Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
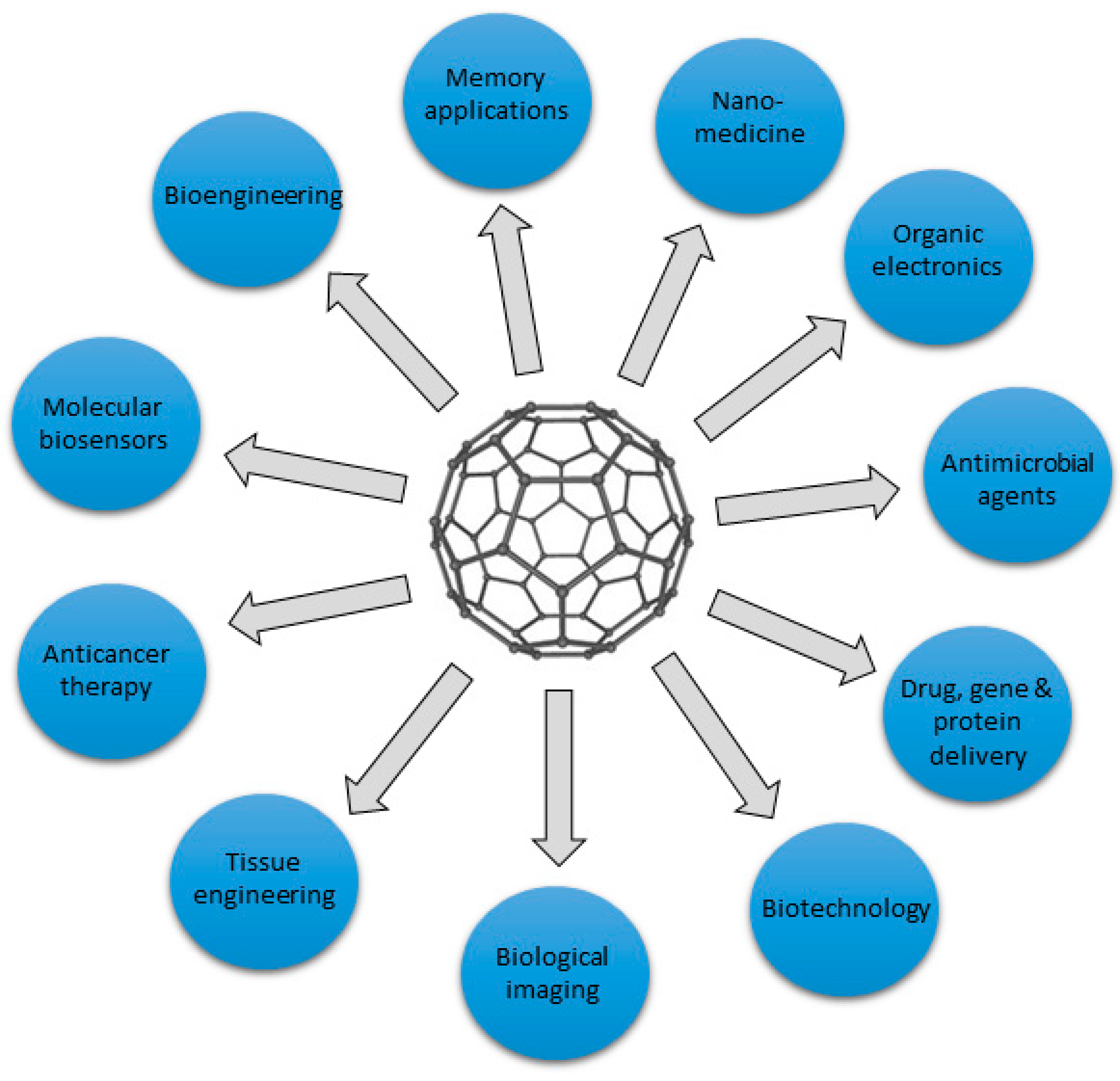
2. Graphene-based materials
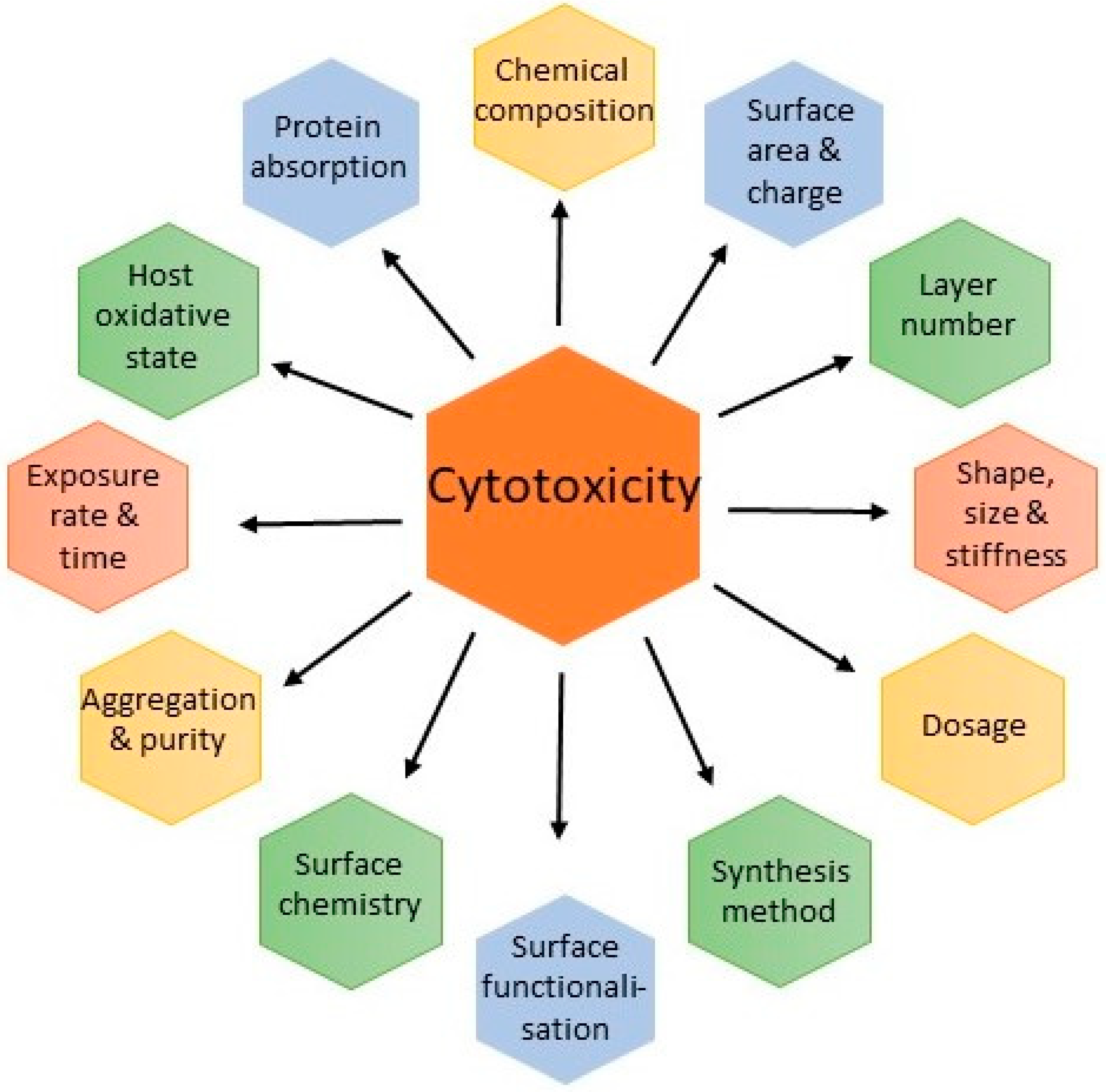
3. Safety Concerns
3.1. Adsorption, distribution and excretion
3.2. Membrane and Cellular Damage
3.3. Oxidative Stress
3.4. Inflammation
3.5. Aggregation
3.6. Environmental Exposure
4. Degradation of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sharma, A.; Kontodimas, K.; Bosmann, M. Nanomedicine: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach to COVID-19. Frontiers in Medicine 2021, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.648005. [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-M.; Zheng, K.-W.; Wang, R.-L.; Yue, S.-F.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.-W.; Song, F.; Su, Y.; Ma, Q. Functionalization and optimization-strategy of graphene oxide-based nanomaterials for gene and drug delivery. Am J Transl Res 2020, 12, 1515-1534.
- He, Y.; Yi, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Yu, D. Magnetic graphene oxide: Synthesis approaches, physicochemical characteristics, and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2021, 136, 116191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116191. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, D.; Sa, P.; Mohapatra, P.; Khuntia, A.; K Sahoo, S. Insights from nanotechnology in COVID-19: prevention, detection, therapy and immunomodulation. Nanomedicine (London, England) 2021, 16, 1219-1235. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2021-0004. [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, S.; Zahmatkeshan, M.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Mehrzadi, S.; Joghataei, M.T.; Alavijeh, M.S.; Seifalian, A. The role of nanotechnology in current COVID-19 outbreak. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06841. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gustafsson, O.J.R.; Siddiqui, G.; Javed, I.; Kelly, H.G.; Blin, T.; Yin, H.; Kent, S.J.; Creek, D.J.; Kempe, K.; et al. Human plasma proteome association and cytotoxicity of nano-graphene oxide grafted with stealth polyethylene glycol and poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). Nanoscale 2018, 10, 10863-10875. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr00835c. [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Choe, G.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y. Graphene oxide-incorporated hydrogels for biomedical applications. Polymer Journal 2020, 52, 823-837. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-020-0350-9. [CrossRef]
- Alphandéry, E. Nano dimensions/adjuvants in COVID-19 vaccines. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2022, 10, 1520-1552. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tb02408f. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Dwivedi, N.; Dhand, C.; Khan, R.; Sathish, N.; Gupta, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S. Potential of graphene-based materials to combat COVID-19: properties, perspectives, and prospects. Mater Today Chem 2020, 18, 100385-100385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100385. [CrossRef]
- Kumar Raghav, P.; Mohanty, S. Are graphene and graphene-derived products capable of preventing COVID-19 infection? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110031. [CrossRef]
- Albaz, A.A.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Sain, Z.M.; Almutairi, W.A.; Alamri, A.S.; Aloufi, A.H.; Almalki, W.H.; Tarique, M. Nanotechnology-based approaches in the fight against SARS-CoV-2. AIMS Microbiology 2021, 7, 368-398. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2021023. [CrossRef]
- Khedri, M.; Maleki, R.; Dahri, M.; Sadeghi, M.M.; Rezvantalab, S.; Santos, H.A.; Shahbazi, M.-A. Engineering of 2D nanomaterials to trap and kill SARS-CoV-2: a new insight from multi-microsecond atomistic simulations. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2022, 12, 1408-1422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-01054-w. [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, O.; Yasamineh, S.; Amini, P.; Afkhami, H.; Delarampour, A.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Karimi Matloub, R.; Zahedi, M.; Hosseini, P.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; et al. Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of nanoparticles in the management of COVID-19: a comprehensive overview. Virol J. 2022, 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-022-01935-7. [CrossRef]
- Seifi, T.; Reza Kamali, A. Antiviral performance of graphene-based materials with emphasis on COVID-19: A review. Med Drug Discov 2021, 11, 100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2021.100099. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Azizighannad, S.; Farinas, E.T.; Mitra, S. Antiviral properties of select carbon nanostructures and their functionalized analogs. Materials Today Communications 2021, 29, 102743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102743. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Esmailpour, M.; Mohammadi, M. Chloroquine drug and Graphene complex for treatment of COVID-19. 2020. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-29418/v1. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Hou, X.; Bohmer, M.; Dong, Y. Advances of nanomaterials-based strategies for fighting against COVID-19. VIEW 2021, 2, 20200180. https://doi.org/10.1002/viw.20200180. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lim, E.-K.; Park, G.; Park, C.; Lim, J.-W.; Lee, H.; Na, W.; Yeom, M.; Kim, J.; Song, D.; et al. Advanced Nanomaterials for Preparedness Against (Re-)Emerging Viral Diseases. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2005927. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005927. [CrossRef]
- Reina, G.; Iglesias, D.; Samorì, P.; Bianco, A. Graphene: A Disruptive Opportunity for COVID-19 and Future Pandemics? Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2007847. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202007847. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Functionalized graphene oxide serves as a novel vaccine nano-adjuvant for robust stimulation of cellular immunity. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3785-3795. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr09208f. [CrossRef]
- Chintagunta, A.D.; M, S.K.; Nalluru, S.; N. S, S.K. Nanotechnology: an emerging approach to combat COVID-19. Emergent Materials 2021, 4, 119-130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00178-6. [CrossRef]
- Daxiang, C.; Ang, G.; Hui, L.; Jing, T.; Xueling, L.; Qi, S. Nano coronavirus recombinant vaccine taking graphene oxide as carrier. Patent CN112220919A. Shanghai National Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology Co Ltd. 2020, CN112220919A, 1-10.
- Zhou, Q.; Gu, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, P.; Lv, L.; Aji, S.; et al. Large-Sized Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Increase DC-T-Cell Synaptic Contact and the Efficacy of DC Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Adv Mater 2021, 33, e2102528. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202102528. [CrossRef]
- Jihad, M.A.; Noori, F.T.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Albukhaty, S.; Almalki, F.A.; Alyamani, A.A. Polyethylene Glycol Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Nigella sativa Extract: A Smart Antibacterial Therapeutic Drug Delivery System. Molecules 2021, 26, 3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113067. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F. Biodegradation of Polyethers (Polyethylene Glycol, Polypropylene Glycol, Polytetramethylene glycol, and Others). In Biopolymers Online.
- Łoczechin, A.; Séron, K.; Barras, A.; Giovanelli, E.; Belouzard, S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Metzler-Nolte, N.; Boukherroub, R.; Dubuisson, J.; Szunerits, S. Functional Carbon Quantum Dots as Medical Countermeasures to Human Coronavirus. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2019, 11, 42964-42974. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b15032. [CrossRef]
- Kitko, K.E.; Zhang, Q. Graphene-Based Nanomaterials: From Production to Integration With Modern Tools in Neuroscience. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2019, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2019.00026. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Yang, J.; Choi, J. Differential genotoxic and epigenotoxic effects of graphene family nanomaterials (GFNs) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2016, 798-799, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.01.006. [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, F.; Qiyue, C.; Weihong, G.; Yaqing, Z.; Chen, H.; Junrong, W.; Longquan, S. Toxicology data of graphene-family nanomaterials: an update. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1915-1939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02717-2. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yan, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, A. Toxicological Evaluation of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2020, 20, 1993-2006. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17364. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological Interactions of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials: An Interdisciplinary Review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 15-34. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx200339h. [CrossRef]
- Ban, G.; Hou, Y.; Shen, Z.; Jia, J.; Chai, L.; Ma, C. Potential Biomedical Limitations of Graphene Nanomaterials. Int J Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 1695-1708. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S402954. [CrossRef]
- Chiticaru, E.A.; Ionita, M. Graphene toxicity and future perspectives in healthcare and biomedicine. FlatChem 2022, 35, 100417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flatc.2022.100417. [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, A.-I.; Aghasoleimani, K.; Semertsidou, A.; Vyas, J.; Roșca, A.-L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A. Graphene-Related Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061092. [CrossRef]
- Rudnytska, O.V.; Kulish, Y.V.; Khita, O.O.; Minchenko, D.O.; Tsymbal, D.O.; Viletska, Y.M.; Sliusar, M.Y.; Trufanova, D.D.; Minchenko, O.H. Exposure to nanographene oxide induces gene expression dysregulation in normal human astrocytes. Endocr. Regul. 2022, 56, 216-226. https://doi.org/10.2478/enr-2022-0023. [CrossRef]
- Aguado-Henche, S.; Escudero, M.L.; García-Alonso, M.C.; Lozano-Puerto, R.M.; Clemente De Arriba, C. Biological Responses in the Blood and Organs of Rats to Intraperitoneal Inoculation of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Materials 2022, 15, 2898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082898. [CrossRef]
- Bantun, F.; Singh, R.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Almalki, A.H.; Alshammary, F.; Khan, S.; Haque, S.; Srivastava, M. Gut microbiome interactions with graphene based nanomaterials: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154789. [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Dou, T.-T.; Chen, J.-Y.; Duan, M.-X.; Zhen, Q.; Wu, H.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-L. Sublethal toxicity of graphene oxide in Caenorhabditis elegans under multi-generational exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113064. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Qiu, D. A comparative study of toxicity of graphdiyne and graphene oxide to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 2021-2030. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.4182. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Bai, L.; Quan, X. Effects of nanomaterials on metal toxicity: Case study of graphene family on Cd. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110448. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhou, Q.; Ouyang, S. Direct and Indirect Genotoxicity of Graphene Family Nanomaterials on DNA—A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112889. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Mei, N. Assessment of the toxic potential of graphene family nanomaterials. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis 2014, 22, 105-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.009. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Pu, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, T. Environmental and health effects of graphene-family nanomaterials: Potential release pathways, transformation, environmental fate and health risks. Nano Today 2022, 42, 101379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101379. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 101-124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8. [CrossRef]
- Facciolà, A.; Visalli, G.; Laganà, P.; La Fauci, V.; Squeri, R.; Pellicanò, G.F.; Nunnari, G.; Trovato, M.; Di Pietro, A. The new era of vaccines: the "nanovaccinology". Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7163-7182. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201908_18763. [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nature Reviews Materials 2021, 6, 1078-1094. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00358-0. [CrossRef]
- du Preez, H.N.; Lin, J.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Aldous, C.; Kruger, H.G. COVID-19 Vaccine Adverse Events: Evaluating the Pathophysiology from an Undersulfated and Degraded Glycocalyx Perspective. ESS Open Archive 2023. https://doi.org/10.22541/essoar.169203072.26336613/v1. [CrossRef]
- Pelin, M.; Sosa, S.; Prato, M.; Tubaro, A. Occupational exposure to graphene based nanomaterials: risk assessment. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15894-15903. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr04950e. [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: a general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-016-0168-y. [CrossRef]
- Plachá, D.; Jampilek, J. Graphenic Materials for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121758. [CrossRef]
- Dasari Shareena, T.P.; McShan, D.; Dasmahapatra, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B. A Review on Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications and Risks in Environment and Health. Nano-Micro Letters 2018, 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-018-0206-4. [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Fanchini, G.; Chhowalla, M. Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nature Nanotechnology 2008, 3, 270-274. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.83. [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Evolving scientific aptitude of poly(ethylene glycol) filled with carbonaceous nanofillers. Journal of Plastic Film & Sheeting 2021, 37, 490-509. https://doi.org/10.1177/8756087921999094. [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Chen, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, G.; Cui, J.; Yan, Y. The interaction between N,N-dimethylacrylamide and pristine graphene and its role in fabricating a strong nanocomposite hydrogel. Journal of Materials Science 2020, 55, 7652-7664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04542-5. [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.M.T.; Vo, T.A.T.; Hoang, T.X.; Cho, S. Graphene Integrated Hydrogels Based Biomaterials in Photothermal Biomedicine. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040906. [CrossRef]
- Ghawanmeh, A.A.; Ali, G.A.M.; Algarni, H.; Sarkar, S.M.; Chong, K.F. Graphene oxide-based hydrogels as a nanocarrier for anticancer drug delivery. Nano Research 2019, 12, 973-990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2300-4. [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Feng, Q.; Tang, N.; Du, Y. Identifying the magnetic properties of graphene oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 123104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4869827. [CrossRef]
- Ženata, O.; Vrzalová, A.; Bachleda, P.; Janečková, J.; Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Vrzal, R. The effect of graphene oxide on signalling of xenobiotic receptors involved in biotransformation. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126753. [CrossRef]
- Tufano, I.; Vecchione, R.; Netti, P.A. Methods to Scale Down Graphene Oxide Size and Size Implication in Anti-cancer Applications. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.613280. [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, G.; D'Agati, M.; Khan, A.M.; Sitharaman, B. Toxicology of graphene-based nanomaterials. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 105, 109-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.028. [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q.T.; Haq, S.H.; Alshammari, A.; Al-Mutlaq, M.A.; Anjum, M.N. The systemic effect of PEG-nGO-induced oxidative stress in vivo in a rodent model. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2019, 10, 901-911. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.10.91. [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, R.; Boholm, M.; Johansson, M.; De Montoya, M.L. “Just Carbon”: Ideas About Graphene Risks by Graphene Researchers and Innovation Advisors. NanoEthics 2018, 12, 199-210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11569-018-0324-y. [CrossRef]
- Algadi, H.E. Effects of Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles on the Immune System Biomarkers Produced by RAW 264.7. University of the Western Cape, Cape Town, South Africa, 2019.
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, M.K.; Kulkarni, P.P.; Sonkar, V.K.; Grácio, J.J.A.; Dash, D. Amine-Modified Graphene: Thrombo-Protective Safer Alternative to Graphene Oxide for Biomedical Applications. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2731-2740. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300172t. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.T.; He, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yu, T.Y.; Qin, Y.; Lin, S.J. Differential effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on zebrafish embryos and developing larvae. Environmental Science-Nano 2018, 5, 1200-1207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en00190a. [CrossRef]
- Kenry. Understanding the hemotoxicity of graphene nanomaterials through their interactions with blood proteins and cells. Journal of Materials Research 2018, 33, 44-57. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.388. [CrossRef]
- Ahlinder, L.; Henych, J.; Lindström, S.W.; Ekstrand-Hammarström, B.; Stengl, V.; Österlund, L. Graphene oxide nanoparticle attachment and its toxicity on living lung epithelial cells. RSC Advances 2015, 5, 59447-59457. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra09351a. [CrossRef]
- du Preez, H.N.; Aldous, C.; Hayden, M.R.; Kruger, H.G.; Lin, J. Pathogenesis of COVID-19 described through the lens of an undersulfated and degraded epithelial and endothelial glycocalyx. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22052. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202101100RR. [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.K.; Awasthi, K.K.; John, P.J. Effects of Nano-Graphene Oxide on Testis, Epididymis and Fertility of Wistar Rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 202-210. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12782. [CrossRef]
- Jović, D.; Jaćević, V.; Kuča, K.; Borišev, I.; Mrdjanovic, J.; Petrovic, D.; Seke, M.; Djordjevic, A. The Puzzling Potential of Carbon Nanomaterials: General Properties, Application, and Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081508. [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, F.; Benzi, R.; Gianpaolo, P. Darkfield microscope analysis of the blood of 1086 symptomatic subjeccts after vaccination with two types of mRNA vaccines; 2022; pp. 1-73.
- Kostarelos, K.; Lacerda, L.; Pastorin, G.; Wu, W.; Wieckowski, S.; Luangsivilay, J.; Godefroy, S.; Pantarotto, D.; Briand, J.P.; Muller, S.; et al. Cellular uptake of functionalized carbon nanotubes is independent of functional group and cell type. Nat Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 108-113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2006.209. [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Chandran, P.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2461-2464. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NR10172B. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.-F.; Dai, L. Can graphene quantum dots cause DNA damage in cells? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9894-9901. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR01734C. [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, E.; Akhavan, O.; Shamsara, M.; Valimehr, S.; Rahighi, R. DNA and RNA extractions from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells by graphene nanoplatelets. RSC Advances 2014, 4, 60720-60728. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA11458B. [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Carmela Lauriola, M.; Ciasca, G.; Conti, C.; De Spirito, M.; Papi, M. The graphene oxide contradictory effects against human pathogens. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 152001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa6150. [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Ge, C.; Yang, Z.; Garate, J.A.; Gu, Z.; Weber, J.K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, R. Reduced Cytotoxicity of Graphene Nanosheets Mediated by Blood-Protein Coating. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5713-5724. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn5066606. [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Thong, K.L.; Ali, M.E.; Appaturi, J.N.; Dinshaw, I.J.; Ong, Z.Y.; Leo, B.F. Graphene oxide exhibits differential mechanistic action towards Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 6-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.023. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Lazzaretto, B.; Hultenby, K.; Newman, L.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Lozano, N.; Kostarelos, K.; Malmberg, P.; Fadeel, B. Graphene Oxide Elicits Membrane Lipid Changes and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Chem 2018, 4, 334-358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2017.12.017. [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yang, K.; Yao, K.; Zhang, S.; Tao, H.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Functionalized Graphene Oxide in Enzyme Engineering: A Selective Modulator for Enzyme Activity and Thermostability. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4864-4875. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300217z. [CrossRef]
- Kaloudis, N.; Zygouri, P.; Chalmpes, N.; Spyrou, K.; Gournis, D.; Pavlidis, I.V. Effect of Graphite Oxide on the Catalytic Behavior of (S)-Selective Amine Transaminases. Frontiers in Catalysis 2022, 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fctls.2021.803850. [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.-H.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, H.; Yu, J.; Jang, S.G.; Ku, B.-C.; Moon, B.; You, N.-H. Sustainable production of reduced graphene oxide using elemental sulfur for multifunctional composites. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 176, 107236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107236. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wen, G.; Ding, Y.; Wu, K.-H.; Chen, C.; Su, D. Reduced graphene oxide: a metal-free catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1175-1181. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC02894B. [CrossRef]
- du Preez, H.N.; Aldous, C.; Kruger, H.G.; Johnson, L. N-Acetylcysteine and Other Sulfur-Donors as a Preventative and Adjunct Therapy for COVID-19. Advances in Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2022, 2022, 4555490. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4555490. [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Guo, S.; Nishina, Y.; Bianco, A. Reaction between Graphene Oxide and Intracellular Glutathione Affects Cell Viability and Proliferation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, 13, 3528-3535. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c17523. [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Huynh, A.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P. Protective Effect of Edaravone against Cationic Lipid-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 144-149. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b20-00679. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Eom, H.-J.; Choi, J. A systems toxicology approach to the surface functionality control of graphene–cell interactions. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1109-1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.108. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Valle, R.P.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Xia, T.; Liu, S. Crucial Role of Lateral Size for Graphene Oxide in Activating Macrophages and Stimulating Pro-inflammatory Responses in Cells and Animals. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10498-10515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b04751. [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan, M.A.; Dillon, C.P.; Tait, S.W.; Moshiach, S.; Dorsey, F.; Connell, S.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cleveland, J.L.; Withoff, S.; et al. Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis. Nature 2007, 450, 1253-1257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06421. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, W.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, T. The interactions between pristine graphene and macrophages and the production of cytokines/chemokines via TLR- and NF-κB-related signaling pathways. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6933-6942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.064. [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.K.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Schreiber, R.D. Interleukin-10 receptor signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway. Requirement for two distinct receptor-derived signals for anti-inflammatory action. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16513-16521. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.23.16513. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Mai, Y.-W.; Liao, C.; Lu, Z.; Liao, Y. Core-shell structured polyethylene glycol functionalized graphene for energy-storage polymer dielectrics: Combined mechanical and dielectric performances. Composites Science and Technology 2020, 199, 108341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108341. [CrossRef]
- Falahati, M.; Attar, F.; Sharifi, M.; Haertlé, T.; Berret, J.-F.; Khan, R.H.; Saboury, A.A. A health concern regarding the protein corona, aggregation and disaggregation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2019, 1863, 971-991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.02.012. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Raul, K.K.; Pradhan, S.S.; Basu, S.; Nayak, A. Magnetic properties of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures 2014, 64, 78-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2014.07.014. [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, C.; Jurgons, R.; Schmid, R.J.; Bergemann, C.; Henke, J.; Erhardt, W.; Huenges, E.; Parak, F. Magnetic drug targeting--biodistribution of the magnetic carrier and the chemotherapeutic agent mitoxantrone after locoregional cancer treatment. J. Drug Target. 2003, 11, 139-149. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186031000150791. [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, N.M.; Jansen, P.; Belcher, A.M. Graphene, Carbon Nanotube and Plasmonic Nanosensors for Detection of Viral Pathogens: Opportunities for Rapid Testing in Pandemics like COVID-19. Frontiers in Nanotechnology 2021, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnano.2021.733126. [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, H.; Rasmussen, K.; Sokull-Klüttgen, B. Regulatory Aspects of Nanomaterials in the EU. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 2017, 89, 224-231. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.201600076. [CrossRef]
- Joghataei, M.; Ostovari, F.; Atabakhsh, S.; Tobeiha, N. Heterogeneous Ice Nucleation by Graphene Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66714-2. [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liang, H. 3d reduced graphene oxide/sio 2 composite for ice nucleation. Patent US 2022/0002159 A1. 2020.
- Waltz, E. How nasal-spray vaccines could change the pandemic. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-02824-3 (accessed on 07 November ).
- Dong, C.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez, G.X.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Kang, S.-M.; Compans, R.W.; Wang, B.-Z. Intranasal vaccination with influenza HA/GO-PEI nanoparticles provides immune protection against homo- and heterologous strains. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118, e2024998118, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2024998118. [CrossRef]
- Mamamoor. FDA Registered Graphene Face Mask. Available online: https://www.mamamoor.com/products/fda-registered-graphene-mask?variant=32234398220375 (accessed on 17 March).
- Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Song, K. COVID-19: Performance study of microplastic inhalation risk posed by wearing masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124955. [CrossRef]
- Dervin, S.; Murphy, J.; Aviles, R.; Pillai, S.C.; Garvey, M. An in vitro cytotoxicity assessment of graphene nanosheets on alveolar cells. Applied Surface Science 2018, 434, 1274-1284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.217. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, D. Biocompatibility of Graphene Oxide. Nanoscale Res Lett 2010, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9751-6. [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C.; Ku, B.K.; Kulkarni, P.; Cheng, Y.S. Deposition of graphene nanomaterial aerosols in human upper airways. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2016, 13, 48-59. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459624.2015.1076162. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Peng, C.; Hu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Distribution and biocompatibility studies of graphene oxide in mice after intravenous administration. Carbon 2011, 49, 986-995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.11.005. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Baek, J.E.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, G.H.; et al. 28-Day inhalation toxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in Sprague-Dawley rats. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 891-901. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2015.1133865. [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Hu, M.; Pan, B.; Xie, Y.; Petersen, E.J. Biodistribution and toxicity of radio-labeled few layer graphene in mice after intratracheal instillation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-016-0120-1. [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Liang, Q.; Meng, X. Effects of graphene oxide on the development of offspring mice in lactation period. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 23-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.014. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yin, L.; Li, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D. Contributions of altered permeability of intestinal barrier and defecation behavior to toxicity formation from graphene oxide in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9934-9943. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02084C. [CrossRef]
- Hein, T. One atom thick – The top four most promising uses of graphene in agriculture. Available online: https://www.futurefarming.com/article/one-atom-thick-the-top-four-most-promising-uses-of-graphene-in-agriculture (accessed on 09 November ).
- Anthony, S. Bill Gates funds creation of thin, light, impenetrable graphene condoms. Available online: https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/171417-bill-gates-funds-creation-of-thin-light-impenetrable-graphene-condoms (accessed on 19 November).
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, T.; Shi, L.; Guo, X.; Si, X.; Yang, R.; Quan, X. The effects of humic acid on the toxicity of graphene oxide to Scenedesmus obliquus and Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.280. [CrossRef]
- Fadeel, B.; Bussy, C.; Merino, S.; Vázquez, E.; Flahaut, E.; Mouchet, F.; Evariste, L.; Gauthier, L.; Koivisto, A.J.; Vogel, U.; et al. Safety Assessment of Graphene-Based Materials: Focus on Human Health and the Environment. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10582-10620. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b04758. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Liang, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B. Impact of humic/fulvic acid on the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using nanomaterials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468-469, 1014–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.044. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Mu, L.; Kang, J.; Lu, K.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Q. Humic Acid Acts as a Natural Antidote of Graphene by Regulating Nanomaterial Translocation and Metabolic Fluxes in Vivo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6919-6927. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5012548. [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Tóth, I.Y.; Kovács, K.; Illés, E.; Szekeres, M.; Barna, B.; Csicsor, A.; Szabó, T. Striking analogies and dissimilarities between graphene oxides and humic acids: pH-dependent charging and colloidal stability. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306, 112948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112948. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, C.; Ouyang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Q. Mitigation in Multiple Effects of Graphene Oxide Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryogenesis Driven by Humic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10147-10154. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02220. [CrossRef]
- Hafez, M.; Popov, A.I.; Zelenkov, V.N.; Teplyakova, T.V.; Rashad, M. Humic substances as an environmental- friendly organic wastes potentially help as natural anti-virus to inhibit COVID-19. Science Archives 2020, 1, 53-60. https://doi.org/10.47587/SA.2020.1202. [CrossRef]
- Koul, D.; Khosla, J.K.; Manhas, R.S.; Chander, D.; Chaubey, A. COVID-19 prevention and management: Potential applications of humic substances. JIMCR 2021, 2, 61-68. https://doi.org/10.38205/imcr.020261. [CrossRef]
- Rozhina, E.; Batasheva, S.; Danilushkina, A.; Kryuchkova, M.; Gomzikova, M.; Cherednichenko, Y.; Nigamatzyanova, L.; Akhatova, F.; Fakhrullin, R. Kaolin alleviates the toxicity of graphene oxide for mammalian cells. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1457-1464. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8md00633d. [CrossRef]
- Di Ianni, E.; Møller, P.; Vogel, U.B.; Jacobsen, N.R. Pro-inflammatory response and genotoxicity caused by clay and graphene nanomaterials in A549 and THP-1 cells. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2021, 872, 503405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2021.503405. [CrossRef]
- Kurapati, R.; Martìn, C.; Palermo, V.; Nishina, Y.; Bianco, A. Biodegradation of Graphene Materials Catalyzed by Human Eosinophil Peroxidase. Faraday Discuss. 2021, 227, 189–203. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fd00094a. [CrossRef]
- Kotchey, G.P.; Allen, B.L.; Vedala, H.; Yanamala, N.; Kapralov, A.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Kagan, V.E.; Star, A. The Enzymatic Oxidation of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2098-2108. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn103265h. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.F.; Montenegro, M.M.; Ntola, C.N.; Vranic, S.; Kostarelos, K.; Vogt, C.; S. Toprak, M.; Duan, T.; Leifer, K.; Bräutigam, L.; et al. Nitric Oxide-Dependent Biodegradation of Graphene Oxide Reduces Inflammation in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16730–16737. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR03675G. [CrossRef]
- Kurapati, R.; Bonachera, F.; Russier, J.; Sureshbabu, A.R.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A. Covalent Chemical Functionalization Enhances the Biodegradation of Graphene Oxide. 2D Mater. 2017, 5, 015020. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/aa8f0a. [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.-C.; Henderson, W.M.; Chowdhury, I.; Goodwin, D.G.; Chang, X.; Martin, S.; Fairbrother, D.H.; Bouchard, D.; Zepp, R.G. The Contribution of Indirect Photolysis to the Degradation of Graphene Oxide in Sunlight. Carbon 2016, 110, 426–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.013. [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Shen, W.; Pei, X.; You, S.; Yin, Q.; Li, X. A Novel Environmental Fate of Graphene Oxide: Biodegradation by a Bacterium Labrys Sp. WJW to Support Growth. Water Research 2018, 143, 260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.070. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Diko, C.S.; Qu, Y. Biogenic Fenton-like Reaction Involvement in Aerobic Degradation of C60 by Labrys Sp. WJW. Environmental Pollution 2021, 272, 115300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115300. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Z.; Li, T.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J. An Efficient and Environment-Friendly Method of Removing Graphene Oxide in Wastewater and Its Degradation Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 531–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.094. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Fang, H.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Q. Exposure to graphene oxide at environmental concentrations induces thyroid endocrine disruption and lipid metabolic disturbance in Xenopus laevis. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124834. [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Song, J.; Hong, B.H. Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112816. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Adam, V.; Richtera, L. Graphene Oxide as a Nanocarrier for Biochemical Molecules: Current Understanding and Trends. Processes 2020, 8, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121636. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Ghalandari, B.; Hao, L.; Huang, C.; Su, W.; Ke, Y.; Cui, D.; Zhi, X.; et al. Encountering and Wrestling: Neutrophils Recognize and Defensively Degrade Graphene Oxide. Adv Healthc Mater 2022, 11, e2102439. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202102439. [CrossRef]
- Chemsec. Carbon nanotubes. Available online: https://sinsearch.chemsec.org/chemical/308068-56-6 (accessed on 17 March).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




