Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Power System State Estimation
2.1. Static State Estimation
2.2. Dynamic State Estimation
3. Bad Data Types and Considerations
3.1. Measurement Error
3.2. Parameter Error
3.3. Topology Error
4. Bad Data Detection
4.1. Chi-Squared Test
4.2. Residual-Based Methods
4.3. Hypothesis Testing
- is a valid measurement.
- is a measurement in error.
5. When Bad Data Becomes Malicious
6. Recent Approaches
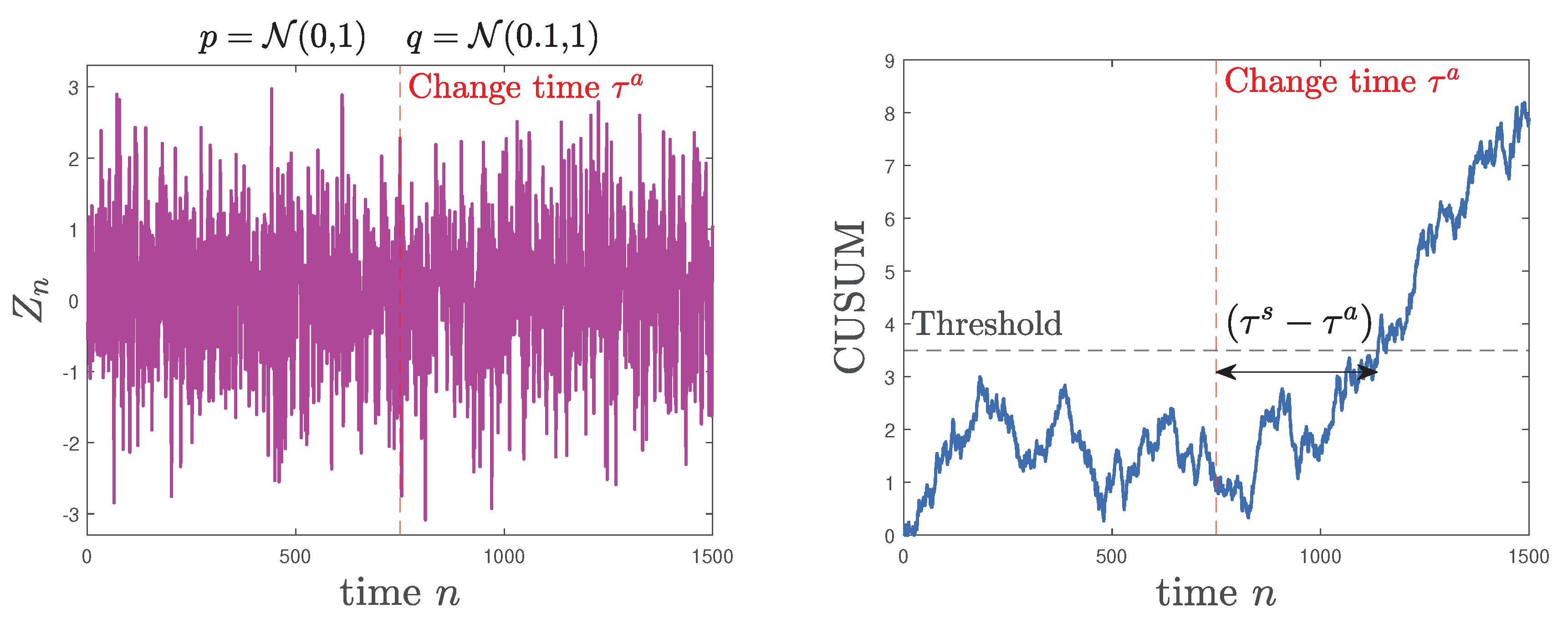
6.1. Quickest Change Detection
- H0: X has pdf p.
- H1: X has pdf q.
6.2. AI Approaches
7. Conclusions and Suggestions for Future Work
7.1. Climate changes and impacts on power and energy systems
References
- Schweppe, F.C.; Wildes, J. Power System Static-State Estimation, Part I: Exact Model. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, -89. [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.; da Silva, A.; Falcao, D. Bibliography on power system state estimation (1968-1989). IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1990, 5, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellstede, G.; Beissler, G. A Software Package for Security Assessment Functions. In Power Systems and Power Plant Control; Pingyang, W., Ed.; IFAC Symposia Series; Pergamon: Oxford, 1987; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, H.M.; Schweppe, F.C. Bad Data Suppression in Power System Static State Estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 2718; -90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschin, E.; Schweppe, F.; Kohlas, J.; Fiechter, A. Bad data analysis for power system state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems 1975, 94, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, A. State estimation in electric power systems: a generalized approach; Springer, 2012.
- Abur, A.; Expósito, A.G. Power System State Estimation: Theory and Implementation, 1 ed.; CRC Press, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Bretas, A.; Bretas, N.; London Jr, J.B.; Carvalho, B. ; others. Cyber-Physical Power Systems State Estimation, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Gómez-Expósito, A.; Netto, M.; Mili, L.; Abur, A.; Terzija, V.; Kamwa, I.; Pal, B.; Singh, A.K.; Qi, J.; Huang, Z.; Meliopoulos, A.P.S. Power System Dynamic State Estimation: Motivations, Definitions, Methodologies, and Future Work. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2019, 34, 3188–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A. Synchronized phasor measurements-a historical overview. IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exhibition, 2002, Vol. 1, pp. 476–479 vol.1. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ning, P.; Reiter, M.K. False Data Injection Attacks against State Estimation in Electric Power Grids 2011. 14.
- Musleh, A.S.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z.Y. A Survey on the Detection Algorithms for False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E.; Bucy, R.S. New Results in Linear Filtering and Prediction Theory. Journal of Basic Engineering 1961, 83, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Singh, A.K.; Mir, A.S.; Taha, A.; Rouhani, A.; Gomez-Exposito, A.; Meliopoulos, A.; Pal, B.; Kamwa, I.; Qi, J.; Mili, L.; Mohd Ariff, M.A.; Netto, M.; Glavic, M.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Bi, T.; Van Cutsem, T.; Terzija, V.; Huang, Z. Power system dynamic state and parameter estimation-transition to power electronics-dominated clean energy systems: IEEE task force on power system dynamic state and parameter estimation 2021.
- Liu, Y.; Singh, A.K.; Zhao, J.; Meliopoulos, A.P.S.; Pal, B.; Ariff, M.A.b.M.; Van Cutsem, T.; Glavic, M.; Huang, Z.; Kamwa, I.; Mili, L.; Mir, A.S.; Taha, A.; Terzija, V.; Yu, S. Dynamic State Estimation for Power System Control and Protection. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021, 36, 5909–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, N. An iterative dynamic state estimation and bad data processing. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 1989, 11, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debs, A.S.; Larson, R.E. A Dynamic Estimator for Tracking the State of a Power System. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1670; -89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, K.I.; Takagi, H.; Hasegawa, J.; Koike, T. Dynamic state estimation for electric power systems—introduction of a trend factor and detection of innovation processes. Electrical Engineering in Japan 1976, 96, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, K.; Hasegawa, J.; Koike, T. Dynamic state estimation including anomaly detection and identification for power systems. IEE Proceedings C Generation, Transmission and Distribution 1982, 129, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, A.S.; Bretas, N.G.; Massignan, J.A.D.; London Junior, J.B.A. Hybrid Physics-Based Adaptive Kalman Filter State Estimation Framework. Energies 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ding, L.; Chakrabarti, S.; Gryazina, E.; Terzija, V. Power system anomaly detection using innovation reduction properties of iterated extended kalman filter. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 136, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, L.; Phaniraj, V.; Rousseeuw, P. Least median of squares estimation in power systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1991, 6, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.; Abur, A. A robust WLAV state estimator using transformations. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1992, 7, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Pal, B.C. Bad Data Detection in the Context of Leverage Point Attacks in Modern Power Networks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, L.; Cheniae, M.; Vichare, N.; Rousseeuw, P. Robust state estimation based on projection statistics [of power systems]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1996, 11, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mili, L. Vulnerability of the Largest Normalized Residual Statistical Test to Leverage Points. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2018, 33, 4643–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Z.; Diao, R. Assessing Gaussian Assumption of PMU Measurement Error Using Field Data. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2018, 33, 3233–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Thimmisetty, C.; Chen, X.; Stewart, E.; Top, P.; Korkali, M.; Donde, V.; Tong, C.; Min, L. Power Distribution System Synchrophasor Measurements With Non-Gaussian Noises: Real-World Data Testing and Analysis. IEEE Open Access Journal of Power and Energy 2021, 8, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco, P.; Exposito, A. Power system parameter estimation: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2000, 15, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.A.; Herczet, C.J. A Sensitivity Analysis of Weighted Least Squares State Estimation for Power Systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1696; -92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, A.S.; Bretas, N.G.; Carvalho, B.E. Further contributions to smart grids cyber-physical security as a malicious data attack: Proof and properties of the parameter error spreading out to the measurements and a relaxed correction model. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2019, 104, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.E.; Lim, S.L. Parameter error identification and estimation in power system state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1995, 10, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.; Leao, J. Identification of topology errors in power system state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1993, 8, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, W.H. Detection of topology errors by state estimation (power systems). IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1989, 4, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korres, G.N.; Manousakis, N.M. A state estimation algorithm for monitoring topology changes in distribution systems. 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, 2012, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Koglin, H.J.; Neisius, T.; Bei<i>β</i>ler, G.; Schmitt, K. Bad data detection and identification. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 1990, 12, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.A.; Davis, P.W. Multiple Bad Data Detectability and Identifiability: A Geometric Approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 1986, 1, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutsem, T.V.; Ribbens-Pavella, M.; Mili, L. Hypothesis Testing Identification: A New Method For Bad Data Analysis In Power System State Estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, L.; Van Cutsem, T.; Ribbens-Pavella, M. Decision Theory Applied to Bad Data Identification in Power System State Estimation. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1985, 18, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, L.; Van Cutsem, T. Implementation of the hypothesis testing identification in power system state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 1988, 3, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, E.; Costa, A.; Clements, K. Bayesian-based hypothesis testing for topology error identification in generalized state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2004, 19, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Cheng, M.X.; Gou, B. A Hypothesis Testing Approach for Topology Error Detection in Power Grids. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2016, 3, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Mo, Y.; Sinopoli, B. Integrity Data Attacks in Power Market Operations. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2011, 2, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Cárdenas, A.A.; Sastry, S.S. Safe and Secure Networked Control Systems under Denial-of-Service Attacks. Hybrid Systems: Computation and Control; Majumdar, R., Tabuada, P., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; pp. 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Tong, L. On Topology Attack of a Smart Grid: Undetectable Attacks and Countermeasures. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2013, 31, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z. Local Topology Attacks in Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Weller, S.R.; Luo, F.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.Y. Generalized FDIA-Based Cyber Topology Attack With Application to the Australian Electricity Market Trading Mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3820–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosut, O.; Jia, L.; Thomas, R.J.; Tong, L. Malicious Data Attacks on Smart Grid State Estimation: Attack Strategies and Countermeasures. 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, 2010, pp. 220–225. [CrossRef]
- Hug, G.; Giampapa, J.A. Vulnerability Assessment of AC State Estimation With Respect to False Data Injection Cyber-Attacks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuthalapati, S. State Estimation Performance Monitoring. https://www.nerc.com/pa/rrm/Resources/Monitoring_and_Situational_Awareness_Conference1/10.%20Monitoring%20SE%20Performance%20at%20ERCOT_Sarma%20Nuthalapati_ERCOT.pdf, 2015. Accessed: 2023-06-03.
- ETAP State Estimation Software. https://etap.com/product/state-estimation-software, 2015. Accessed: 2023-06-03.
- Yang, Q.; Chang, L.; Yu, W. On false data injection attacks against Kalman filtering in power system dynamic state estimation. Security and Communication Networks 2016, 9, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, G.; Terzija, V. Unscented Kalman filter for power system dynamic state estimation. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2011, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, E.; Kamwa, I. Dynamic State Estimation in Power System by Applying the Extended Kalman Filter With Unknown Inputs to Phasor Measurements. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2011, 26, 2556–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.R.; Huang, S.J. Application of a robust algorithm for dynamic state estimation of a power system. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2002, 17, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, K.; Cao, X.; Hu, F.; Liu, Y. Detection of Faults and Attacks Including False Data Injection Attack in Smart Grid Using Kalman Filter. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems 2014, 1, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Shah, S.; Butt, R.; Raza, B.; Anwar, M.; Ashraf, M.; Ngadi, M.; Gungor, V. Smart grid communication and information technologies in the perspective of Industry 4.0: Opportunities and challenges. Computer Science Review 2018, 30, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Uludag, S. Mitigating IoT-based Cyberattacks on the Smart Grid. 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), 2017, pp. 517–522. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A Survey on Cyber Security for Smart Grid Communications. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2012, 14, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.N.; Yılmaz, Y.; Wang, X. Secure Distributed Dynamic State Estimation in Wide-Area Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2020, 15, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zou, S.; Xie, Y.; Veeravalli, V.V. Sequential (Quickest) Change Detection: Classical Results and New Directions. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory 2021, 2, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeravalli, V.V.; Banerjee, T. , Quickest change detection. In Academic Press Library in Signal Processing; Elsevier, 2014; Vol. 3, pp. 209–255. [CrossRef]
- Poor, H.V. An introduction to signal detection and estimation, 2 ed.; Springer Texts in Electrical Engineering, Springer-Verlag: New York, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Neyman, J.; Pearson, E.S. IX. On the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical or Physical Character 1933, 231, 289–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, P.; Veeravalli, V.V. Statistical Inference for Engineers and Data Scientists; Cambridge University Press, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Page, E.S. Continuous Inspection Schemes. Biometrika 1954, 41, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polunchenko, A.S.; Tartakovsky, A.G. On Optimality of the Shiryaev-Roberrts Procedure for Detecting a Change in Distribution. The Annals of Statistics 2010, 38, 3445–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Chen, Y.C.; Dominguez-Garcia, A.D.; Veeravalli, V.V. Power system line outage detection and identification — A quickest change detection approach. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2014, pp. 3450–3454. [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, G.; Jiang, X.; Domínguez-García, A.D.; Veeravalli, V.V. Comparison of statistical algorithms for power system line outage detection. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2016, pp. 2946–2950. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, N.; Zhai, C. A Control Chart Approach to Power System Line Outage Detection Under Transient Dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021, 36, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Campbell, K.A.; Han, Z. Defending false data injection attack on smart grid network using adaptive CUSUM test. 2011 45th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, 2011, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Campbell, K.A.; Han, Z. Real-Time Detection of False Data Injection in Smart Grid Networks: An Adaptive CUSUM Method and Analysis. IEEE Systems Journal 2016, 10, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A. Rao Test for Adaptive Detection in Gaussian Interference With Unknown Covariance Matrix. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2007, 55, 3577–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akingeneye, I.; Wu, J. Low Latency Detection of Sparse False Data Injections in Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58564–58573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yılmaz, Y.; Wang, X. Quickest Detection of False Data Injection Attack in Wide-Area Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekatos, V.; Giannakis, G.B. Distributed Robust Power System State Estimation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2013, 28, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.N.; Yılmaz, Y.; Wang, X. Distributed Quickest Detection of Cyber-Attacks in Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2018, 13, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.N.; Yılmaz, Y.; Wang, X. Real-Time Detection of Hybrid and Stealthy Cyber-Attacks in Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2019, 14, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Low-Complexity Quickest Change Detection in Linear Systems With Unknown Time-Varying Pre- and Post-Change Distributions. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2021, 67, 1804–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Akingeneye, I.; Wu, J.; Han, Z. Quickest Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid with Dynamic Models. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics 2022, 10, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.N. Data-Driven Quickest Change Detection. PhD thesis, Columbia University, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Moustakides, G.V.; Polunchenko, A.S.; Tartakovsky, A.G. Numerical Comparison of CUSUM and Shiryaev–Roberts Procedures for Detecting Changes in Distributions. Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods 2009, 38, 3225–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.; Tartakovsky, A.G. Exact optimality of the Shiryaev-Roberts procedure for detecting changes in distributions. 2008 International Symposium on Information Theory and Its Applications, 2008, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Polunchenko, A.S.; Raghavan, V. Comparative performance analysis of the Cumulative Sum chart and the Shiryaev-Roberts procedure for detecting changes in autocorrelated data. Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry 2018, 34, 922–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozay, M.; Esnaola, I.; Yarman Vural, F.T.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Poor, H.V. Machine Learning Methods for Attack Detection in the Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2016, 27, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Tang, B.; He, H. Detection of false data attacks in smart grid with supervised learning. 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2016, pp. 1395–1402. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Amin, M.M.; Fu, J.; Moussa, H.B. A Novel Data Analytical Approach for False Data Injection Cyber-Physical Attack Mitigation in Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26022–26033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Chin, W.L. Blind False Data Injection Attack Using PCA Approximation Method in Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Piechocki, R.J.; Kaleshi, D.; Chin, W.H.; Fan, Z. Sparse Malicious False Data Injection Attacks and Defense Mechanisms in Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2015, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmalifalak, M.; Liu, L.; Nguyen, N.; Zheng, R.; Han, Z. Detecting Stealthy False Data Injection Using Machine Learning in Smart Grid. IEEE Systems Journal 2017, 11, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevizan, R.D.; Ruben, C.; Nagaraj, K.; Ibukun, L.L.; Starke, A.C.; Bretas, A.S.; McNair, J.; Zare, A. Data-driven Physics-based Solution for False Data Injection Diagnosis in Smart Grids. 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), 2019, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Ruben, C.; Dhulipala, S.; Nagaraj, K.; Zou, S.; Starke, A.; Bretas, A.; Zare, A.; McNair, J. Hybrid data-driven physics model-based framework for enhanced cyber-physical smart grid security. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, K.; Zou, S.; Ruben, C.; Dhulipala, S.; Starke, A.; Bretas, A.; Zare, A.; McNair, J. Ensemble CorrDet with adaptive statistics for bad data detection. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Martinez, V.; Cooper, A.; Vera, B.; Aljohani, N.; Bretas, A. Hybrid Data-Driven Physics-Based Model Framework Implementation: Towards a Secure Cyber-Physical Operation of the Smart Grid. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2022 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC / I&CPS Europe), 2022, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.N.; Ogundijo, O.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Online Cyber-Attack Detection in Smart Grid: A Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 5174–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsiklis, J.; van Roy, B. Optimal stopping of Markov processes: Hilbert space theory, approximation algorithms, and an application to pricing high-dimensional financial derivatives. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 1999, 44, 1840–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Devraj, A.M.; Bušić, A.; Meyn, S. Zap Q-Learning for Optimal Stopping. 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), 2020, pp. 3920–3925. [CrossRef]
- Meyn, S. Control Systems and Reinforcement Learning; Cambridge University Press, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Yang, S.; McCann, J.A.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. Detection of false data injection attacks in smart-grid systems. IEEE Communications Magazine 2015, 53, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Mendis, G.J.; Wei, J. Real-Time Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid: A Deep Learning-Based Intelligent Mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.; Farag, H.E.Z.; Youssef, A.; El-Saadany, E.F. Detection of false data injection attacks in smart grids using Recurrent Neural Networks. 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), 2018, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Ganjkhani, M.; Fallah, S.N.; Badakhshan, S.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.w. A Novel Detection Algorithm to Identify False Data Injection Attacks on Power System State Estimation. Energies 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Detecting False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids: A Semi-Supervised Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bresler, F.S.; Bryson, M.E.; Seiler, K.; Monken, J. Toward Bulk Power System Resilience: Approaches for Regional Transmission Operators. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine 2020, 18, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.M.; Sippel, S.; Knutti, R. Increasing probability of record-shattering climate extremes. Nature Climate Change 2021, 11, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, V.; Miu, K.; Leger, A.S.; Nwankpa, C. Study of the impacts of ambient temperature variations along a transmission line using temperature-dependent line models. 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, 2011, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, V.; Knudson, M.; Miu, K. System impacts of temperature-dependent transmission line models. 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting | Conference & Exposition, 2014, pp. 1–1. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




