019, 8, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Vital signs: Overdoses of prescription opioid pain relievers. United States, 1999–2008. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2011, 60, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44519.
- Duthey, B.; Scholten, W. Adequacy ofopioid analgesic consumption at country, global, and regional levels in 2010, its rela-tionship with development level, and changes compared with 2006. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2014, 47, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2008/022304s000_TOC.cfm.
- https://www.info.pmda.go.jp/go/pack/8219003G1024_1_08/. 8219.
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/021217s005lbl.pdf.
- https://www.info.pmda.go.jp/go/pack/8119003F1023_1_06. 8119.
- Swegle, J.M.; Logemann, C. Management of common opioid-induced adverse effects. Am. Fam. Phys. 2006, 74, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar]
- R. ; Adlaka, R.; Sehgal, N.; Glaser, S.E.; Vallejo, R.Opioid complications and side effects. Pain Phys. 2008, 11, S105–S120. [Google Scholar]
- Naeim, A.; Dy, S.M.; Lorenz, K.A.; Sanati, H.; Walling, A.; Asch, S.M. Evidence-based recommendations for cancer nausea and vomiting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiffen, P.J.; Wee, B.; Derry, S.; Bell, R.F.; Moore, R.A. Opioids for cancer pain – an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD012592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Els, C,; Jackson, T.D.; Kunyk, D.; Lappi, V.G.; Sonnenberg, B.; Hagtvedt, R.; Sharma, S.; Kolahdooz, F.; Straube, S. Adverse events associated with medium- and long-term use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: an overview of cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, CD012509. [CrossRef]
- Lichter, I. Results of antiemetic management in terminal illness. J. Palliat. Care. 1993, 9, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passik, S.D.; Lundberg, J.; Kirsh, K.L.; Theobald, D.; Donaghy, K.; Holtsclaw, E.; Cooper, M.; Dugan, W. A pilot exploration of the antiemetic activity of olanzapine for the relief of nausea in patients with advanced cancer and pain. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2002, 23, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra, Y.; Sacristán, A.; González, M.; Ferrari, M.; Portugués, A.; Calvo, M.J. Efficacy of senna versus lactulose in terminal cancer patients treated with opioids. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1998, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mystakidou, K.; Tsilika, E.; Parpa, E.; Kouloulias, V.; Kouvaris, I.; Georgaki, S.; Vlahos, L. Long-term cancer pain management in morphine pre-treated and opioid naive patients with transdermal fentanyl. Int. J. Cancer. 2003, 107, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitbart, W.; Marotta, R.; Platt, M.M.; Weisman, H.; Derevenco, M.; Grau, C.; Corbera, K.; Raymond, S.; Lund, S.; Jacobson, P. A double-blind trial of haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and lorazepam in the treatment of delirium in hospitalized AIDS patients. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1996, 153, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candy, B.; Jackson, K.C.; Jones, L.; Leurent, B.; Tookman, A.; King, M. Drug therapy for delirium in terminally ill adult patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD004770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enting, R.H.; Oldenmenger, W.H.; van der Rijt, C.C.; Wilms, E.B.; Elfrink, E.J.; Elswijk, I.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A. A prospective study evaluating the response of patients with unrelieved cancer pain to parenteral opioids. Cancer. 2002, 94, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/jpm.2021.0438. 0438.
- FDA. FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS); AERS, 2012.
- United States Food and Drug Administration, 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/surveillance/fda-adverse-event-reporting-system-faers (accessed on 9 August 2019).
- FDA. Potential Signals of Serious Risks/New Safety Information Identified from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) (Formerly AERS), 2014, pp. 6–7.
- Sakaeda, T.; Kadoyama, K.; Minami, K.; Okuno, Y. Commonality of drug-associated adverse events detected by 4 commonly used data mining algorithms. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronin, M.A.; Schumaker, R.P.; Dixit, R.R.; Elath, H. Opioids and frequency counts in the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database: a quantitative view of the epidemic. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2019, 11, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, K.B.; Demakas, A.R.; Dimbil, M.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Erdman, C.B. Stimulated reporting: the impact of US Food and Drug Administration-issued alerts on the Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Drug Saf. 2014, 37, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Mining of the Public Version of the FDA; Adverse Event Reporting System.
- FDA. Follow-Up to the 09 Early Communication about an Ongoing Safety Review of Sibutamine, Marketed as Me-ridia.2010. 20 November.
- WHO analgesic ladder - StatPearls - NCBI bookshelf, , 2022. Anekar; Marco Cascella. Last Update. Available online: nih.govWHO Analgesic Ladder Aabha A. 15 May.
- Schuster, M.; Bayer, O.; Heid, F.; Laufenberg-Feldmann, R. Opioid rotation in cancer pain treatment. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2018, 115, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, E.; Kobayashi, T.; Dexter, E.; Marino, M.; Maeno, T.; Deyo, R.A. Comparison of opioid prescribing patterns in the United States and Japan: primary care physicians' attitudes and perceptions. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2017, 30, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.info.pmda.go.jp/go/pack/8211400A1049_1_06/?view=frame&style=SGML&lang=ja.
- Vetel, J.M.; Berard, H.; Fretault, N.; Lecomte, J.M. Comparison of racecadotril and loperamide in adults with acute diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 13, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toce,M. S.; Chai, P.R.; Burns, M.M.; Boyer, E.W. Pharmacologic treatment of opioid use disorder: a review of pharma-cotherapy, adjuncts, and toxicity. J. Med. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, H.G. Tapentadol and its two mechanisms of action: is there a new pharmacological class of centrally-acting analgesics on the horizon? Eur. J. Pain. 2010, 14, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, M.S.; Fife, D.; Ma, Q.; Ryan, P.B. Comparison of the risks of opioid abuse or dependence between tapentadol and oxycodone: results from a cohort study. J. Pain. 2013, 14, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanxu Ren, Takashi Matsusaki, Abugri Osman Bright, et al. Association between the Remifentanil Dose during Anesthesia and Postoperative pain 2013 Oct;14(10):1227-41. [CrossRef]
- M.T.; Hawley, C.E.; Triantafylidis, L.K.; Paik, J.M. Opioid management in older adults with chronic kidney disease: a review. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1386–1393. [CrossRef]
- Tina Lam, Jane Hayman, Janneke Berecki-Gisolf, et al. Pharmaceutical opioid poisonings in Victoria, Australia: Rates and characteristics of a decade of emergency department presentations among nine pharmaceutical opioids. Addiction 2022, 117, 623–636. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muellejans, B.; Matthey, JoachimT.; Scholpp, J.; Schill, M. Sedation in the intensive care unit with remifentanil/propofol versus midazolam/fentanyl: a randomised, open-label, pharmacoeconomic trial. Crit. Care. 2006, 10, R91. [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, L.C.; Nation, R.L.; Somogyi, A.A. Characterization of the human cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the metabolism of dihydrocodeine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 44, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.R.; Menelaou, A.; Foster, D.J.R.; Coller, J.K.; Somogyi, A.A. CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 involvement in the primary oxidative metabolism of hydrocodone by human liver microsomes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.F.; Hofmann, U.; Griese, E.U.; Mikus, G. Dihydrocodeine: a new opioid substrate for the polymorphic CYP2D6 in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 58, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciani,R.A. Methadone: ECG or not to ECG…that is still the question. Open Accesspubl. 2008, 36, 545–552. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/methadone-hydrochloride-marketed-dolophine-information.
- Modesto-Lowe.,V.; Brooks, D., MS; Petry, N. Methadone deaths: risk factors in pain and addicted populations. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 305–309. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.; Cruciani, R.A., et al. Methadone safety guidelines methadone safety: A clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society and College on Problems of Drug Dependence. In Collaboration With the Heart Rhythm Society.
- Delirium Jo Ellen Wilson, J.E.; Mart, M.F.; Cunningham, C.; Shehabi, Y.; Girard, T.D.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Ely, E.W. available in PMC 2022 Apr 15. Delirium. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2020, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea Wagmann, L.; Gampfer, T.M.; Meyer, M.R. Recent trends in drugs of abuse metabolism studies for mass spectrome-try-based analytical screening procedures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5551–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano Pieretti, S.; Di Giannuario, A.; Di Giovannandrea, R.; Marzoli, F.; Piccaro, G.; Minosi, P.; Aloisi, A.M. Gender dif-ferences in pain and its relief. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita. 2016, 52, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.M.; Duron, D.I.; Womer, D.; Fell, R.; Streicher, J.M. Comprehensive molecular pharmacology screening reveals potential new receptor interactions for clinically relevant opioids. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0217371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiński, P.F.J.; Kosson, P.; Matalińska, J.; Roszkowski, P.; Czarnocki, Z.; Jarończyk, M.; Misicka, A.; Dobrowolski, J.C.; Sadlej, J. Fentanyl family at the mu-opioid receptor: uniform assessment of binding and computational analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Santhakumar, R.; Dewey,W.; Kelly, E.; Henderson, G. Fentanyl depression of respiration: comparison with heroin and morphine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 254–266. [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Klein, T.E.; Shen, D.D.; Callaghan, J.T.; Kharasch, E.D.; Skaar, T.C.; Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for codeine therapy in the context of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype 2011 Dec 28. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang,; Yin, X.; Sun, H.; Uhl, G.R.; Wang, J.B. Mu opioid receptor phosphorylation, desensitization, and ligand efficacy. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28869–28874. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Tzschentke, T.M.; Christie, M.J. μ-Opioid receptor activation and noradrenaline transport inhibition by tapentadol in rat single locus coeruleus neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; He, Y.; Jin, W.Q.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, H.P.; Shen, Q.X.; Chi, Z.Q. , Wen-Qiao Jin, et al. Binding affinity to and dependence on some opioids in Sf9 insect cells expressing human mu-opioid receptor. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wency Chen, W.; Chung, H.-H.; Cheng, J.-T. Opiate-induced constipation related to activation of small intestine opioid μ2-receptors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, R. Small sample confidence intervals for the odds ratio. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2004, 33, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).