Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
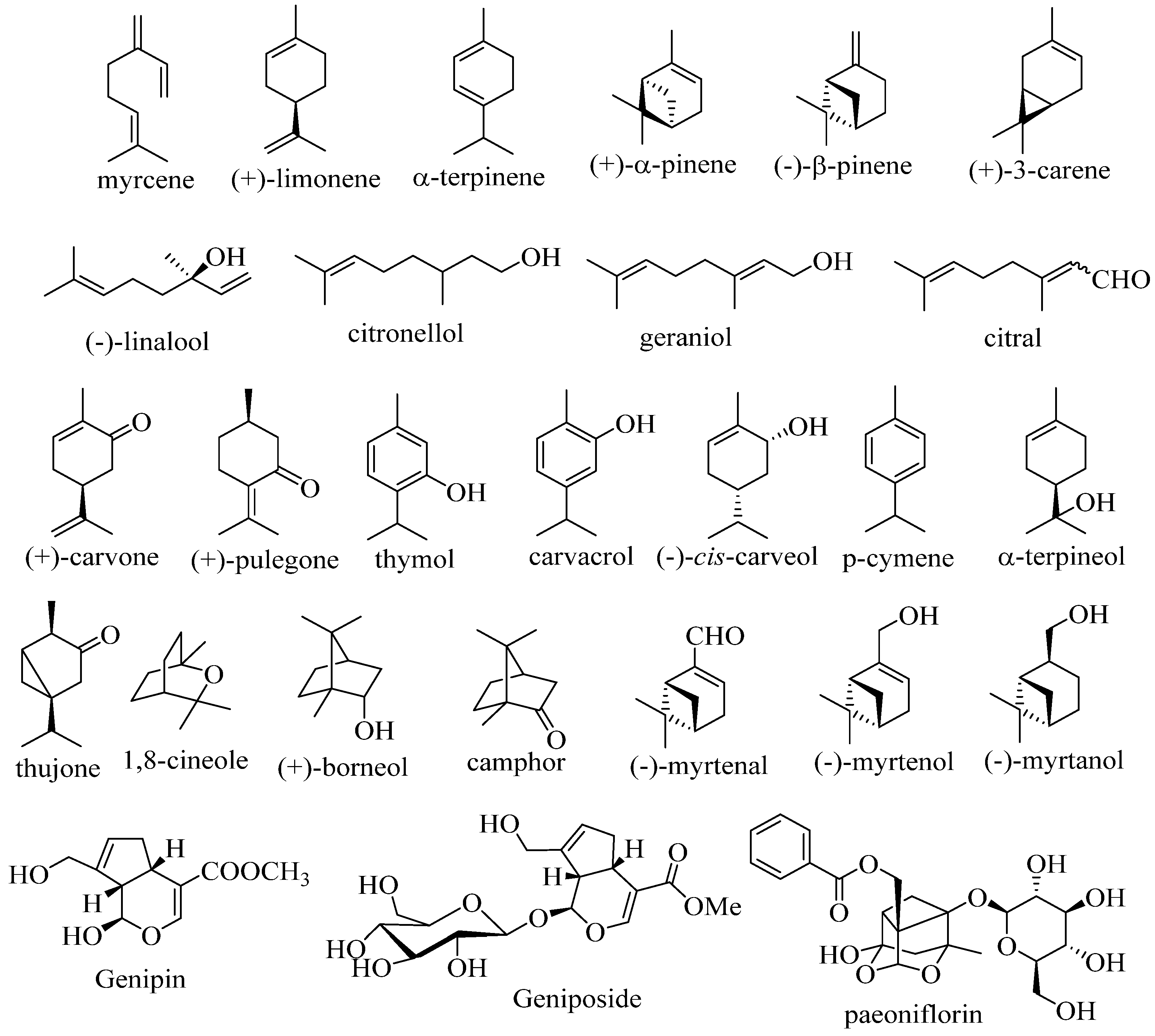
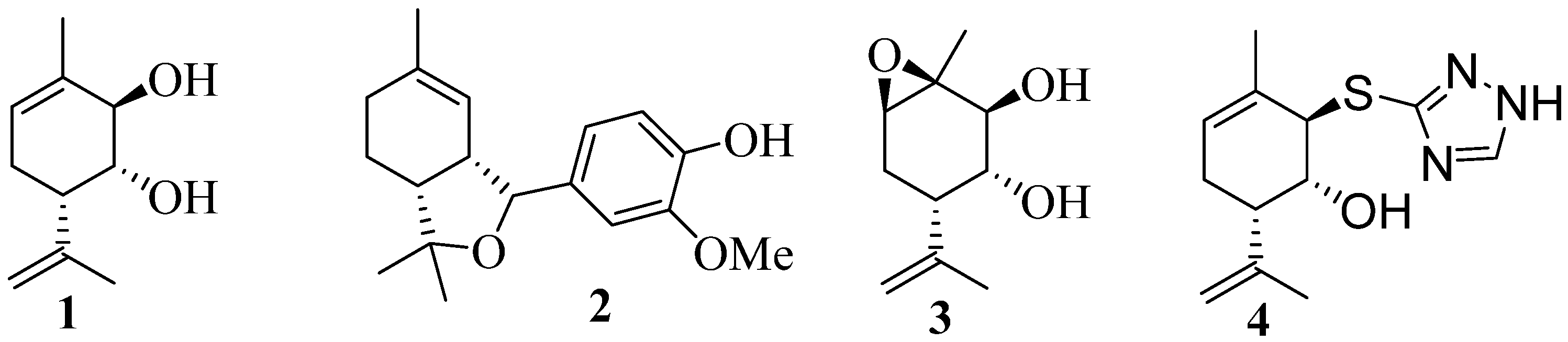
2. Therapeutic potential of monoterpenoid derivatives
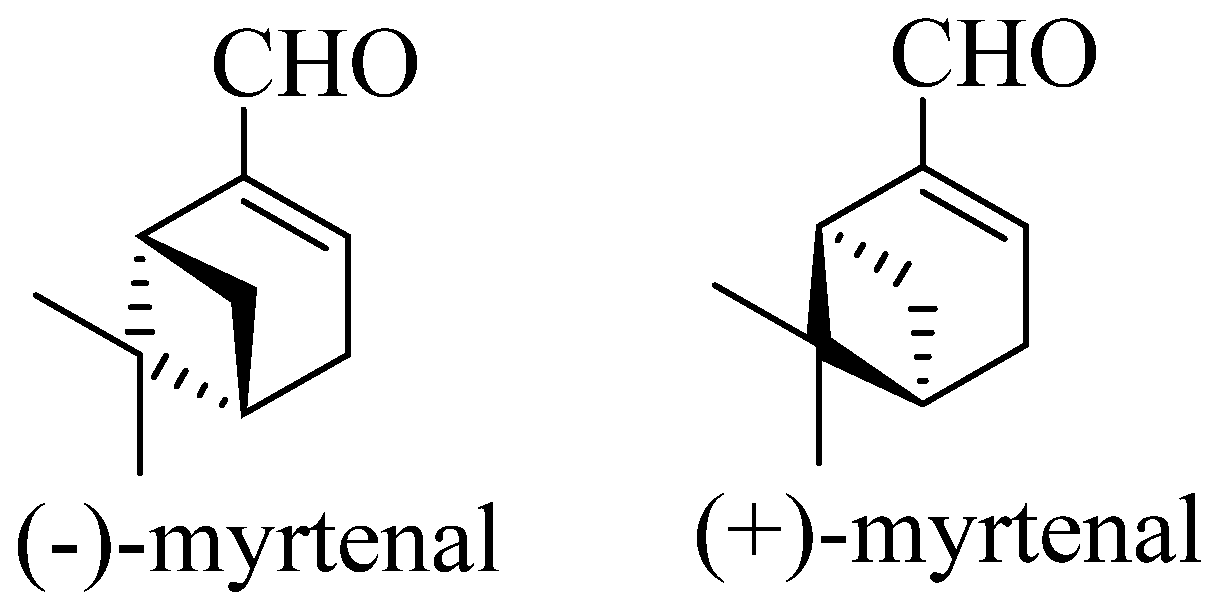
3. Therapeutic potential of myrtenal
| Natural source | Reference |
|---|---|
| Artemisia spp. | [98] |
| Coriandrum sativum | [99] |
| Cuminum cyminum | [100,101] |
| Curcuma amada, Curcuma aromatica | [102] |
| Glycyrrhyza glabra | [103] |
| Helianthus annuus | [104] |
| Hyssopus officinalis | [105] |
| Juglans regia | [106] |
| Laurus nobilis | [103] |
| Lavandula spp. | [107] |
| Ledum palustre | [108] |
| Myrtus communis | [109] |
| Origanum majorana, Origanum vulgare | [110] |
| Peumus boldus | [103] |
| Piper nigrum | [103] |
| Propolis | [111] |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | [112] |
| Thymus spp. | [113] |
4. Therapeutic potential of myrtenal derivatives
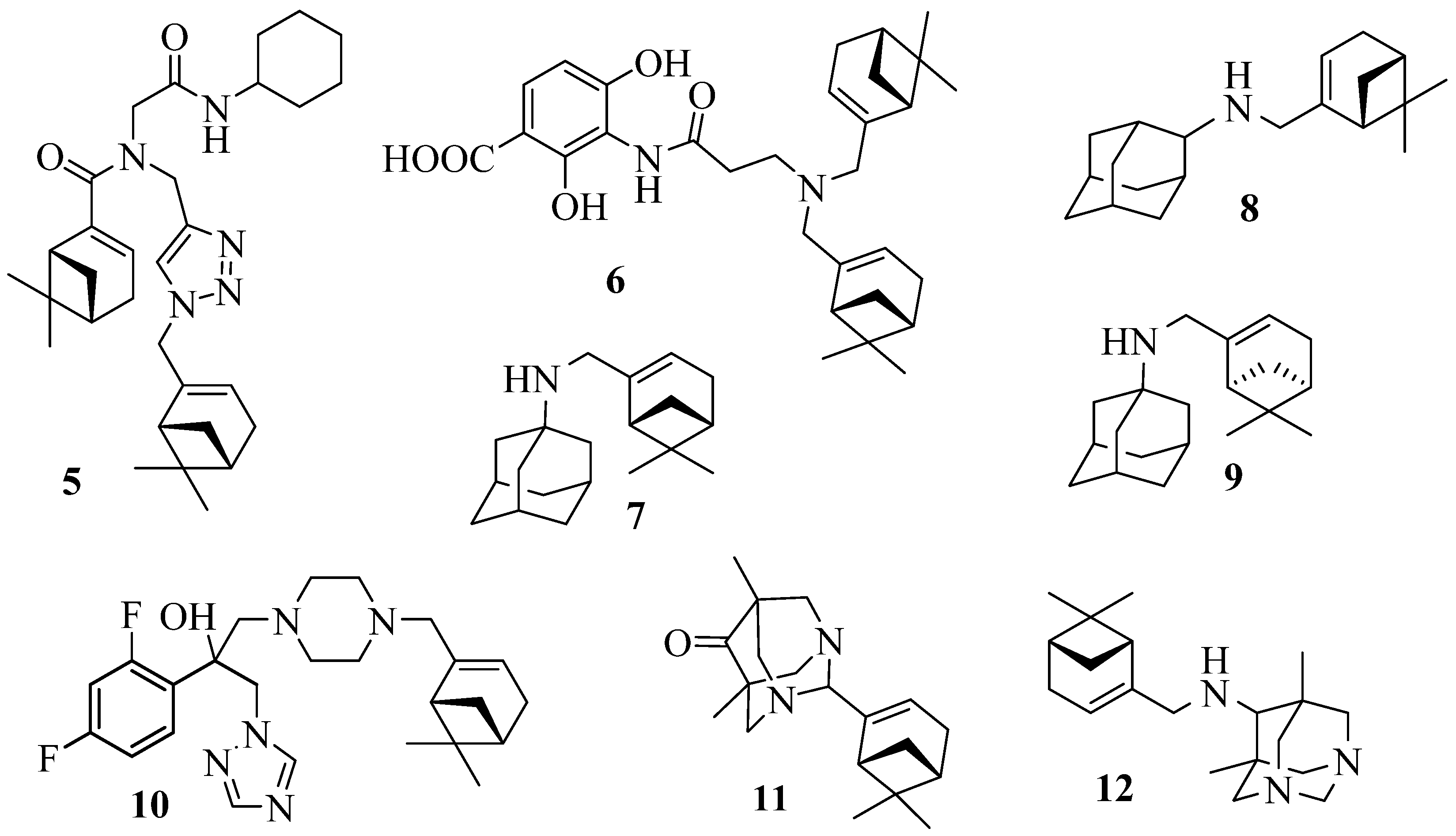
5. Conclusions and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaaban, H.A.E.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Shibamoto, T. Bioactivity of essential oils and their volatile aroma components: Review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorati, R.; Foti, M.C.; Valgimigli, L. Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10835–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.D.A.; Andrade, L.N.; De Sousa, É.B.V.; De Sousa, D.P. Anti-Ulcer Activity of Essential Oil Constituents. Molecules 2014, 19, 5717–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oils’ Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Jamous, R.M.; Abu-Zaitoun, S.Y.; Khasati, A.I.; Kalbouneh, S.R. Biological Properties and Bioactive Components of Mentha spicata L. Essential Oil: Focus on Potential Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity, Alzheimer’s Disease, Dermatophytosis, and Drug-Resistant Infections. eCAM 2019, 3834265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Ebani, V.V. (2020). Biological activity of essential oils. Molecules 2020, 25(3), 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radice, M.; Durofil, A.; Buzzi, R.; Baldini, E.; Martínez, A.P.; Scalvenzi, L.; Manfredini, S. Alpha-Phellandrene and Alpha-Phellandrene-Rich Essential Oils: A Systematic Review of Biological Activities, Pharmaceutical and Food Applications. Life 2022, 12, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuka, P.M.; Mayoka, G.; Mutai, P.; Chibale, K. The Role of Natural Products in Drug Discovery and Development against Neglected Tropical Diseases. Molecules 2017, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Hu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Q. Natural Products as Anticancer Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanforlin, E.; Zagotto, G.; Ribaudo, G. The Medicinal Chemistry of Natural and Semisynthetic Compounds against Parkinson’s and Huntington’s Diseases. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8(11), 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharate, S.S.; Mignani, S.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Why Are the Majority of Active Compounds in the CNS Domain Natural Products? A Critical Analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61(23), 10345–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskal, T.; Weng, J.-K. Natural product modulators of human sensations and mood: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.R.; Grosso, C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rocha, J.M. Comprehensive review on the interaction between natural compounds and brain receptors: Benefits and toxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 174, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Roy, K.; Pal, C. Terpenoids Against Infectious Diseases. Roy D. (Ed.), 2019 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC; ISBN 3: 978-0-8153-7066-6; 270 pp. [CrossRef]
- de Alvarenga, J.F.R.; Genaro, B.; Costa, B.L.; Purgatto, E.; Manach, C.; Fiamoncini, J. Monoterpenes: current knowledge on food source, metabolism, and health effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021, 63, 1352–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, X. Citral inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by activating PPAR-γ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 747, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, P.R.R.; Da Fonsêca, D.V.; Braga, R.M.; De Melo, C.G.F.; Andrade, L.N.; De Almeida, R.N.; De Sousa, D.P. Comparative Anticonvulsant Study of Epoxycarvone Stereoisomers. Molecules 2015, 20, 19660–19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Filho, H.V.; de Silva, S.C.M.; de Siqueira, R.J.B.; Lahlou, S.; dos Santos, A.A.; Magalhães, P.J.C. Biphasic cardiovascular and respiratory effects induced by β-citronellol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 775, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.B.; Simões, L.O.; de Medeiros, A.C.F.; de Jesus, M.A.; Fregoneze, J.B.; Evangelista, A.; Villarreal, C.F.; de Araújo, S.A.A.; Quintans-Jr, L.J.; Silva, D.F. Antihypertensive potential of linalool and linalool complexed with β-cyclodextrin: Effects of subchronic treatment on blood pressure and vascular reactivity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, T. Medicinal properties of terpenes found in Cannabis sativa and Humulus lupulus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 198–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.C.; Meireles, L.M.; Lemos, M.F.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Endringer, D.C.; Fronza, M.; Scherer, R. Antibacterial Activity of Terpenes and Terpenoids Present in Essential Oils. Molecules 2019, 24, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, F.; Khan, M.B.N.; Musharraf, S.G. Monoterpenes as therapeutic candidates to induce fetal hemoglobin synthesis and up-regulation of gamma-globin gene: An in vitro and in vivo investigation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Rudkowska, M.; Kasprzak-Drozd, K.; Oniszczuk, A.; Borowicz-Reutt, K. Activity of Selected Group of Monoterpenes in Alzheimer’s Disease Symptoms in Experimental Model Studies—A Non-Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, B.N.; da Silva, G.N.S.; Araújo, F.F.; Néri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M.; Bicas, J.L.; Molina, G. Beyond natural aromas: The bioactive and technological potential of monoterpenes. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2022, 128, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccialli, I.; Tedeschi, V.; Caputo, L.; D’Errico, S.; Ciccone, R.; De Feo, V.; Secondo, A.; Pannaccione, A. Exploring the therapeutic potential of phytochemicals in Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on polyphenols and monoterpenes. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 876614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhong, C.; Yu, J. Natural Monoterpenes as Potential Therapeutic Agents against Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(3), 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. Advances in Pharmacological Activities of Terpenoids. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15(3), 1934578X2090355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Dash, D.; Kishore Tyagi, C.; Kumar Sahu, A.; Tripathi, V. Revisiting the Medicinal Value of Terpenes and Terpenoids [Internet]. Revisiting Plant Biostimulants. IntechOpen 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Antidiabetic Potential of monoterpenes: A case of small molecules punching above their weight. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 19, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kury, L.T.; Abdoh, A.; Ikbariah, K.; Sadek, B.; Mahgoub, M. In Vitro and In Vivo Antidiabetic Potential of Monoterpenoids: An Update. Molecules 021, 27, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhong, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Bai, T.; Ren, L.; Guo, Y.; Jiao, X.; Liu, Y. Geniposide acutely stimulates insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells by regulating GLP-1 receptor/cAMP signaling and ion channels. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 430, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Ramalingam, S. Antidiabetic effect of d-limonene, a monoterpene in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed Prevent Nutr. 2012, 2, 269–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, V.C.; Schmidt, M.I.; Pankow, J.S.; Couper, D.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Young, J.H.; Duncan, B.B. Chronic inflammation role in the obesity-diabetes association: a case-cohort study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cássia da Silveira e Sá, R.; Andrade, L.N.; de Sousa, D.P. A review on anti-inflammatory activity of monoterpenes. Molecules 2013, 18(1), 1227–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.; Chi, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y. Effects of paeoniflorin on tumor necrosis factor-α-induced insulin resistance and changes of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Fitoterapia 2013, 91, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, D.P. Analgesic-like activity of essential oils constituents. Molecules 2011, 16, 2233–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo, A.T.; Dos Passos, M.P.; de Carvalho, Y.M.B.G.; Dos Santos, L.B.; de Souza, E.P.B.S.S.; de Souza, A.A.A.; Melo, M.A.O.; Quintans-Jr, L.J.; de Souza, S.Q.J.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Shanmugam, S.; Frank, L.A.; Serafini, M.R. (−)-linalool-Loaded Polymeric Nanocapsules Are a Potential Candidate to Fibromyalgia Treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.; Abdelhameed, M.F.; Abdou, R.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Dawoud, M.; Alasmari, S.M.; El Raey, M.A.; Attia, H.G. Mechanistic action of linalyl acetate: Acyclic monoterpene isolated from bitter orange leaf as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic agent: Role of TNF-α, IL1β, PGE2, and COX-2. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 203, 117131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.O.C.; Rego, R.I.A.; Andrade, H.H.N.; Costa, T.K.V.L.; Salvadori, M.G.S.S.; Almeida, R.N.; Castro, R.D. Evaluation of the antinociceptive effect generated by citronellal monoterpene isomers. Braz J Biol. 2023, 83, e271781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.B.R.; Melo, M.A.O.; Alves, R.S.; de Brito, R.G.; Rabelo, T.K.; Prado, L.D.S.; Silva, V.K.D.S.; Bezerra, D.P.; de Menezes-Filho, J.E.R.; Souza, D.S.; de Vasconcelos, C.M.L.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; Lucca Jr, W.; Quintans-Jr, L.J.; Guimarães, A.G. p-Cymene attenuates cancer pain via inhibitory pathways and modulation of calcium currents. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.B.R.; Pina, L.T.S.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Santos, L.A.B.O.; Batista, M.V.A.; Trindade, G.G.G.; Duarte, M.C.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.S.S.; et al. Antinociceptive Effect of a p-Cymene/β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex in a Murine Cancer Pain Model: Characterization Aided through a Docking Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gan, Y.; Kang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Ke, B. Camphor Attenuates Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Pain Models in Mice. J Pain Res. 2023, 16, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, D.N.; Costa, J.S.; Oliveira, M.A.; Rabelo, T.K.; Silva, A.M.O.E.; Carvalho, A.A.; Miguel-Dos-Santos, R.; Lauton-Santos, S.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; Santos, M.R.V.D.; Quintans-Jr, L.J.; Albuquerque Jr, R.L.C.; Guimarães, A.G. α-Terpineol reduces cancer pain via modulation of oxidative stress and inhibition of iNOS. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, M.; Sheikholeslami, M.A.; Ghafghazi, Sh.; Pouriran, R.; Parvardeh, S. Analgesic effect of α-terpineol on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rat sciatic nerve: Involvement of spinal microglial cells and inflammatory cytokines. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019, 22, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbrey, J.A.; Ortiz, Y.T.; Felix, J.S.; McMahon, L.R.; Wilkerson, J.L. Evaluation of the terpenes β-caryophyllene, α-terpineol, and γ-terpinene in the mouse chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain: possible cannabinoid receptor involvement. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, D.; Guimarães, A.; Oliveira, M.; Rabelo, T.K.; Lts, P.; Rocha, W.; Almeida, I.; Andrade, T.; Serafini, M.; Lima, B.; Araújo, A.; Menezes-Filho, J.E.; Santos-Miranda, A.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.; Coutinho, H.; Quintans, J.; Capasso, R.; Quintans-Júnior, L. Nanoencapsulated α-terpineol attenuates neuropathic pain induced by chemotherapy through calcium channel modulation. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, H.; Heberle, E.; Hilfiger, L.; Łapie´s, O.; Rodrigue, G.; Charlet, A. TRP channels and monoterpenes: Past and current leads on analgesic properties. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 945450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, J.J.; McKenna, M.K. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Properties of the Cannabis Terpene Myrcene in Rat Adjuvant Monoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.W.M.; Heimfarth, L.; Santos, T.K.B.; Passos, F.R.S.; Siqueira-Lima, P.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; Campos, A.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Martin, P.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; Quintans, J.S.S. Limonene, a Citrus monoterpene, non-complexed and complexed with hydroxypropyl-_-cyclodextrin attenuates acute and chronic orofacial nociception in rodents: evidence for involvement of the PKA and PKC pathway. Phytomedicine 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriana Estrella, G.R.; María Eva, G.T.; Alberto, H.L.; María Guadalupe, V.D.; Azucena, C.V.; Sandra, O.S.; Noé, A.V.; Francisco Javier, L.M. Limonene from Agastache mexicana essential oil produces antinociceptive effects, gastrointestinal protection and improves experimental ulcerative colitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilfiger, L.; Triaux, Z.; Marcic, C.; Héberlé, E.; Emhemmed, F.; Darbon, P.; Marchioni, E.; Petitjean, H.; Charlet, A. Anti-Hyperalgesic Properties of Menthol and Pulegone. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 753873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.L.; Rabelo, T.K.; Matos, J.P.S.C.F.; Anjos, K.S.; Melo, M.A.O.; Carvalho, Y.M.B.G.; Lima, B.S.; Menezes, P.P.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Picot, L.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Brito, R.G.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Involvement of nuclear factor κB and descending pain pathways in the anti-hyperalgesic effect of β-citronellol, a food ingredient, complexed in β-cyclodextrin in a model of complex regional pain syndrome - Type 1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021, 153, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.A.; Ghafghazi, S.; Parvardeh, S.; Koohsari, S.; Aghajani, S.H.; Pouriran, R.; Vaezi, L.A. Analgesic effects of cuminic alcohol (4-isopropylbenzyl alcohol), a monocyclic terpenoid, in animal models of nociceptive and neuropathic pain: Role of opioid receptors, L-arginine/NO/cGMP pathway, and inflammatory cytokines. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021, 900, 174075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.D.; Zheng, X.B.; Yang, B.L.; Wan, B.; Ma, J.M.; Liu, Z.X. 1,8-cineole decreases neuropathic pain probably via a mechanism mediating P2X3 receptor in the dorsal root ganglion. Neurochem Int. 2018, 121, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araruna, M.E.; Serafim, C.; Alves Júnior, E.; Hiruma-Lima, C.; Diniz, M.; Batista, L. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Terpenes in Experimental Models (2010–2020): A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaila, D.; Toy, B.J.; Wang, R.C.; Elegbede, J.A. Monoterpenes enchanced the sensitivity of head and neck cancer cells to radiation treatment in vitro. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 3089–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.A. Toxicity of Selected Monoterpenes and Essential Oils Rich in These Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Correa, C.R.; Campos-Reyna, J.L.; Villarreal-La Torre, V.E.; Calderón-Peña, A.A.; Sagástegui-Guarniz, W.A.; Guerrero-Espino, L.M.; González-Siccha, A.D.; Aspajo-Villalaz, C.L.; González-Blas, M.V.; Cruzado-Razco, J.L.; Hilario-Vargas, J. Potential Neuroprotective Activity of Essential Oils in Memory and Learning Impairment. Pharmacogn. J. 2021, 13, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, H.; Qin, T.; Li, M.; Ma, S. Thymol improves high-fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in mice via ameliorating brain insulin resistance and upregulating NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Metab Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Lu, H.; Teng, J. Carvacrol attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats. J Mol Neurosci. 2013, 51, 813–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Yamafuji, C. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity by bicyclic monoterpenoids. J Agric Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1765–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, K.R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Santha, K.; Sivakamasundari, R.I. Geraniol attenuates α-synuclein expression and neuromuscular impairment through increase dopamine content in MPTP intoxicated mice by dose dependent manner. BBRC 2013, 4, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, K.R.; Selvakumar, G.P. Gene expression regulation of Bcl2, Bax and cytochrome-C by geraniol on chronic MPTP/probenecid induced C57BL/6 mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 217, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardashov, O.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Il’ina, I.V.; Morozova, E.A.; Korchagina, D.V.; Karpova, E.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Highly Potent Activity of (1R,2R,6S)-3-Methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol in Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 3866–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, A.; Il’ina, I.; Morozova, E.; Korchagina, D.; Kurbakova, S.; Sorokina, I.; Tolstikova, T.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N. Potent neuroprotective activity of monoterpene derived 4-[(3aR, 7aS)-1, 3, 3a, 4, 5, 7a-hexahydro-3, 3, 6-trimethylisobenzofuran-1-yl]-2-methoxyphenol in MPTP mice model. Lett Drug Des Discov. 2014, 11, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotliarova, A.; Podturkina, A.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Gorina, D.S.; Lastovka, A.V.; Ardashov, O.V.; Rogachev, A.D.; Izyurov, A.E.; Arefieva, A.B.; Kulikov, A.V.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Sidorova, Y.A. A Newly Identified Monoterpenoid-Based Small Molecule Able to Support the Survival of Primary Cultured Dopamine Neurons and Alleviate MPTP-Induced Toxicity In Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrova, Y.; Chaprov, K.; Podturkina, A.; Ardashov, O.; Yandulova, E.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Neganova, M. Monoterpenoid Epoxidiol Ameliorates the Pathological Phenotypes of the Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Model by Alleviating Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.; Choi, B.Y.; Suh, S.W. Carvacrol Inhibits Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 7 Channels and Alleviates Zinc Neurotoxicity Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amooheydari, Z.; Rajaei, Z.; Alaei, H.; Esmaeil, N. Supplementation of Carvacrol Attenuates Hippocampal Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Level, Oxidative Stress, and Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Lipopolysaccharide-Exposed Rats. Adv Biomed Res. 2022, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, H.; Fizur, N.M.M.; Jha, N.K.; Ashraf, G.Md.; Ojha, S. Neuroprotective Potential and Underlying Pharmacological Mechanism of Carvacrol for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddin, L.B.; Jha, N.K.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Kesari, K.K.; Beiram, R.; Ojha, S. Neuroprotective Potential of Limonene and Limonene Containing Natural Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccialli, I.; Tedeschi, V.; Caputo, L.; Amato, G.; De Martino, L.; De Feo, V.; Secondo, A.; Pannaccione, A. The Antioxidant Activity of Limonene Counteracts Neurotoxicity Triggered byAβ1-42 Oligomers in Primary Cortical Neurons. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddin, L.B.; Azimullah, S.; Jha, N.K.; Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Beiram, R.; Ojha, S. Limonene, a Monoterpene, Mitigates Rotenone-Induced Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration by Modulating Neuroinflammation, Hippo Signaling and Apoptosis in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.; Rashno, M.; Salehi, I.; Karimi, S.A.; Raoufi, S.; Komaki, A. Geraniol improves passive avoidance memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 951, 175714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, P.; Sharma, T.; Airao, V.; Vaishnav, D.; Mani, S.; Rachamalla, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Upadhye, V.; Jha, S.K.; Jha, N.K.; Parmar, S. Geraniol protects hippocampal CA1 neurons and improves functional outcomes in global model of stroke in rats. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 102, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Parekh, K.A.; Ojha, S.K.; Beiram, R. Effect of citronellol on oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and autophagy pathways in an in vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Heliyon 2022, 11, e11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Khan, A.-u.; Saleem, M.W.; Shah, F.A.; Ali, F.; Khan, A.W.; Li, S. Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Compounds in Paclitaxel-Induced Chronic Inflammatory Pain. Molecules 2022, 27, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.; Bai, Y.; Xuan, X.; Bian, M.; Zhang, G.; Wei, C. 1,8-Cineole Ameliorates Advanced Glycation End Products-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; An, H.; Yu, F.; Yang, J.; Ding, H.; Bao, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, D. The neuroprotective effects of paeoniflorin against MPP+-induced damage to dopaminergic neurons via the Akt/Nrf2/GPX4 pathway, J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2022, 122, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan-Mohammadi-Khorrami, M.-K.; Asle-Rousta, M.; Rahnema, M.; Amini, R.J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lucena, J.D.; Gadelha-Filho, C.V.J.; da Costa, R.O.; de Araújo, D.P.; Lima, F.A.V.; Neves, K.R.T.; de Barros Viana, G.S. L-linalool exerts a neuroprotective action on hemiparkinsonian rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Gutiérrez, S.L.; Gómez-Cansino, R.; García-Zebadúa, J.C.; Jiménez-Pérez, N.C.; Reyes-Chilpa, R. Antidepressant activity of Litsea glaucescens essential oil: Identification of β-pinene and linalool as active principles. J. Ethnopharm. 2012, 143, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Li, R.P.; Qu, R.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S.P. Thymol produces an antidepressant-like effect in a chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 291, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, R. Exploring the Role of Cannabidiol-Monoterpene Formulations in Modulating Anxiety Symptoms. PhD thesis. 2020, Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository. 7090. https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/7090.
- Shi, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Ge, Y.W.; He, Y.M.; Kazuma, K.; Wang, Z.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Komatsu, K. Monoterpene derivatives with anti-allergic activity from red peony root, the root of Paeonia lactiflora. Fitoterapia 2016, 108, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Volcho, K.P.; Yarovaya, O. I. Monoterpenes as a renewable source of biologically active compounds. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitsa, I.G.; Suslov, E.V.; Teplov, G.V.; Korchagina, D.V.; Komarova, N.I.; Volcho, K.P.; Voronina, T.A.; Shevela, A.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Synthesis and anxiolytic activity of 2-aminoadamantane derivatives containing monoterpene fragments. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.A.P.; Santos, D.M.; de Carvalho, F.O.; Menezes, I.A.C.; Barreto, A.S.; Souza, D.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Santos, M.R.V. Monoterpenes and their derivatives as agents for cardiovascular disease management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2021, 88, 153451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.E.; Franks, A.E.; Phillips, M.A. Biosynthesis, natural distribution, and biological activities of acyclic monoterpenes and their derivatives. Phytochem Rev. 2023, 22, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, T.M.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Orshanskaya, I.R.; Kadyrova, R.A.; Sannikova, V.A.; Korchagina, D.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Anti-influenza activity of monoterpene-containing substituted coumarins. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, T.M.; Shtro, A.A.; Galochkina, A.V.; Nikolaeva, Y.V.; Garshinina, A.V.; Borisevich, S.S.; Korchagina, D.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. New Inhibitors of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Replication Based on Monoterpene-Substituted Arylcoumarins. Molecules 2023, 28, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, T.M.; Zakharenko, A.L.; Chepanova, A.A.; Ilina, E.S.; Zakharova, O.D.; Kaledin, V.I.; Nikolin, V.P.; Popova, N.A.; Korchagina, D.V.; Reynisson, J.; Chand, R.; Ayine-Tora, D.M.; Patel, J.; Leung, I.K.H.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Lavrik, O.I. Promising New Inhibitors of Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase I (Tdp 1) Combining 4-Arylcoumarin and Monoterpenoid Moieties as Components of Complex Antitumor Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, T.M.; Zakharenko, A.L.; Kornienko, T.E.; Chepanova, A.A.; Dyrkheeva, N.S.; Artemova, A.O.; Korchagina, D.V.; Achara, C.; Curtis, A.; Reynisson, J.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Lavrik, O.I. New 5-Hydroxycoumarin-Based Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase I Inhibitors Sensitize Tumor Cell Line to Topotecan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkuev, A.A.; Dyrkheeva, N.S.; Kornienko, T.E.; Ilina, E.S.; Ivankin, D.I.; Suslov, E.V.; Korchagina, D.V.; Gatilov, Y.V.; Zakharenko, A.L.; Malakhova, A.A.; Volcho, K.P.; et al. Adamantane-Monoterpenoid Conjugates Linked via Heterocyclic Linkers Enhance the Cytotoxic Effect of Topotecan. Molecules. 2022, 27, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivankin, D.I.; Kornienko, T.E.; Mikhailova, M.A.; Dyrkheeva, N.S.; Zakharenko, A.L.; Achara, C.; Reynisson, J.; Golyshev, V.M.; Luzina, O.A.; Volcho, K.P.; et al. Novel TDP1 Inhibitors: Disubstituted Thiazolidine-2,4-Diones Containing Monoterpene Moieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, D.S.P.; Kincses, A.; Nové, M.; Spengler, G.; Mulhovo, S.; Aires-de-Sousa, J.; Dos Santos, D.J.V.A.; Ferreira, M.U. Alkylated monoterpene indole alkaloid derivatives as potent P-glycoprotein inhibitors in resistant cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2021, 210, 112985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, A.; Borralho, P.M.; Gomes, S.E.; Mulhovo, S.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Ferreira, M.J.U. Monoterpene indole alkaloid hydrazone derivatives with apoptosis inducing activity in human HCT116 colon and HepG2 liver carcinoma cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25(17), 3556–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, N.S.; Randjelović, P.J.; Stojanović, N.M.; Blagojević, P.D.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Ilić, I.R.; Djordjević, V.B. Toxic essential oils. Part II: Chemical, toxicological, pharmacological and microbiological profiles of Artemisia annua L. Volatiles. FCT 2013, 58, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, J.A.; Rosado, A.; Fuentes, V. Chemical composition of the seed oil of Coriandrum sativum L. from Cuba. J. Essent. Oil Res 1996, 8, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajlaoui, H.; Mighri, H.; Noumi, E.; Snoussi, M.; Trabelsi, N.; Ksouri, R.; Bakhrouf, A. Chemical composition and biological activities of Tunisian Cuminum cyminum L. essential oil: A high effectiveness against Vibrio spp. Strains. FCT 2010, 48, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraghebi, F. Introduction of myrtenal as an indicator component in essential oil of Cuminum cyminum Isfahan variety. JBES 2013, 3, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Chong, T.; Chee, S. Essential oil of Curcuma mangga Val. and van Zijp rhizomes. J. Essent. Oil Res 1999, 11, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, S. Medicinal Plant Constituents. LifeLong Press www.NaturalHealthWizards.com, 2004. Copyright 2004 Steve Blake.
- Etievant, P.X.; Azar, M.; Pham-Delegue, M.H.; Masson, C.J. Isolation and identification of volatile constituents of sunflowers (Helianthus annuus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem 1984, 32, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizil, S.; Haşimi, N.; Tolan, V.; Kilinç, E.; Karataş, H. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Hyssop (Hyssopus officinalis, L) essential oil. Not. Bot. Hort. Agrobot. Cluj. 2010, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rather, M.A.; Dar, B.A.; Dar, M.Y.; Wani, B.A.; Shah, W.A.; Bhat, B.A.; Ganai, B.A.; Bhat, K.A.; Anand, R.; Qurishi, MA. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of the leaf essential oil of Juglans regia L. and its constituents. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smigielski, K.; Raj, A.; Krosowiak, K.; Gruska, R. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of Lavandula angustifolia Cultivated in Poland. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2009, 12, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattje, D.H.E.; Bos, R. Composition of Essential Oil of Ledum palustre. Planta Med. 1981, 41, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardeli, C.; Vassiliki, P.; Athanasios, M.; Kibouris, T.; Komaitis, M. Essential oil composition of Pistacia lentiscus L. and Myrtus communis L.: Evaluation of antioxidant capacity of methanolic extracts. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, E.; Mancini, E.; Roscigno, G.; Mignola, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Senatore, F. Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Essential Oils of Origanum vulgare L. subsp. vulgare L. under Different Growth Conditions. Molecules 2013, 18, 14948–14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esin, H.K.E.; Demirci, B.; Uzel, A.; Demirci, F. Volatile composition of Anatolian propolis by headspace-solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME), antimicrobial activity against food contaminants and antioxidant activity. J. Med. Plant Res. 2013, 7, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghadraoui, L.; Essakhi, D.; Benjelloun, M.; Errabhi, N.; El Harchli, E.H.; Alaoui, M.M.; Petit, D. Chemical Composition of Essential Oils from Rosmarinus officinalis L. and Acridicide Activity on Dociostaurus maroccanus Thunberg, 1815 in Morocco. IJSER 2015, 6, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Salgueiro, L.R.; Vila, R.; Tomàs, X.; Cañigueral, S.; Paiva, J.; da Cunha, A.P.; Adzet, T. Essential oil composition and variability of Thymus lotocephalus and Thymus×mourae. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2000, 28, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegezzi, D. ; United States Patent 1980; http://www.google.fr/patents/US4190675?
- Dragomanova, S.; Tancheva, L.; Georgieva, M. A review: Biological activity of myrtenal and some myrtenal-containing medicinal plant essential oils. Scr. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 31, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Okabe, T.; Inamori, Y.; Tsujibo, H.; Miyake, Y.; Hiraoka, K.; Ishida, N. The biological properties of monoterpenes: Hypotensive effects on rats and antifungal activities on plant pathogenic fungi of monoterpenes. Mokuzai Gakkaishi. 1996, 42, 677–80. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.R.V.; Moreira, F.V.; Fraga, B.P.; de Souza, D.P.; Bonjardim, L.R.; Quintans-Junior, L.J. Cardiovascular effects of monoterpenes: a review. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2011, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, A.; Pari, L. Myrtenal ameliorates hyperglycemia by enhancing GLUT2 through Akt in the skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2016, 256, 161–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, H.L.; Perumal, S.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Myrtenal, a natural monoterpene, down-regulates TNF-α expression and suppresses carcinogen-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012, 369, 183–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, L.H.; Perumal, S.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Myrtenal attenuates diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by stabilizing intrinsic antioxidants and modulating apoptotic and anti-apoptotic cascades. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2012, 35, 269–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, L.H.; Natarajan, N.; Thamaraiselvan, R.; Srinivasan, P.; Periyasamy, B.M. Myrtenal ameliorates diethylnitrosamine-induced hepato-carcinogenesis through the activation of tumor suppressor protein p53 and regulation of lysosomal and mitochondrial enzymes. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2013, 27, 443–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, S.; Boobathi, L.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Salubrious therapeutic efficacy of myrtenal on colon carcinoma induced by 1,2-dimethyl-hydrazine studied in experimental albino rats. Res J Pharmacol Pharmacodyn. 2014, 6, 146–52. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, B.X.; Arruda, R.F.; Costa, G.A.; Jerdy, H.; de Souza, S.B.; Santos, J.M.; de Freitas, W.R.; Kanashiro, M.M.; de Carvalho, E.C.Q.; Sant’Anna, N.F.; Antunes, F.; Martinez-Zaguilan, R.; Souad, S.; Okorokova-Façanha, A.L.; Façanha, A.R. Myrtenal-induced V-ATPase inhibition – A toxicity mechanism behind tumor cell death and suppressed migration and invasion in melanoma. BBA-General Subjects. 2019, 1863, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshkumar, B.; Sathishkumar, V.; Nandakumar, N.; Rengarajan, T.; Madankumar, A.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Anti-Oxidative Effect of Myrtenal in Prevention and Treatment of Colon Cancer Induced by 1, 2-Dimethyl Hydrazine (DMH) in Experimental Animals. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshkumar, B.; Sathishkumar, V.; Nandakumar, N.; Rengarajan, T.; Madankumar, A.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Chemopreventive effect of myrtenal on bacterial enzyme activity and the development of 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine-induced aberrant crypt foci in Wistar rats. J Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trytek, M.; Paduch, R.; Pięt, M.; Kozieł, A.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M.; Szajnecki, Ł.; Gromada, A. Biological activity of oxygenated pinene derivatives on human colon normal and carcinoma cells. Flavour Fragr. J. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Lazarova, M.; Tancheva, L. Myrtenal effects on memory in experimental rats. J of IMAB 2021, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Tancheva, L.; Georgieva, M.; Klisurov, R. Аnalgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of monoterpenoid myrtenal in rodents. J of IMAB 2019, 25, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S. Pharmacological, toxicological and neurobiological studies of Myrtenal – a bicyclic monoterpenoid of natural origin. Ph.D. Thesis. 2020; https://ras.nacid.bg/api/reg/FilesStorage?key=6b37588e-6c9b-4708-bb22-e5872dca6bd3&mimeType=application/pdf&fileName=Authoreferate%20S%20Dragomanova.pdf&dbId=1.
- Hailu, E.; Engidawork, E.; Asres, K. Essential oil of Myrtus communis L. produces a non-sedating anxiolytic effect in mice model of anxiety. Ethiopian Pharm J. 2011, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancheva, L.P.; Lazarova, M.I.; Alexandrova, A.V.; Dragomanova, S.T.; Nicoletti, F.; Tzvetanova, E.R.; Hodzhev, Y.K.; Kalfin, R.E.; Miteva, S.A.; Mazzon, E.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Atanasov, A.G. Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Three Natural Antioxidants on a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease: A Comparative Study. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Pavlov, S.; Marinova, D.; Hodzev, Y.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Lazarova, M.; Tzvetanova, E.; Alexandrova, A.; Kalfin, R.; Tancheva, L. Neuroprotective Effects of Myrtenal in an Experimental Model of Dementia Induced in Rats. Antioxidants 2022–11. [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, D.; Dogra, A.K.; Wink, M. Myrtenal inhibits acetylcholinesterase, a known Alzheimer target. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1368–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Tancheva, L.; Georgieva, M.; Georgieva, A.; Dishovsky, C.; Stoeva, S. Effect of monoterpene myrtenal on experimental dementia in mice. 31st ICAD, 2016, Budapest, Hungary. https://www.alz.co.uk/ADI-conference-2016.
- Concepción, O.; Belmar, J.F.; de la Torre, A.; Muñiz, F.M.; Pertino, M.W.; Alarcón, B.; Ormazabal, V.; Nova-Lamperti, E.; Zúñiga, F.A.; Jiménez, C.A. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Analysis of Novel Myrtenyl Grafted Pseudo-Peptides Revealed Potential Candidates for Anticancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska-Błajet, M.; Feder-Kubis, J. Monoterpenes and Their Derivatives-Recent Development in Biological and Medical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garberová, M.; Potočňák, I.; Tvrdoňová, M.; Bago-Pilátová, M.; Bekešová, S.; Kudličková, Z.; Samoľová, E.; Kešeľáková, A.; Elečko, J.; Vilková, M. Spectral, structural, and pharmacological studies of perillaldehyde and myrtenal based benzohydrazides. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1271, 134112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozioł, A.; Stryjewska, A.; Librowski, T.; Salat, K.; Gawel, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Lochynski, S. An overview of the pharmacological properties and potential applications of natural monoterpenes. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, R.S.S.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.C.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Santos, M.R.V.; Barreto, A.S.; DeSantana, J.M.; Siqueira-Lima, P.S.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. A Systematic Review of the Wound-Healing Effects of Monoterpenes and Iridoid Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of thymol: A brief review of the literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.A.; Kasprzak, K.; Oniszczuk, T.; Oniszczuk, A. Natural monoterpenes: Much more than only a scent. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheer, D.; Singh, D.; Kumar, G.; Karnatak, M.; Chandra, S.; Prakash Verma, V.; Shankar, R. Thymol chemistry: A medicinal toolbox. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2019, 15(5), 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephane, F.F.Y.; Jean Jules, B.K. Terpenoids as Important Bioactive Constituents of Essential Oils [Internet]. Essential Oils - Bioactive Compounds, New Perspectives and Applications. IntechOpen 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coêlho, M.L.; Islam, M.T.; da Silva Oliveira, G.L,.;de Alencar, M.V.O.B.; de Oliveira Santos, J.V.; dos Reis, A.C.; da Mata, A.M.O.F.; Paz, M.F.C.J.; Docea, A.O.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; de Carvalho, M.C.A.A. Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Properties of Natural Bioactive Monoterpenes Nerol, Estragole, and 3,7-Dimethyl-1-Octanol. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 8002766. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sintim, H.O. Dialkylamino-2, 4-dihydroxybenzoic Acids as Easily Synthesized Analogues of Platensimycin and Platencin with Comparable Antibacterial Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17(12), 3352–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslov, E.; Ponomarev, K.; Rogachev, A.; Pokrovsky, M.; Pokrovsky, A.; Pykhtina, M.; Beklemishev, A.; Korchagina, D.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N. Compounds combining aminoadamantane and monoterpene moieties: Cytotoxicity and mutagenic effects. Med. Chem. 2015, 11, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, K.Y.; Suslov, E.V.; Zakharenko, A.L.; Zakharova, O.D.; Rogachev, A.D.; Korchagina, D.V.; Zafar, A.; Reynisson, J.; Nefedov, A.A.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Lavrik, O.I. Aminoadamantanes containing monoterpene-derived fragments as potent tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, T.; Szakonyi, Z. (2018). Stereoselective synthesis and application of bi-and trifunctional monoterpene-based compounds. PhD thesis, 2018, https://web.archive.org/web/20190429033511id_/http://doktori.bibl.u-szeged.hu/9832/1/Gonda20Timea20disszertacio.
- Gonda, T.; Bérdi, P.; Zupkó, I.; Fülöp, F.; Szakonyi, Z. Stereoselective Synthesis, Synthetic and Pharmacological Application of Monoterpene-Based 1,2,4- and 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitsa, I.G.; Suslov, E.V.; Teplov, G.V.; Korchagina, D.V.; Komarova, N.I.; Volcho, K.P.; Voronina, T.A.; Shevela, A.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Synthesis and anxiolytic activity of 2-aminoadamantane derivatives containing monoterpene fragments. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplov, G.; Suslov, E.; Zarubaev, V.; Shtro, A.; Karpinskaya, L.; Rogachev, A.; Korchagina, D.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Kiselev, O. Synthesis of new compounds combining adamantanamine and monoterpene fragments and their antiviral activity against influenza virus A (H1N1) pdm09. Lett Drug Des Discov. 2013, 10, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Zhulanov, N.S.; Zaikova, N.P.; Sari, S.; Gülmez, D.; Sabuncuo ̆glu, S.; Ozadali-Sari, K.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Nefedov, A.A.; Rybalova, T.V.; Volcho, K.P.; et al. Rational Design of New Monoterpene-Containing Azoles and Their Antifungal Activity. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarev, K.; Pavlova, A.; Suslov, E.; Ardashov, O.; Korchagina, D.; Nefedov, A.; Tolstikova, T.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N. Synthesis and analgesic activity of new compounds combining azaadamantane and monoterpene moieties. Med Chem Res. 2015, 24, 4146–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, K.; Morozova, E.; Pavlova, A.; Suslov, E.; Korchagina, D.; Nefedov, A.; Tolstikova, T.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N. Synthesis and analgesic activity of amines combining diazaadamantane and monoterpene fragments. Med. Chem. 2017, 13(8), 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Andonova, V.; Lazarova, M.; Munkuev, A.; Suslov, E.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Stefanova, M.; Gavrilova, P.; Uzunova, D.; Kalfin, R.; Tancheva, L. Memory-improving effects of myrtenal-adamantane conjugates. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2023, 58, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomanova, S.; Lazarova, M.; Munkuev, A.; Suslov, E.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Bibi, A.; Reynisson, J.; Tzvetanova, E.; Alexandrova, A.; et al. New Myrtenal–Adamantane Conjugates Alleviate Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia in Rat Model. Molecules 2022, 27, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





